Water soluble Vitamins & C (mine)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Vitamins are...
organic compounds w/ regulatory functions (essential in diet)
organic means what
it contains carbon (ex: water (H2O) is not organic)
vitamins and energy yielding
yield no energy
Preservation of vitamins (what are they sensitive to)
exposure to light, heat, air, water & alkaline
**water can cause vitamins to leach out of food
Fat soluble vitamins are generally...
stored (except K)
Water soluble vitamins are generally...
excreted (except B12 & B6)
Deficiency occurs when...
lacking in diet & stores are depleted
according to Juma, deficiency occurs when and suboptimal occurs when?
deficiency: storage depletion in body
suboptimal: lack of intake from diet
How to preserve?
eat ASAP, the sooner the less chance of nutrient loss
if absorption is defective... what will likely occur
Deficiency is likely
ex: fat malabsorption, alcohol abuse, intestinal disease (CF, Crohn's, Celiac)
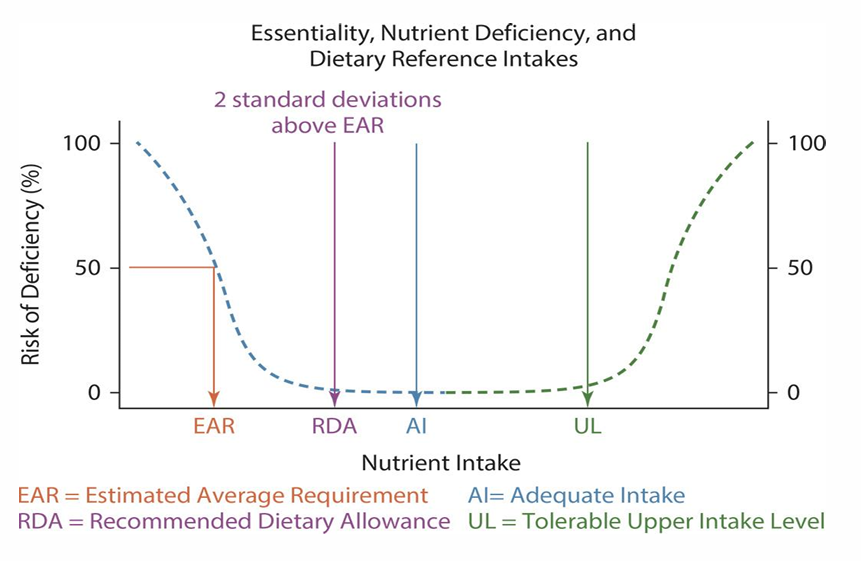
EAR:
RDA:
AI:
UL:
what do they stand for and what are they
List Fat soluble vitamins
A, D, E, K
List water soluble vitamins
B complex:
- Folate
- B12
- B6
- thiamin
- riboflavin
- niacin
- biotin
- pantothenic
vitamin C
vitamin C is a... (function)
antioxidant & enzyme substrate
Forms of vitamin C
Reduced: Ascorbic acid/ascorbate
Oxidized: dehydroascorbic acid
Vitamin C is synthesized by ____ except _____
synthesized by most animals, except some primates, birds, humans
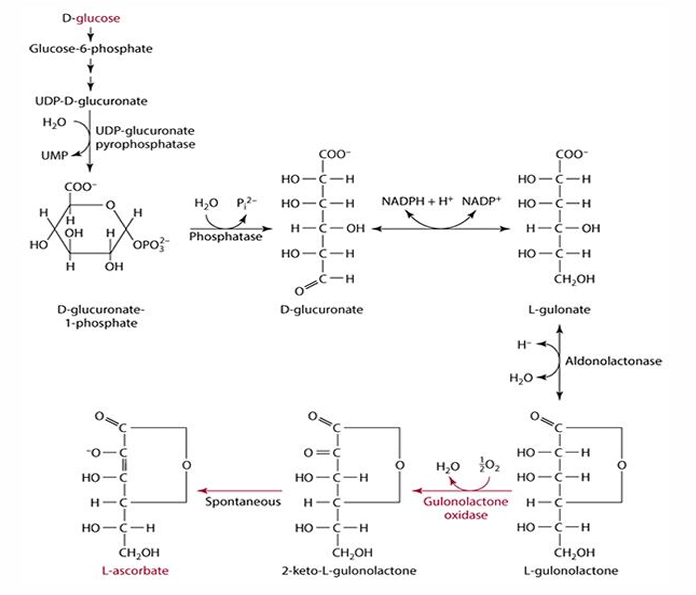
why can we not synthesize vitC
absence of gluconolactone oxidase
(glucose—> L-gulonolactone—> needed enzyme—> L-ascorbate)
reduced form (what does this mean)
gains -e
is more negative
oxidized form (what does this mean)
loses -e
becomes more +
reducing agent does what/ what happens to it
the reducing agent will lose electrons
the molecule being reduced gains electron
oxidizing agent does what/ what happens to it
the oxidizing agent will gain electrons
the molecule being oxidized loses electrons
D-glucose pathway/vitaC synthesis pathway
- starts w/ glucose
- halts after l-glulonolactone bc we lack enzyme
-then becomes another molecule that spontaneously becomes L-ascorbate (C)
- enzyme: gulonolactone oxidase
how is vitamin C commonly found in food (in what form)
mostly as reduced (ascorbate)
Vit C is destroyed by what? stable when?
- destroyed by heat, light, oxidation, alkaline
- stable in acid conditions
what can push vitas to brink of destruction?
metallic minerals (Fe, Cu) cause oxidative destruction yielding diketogulonic acid
Ascorbic acid digestion...
- not required
ascorbic acid absorption
uses what carriers
- absorption by SVCT1 (main carrier) & SVCT2 (meta active tissue)
what are SVCT carriers dependent on?
sodium! (SVCT= sodium dependent vit C transporter)
what is the difference between SVCT1 and SVCT2?
SVCT2 active in metabolically active tissue while SVCT1 in mostly active in the gut (main carrier)
how is absorption related to intake
decreases with intake
ex: if take a huge supplement it wont do any good, it will just be excreted and barely any will be absorbed
what may occur to ascorbate prior to absorption
may be oxidized (into dehydroascorbate)
transport of ascorbic acid in blood (how is it transported?)
in free form
storage of ascorbic acid
- tissues concentration is > plasma
Dehydroascorbic acid found in...
food or oxidized in GI
dehydroascorbic acid absorption occurs how
- via GLUT 1 & 3
how may vit C be absorbed if oxidized before absorption and intake is high (what transport may it use)?
absorbed by passive transport if intake is high
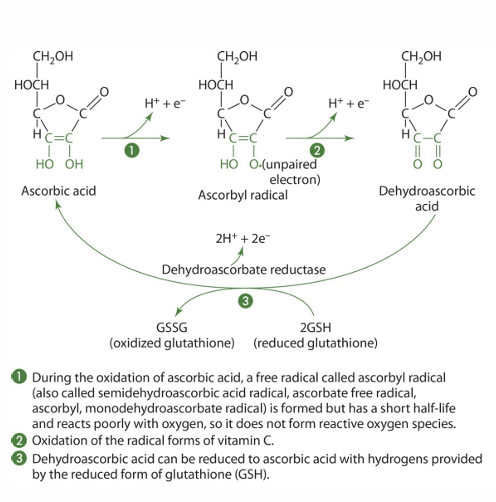
what occurs to dehydroascorbate once it is absorbed
it is reduced back into ascorbate by dehydroascorbate reductase (glutathione dependent)
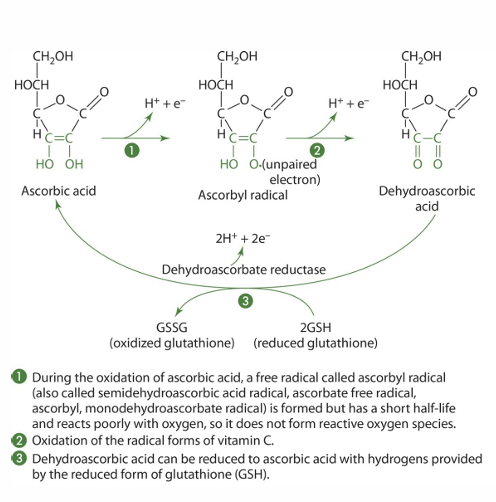
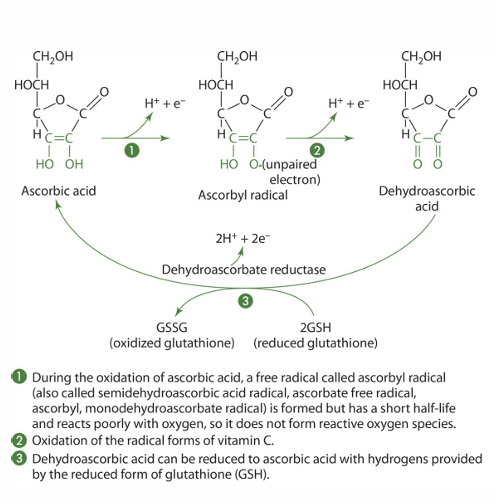
how is vit C absorbed mostly (in what form; by what transport system)
as ascorbate in specific energy dependent transport system
(SVCT’s are Na dependent which usually indicates energy)
how is dehydroascorbate reduced to ascorbate (and what cells do this)
- Intestinal cells
- under action of dehydroascorbate reductase (glutathione is critical but NADPH & dithiol glutaredoxin can be used instead)
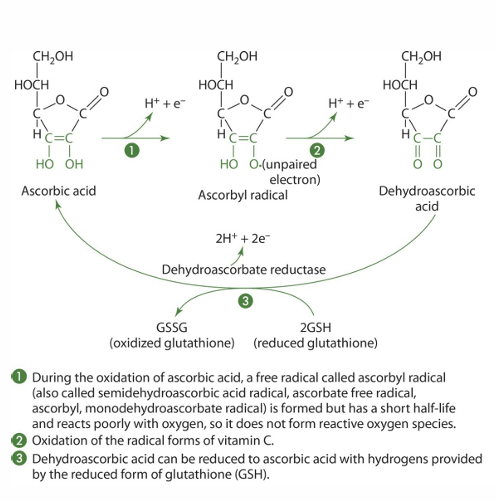
what other molecules can be used by dehycroscarbotate reductase instead of glutathione?
