HL Biology Paper 2: Mistake's I've Made
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Nitrogen is part of many important substances in living organisms.
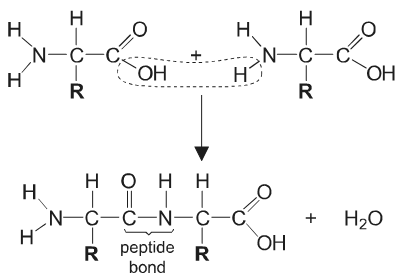
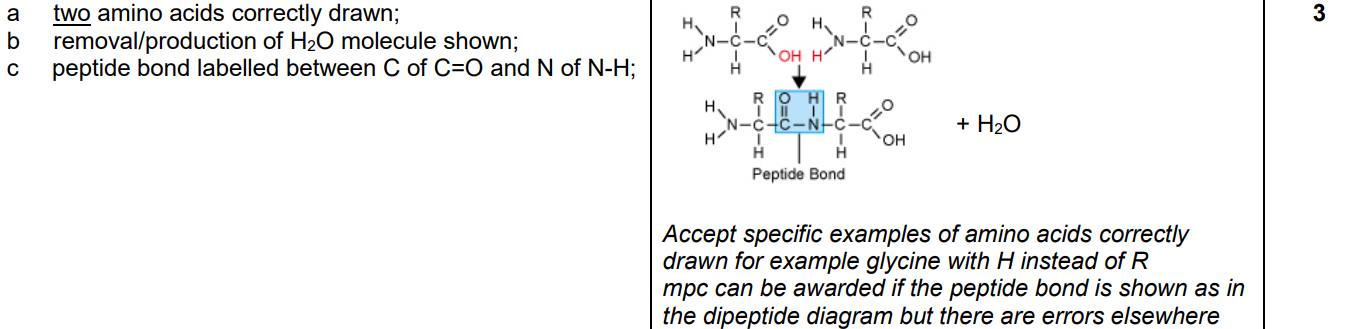
Draw labelled diagrams to show a condensation reaction between two amino acids.
a. at least one of the amino acid structures completely correct
b. peptide bond shown with N–C and C=O and N–H correct
c. release of water clearly shown
TOP TIPS for a distinguish question, e.g “Distinguish between transcription and translation.”
really highlight the differences
what does one thing have that the other doesn’t
Explain what the Rf values represent in chromatography.
see image
each pigment has/is represented by a specific Rf «value»
used to identify different pigments
Rf «value» depends on solubility of the pigment in the solvent

