[PART 1] [Microscopic Examination of Urine] Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fuids [MTAP][Strasinger][LABORATORY]
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Standard amount of urine
Between 10 and 15 mL
How many mL is used because multiparameter reagent strips are easily immersed in this volume
12-mL volume
How many mL of sediment after DECANTATION are frequently used
0.5 and 1.0 mL
What microscopic OBJECTIVES is used r to detect casts?
Low power (40x) -Yel[LOW]
![<p>Low power (40x) -Yel[LOW]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/da32d318-7b42-47da-a90a-f0a58556982c.jpg)
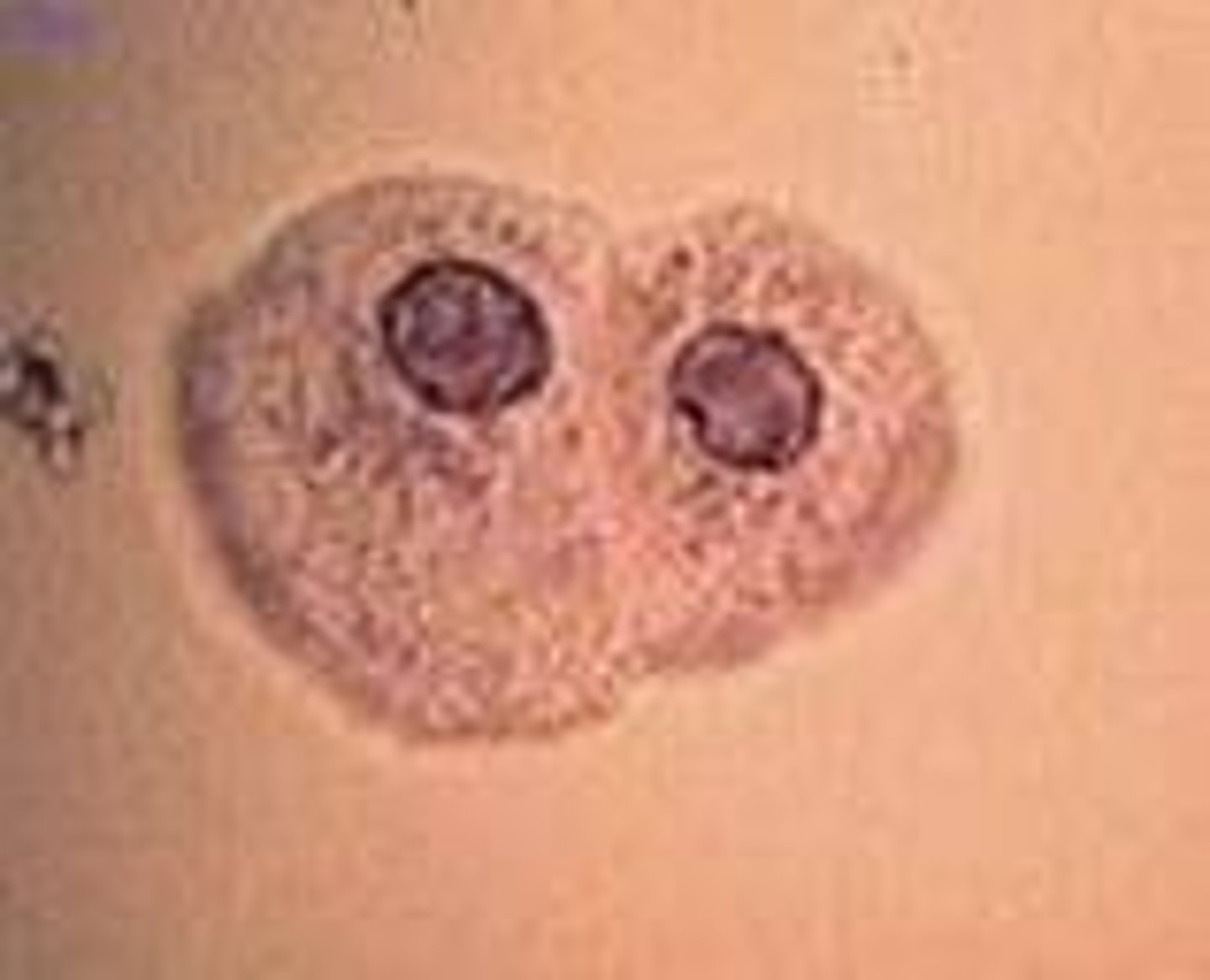
What STAIN delineates structure and contrasting colors of the nucleus and cytoplasm
Sternheimer-Malbin
Sternheimer-Malbin FUNCTION
Identifies WBCs, epithelial cells, and casts
What STAIN Enhances NUCLEAR detail
Toluidine blue
Toluidine blue FUNCTION
Differentiates WBCs from RTE cells
What STAIN Lyses RBCs and enhances nuclei of WBCs
2% acetic acid
2% acetic acid FUNCTION
