8 Anatomy of the maxillofacial skeleton and introduction to radiological interpretation
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
dental radiographic images are 2D representations of the 3D teeth and bones of the skull
soft tissue shadowing, is for the most part, not relevant
it is important that you are aware of the whole skull but particularly the maxilla and the mandible
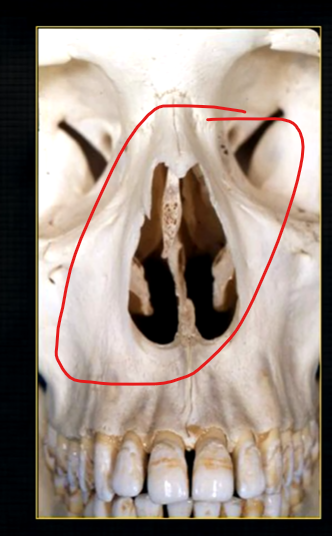
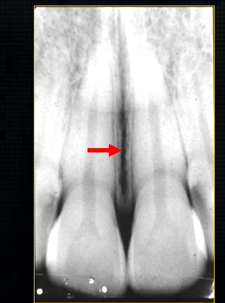
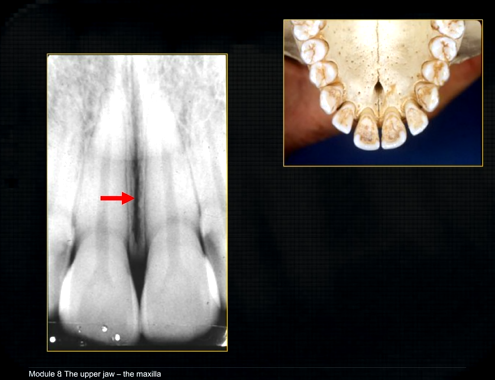
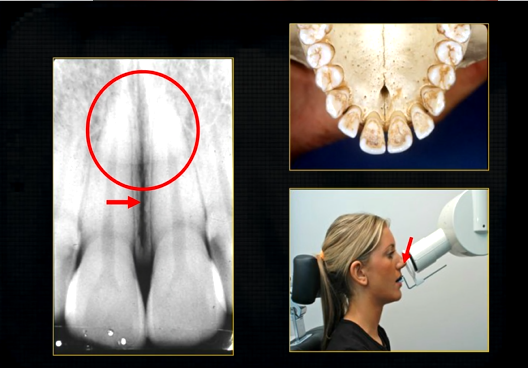
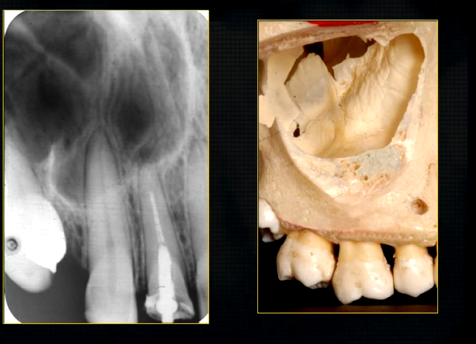
the upper jaw - the maxilla - what is circled in red?
the nasal cavity
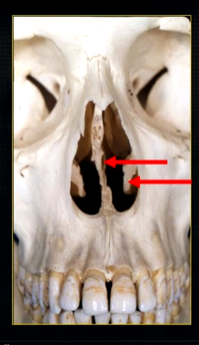
what is seen here?
the nasal septum and the inferior nasal concha
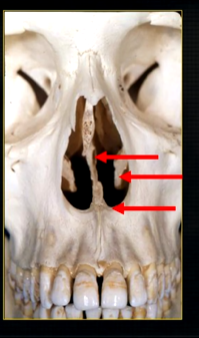
what is the bottom arrow showing?
the floor of the nose - just above the apices of the upper anterior teeth
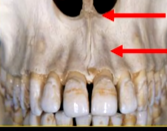
what can you say about the surface anatomy of the maxilla around the teeth themselves?
very undulating - prominences over roots
bony spike of the anterior nasal spine
becomes visible at the side view
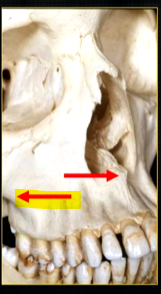
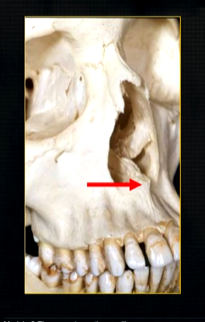
posteriorly, the maxilla….
widens as it articulates with the zygoma or cheekbone
The zygomatic buttress is a key vertical support structure of the midface, formed by the junction of the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the zygomatic bone
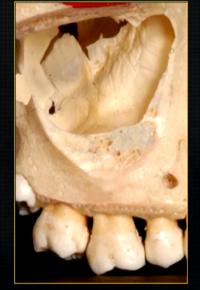
underneath the surface layer of the maxilla
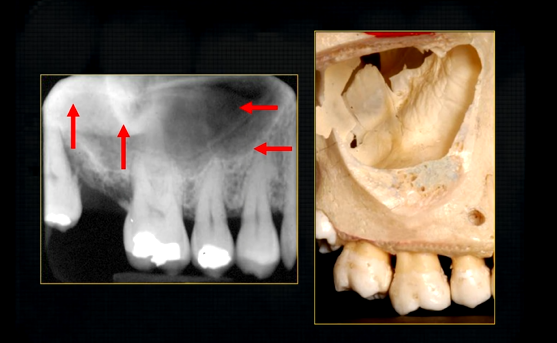
large cavity - maxillary air sinuses /antrum -can extend anteriorly almost to the midline or posteriorly, to hollow out the zygoma
maxillary sinus is evident radiographically when the upper posterior teeth are shown

internally, the maxillary sinus is not smooth ….
