quiz #1: digestion
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
about how much of production costs is feed?
60-75%
who’s feed costs the most out of livestock animals?
swine (60-80%)
finisher cattle (70%)
broilers/turkeys (65%)
dairy/cow calf (50-60%)
poultry (55%)
feeder lambs (50%)
how much fructose is in corn?
not a large amount (<1%)
we get fructose from converting corn starch to fructuose
what is nutrition?
a function of living plants and animals consisting of the taking in and metabolism of food material whereby tissue is built up and energy is liberated
what is metabolism?
the sum of the chemical and physical changes occuring in tissue, consisting of anabolism and catabolism
what is anabolism?
the building up in the body of complex chemical compounds from simpler compounds, usually with the use of energy
what is catabolism?
the breaking down in the body of complex chemical compounds into simpler ones, often accompanied by the release of energy
what is homeostasis?
the state of equilibrium in the body with respect to various functions and to the chemical compositions of the fluids and tissues
what is a nutrient?
any chemical (element or compound) in the diet/ration/feed that supports normal reproduction, growth, lactation, or maintenance of life processes
energy values of feedstuffs are difference for various species primarily due to the animals ability to utilize __
fiber
what are the 2 types of nutrients?
essential nutrients and non-essential nutrients
what is an essential nutrient?
can NOT be made at all or in great enough quantities in the body and it (or a derivative) must have a critical biological function
ex: lysine, calcium, vitamin E
what are the classes of essential nutrients? (5)
water
amino acids
essential fatty acids
energy
minerals
what is a non-essential nutrient?
can be made in the body and is not needed in the diet - function is for flavor
ex: alanine, glucose (carbs), vitamin C (in most species)
what are the 10 essential amino acids?
PVT TIM HALL
Phenylalanine
Valine
Threonine
Tryptophan
Isoleucine
Methionine
Histidine
Arginine
Leucine
Lysine
what nutrients do humans need but not ruminants?
vitamin C, possibly fiber
what is the water composition of plants vs animals?
plants - 70%
animals - 54%
animals store energy as _, but plants store energy as _
fat ; carbohydrates
what are the essential macrominerals?
Ca, Cl, Mg, P, K, Na, S
what are the essential microminerals?
Cu, I, Fe, Mn, Se, Zn
what are the fat soluble minerals?
A, D, E, K
on a dry matter basis, how much of plants is carbohydrates (CHO)?
75%
what is the carbohydrate composition of plants vs animals?
plants - 25%
animals - <1%
what is the lipid composition of plants vs animals?
plants - <1%
animals - 26%
what are sugars, starches, and fiber?
carbohydrates (CHO)
how much of animals is carbohydrates (CHO)?
essentially none
how does animal composition vary with age?
lipid content is low at birth
what is an autotroph?
an organism that produces organic compounds from carbon dioxide as a carbon source, using either light or reaction of inorganic chemical compounds, as a source of energy
ex: plants
what is a heterotroph?
an organism that requires organic substrates to get its carbon for growth and development
ex: animals
how do heterotrophs and autotrophs relate?
both depend on one another and can’t function without each other
are energy values and other chemical components dependent on the species?
energy values are a biological value and vary between species but all other values are a chemical determination that is independent of species
energy is determined by how an animal digests fiber, which differs greatly between species
alfalfa meal has the most energy in _ and the least in _
horses ; swine
are labels on food completely accurate?
no, they give us a good idea but are not entirely accurate
how to find the proximate calorie count?
[fat x9] + [carbs x4] + [protein x4]
what are 3 components of animal feed labels?
guaranteed analysis (based on proximate analysis)
ingredient list (in order of abundance)
quality assurance (for pet food only)
what is nutrient analysis?
analysis of the chemical composition of a feed or feed ingredient
the most common is proximate analysis
what is proximate analysis?