Distinguishes RBCs from WBCs, yeast, oil droplets, and crystals
- Anucleated si RBC kaya madidifferentiate sya sa WBC and other
What STAIN stains triglycerides and neutral fats orange-red; do not stain cholestero
Lipid stains: Oil Red O and Sudan III
Lipid stains: Oil Red O and Sudan III FUNCTION
Identify free fat droplets and lipidcontaining cells and casts
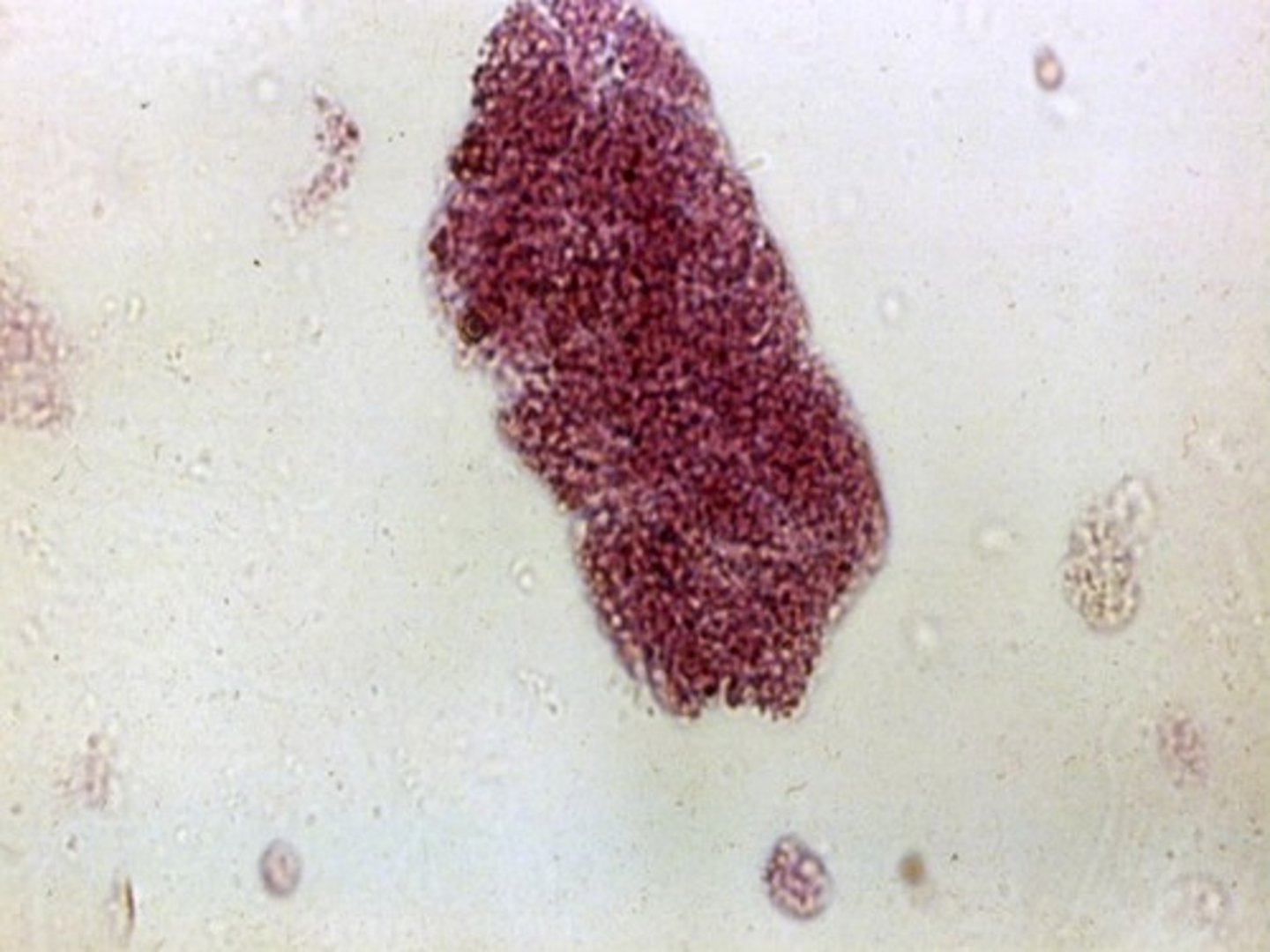
What STAIN Differentiates grampositive and gramnegative bacteria
Gram stain
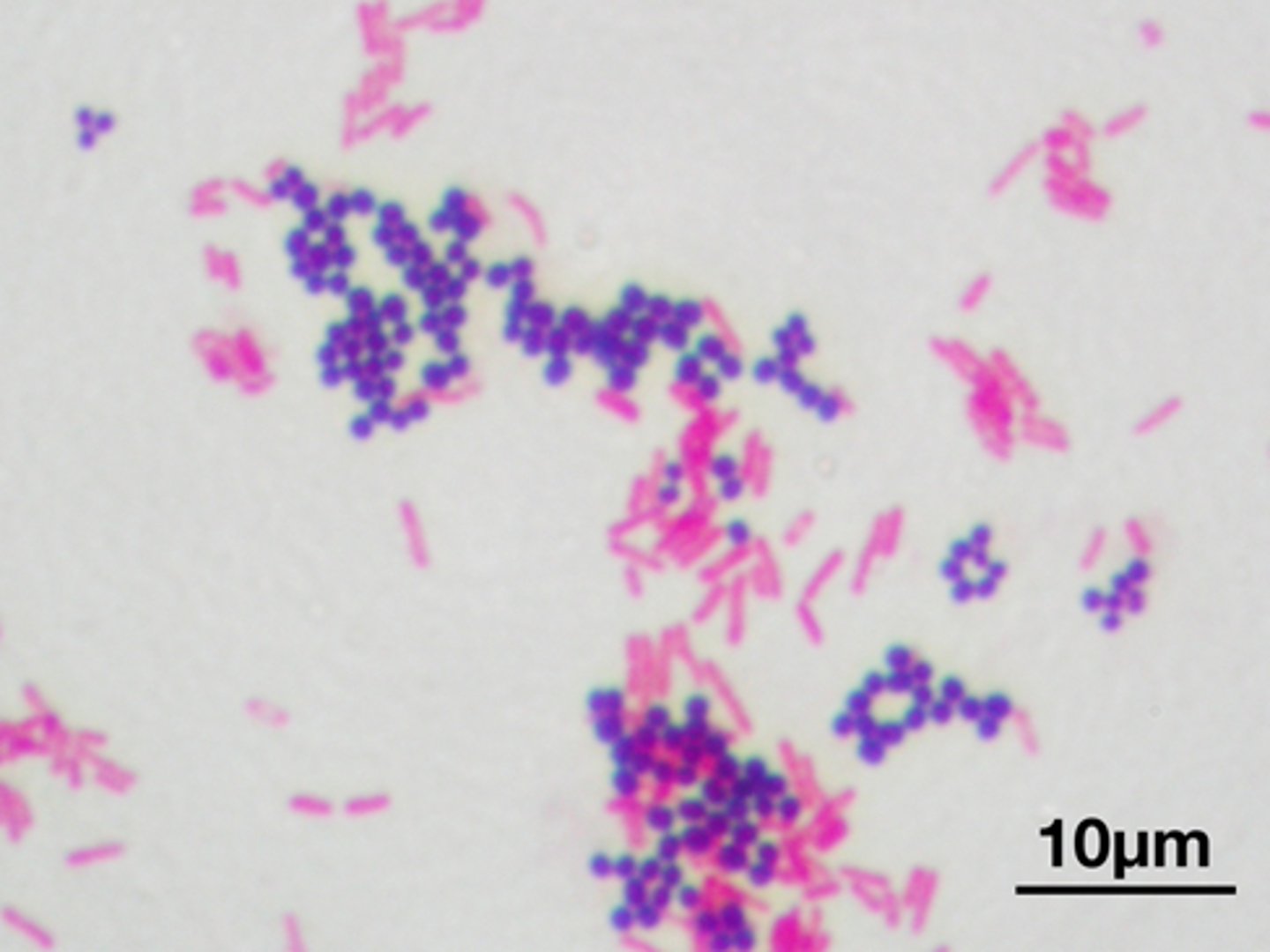
Gram stain FUNCTION
