MI - M5 - Gram-Positive Pathogens Streptococcus Pyogenes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is a-haemolysis?
Oral or viridans streptococci
- Partial hemolysis or blood agar plates
- S.pneumonia
- Most oral streptococci
GREEN
What is B-haemolysis? Not key
Pathogenic streptococci
- Complete hemolysis on blood agar plates
- S,pyogenes and anginosus group of oral streptococci
Clear haemolysis
What is Haemolysis? Not key
Is the destruction of red blood cells (erythrocytes)
- How to identify streptococcus
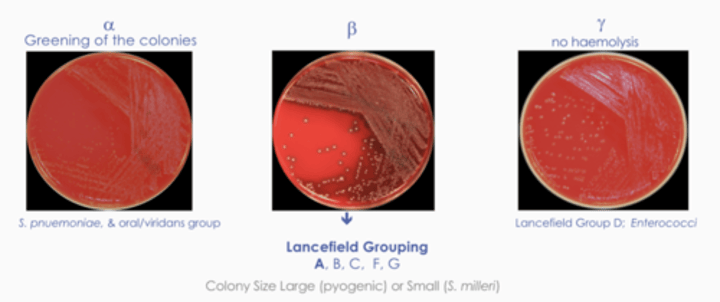
What is y-harmolysis?
Enterococci
- No hemolysis of blood agar plates
- Enterococcus faecals
No Haemolysis
What is Group A Streptococcus as a reference to?
Numerous types of associated diseases
- Most significant pathogenic streptococci

How are Streptococcus pygoenes identified? (Pharyngitis or streptococcal sore throat, scarlet fever)