there are small ridges and bumps- thin in cross sections - can appear as dense white opaque lines radiographically
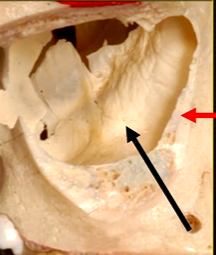
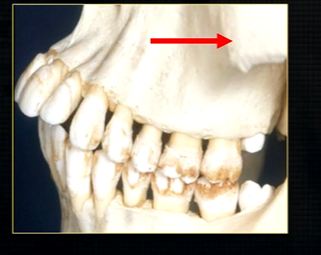
bulk/prominence of the zygomatic cheekbone - radiographically this can overly the apical tissues of the upper molar teeth - solid, dense, white shadow
if its hollowed out by the maxillary sinus, it casts a white, radiopaque U shaped shadow - radiolucent centre
what is the canine prominence?
bony undulation over the canine root that is especially prominent
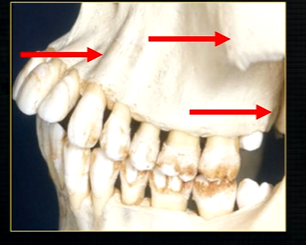
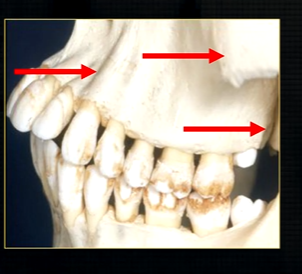
the end of the maxilla can be described as,
smooth, rounded end - called the tuberosity
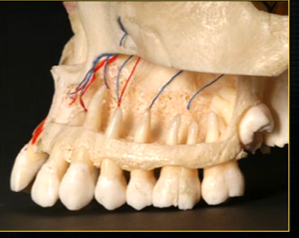
when the thin, surface bone of the maxilla is removed …
can see the roots of the teeth as they are positioned in the alveolar part of the maxilla
the alveolar bone has an internal trabecular, honeycomb appearance - wide enough to envelope all the roots of the posterior teeth
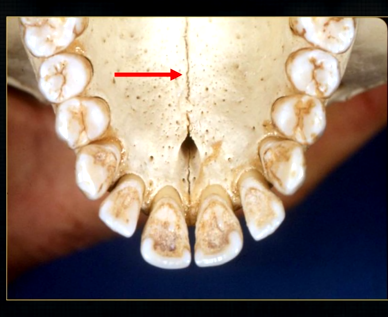
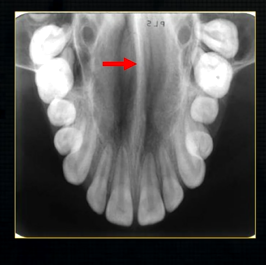
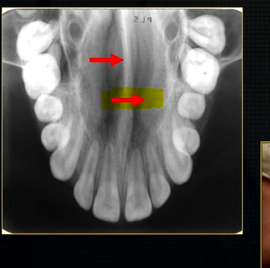
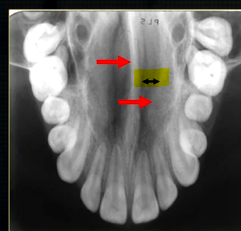
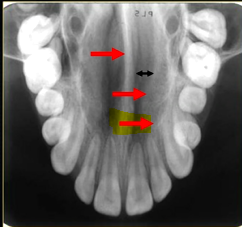
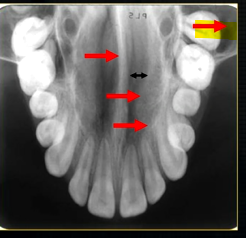
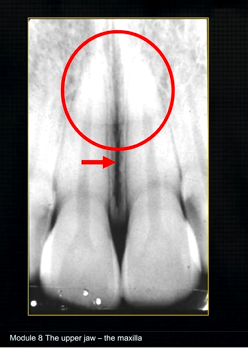
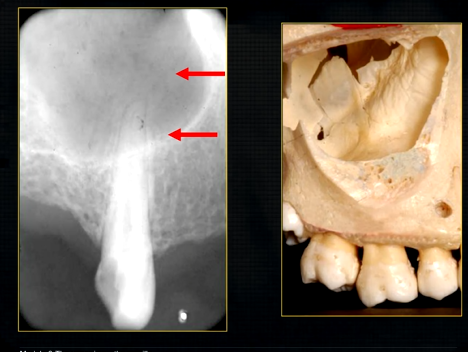
what is this thin line over the palate?
mid-palatal suture
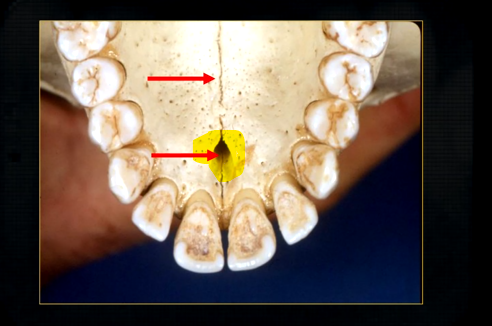
what is this large hole?
