Alberta Science 10 Biology
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
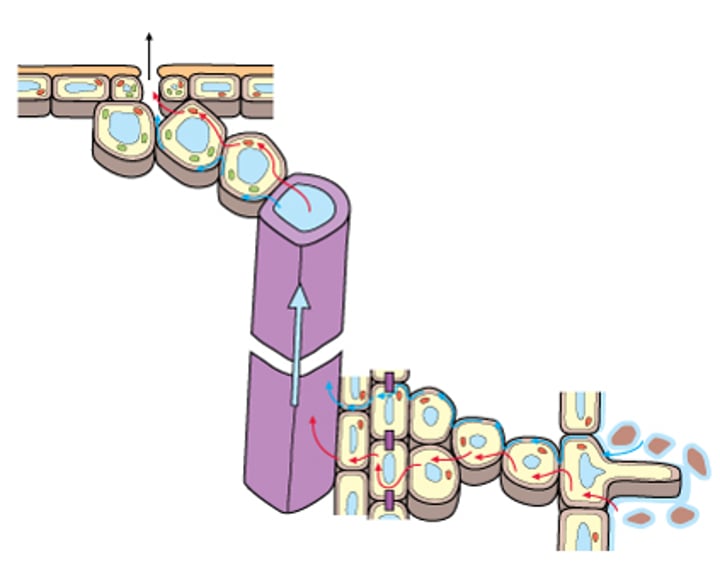
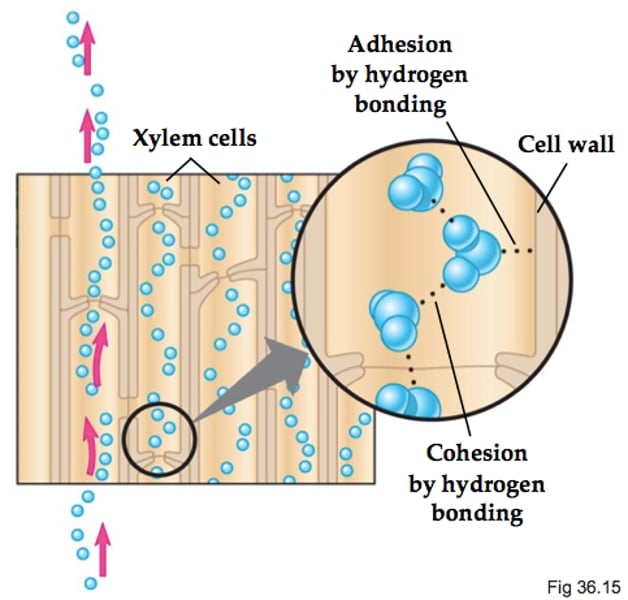
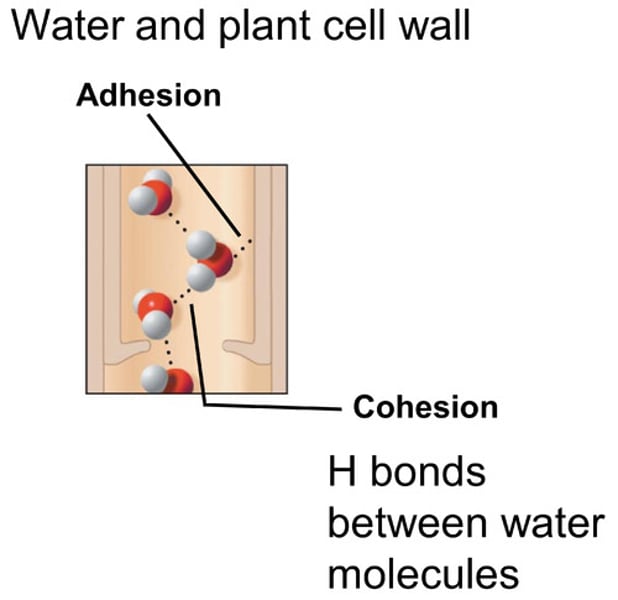
adhesion
The attraction of water to molecules of other substances.
Is used in plants to move water and dissolved minerals up the xylem.
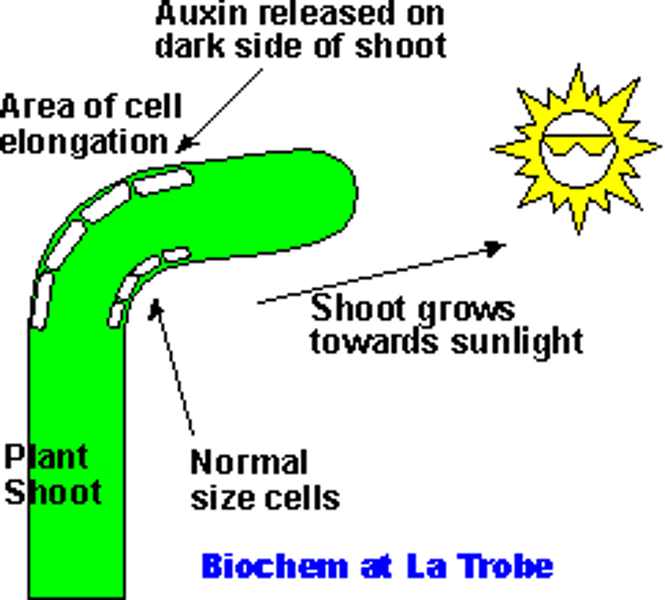
auxin
A photonegative plant hormone that promotes cell elongation.
Is responsible for phototropism.
cell theory
1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
3. Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen.
36ADP(aq) + 36Pi(aq) + C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) = 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) + 36ATP(aq)
cohesion
The attraction of water to other molecules due to hydrogen bonds formed by the polar nature of water molecules.
Is used in plants to move water and dissolved minerals up the xylem.
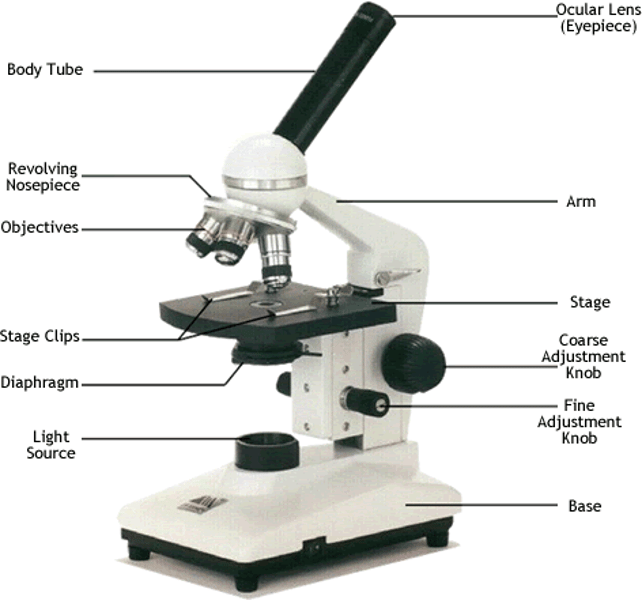
compound light microscope
A microscope that shines light through a specimen and has two lenses to magnify an image.
