Organic Chemistry ACS Review (Mechanisms)
1/269
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
270 Terms
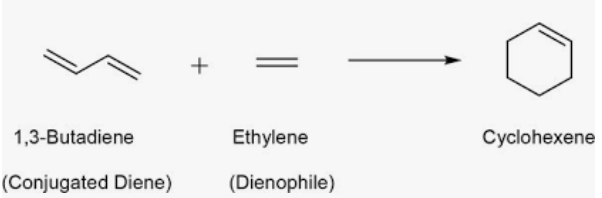
Diels Alder
forms cyclic hexane from a diene and a dienophile.
Friedel-Crafts
Add acyl or akyl group
Grinard
add alkyl or aryl group
Wolf-Kirschner, Clemmenson
Reduce ketone to alkane
Wittig
Convert aldehyde/ketone to alkene
Hammond-Leffler postulate
The TS is more like the reactant or product that is closer in energy
An endothermic TS is like
the product
An exothermic TS is like
the reactant
Exergonic
large and negative expelling of energy
A reaction with exergonic DG
has a product likely controlled by thermodynamics
Large Keq corresponds to
large amount of product relative to the reactant
If a reaction has a large Ea
TS controls the reaction instead of product-reactant thermodynamics
When a solvent stabilizes an intermediate
Ea decreases and rate of reaction increases
Charged complexes are stabilized
by polar solvents
Lewis acid
electron pair acceptor
Bronsted lowry acid
proton donor
Lewis base
electron pair donor
bronsted lowry base
proton acceptor
inductive effect of substituent on A (in HA)
decreases the strength of the H-A bond, making it easier for the acid to donate its proton. (electron withdrawl)
Inductive effect
the electron-withdrawing effect of substituents that stabilizes the conjugate base, enhancing acid strength.
More “s” character in a hybrid orbital
weakens the H-A bond, making the acid stronger.
A resonance stabilized conjugate base A-
Increases acid strength in corresponding HA by delocalizing the negative charge through resonance, thus stabilizing the conjugate base.
A base is
a nucleophile
Nucleophile
