Cognitive Science 1 - Lec 7
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Computational Neuroscience
Based on modeling biological neurons and populations of neurons
Constructs models by abstracting away from some biological details while preserving others
Connectionist Modelers
Aim to stimulate and reproduce well-documented psychological phenomena like a child’s pattern of development or ways cognitive processes break down in brain-damaged patients
86 billion
How many neurons the human brain has
Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
a computer program that mimics the human brain's network of neurons.
used to solve problems, make decisions, and learn from experience with an organized layers of nodes/neurons
Weights
Determine signal strength of node (positive = excitatory, negative = inhibitory)
The Part of ANNs that are attached to the connections between pairs of units in adjacent layers to determine the behavior of the network
Similar to how excitatory and inhibitory neural connection of various strengths connect to a particular neuron in human neural networks
Bias term
Adjusts activation threshold/Indicates what weighted sum needs to be before node/neuron activates
Similar to threshold necessary for activation of a neuron in human neural networks
Input Layer
First part of ANN processing of an image
Pixels have values between 0 (back) and 1 (white) for its intensity in a grayscale
Each pixel corresponds to a neuron that holds that grayscale value as its activation level
First hidden layer (edge detection)
Neurons recognize edges or basic shapes & calculates a weighted sum with the assigned weights of the input layer pixel
Bias is added to adjust when a neuron activates (ex: only if the sum exceeds 10)
Second hidden layer (feature assembly)
Neurons recognize complex patterns by combining edges
Ex: detect lines or curves that distinguish “9” from “3”
Output layer (digit prediction)
Last ANN layer
Each neuron outputs a number 0-1 for the confidence level of each digit and the highest activation neuron determines the predicted digit
Backpropagation
Learning algorithm that fine-tunes weights and biases
compares predictions with actual labels, calculates errors, and updates weights accordingly
Overtime network learns to correctly classify different images
Multilayer neural network
Network’s knowledge is distributed across the relative strengths of the connections between different units and is constantly changing rather than being encoded in discrete symbol structures
Flow of information is determined by what happens in all of the units in a given layer
Suitable for pattern recognition tasks like image classification
Single-layer network
Simplest form of a neural network w/ one layer of artificial neurons
Works for linearly separable data (ex: given sentence A and B, the only circumstance which A and B is true is if both A and B are true) and can use traditional programming
Hebbian Learning
Donald Hebb (1949) speculated that learning takes place in the brain through an associative process
“neurons that fire together wire together”
If two neurons fire simultaneously, their interconnecting weights will be reinforced
Can engage in unsupervised learning
Perception Convergence Rule
Frank Rosenblatt (1958) came up with learning rule that would allow a single layer network or perceptron w/ random weights and thresholds that would allow it to produce the right output for every input.
Involved supervised learning
Underfitting
Network tries to fit a function to the data but the function is not complex enough to correctly represent the data
Optimum
Network fit function that has the appropriate complexity to accurately represent the data and generalize since it learned the trend the data follows
Overfitting
Network’s function fits data but hasn’t learned the trend and it unable to generalize to new data
Autoencoder
Learns to produce a simplified representation of the input
Ex: in computer visual processing, it learns to encode images as complexes of edges
Can improve performance on different types of tasks like classification
Compresses then decompresses an input signal
Convolutional neural network (AKA CNNs or ConvNets)
An artificial system that performs complex visual information processing that humans do every second
Used for natural language processing, facial recognition software, self-driving cars, SuperVision program to identify things in a box
Creates filter that functions as a localized feature detector
filters out everything except feature its trained to detect
Small-world network
Any network where one can get from any single point to any other point only in a small number of steps even though the total number of elements may be huge
“Six-degrees of separation”
Allows efficient information transfer and neuroplasticity
Six-world network
All people are six, or fewer, social connections away from each other
Supported by research from Duncan Watt
Bayesian Probability
Probability is interpreted as reasonable expectation representing a state of knowledge or as quantification of a personal belief
Updates probability of an event based on new evidence

Fuzzy Logic
Probabilistic approach to logic where truth values are on a spectrum (0 to 1) instead of binary (True/False)
Ex: 0.7 = mostly true; 0.3 = mostly false
Used in AI, robotics, and expert systems to model uncertain environments
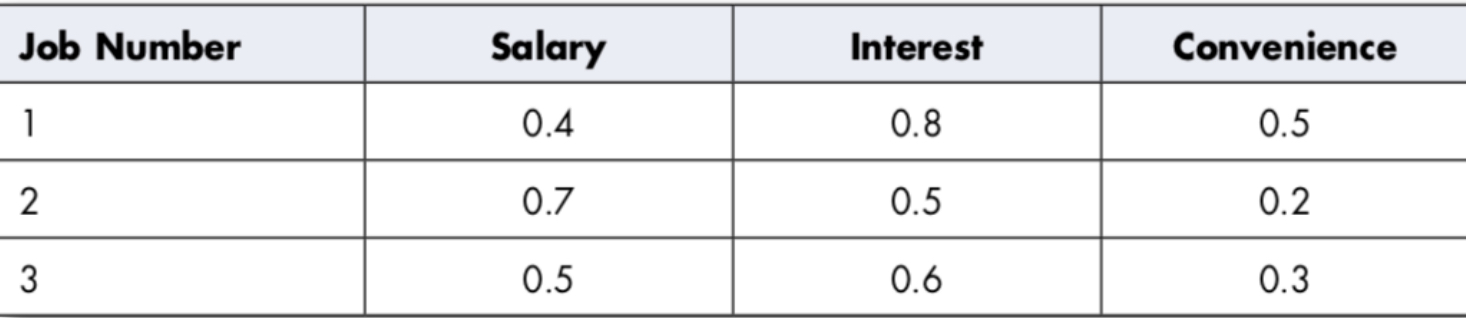
Ex: operation consists of taking the lowest rating among all variables:
− Job 1 quality = 0.4
− Job 2 quality = 0.2
− Job 3 quality = 0.3
➜ Choice of best job = Job 1