Science Test-May 8th
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
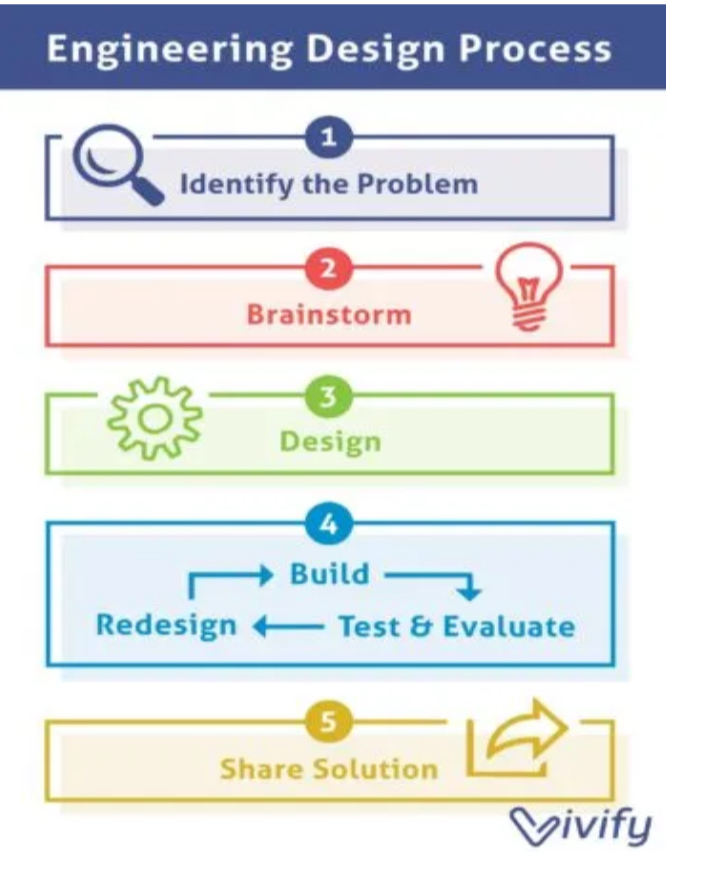
Engineering Design Process
A series of steps that engineers follow to come up with a solution to a problem
Force
A push or a pull
Field
An area that surrounds an object and extends though space, which may exert a force on another object.
Non-contact force
Forces that affect objects without touching
Gravitational force
The amount of gravitational pull between objects
Balanced force
When the opposite forces acting on either side of the object are equal (net force of zero)
Unbalanced force
When the opposite forces acting on either side of tge object are NOT equal (net force greater than zero)
Net force
The combined force (in strength and direction) acting on an object
Newton (N)
The unit for measuring the strength of a force
Force Diagram
A simple labeled diagram that shows the forces acting on an object as arrows that indicate the magnitude and direction of the force
Newton’s first law of motion
An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force

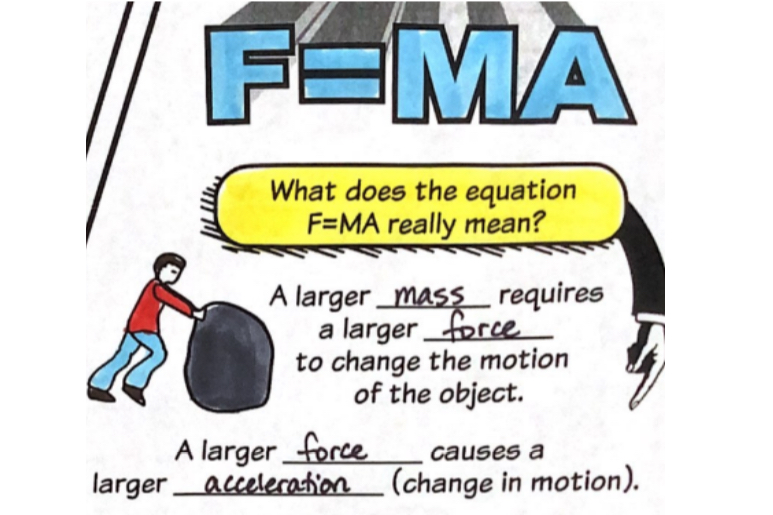
Newton’s second law of motion
The acceleration of an object depends on the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object (F = MA)
Newton’s third law of motion
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction

Conductor
An object that supports the transfer of thermal/electrical energy
Insulators
Any material resistant to the flow of thermal/electrical energy
Electron
An negatively charged particle found outside the center of the nucleus of an atom
Proton
A positively charged particle found within the nucleus of an atom
Static Discharge
A quick flow of electricity from one object with static electricity to another
Electric charge
A tiny particle that interacts with other charges (positive or negative)
Electric Field
A field that exerts a force on charged particles or a charged object
Electromagnetism
The phenomenon of generating an electric field from a magnetic field. Likewise, a magnetic field can be generated by an electric field
Magnetic Force
A force between objects due to the magnetic properties of each object
Magnetic Field
A field that affects objects with magnetic properties
Permanent Magnet
A magnet in which the domains are well aligned in the material and are no easily changed
Temporary magnet
An object that is unmagnetized in its natural state but can become magnetized when placed in a magnetic field
Attract
Force that causes objects to come together, even if those objects are not close or even touching each other
Repel
To force (something) to move away or apart
Friction (Ff)
A force that opposes motion, working in the opposite direction of the moving object
Tension (Ft)
A force created when two objects pull on a rope, string, or wire in opposite directions
Normal (Fn)
A force exerted by a surface on an object resting on that surface
Air Resistance (Far)
A force working in the opposite direction of a falling object, like “air friction”
Applied (Fa)
A force applied by a person or object onto another object
Spring (Fs)
A force created by a stretched or compressed spring
Buoyancy (Fb)
A force that pushes fluid upward on a immersed object, or floating object
Gravitational (Fg)
A force of attraction between any two objects with mass
Electrical (Fe)
An invisible force created by electrically charged objects
Magnetic (Fm)
A force created by magnets or objects with magnetic properties