naso-palatine foramen
resultant radiographs are always 2d demonstrations of a 3d object - all structures, internal and external will be superimposed on one another
how the anatomy is presented geometrically is dependent on the relative positions of the patient, image receptor and the X ray beam
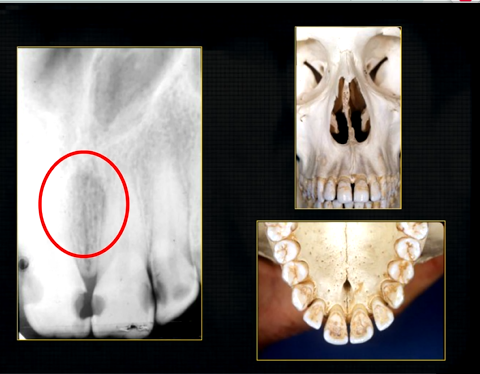
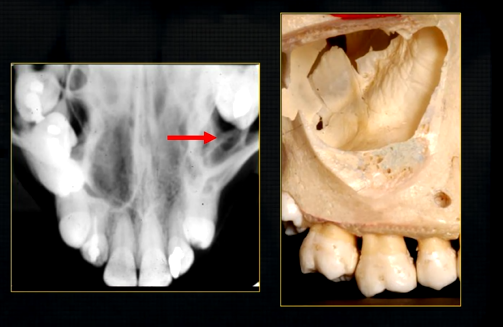
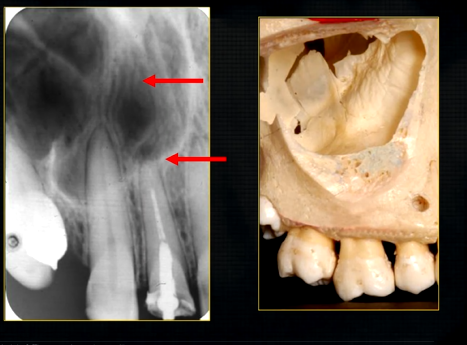
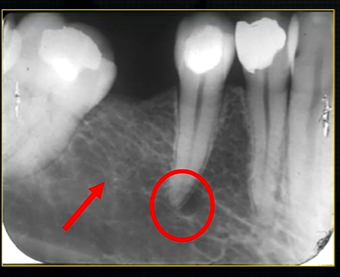
what does this anterior periapical graph show?
oval radiolucent area between the central incisors - is it Infront of the teeth (buccally?) or is it behind them? - you can’t tell radiographically
but its shape and position is compatible with the palatally positioned with the nasopalatine formaina
more posteriorly - radiopacities indicate the nasal septum and floor of the nose
dense, thin , white line in the middle of the image is the nasal septum
less dense opacity is caused by the
inferior nasal concha
radiolucency - nasal septum
lateral wall of the nose
maxillary air sinus
mid-palatal suture
this increased radiopacity is caused by the soft tissues at the tip of the nose - shadow - dense tissue
occlusal view shows how maxillary air sinus varies in size
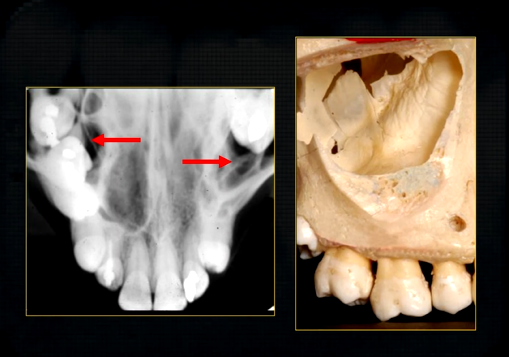
density of the maxillary sinus varies
blacker in some parts than in others
shape varies and the density of the overlying bone varies
radiolucent, antral air cavity and the radiopaque white line of the anterior wall and floor
faint lines in the maxillary air sinus represents the irregularities in the wall
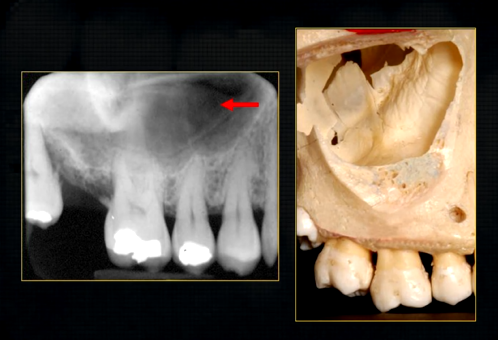
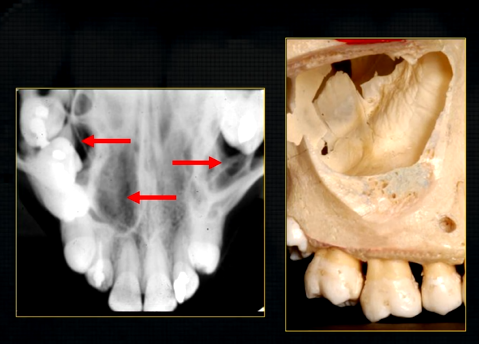
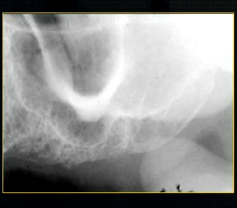
