digestive system
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANAT3651
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Alimentary canal or GastroIntestinal (GI) tract includes…
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus.
Accessory organs
assist in digestion of food but NOT required. includes teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver and pancreas.
Purpose of the digestive system
acquire nutrients and water.
alcohol and asprin are absorbed through
stomach
Glucose, lipids, and amino acids are absorbed through
the small intestine
vitamins, water, and minerals are absorbed through the
Large intestine
absorbed nutrients are passed to…
veins of digestive system and then to liver
Fats are absorbed through the ______ and passed into _______, then transported to ____.
small intestine; lacteal ducts; veins of circulatory system
sigmoid colon
storage for feces
6 essential food-processing activities of the Digestive System
Ingestion (taking food in mouth)
2. Propulsion = swallowing (voluntary) and peristalsis (involuntary movement of food)
3. Mechanical digestion = chewing, churning food in stomach, and segmentation (Occurs in the mouth, stomach and small intestine).
4. Chemical digestion (breaks down the food material to molecules). (Occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine.)
5. Absorption = transporting nutrients, electrolytes, and water into veins; and fats into the lymphatics.
6. Defecation = elimination of indigestible substances
Peristalsis versus Segmentation
The intestine contains circular and longitudinal smooth muscle.
Peristalsis is a wave-like muscle contraction that moves food along the digestive tract (through the lumen), while segmentation involves contraction to mix food contents.
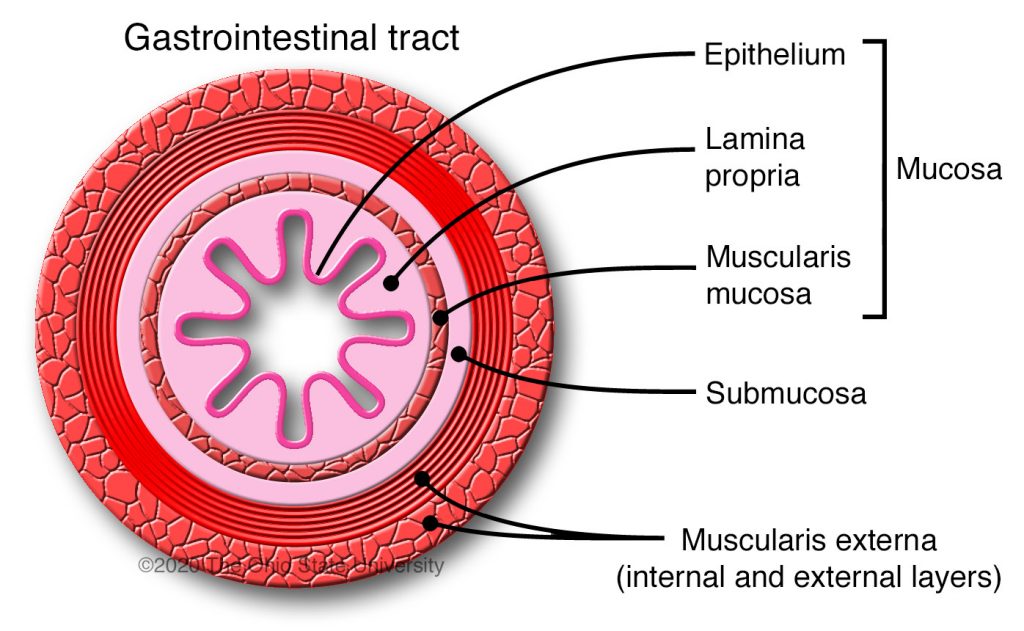
Histological organization of the Digestive System:
Mucosa (true epithelium + lamina propria + muscularis mucosae)
- Note: Epithelium is either stratified squamous or simple columnar.Submucosa - contains arteries, veins, nerves, lymphatics, sometimes mucus glands
3. Muscularis externa - smooth muscle (inner circular layer + outer longitudinal layer)
4. Serosa (mesothelium) or adventitia
Submucosal nerve plexus
signals submucosal glands to secrete and muscularis mucosae to contract.
Myenteric
-located between the circular and longitudinal layers of muscularis externa
- controls peristalsis and segmentation.
4 types of mucus membranes
a. Protective - stratified squamous epithelium
- Found in the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus and anus
b. Secretory - simple columnar epithelium
- specialized for secreting mucus
- Found only in the Stomach as Mucus-secreting cells and mucus-neck cells
c. Absorptive (Nutrients) - Simple columnar cells
- modified with increased surface area for absorbing nutrients – found in the small
intestine
d. Absorptive (Water & Electrolytes) - Simple columnar cells
- for absorbing water and electrolytes
- found in large intestine
- will switch to stratified squamous in anus.
alveolar ridge
The line between the tooth and gum

Vestibule
the space between the lip and the alveolar ridge.
labial frenulum, or frenulum of the lip
lip to the gum
lingual frenulum
tongue to floor of oral cavity
uvula
dangles from soft palate
palatoglossal arch
palate to the tongue
palatopharyngeal arch
palate to pharnyx
palatine tonsil
located in between the palatopharyngeal and palatoglossal arches
Filiform papilla
pointed cones on tongue, most numerous and no taste buds,
Fungiform
papillae on tongue with taste buds, round in shape (mushrooms)
Circumvallate
papillae surrounded by a wall, possess taste buds.
sulcus termanalis
separates circumvallate papilla and lingual tonsil.
fauces
opening between the oral cavity and the oropharynx. Borders are palatoglossal arch, uvula, and sulcus terminalis.
tonsilar ring
ring of protective tonsils in the oropharynx (palatine and lingual tonsils)
parotid gland
serous cells secrete amalyse and lysosomes.
sublingual
mucus cells secrete mucus for lubrication
submandibular
serous and mucus cells secrete
Types of teeth (2123)
2 incisiors, 1 canine (cuspid), 3 bicuspid (premolar), and 3 molar
esophagus
carries bolus from oral cavity to stomach. transitions from skeletal muscle to smooth.
type of esophagus epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium
external layer of esophagus
adventitia not serosa
Inferior vena cava passes through
respiratory diaphragm (caval foramen) at level of thoracic vertebra 8
esophagus passes through
diaphragm (esophageal hiatus) at the level of thoracic vertebra 10 (T10)
cardiac sphnicter
Muscle fibers of the respiratory diaphragm that serve as functional sphincter muscles of the esophagus
Lower esophageal sphincter
The inner circular layer of muscularis externa functions as the sphincter muscle of the
esophagus.
aorta passes through
the respiratory diaphragm at T12
stomach is a site for
chemical and mechanical digestion
regions of the stomach
cardiac, fundus, body, pyloris, greater and lesser curvature, rugae,
pyloric sphincter
prevents food from leaving the stomach. Formed by thickened middle circular layer.
3 layers of the muscularis externa
innermost oblique, middle, circular, and outer longitudinal
what type of cells line the gastric pits?
simple columnar