Identifies bacterial casts
What STAIN is composed of Methylene blue and eosin Y stains eosinophilic granules
Hansel stain
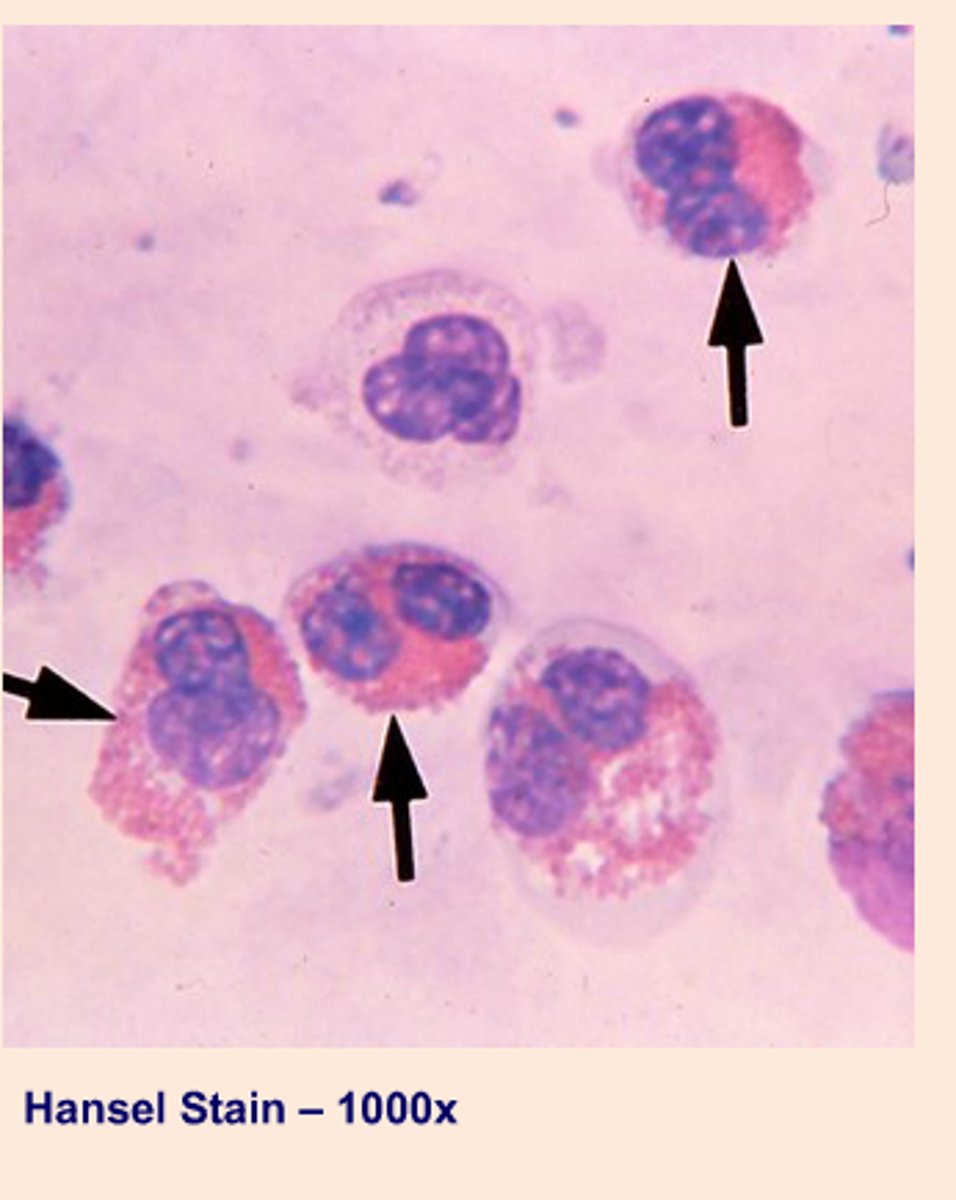
Hansel stain FUNCTION
Identifies urinary eosinophils
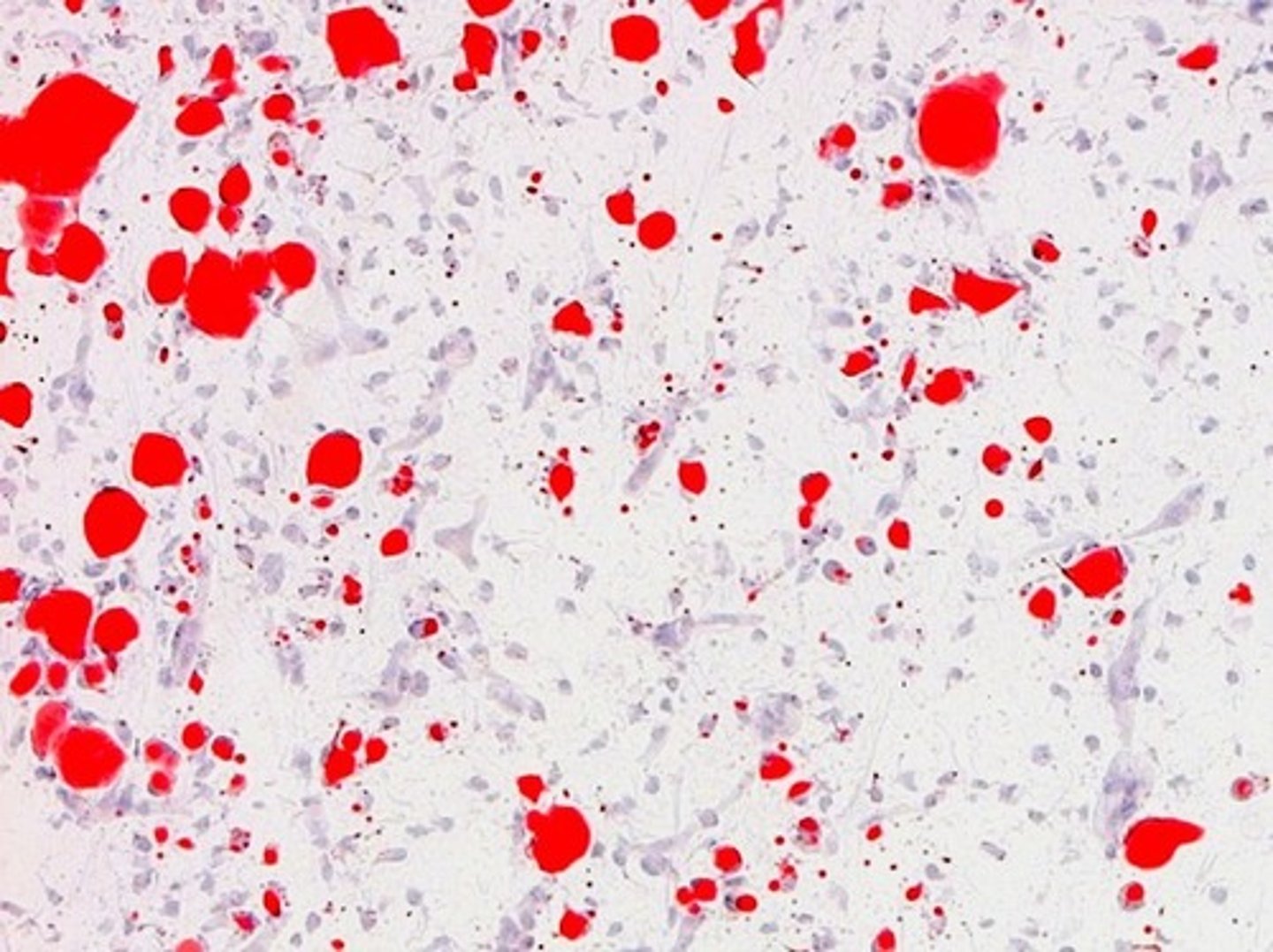
What STAIN stains structures containing iron
Prussian blue stain
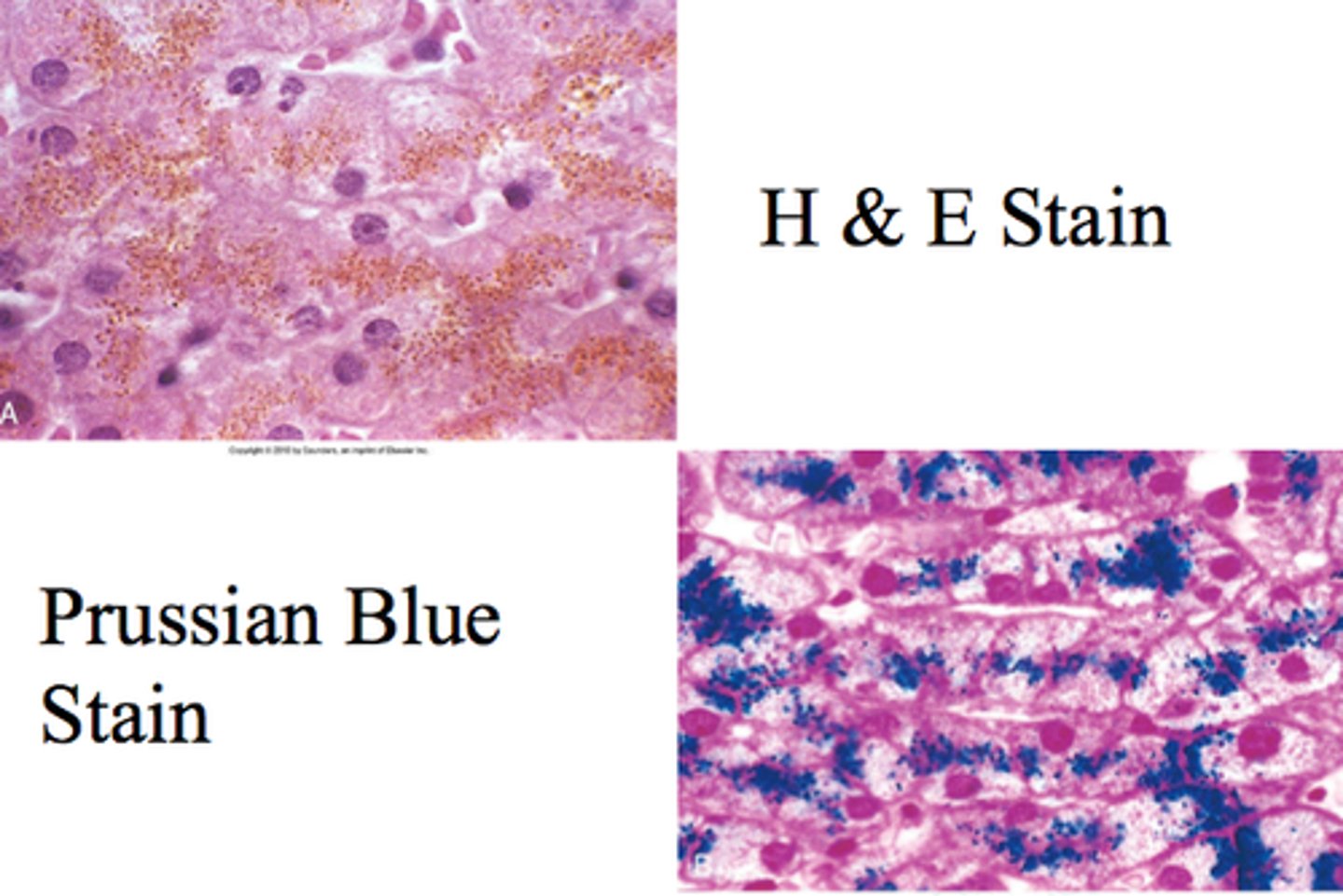
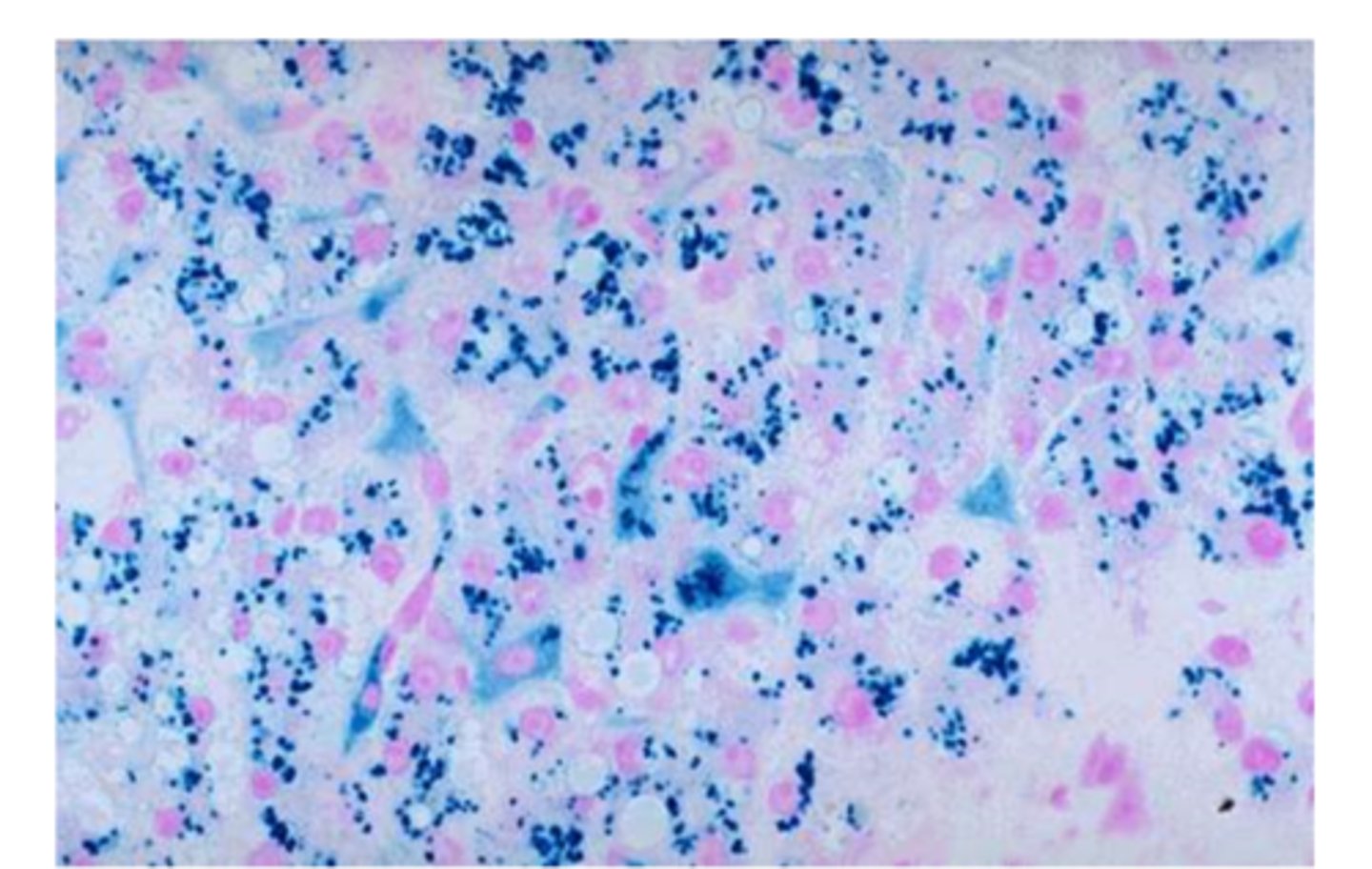
Prussian blue stain FUNCTION
Identifies yellow-brown granules of hemosiderin in cells and casts
Sternheimer Malbin stain is comopsed of?