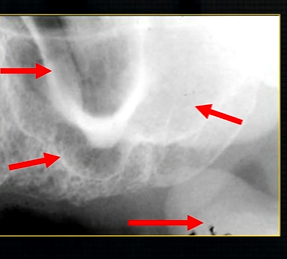
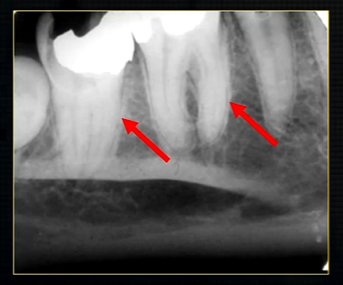
periapical radiograph → posterior maxilla
radiolucent maxillary sinus and radiopaque floor
radiopaque shadow cast by zygoma, hollowed out by maxillary sinus
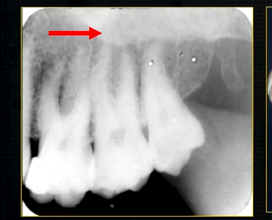
lower end of the dense, zygomatic bone
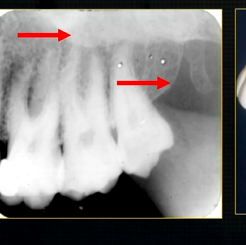
posterior aspect of the maxilla - smooth round tuberosity
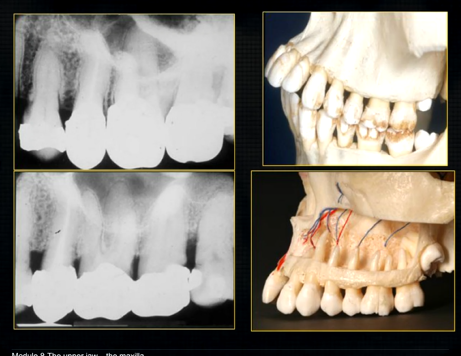
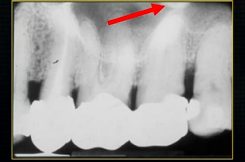
1st image taken using the bisected angle technique
2nd was taken using the geometrically accurate, paralleling technique
upper image is geometrically distorted
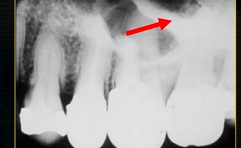
shadow caused by zygoma
this was taken using the bisected angle technique
x ray beam was directed below the zygoma
very lower of the zygoma is seen - projected above the apices
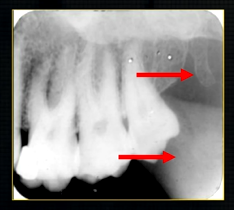
pterygoid hammulus - supports the muscles of the soft palate
coronoid process of the mandible
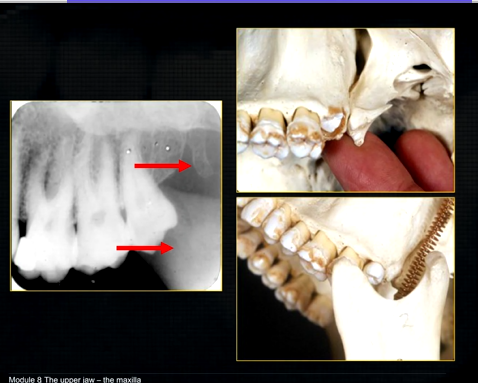
edentulous patient
can see u shaped edge of hollowed out zygomatic bone
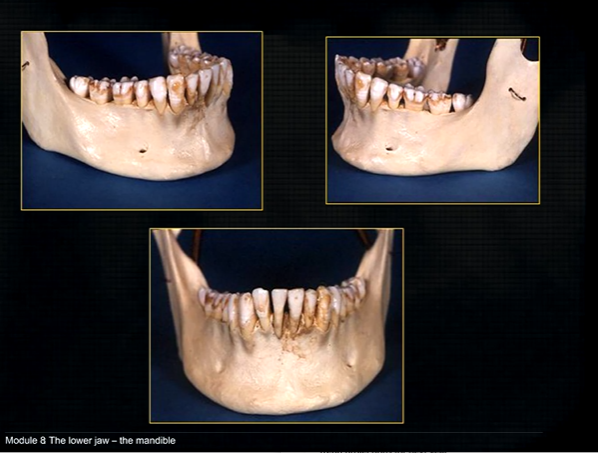
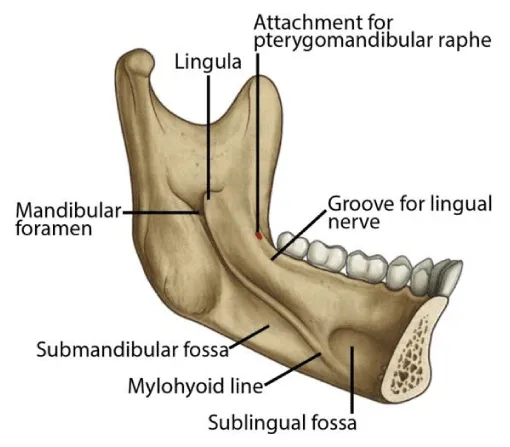
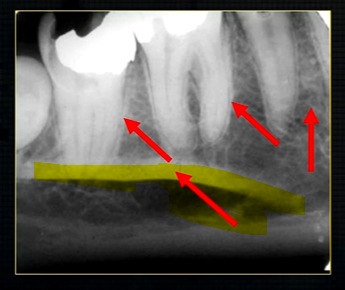
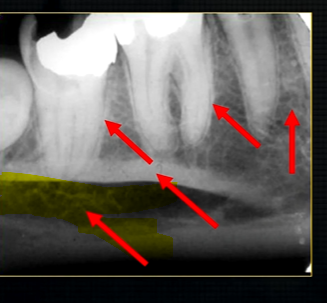
mandible - the lower jaw
mental prominence
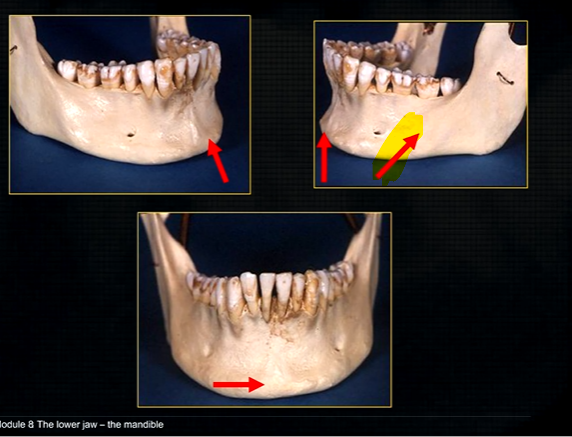
body
mental foramina
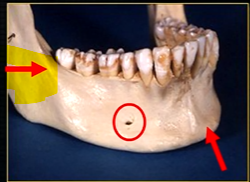
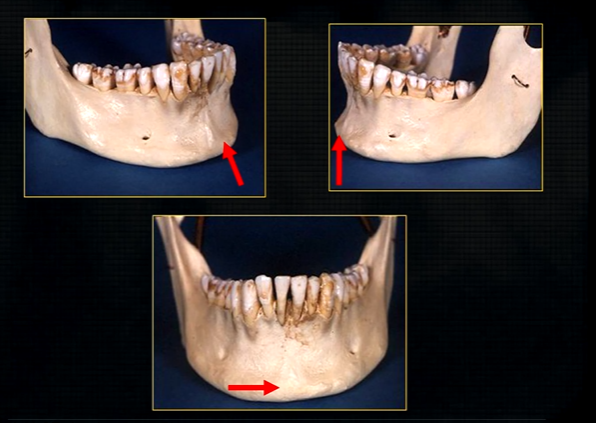
dense bony prominence of the external oblique ridge
angle
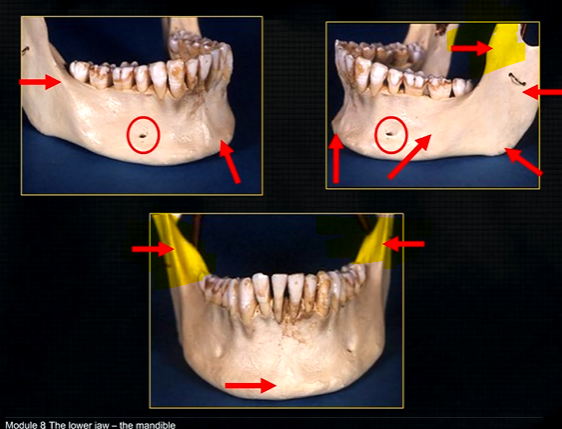
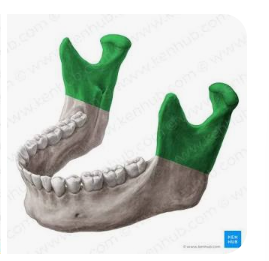
coronoid process - and ascending rami on both sides????