DNA codes for the amino acid sequence of polypeptides. List two other functions of DNA.
Telomeres (form caps at the end of chromosomes)
Coding for tRNAs/rRNAs
Allows genes/traits/heritable characteristics to be passed to offspring
Hydrogen bonds can exist both within and between molecules in living organisms and have an impact on their structure and function. Explain the importance of hydrogen bonding for living organisms. (7)
Cohesion in wate stick together (due to hydrogen bonds)
Adhesion between water and cell walls
Solvent properties (due to hydrogen bonds) with polar/hydrophilic molecules
High (specific) heat capacity so water temperature changes less
Base pairing between bases in DNA by hydrogen bonding
Base pairing between bases in RNA and DNA for transcription between codon and anticodon for translation
Proteins have hydrogen bonding in secondary structure/α helix/β pleated sheet
Proteins have hydrogen bonding between R groups in tertiary structure to maintain conformation
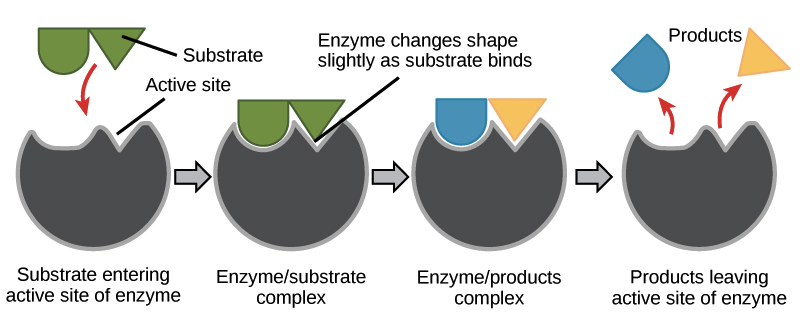
Explain how enzymes catalyse chemical reactions. (3)
enzymes work by forming enzyme–substrate complexes
binding of substrate to active site of enzyme
enzyme changes shape slightly
decreases activation energy → increases rate of reaction
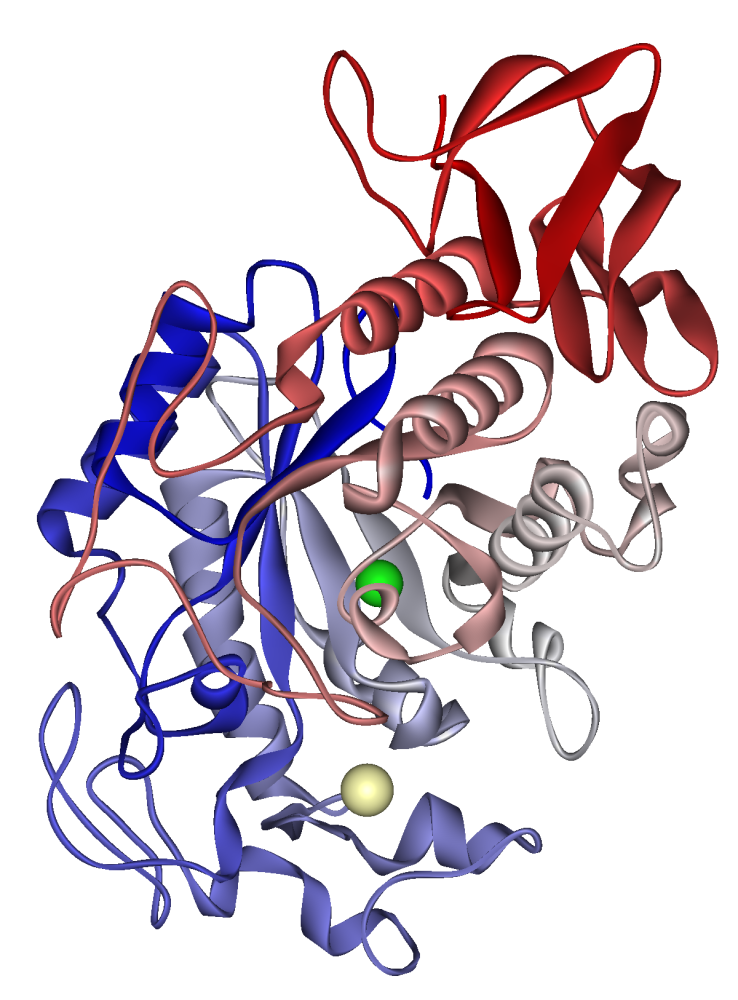
explain the secondary structure of this protein molecule (3)
the secondary structure includes alpha helices/beta pleated sheets
spiral coils of this protein consist mainly of alpha helices
between oxygen and hydrogen atoms of amino acids on backbone
explain how enzymes catalyse chemical reactions
binding of substrate to the active site of the enzyme, forming enzyme-substrate complexes
enzymes bind to specific substrates
AE decreases and ROR increases
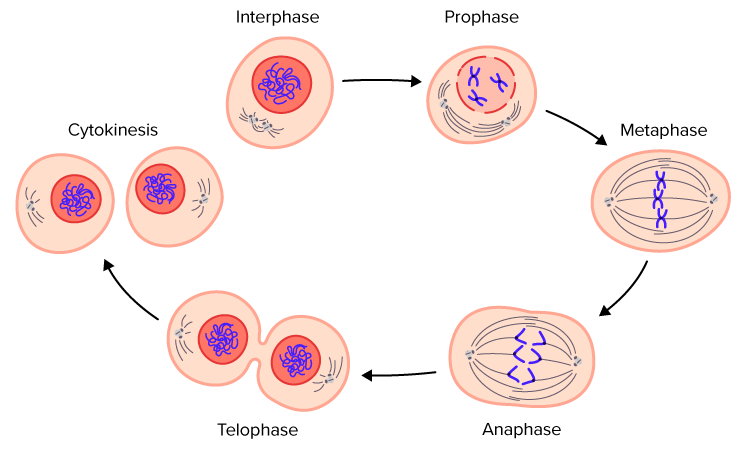
describe what happens to the membranes of an animal cell, during and immediatley after mitosis
nuclear membrane breaks down in prophase
nuclear membrane reforms around two new nuclei
plasma membrane pulled inwards at equator / cleavage furrow formed
membrane pinches apart to form two cells
explain transcription
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter
RNA nucleotides linked together to form a strand
RNA strand assembled on DNA template
RNA polymerase carries out transcription
uncoiling of DNA strands
5’ end of nucleotides linked to 3’ end of growing RNA strand
complementary bas pairing
uracil instead of thymine in RNA
regulated by transcription factors
what happens to the membranes of an animal cell during mitosis
plasma membrane pulled inwards at equator / cleavage furrow formed;
membrane pinches apart to form two cells / cytoplasm divided / cytokinesis;
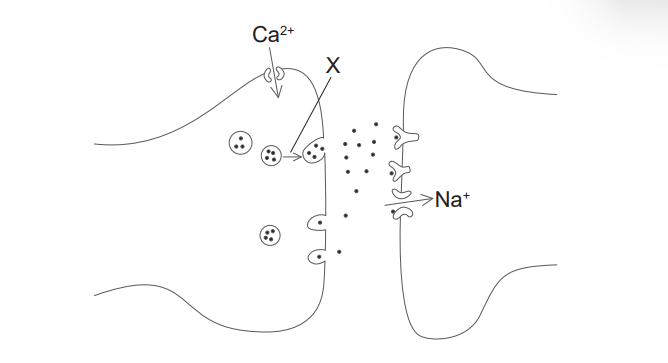
state the name of the structure shown
synapse
label the mitochondria
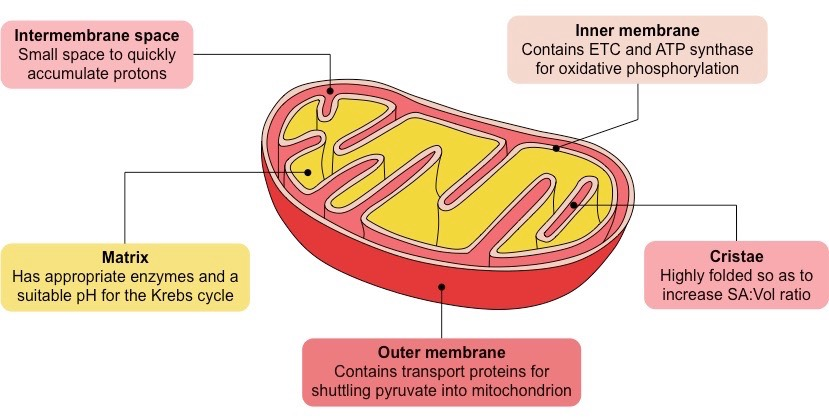
what is the role of the intermembrane space in the mitochondira
