Unit 5- Lions Test
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Organism
Individual living thing
Ecology
The study of how organisms interact with each other and with their environment
Population
all the individuals of the same species living in a defined area
Habitat
a defined area where a species lives
Community
All living organisms living close enough together for potential interactions
ecosystem
includes both the biotic and abiotic factors of the environment
biotic factors
living factors of an environment
abiotic factors
non-living factors of an environment
biosphere
every place on earth that is inhabited by life
autotrophs
“self-feeders”/ make their own organic nutrients using external energy sources/ also called producers
heterotroph
“Different feeder”/obtain organic nutrients from other organisms, also called consumers
Food chain
linear sequence of matter and energy flow through an ecosystem. Arrows point in the direction of flow
food web
a network of interconnected food chains
decomposers
feed on all trophic levels, convert organic matter into inorganic matter
10% rule
as you move from one tropic level to the next, only 10% of the energy at one level is available at the next. This means that 90% of energy is lost as heat or metabolic process
niche
role of an organism in its habitat
keystone species
plays an especially important role in its community/ if removed, has drastic effects
predators
help control prey populations, which in turn affects other trophic levels
ecosystem engineers
create, destroy, or change a habitat
mutualists
two or more species who interact with each other for each other’s benefits
population size
number of individuals in a population
population density
the average number of individuals in a population per unit of area or volume
population distribution
average number of individuals per unit of area or volume
limiting factors
density-dependent factors, density- independent factors
density-dependent factors
increase as population density increases
density-independent factors
do not vary with population density
Carrying capacity
the maximum population size that a particular environment can sustain
r-selected
species who live in unstable environments. There is a large number of offspring produced, but individuals often die young
k-selected
species who live in stable environments. their population is often at or near carrying capacity
population pyramid
a bar graph that measures age and sex data
survivorship curves
number of individuals still alive at each age
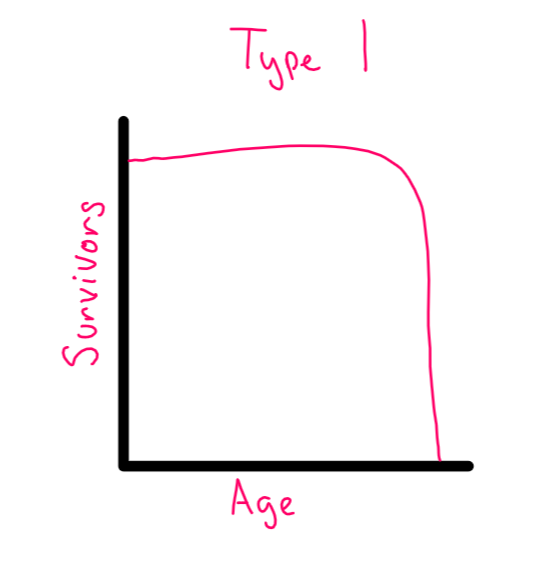
Survivorship Curve- Type 1
low death rate- most live until old age
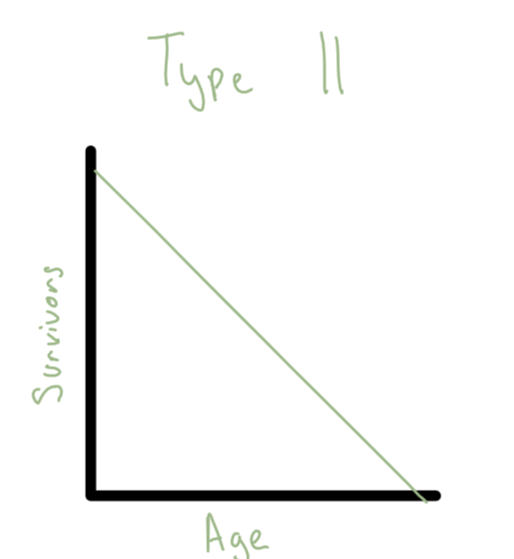
Survivorship Curve- Type 2
moderate death rate- all ages die
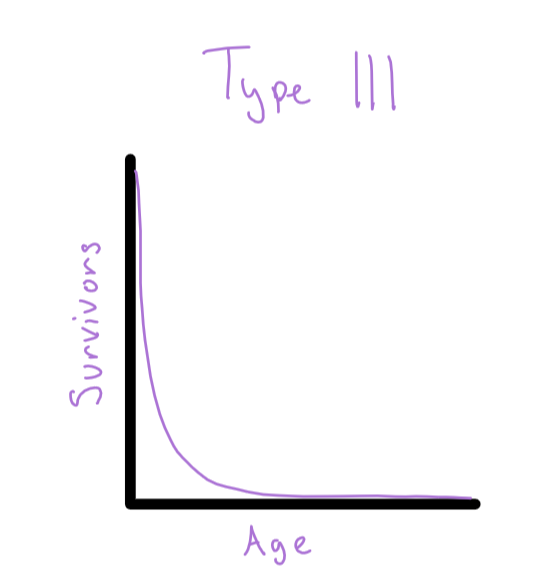
Survivorship Curve- Type 3
high death rate- most die young
competition
a relationship between organisms that strive for the same resources in the same environment
intraspecific competition
two members of the same species fight for a resource
interspecific competition
members of different species fight for a resource
Symbiosis
A close relationship between two species in which at least one specifies benefits
symbiosis- mutualism
both species benefit
symbiosis- commensalism
one benefits, the other is unaffected
symbiosis- parasitism
one species benefits, the other species is harmed