A and P chapter 6 bones
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
before 8 weeks of development the fetal skeleton is composed of ?
hyaline cartilage and fibrous membranes
After 8 weeks of development the fetal skeleton is composed of ?
bone
By adulthood what is the human body composed of ?
Bone and Cartilage at the Joints
Skeleton cartilage
contains no blood vessels
hugh perecnt of water - give resiliency
surrounded by the perichondrium (dense irregular tissue) that resists outward expansion
Skeletal cartilage types (3)
•Hyaline – support/flexibility, most abundant
•Elastic – takes repeated bending
•Fibrocartilage – e.g.intervertebral discs
Appositonal
cells of perichondrium secrete matrix; growth from outside edge
Interstitial
lacunae-bound chondroblasts; expanding the cartilage from within
Calcification of cartilage occurs ….?
•During normal bone growth
•During old age
Functions of the bones
§Support - form the framework that supports the body and cradles the soft organs
§Protection - provide a protective case for the brain, spinal cord, and vital organs
§Anchorage- muscle to bone (levers)
§Mineral storage - reservoir for minerals, especially calcium and phosphorus
§Blood cell formation - hematopoiesis occurs within the marrow cavities of bones
§Fat storage – yellow marrow
§Hormone production – osteocalcin
•Regulates insulin release, glucose homeostasis
levels of bone structure
•Gross
•Microscopic
•Chemical
structure of bone
•Bone
•Cartilage
•Nerve
•Fibrous connective
Epithelial and smooth muscle
Gross anatomy of bones : markings
•Bulges, depressions, and holes (Table 6.1) that serve as:
wSites of attachment for muscles, ligaments, and tendons
wJoint surfaces
wPassages for blood vessels and nerves
Gross anatomy of bones: textures
•Compact bone – dense outer layer
•Spongy bone – honeycomb of trabeculae filled with red or yellow bone marrow
Diaphysis
the tubular shaft of long bones
•Compact bone surrounds the medullary cavity
Medullary cavity
cavity that contains yellow bone marrow
Epiphyses
§ Ends of long bones
•Exterior compact bone, interior spongy bone
•Joint surface is covered with articular (hyaline) cartilage
Epiphyseal line
separates diaphysis and epiphyses
articular cartilage
Joint surface is covering
(made of hyaline cartilage )
Periosteum
outer membrane
• The outer fibrous layer is dense, irregular connective tissue
•Inner osteogenic layer (osteoblasts, osteoclasts)
•Richly supplied with nerve fibers, blood, and lymphatic vessels
•Secured to the bone by perforating fibers (strongest at tendon/ligament attachment)
Endosteum
internal surfaces of bone
tendons
attach bone to muscle
ligaments
attach bone to bone
Location of hematopoietic tissue (Red marrow)
IN INFANTS
•Found in the medullary cavity and all areas of spongy bone
Location of hematopoietic tissue (Red marrow)
IN ADULTS
•Found in the spongy region (diploë) of flat bones, some irregular bones, and the head of the femur and humerus
The chemical composition of the bone
ORGANIC PORTION
§Cells - living
§Osteogenic
§Osteoblasts
§Osteocytes
§Osteoclasts
§Osteoid (35% by mass) - non living
§Collagen fibers ( between lamella)
§Proteoglycans, glycoproteins
Osteogenic cell
synthesis bone ; stem cell

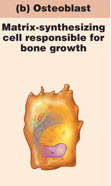
Osteoblasts
make up the majority of the matrix
cell responsible for bone growth
cell that creates bone
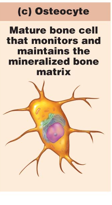
Osteocytes
maintain the matrix
matured bone cells that maintain the mineralized bone matrix
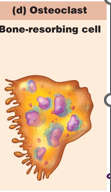
Osteoclasts
break down the matrix
breaks down the bone for calcium
bone resorbing cell
what do Collagen fibers, proteoglycans and glycoproteins provide to the bone?
flexibility
hydration
*glycoproteins are a polar nature that attaches water and hydrates the bone
Chemical composition of bone
INORGANIC PORTION
§Mineral salts (65% by mass)
§Mainly calcium phosphates
§Responsible for bone hardness and its resistance to compression
Formation of bony skeleton occurs…?
Before birth
Bone growth occurs..?
Until early adulthood
Remodeling and repair of bone occurs…?