small space to quickly accumulate protons
what is the role of the matrix in mitochondria
It's a crucial site for several metabolic processes, most notably thekrebs cycle, where enzymes and cofactors are concentrated to oxidise fuel molecules like pyruvate and fatty acids.
The matrix also houses the mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, and other components necassary for these processes
what’s the role of the outer membrane in mitochondria
The outer membrane of a mitochondrion primarily acts as a permeable barrier, facilitating the exchange of small molecules and ions between the mitochondrion and the surrounding cytoplasm. contains transport proteins for shuttling pyruvate into the mitochondiron
what is the role of the cristae in the mitochondrion
The cristae in mitochondria are folds in the inner membrane that significantly increase its surface area.
This increased surface area is crucial for efficient energy production, as it allows for a greater number of protein complexes involved in the electron transport chain and ATP synthase to be housed on the cristae membranes.
what is the role of the inner membrane in photosynthesis
The inner mitochondrial membrane plays a crucial role in generating cellular energy through oxidative phosphorylation.
It functions as a barrier, maintains a proton gradient, and houses the electron transport chain and ATP synthase, which are essential for energy production in oxidative phosphorylation.
Explain how ATP is generated in mitochondria by chemiosmosis.
a protons pumped across inner membrane of mitochondria/into intermembrane space;
b using energy released by flow of electrons/by electron transport/by electron carriers;
c proton gradient established/maintained / proton motive force generated;
d protons pass/diffuse back through inner membrane/membrane of cristae/to matrix;
e through ATP synthase;
f ATP production coupled to flow of protons / ATP from ADP and Pi using energy from protons;
Distinguish between the transfers of energy and inorganic nutrients in ecosystems.
energy is lost (between trophic levels) / not all passed on / not reused / must be supplied;
nutrients are recycled/reused;
Outline the role of methanogenic archaeans in the movement of carbon in ecosystems.
a methane produced from organic matter;
b in anaerobic conditions;
c methane diffuses into atmosphere/accumulates in ground/soil;
d oxidized/converted to carbon dioxide (in atmosphere);
Describe how autotrophs absorb light energy
a light absorbed by (photosynthetic) pigments;
b chlorophyll absorbs blue and red / drawing of absorption spectrum for chlorophyll;
c photosystems are groups of pigment molecules/are light harvesting complexes;
d photosystems are located in thylakoid membranes;
e electrons excited/raised to higher energy level;
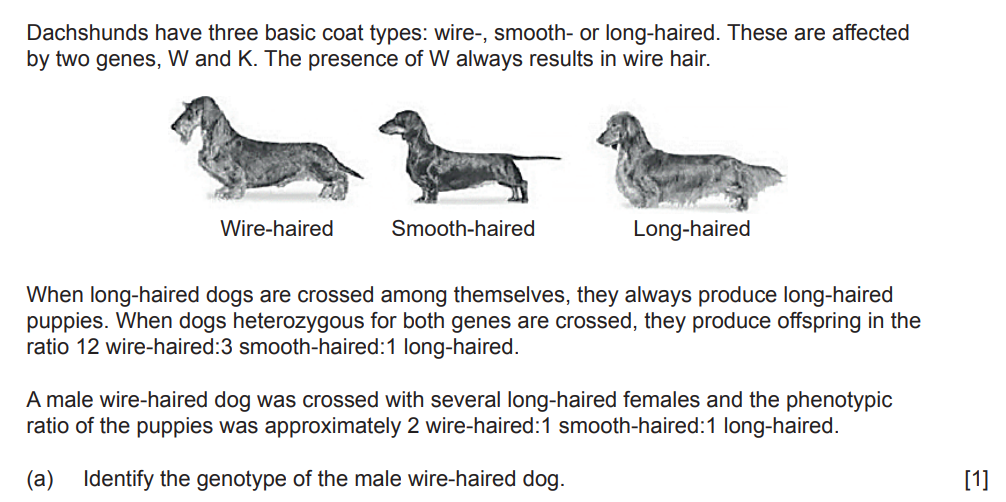
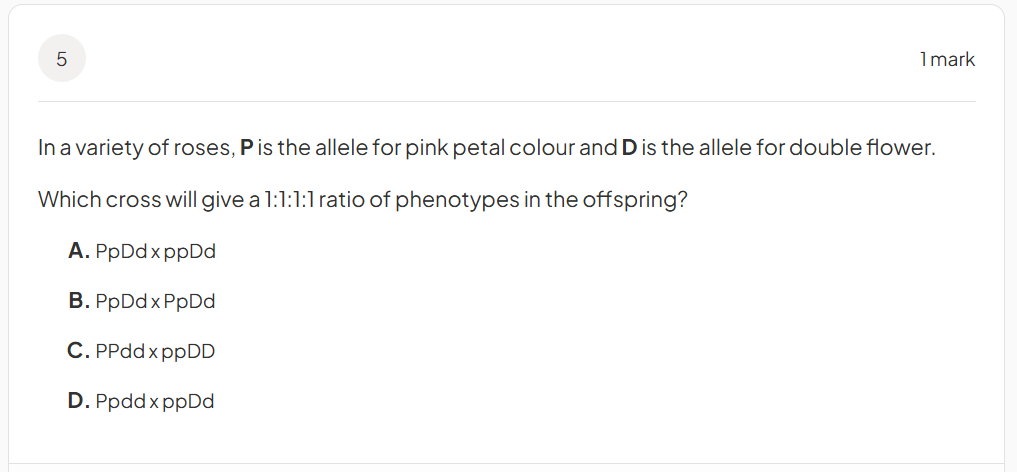
Identify the genotype of the male wire-haired dog.
WwKk

