STEP 2 Smartbook
1/516
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
517 Terms
How do you manage asymptomatic BV in a nonpregnant woman?
No treatment indicated (monitor only).
Why is vaginal culture for Gardnerella vaginalis not recommended to diagnose BV?
Gardnerella can be normal part of flora; culture does not differentiate colonization from overgrowth. Diagnosis is clinical.
When do you treat bacterial vaginosis?
when symptomatic (fishy order, increased discharge) or in pregnancy
What drug effect is most likely when a patient on chronic high-dose prednisone develops slowly progressive proximal muscle weakness with normal CK and ESR?
Glucocorticoid-induced myopathy → catabolism of type II muscle fibers → proximal muscle atrophy.
Which muscle fibers are preferentially affected in glucocorticoid myopathy?
Type II (fast twitch) fibers—mostly in proximal limb muscles → atrophy leads to hip/shoulder weakness.
What is the first‐line treatment for molluscum contagiosum in adults
Cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen (or curettage, or topical cantharidin).
What does topical triamcinolone treat?
(what drugs class)
topical corticosteroid
treat pruritus and inflammation
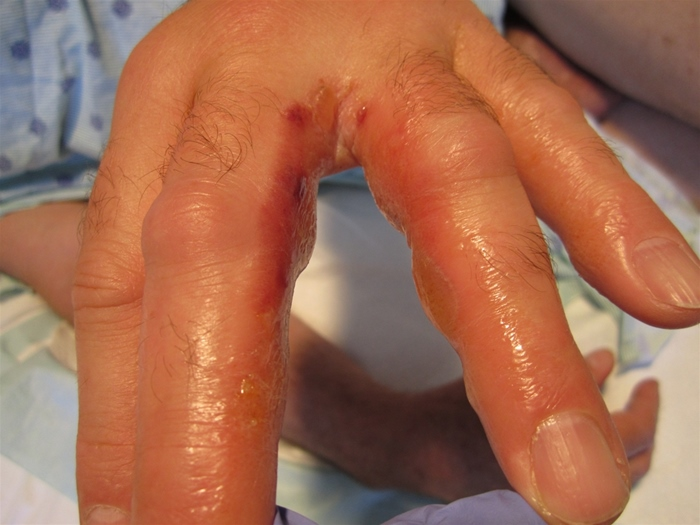
person with 2 day pruritic rash after clearing bushes around house. Diagnosis and cause?
Allergic contact dermatitis (Type IV hypersensitivity)
from Toxicodndron spec (poison ivy)
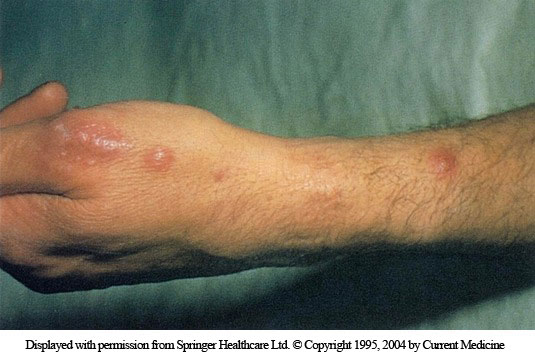
person ulcerating, pusutular nodules , associated lymphatic channels. asymptomatic, after plants (rose bush)
Sporotrichosis (fungus)
What is the first step in evaluating new iron deficiency anemia in a man or a postmenopausal woman?
Upper endoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy to identify potential sources of GI blood loss (peptic ulcer disease, malignancy, angiodysplasia, etc.).
Age > 50, ↓Hb, ↓MCV, ↓ferritin, ↑TIBC, negative guaiac test, 2/6 mid-systolic murmur with normal S2 split, sinus tachycardia and nonspecific ST-T changes. Dx . and most probable cause?
Iron def anemia → from GI blood loss
Pt with random pill count and urine drug screen for hydrocodone/acetaminophen. Pill count shows fewer pills remaining than expected, urine drug test is negative for prescribed opioid. Prescription Drug Monitoring shows on-time refills. What should you do next?
stop future opioid prescriptions (opoid diversion → not taking pills (- urine test) then selling them (less pills)
What is the first-line pharmacotherapy for acute urticaria?
Second-generation H₁ antihistamines (e.g., cetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine), given once daily.
