Chapter 1: Celestial Sphere, Seasons, and the Moon
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
The totality of all space, time, matter, and energy.
What is the universe?
There would be no dramatic change.
How would the number of hours of sunlight and the height of the Sun in the sky at noon change over the course of the year on the equator?
The study of the universe.
What is astronomy?
The distance light travels in one year. Not a unit of time, it’s a unit of DISTANCE.
What is a light-year?
Theory
The framework of ideas and assumptions used to explain some set of observations and make predictions about the real world.
Theoretical models
Theories must be continuously tested with ______ of physical objects (like a planet or star) or phenomena (such as gravity or light) that account for the physical properties seen.
Testable
Scientific theories must be ______.
Scientific method
Scientists use this to test theories.
Observation/question → Research the topic area → Hypothesis → Test with experiment → Analyze data → Report conclusions
What are the steps of the scientific method?
Big Bang, Gravity, Electromagnetism, Quantum Mechanics
What are some examples of scientific theories?
One possible explanation for some observed characteristics or effects.
What is a hypothesis?
3000
The amount of visible stars at any one time.
The name for a group of stars.
What are constellations?
88
The amount of recognized constellations.
The North Star, it is directly over Earth’s north rotational pole, so it does not appear to rise or set.
What is Polaris?
A commonly recognized pattern in the night sky.
What is an asterism?
Located in the constellation Ursa Minor, which also contains the little dipper.
What asterism is Polaris a part of?
An imaginary sphere surrounding Earth where stars seem to be on the inner surface for observational purposes.
What is the celestial sphere?
An imaginary great circle of the celestial sphere that is an extension of Earth’s equator into space.
What is the celestial equator?
The point on the celestial sphere directly above Earth’s North Pole, where Earth’s axis of rotation intersects the sky.
What is the North Celestial Pole?
The point of the celestial sphere directly above the Earth’s South Pole, where Earth’s axis of rotation intersects the sky.
What is the South Celestial Pole?
Stars that remain continuously above the horizon for a specific observer on Earth.
What are circumpolar stars?
Counterclockwise
The Earth rotates in this direction, causing things on the celestial sphere to appear to rise in the east and set in the west.
It reaches their highest point in the sky.
What happens when an object transits?
The meridian of the celestial sphere
When an object transits, it is found on this.
The point directly overhead.
What is the zenith?
The North Pole
Where on Earth would you be if Polaris were at your zenith?
Zodiac constellations
The twelve constellations the Sun moves through during the year.
The path that the Sun travels along on the celestial sphere throughout the year.
What is the ecliptic?
Zodiac constellations, the moon, planets, and asteroids.
What can be found near the ecliptic?
When an object spins
What is a rotation?
Movement around an object
What is a revolution?
The belief that suggests the positions of the sun, moon, and planet at the time of a person’s birth influences their personality and life.
What is astrology?
Approximately 23.5º
The ecliptic is the plane of the Earth’s path around the Sun. The plane is tilted at what angle to the celestial equator?
The northernmost point in the path of the Sun. This is also the longest day of the year (>12 hours) where its hot and the Sun is the highest in the sky.
What is the summer solstice?
The southernmost point in the path of the Sun. This is also the shortest day of the year (<12 hours) where its cold and the Sun is the lowest in the sky.
What is the winter solstice
The points where the path crosses the celestial equator. Happen between the summer and winter solstices, with equal day and night. 12 hours of daylight everywhere on Earth.
What is the vernal equinox and autumnal equinox?
The Earth’s 23.5º tilt of the Earth’s rotational axis, causing the sun to hit Earth at different angles.
What is the primary reason for the seasons?
In summer, longer days and more direct sunlight make it warmer, and winter, shorter days and less direct light make it colder.
What is the secondary reason for seaons?
Constant, this planet would experience no significant seasonal changes, as the angle of sunlight would remain constant throughout its orbit.
Imagine a planet whose rotational axis is perpendicular to its orbital plane. How would you describe its seasons?
Approximately 29.5
How many days does it take the moon to go through whole cycles?
The time it takes for the moon to complete one full cycle of phases.
What is a synodic month?
the position of the Moon with respect to the Sun and the Earth.