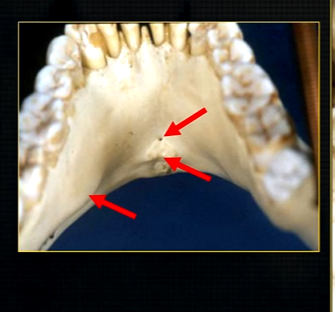
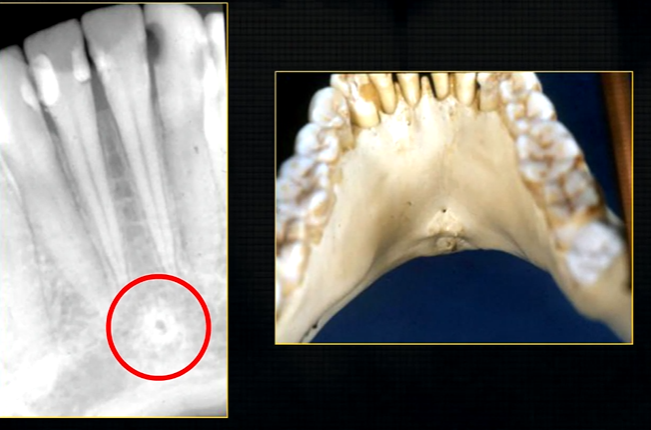
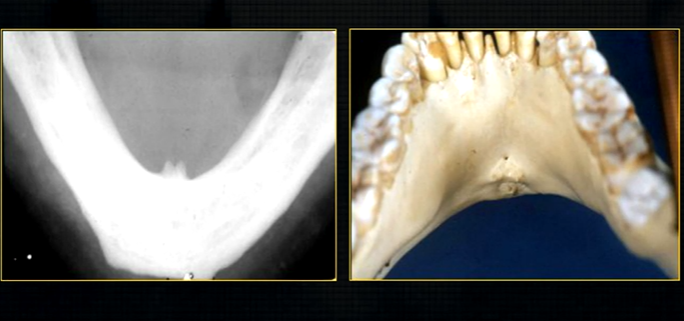
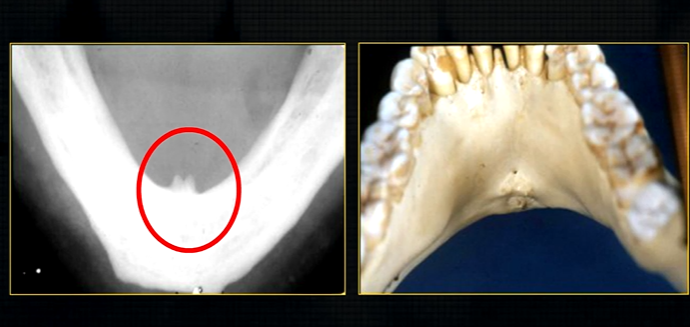
anterior lingual/inner aspect of the mandible
bony spurs
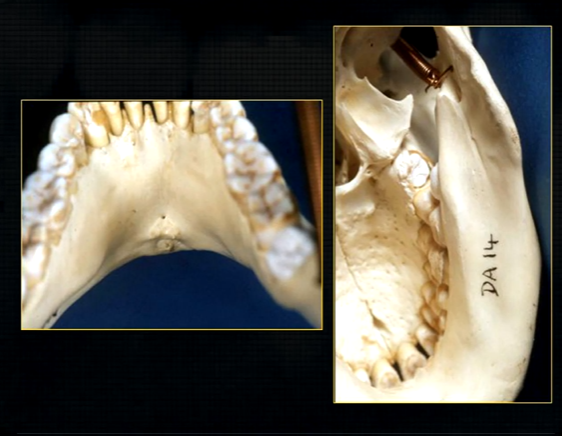
genial tubercules - muscles of the tongue and neck attach here
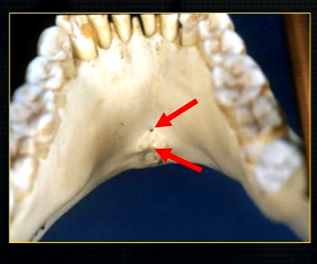
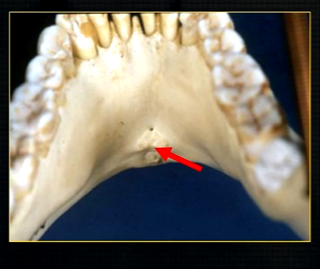
lingual pit
mylohyoid ridge - mylohyoid attaches to form the floor of mouth
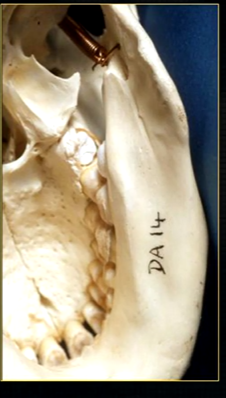
mandible varies in cross sectional thickness
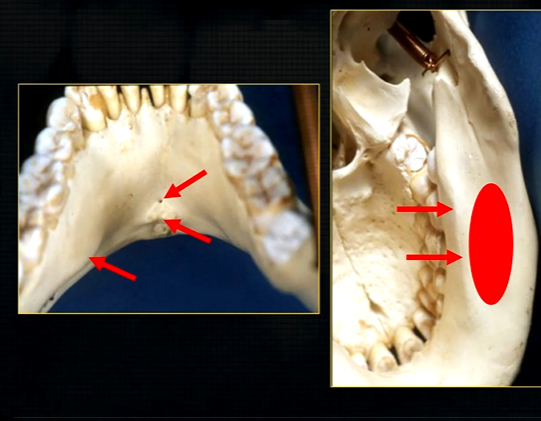
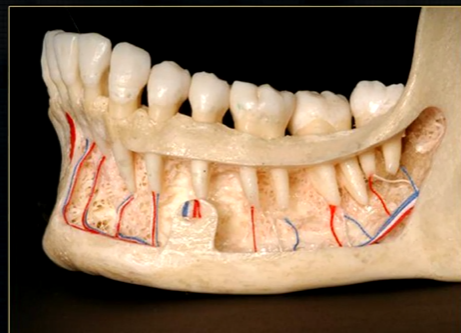
left hand side of the mandible buccal surface has been removed
roots of the teeth protrude in the underlying trabecular bone
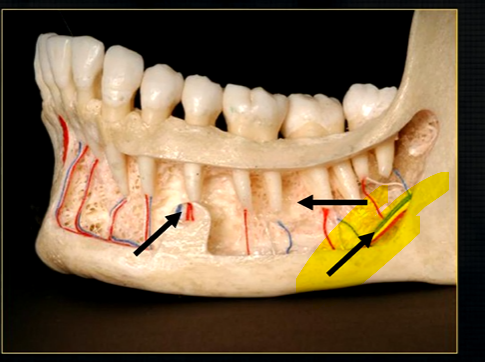
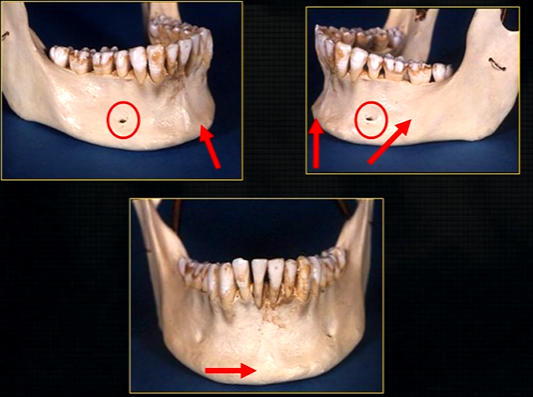
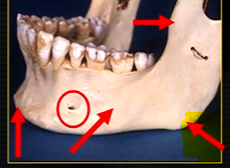
inferior dental nerve
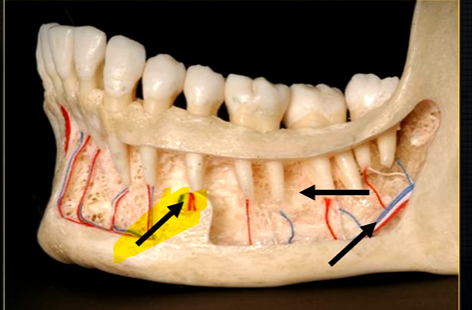
