Week 3,4,5 - Carbonates
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Conditions for high carbonate production
Light
Nutrients
Warm water
High salinity
Shallow subtropical shelves
Lithofacies
Modern sediments reflect different physical environments (water depth, energy, nutrient supply)
Biogenic and/or abiogenic sediment composition
Analysis reconstructs depositional environments and processes
Order of tidal zones
Peritidal (Supratidal → Intertidal)
Subtidal
Features of the peritidal zone
Range <2m
Low faunal diversity
Subtidal sediment source
Regions of intertidal channels
Algal mats
Structures depend on climate
Why does the peritidal zone have low faunal diversity
2x a day organisms go from being under saline water to exposure to the air -> stressed environment -> lower biodiversity
How do textures in clays form
Clays expand when wet then contract when dry leading to mudcracks, desiccation polygons, fenestrae, lamination and bioturbation
Features of the subtidal zone
Ponds and tidal channels
High biodiversity with high abundance of skeletal fauna
Bioturbation
Fining upwards and levee deposits
Peritidal zone in an arid climate
Halite crusts, gypsum, anhydrite
Dolomite
Algal mats
Dessication cracks
Windblown deposits
Formation of karsts
Low pH water percolates through limestone -> dissolution of limestone -> infill of sandstone above -> diagenesis
Features of open shelves and lagoons
Moderate-low energy environments
Muddy sediments, bioclasts
Often burrowed
Separation based on degree of connection to the open ocean
Features specific to open shelves
Normal salinity
Abundant and diverse fauna
Features unique to lagoons
Elevated salinity
Abundant but low diversity fauna which can tolerate salinity fluctuations
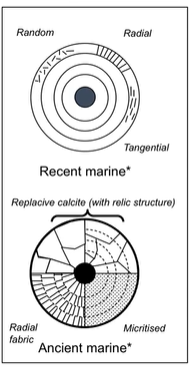
Micritisation
The action of cyanobacteria in the clasts of carbonate sediments retract nutrients from theing carbonate
Features of sand bars and shoals
High energy
High carbonate production
Grainy sediments
Important reservoirs
Restrictions on echinoderms
Must be normal salinity
Implications of cross stratification
Current was present as there was energy moving the sediment
Appearance of bivalves in thin section
Line of symmetry between two shells
Long and curved grains
Appearance of gastropods in thin section
Variable shape
Common shallow marine and terrestrial

Corals in samples
Rugose + tabulate (Paleozoic) - high Mg calcite with high preservation potential
Scleractinian corals - aragonite skeletons with lower preservation potentials
Septa -> Rugose/Scleractinia
Tabulae -> Tabulate
Warm clear waters
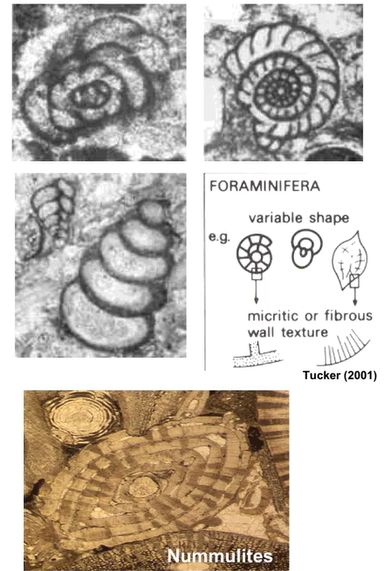
Echinoderms in samples
Crinoids, starfish, sea urchins
Internal calcite skeleton
Normal salt content
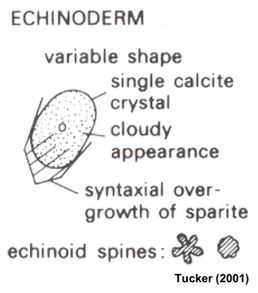
Foraminifera
Small calcitic organisms
Benthic
Cambrian - recent
Algae in samples
Green -> visible filaments and no ordered internal structures, productive <15m depth
Red algae -> tiny rectangular pores, greater depths
Ooids
Spherical grains with concentric layers surrounding the nucleus
<2mm
Usually marine
High energy environments
Oncoids
Coated grains with concentric but irregular layers
Lack distinct nucleus
Usually shallow marine
Peloids
Structureless grains
100-500 microns
Well rounded and ellipsoidal