a chemical species that donates an electron pair to form a chemical bond in reaction.
Electronic effects shifting electron density
increases base strength
Alkanes are non
cyclic (formula C_nH_2n+2)
Bicyclic
two fused/bridged carbon rings
Cyclopropane distance of an e- from the nucleus
n = 3
cyclobutane distance of e- from nucleus
n = 4
cyclopentane distance e- from nucleus
n = 5
cyclohexane distance of e- from nucleus
n = 6
Cyclopropane structure is
highly strained
cyclobutane structure is
flexible
cyclopentane structure has
slight puckering to minimize angle strain.
cyclohexane stable conformer structure is
chair
cyclohexane less stable structure is
boat
cyclohexane structure perpendicular to plane of the ring is
axial position
cyclohexane structure in plane with the ring is
equitorial position
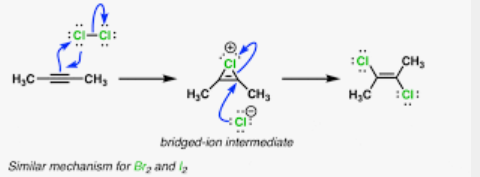
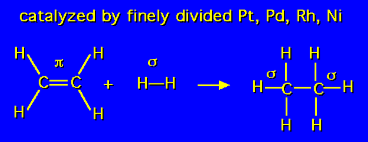
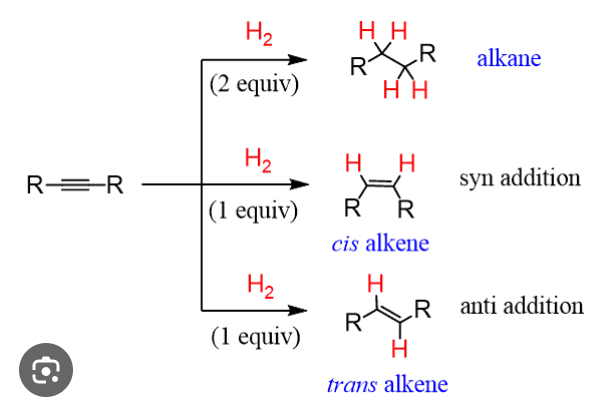
hydrogenation of alkynes to form alkanes
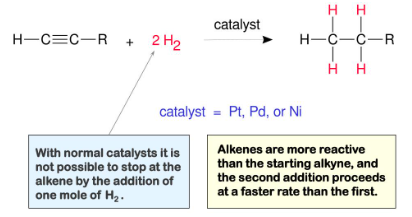
Possible catalysts for hydrogenation of alkynes and alkenes
H2, Pd, Pt, Ni
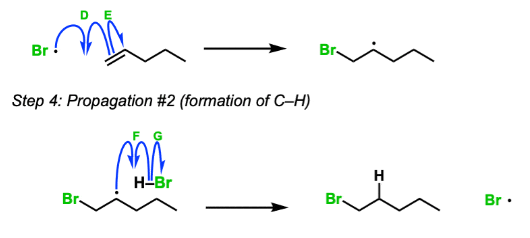
Free radical reaction of alkene
Reduce haloalkane
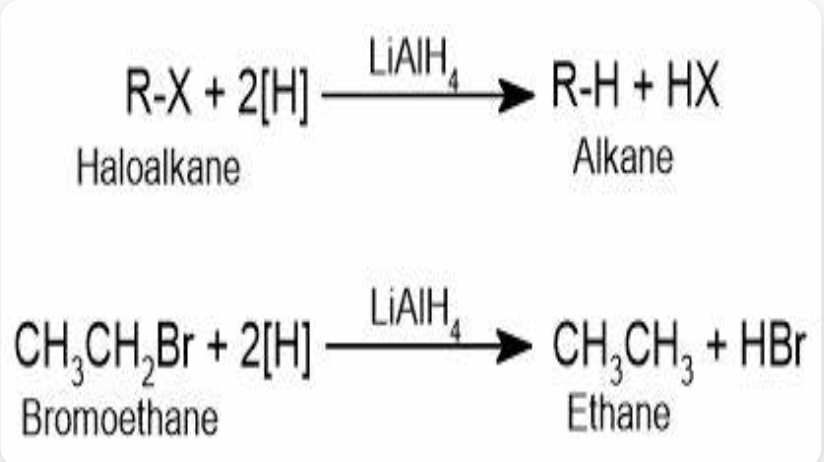
possible catalysts in the reduction of haloalkanes to alkanes
Metal hydrides, and metals alongside H giving species (like Mg+H2O), Plutonium, Nickel
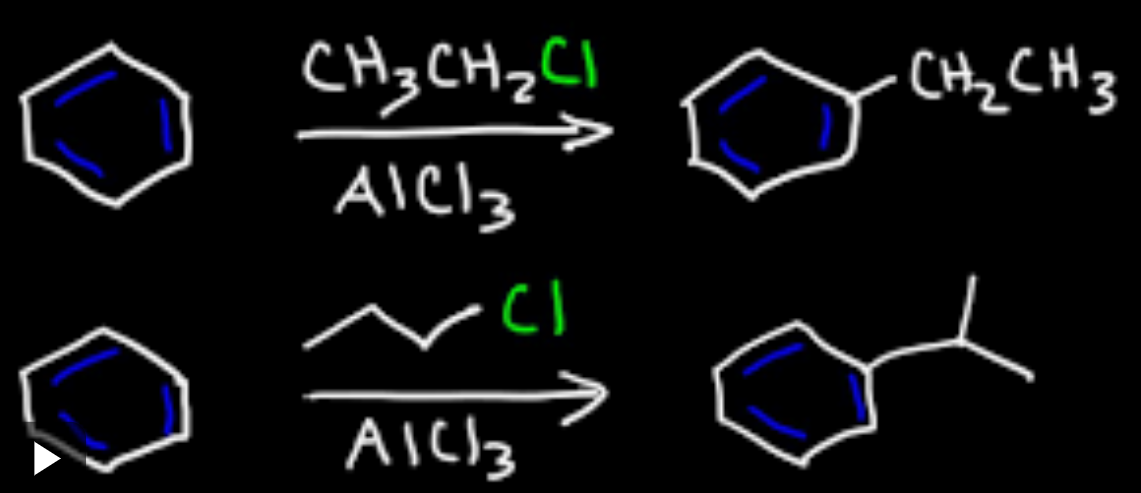
Friedel-Crafts alkylation
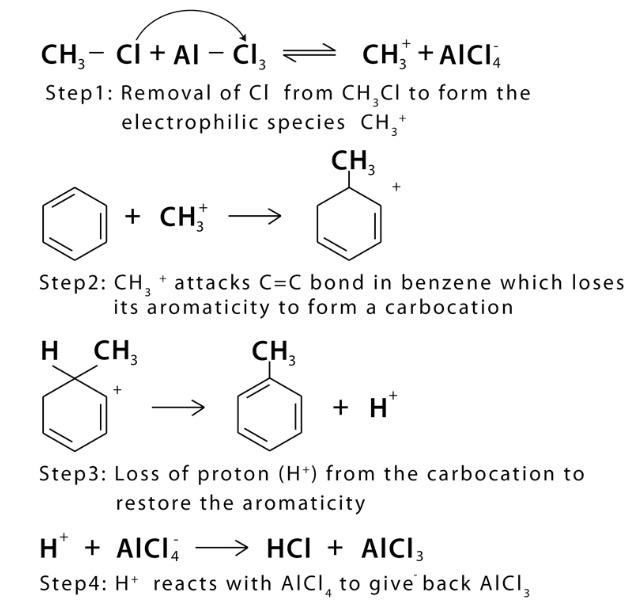
Friedel Crafts alkylation catalyst
Aluminum Chloride (AlCl3)
Combustion of alkanes

Free radical halogenation of alkene to haloalkane
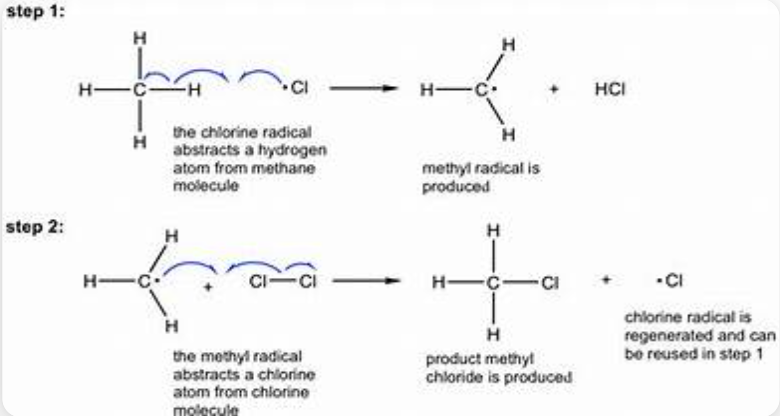
Properties of Alkene
Non-polar, flammable
Alkadiene
An alkene containing two double bonds, typically in a chain arrangement.