crystal violet + safranin O - una at dulo ng gram stain "[V]IA[S]"
Bacteria COLOR when non-motile?
PURPLE
Bacteria COLOR when motile?
Do not Stain
Trichomonas vaginalis COLOR
Light blue-green
Is the most common type of microscopy performed in the urinalysis laboratory.
Bright-field microscopy
What microscope is Used for routine urinalysis?
Bright-field microscopy
What microscope enhances visualization of elements with LOW REFRACTIVE INDICES , such as hyaline casts, mixed cellular casts, mucous threads, and Trichomonas vaginalis
Phase-contrast microscopy
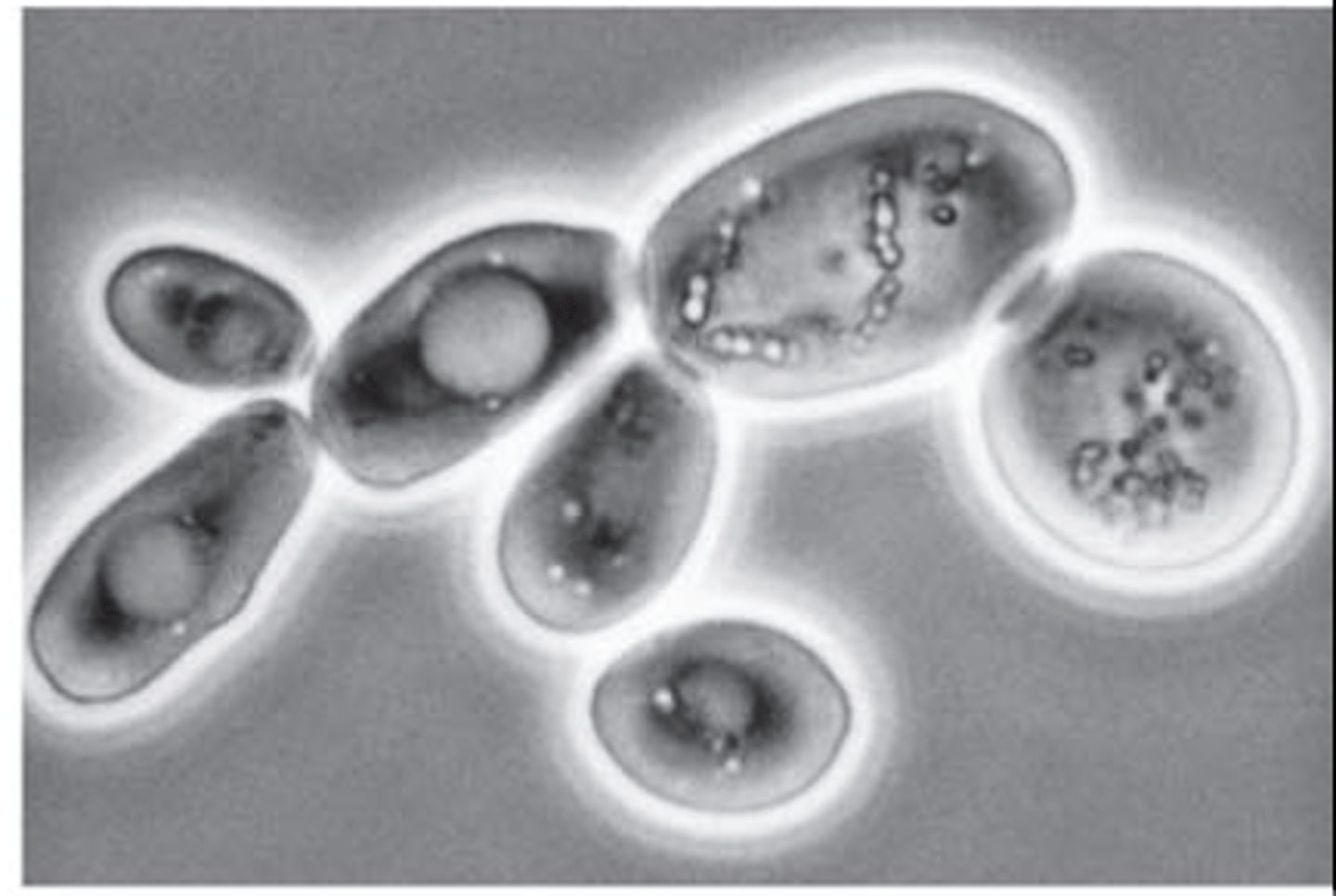
What microscope Aids in identification of cholesterol in oval fat bodies, fatty casts, and CRYSTALS
Polarizing microscopy
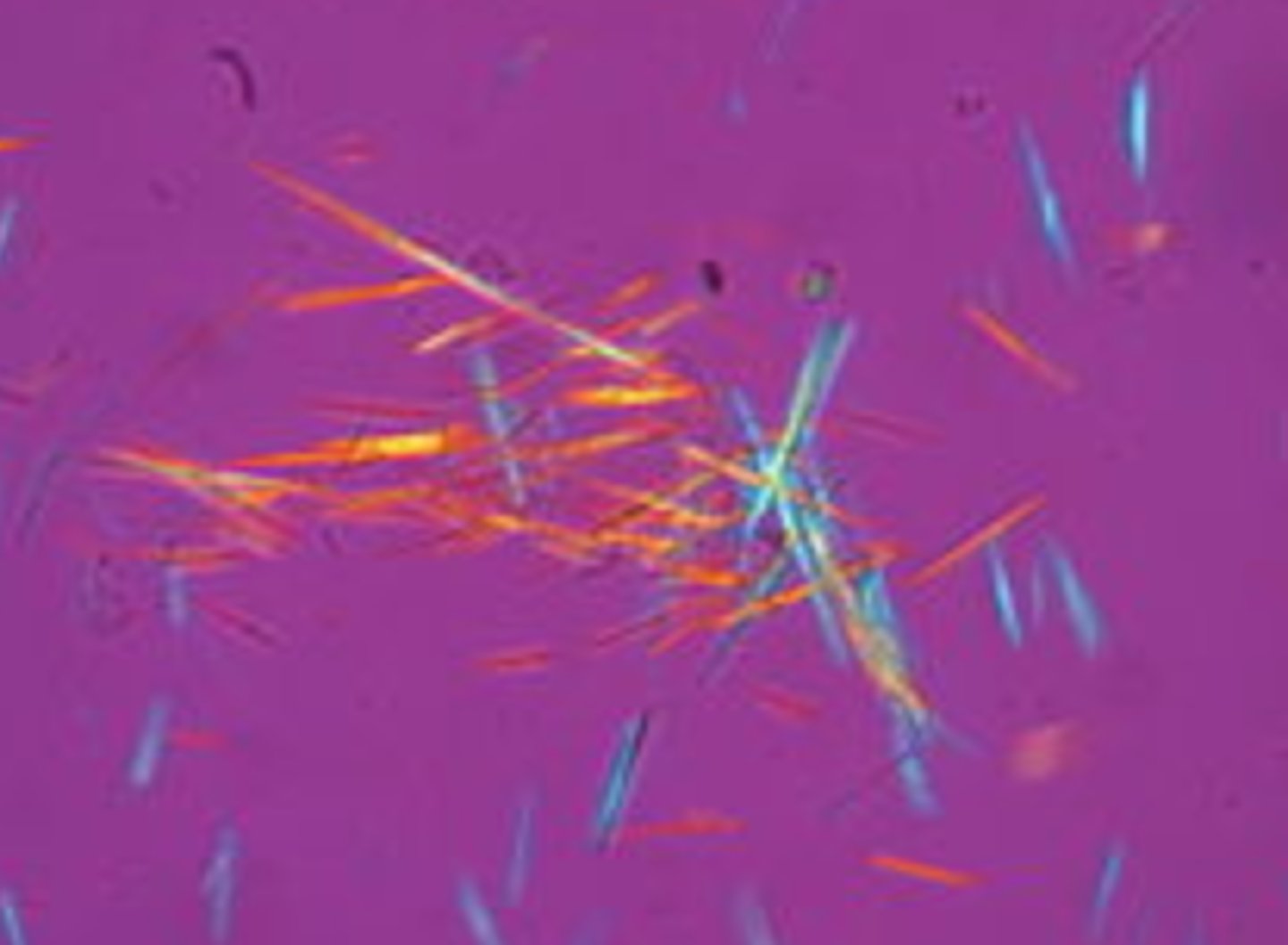

What microscope Aids in identification of Treponema pallidum
Dark-field microscopy
What microscope allows visualization of naturally FLUORESCENT microorganisms or those stained by a fluorescent dye, including labeled antigens and antibodies