b

Draw a molecular diagram to show the formation of a peptide bond.
Outline how proteins are digested and the products of protein digestion absorbed in humans
a digested by peptidases/proteases;
b pepsin/pepsinogen/endopeptidase secreted by
stomach (lining)/digests proteins in stomach;
c pancreas secretes/pancreatic juice contains
endopeptidase/trypsin/peptidase;
d endopeptidase digest proteins/polypeptides to shorter
chains of amino acids/shorter peptides;
e amino acids absorbed by active uptake/transport;
f in small intestine/ileum;
g villi increase the surface area for absorption;
h absorbed into bloodstream/into capillaries;
Outline how hydrogen bonds form in water.
a water (molecules) are polar/dipolar/have partially positive and negative poles/have δ+ and
δ-;
b attraction/bonding between positive and negative (poles);
c hydrogen bond formed between hydrogen and oxygen; Reject if H and O in same molecule
d bond/attraction between different water molecules/intermolecular;
Describe the processes that cause water to move from the roots of plants to their leaves. [4]
a water moved/transported in xylem vessels;
b transported under tension/suction/pulled up (in xylem vessels);
c transpiration/loss of water (vapour) generates pulling forces/low pressure/tension;
d tension/pull generated when water evaporates from cell walls (in mesophyll);
e transpiration is loss of water vapour from leaf (surface)/stomata;
f cohesivity/cohesion in water due to hydrogen bonding/attractions between water
molecules;
g cohesion/WTTE so chain/column of water (molecules) doesn’t break/remains continuous;
h transpiration stream is a column of/flow of water in xylem from roots to leaves;
Explain the role of the kidney in osmoregulation. [8]
a osmoregulation is regulation of water and solute/salt balance/solute concentrations;
b nephron (is the functional unit of the kidney/osmoregulates);
c ultrafiltration in glomerulus / glomerular filtrate collected by Bowman’s capsule;
d loop of Henle establishes/maintains hypertonic conditions in medulla;
e osmosis/reabsorption of water (from filtrate) in the collecting duct;
f brain/hypothalamus monitors blood solute concentration / pituitary secretes ADH;
g ADH secreted when solute concentration of blood is too high/hypertonic/when dehydrated;
h ADH increases permeability of collecting duct to water;
i ADH causes more aquaporins (in membranes of collecting duct wall cells);
j more water reabsorbed resulting in more concentrated/hypertonic urine/less volume of
urine;
k less/no ADH secreted when solute concentration (of blood) is too low/hypotonic;
l less water reabsorbed resulting in dilute/hypotonic urine/large volume of urine;
define speciation
the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.
Describe the changes that occur in gene pools during speciation. [5]
a gene pool is all genes/alleles in an (interbreeding) population;
b gene pool splits/divides/separated during speciation;
c due to reproductive isolation (of groups within a species);
d temporal/behavioral/geographic isolation (can cause reproductive isolation);
e divergence of gene pools;
f allele frequencies change;
g natural selection different (in the isolated groups so there is divergence);
h different (random) mutations occur (in the isolated populations so there is divergence);
i speciation has occurred when differences between populations prevent interbreeding
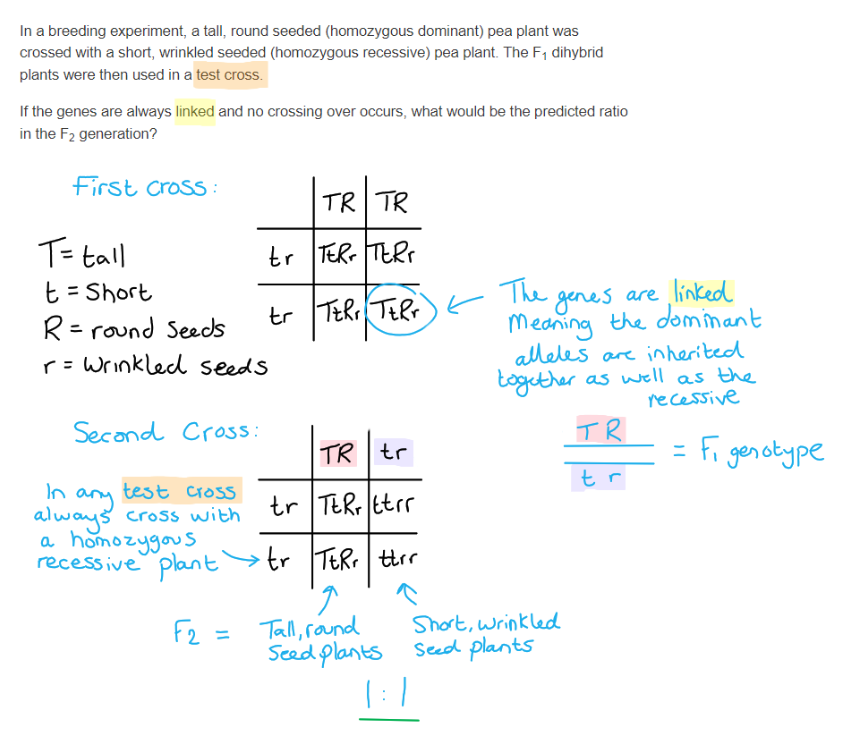
outline the process of genetic modification of plants
a genetic modification by gene transfer between species;
b gene/Bt gene/DNA segment transferred from bacterium to plant/crop;
c gene/DNA codes for/responsible for desired protein/gene product;
d bacteria have/produce plasmids / gene/DNA inserted into plasmid;
e using restriction enzymes/endonucleases to cut DNA;
f using DNA ligase to join DNA;
g bacterium transfers (modified) plasmid to plant cell;
benefits of genetic modification
h increase crop yields / more food produced / less land needed to grow food;
i increase pest/disease resistance / use less pesticides/insecticides/fungicides;
j improves crops to be more nutritious/increased vitamin content;
k increased tolerance to saline soils/drought/high temperatures/low temperatures;
risks of genetically modified crops
GM organisms could spread to sites (where they will cause harm);
transferred gene could spread to other species / spread of herbicide resistance to weeds;
GM crops that produce pesticide could kill non-pest insects/monarch butterflies / insect pests could develop resistance to pesticides/insecticides/Bt toxin;



