Guinea Pig Flashcards
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for VET 215 - Laboratory Animal Medicine: Guinea Pigs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Scientific Name of Guinea Pig
Cavia porcellus (Cavy)
Order of Guinea Pig
Rodentia
Common Guinea Pig Varieties
English/American (short, smooth, straight hair)
Abyssinian (short, coarse hair growing in whorls/colics)
Peruvian (long, fine, silky hair)
13 Different breeds according to the American Cavy Breeders Association an affiliate of the American Rabbit Breeders Association
Common Guinea Pig Research Stocks
Dunkin-Hartley, Hartley (outbred)
Strain 2, Strain 13 (inbred)
Guinea Pig Use in Research
Nutrition studies, allergies & respiratory diseases, infectious diseases, audiology, immunology
Infectious disease studies (especially Tuberculosis)
Guinea Pig Behavior
Docile, social, barbering, active during the day, vocal, dislike change, can't climb or jump
Guinea Pig Housing Preferences
Solid bottom w/bedding, open-top cages if >10" high, rectangular cages
Guinea Pig Diet
•Ascorbic acid/Vitamin C supplement not needed if on a good quality diet
(light breaks it down making it unstable)
•Ascorbic acid is unstable – degrades
•L-ascorbyl 2 phosphate is double bonded and stable
•Vitamin C can flavor water and cause guinea pigs to not drink plain water
•Water in bottle, bowl, or automatic watering system
Guinea pigs prefer a water bottle (environmental enrichment)
•Treats should be low in sugar, high in fiber
–Yogurt drops - BAD
–Hay based/freeze dried fruits - GOOD
–Greens and veggies - BEST
Guinea Pig Water Considerations
Avoid ascorbic acid supplements, use L-ascorbyl 2 phosphate, prefer water bottle
Males
boars
Females
sows
Babies
pups
Adult Male Guinea Pig Weight
900-1200 g
Adult Female Guinea Pig Weight
700-900 g
Guinea Pig Lifespan
5-6 years
Guinea Pig Body Temperature
99-103.1° F
Guinea Pig Heart Rate
240-310 bpm
Guinea Pig Respiratory Rate
7-130 bpm
Guinea Pig Anatomy
Compact body, short legs, no tail, 4 digits on forelimbs, 1 pair of nipples, 3 digits on hind
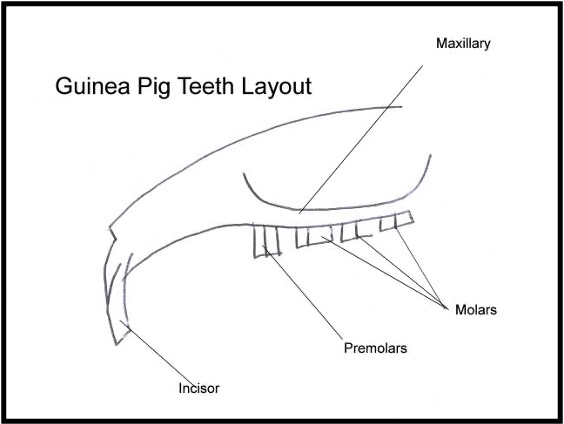
Dental formula, 2(I 1/1,C 0/0,P 1/1, M 3/3)
All teeth are open rooted
Large tympanic bullae
Unique pharynx
Soft palate is continuous with the base of the tongue and has a hole in it, called palatal ostium.
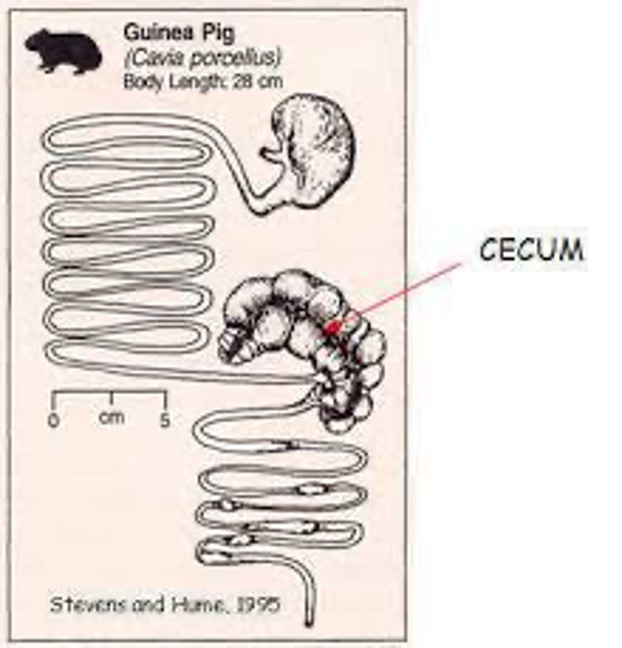
Guinea Pig Digestive System
Undivided stomach, large cecum, large intestine occupies most of the abdominal cavity, coprophagic, cannot synthesize Vitamin C
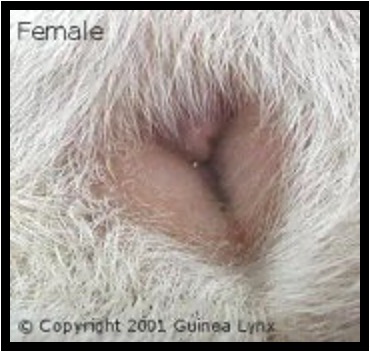
Sexing
Females: Males:
“Y” Shaped opening Prominent scrotal sacs, can extrude penis
Guinea Pig Breeding Onset - Male
3-4 months
Guinea Pig Breeding Onset - Female
2-3 months
Guinea Pig Estrous Cycle Length
15-17 days
Guinea Pig Gestation Period
59-72 days
Guinea Pig Litter Size
2-4
Guinea Pig Weaning Age
21 days
Why breed a sow before 6 months?