provides an approximation of the chemical composition of a feed
has a lot of gravimetric determinations
what are the components of proximate analysis? (6)
dry matter
ash
crude protein
ether extract
crude fiber
nitrogen free extract
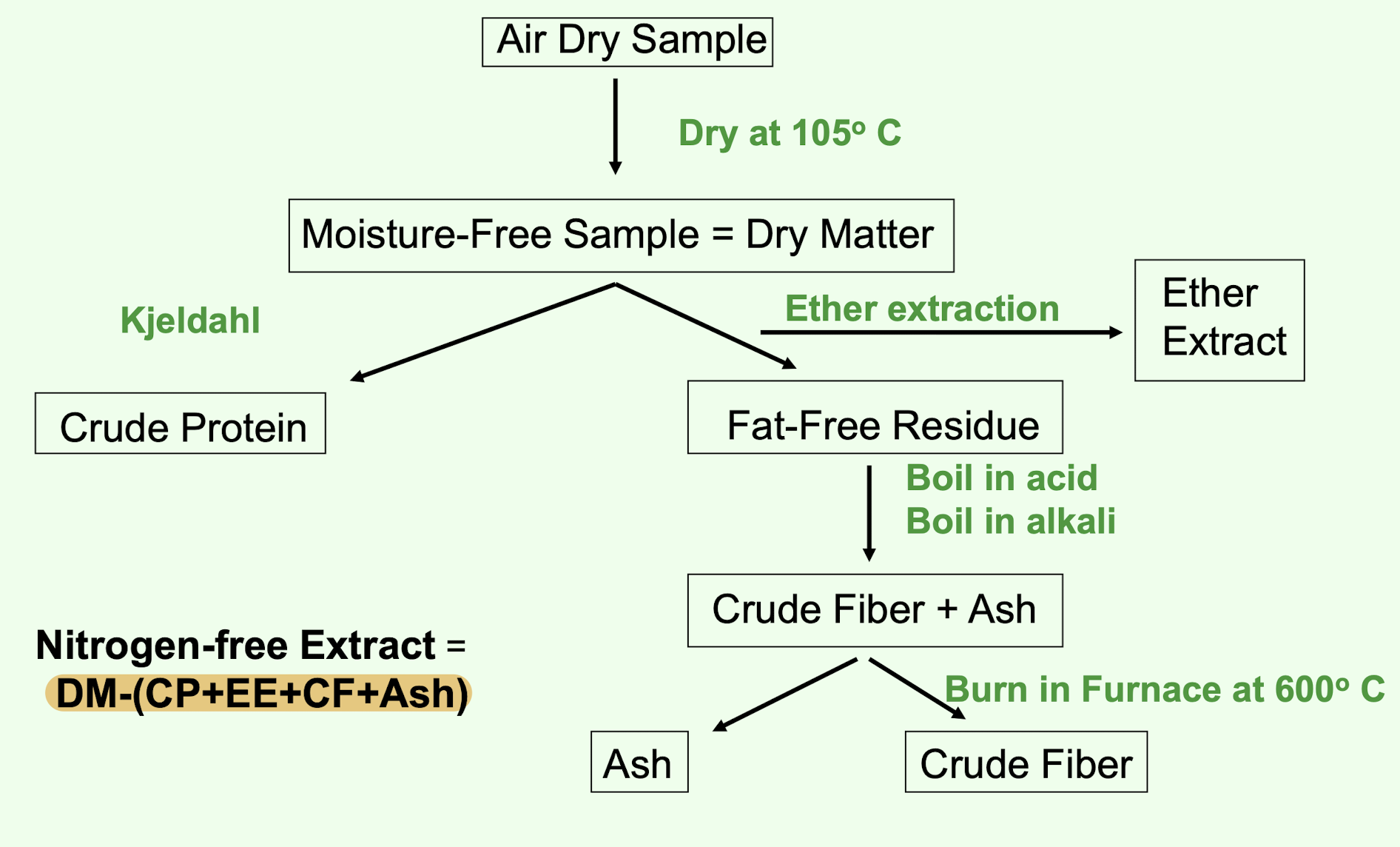
what is dry matter?
the moisture content of a sample
process includes weighing before and after being heated, and the different is equal to the moisture loss
what temperature is dry matter typically heated at?
100-105 °C
what are factors that can affect dry matter?
time and temperature can afffect the results
volatile compounds other than water can be lost (VFA) when at temperatures less than 100°
what is crude protein?
the nitrogen content of a sample to indicate protein
what method is used to measure crude protein?
kjeldahl procedure
what is the kjeldahl procedure?
a process where a sample is digested in concentrated sulfuric acid, which converts all nitrogen to ammonium sulfate
the ammonium ion is then determined by titration with KOH
the analysis determines the N content, NOT the protein (N x 6.25 = CP)
what are some faults with the crude protein process?
it does not distinguish between types of nitrogen (it assumes all N is amino acids)
does not indicate the quality of the protein
can only run a limited number of samples per day
why is N multiplied by 6.25 in crude protein analysis?
the average protein content is 16% (16/100 = 6.25)
a different number is used based on the amino acid content in the food
is not an entirely accurate calculation
what was the 2007 pet food recall?
many cases of kidney failure as a result of contaminants in vegetable proteins imported into the US from china
caused by melamine, which is 66% N and toxic particularly to cats
what was the 2008 chinese milk scandal?
a food safety incident in china where melamine was added to milk to cause it to appear to have a higher protein content, resulting in kidney damage
what has recently replaced the kjeldahl procedure to measure crude protein?
the dumas method, which is a nitrogen analysis which is less expensive and has no acid waste since the method is based on combustion where the N gas given off is measured
what is ether extract?