“Raised, erythematous, pruritic plaques” + rapid spread over hours (24 hours) Dx.
urticaria (hives)
fixed, erythematous, often scaly or vesicular plaques that evolve over days. Dx.
contact dermatitis
Photosensitive rash + arthralgias + cytopenias + low-grade fever + lymphadenopathy + hypertension + diastolic murmur + mild splenomegaly. Dx. and next step for diagnosis?
SLE, antinuclear antibody assay
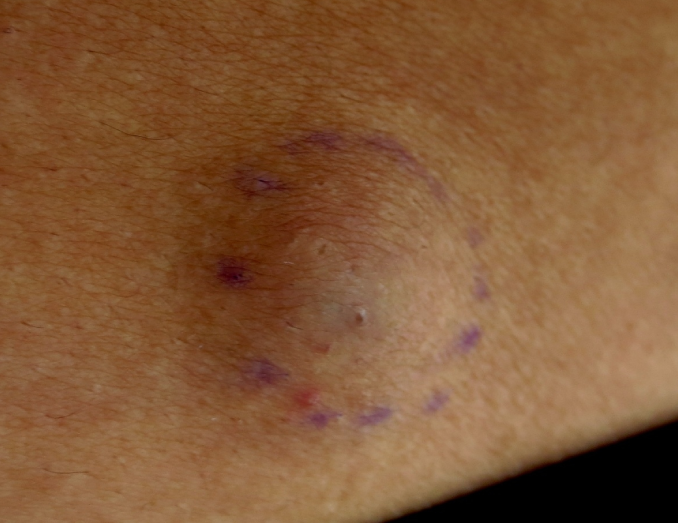
2 month history of bump in lower back, same bump 6 month ago resolved spontaneous in 3 weeks. no pruitus,’, pain, other symptoms.
firm, mobile nodule, no drainage from lesion or tenderness to palpation. does not change shape when pressed. Dx?
Epidermal inclusion cyst
[Bonus: epidermal cells trapped in dermis and proliferate → create sac lined by squamous ep → produce keratin —> central punctum = plugged pilosebacous where keratin accum
mobile → not deep invasion
firm → surrounded by fibrous capsule in dermis/subcuatenous tissue]
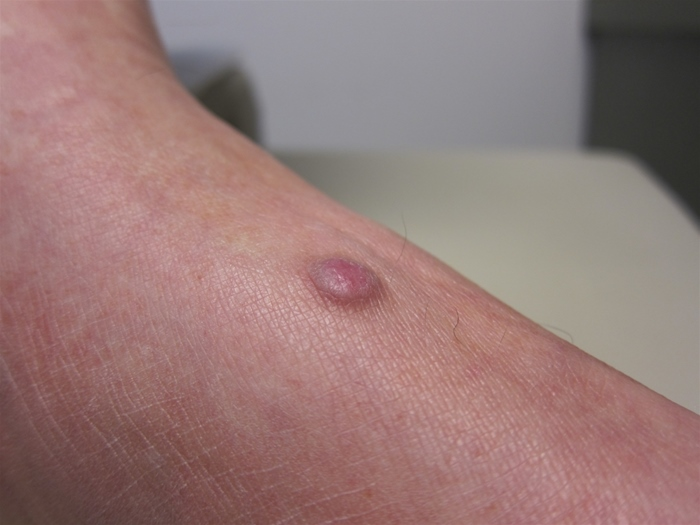
firm, hyperpigmented nodule , lower extremities, fibrous component with dimpling in center when pinched. Dx.
dermatofibroma
Which pharmacologic class is used to facilitate passage of a 5–10 mm ureteral stone?
Alpha‐1 adrenergic antagonists (e.g., tamsulosin, alfuzosin).
They relax distal ureteral smooth muscle, reduce spasms, and increase stone‐passage rates.
Why are α₁‐blockers most effective for distal ureteral stones?
The distal ureter has the highest density of α₁ receptors. Blocking those receptors relaxes the muscle there, transiently dilates the lumen, and lowers intraureteral pressure around the stone.
What does bethanechol do, and why is it inappropriate for ureteral stones?
Mechanism: Muscarinic (M₃) agonist → stimulates detrusor muscle contraction to relieve urinary retention (e.g., postoperative atony).