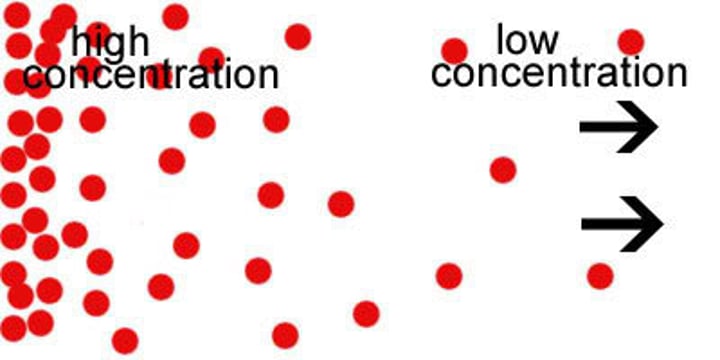
concentration gradient
In cells: the difference of concentrations between areas of the cytoplasm.
Determines the direction in which particles tend to flow across the cell membrane.
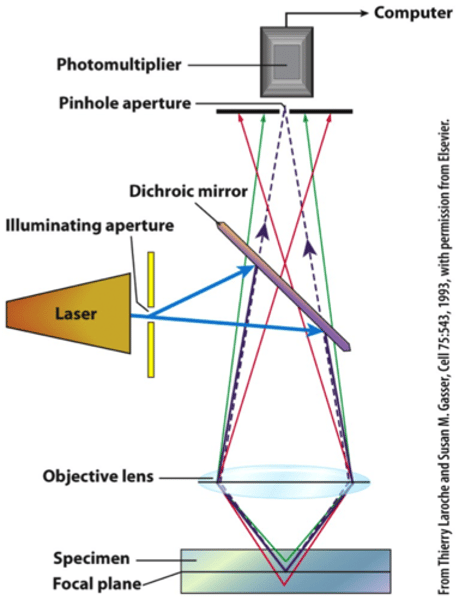
confocal laser scanning microscope
A microscope in which a laser beam is directed at various planes of the specimen, producing a series of two-dimensional images that can be stacked to produce a three-dimensional image.
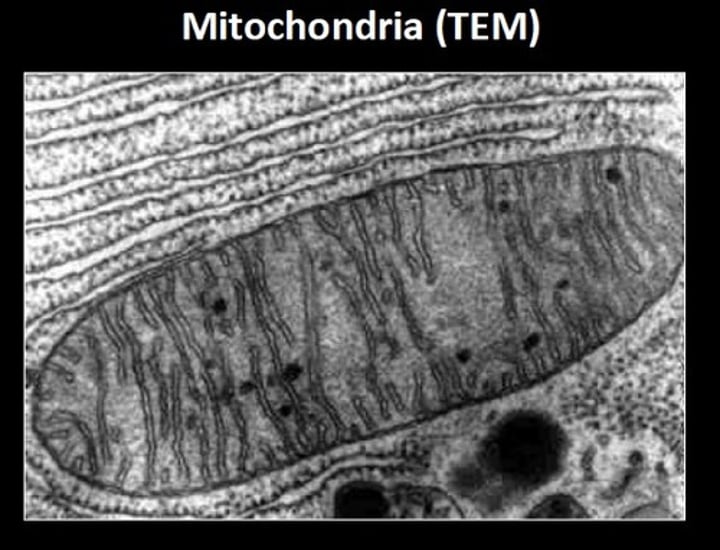
transmission electron microscope
A microscope that uses an electron beam to study the internal structure of thinly sectioned specimens.
Creates high-resolution and magnification 2D images.
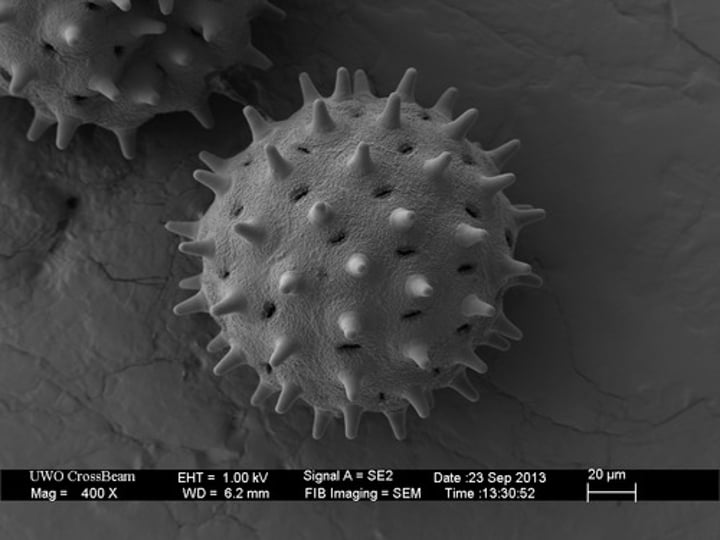
scanning electron microscope
A microscope that produces an enlarged, three-dimensional image of an object by using a beam of electrons across the surface of an object.
Creates lower resolution and magnification (compared to TEM) images in 3D.

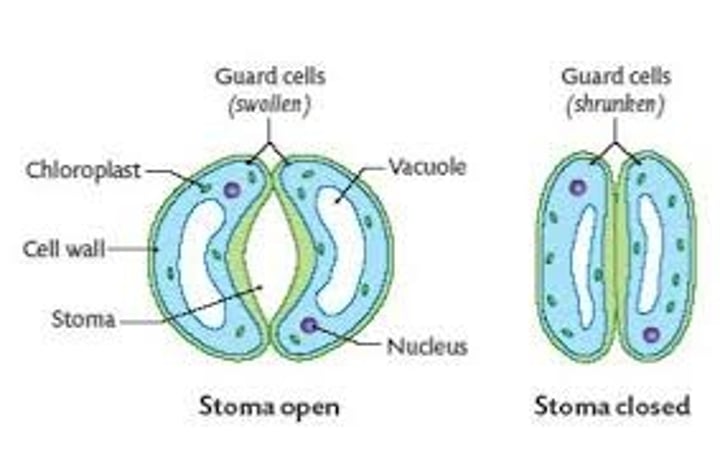
guard cells
The two cells that flank the stomatal pore and regulate the opening and closing of the pore.
Opens through a process in which potassium ions are drawn in via active transport and water follows via osmosis, making the cells turgid.
gravitropism
Direction of plant growth in response to gravity.
Stem: negative gravitropism (grow away from gravity)
Root: positive geotropism (grow towards gravity)

phototropism
Direction of plant growth in response to light.
Stem: positive phototropism (grow towards light)
Root: weak negative phototropism (grow away from light)
open system
A system that interacts with its environment.
Cells are open systems.
organ
A collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body.
organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell.
photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars.
6H2O(l) + 6CO2(g) --(chlorophyll and light)--> C6H1206 + 6O2(g)
pressure difference
The force that drives movement of water throughout a plant.