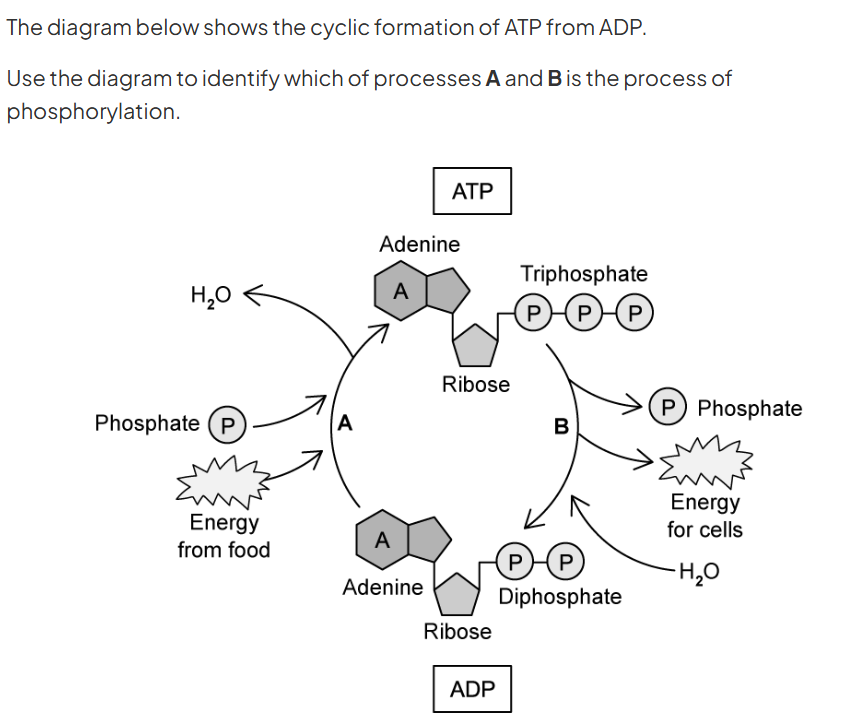
a - phosphorylation
b - hydrolysis
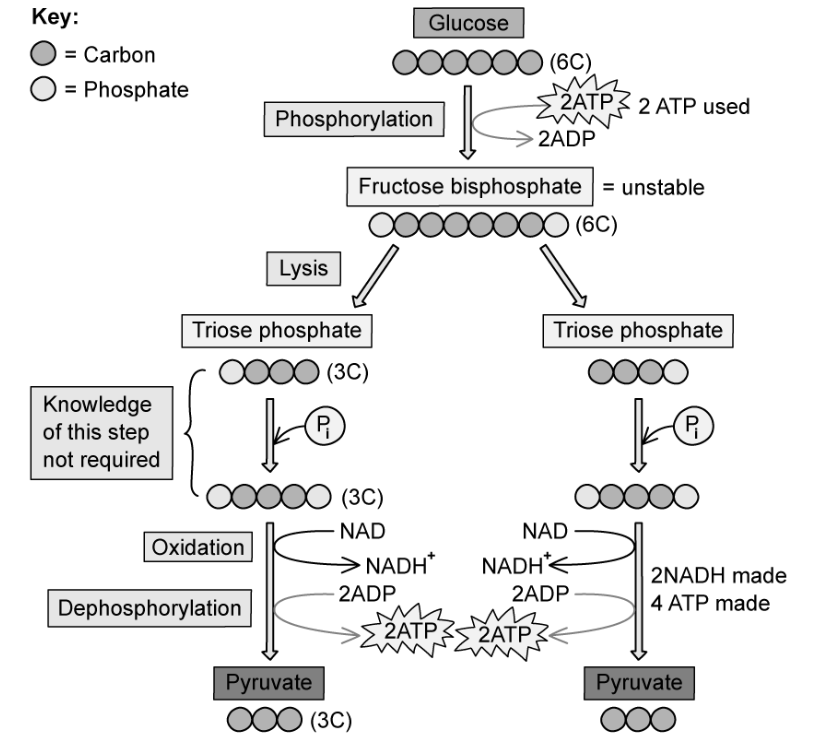
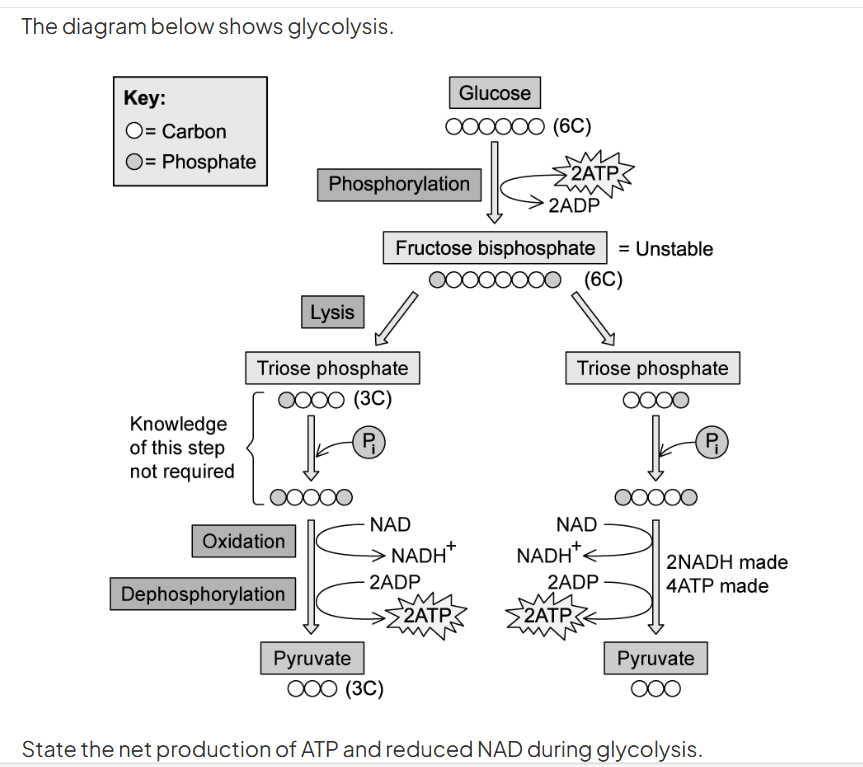
use the diagram to describe phosphorylation during glycolysis