NADPH and dithiol glutaredoxin
Rate of absorption of vit C
16-98% based on needs
avg from 70-100mg is 70-90%
- falls rapidly w/ supplement use
uptake into tissues of vit C via what
SVCT1 and SVCT2
Difference in SVCT 1 & 2
2 is MUCH more metabolically involved
Tissue Levels of Vitamin C
exceed plasma by x3-10 fold
Blood Levels of Vitamin C
Plasma & RBC 70%; WBC 30%
WBC is x80 fold higher than plasma
Vitamin C storage (how long, major tissues, major organ, max body pool)
- quickly excreted, no major long term storage
- major tissue sites: pituitary & adrenal glands
- major organ sites: liver, spleen, kidneys, pancreas & heart
- max body pool of 2g
Ascorbic acid function's & mechanisms (6) — know because it then leads to those roles
-Antioxidant
-Cosubstrate
-Collagen synthesis
-Carnitine synthesis
- Tyrosine catabolism
- Neurotransmitter synthesis
What role does vitamin C play in collagen synthesis?
Vitamin C is involved in 3 hydroxylation reactions
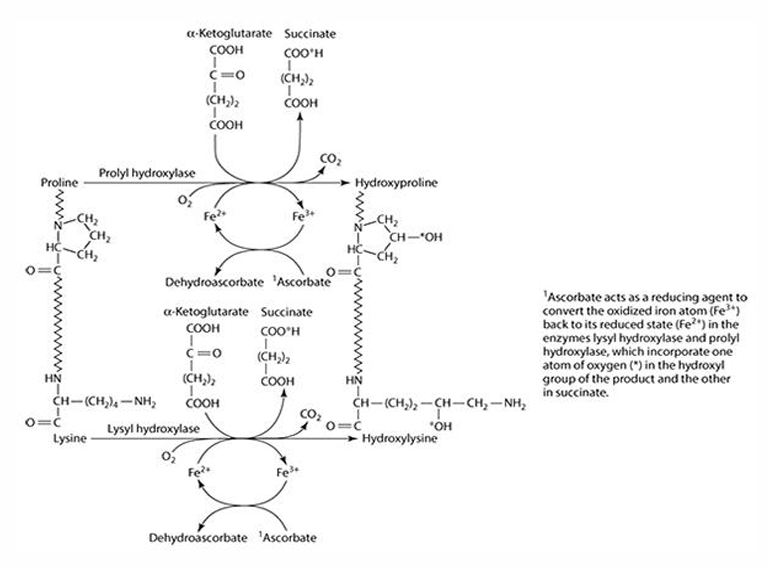
What amino acids are precursors for collagen synthesis?
Proline and lysine.
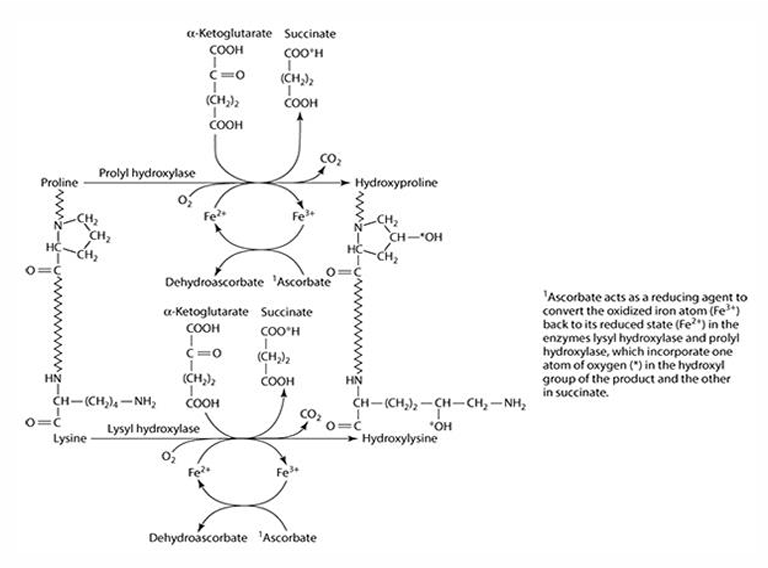
What are the key enzymes involved in collagen synthesis?
Prolyl hydroxylase (4- & 3-) and lysyl hydroxylase.
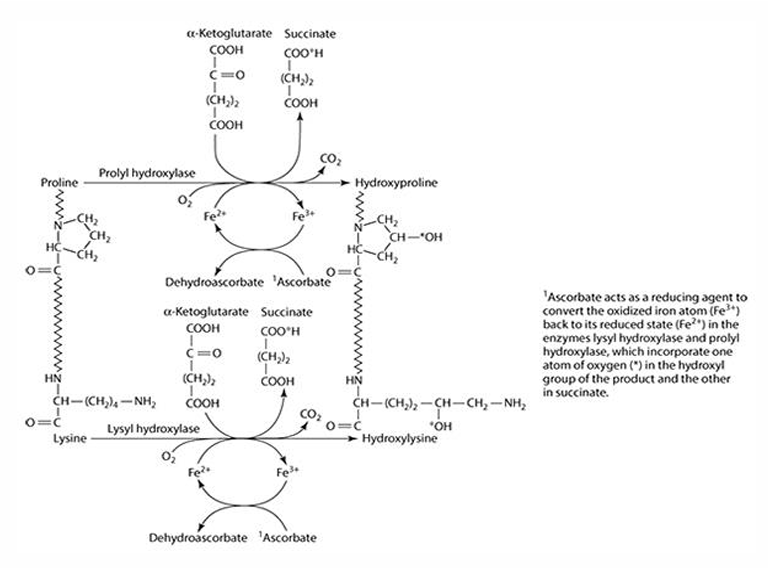
What is the cofactor required for collagen synthesis?
Iron (Fe) is the cofactor, which is reduced by ascorbate.
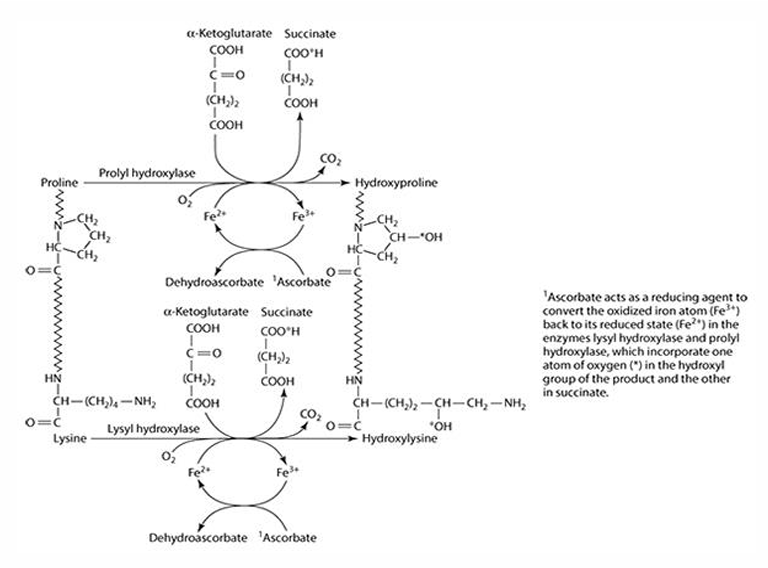
What does ascorbate convert iron into during collagen synthesis? What is ascorbate converted to?
Fe3 + —> Fe2+
Ascorbate —> dehydroascorbate
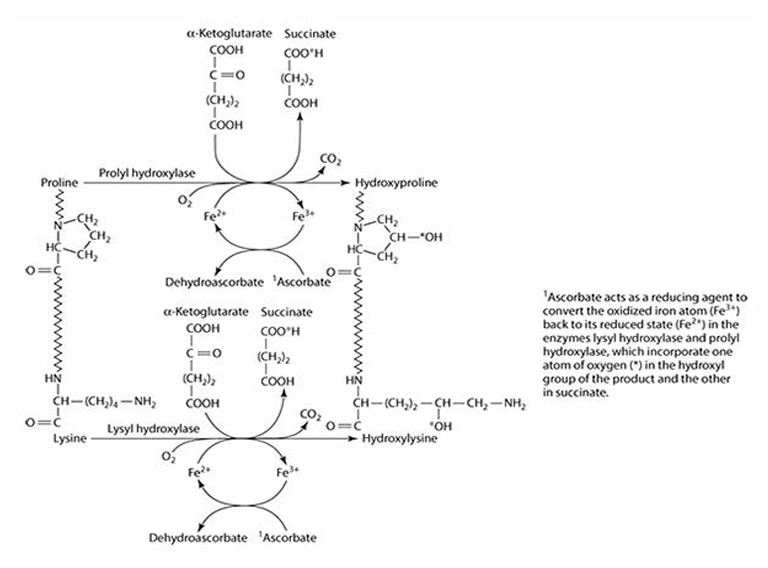
What is the precursor for carnitine synthesis?
Lysine
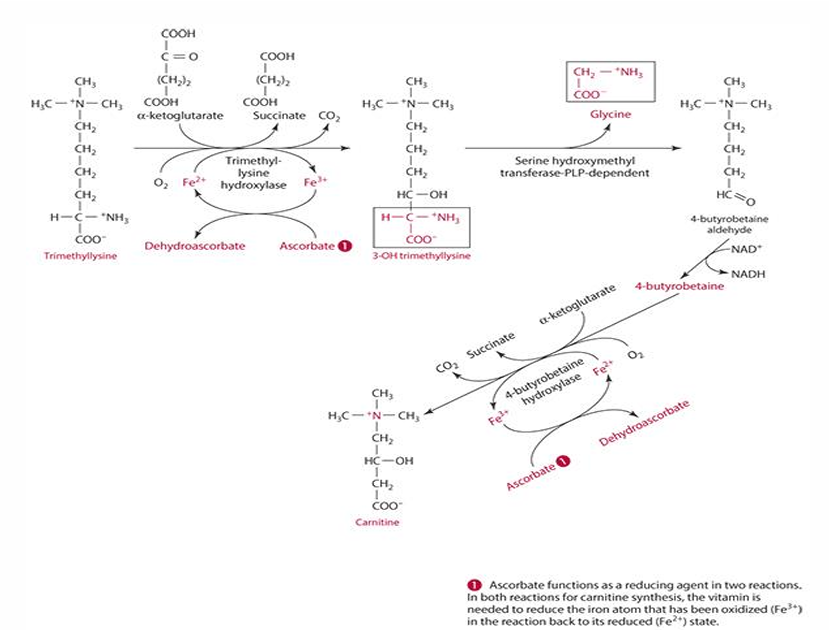
What methylates lysine in carnitine synthesis?