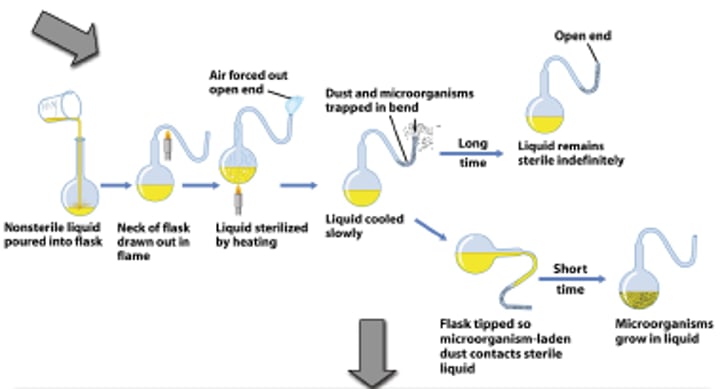
spontaneous generation
Hypothesis stating that life could arise from nonliving matter.
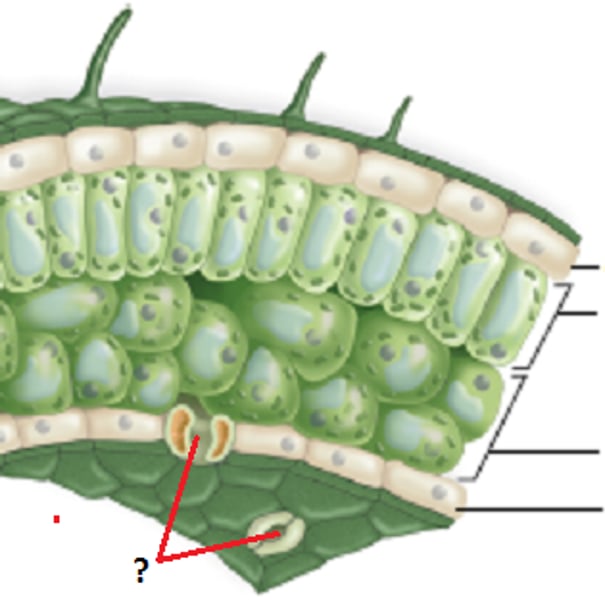
stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move.
system
A group of parts that work together as a whole.
tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
hyper, hypo, iso -tonic
The ability of a solution surrounding a cell to cause that cell to gain or lose water.
Hyper-: more solute
Iso-: balanced solute
Hypo-: less solute
transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant, mainly through the stomata.
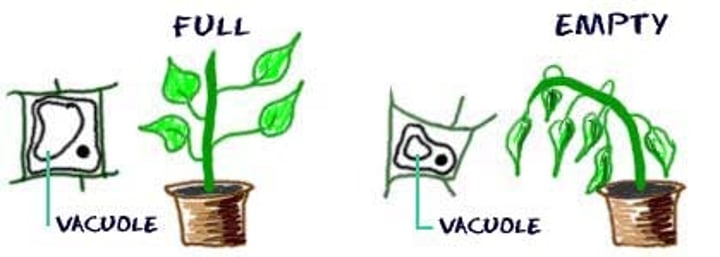
turgor pressure
The pressure inside of a cell as a cell pushes itself against the cell wall, creating a firm state.
Hans and Zacharias Janssen (1590)
Invented the first compound microscope.
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
Observed single-celled organisms.
Robert Hooke (1665)
Studied cork and and named the structures he saw "cells".
Francesco Redi (1668)
Showed maggots do not arise from decaying meat (disproving spontaneous generation theory).
John Needham (1745)
Boiled broth, sealed vessel, showed things still grew.
Lazzaro Spallanzani (1765)
Repeated Needham's experiments but sealed flask before boiling.
Louis Pasteur (1859)
Repeated Needham's experiment with swan neck beakers, disproving spontaneous generation for good.
Robert Brown (1831)
Discovered the nucleus.
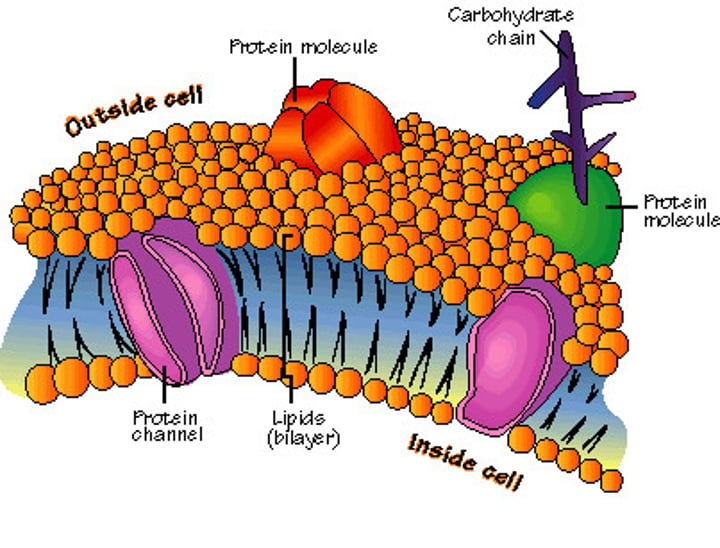
cell membrane
Protective barrier, transport in/out of cell, cell communication, molecule recognition.
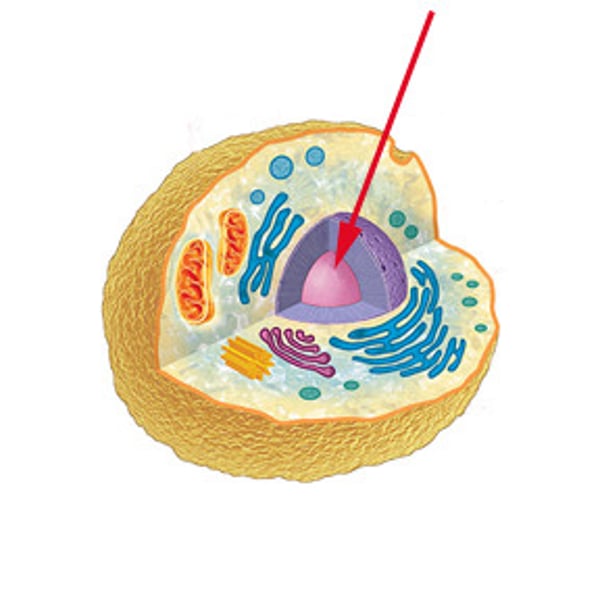
nucleus
Contains DNA, directs cellular activity, surrounded by nuclear envelope (thick, porous).
cytoplasm
Gel-like, contains essential nutrients, suspends organelles and allows movement (cytoplasmic streaming).
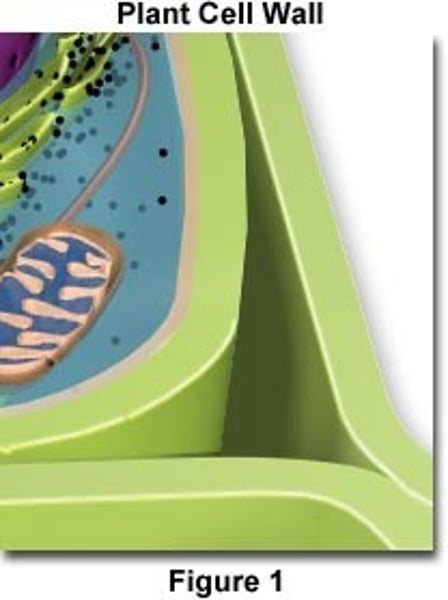
cell wall
Rigid, nonliving layer of support and strength in plants, bacteria, some protists, and fungi.
chloroplats
Site of photosynthesis, contains chlorophyll.