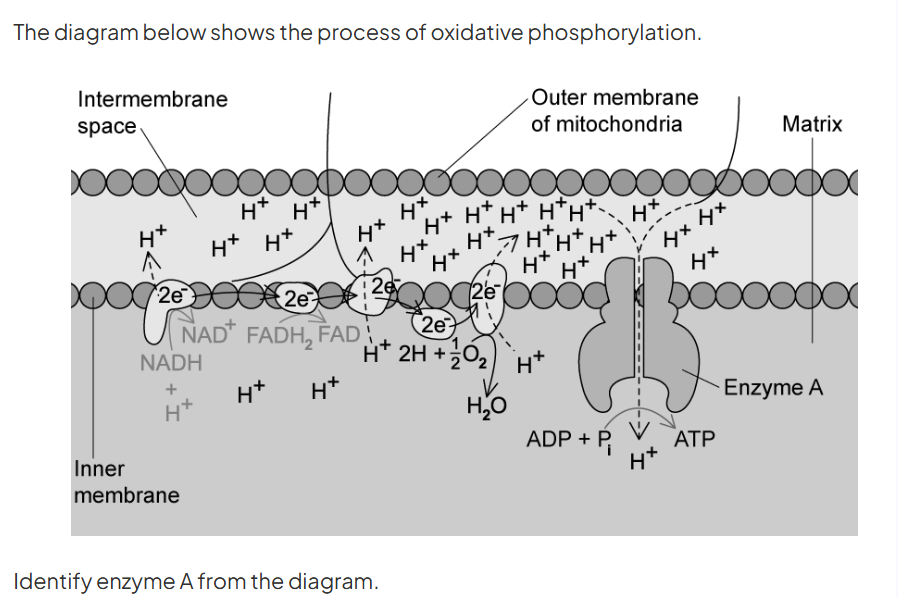
atp synthase





mitchondria _____ ATP and ______ energy
mitochondira produce ATP and release energy




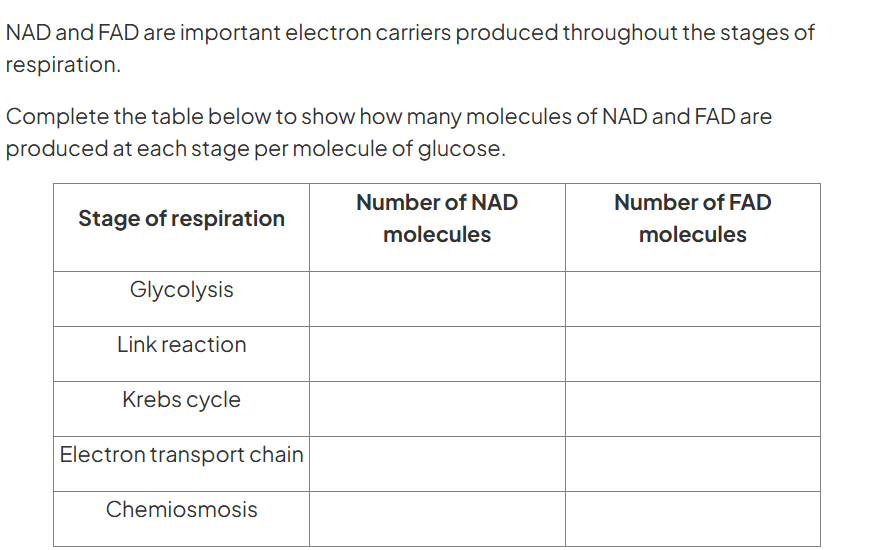
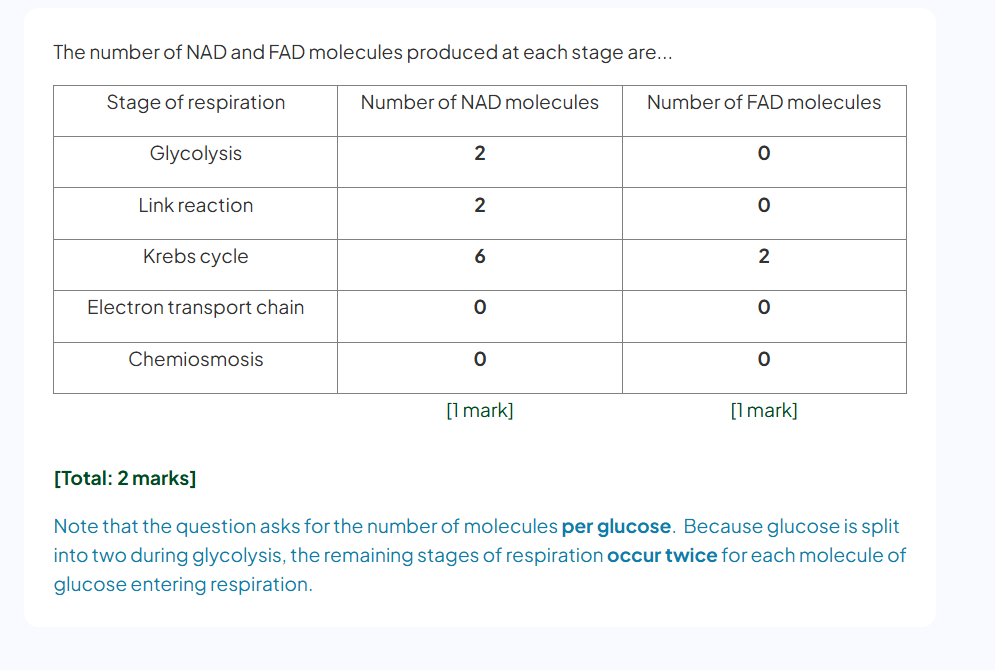
describe the role of oxygen in respiration