S-adenosyl methionine (SAM)
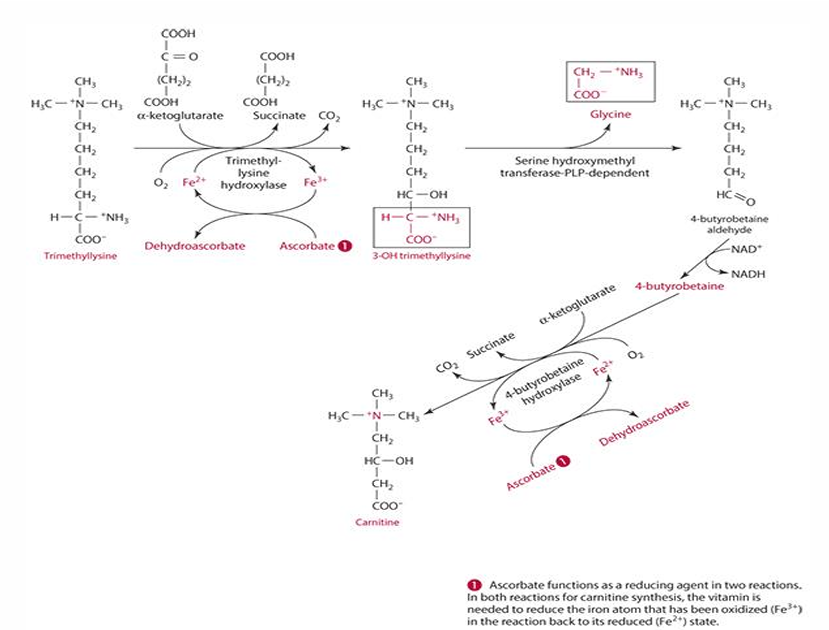
What role does Vitamin C play in the reduction of iron? (in carnitine synthesis)
It acts as a reducing agent, converting Fe3+ to Fe2+.
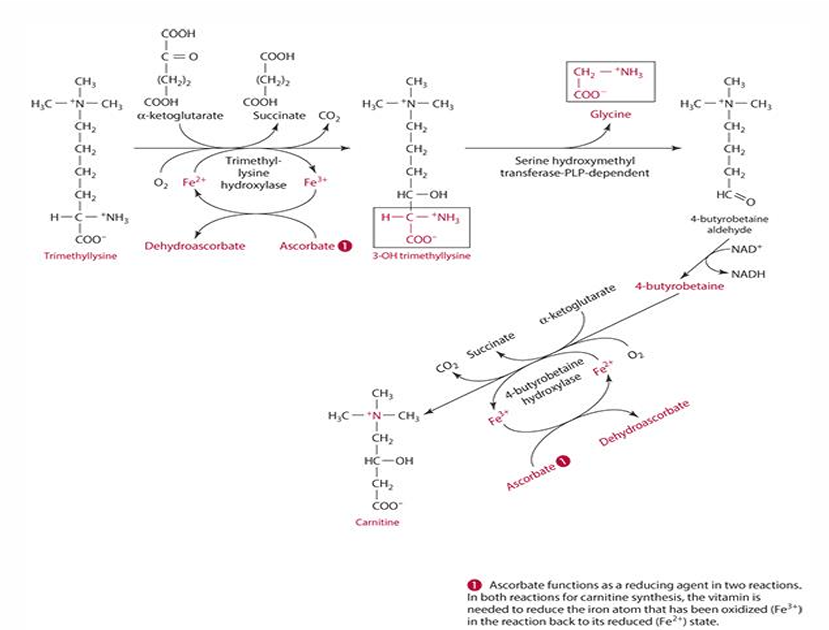
What is the first step in the conversion of trimethyllysine to 3-hydroxytrimethyllysine?
It is catalyzed by trimethyllysine dioxygenase/hydroxylase.
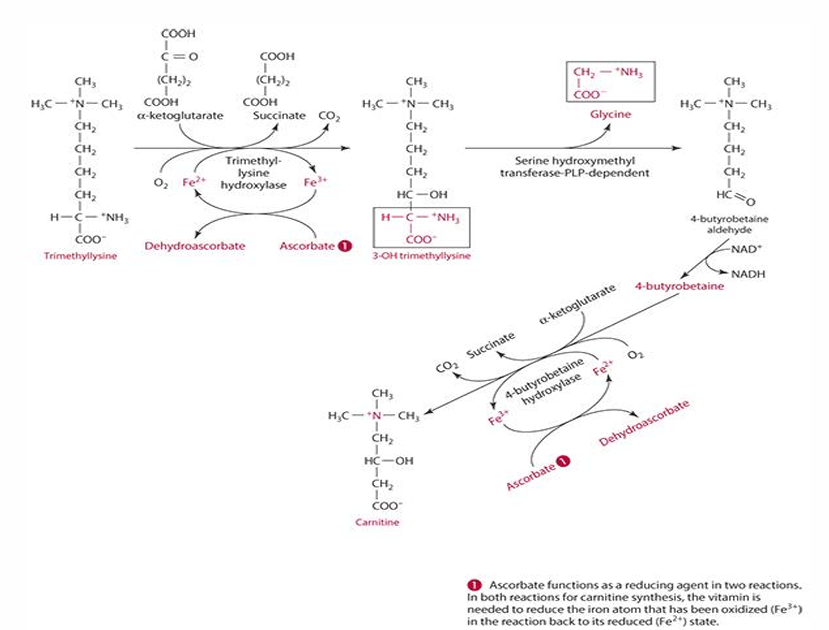
What is the last step in carnitine synthesis involving ascorbate?
Ascorbate acts on the enzyme 4-butyrobetaine dioxygenase to produce carnitine.
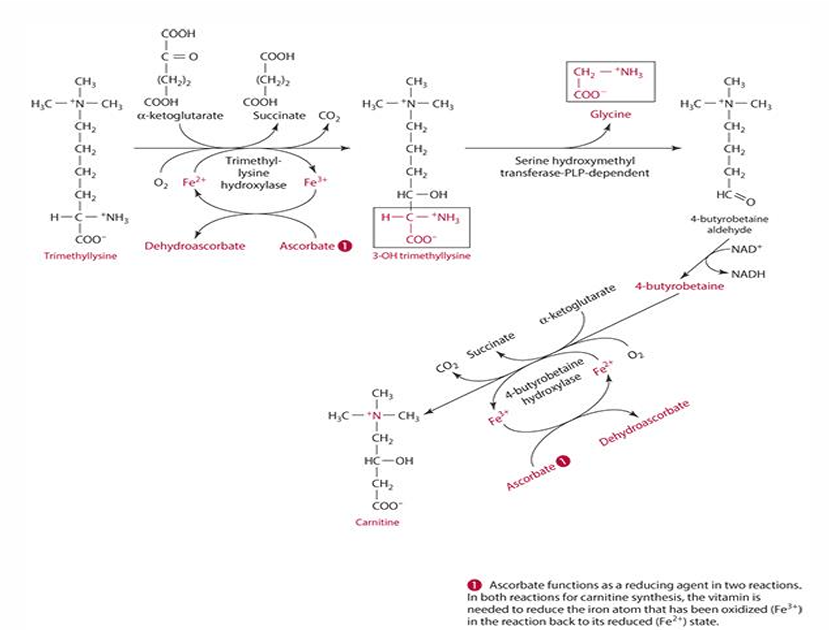
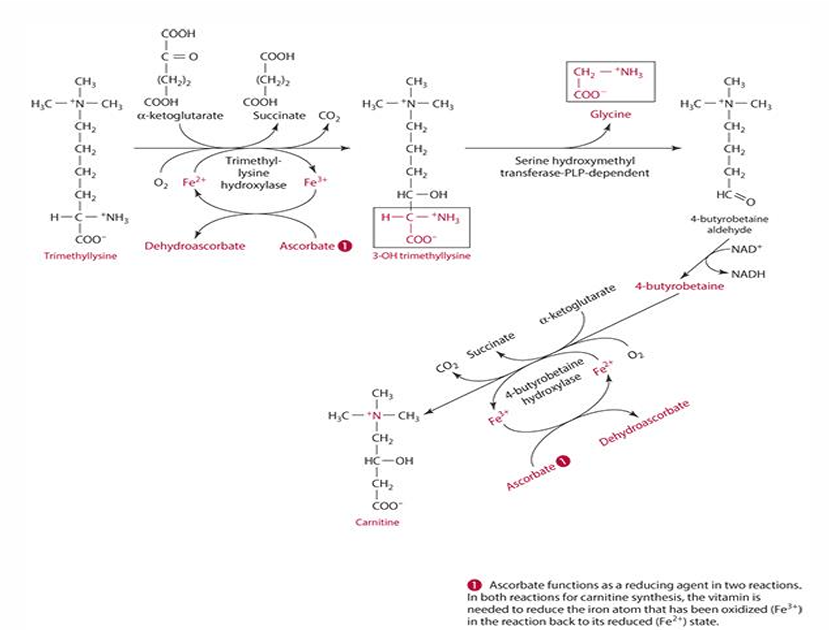
ascorbates role in carnitine synthesis (explain what occurs)
step 1: trimethyllysine is converted into 3-hydroxytrimethyllysine by trimethyl-lysine hydroxylase. For this to occur ascorbate reduces iron (Fe3+ —> Fe2+) and is oxidized into dehydroascorbate
last step: 4-butryobetaine is converted into carnitine by 4-byturobetaine hydroxylase. For this to occur ascorbate reduces iron (Fe3+ —> Fe2+) and is oxidized into dehydroascorbate
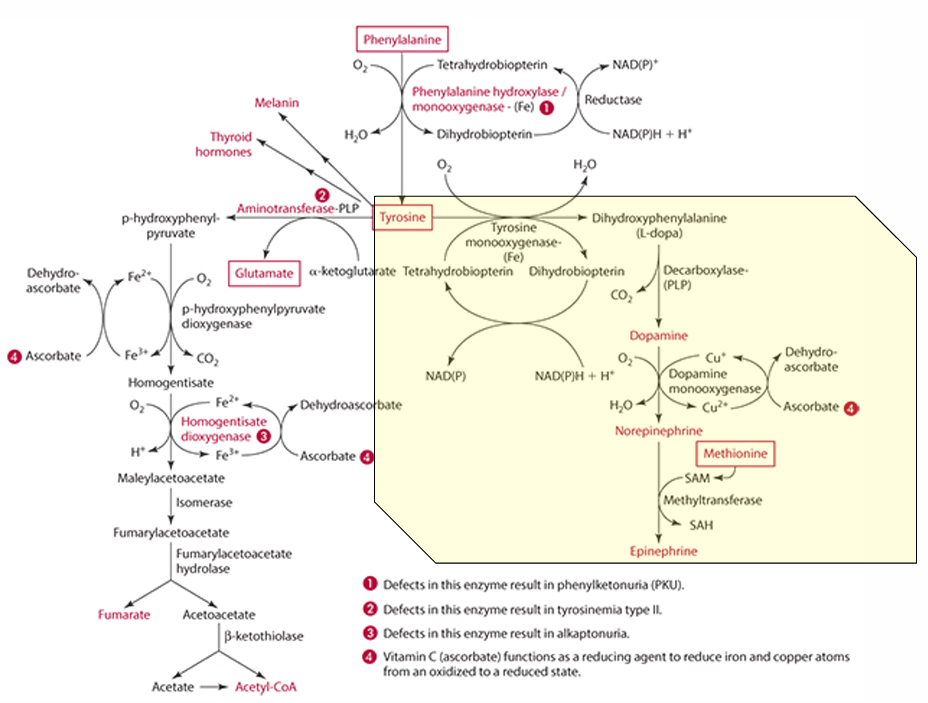
What amino acid is required for tyrosine synthesis?