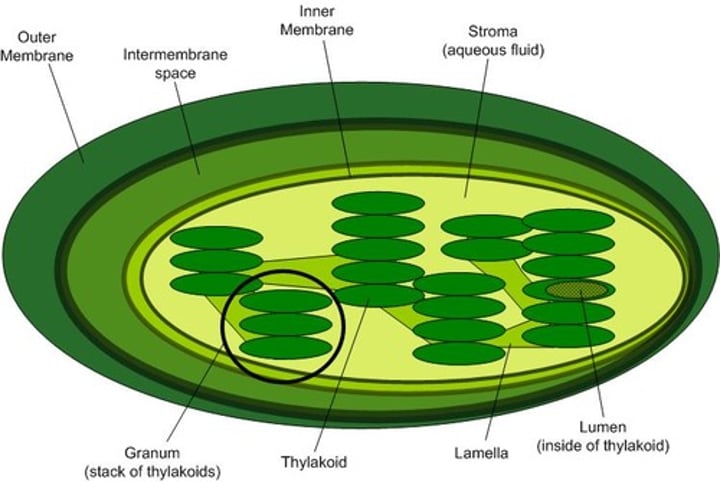
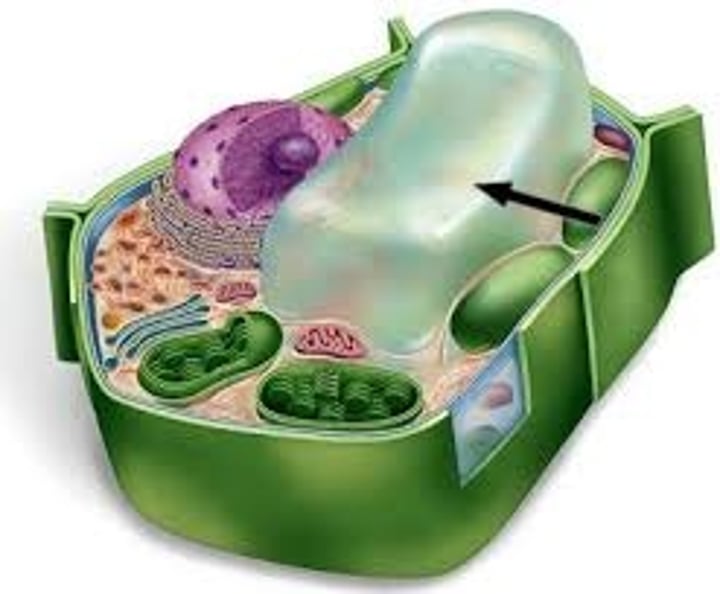
vaculoes
Membrane-bound, storage (in plants, central vacuole stores water), swells to create turgor pressure. Vesicles are smaller and used in endo/exocytosis.
endoplasmic reticulum
Connected tubes branching from nuclear envelope for transportation. Rough ER has ribosomes - protein synthesis. Smooth ER - fat and oil (lipid) production.
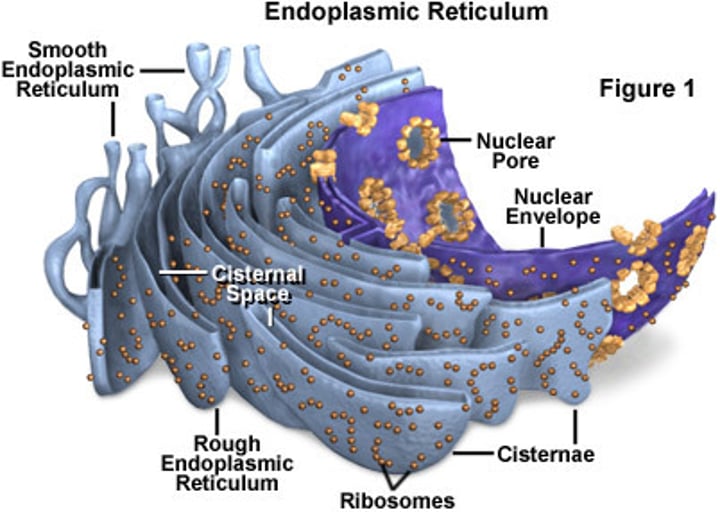
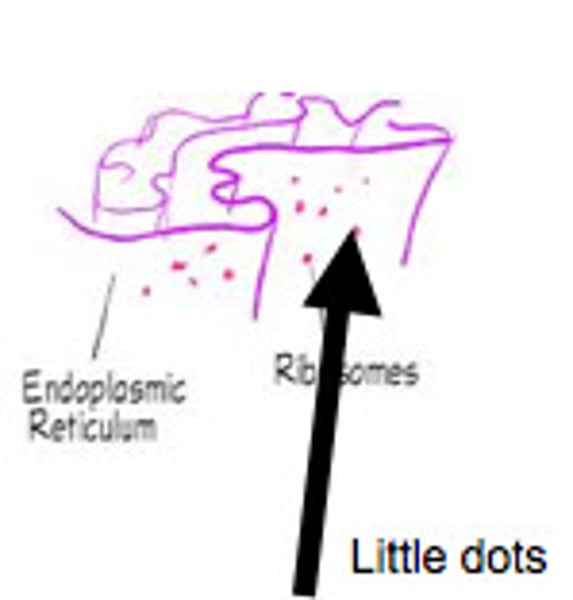
ribosomes
Dense granules, attached to ER or free is cytoplasm, protein synthesis.
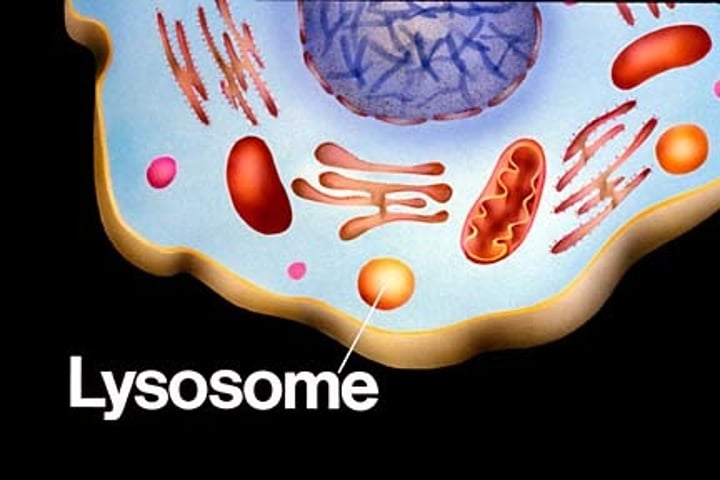
lysosomes
Membrane-bound, digestion and destruction of damaged organelles, defense against hostile bacteria.