Fusion of pelvic symphysis
Breeding and Reproduction
Non-seasonal, continuous polyestrous
Post-partum estrus (2-10 hours post parturition)
Do not build nests
Farrowing takes 30 minutes
Young are precocious
Begin eating solid food at 1 week, weaned by 3 weeks
Guinea Pig Identification Methods
Ear notching, ear tag, tattooing, microchipping
Guinea Pig Blood Collection Sites for Small volume
Toenail bed
Marginal ear vein
Saphenous vein
Cephalic vein
Guinea Pig Blood Collection Sites for Large volume
Jugular
Femoral artery/vein
Cranial vena cava
Cardiac puncture

Blood Collection
Guinea Pig Urine Characteristics
Opaque, creamy yellow, alkaline pH 8-9, contains crystals
Guinea Pig Urine Collection
Metabolic cage
Cystocentesis
Bladder expression
Placing the animal on a cold surface (examination table)
Guinea Pig Drug Administration Routes
Meds in food or water; will often refuse if unfamiliar taste or odor
Oral meds with syringe, gavage needle
SQ – over the shoulders, max vol. 5-10 ml (tough skin > 25g needle)
IM- quadriceps or gluteals – 0.5 ml max
IP – 5-8 ml
IV- (rarely used) saphenous vein, cephalic vein or marginal ear vein
Guinea Pig Anesthesia Considerations
Fast 2-3 hours
Variable responses to anesthetics, difficult to intubate
Suggested injectable route IP due to drugs irritating when administered IM
Mask down for inhalation anesthetics
Difficult to intubate due to anatomy of pharynx and small trachea (palatal ostium)
Monitor via, ear pinch, toe pinch RR, HR
Pulse oximeter
Ophthalmic ointment
Circulating H20 pad
Guinea Pig Post-Op Care
Hydration, analgesics, frequent flipping
Guinea Pig Euthanasia Methods
Overdose of inhalation anesthetic
overdose of injectable anesthetic
70% CO2 in prefilled chamber
Common Bacteria Diseases of Guinea Pigs
Pneumonia, cervical lymphadenitis, intestinal infections, Tyzzer's disease, mastitis, conjunctivitis
Guinea Pig Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Latent viral infection, swelling of salivary glands, transmitted through saliva or urine
Guinea Pig Fungal Disease
Dermatophytosis (ringworm), pruritic, zoonotic
Protozoal Parasites of Guinea Pigs
Cryptosporidium wrairi & Eimeria caviae (coccidia)
Mites Parasitic to Guinea Pigs
Trixacarus caviae (burrowing mite), Chirodiscoides caviae (fur mite)
Trixacarus caviae
burrowing mite
Sarcoptic mange
Signs: Alopecia, crusting, pruritus
Treatment: Ivermectin, pyrethrin powders(cat friendly)
Zoonotic
Chirodiscoides caviae
fur mite
Usually no clinical signs
Treatment: Ivermectin, pyrethrin powders(cat friendly)
Biting Lice Parasitic to Guinea Pigs
Gliricola porcelli & Gyropus ovalis
–Clinical signs: alopecia, rough hair coat & mild pruritus
–Spread by direct contact
Guinea Husbandry Related Diseases
Ulcerative Pododermatitis (Bumblefoot)
Antibiotics toxic to Guinea Pigs
Bad (kill gram +)— Ampicillin, penicillin, bacitracin, erythromycin, lincomycin, gentamicin, clindamycin, streptomycin
Highly sensitive to antibiotics
Upsets natural gut flora allowing “bad” bacteria to proliferate
Better Antibiotics for Guinea Pigs
(kill mainly gram -) Tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and sulfonamides
Miscellaneous Conditions of Guinea Pigs
Includes: Neoplasia, Malocclusion, Heat Stress, Scurvy, Dystocia, Pregnancy Toxemia, Muscular Dystrophy, and Metastatic mineralization
Guinea Pig Urogenital Issues
Cystitis, uroliths, perianal sebaceous material accumulation, preputial infection, and vaginitis