Phenylalanine
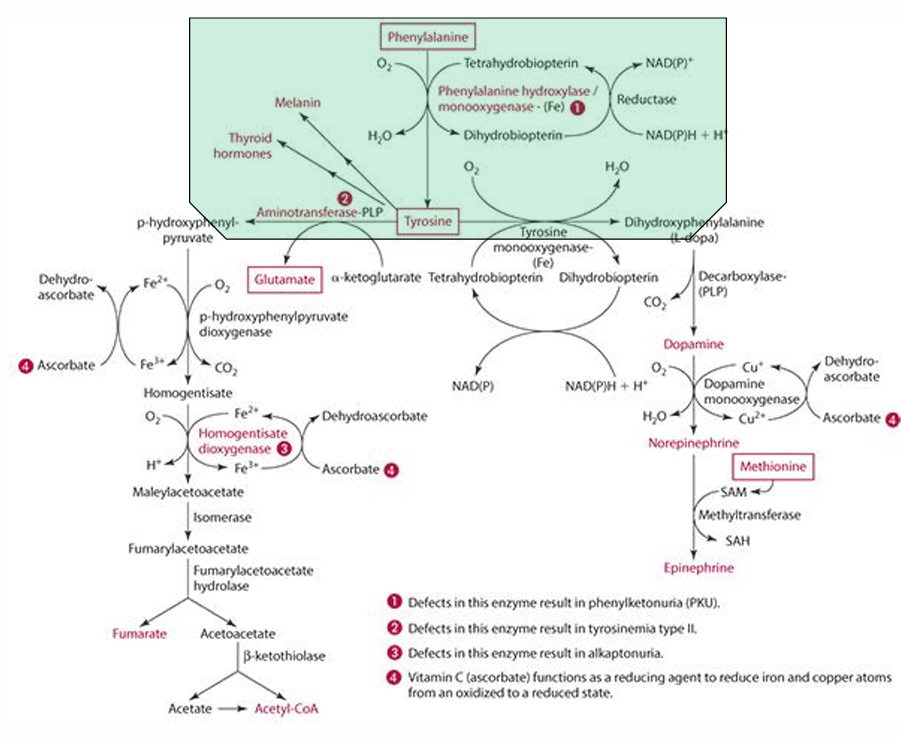
What enzyme facilitates the synthesis of tyrosine from phenylalanine?
Phenylalanine monooxygenase (which is iron dependent)
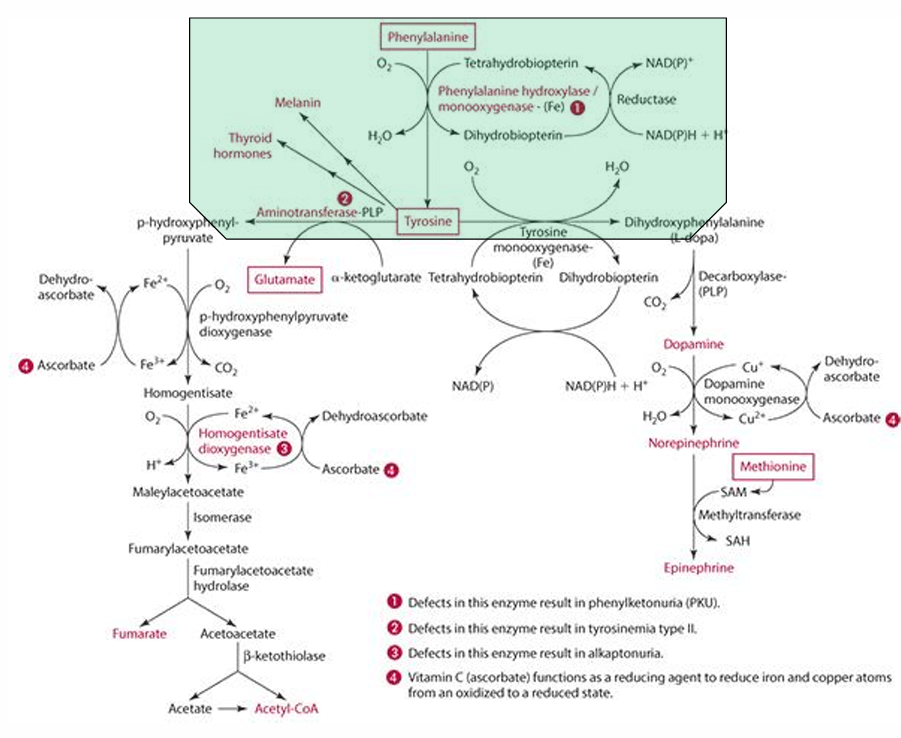
In which organs does tyrosine synthesis occur?
Liver and kidneys
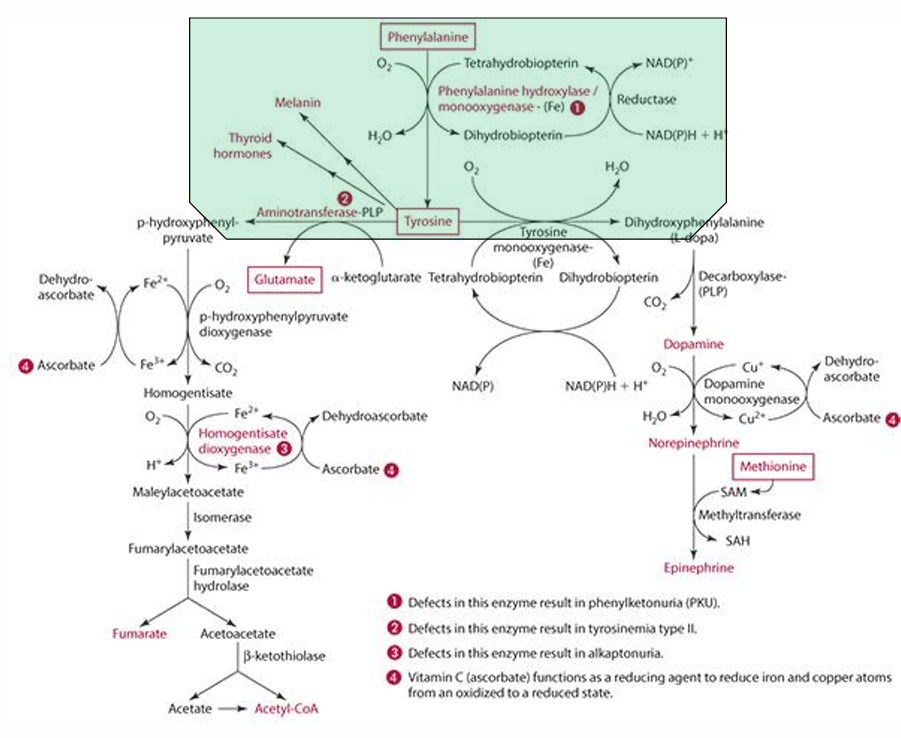
what must be regenerated in the process; what does this
tetrahydrobiopterin must be regenerated
vit C does regenerates it
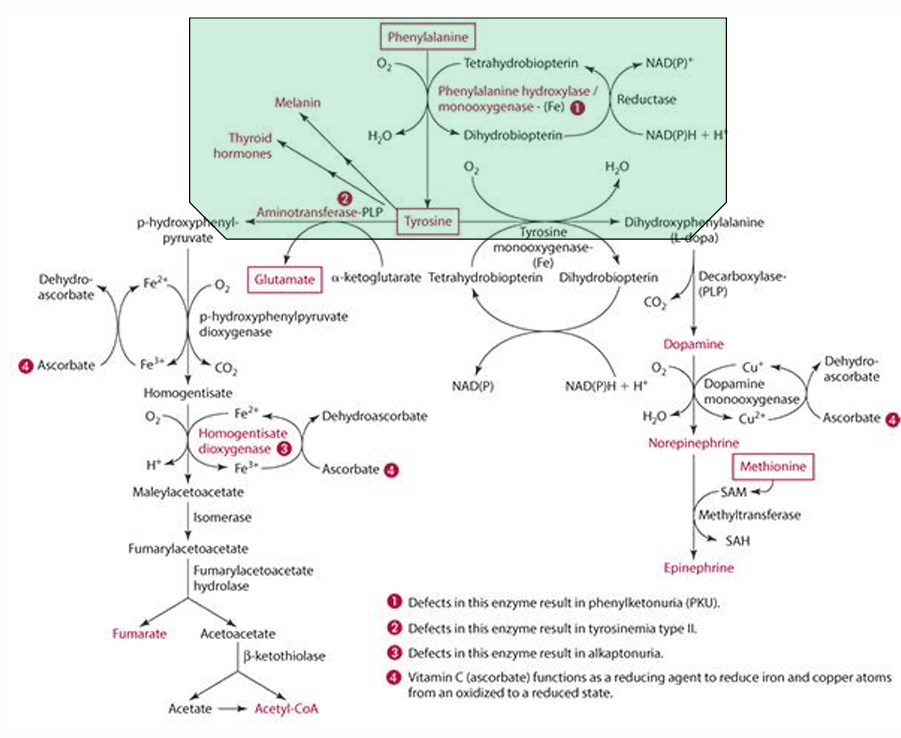
What is the role of Vitamin C in the regeneration of tetrahydrobiopterin?