- Gram +ve cocci
- Chains = Liquid media
- Catalase negative
- Haemolysis
* GAS = B haemolysos (S.pyogenes, bacitracin sensitive)
What is the pathology of Streptococcus pygoenes? (Pharyngitis or streptococcal sore throat, scarlet fever)
- Skin infections
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- Rheumatic fever = Heart
- Glomerularnephritits
What does the origin of Group A refer to?
To antibodies raised to the surface carbohydrates
- Subdivided according to M protein antigens
What is the reservoir in the Oropharynx?
- Very complex microflora
- Contains organisms found in the nasopharynx plus others such as mycoplasma spp. and B-haemolytic streptococci
- Dominated by a-haemolytic streptococci
How is streptococcus pyrogens similar to staphylococci?
Flexible with multiple virulence factors
What are the main diseases associated with streptococcus pyrogens?
- GAS Skin disease
- Invasive GAS Diseases
- Classical Strep Throat
- Sore Throat
- Bacterial Sore throat
- GAS specific diseases
- Rheumatic fever
What is GAS Skin diseases?
Pathogens that cause skin infections and can present in mouth and throat (Uncommon to have a cough, minus bacterial sore throat)
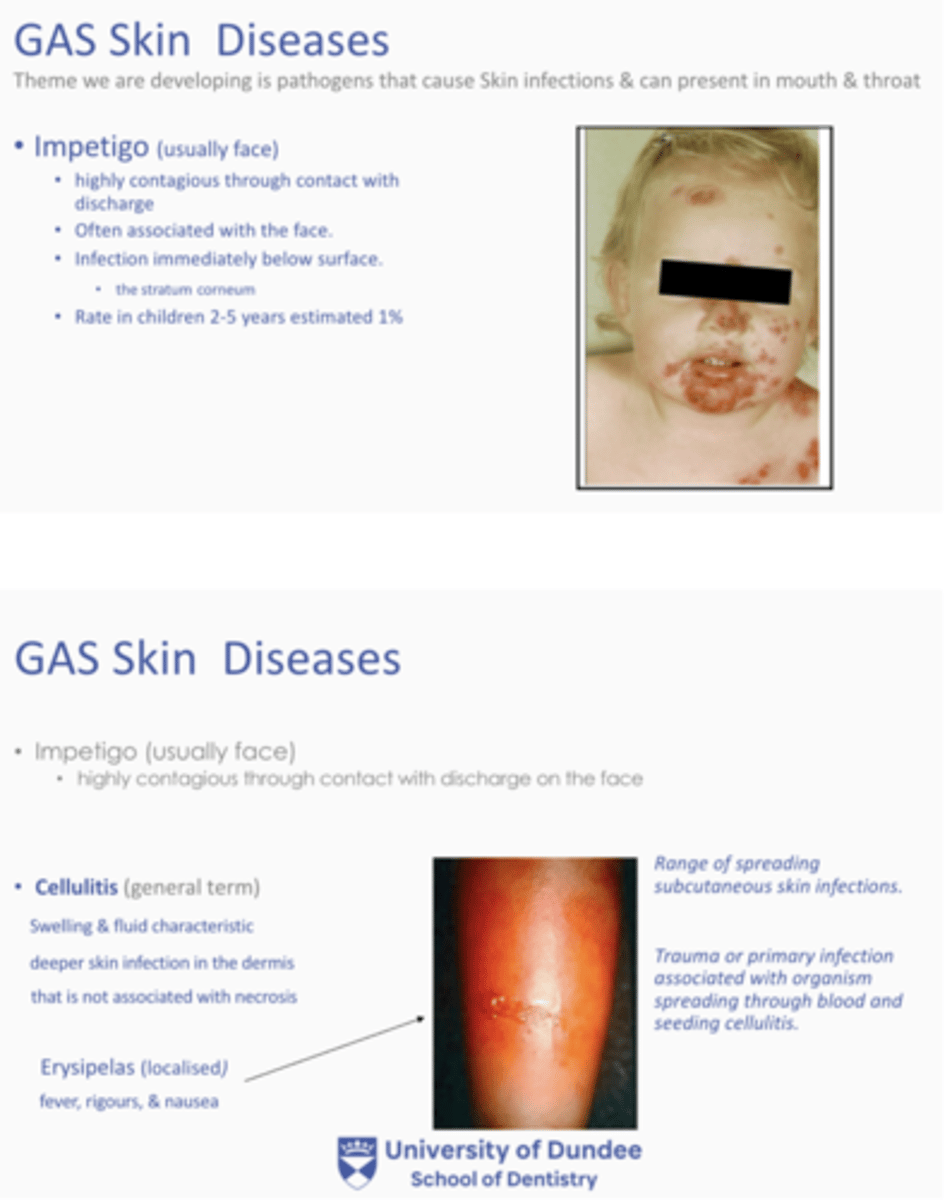
What is Invasive GAS Diseases (iGAS)?
- Impetigo, cellulitis = Invasive strepto A strains penetrate the mucous membrane and develop in lesions
- Necrosting factor (Type 2) = Rapidly destroys connective tissue
- Acute stepto gingivitis

What is classical strep throat?
Bacterial infection from pharyngitis to tonsillitis

What is sore throat?
Viral pharyngitis "Strep throat"

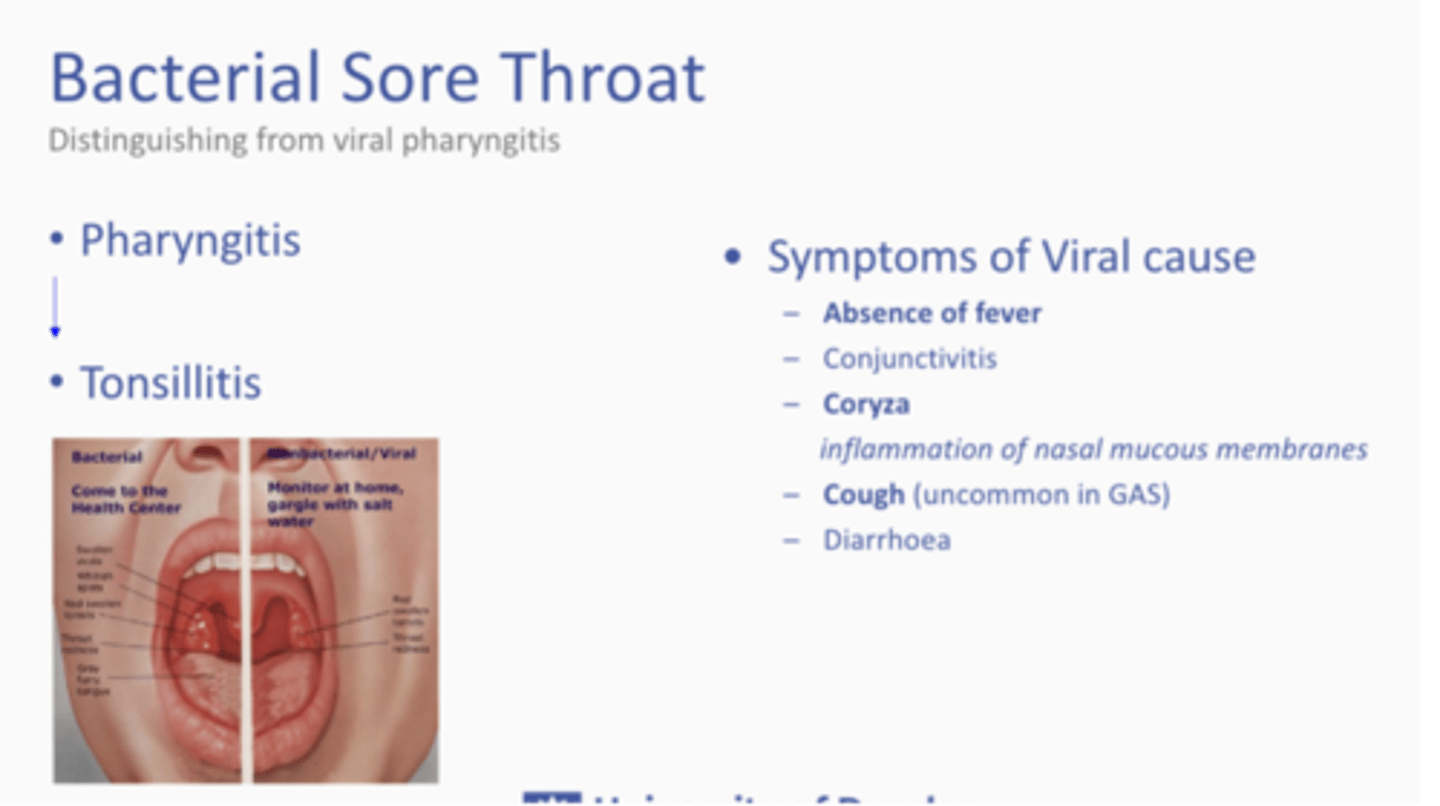
What is bacterial sore throat?
Pharyngitis>Tonsillitis
- Abscence of fever
- Coryza = Inflammation of nasal mucous membranes
- Cough (Uncommon in GAS)
What is GAS specific diseases?