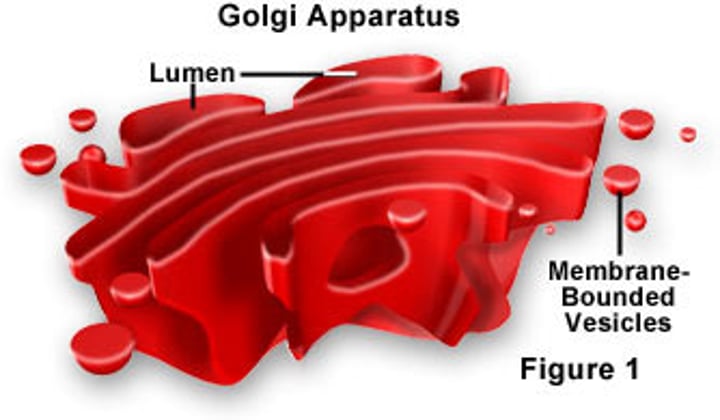
golgi apparatus
Flat, disc-shaped, packages substances from ER for transport out of cell.
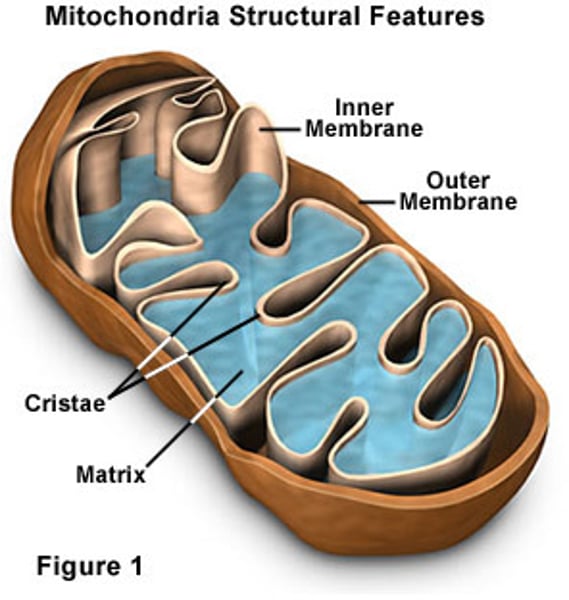
mitochondria
Rod-like, converts chemical energy in sugars into energy the cell can use (cellular respiration).
centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only.
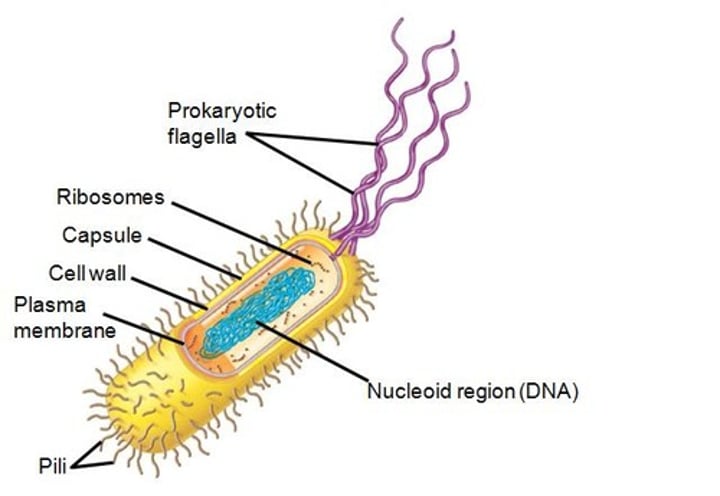
nucleoid region
The region in a prokaryotic cell consisting of a concentrated mass of DNA.
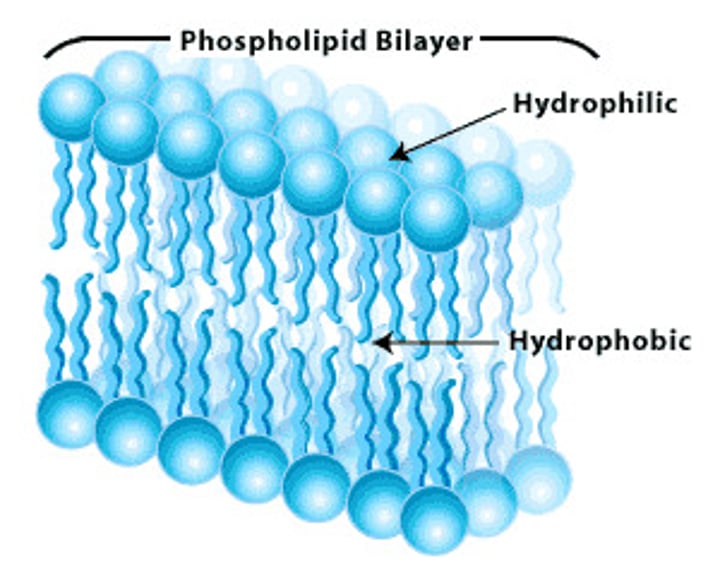
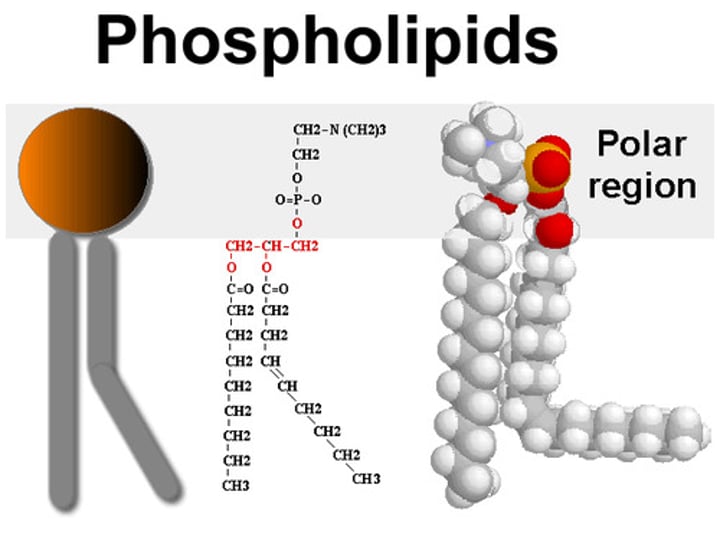
phospholipids
Main fabric of cell membrane, has hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails.
saturated/unsaturated fatty acids in hydrophobic tails
Unsaturated tails have one or more double bonds, creating a bent tail. They cannot pack together as tightly in cold temperatures, keeping the cell more fluid.