Derived from clasts
Grain aggregates
Form by algal binding and cementation
Binding and grapestone stage → lump stage
Intraclasts
Reworked partially lithified local material from within the basin
Extraclasts
Lithified material from outside the immediate depositional area
Lime mud
Micrite (calcium carbonate crystals <62 microns)
Originally aragonite or calcite replaced by low Mg calcite
Fills pores, borings and burrows to form rocks
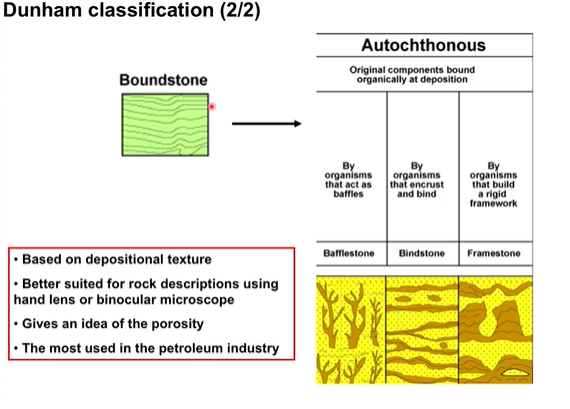
Dunham classification
Organic/skeletal reefs
Rigid calcareous organisms
Matrix or skeleton supported
Deposited in warm or cold water
Able to withstand high energy wind/wave action
Reef/mud mounds
Inorganically and/or biogenically constructed
Lack a rigid skeletal framework
Unable to withstand high energy wind/wave action → deeper water settings
‘Fine grained, mud (micrite)-dominated build-ups
Stability provided by matrix, limited cementation
Organic components include bivalves, corals, sponges, bryozoa, microbes, stromatoporoids
Heterotrophic and biologically influenced/induced carbonate precipitation
Low topographic relief
Bioherm
Massive reef structure which forms distinct topography
Biostrome
Massive core which passes laterally consistent with the bedding
Constructive processes
Biological processes through direct growth, baffling and binding
Destructive processes
Wave damage and biological destruction
Cementation
Early cementation from seawater
Sedimentation
Accumulation of biogenic matter and reed derived detritus
4 stages of reef building
Pioneer
Colonisation
Diversification
Domination
Corals in high sedimentation rate areas
Long branches working upwards to reach the light
Corals in high energy rate areas
Strong and robust to withstand wind and wave action
Areas of a reef
Back reef
Reef flat
Reef front
Fore reef
Reef flat
Depths up to 10m
Reworked reef debris
Carbonate sand
Bioerosion
Reef crest
Encrusting organisms
Bioerosion
Periodic subaerial exposure
Bindstones and framestones
Reef front
Extensive coral growth seaward of reef crest
High energy zone
Low preservation potential
Forereef
Transition to basin
Sedimentation from grabity flows
Rudist
Cretaceous bivalve which appears like a coral
Basin deposition
Deep water
Low energy
Settling out of suspended material
Main extrinsic force causing lateral migration of facies
Sea level fluctuation
Transgression
Shallow water environments get progressively deeper
Regression
Deep water environments get progressively shallower
Eustacy
Over time sea level changes relative to the center of the Earth
Driven by the volume of water in the ocean due to change in glacial ice volume
Volume of ocean basins related to tectonic spreading rates
Time scale >10^6 years
Subaerial exposure
When sea levels drops below the top of the system
Formation of karsts on the surface from the slightly acidic rainwater leading to dissolution of carbonates
Effect of influx of silicilastics on reef growth
Suspended mud limits light penetration in the water column → inhibits carbonate formation
Mud settles slower than sand
What forms chalk
Coccoliths (cretaceous onwards)
Hothouse climates
High tectonic spreading rate
Dispersed continents
High sea level
Increased CO2
Calcite dominated seas
Icehouse climates
Low spreading rate
Supercontinents
Decreased CO2
Aragonite seas