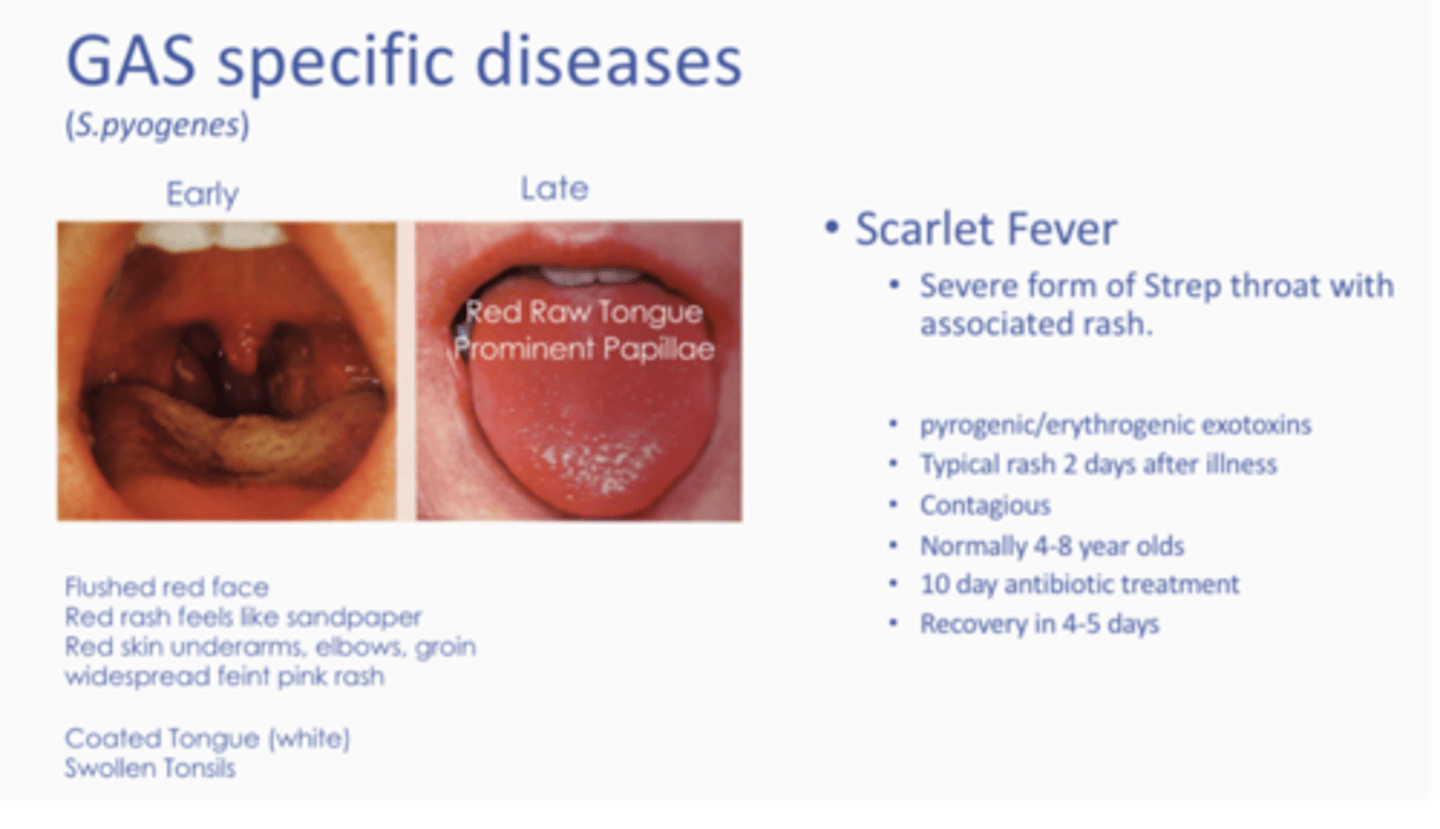
What is rheumatic fever?
- Autoimmune diseases = Increased risks of infective endocarditis
- Delayed reaction due to inadequate recovery from GAS

What are the identifications of streptococcus pyogenes?
- Gram +ve cocci
- B-haemolysis, bacitracin sensitive
- Group A carbohydrate
- Typed by M proteins
- Toxins (SLS, iGAS, Scarlett fever)
What are the pathologies of streptococcus pyogenes?
- Skin conditions
*Impetigo, cellulitis, necrotising fasciitis
- Pharynx
* Strep sore throat
* Scarlett fever
* Acute streptococcal gingivitis
- Autoimmune diseases
* Rheumatic fever
* Glomerular nephritis
What are the 3 antibiotic treatments?
GAS still relatively sensitive to antibiotics but erythromycin resistance growing
- Penicillin V = 10 day course
- Amoxicillin = Acceptable to children
- Erythromycin = Patients sensitive to penicillin
4 defences of the upper respiratory tract defence?
- Mechanical washing
- Cough response
- Mucociliary clearance
- Microbiotica/flora
What are the 3 infectious organisms in the respiratory tract?
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Fungi
What does M protiens help diseases?