As adults
Intramembranous ossification
*Hardening of tissue
§bone develops from a fibrous membrane(perichondrium ) formed from mesenchyme
•All flat bones of the skull, clavicles
(outside —— in)
Endochondral ossification
*hardening of bone tissue
§bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage
Majority of bone formation
(inside —— out)
§Growth in length of long bones
•Elongation occurs at the epiphyseal plate, bone grows toward diaphysis
•Epiphyseal plates are eventually replaced by bone tissue once growth in length has stopped (~18 in females, ~21 males)
Epiphyseal plates
where cartilage cell divides, and is replaced by bone
§Growth in thickness throughout life
Appositional growth (outside —- inside)
cells lining inner periosteum
Hormonal control
•Growth hormone, thyroid hormone
•Steroid hormones (sex hormones during adolescence)
Bone Remodeling (change in shape and density)
§consists of both deposit and resorption of bone tissue.
•Occurs during growth and throughout life
•Controls on remodeling
wCa+ levels in blood
wMechanical and gravitational forces
Blood Ca levels are regulated calcitonin and parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Bone fractures are classified by:
•The position of the bone ends after fracture
•The completeness of the break
•The orientation of the break to the long v.s short axis
•Whether or not the bones ends penetrate the skin
Nondisplaced bone fracture
bone ends retain their normal position.
Displaced bone fracture
§bone ends are out of normal alignment
Complete fracture
broken all the way through.
*Referring to a break
Incomplete fracture
not broken all the way through
*Referring to a break
Linear fracture
parallel to the long axis of the bone
looks like when you are cutting sub-bread
Transverse fracture
along transverse plane
can cause an infection and infect the red blood cells (which is more dangerous because infection can spread to whole body)
Compound( open) fracture
§bone ends penetrate the skin
simple ( close) fracture
bone ends do not penetrate the skin
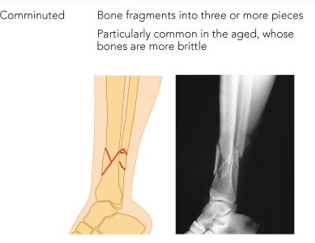
Comminuted fracture
bone is broken into 3 or more pieces.
commonly found in old people who have brittle bone.
long and short bones are mostly affected
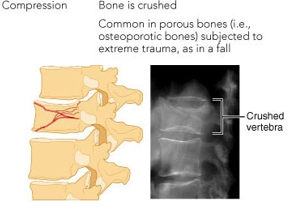
Compression fracture
bone is crushed
vertebral and knee bone are mostly affected
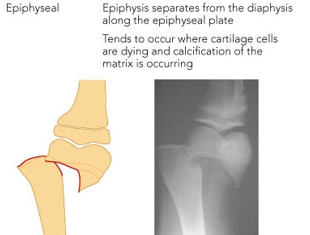
epiphyseal fracture
only happens in long bone
when epiphysis separates from the diaphysis along the epiphyseal plate
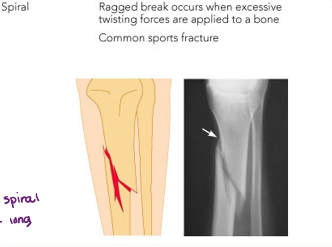
spiral fracture
ragged break that occurs when excessive twisting forces are applied to the bone
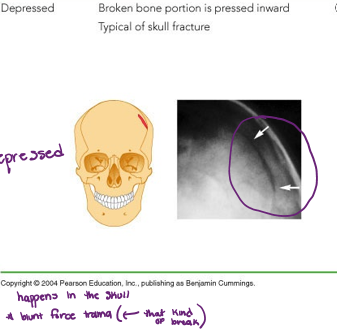
Depressed fracture
broken broke portion is pressed inward
typical fracture for the skull
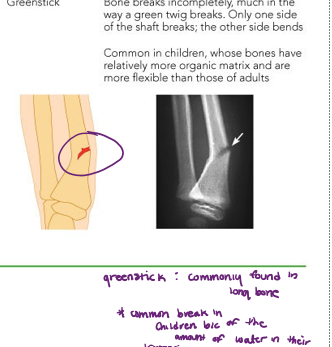
Greenstick fracture
bone breaks incompletely.
one side of the shaft breaks, while the other side bends
commonly occurs in children because of the amount of water in their bones.