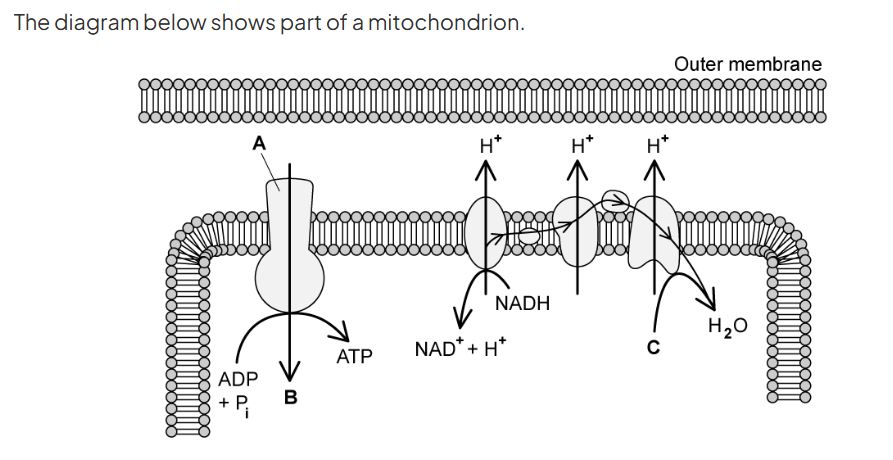
label C
oxygen






the calvin cycle takes place in the ________
stroma



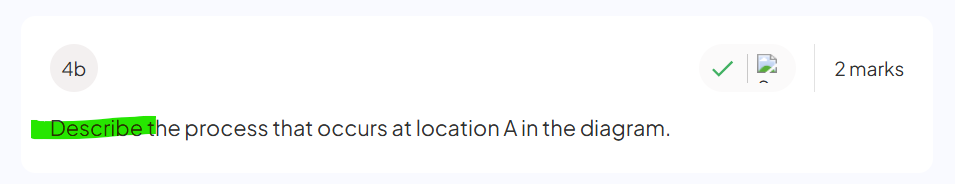

what type of reactions take place at B
redox
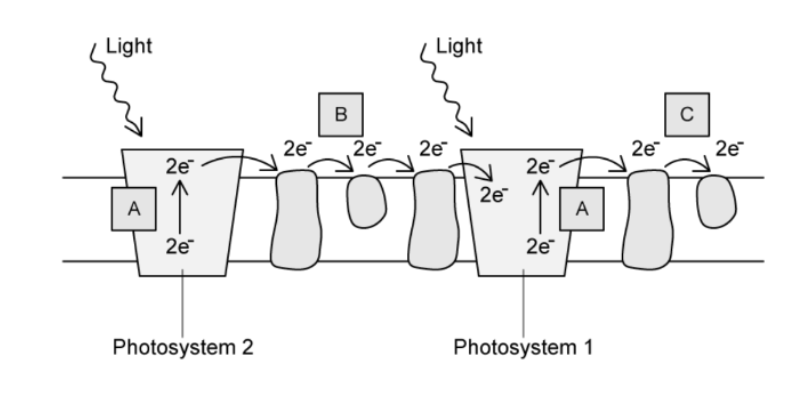
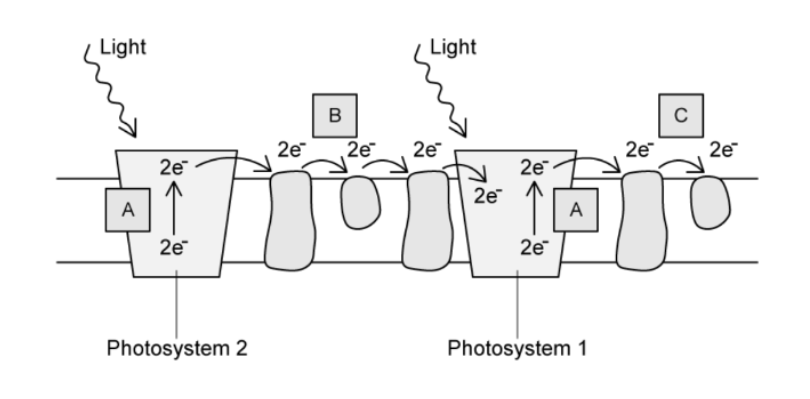
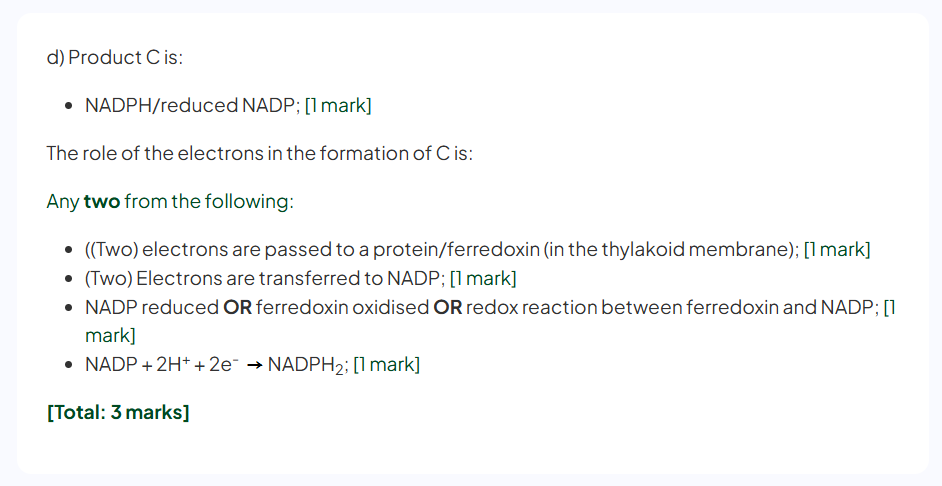
identify C and the role of electrons in the formation of C
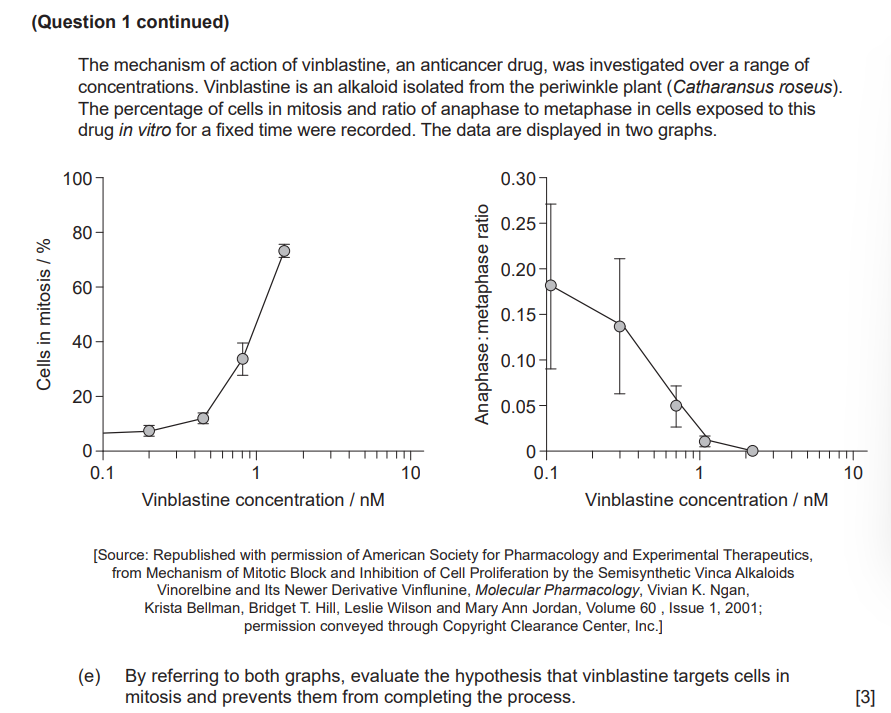