mental nerve - coming out of the mental foramen
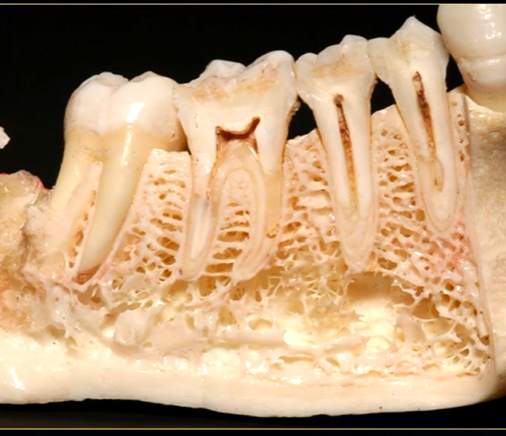
reveals honeycombed pattern of trabecular bone
dense outline of the individual sockets of the teeth
cortical bone which forms the lower border
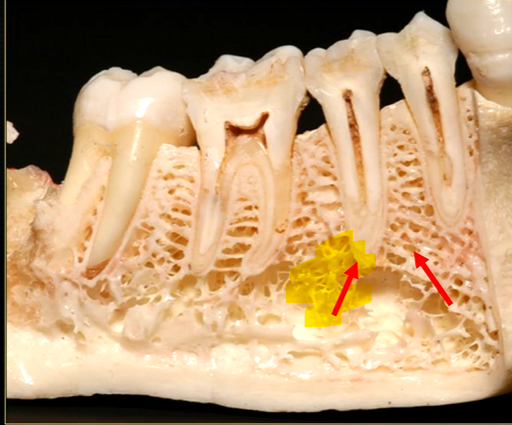
periapical region
can see honeycombed pattern
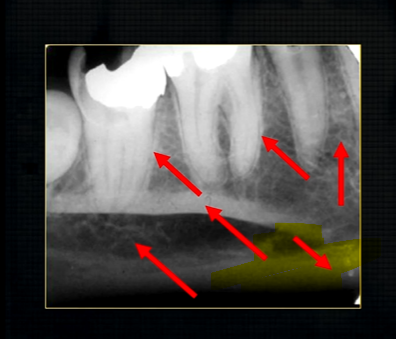
mental foramen - black radiolucency - near 1st and 2nd premolars
sockets of the teeth are represented by thin, white, opaque lines → ‘ lamina dura’
dense, white, radiopaque line → dense bone of mylohyoid ridge
underneath mylohyoid ridge - looks more radiolucent → this is due to the lingual indentation of submandibular fossa
dense cortical bone of the lower border
radiolucent shadow created by the lingual pit
lower occlusal
small bony spurs of the genial tubercles
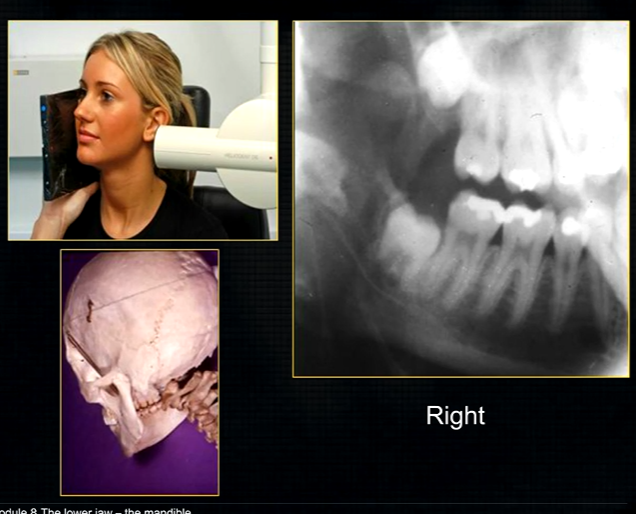
oblique lateral technique allows you to take extraoral radiographs