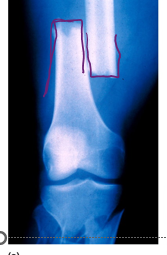
Closed reduction
•Broken ends are manipulated back into place without surgery
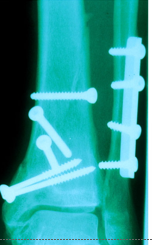
Open reduction
•Fragments are exposed by surgery and fixed in place with hardware
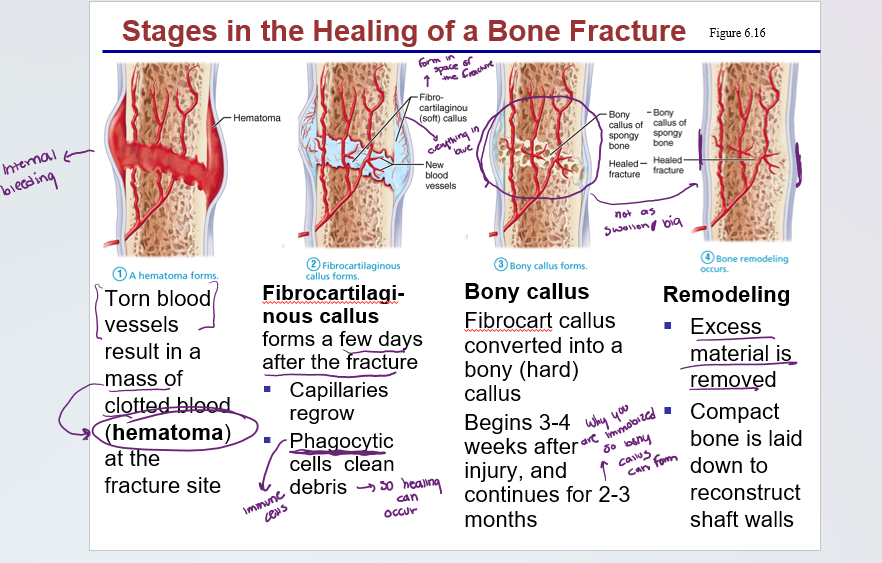
Stages in healing of a bone
1) hematoma forms
2) fibrocartilaginous callous forms
3) bony callus forms
4) bone remodeling occurs
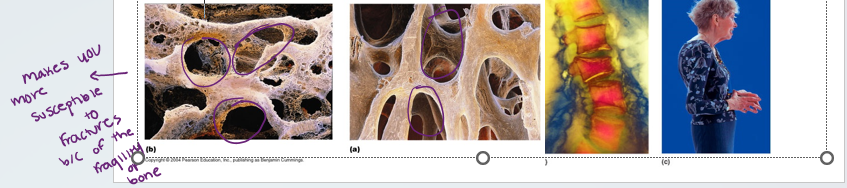
Osteoporosis
•Group of diseases in which bone reabsorption outpaces bone deposit
•Spongy bone of the spine is most vulnerable
•Occurs most often in postmenopausal women
•Bones become so fragile that sneezing or stepping off a curb can cause fractures
osteomalacia
mostly affects adults
•Bones are inadequately mineralized causing softened, weakened bones
•Main symptom is pain when weight is put on the affected bone
•Caused by insufficient calcium in the diet, or by vitamin D deficiency
Rickets
is osteomalacia but in children
•Bones of children are inadequately mineralized causing softened, weakened bones
•Bowed legs and deformities of the pelvis, skull, and rib cage are common
•Caused by insufficient calcium in the diet, or by vitamin D deficiency
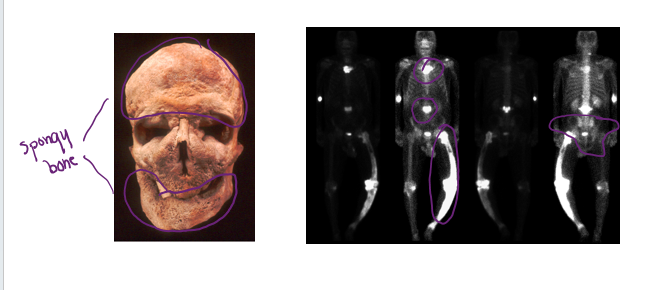
Paget’s disease
§Excessive bone formation and breakdown: uncontrolled remodeling
§Pagetic bone = excessively high ratio of spongy to compact bone is formed
•Weaker than normal bone
§Osteoclast activity wanes, but osteoblast activity continues to work
§Often affects the spine, pelvis, femur, and skull
§Unknown cause (possibly viral)
§Treatment includes bisphosphonate drugs and calcitonin
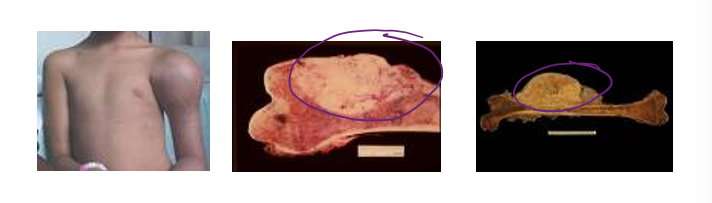
Osteosarcoma
homeostatic imbalance
uncontrolled growth of malignant tissue
primarily in children and young adults
Gorham-Stout Syndrome (Vanishing Bone DO)
Progressive bone loss (osteolysis)
Commonly affected areas: ribs, spine, pelvis, skull, collarbone (clavicle), and jaw
Symptoms: pain and swelling, disfigurement and functional disability of affected areas. Severity varies.
Cause unknown