Some anticancer drugs inhibit mitosis by blocking the formation of the spindle. Suggest one other way in which vinblastine could block mitosis.

Discuss one disadvantage of using plant tissue to investigate drugs intended to treat cancer in humans.

State two structural similarities between mitochondria and chloroplasts.

Compare and contrast mitochondria and chloroplasts in terms of the substrates they use and the products they produce.

Outline how the compounds produced by chloroplasts are distributed throughout the plant [3]
a. in phloem ✔
b. loading into sieve tubes/by active transport/by cotransport/by companion cells ✔
c. entry of water (to phloem) by osmosis/because of high solute concentration ✔
d. causes high/hydrostatic pressure ✔
e. flow from high pressure to lower pressure down pressure gradient ✔
from source to sink ✔
Do not award mpa if xylem included with phloem. Do not award a mark solely for mentioning the term ‘translocation’.
Detritus accumulates on coral reefs damaged by ocean acidification. Suggest two possible impacts of an increase in detritus on the organisms in this food web.

Plasma cells secrete antibodies against specific antigens. Outline how plasma cells become activated.

A hybridoma is a cell produced by the fusion of a plasma cell with a tumour cell. Explain the advantages of using hybridoma cells in the production of monoclonal antibodies.

Outline the functions of the villi in the small intestine. [2]
a. increase the surface area for absorption ✔ b. absorption of digested foods/nutrients ✔ c. absorption of mineral ions/vitamins ✔
Explain the consequences of celiac disease for absorption of digested nutrients

Wheat, barley and rye all contain gluten. Outline how a protein such as gluten is digested

Describe the genetic and hormonal control of male sexual characteristics in a human. [3]

Outline how the hormone auxin controls phototropism in plant shoots [5]

Compare and contrast hormonal and nervous communication. [7]
Outline the process of DNA profiling. [4]
in DNA replication ____ _______ ___ links nucleotides with sugar-phosphate/phosphodiester bonds.
DNA polymerase III




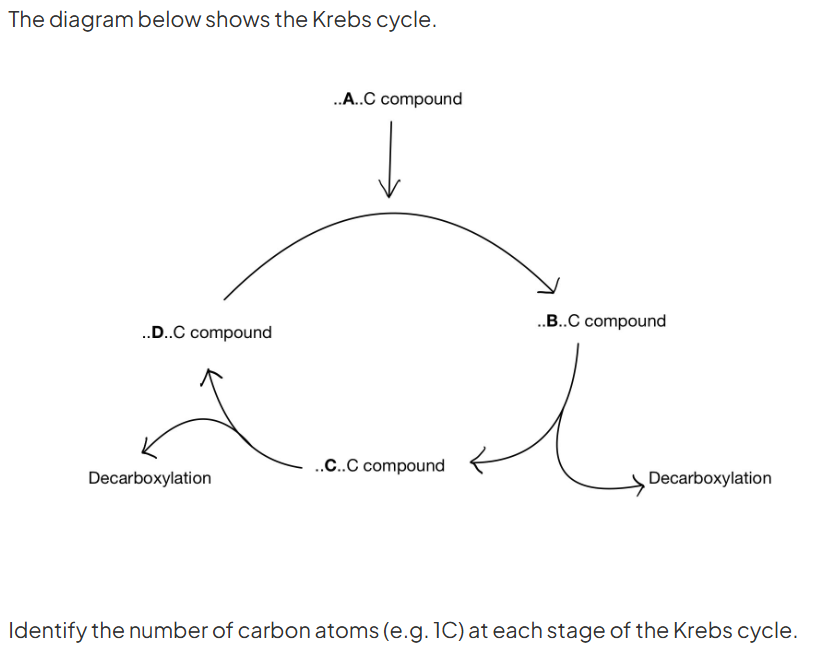
what are the adaptations of A and B

explain the processes that occur at photosystem II

what is independent segregation
the random separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I




ammonia is highly _____
toxic










The DNA molecule: The double helix structure of the DNA will be clearly visible, showing the two strands winding around each other. The path and the number of turns the DNA makes around the protein core can be observed.
The histone core: The octamer of histone proteins (two each of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) will be seen as a central, roughly disc-shaped structure. The individual histone proteins within the octamer may be distinguishable.
The interaction between DNA and histones: The way the DNA wraps tightly around the histone core can be visualised, highlighting the points of contact and the regions where the DNA is closely associated with the protein surface.
The path of the DNA grooves: The major and minor grooves of the DNA that are exposed or in contact with the histone proteins can be observed.
The histone tails: The N-terminal tails that extend from the histone core will be visible. These tails are important for interactions with other nucleosomes and for chromatin regulation.
Overall 3D structure: The overall three-dimensional arrangement of the DNA wrapped around the histone octamer, forming the fundamental repeating unit of chromatin, will be evident.