image receptor is placed outside the mouth and against the side of the face
resultant radiographs are larger and show anatomical structures in both jaws
direction of Xray beam on this skull
for right hand side - tube head left and receptor opposite - passes between the cervical spine and the left ascending ramus of the mandible - viewed like you are looking at the patient’s right cheek
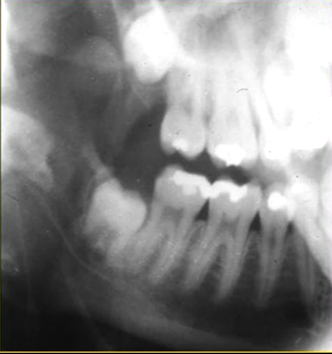
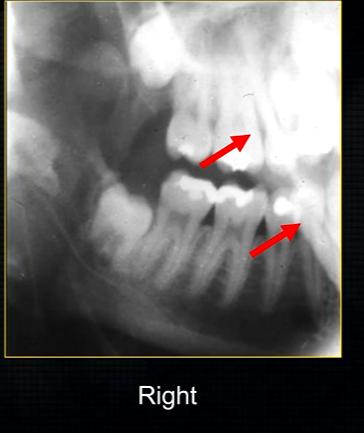
posterior edge of left side
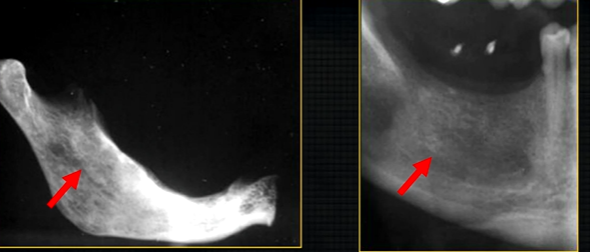
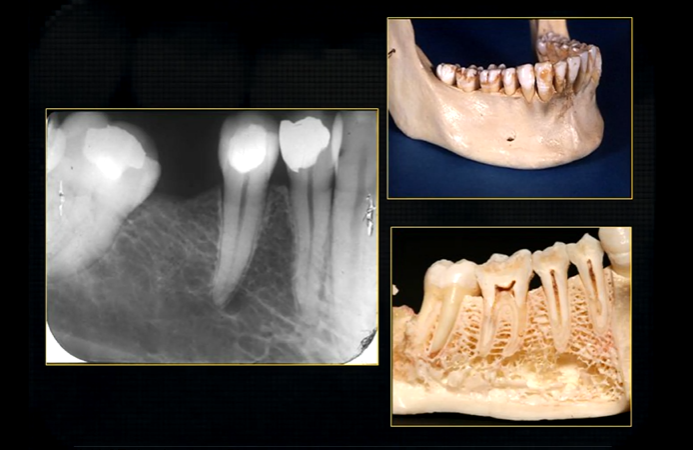
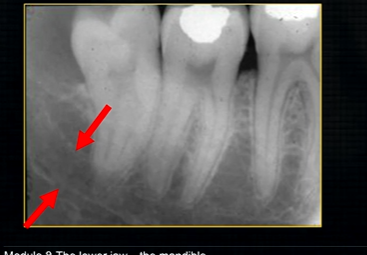
radiolucent band around the posterior part of the body of the mandible
created by inferior dental nerve and blood vessel, created by the inferior dental canal
the edges of the canal can be seen as thin, white radiopaque lines → ‘tram lines’
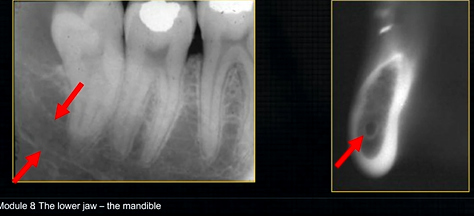
inferior dental canal can easily be seen in cross sectional dental images