Attach to the upper throat
- Fibronectin and specific binding sites
What is streptolysin (SLS) (Hae
- Tissues/Cell destruction
- Pore-forming cytolysin
- Toxin to PMN, organelles, platelets
- Important in animal models
What are key in proteins for the colonising throat?
Surface proteins = Needed for adhesion in:
- Oropharynx and nasopharynx
- Non ciliated cells covered in mucus
- Range of adhesins
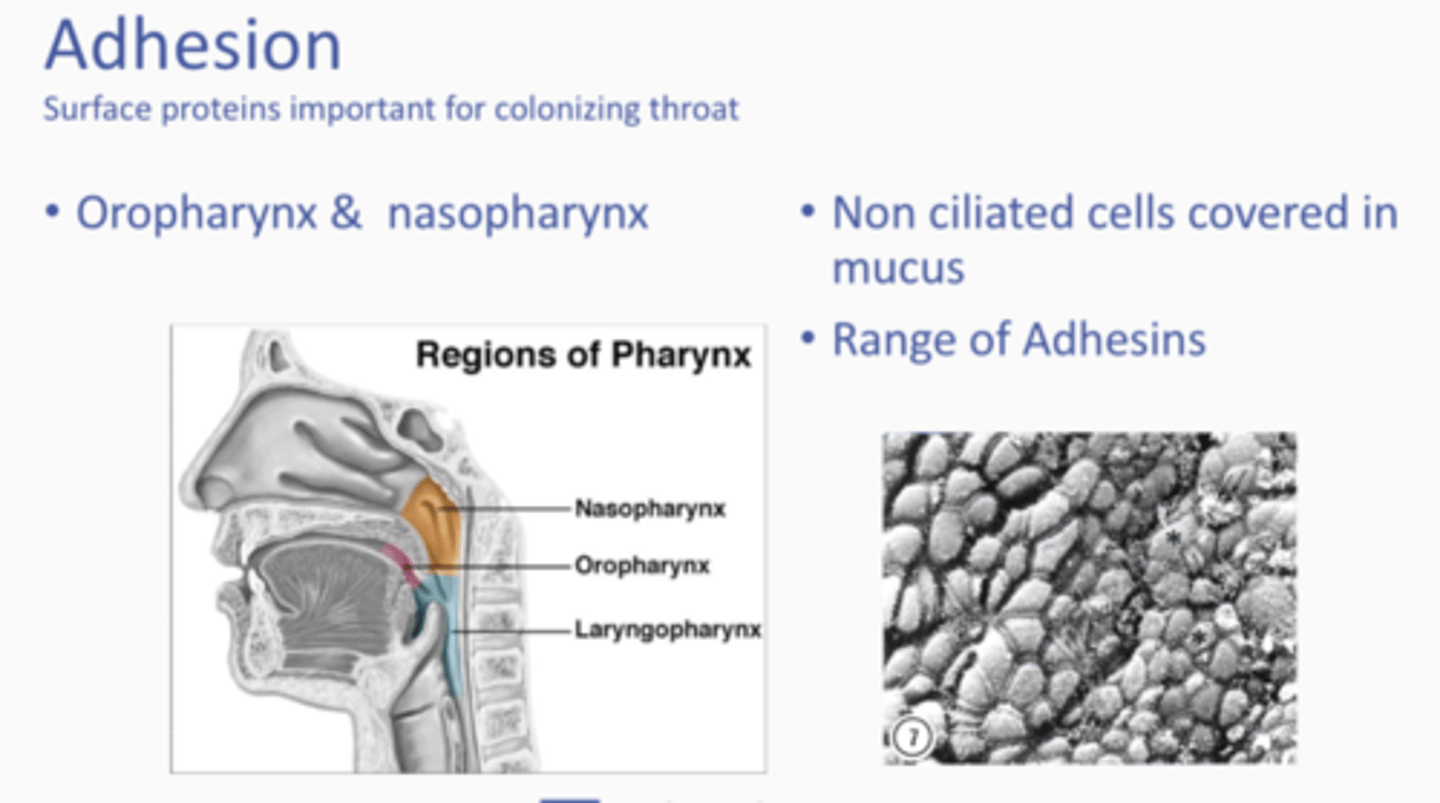
What are these in relation to the colonisation of the pharynx and skin?