Why wrong: It increases bladder contractions, not ureteral relaxation. May worsen backpressure on a blocked ureter.
What is oxybutynin used for, and why is it contraindicated in stone passage?
Mechanism: Antimuscarinic → relaxes detrusor overactivity (overactive bladder).
Why wrong: Relaxing bladder outlet doesn’t help a ureteral stone. Antimuscarinics can also reduce ureteral peristalsis, potentially hindering stone movement.
What is phenazopyridine used for, and why won’t it help pass a stone?
Mechanism: Topical urinary tract analgesic → soothes mucosal lining to relieve dysuria.
Why wrong: Does not affect ureteral peristalsis or stone passage; only masks pain.
34 yo man worse headaches (esp during stress), dizzy, sometimes blurry vision and nausea. BP 170/100 mm Hg supine and 150/90 standing. pulse 90/min reg, BMI 24, elevated glucose. Dx?
pheochromocytoma
(paroxysmal headache and hypertension, elevated BP, unexplained hyperglycemia)
A young woman with voluminous, watery, recurrent diarrhea and a completely negative workup (normal colonoscopy, normal labs). Abnormally low stool osmolarity. Dx?
factitious diarrhea by dilution by water or laxatives
A young woman with voluminous, watery, recurrent diarrhea and a completely negative workup (normal colonoscopy, normal labs), nocturnal bowel movements. Next diagnostic test and Dx?
stool osmolarity
Dx. = factitious diarrhea (most likely)
A young woman with voluminous, watery, recurrent diarrhea and a completely negative workup (normal colonoscopy, normal labs). Elevated osmotic gap in stool. Dx?
factitious diarrhea indicating osmotic laxative use
31 yo woman with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, regular menses, normal vitals and BMI, sig retroverted uterus. most appropriate contraception
Copper containing IUD
nonhormonal, effective, uterine position does not affect insertion, expulsion or failure
(estrogen contraindicated)
64 yo persistent dry cough and worsening dyspnea, mild dyspnea with exertion, previous inferior wall MI. JVP normal, no edema. fine dry inspiratory crackles in lower lung zones. Chest X—ray normal. Dx.
Early interstitial fibrosis (ILD)
Initial imaging modality for suspected early ILD even if normal CXR?
High-resolution CT (thin 1 mm slices, prone imaging).
CHF crackles vs. ILD crackles—key distinguishing feature
CHF = wet/popping crackles with volume overload signs; ILD = fine/dry “Velcro” crackles, often before CXR abnormality.
Hallmark physical exam findings that argue against LV failure in dyspnea?
Normal JVP, absence of peripheral edema, no S3 gallop, no orthopnea/PND.
Most common cause of painless gross hematuria in a smoker > 40 years old
Bladder urothelial carcinoma
Next best step for evaluation of gross hematuria with high suspicion for bladder cancer
Cystoscopy with biopsy
Does BPH (enlarged prostate) and prostate cancer cause hematuria?
no (very rare, look for other factors)
Mixed LMN signs in arms + UMN signs in legs = localization to?
Cervical spinal cord lesion (compression at C5–C8 level).
Why is demyelinating polyneuropathy unlikely if reflexes are increased in lower extremities?
demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) produces symmetric decreased/absent reflexes (LMN neuropathy). Increased reflexes are UMN and point to spinal cord, not peripheral.
Runner with burning pain in the forefoot, worsened, elicits clicking sensation when 3rd and 4th metatarsal heads squeezed together and cause burning pain over plantar surfaece of foot—likely diagnosis?
Motor neuroma (interidigital nerve entrapment)
Behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia vs Alzheimer disease—key difference in symptom timeline
FTD = early personality/behavior changes, relative sparing of memory early; AD = early memory loss, late behavioral changes
In a sickle cell patient with insidious, unremitting hip pain, normal inflammatory markers, and normal plain films, what’s the top diagnosis?
Avascular necrosis (osteonecrosis) of the femoral head
37-year-old woman, 24 h of stabbing RUQ/epigastric pain + nausea/vomiting, now confused and hypotensive, fever, direct hyperbilirubinemia, leukocytosis, metabolic acidosis. Dx
acute cholangitis
(Fever + RUQ pain + jaundice (Charcot triad) plus hypotension & AMS (Reynolds pentad))
lactic acidosis seen in severe sepsis
First-line imaging for suspected cholangitis
RUQ ultrasound → bile duct dilation and stones; follow with ERCP within 24–48 h for biliary decompression
CD4 threshold for live vaccines in HIV patients (like VZV)
≥200 cells/mm³ → live vaccines permitted; <200 → contraindicated.
