Test 9: Soil Glass Paint Analysis, Impressions and Ballistics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Soil Material
Partly organic
Decaying matter
Ex: peat - 100% organic
Partly inorganic
Minerals
Ex: sand - 100% inorganic
Components of Soil
Rocks
Minerals
Vegetation
Animal waste
Glass
construction debris
Asphalt
How do Soils Differ?
Color
1000 different colors
Wet soils appear dark
Texture
Particle size
pH
Density
Fossil types (Diatoms)
Mineral and rock content
pesticides/herbicides
Forensic Geology: Geotracking
different parts of the world have different soil
Minerals
naturally occurring crystals (2200 known)
Look at color, shape, density, refractive index
Fluorescence
Rocks
contain a combination of different minerals
Ingredients of Glass
Sand (mostly silica sand)
Soda (Na2CO3) - lowers melting point
Lime (CaO) - makes it water insoluble
Combination of metal oxides:
Ex: Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Aluminum
Melting point between 1,500 and 2,500 degrees celsius
Tempered (Safety) Glass
glass dices (shatters into small pieces, not splintering) on impact
strong from lamination (plastic between glass layers)
Pyrex Glass
contains boron oxides to be able to withstand high temperatures
Glass Fractures
able to determine the direction of a shot through glass
Concentric — circular fractures that originate on the force side of glass
Radial — right angle fractures that originate on the reverse side of force
Multiple Shot Rule
cracks don’t cross cracks
Problem with Glass Identification
most glass is uniform in its making (with respect to its refractive index)
Density Determination
D = m/V
sink or float
density gradient tubes
volume displacement method
Refractive Index Determination
Becke Line — bright halo that disappears when medium and fragment have the same refractive indexes
Birefringence (aka Double Refraction)
Refraction of light in 2 directions
Sandwich between polarizing filters
Paint and Locard’s Principle
Small pieces of paint are often unwittingly transferred between objects during
Vehicle accidents
Burglaries
Robberies
Assaults
Homicides
Even from simple contact with freshly painted surfaces during a crime
Paint Composition
Pigment: very tiny particles of organic and inorganic colored compounds that give the paint its characteristic hue
Binder: suspends the pigment particles and helps to firmly fix them to the surface
Solvent: such as water or an organic liquid, provides a consistency suitable for spreading the paint on the surface
Recording Impressions
take a photo
make a cast