it reduces it
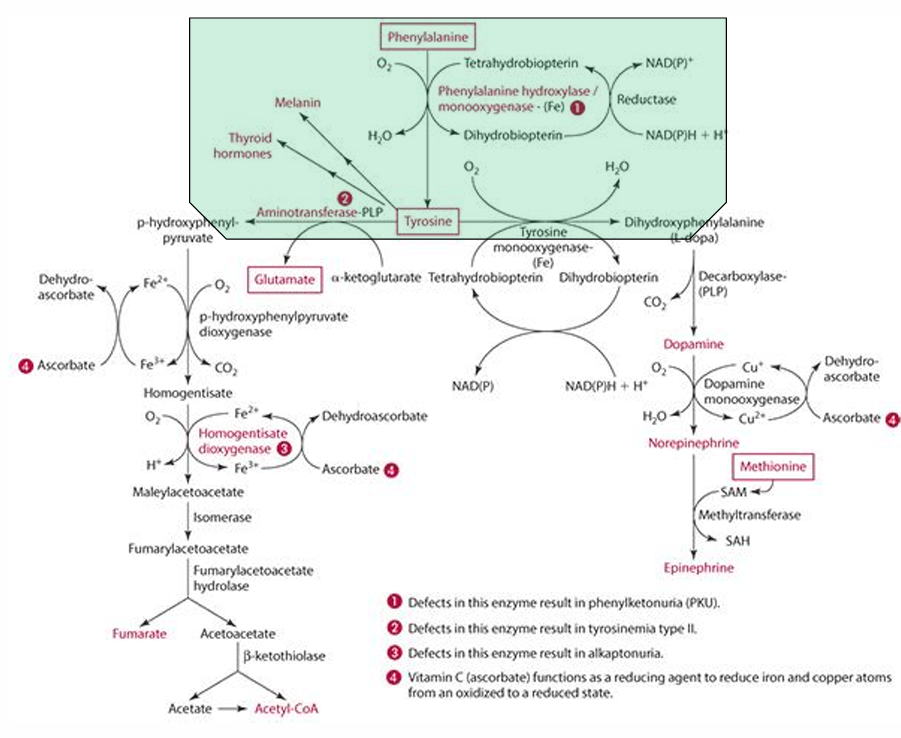
Explain how Vitamin C can regenerate cosubstrate
can help tetrahydrobiopterin become dihydrobiopterin then back to tetrahydrobiopterin
What else Vitamin C reduce in the catabolism process?
Copper (Cu)
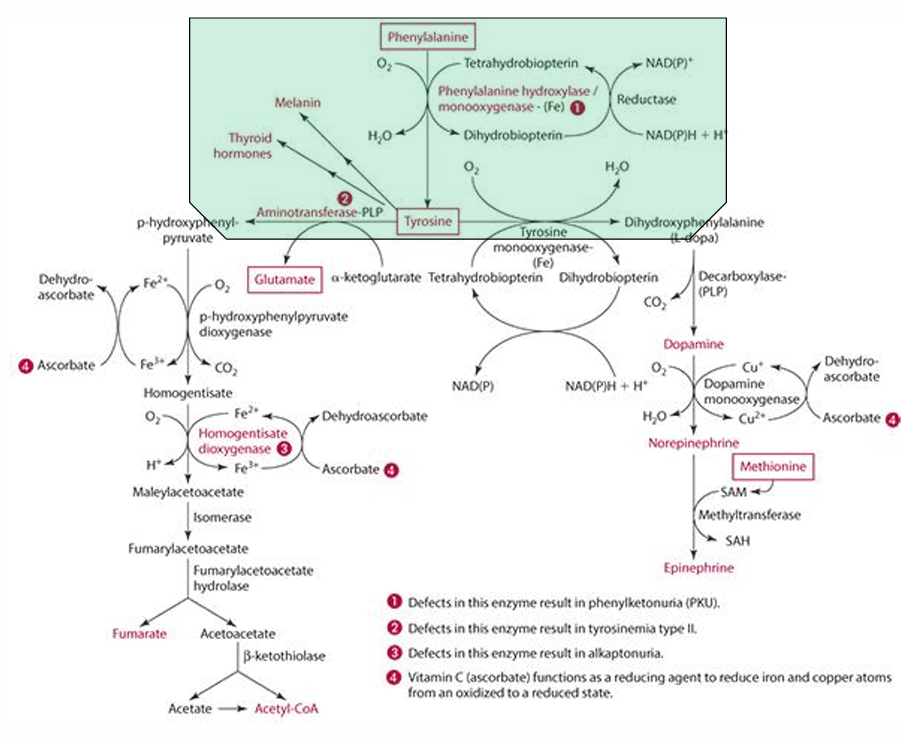
What role does vitamin C play in tyrosine catabolism?
Vitamin C is a reducing agent for Fe.
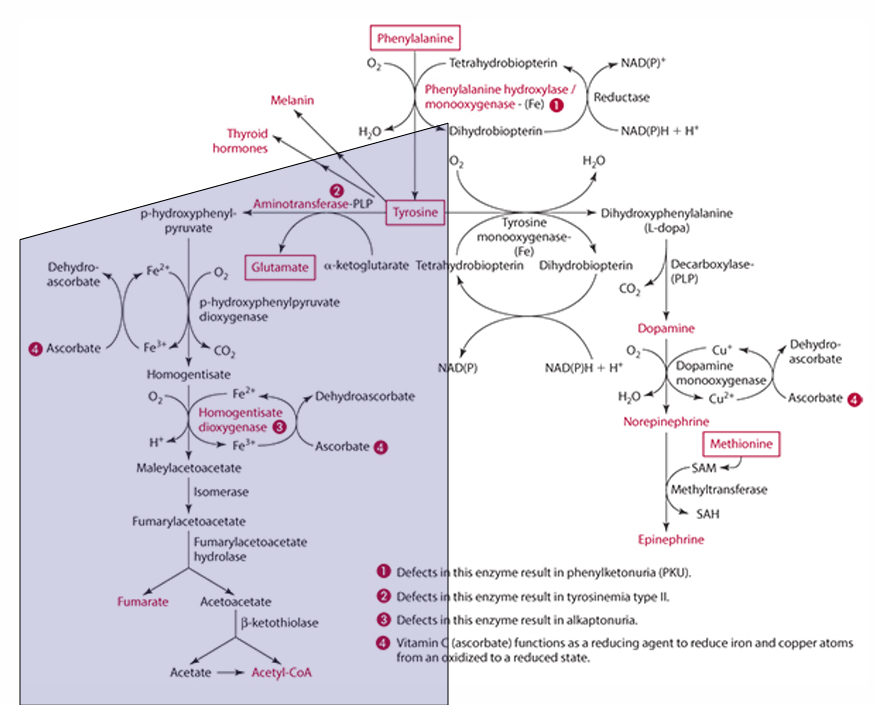
What is the first step in the conversion of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate in tyrosine catabolism?
It is converted to homogentisate.
**ascorbate reduces Fe for this to occur
What does vitamin C convert homogentisate into?
4-maleylacetoacetate via homogentisate dioxygenase.
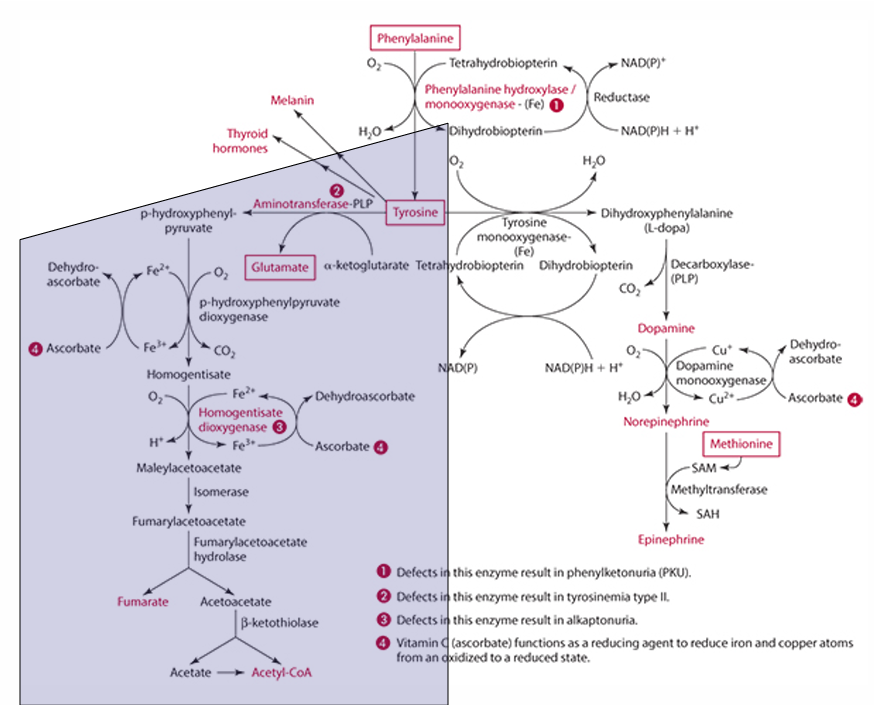
What condition is caused by a defect in the dioxygenase enzyme?