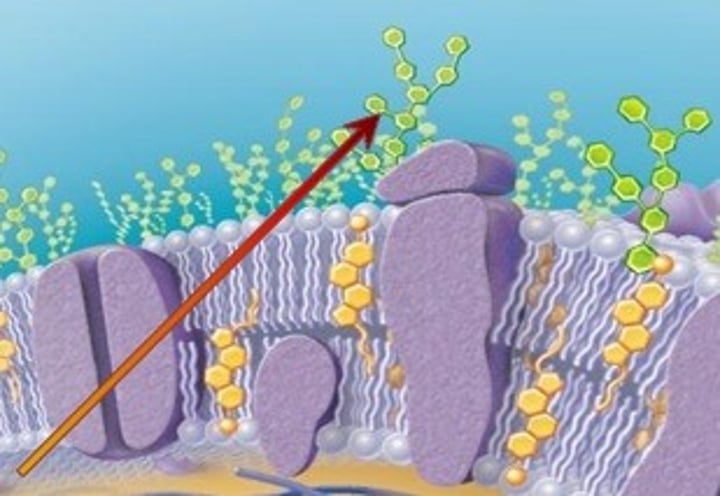
carbohydrates in cell membrane
Attached to proteins (glycoproteins)
Attached to lipids (glycolipids)
Identification markers
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
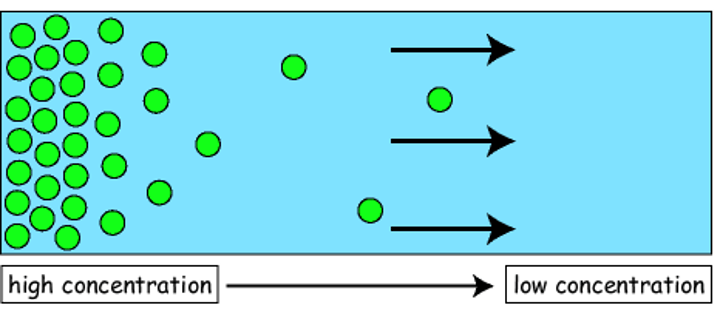
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane.
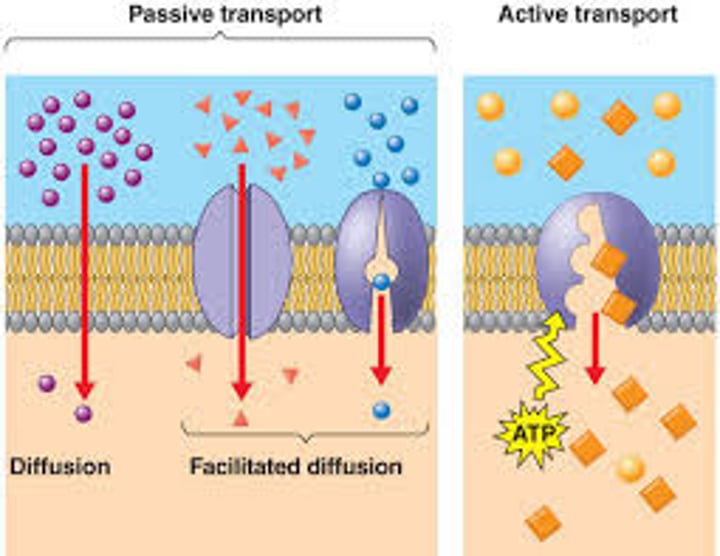
passive transport
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell.
Simple: small, uncharged
Facilitated: large, polar, charged (with the help of channel proteins for smaller and carrier for larger)
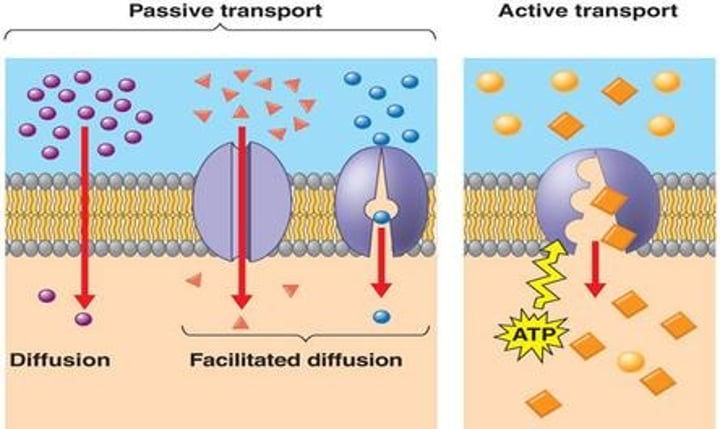
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference.
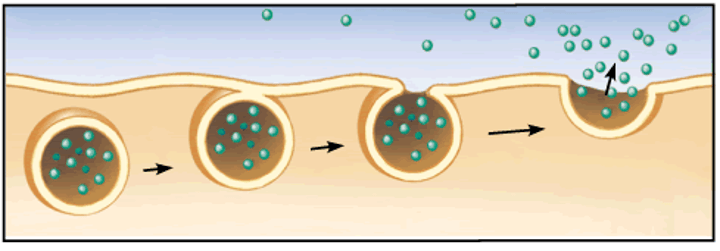
exocytosis
Secreting large particles with vesicles. Active transport.
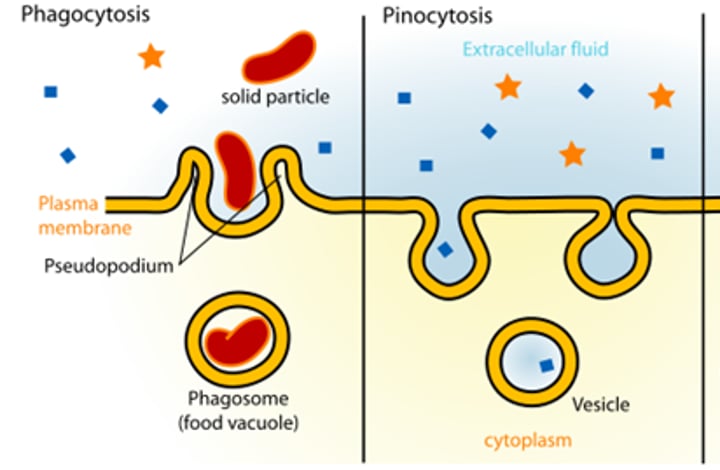
endocytosis
Taking in large particles by forming pseudopods and vesicles.
Phagocytosis: ingestion of large particles - membrane moves out
Pinocytosis: ingestion of small particles and fluid - membrane moves in
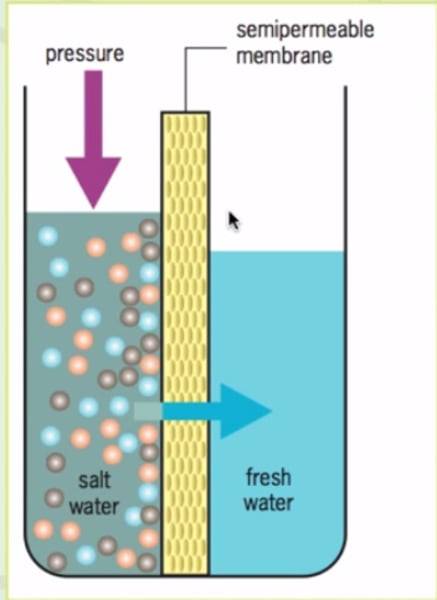
reverse osmosis
A desalinization process that involves forcing salt-water through a membrane permeable to water but not to salt.