Fluorescence microscopy
What microscope produces a three-dimensional (3D) microscopy image and LAYER-by-LAYER imaging of a specimen
Interference-contrast
Laboratory microscopes normally contain oculars capable of increasing the magnification of?
10x
The objectives used for examination of urine sediment are
10× and 40×
What part of MIRCOSCOPE contained in the light source controls the DIAMETER of the light beam reaching the slide
Field diaphragm
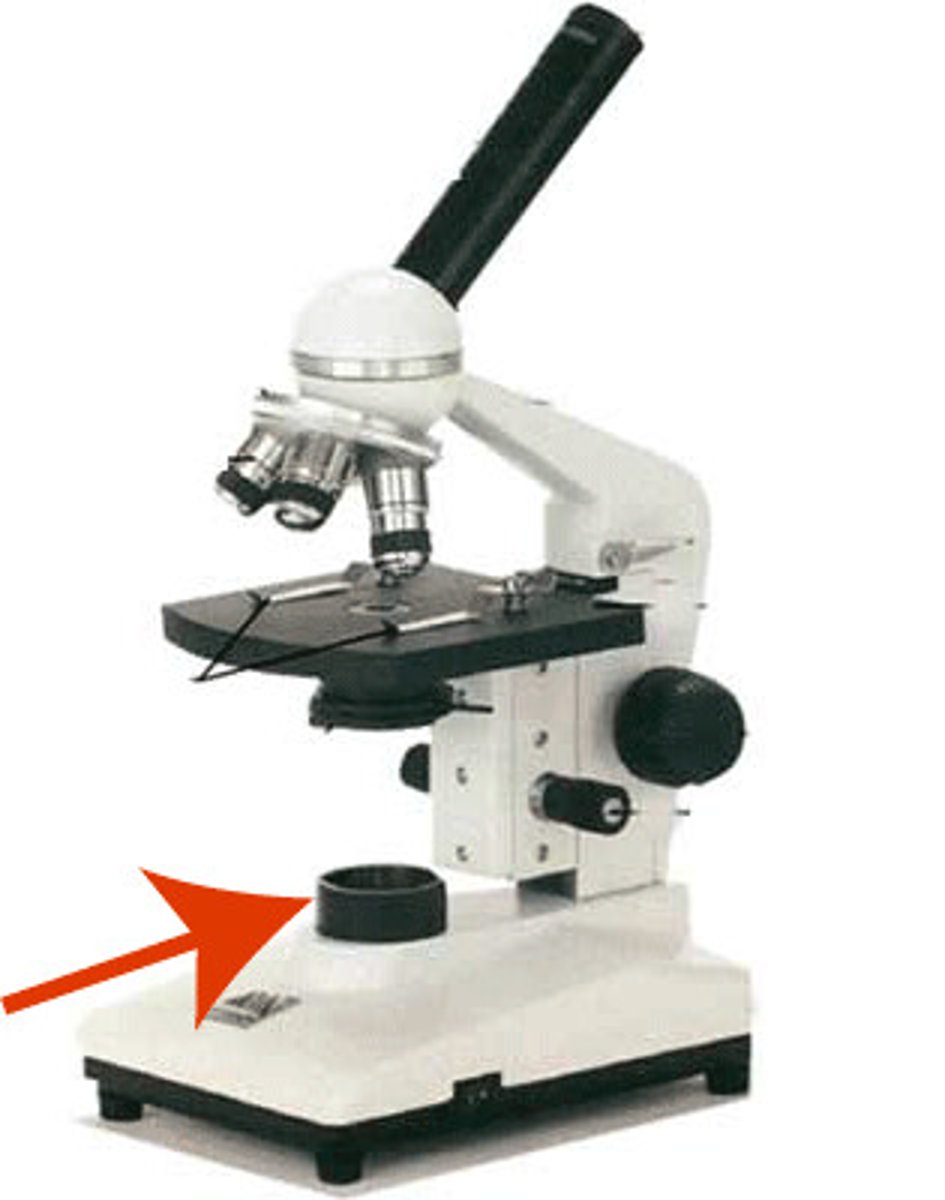

What part of MIRCOSCOPE located below the stage focuses the light on the specimen
Condenser
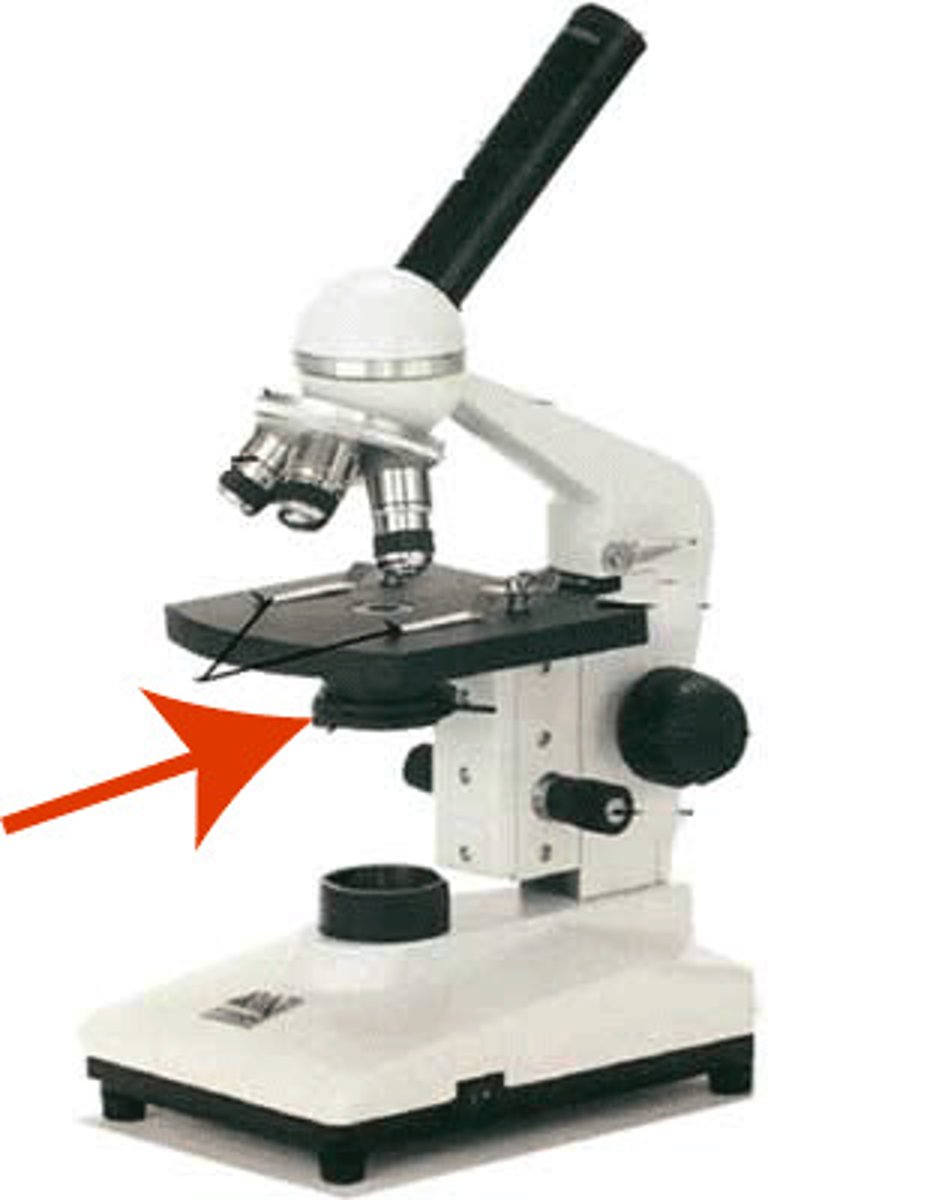
What part of MIRCOSCOPE moves the condenser up and down to focus light on the object
Condenser adjustment (focus) knob
are the largest cells found in the urine sediment.
Squamous cells
WHat cells are indicative of vaginal infection by the bacterium Gardnerella vaginalis.
Clue cells
The cells from the_______________________ (PCT) are larger than other RTE cells
proximal convoluted tubule
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells in PROXIMAL convoluted tubules are what SHAPE?
Rectagular (columnar)
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells in DISTAL convoluted tubules are what SHAPE?
spherical
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells inCOLLECTING DUCT are what SHAPE?
[C]uboidal
- [C]ollecting Duct
rapid darting movement / "rapid jerky tumbling" motility is characteristic of what parasite?
Trichomonas vaginalis
Most common contaminant of URINE from stool
E. vermicularis ova
sperm is expelled into the bladder instead of the urethra.
retrograde ejaculation
a major constituent of mucus. A glycoprotein excreted by the RTE cells of the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle and by the distal convoluted tubules.
Uromodulin
only elements found in the urinary sediment that are unique to the kidney.
Casts
major constituent of casts.