Alkaptonuria.
What is alkaptonuria?
It is the accumulation of homogentisic acid, leading to painful joints and urine oxidation (black).
What is the starting amino acid for the synthesis of DOPA?
Tyrosine
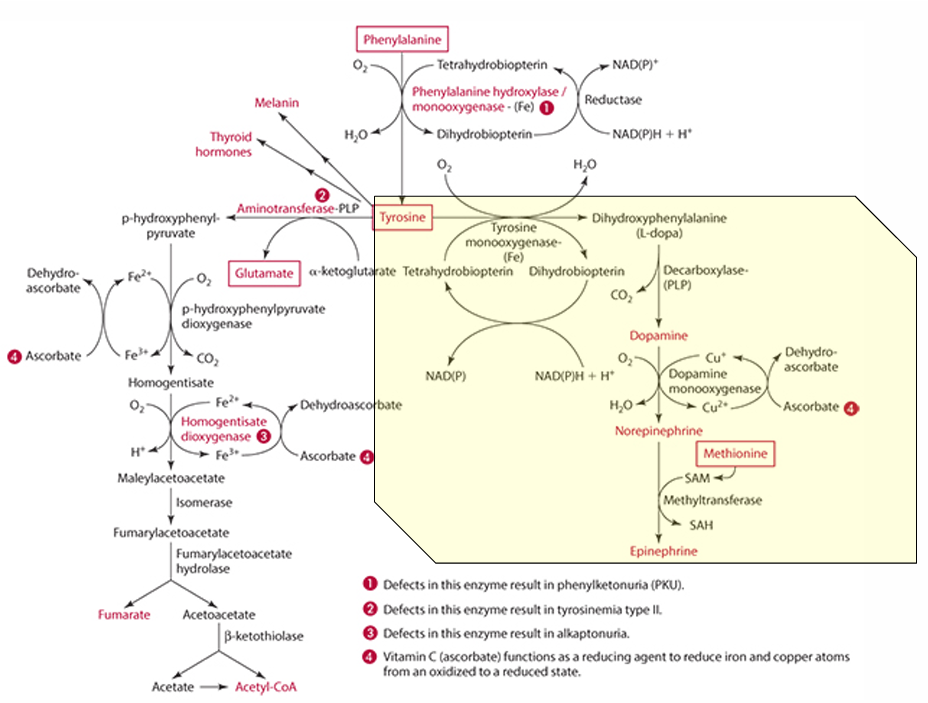
What enzyme converts Tyrosine to DOPA?
Tyrosine monooxygenase
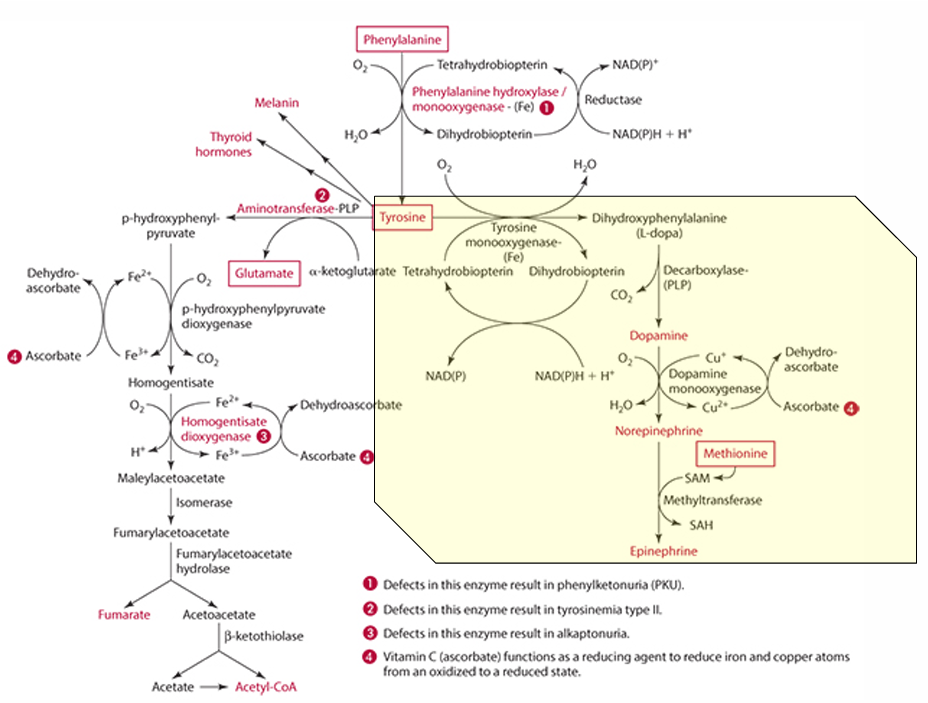
What is the product of the conversion of Tyrosine by tyrosine monooxygenase?
Dihydrophenylalanine (L-Dopa)
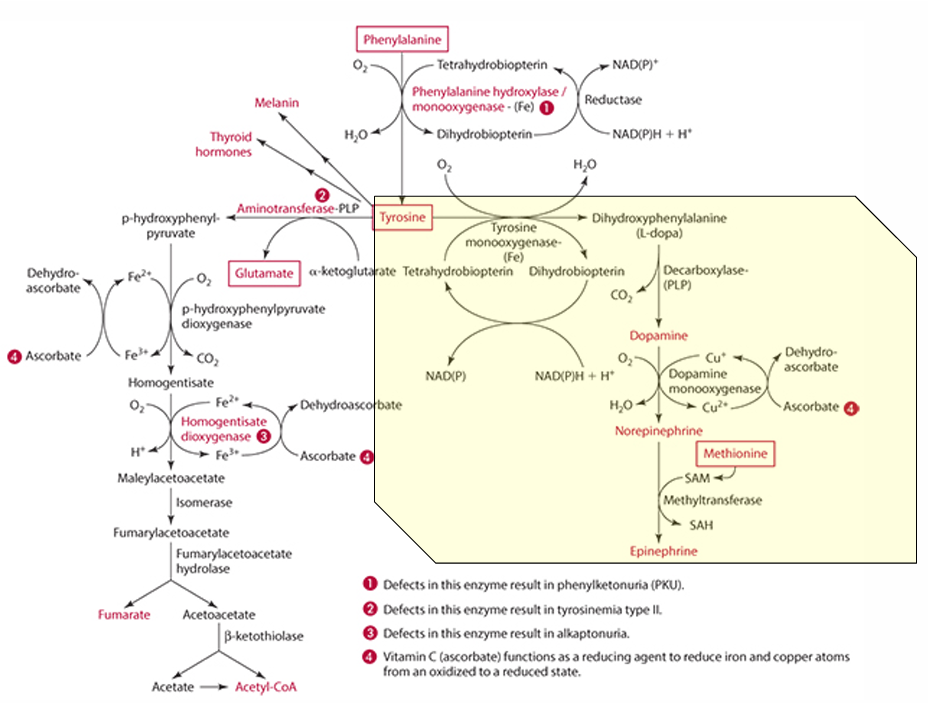
What cosubstrate is involved in the formation of L-Dopa?
Tetrahydrobiopterin (which requires NADPH)
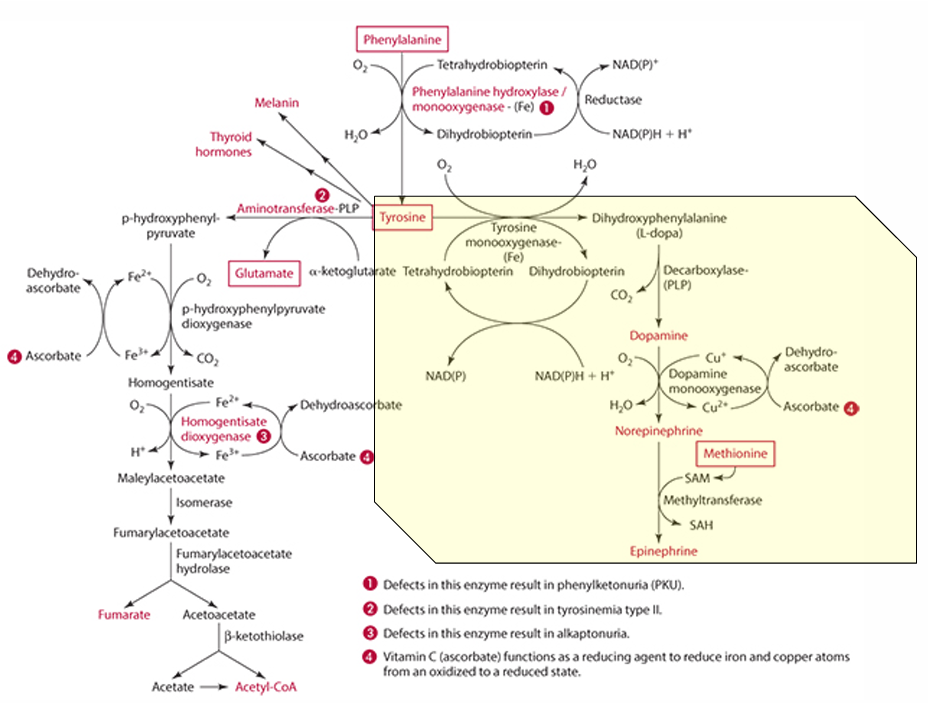
What role does ascorbate play in norepinephrine synthesis?