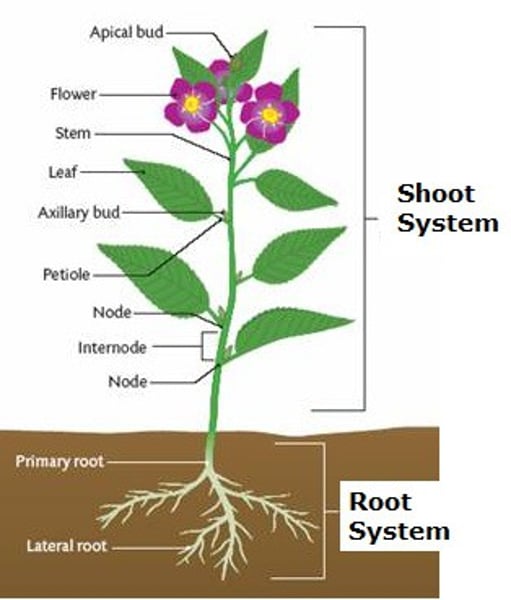
shoot system
The aerial portion of a plant body, consisting of stems, leaves, and (in angiosperms) flowers.
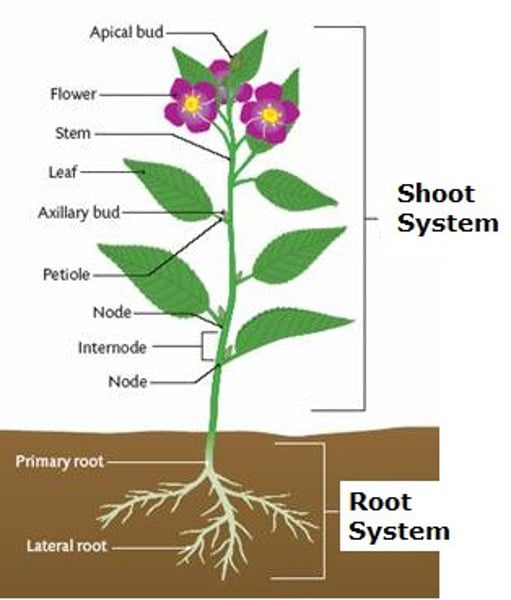
root system
All of a plant's roots, which anchor it in the soil, absorb and transport minerals and water, and store food.
epidermis
Outer layer of non-woody plants, exchange of matter (shoot - gas exchange, root - water and minerals), protection.
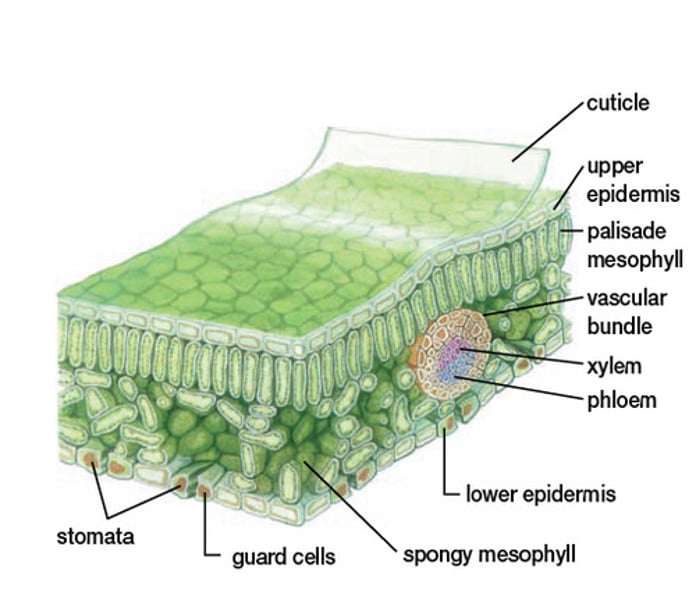
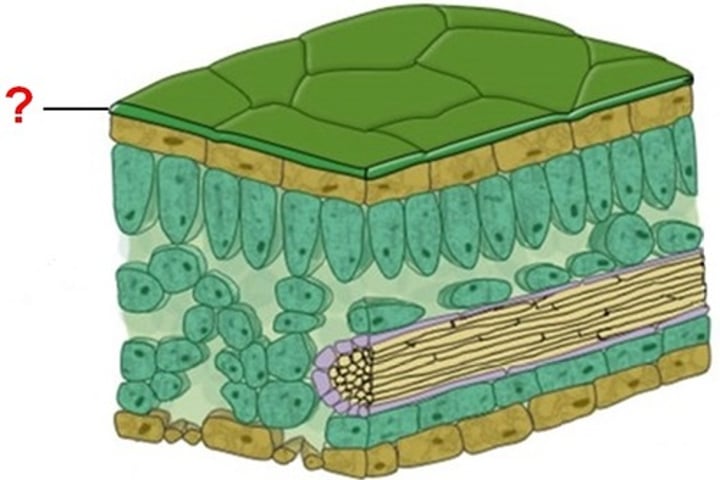
cuticle
A waxy covering on the surface of stems and leaves that acts as an adaptation to prevent desiccation in terrestrial plants.
ground tissue
Tissue system that makes up the majority of a plant
Stem - strength and support
Leaves - site of photosynthesis
Root - storage
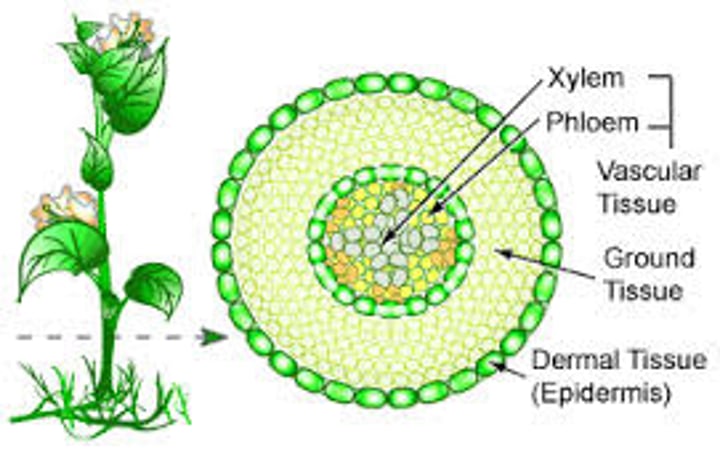
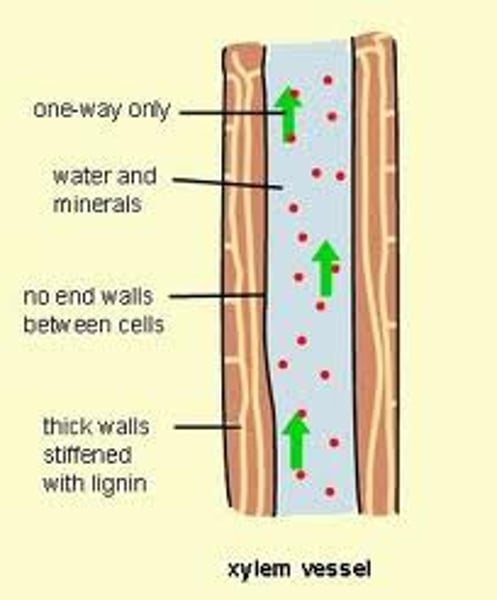
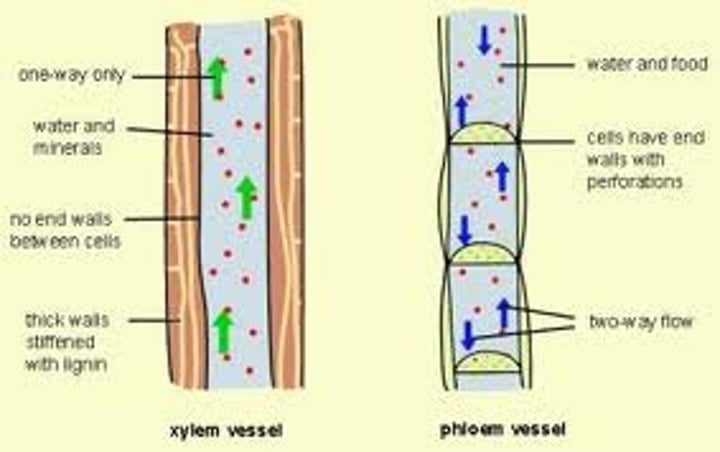
xylem
Vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant.
phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant.