Lateral elbow pain + tenderness distal humerus+ pain on resisted wrist extension (aka grasping tools). No trauma, not swollen, full ROM. Dx.
lateral epicondylitis
Initial treatment for lateral epicondylitis
activity modification, counterforce bracing/ strap , physical therapy
Imaging indications in suspected lateral epicondylitis
Only if red flags (recent trauma, systemic signs, severe ROM limitation) or diagnosis uncertain after exam.
Moderate-intensity statin examples
1)
2)
3)
4)
and doses
Rosuvastatin 5–10 mg
Atorvastatin 10–20 mg
Simvastatin 20–40 mg
Pravastatin 40–80 mg
First step in statin-related myalgias
Switch to a different statin (lower myopathy risk), consider moderate-intensity, check TSH, consider alternate-day dosing
Why avoid high-dose NSAIDs immediately after MI?
Concern (theoretical) for impaired scar formation and higher risk of myocardial free-wall rupture in the early post-infarct period.
Recent MI (<4 days) + pleuritic positional pain + PR-segment depression. dx.
peri-infarction pericarditis
How long do troponin levels stay elevated post-infarct?
Bonus: what is significance
1-2 weeks post-infarct
can’t distinguish new from old injury
Dull, pressure-like, exertional, not improved by position chest pain
dx.
ischemic chest pain
When does rhabdomyolysis cause hypercalcemia?
During recovery phase, due to release of Ca from injured muscles, often with ↑ phosphate.
usually causes hypocalcemia initially
What is the most likely cause of acute limb ischemia after MI?
LV mural thrombus (from stasis in infarcted wall)
What test should you order in suspected LV thrombus?
Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE)
Acute limb ischemia after MI = _______ —> look at ________!
embolic, look at heart
after STEMI, Sudden cold, pulseless leg = _______ occulusion
arterial (Acute limb ischemia)
warm swollen limb = _______ occulusion
venous (DVT)
First step after biopsy-confirmed gastric adenocarcinoma?
CT abdomen/pelvis for staging.
Are tumor markers like CEA or CA-125 used to stage gastric cancer?
No — low sensitivity/specificity, and do not affect management.
When is H. pylori eradication useful in gastric cancer?
In early-stage resectable cancer or MALT lymphoma, but not curative for adenocarcinoma.
What is the best method to prevent infection in burn wounds?
Early excision and grafting (within 5 days)
Why don't you use prophylactic systemic antibiotics in burn patients?
Because they don’t penetrate eschar, don’t prevent infection, and increase resistance risk
painless chronic nodes + normal labs = ________ —> ____ (which gene)
follicular lymphoma —> BCL-2
What genetic translocation is associated with follicular lymphoma?
t(14;18) → BCL-2 overexpression
What is the classic clinical presentation of follicular lymphoma?
Older adult with painless, slowly progressive lymphadenopathy (axillary, cervical, inguinal ± mediastinal), no B symptoms, normal labs
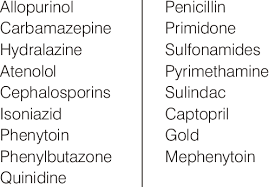
Which drugs can cause drug induced lymphadenopathy (name like one)
phenytoin, carbamepine (antivonvulsants) allopurinol , isoniazid, quinidine.
Which structures are at risk in a supracondylar fracture with posterior displacement?
Brachial artery and median nerve
What structure is at risk in elbow flexion injuries?
Ulnar nerve, due to proximity to posterior medial epicondyle
ocean water exposure, hereditary hemochromatosis, hemorrhagic bullae + necrotizing fasciitis, sepsis within 24 hours. Dx. (which bug)
Vibrio vulnificus
What comorbidity increases risk of Vibrio vulnificus infection?
Hereditary hemochromatosis (iron promotes rapid bacterial growth) [liver disease, ocean water]
What is the main benefit of intensive glycemic control in diabetes?