L-dopa is converted into dopamine,
It acts as a factor in dopamine monooxygenase (enzyme) to form norepinephrine because reduces Cu.
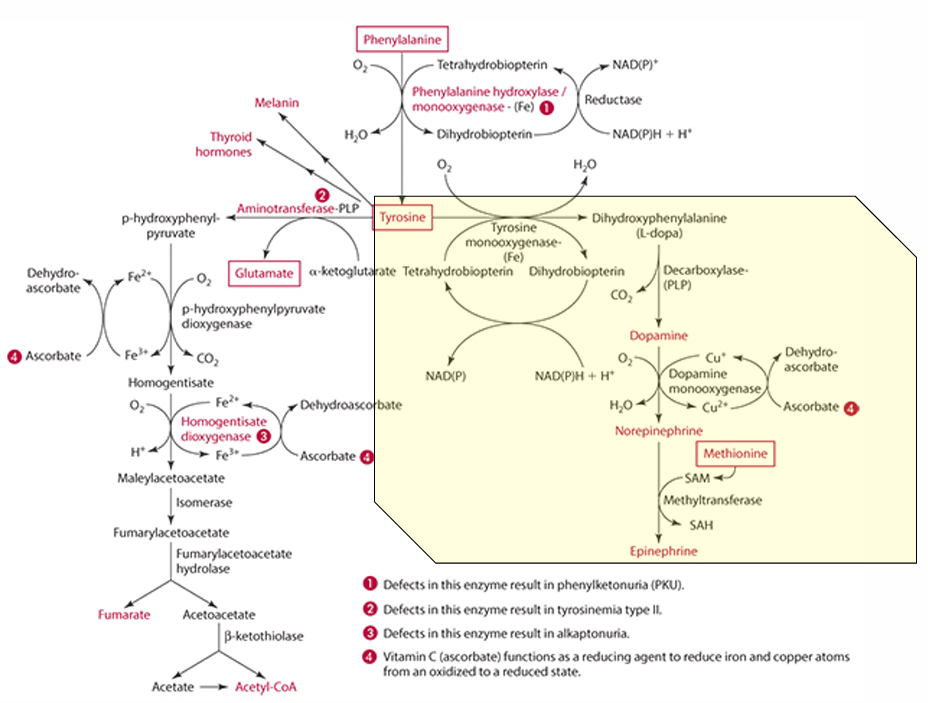
precursor for dopamine
L-Dopa
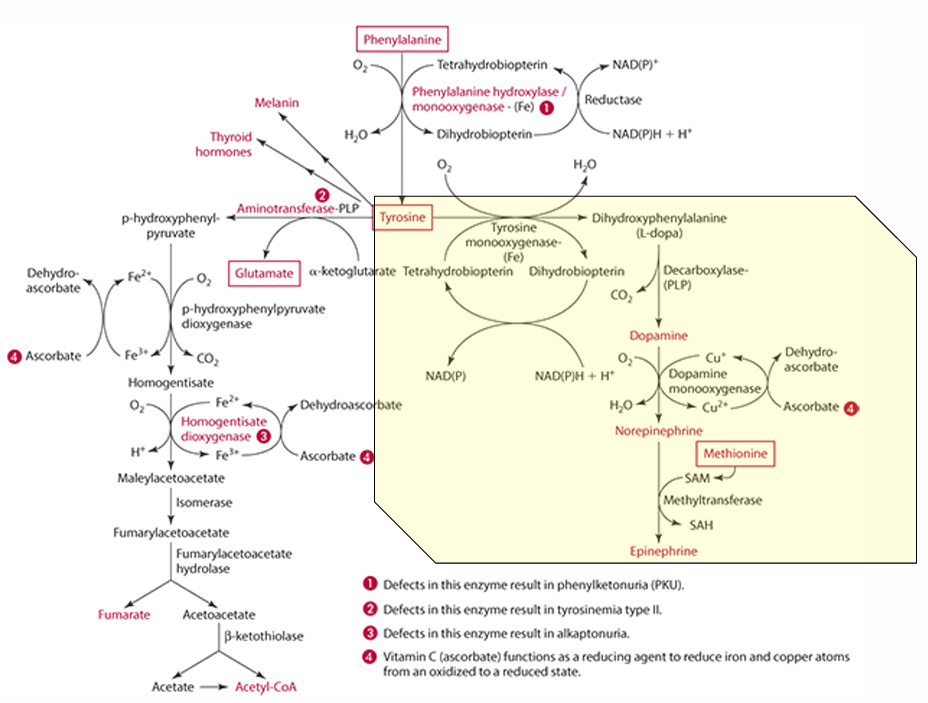
Pathway to make epinephrine & enzyme used
Phenylalanine -> Tyrosine -> Dopamine -> (enzyme: Dopamine monooxygenase) -> Norepinephrine -> (methionine) -> epinephrine
What is the precursor of serotonin?
Tryptophan
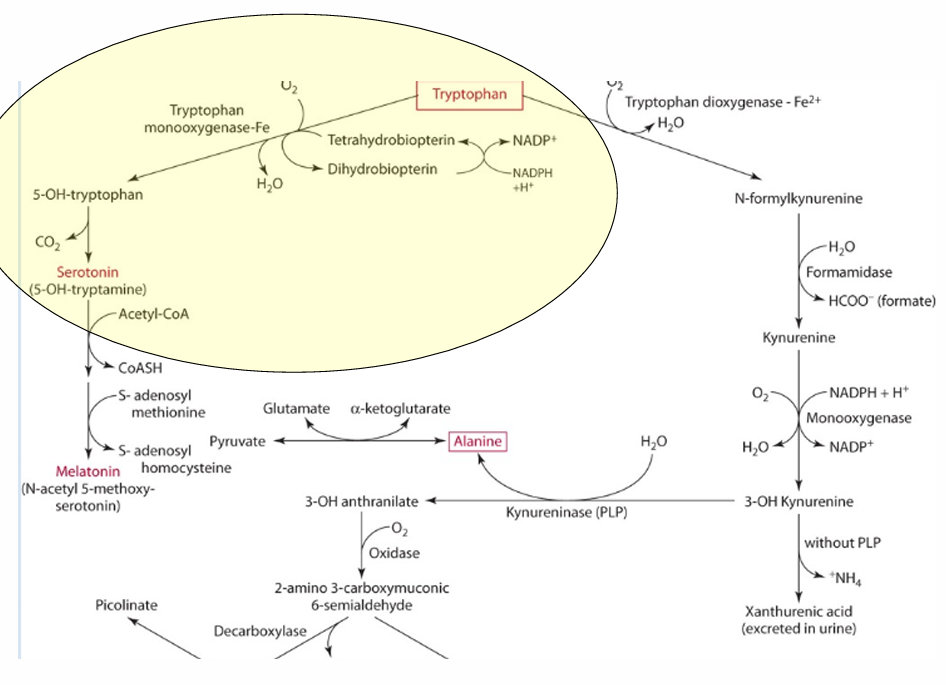
enzyme for converting tryptophan —> serotonin
tryptophan monooxgenase
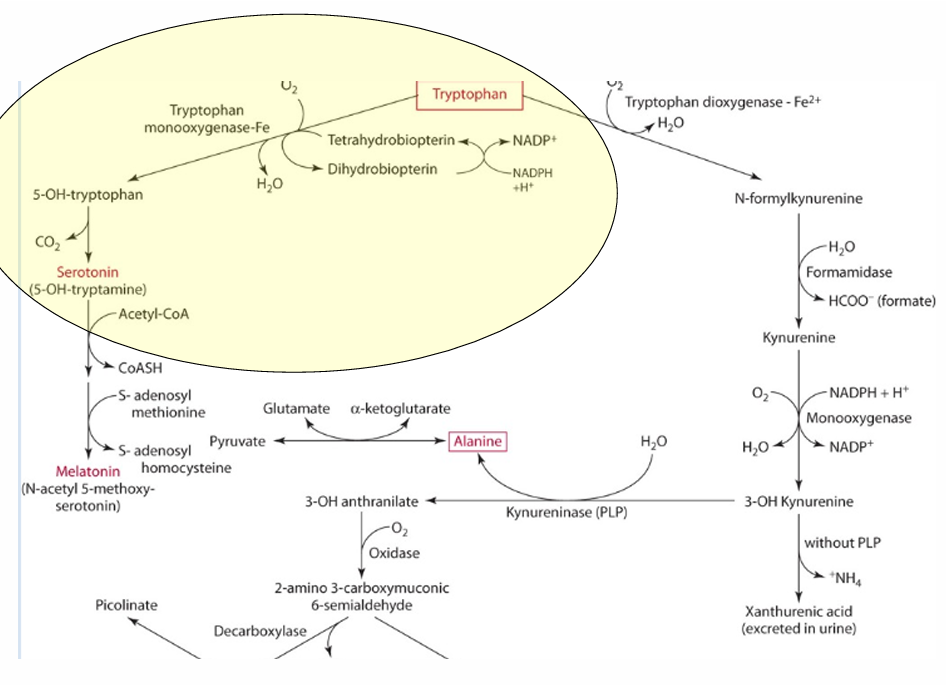
what is the cosubstrate for the reaction
tetrahydrobipterin
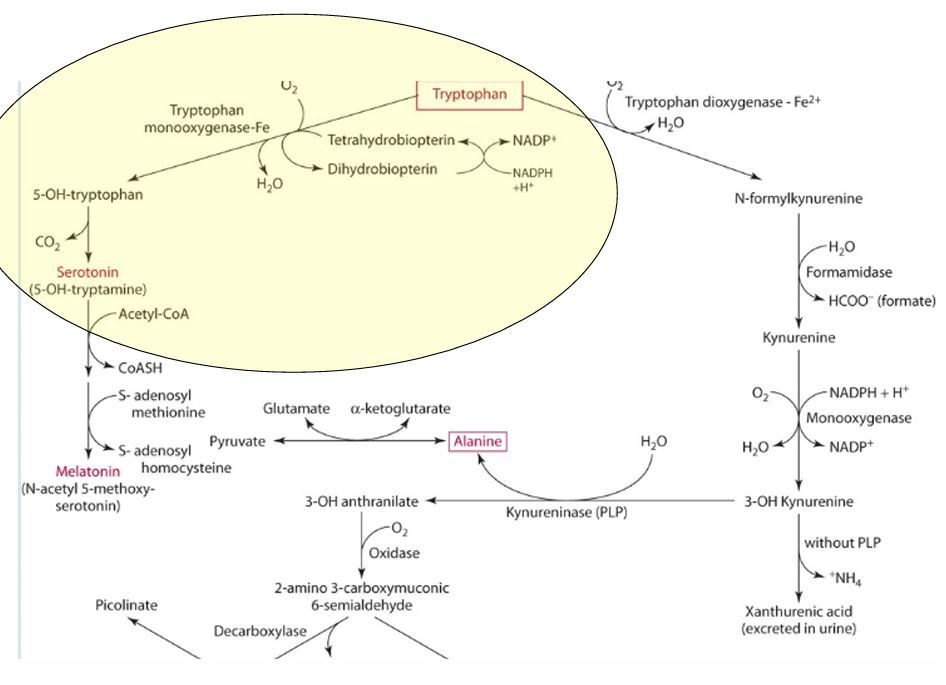
How does vitamin C influence tetrahydrobiopterin?