Alkatriene
An alkene containing three double bonds, typically in a chain arrangement.
Annulene
Conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons with alternating double bonds.
Isomers of alkenes
have no free rotation of C=C
In a non-cyclic alkene
the cis isomer is less stable than the trans isomer due to steric hindrance
In a cyclic alkene
the cis isomer is more stable than the trans isomer due to angle strain and steric interactions.
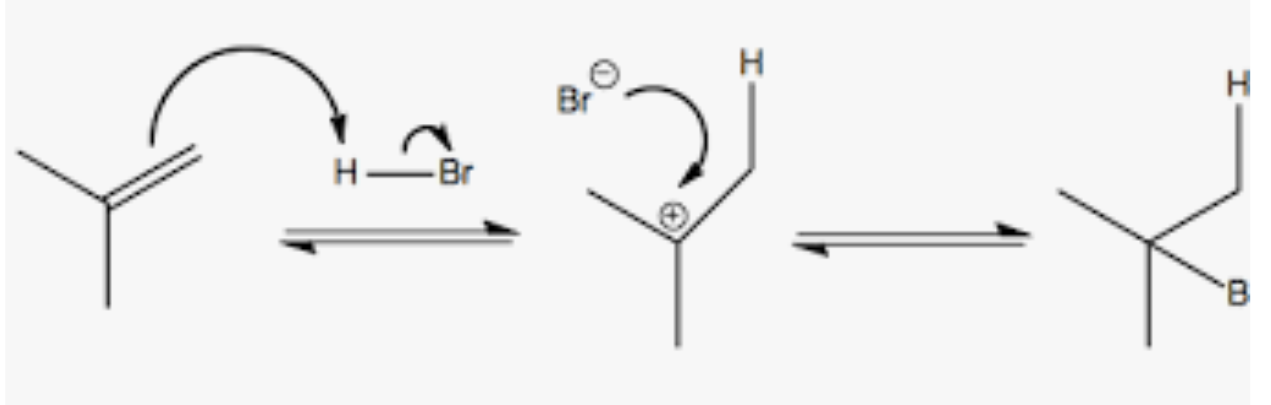
Markovnikof Addition
in addition of HX to an alkene, the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon atom of the double bond that already has the greater number of hydrogen atoms
Zaitsev Elimination
Form the more substituted alkene