Moon phases are due to
Sidereal month
Time for the Moon to make full 360º orbit around Earth, which is about 2 days.
Waxing phase
When light is on the right side of the Moon, what phase is it?
Waning phase
When light is on the left side of the Moon, what phase is it?
4
It takes roughly how many weeks for the Moon to complete a cycle of Moon phases.

New Moon
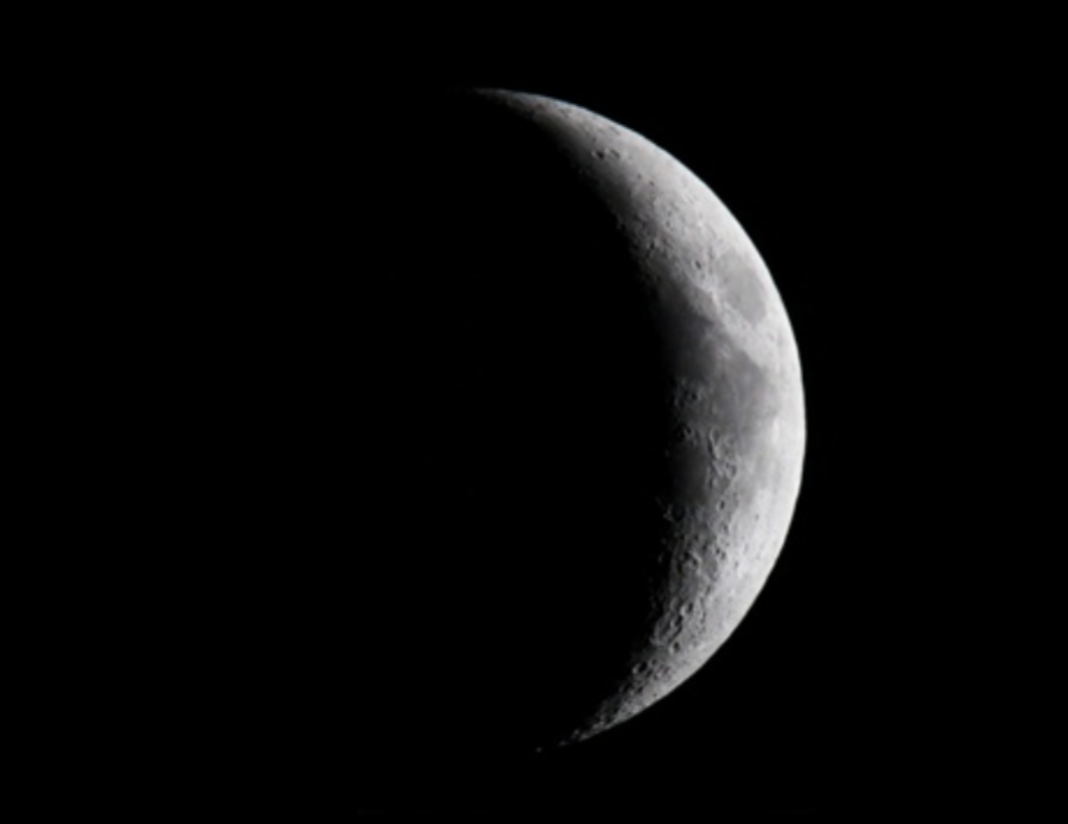

Waxing Crescent