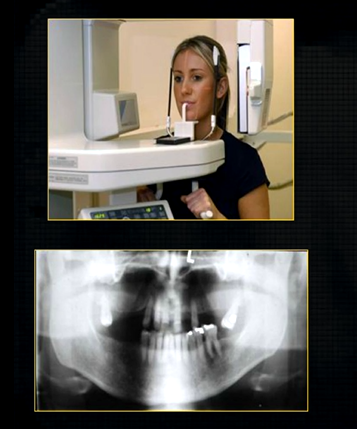
to see both jaws, a panoramic radiograph can be taken
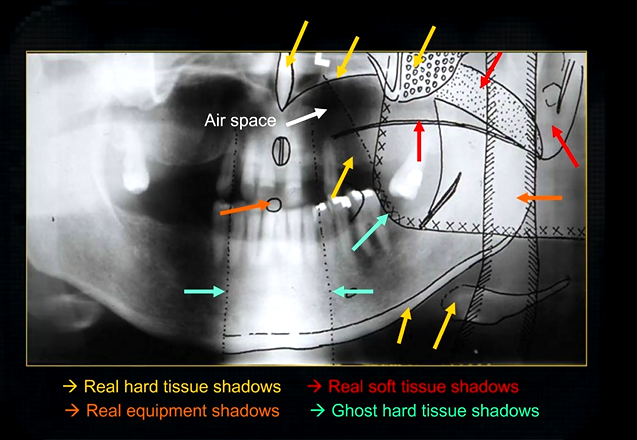
this creates a complicated radiograph with several types of shadows superimposed on top of each other - image shows why the cervical spine appears on both sides of the image - anatomical structures are severely distorted
real hard tissue shadows
real hard tissue shadows of nasal septum, hard palate, maxilla, zygoma, mandible and the hyoid
real soft tissue shadows
real soft tissue shadows of the soft palate, ear lobe and the dorsum of the tongue
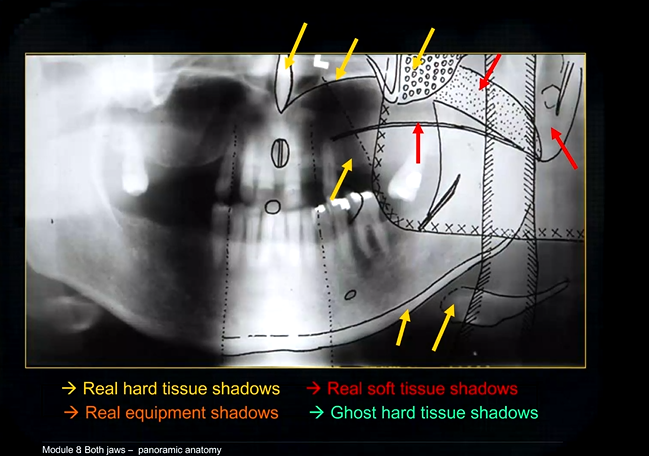
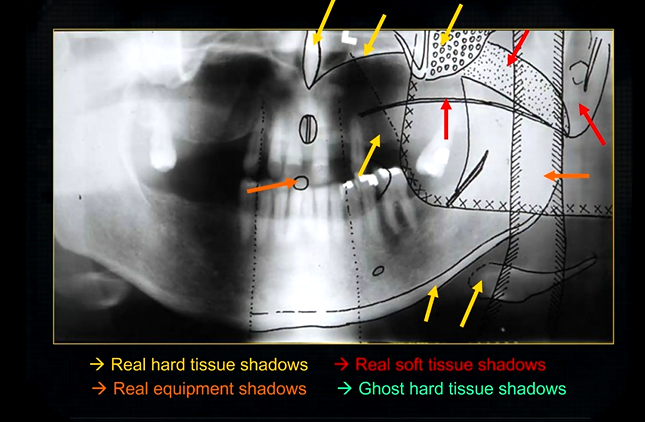
real equipment shadows
bite peg and the plastic head support
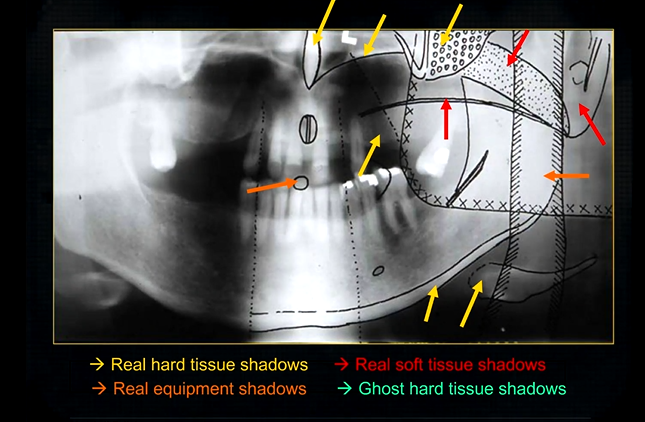
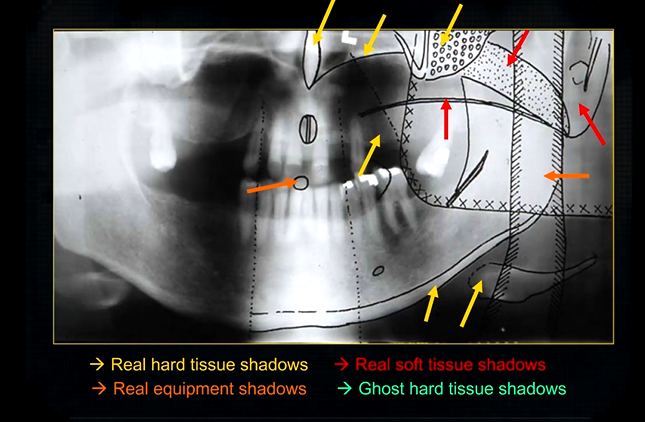
ghost hard tissue shadows
mandible from the opposite side
cervical spine
shadows of the air space - between the tongue and the roof of the mouth