Dehydration of alcohols
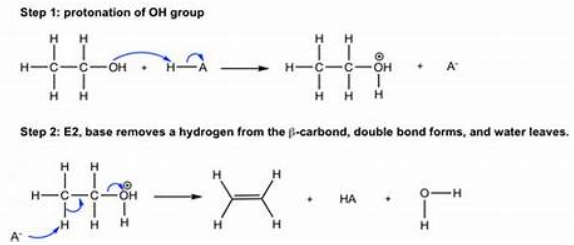
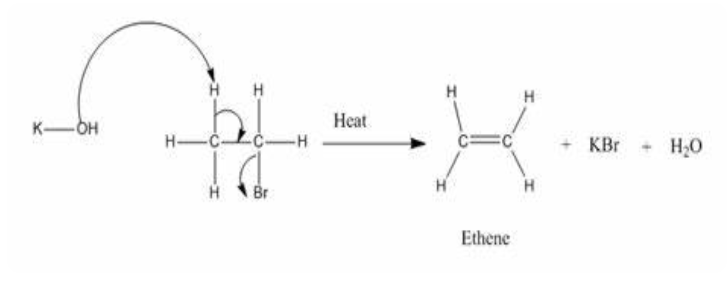
Dehydrohalogenation of haloalkane
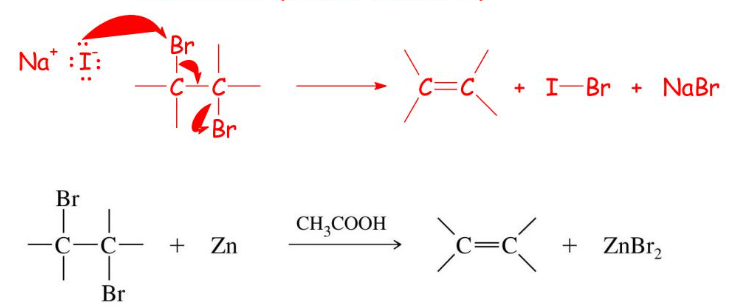
Dehalogenation vicinal dihalide
Hydrogenate alkyne
electrophilic addition
Alkene combustion
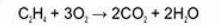
Markovnikov 2 and 3 degree hydration of alkene, 1 degree ethene rearrange
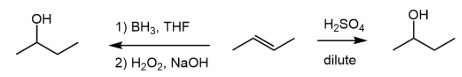
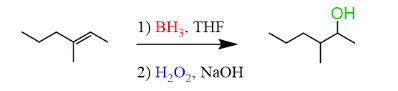
Hydroborate oxidation (anti-markovnikov)
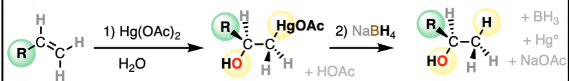
Oxymercuration-demercuration of alkenes to alcohols
markovnikov additionhy
Hydrohalogenation of alkenes
Halogenate vicinal dihaloalkane from alkenes
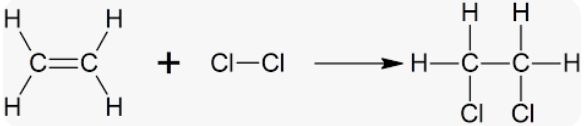