↓ risk of microvascular complications (retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy)
Does tight A1c control lower the risk of MI or stroke in 5 years?
No — macrovascular benefit is uncertain and may require decades
athlete with subactue, localized, activity related pain, swelling and point tnederness on palpation on anterior aspect of shin. X ray normal. Dx.
tibial stress fracture
novice runner with diffuse painful area along shaft of tibia. Dx
medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints)
What is the first-line antidote for muscarinic symptoms in organophosphate poisoning?
Atropine
What reverses both muscarinic and nicotinic symptoms?
Pralidoxime (must be given after atropine)
multiple victims, fruity odor, pinpoint pupils, SOB, drooling, diaphroesis, bradycardia, tachypnea, rhonchi and wheezing. Dx.
cholinergic toxicity (DUMBELS, organophosphate poision)
multiple victims, confusion, headache, syncope, bradycardia, altered mental status, cherry red skin. Dx.
carbon monoxide poisoning
What’s the first-line treatment for confirmed chlamydia in a nonpregnant woman?
Doxycycline for 7 days
When do you use ceftriaxone for STIs?
Confirmed gonorrhea, or empirically when both infections are suspected but test results are pending
ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) patient with orthopnea and morning headaches, low O2 — most appropriate next step?
Noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation
✅ Supports weak muscles
✅ Prevents CO₂ buildup
✅ Improves survival
Patient with history of gastric bypass presents with vague bone/muscle pain and ↑ ALP. What is your next step?
Check 25-hydroxyvitamin D to evaluate for osteomalacia due to vitamin D deficiency.
18 month , nasal congestion, fever, cough increased in frequency. resp 45, O2 sat 96%. active, playful , mild tachypnea, intermittent suprasternal rectractions. auscultations scattered wheezing and crackles over bilateral lung fields. Dx. and next step?
Bronchiolitis, dischaarge with close follow up
Why don’t we use bronchodilators/steroids routinely in bronchiolitis?
Because airway obstruction is not due to bronchospasm or inflammation; bronchiolitis is a viral + obstructive problem.
Key differences between malignant hyperthermia and neuroeleptic malignant syndrome.
MH = triggered by anesthesia, develops in minutes
NMS = antipsychotics, develops over days
What causes primary spontaneous pneumothorax?
rupture of subpleural blebs
What is the first-line treatment for a small Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax in a stable patient?
Supplemental oxygen + observation
Next step in treating asymptomatic gallstones? normal liver and bile duct and passes stone.
no treatment at this time (don’t need to do ultrasound)
What’s the most common cause of empyema with foul-smelling pleural fluid? (specific)
Polymicrobial infection from oral anaerobes (eg, Fusobacterium, Prevotella, Bacteroides, Streptococcus intermedius).
traumatic head injury, worsening mental status over minutes, swelling over left frontoparietal region. Dx
epidural hematoma
What is the first-line treatment for mild cervical radiculopathy without red flags?
NSAIDs + avoid provocative activity
When do you order MRI in neck pain with nerve symptoms?
Only if there is motor weakness, bilateral symptoms, red flags, or failure to improve with conservative therapy
Why avoid imaging right away (MRI) in cervical radiculopathy?
Most improve in 4–6 weeks with NSAIDs and activity mods
Diabetic nephropahty diagnosis can be presumed in patients with renal dysfunction andeither ___________ or ___________, which correlates with teh prescence of DN
prolonged history of diabetes ( over 5 years for Type 1)
proliferative diabetic reintopathy
child with sickle cell has sudden onset unilateral weakness,pain in arms, legs, back and clear CT head. Dx. and treatment?
ischemic stroke
exchange transfusion
What are the three types of polycythemia?
Relative polycythemia = ↓ plasma volume (e.g. dehydration)
Primary polycythemia = ↑ RBC production from marrow itself (e.g. PV)
Secondary polycythemia = ↑ EPO (e.g. OSA, COPD, high altitude, RCC)
What is the most common asymptomatic cause of erythrocytosis in obese men? (high hematocrit, high hemoglobin, normal platlets)
obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
Patient has history of perianal abscess and now has chronic foul-smelling discharge with an indurated lesion near the anus. What’s the diagnosis and next best step?
Anorectal fistula → next step: Surgical evaluation (for fistulotomy)