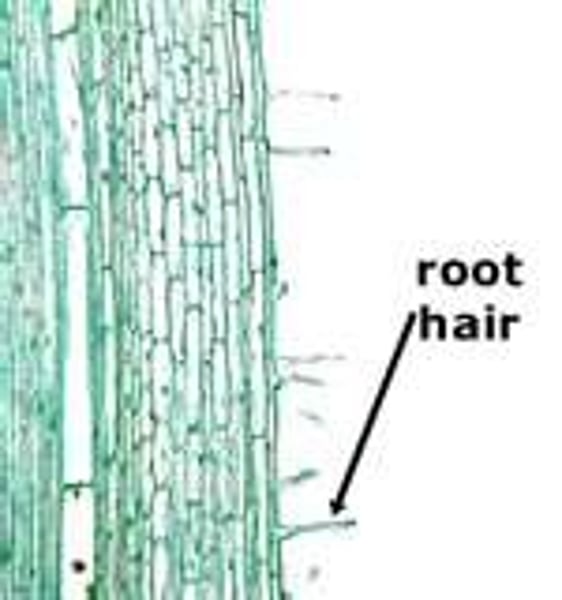
root hairs
Tiny hair-like extensions that increase the surface area of the root allowing it to absorb more water and nutrients.
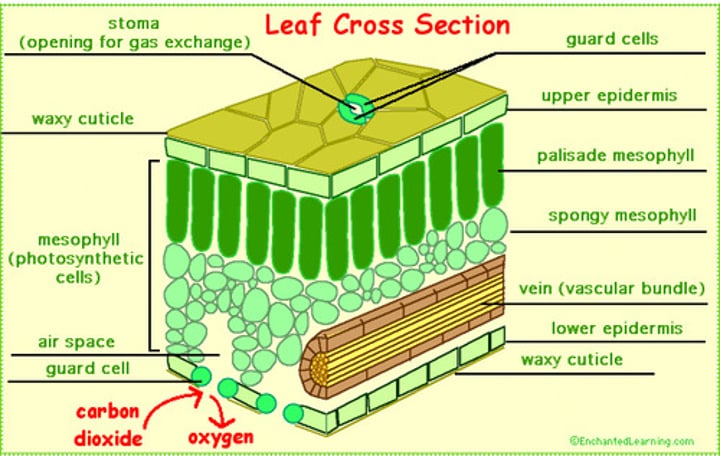
mesophyll
The ground tissue of a leaf, sandwiched between the upper and lower epidermis and specialized for photosynthesis.
Palisade: below upper epidermis, long hard rectangles for photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll: below palisade, irregular and allows for gas exchange
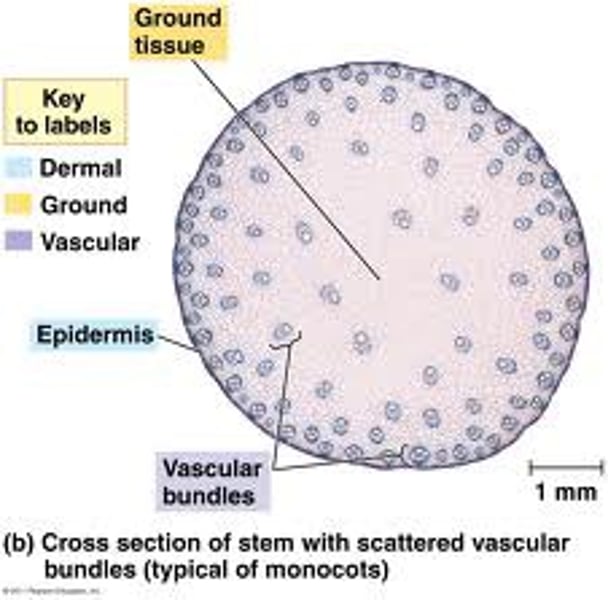
vascular bundle
Plant stem structure that contains xylem and phloem tissue.
pressure-flow theory
Explanation of how a difference in turgor between sieve elements in source and sink regions pushes sugar-rich fluid through a sieve tube.
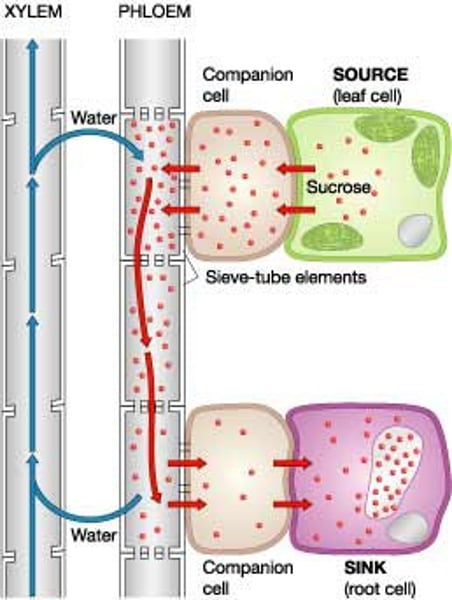
root pressure
The upward push of xylem sap in the vascular tissue of roots. Effective ~1m.
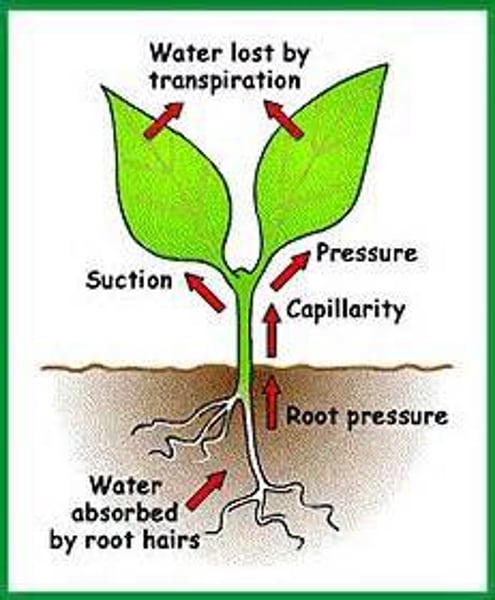
transpiration pull
When water evaporates from the leaves of a plant, water is pulled up to replace what was lost. Effective many m.