Anti addition of halohydrins from alkenes
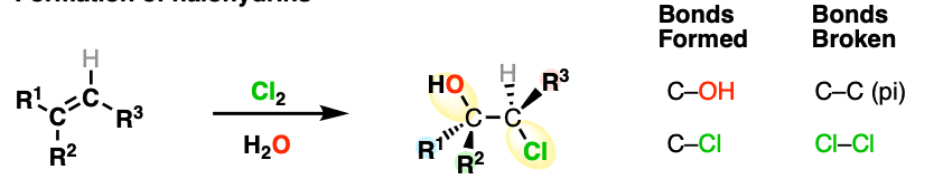
Hydroxylation of alkenes to form 1,2-diol
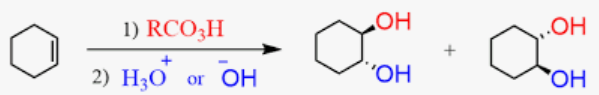
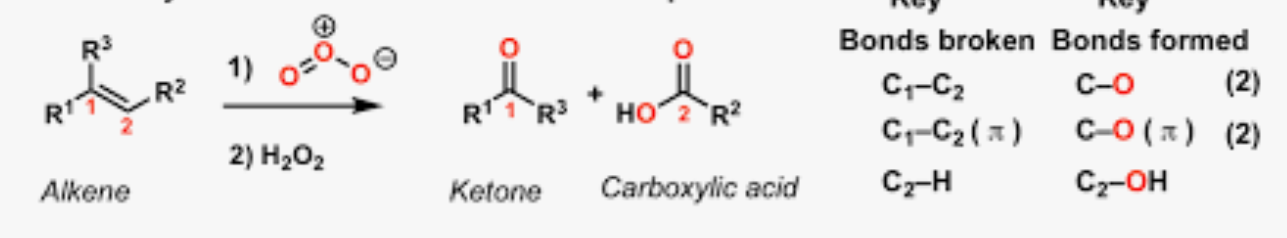
Oxidation of alkenes to carboxylic acid
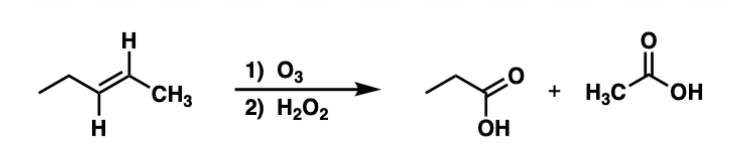
Ozonolysis of alkenes to form ketone
Hydrogenation of alkenes to alkane
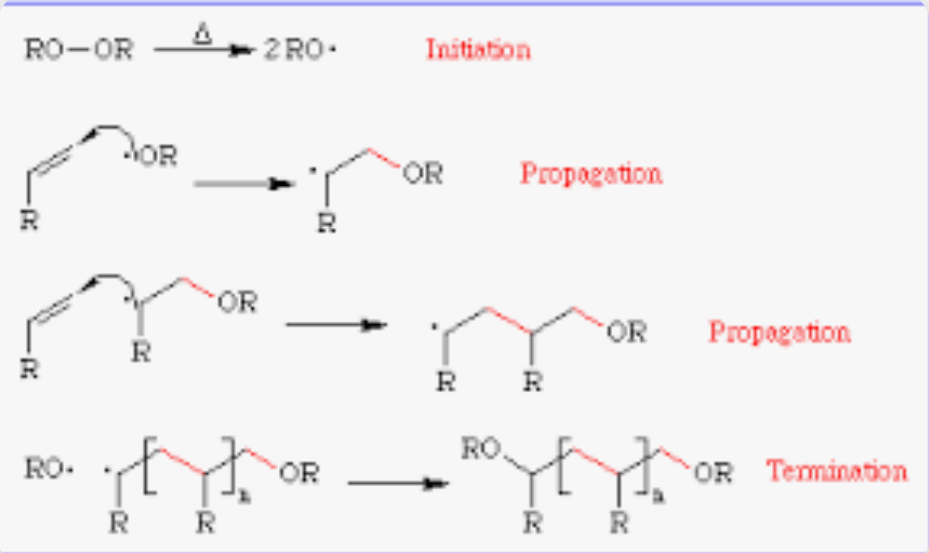
Free radical polymerization of alkenes
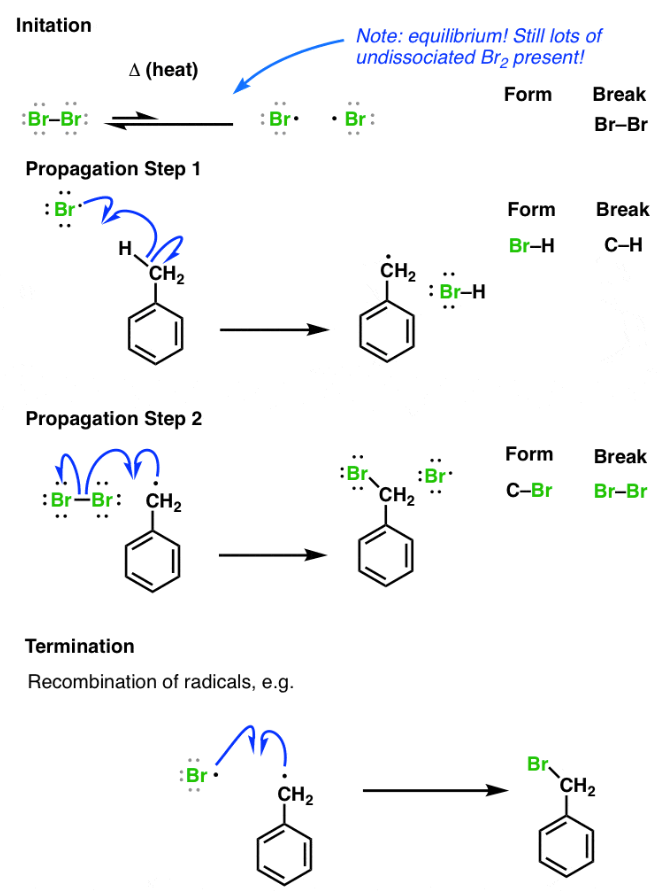
Allylic halogenation of alkenes
Diels alder of alkenes
Properties of benzene/arene
Insoluble in water, miscible with non-polar organic solvents
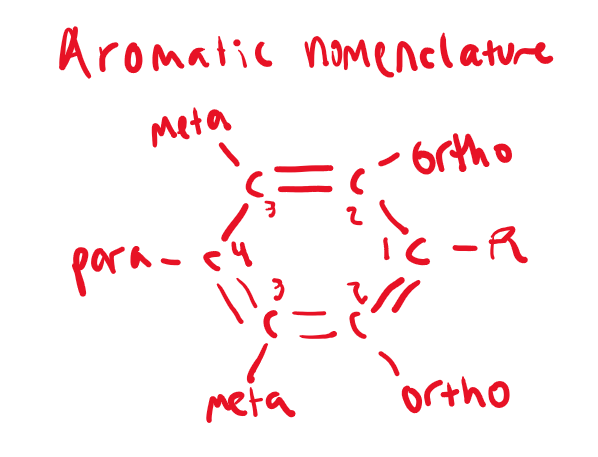
Aromatic nomenclature guideline
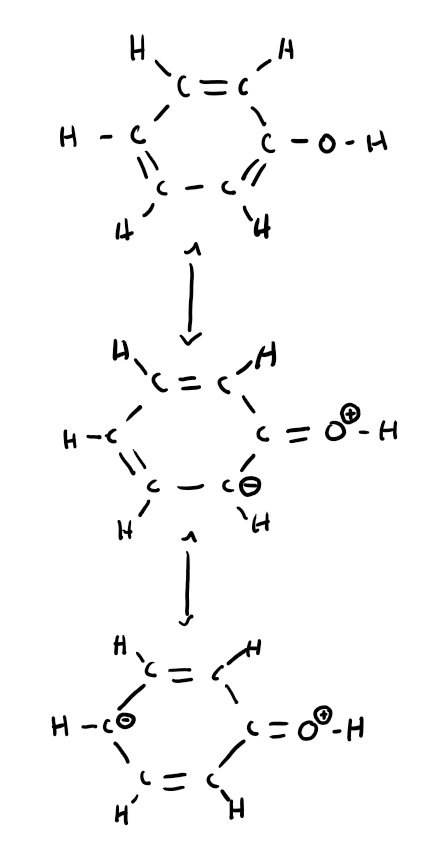