Vitamin C influences the regeneration of tetrahydrobiopterin, which is important in hydroxylation.
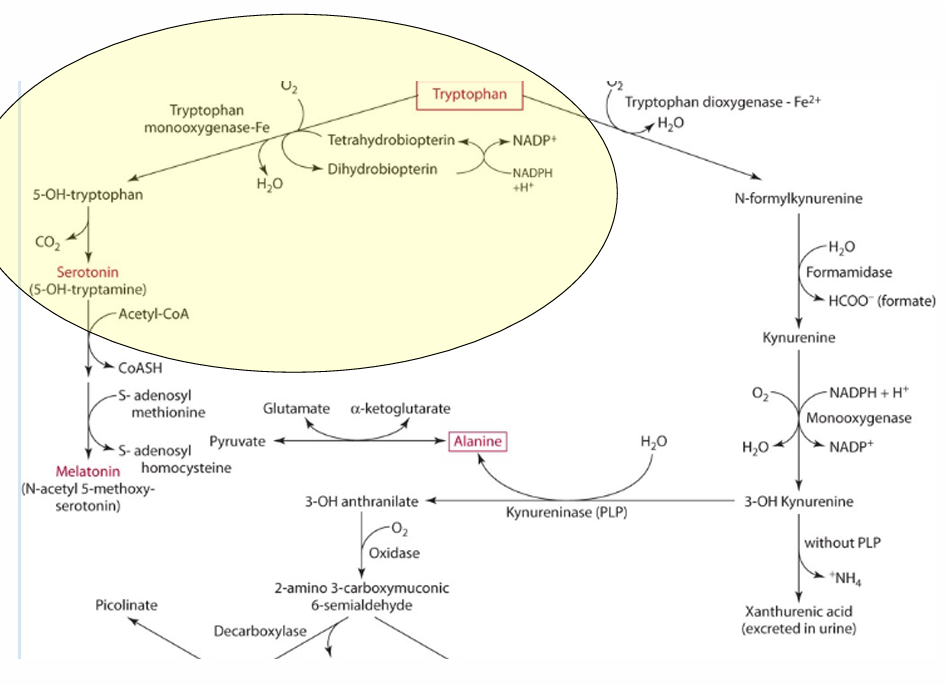
What other role does vit C play in this
reduces iron via an enzyme.
What is the role of ascorbate in peptide amidation?
Ascorbate is important for amidation of peptides with C-terminal glycine, forming amidated peptides, hormones, and hormone-like factors.
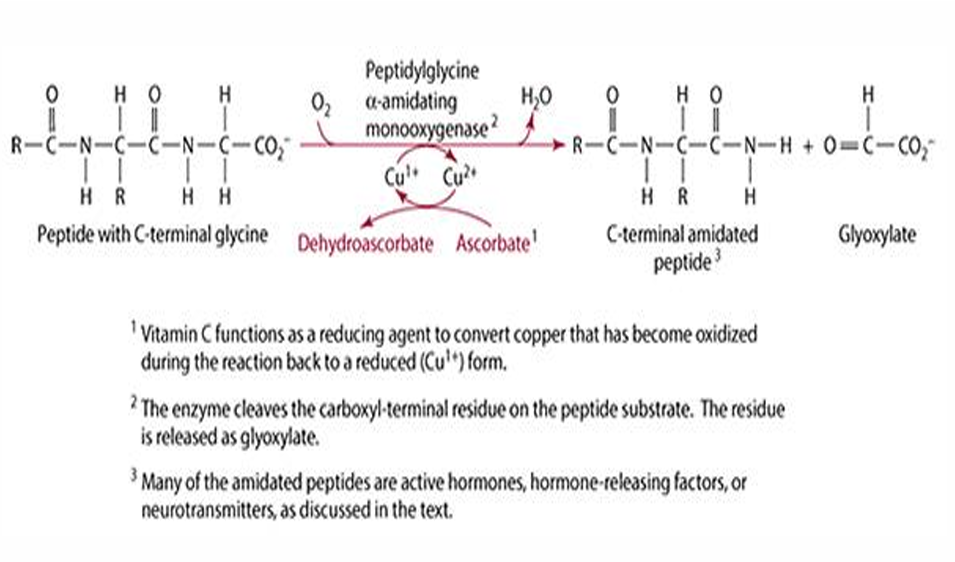
What is the function of vitamin C in relation to glycine-a-amidating monooxygenase?
Vitamin C acts as a reductant for copper associated with glycine-a-amidating monooxygenase.
Name some hormones and hormone-like factors that are neurotransmitters.
GRP, calcitonin, cholecystokinin, growth hormone, oxytocin, vasopressin, and other releasing hormones.
In which tissues are neurotransmitters and hormones active?
They are active in neuroendocrine tissues such as the brain, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
What is one function of vitamin C related to liver metabolism?
Microsomal metabolism in liver microsomes & reticuloendothelial
What types of compounds can vitamin C act on?
Endogenous & exogenous (xenobiotics)
What role does vitamin C play as an antioxidant?
It reduces via hydrogen or electron donation.
it is a reducer so it will reduce the molecule by giving it electrons***
How does vitamin C exhibit pro-oxidant activity?
It becomes oxidized by reducing iron (Fe) and copper (Cu).
**if it becomes oxidized it, it cant oxidize other things
Under what conditions does vitamin C show pro-oxidative activities?
In vitro & at high concentrations.
Vitamin C as a reducing agent
- reduces transitional metals (Fe & Cu)
- acts on ROS (reactive oxygen species) such as:
hydroxyl, hydroperoxyl, superoxide, alkoxyl, peroxyl
why do we take vitamin C for Colds?
proliferation of macrophages and lymphocytes,
increase killer cells (T cells), destroying histamine
effect of vitamin C on cancer
inhibits nitrosamine formation (via nitrite & nitrate)
strongest effect against oral, esophagus, stomach, colon, lung & breast cancer
effect of vitamin C on CVD
decreases monocyte adhesion
enhances collagen IV (prevents apoptosis)
effect of vitamin C on cataracts & macular degeneration
antioxidant
prevents lipid peroxidation & protein crosslinking
Iron & vitamin C absorption
vitamin C enhances nonheme Fe absorption
metabolism & excretion of vitamin C
Excreted or oxidized to dehydroascorbate—> turned to diketogulonic acid—>
intermediate product are excreted as oxalic, threonic, xylonic acid & xylose (sugar moiety)
Oxalic acid Is & can cause
product of diketogulonic acid & can causes stones
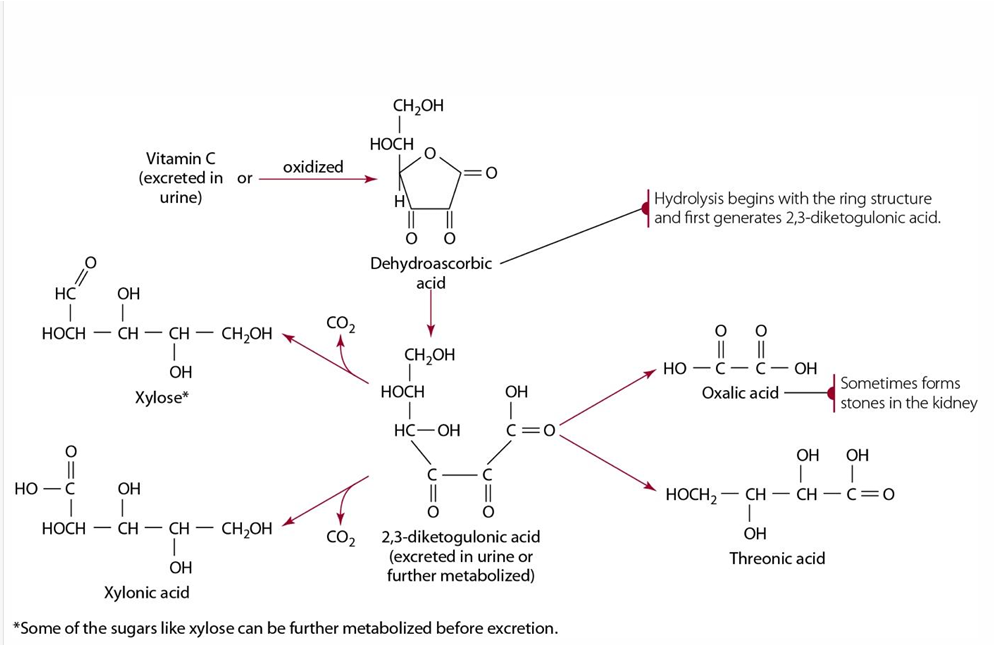
food sources of vitamin c are sensitive too
heat, Fe, Cu & O2