measures the lipid content of the sample
extracts the lipid with ether using the soxhlet procedure using a gravimetric procedure and whats lost is the lipid content
what are some of the faults in ether extract?
does not distinguish between nutritive (triglycerides) and non-nutritive (waxes, etc.)
ether is highly flammable
ether can be anesthetic if there is bad ventilation
what is ash?
measures the total mineral content
heats at 600°C for 16 hours and uses a gravimetric method where the residue is the ash (burns everything else off)
what are some faults in measuring ash?
does not indicate the specific minerals in it (Ca, P, etc. - could be good or bad minerals)
a high value may indicate some kind of contamination of an ingredient with soil, limestone, or salt
what is crude fiber?
represent the structural carbohydrates - cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin
what is the process to extract crude fiber?
a process supposed to resemble digestion where fat free residue is boiled in a dilute base and then a dilute acid and dried
has largely replaced the van soest procedure
what is nitrogen free extract (NFE)?
represents the soluble or readily available carbohydrate fraction of the feedstuff
is a calculated value, not an extract (NFE = DM - CP - EE - CF - ash), whats remaining after everything
is mainly starch
what is the van soest procedure?
a process to replace crude fiber measurement (may show more than what the CF value says)
measures hemicellulose (NDF - ADF = hemicellulose)
what is neutral detergent fiber (NDF)?
boiling in sodium lauryl sulfate under neutral conditions to extract all of the cell contents to leave the cell wall (hemicellulose, cellulose, lignin)
what are the components of the cell wall?
hemicellulose, cellulose, lignin
what is acid detergent fiber (ADF)?
boiling in detergent (cetyl trimethylammonium bromise and sulfuric acid) to leave cellulose and lignin
crude fiber is most similar to ADF value
what is a calorie?
the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 mL of water 1°C
what other analytical procedure is used to measure energy?
bomb calorimeter
what other analytical procedure is used to measure amino acids?
amino acid analyzer
what other analytical procedure is used to measure minerals
atomic absorption spectrophotometer, inductive coupled plasma spectrophotometer
what other analytical procedure is used to measure fatty acids?
gas chromatography
what other analytical procedure is used to measure multiple feed components?
near infrared reflectance (NIR)
what does liquid chromatography measure?
amino acid analysis
what does gas chromatography measure?
fatty acid analysis (saturated, unsaturated, chain length)
what does HPLC measure?
amino acids, steroid hormones (drug residue analysis), vitamins
in a chromatography graph, how do you find concentration?
peak height is proportional to the concentration
the elution time is characteristic for particular amino acids
what does atomic absorption and ICP measure?
mineral profile
what are some considerations to have for analytical procedures? (4)
in feed mill vs commercial lab (speed vs accuracy)
cost
speed
simplicity
what 2 things are necessary for nutrient utilization?
digestion
absorption
what is digestion?
the preparation of food for absorption
what percent of food we eat is actually utilized?
80-85%
what are the 4 processes of digestion?
mechanical (chewing, muscle contractions)
chemical (stomach acid, bile)
enzymatic hydrolysis
microbial (fermentation)
what is fermentation?
the breakdown by bacteria under anaerobic conditions
what is the overall function of digestion?
to reduce food to a molecular size that allows absorption
what is absorption?
processes that result in the passage of small molecules from the lumen of the interstitial tract through the mucosal cells lining the lumen and into the blood or lymphatic system
what are the mechanisms for absorption (4)?
simple diffusion (water)
facilitated diffusion (amino acids)
active transport (glucose)
pinocytosis or endocytosis (immunoglobulins)
what 4 things determine the mechanism for absorption?
size
solubility
concentration
charge
what is simple diffusion?
no carrier required, moves down concentration gradient (high to low)
ex: water
what is facilitated diffusion?
a carrier protein helps to move down a concentration gradient (no energy expended)
ex: amino acids
what is active transport?
a carrier protein uses energy to transport molecules against a concentration gradient
ex: glucose
what molecule uses pinocytosis/endocytosis?
immunoglobulins
digestion + absorption = ?
digestibility
what 2 things determine the digestibility of a nutrient in a feed or an ingredient?
energy digestibility or availability
lysine digestibility or availability
where are mucosal cells found?
in the lumen
why might one look at the composition of feces?
to measure digestibility where everything that disappears has been digested and absorbed
what animals are considered carnivores?
cats and dogs
what animals are considered omnivores?
pig, human, chickens
what animals are considered herbivores?
horse, rodents, cattle, sheep
oligovore vs omnivore?
omnivore - generalist ; oligovore - specialist
what are the 2 types of hind gut fermentors?
cecal fermentors (rat, rabbit)
colonic digestors (horse, pig, human, dog, cat)
what are the 2 types of pregastric fermentors?
ruminants (cattle, sheep, deer)
nonruminants (colobine, monkey, hamster, kangaroo, hippo)