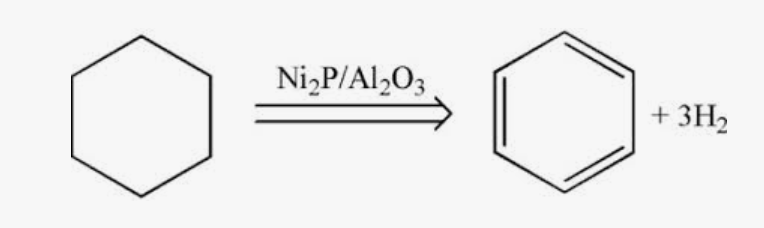
Dehydrogenation of cyclohexane to form benzene
Combustion of benzene
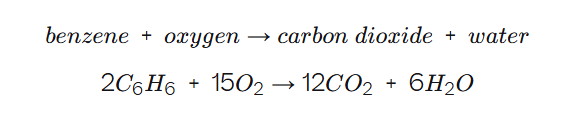
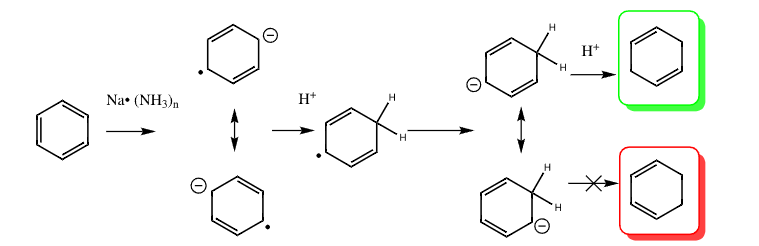
Birch reduction of benzene to form 1,4 cyclohexadiene
Hydrogenation of benzene to form cyclohexane
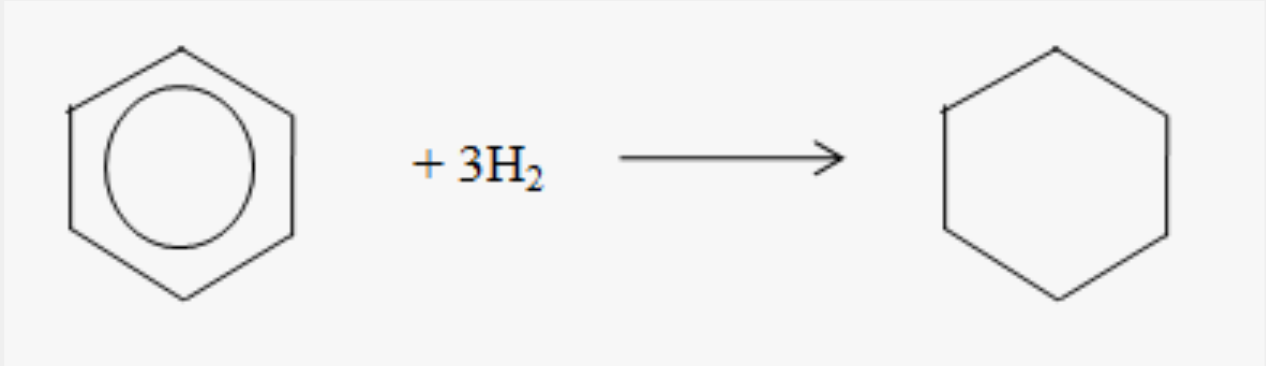
Alkylation of benzene
electrophilic substitution
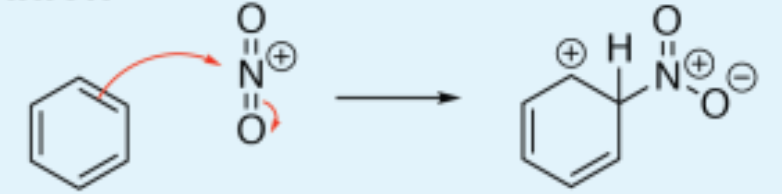
Nitration of benzene
electrophilic substitution
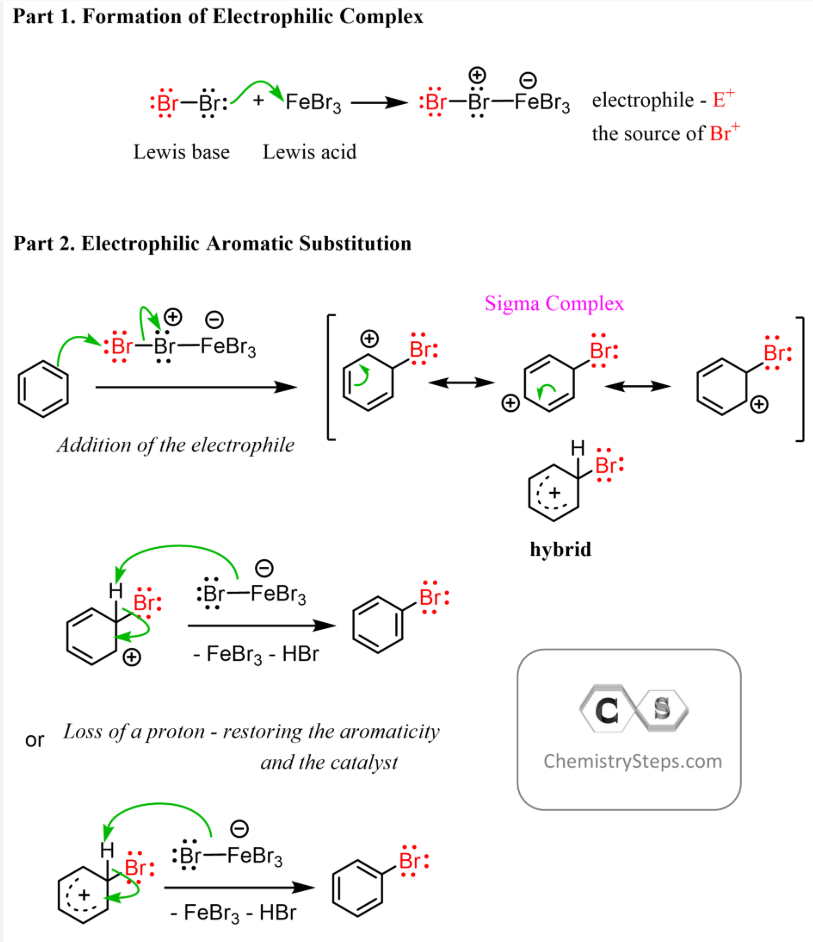
Halogenation of benzene
electrophilic substitution
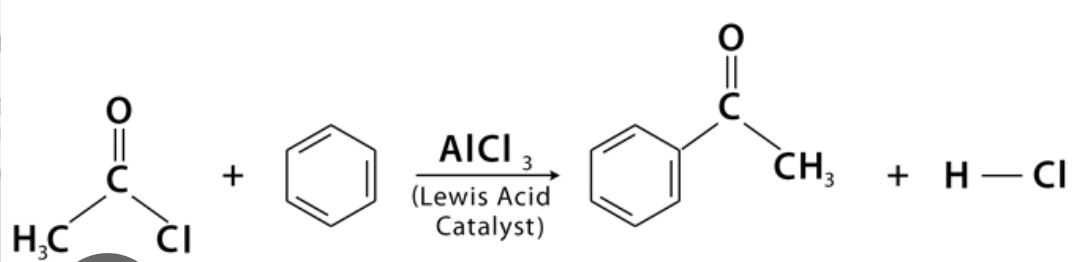
Acylation of benzene
electrophilic substitution
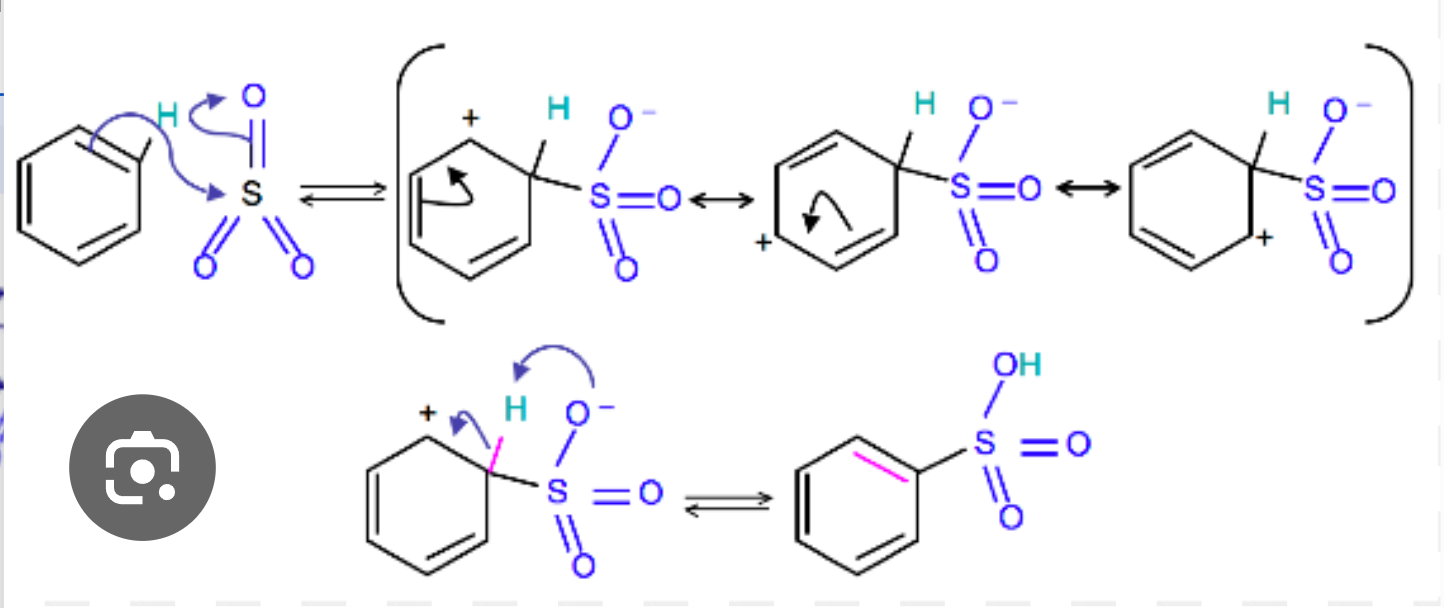
Sulfonation of benzene