- M protein
- Hyaluronic acid = Capsule
Key surface proteins for adhesion
- M proteins = Fibronectin and specific binding sites
- Hyaluronic acid = Capsule, CD44 +ve Keratinocytes
Example of evasion of host defences?
- Protease = Cleaves immunoglobulins
- Cleaves C5a = Cleaves at PMN binding site and hinders their activation
- Binds C5b and C7 = Cleaves at membrane insertion site
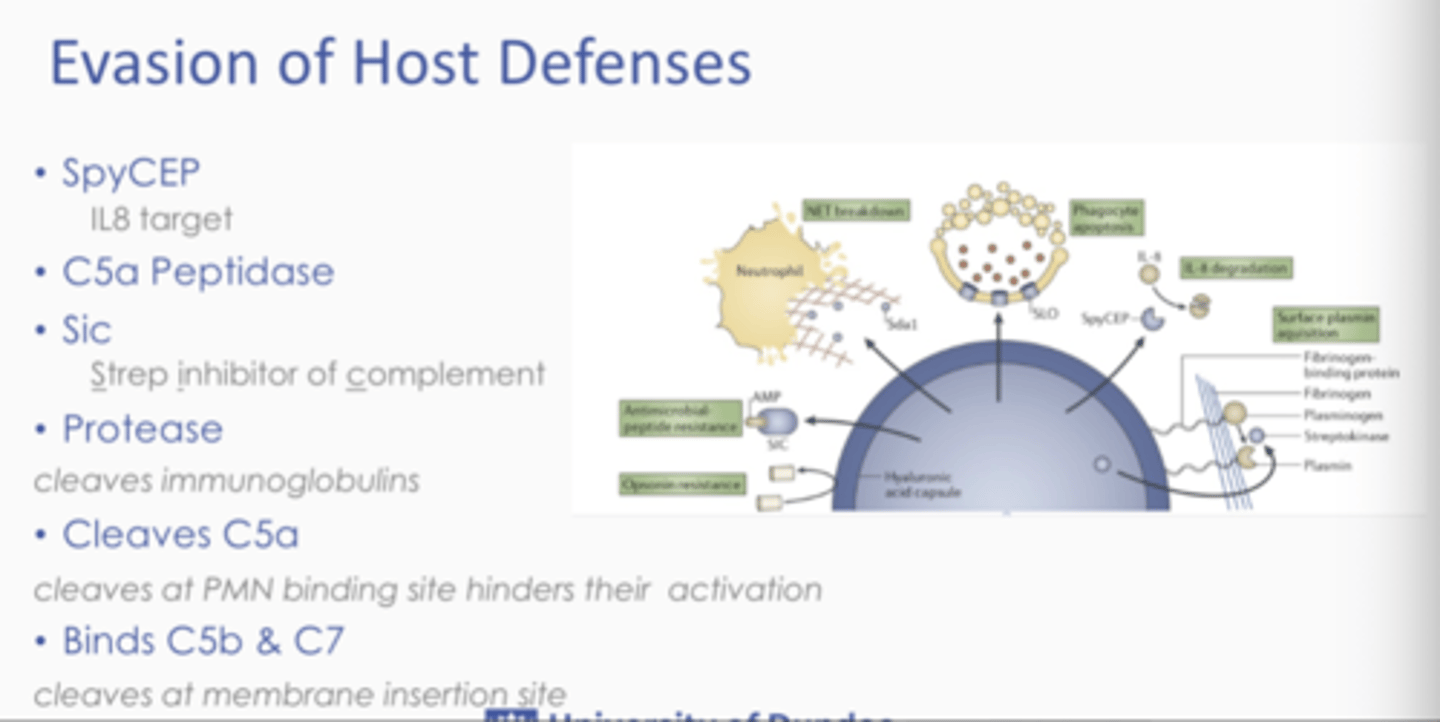
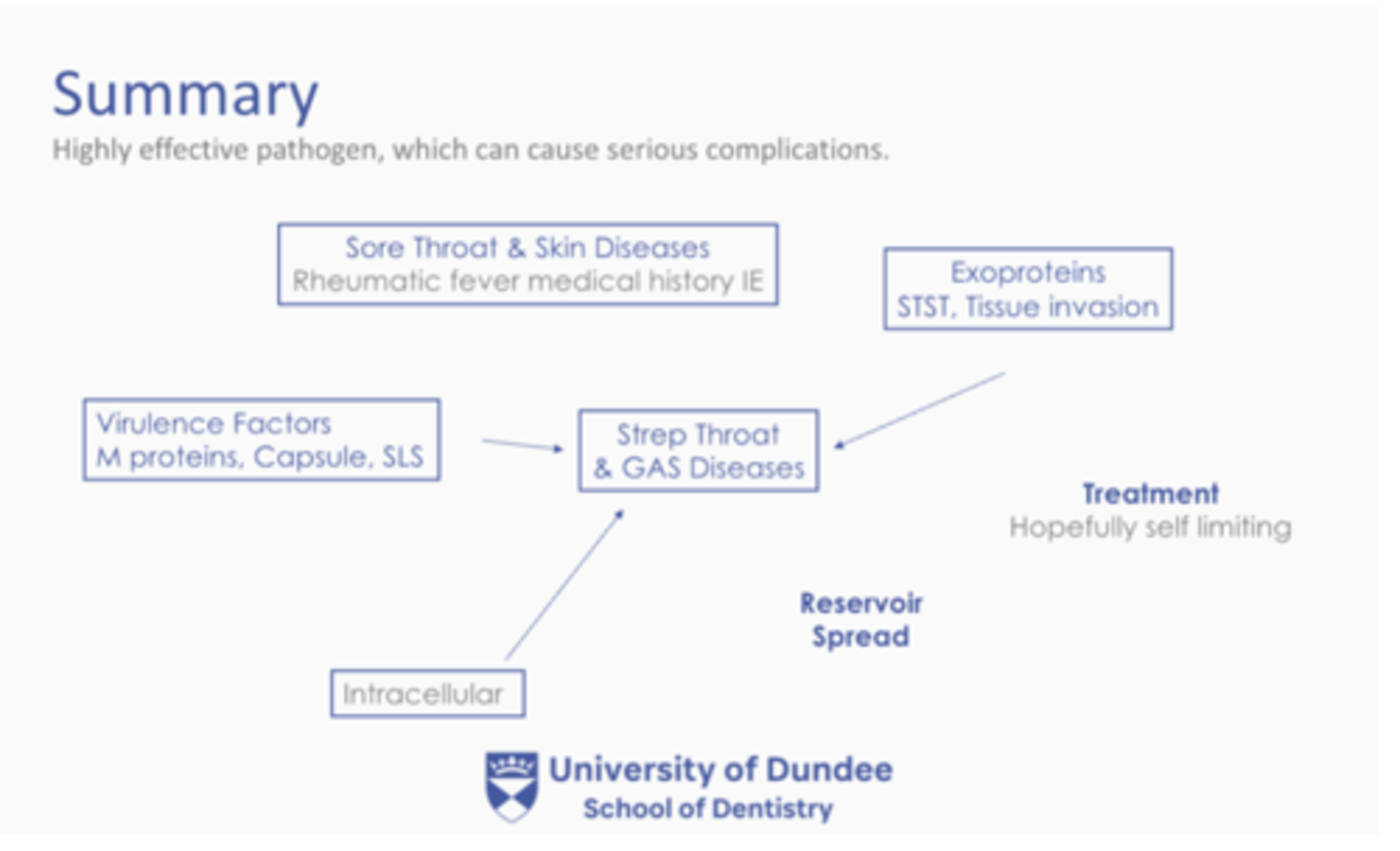
Summary - What leads to strep throat and GAS diseases?
- Virulence factors
- M proteins
- Capsule
- SLS
- Exoproteins
- STST
- Tissue invasion
* Treatment = Hopefully self limiting