Uromodulin
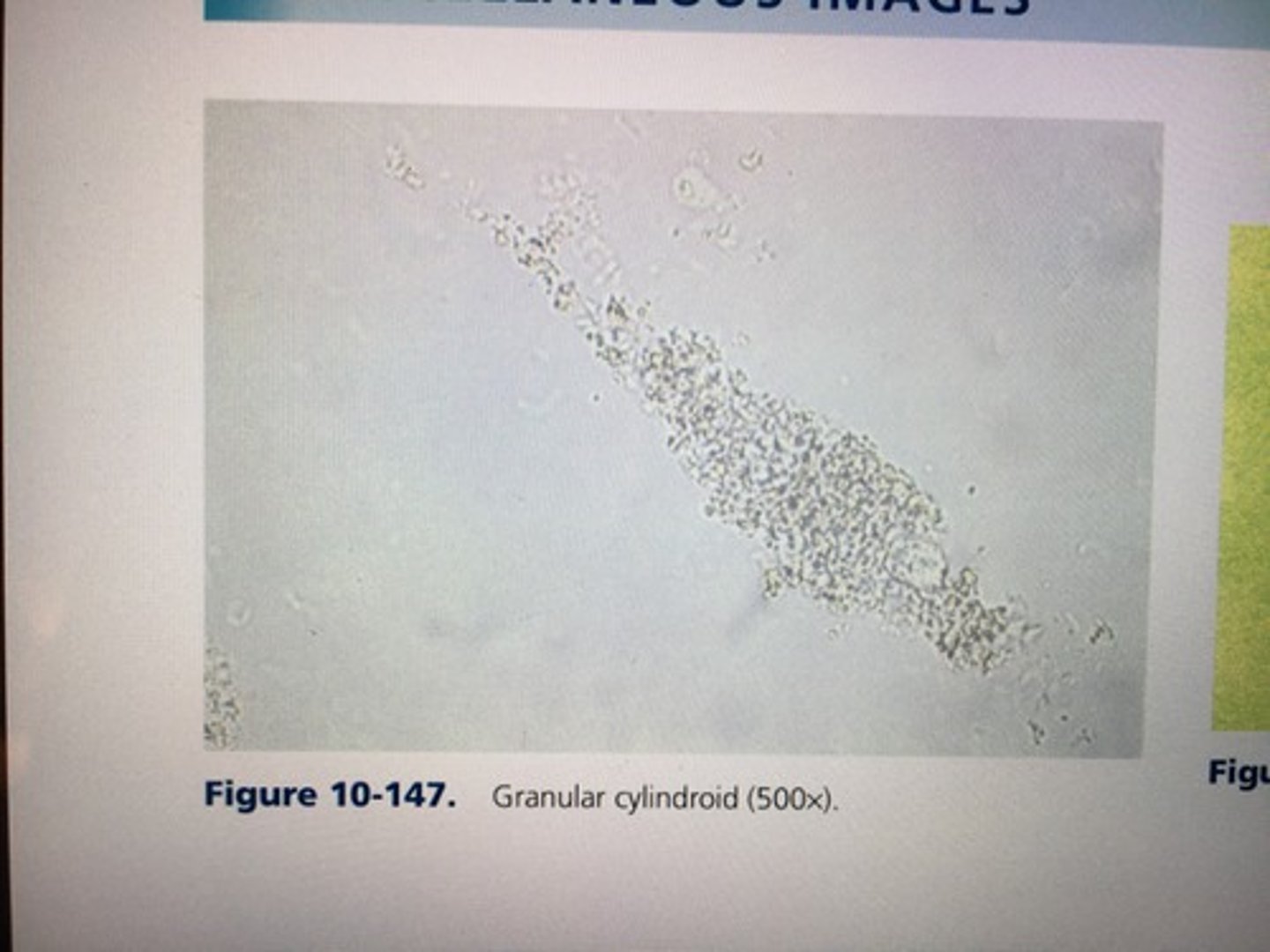
- formation of casts at the junction of the ascending loop of Henle and the DCT may produce structures with a tapered end.
Cylindroids
cast seen most frequently which consists almost entirely of uromodulin.
HYALINE CASTS
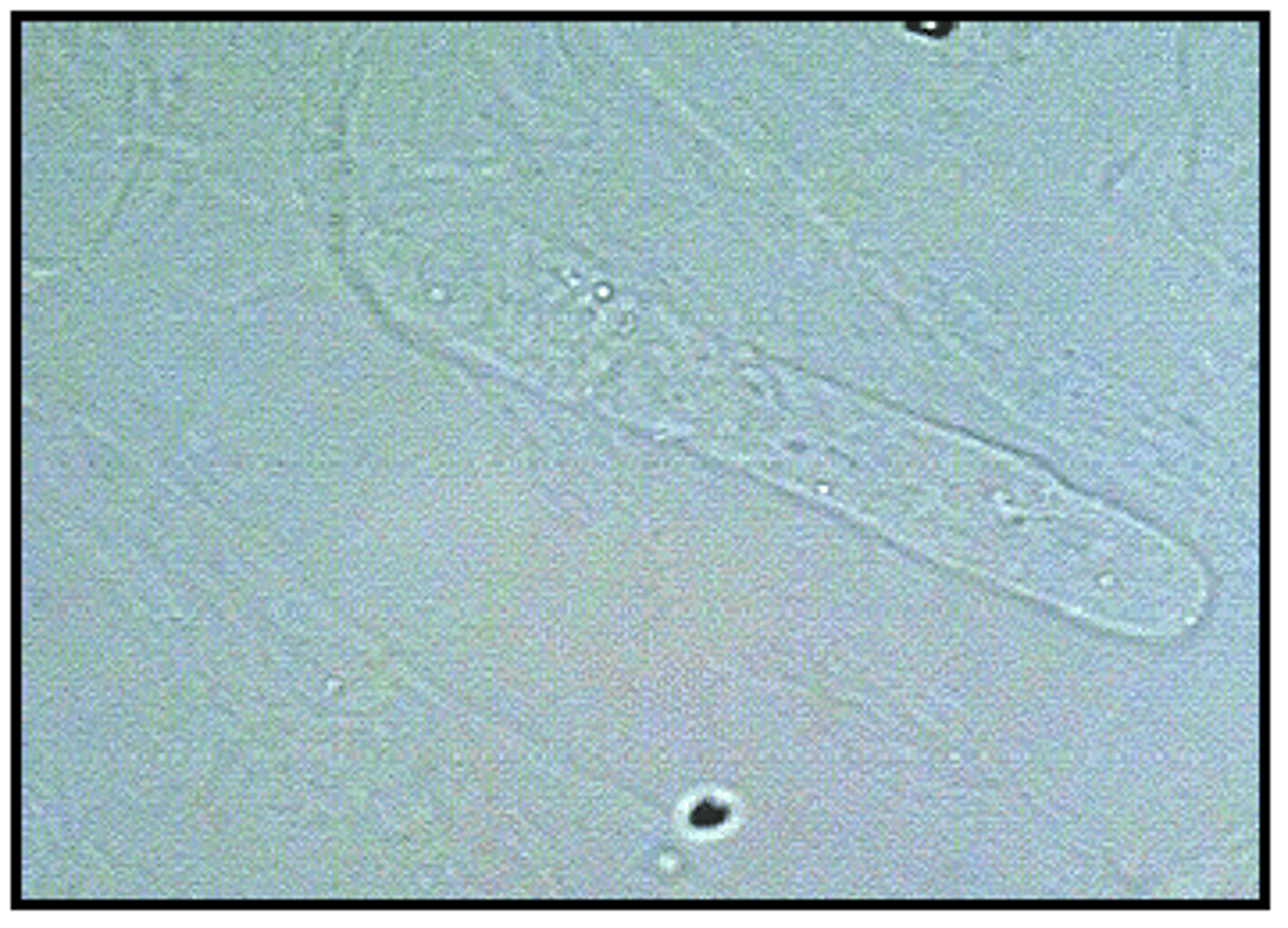
WBC CASTS associated most frequently with what condition?
pyelonephritis
are oval or dumbbell shaped CRYSTALS
Monohydrate calcium oxalate
Prescence of WBC cast
a. Pyelonephritis
b. Cystitis
c. both
d. Neither
a. Pyelonephritis
What is the difference between Cystitis and Pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis has the prescence of WBC cast