electrophilic substitution
Activating group
a substituent that increases the rate of electrophilic substitution reactions on a benzene ring. Adds electrons to the ring, destabilizes the arenium cation.
Deactivating group
a substituent that decreases the rate of electrophilic substitution reactions on a benzene ring. It withdraws electrons from the ring, stabilizing the arenium cation.
Ortho/para director
A substituent that directs incoming electrophiles to the ortho and para positions of a benzene ring, typically activating groups that add electron density.
Examples of ortho/para directors
-NR2, -OH, -R, -OR, -X(halogen)
Meta-director
A substituent that directs incoming electrophiles to the meta position of a benzene ring, typically deactivating groups that withdraw electron density.
Examples of meta-directors
-NO2, -CN, -COOH, -SO3H, -COOR, -CHO, -CRO
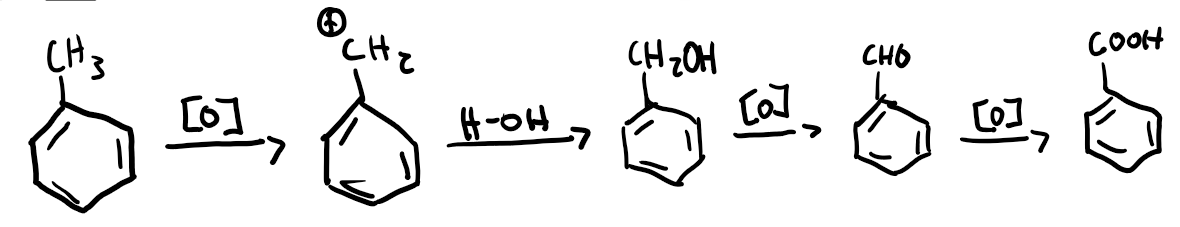
Reaction of toluene to form benzoic acid
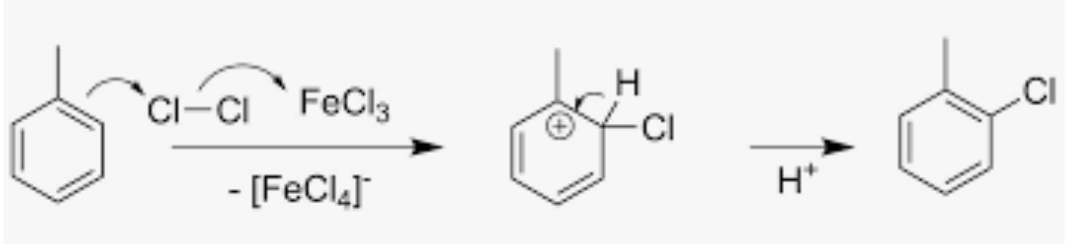
Chlorination of toluene
The number in the name of alkynes
denotes the position of the triple bond
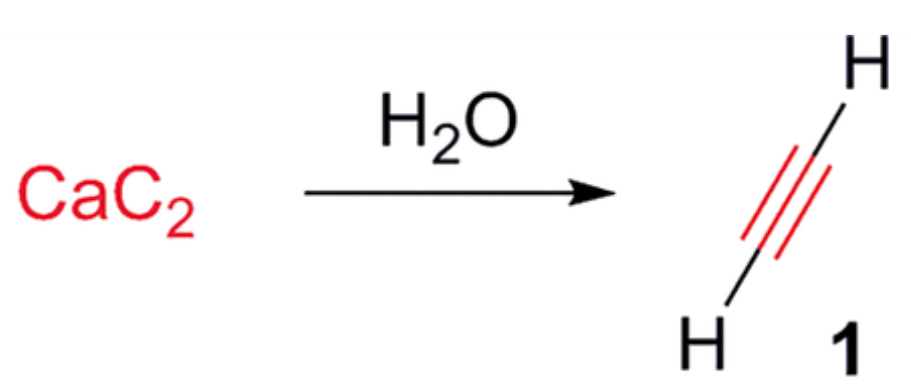
synthesis of alkynes from Calcium Carbide
CAC2 +H2O => Ca(OH)2 + C2H2
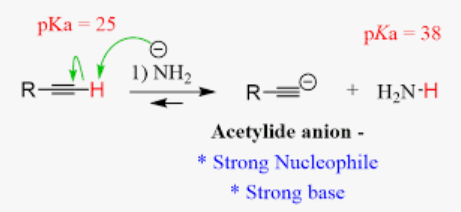
Alkylation of terminal alkyne
Reduction of alkynes
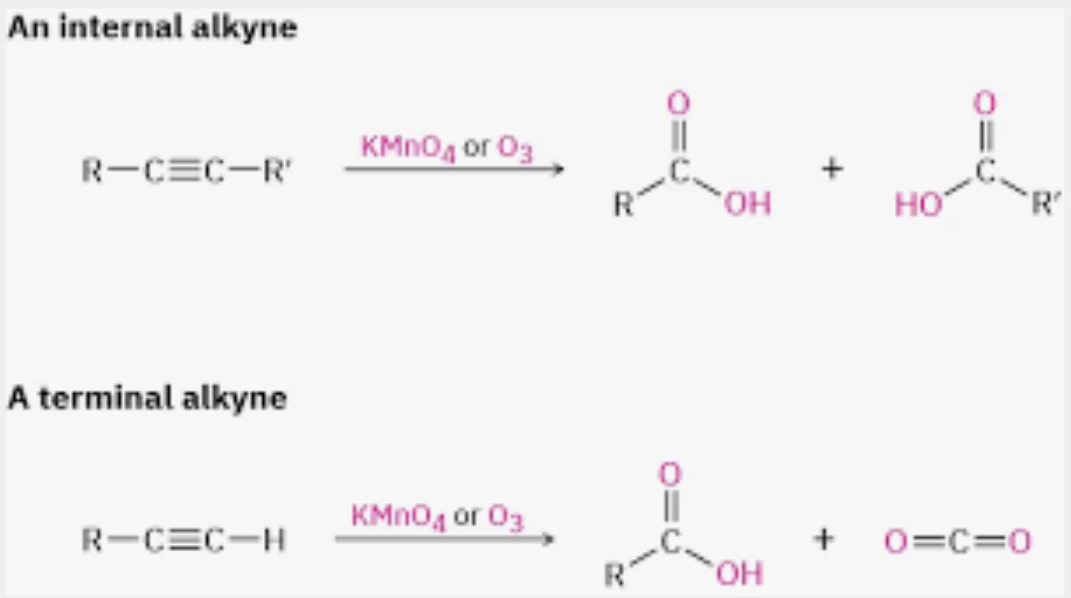
Ozonolyzation of alkynes to form carboxylic acid
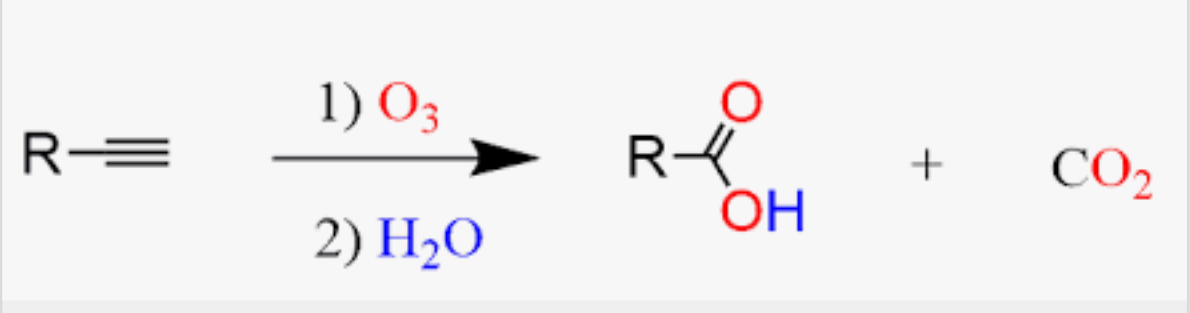
Oxidation of alkynes to form carboxylic acid
O/P director