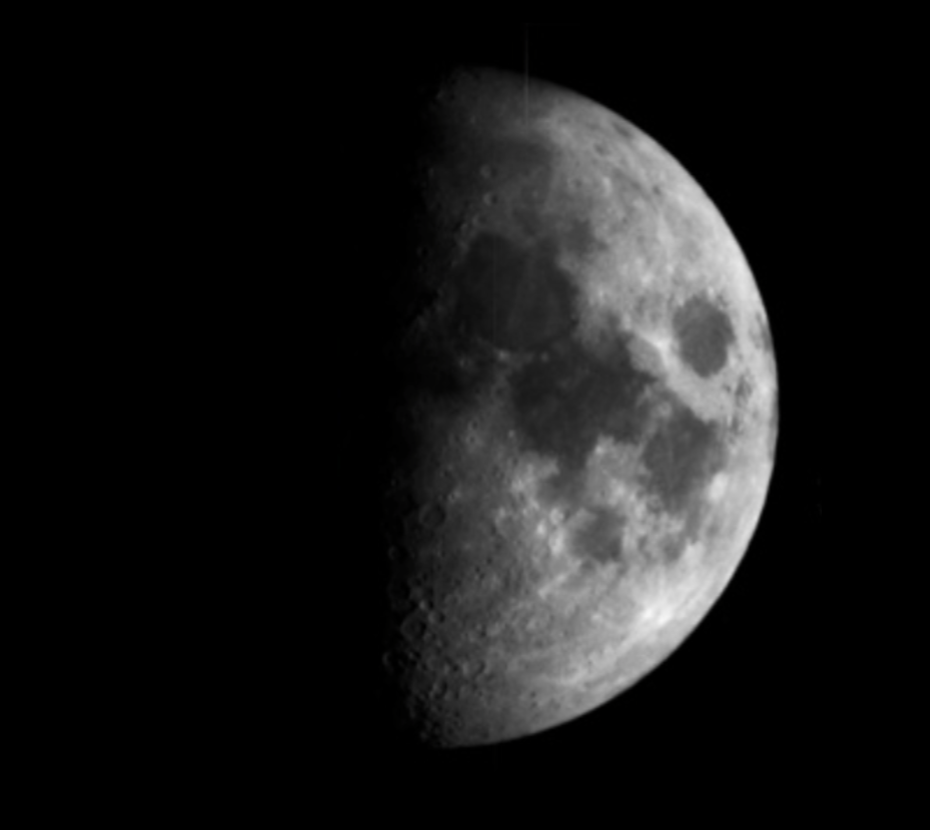

First Quarter
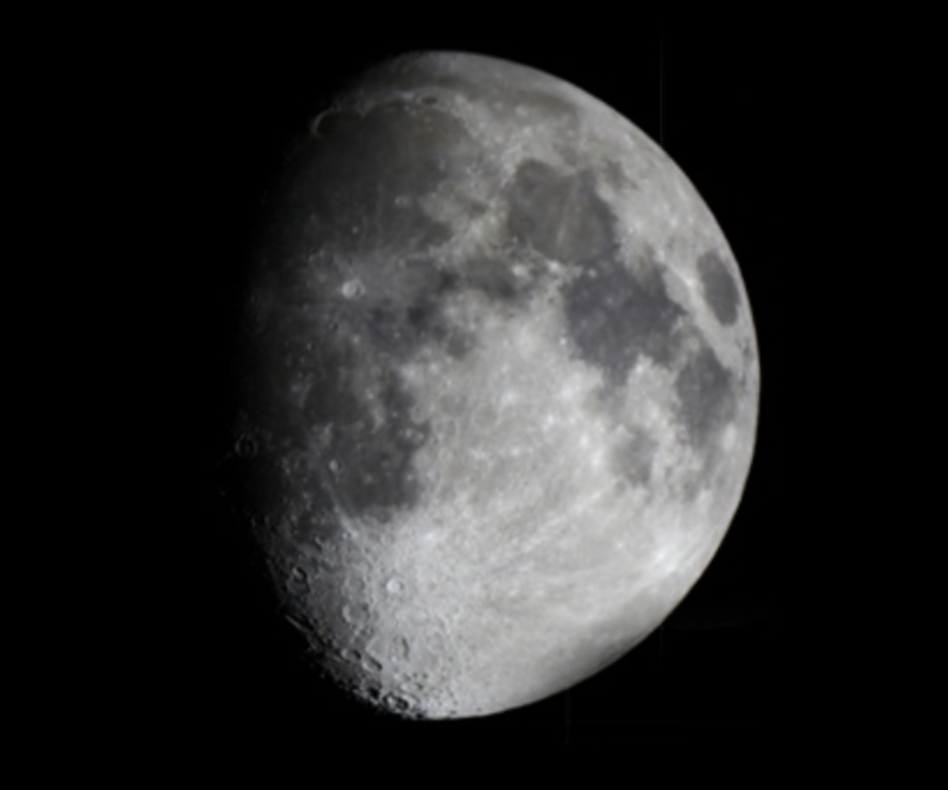

Waxing Gibbous
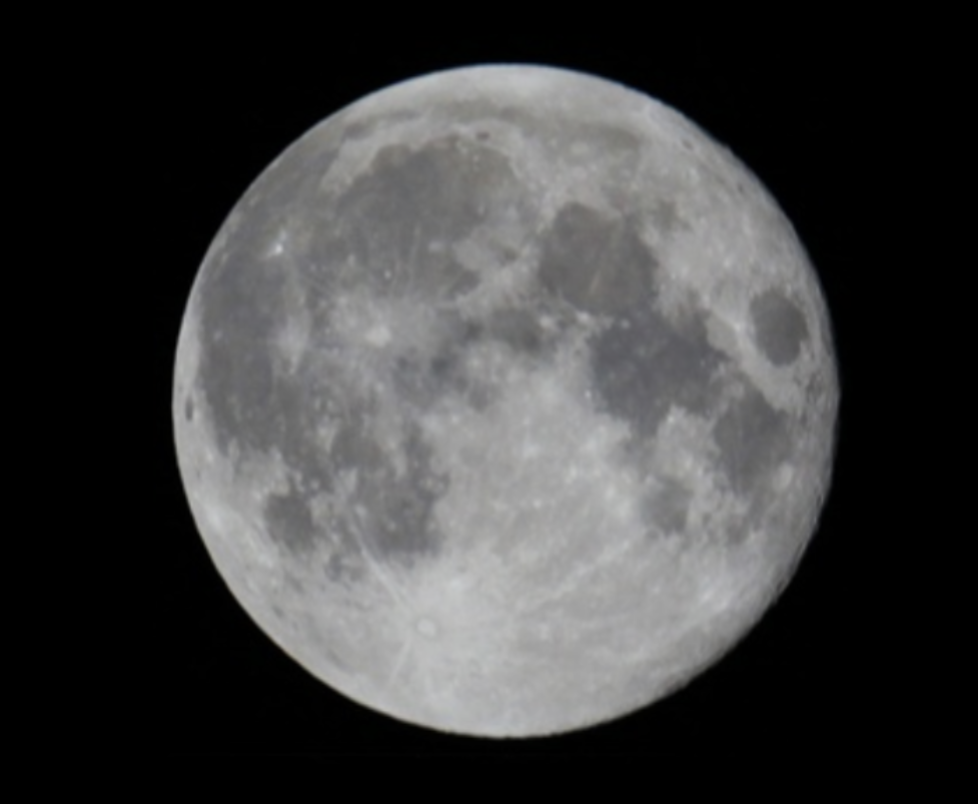

Full Moon
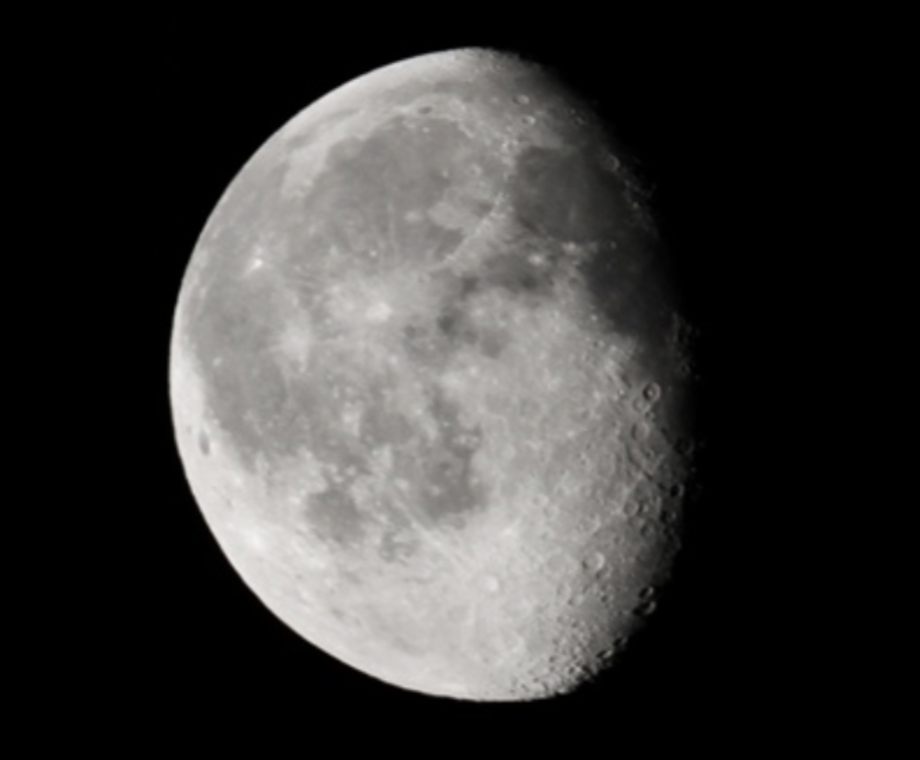

Waning Gibbous
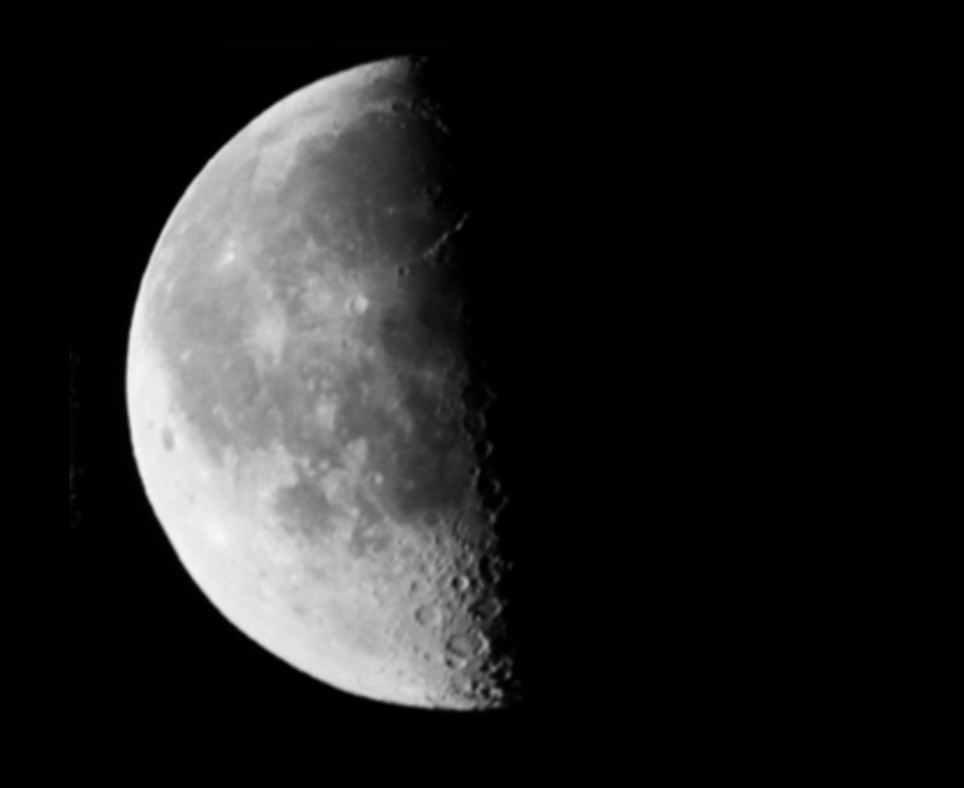

Third Quarter
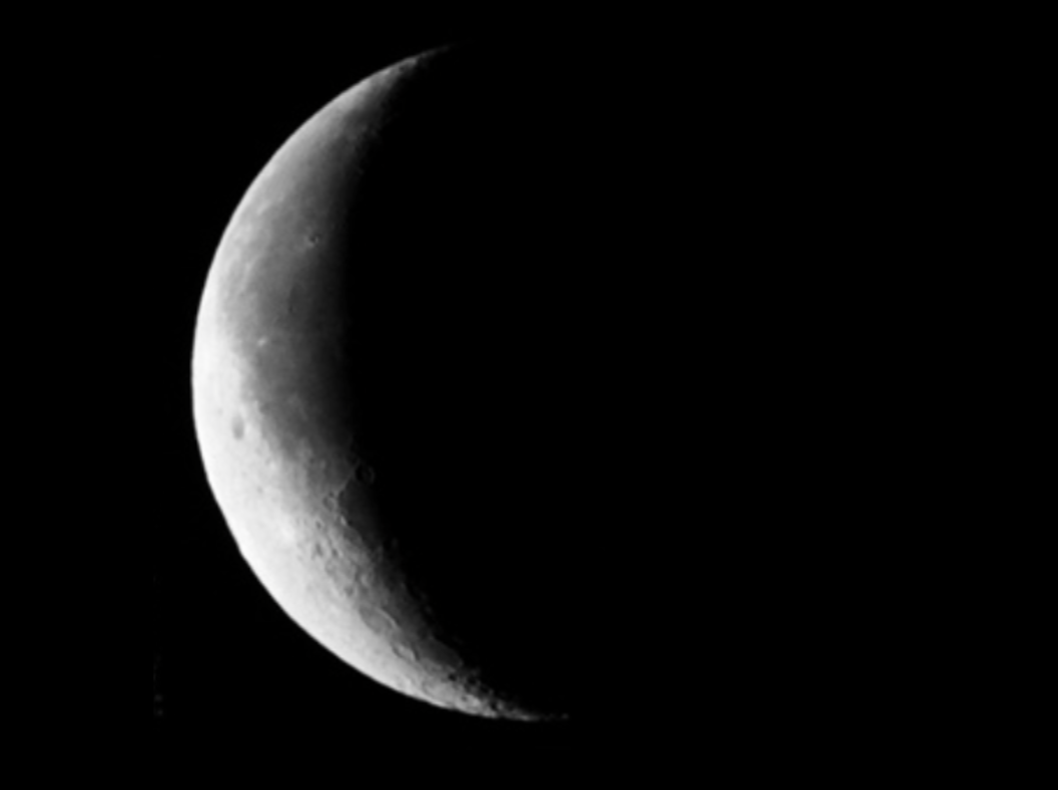

Waning Crescent
Eclipse
Occur when Earth, Moon, and Sun form a straight line.
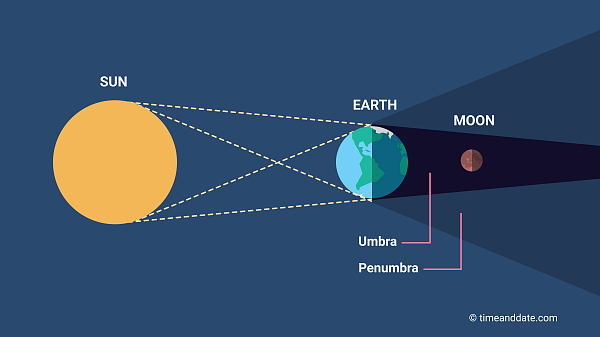
When the Earth is between the Moon and the Sun and all three make a straight line (partial when only part of Moon is in shadow, total when all is in shadow)
When does a lunar eclipse occur?
Can be seen by everyone on the entire nighttime half of the Earth.
Who on Earth can see a lunar eclipse?
Full Moon phase
What phase is the Moon always in during a lunar eclipse?
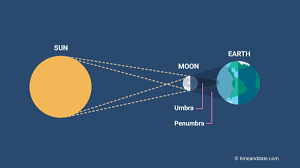
When the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun and all three make a straight line (partial when only part of the Sun is blocked, total when it all is blocked)
When does a solar eclipse occur?
The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is tiled 5.2º with respect to Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
Why don’t eclipses occur every month?
Umbra, where the is sun completely obscured.
Where on Earth do you need to be to see a total solar eclipse?
Penumbra, where the sun is partly visible.
Where on Earth do you need to be to see a partial solar eclipse?
New Moon phase
What phase is the Moon always in during a solar eclipse?
6PM/Sunset
12AM/Midnight
6AM/Sunrise
What times does the Full Moon rise, transit, and set?
12PM/Noon
6PM/Sunset
12AM/Midnight
What times does the First Quarter Moon rise, transit, and set?