Info Learned from Shoe Impressions
Class Info
manufacturer
make
model of footwear (based on sole pattern)
aided by SICAR and TreadMark databases
footwear impressions may be individualized by identifying imperfections
Determination of how many people and objects were involved
description of the movements of the participants and objects
establish a timeline and sequence of actions that occurred during an incident
support or refute eyewitness, suspect, and victim accounts of what occurred
Information Learned from Tire Marks
Class Traits
manufacturer
mode
year of manufacture
Individual Traits
rocks
nails
etc
Tool Marks
Individualized Marks
Class Traits (Typical Features)
Individual Traits (Accidental of Identifying Features)
cuts
tears
gouges
wear marks
Rifling
grooves in the barrel of a gun that spin the bullet to aim it straight
Lands
raised portion of rifling
Grooves
recessed portion of rifling
Striations
linear marks on bullets after they have been fired
Caliber
diameter of a rifle or handgun barrel between opposite lands
Bullet to Bullet to Gun Comparison
use a comparison microscope to compare striation patterns on bullets
Rifles and Handguns
rifled firearms
leaves striations
Shotguns
non-rifled firearms
no striations
pellets as ammunition
Gauge
diameter of barrel of shotgun
Ballistic Mechanics
Trigger pulled
Activates firing pin
Hits primer
Gunpowder ignited
gunpowder stored in cartridge
Gases propel bullet through barrel
Spent casing bashed against breechblock
Spent cartridge removed from barrel by an extractor
Spent cartridge thrown out of gun by the ejector
extractor and ejector are a source of markings
Close Range, <6 in
muzzle fire burns or melts clothes
concentrated burn marks and shot residue immediately around hole
Shot 12 in Away
halo of smoke-soot around hole
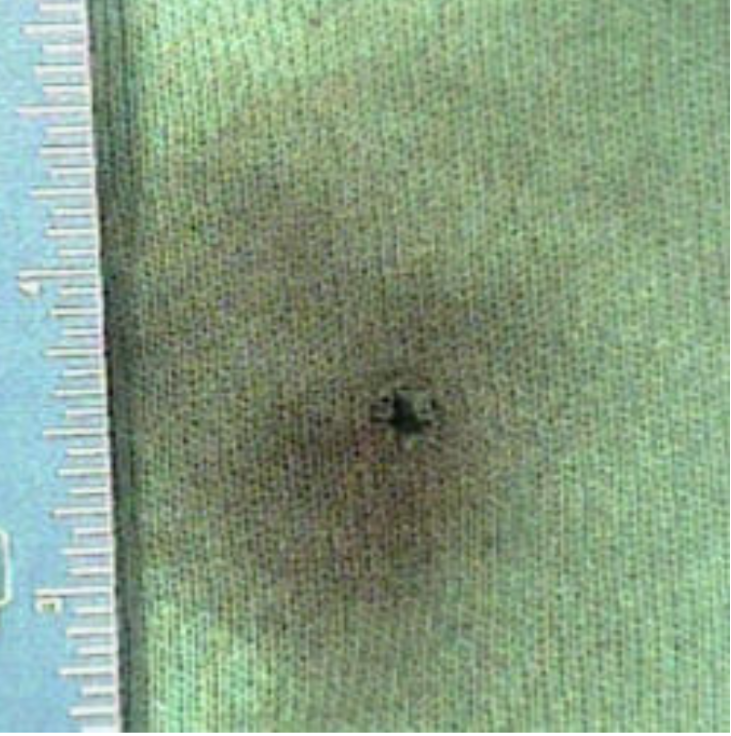
About 18 in Away
scattered specks of shot residue with less soot around hole
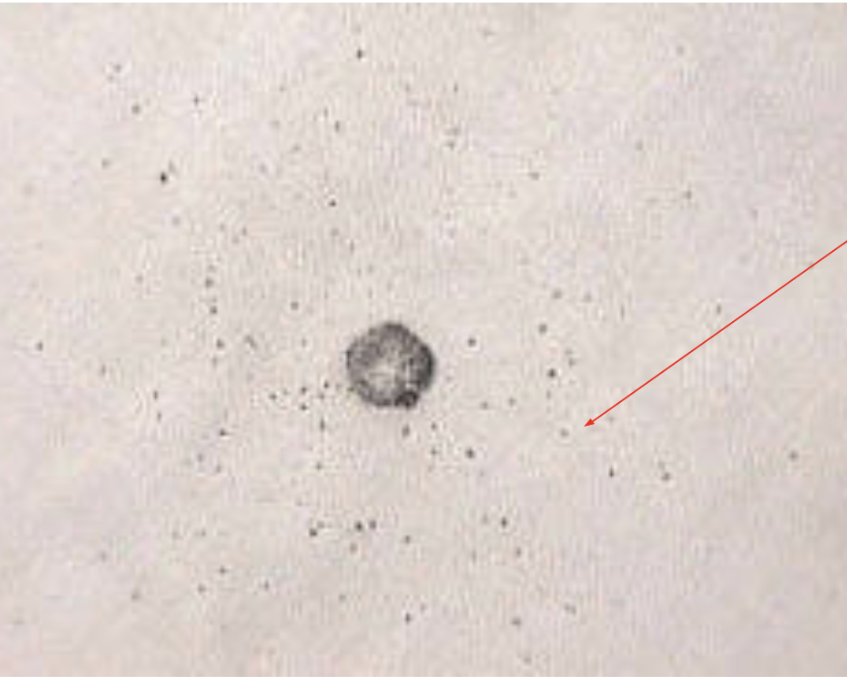
Greiss Test
used to determine the presence of gunpowder residue on clothes
press a treated photo paper against questioned surface with an iron
nitrate residue stuck and chemically enhanced
Bullet Trajectory Analysis
used to determine from where a shot was fired
Integrated Ballistic Identification System (IBIS)
combined FBI and ATF database of fired bullets and cartridges
input and recover digital images of the markings found on fired bullets and cartridge cases either recovered from crime scenes or from test-fired weapons
digital images are then compared with those previously stored
computer matching system