Chapter 12: Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Helminths
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Mycology
The study of fungi
Chemoheterotrophs
Fungi that decompose organic matter
Aerobic
Fungi that require oxygen
Facultative anaerobic
Fungi that can survive with or without oxygen
Chitin
A substance found in the cell walls of fungi
Molds
Fungi with filamentous hyphae
Fleshy fungi
Fungi with a mass of hyphae called mycelium
Mycelium
A mass of hyphae
Vegetative hyphae
Hyphae that obtain nutrients
Aerial hyphae
Hyphae involved in reproduction
Yeasts
Nonfilamentous and unicellular fungi
Fission yeasts
Yeasts that divide evenly
Dimorphic fungi
Fungi that can exist as yeastlike or moldlike forms
Spores
Reproductive structures of fungi
Arthroconidia
Asexual spores formed by the fragmentation of hyphae
Conidia
Asexual spores arranged in chains
Pseudohypha
A chain of yeast cells
Conidiophore
A structure that produces conidia
Blastoconidia
Asexual spores formed from the buds of a parent cell
Sporangiospores
Asexual spores formed within a sporangium
Mycosis
Fungal infection
Systemic mycosis
Deep fungal infection within the body
Subcutaneous mycosis
Fungal infection beneath the skin
Cutaneous mycosis
Fungal infection affecting hair, skin, and nails
Opportunistic mycosis
Fungal infection in a compromised host
Algae
Photosynthetic eukaryotes that inhabit water and soil
Protozoa
Unicellular eukaryotes that inhabit water and soil
Fission
Asexual reproduction by splitting into two
Budding
Asexual reproduction by forming a bud
Schizogony
Asexual reproduction by multiple fission
Euglenozoa
Excavata protozoa, including hemoflagellates transmitted by blood-feeding insects
Amebae
Protozoa that move by extending pseudopods
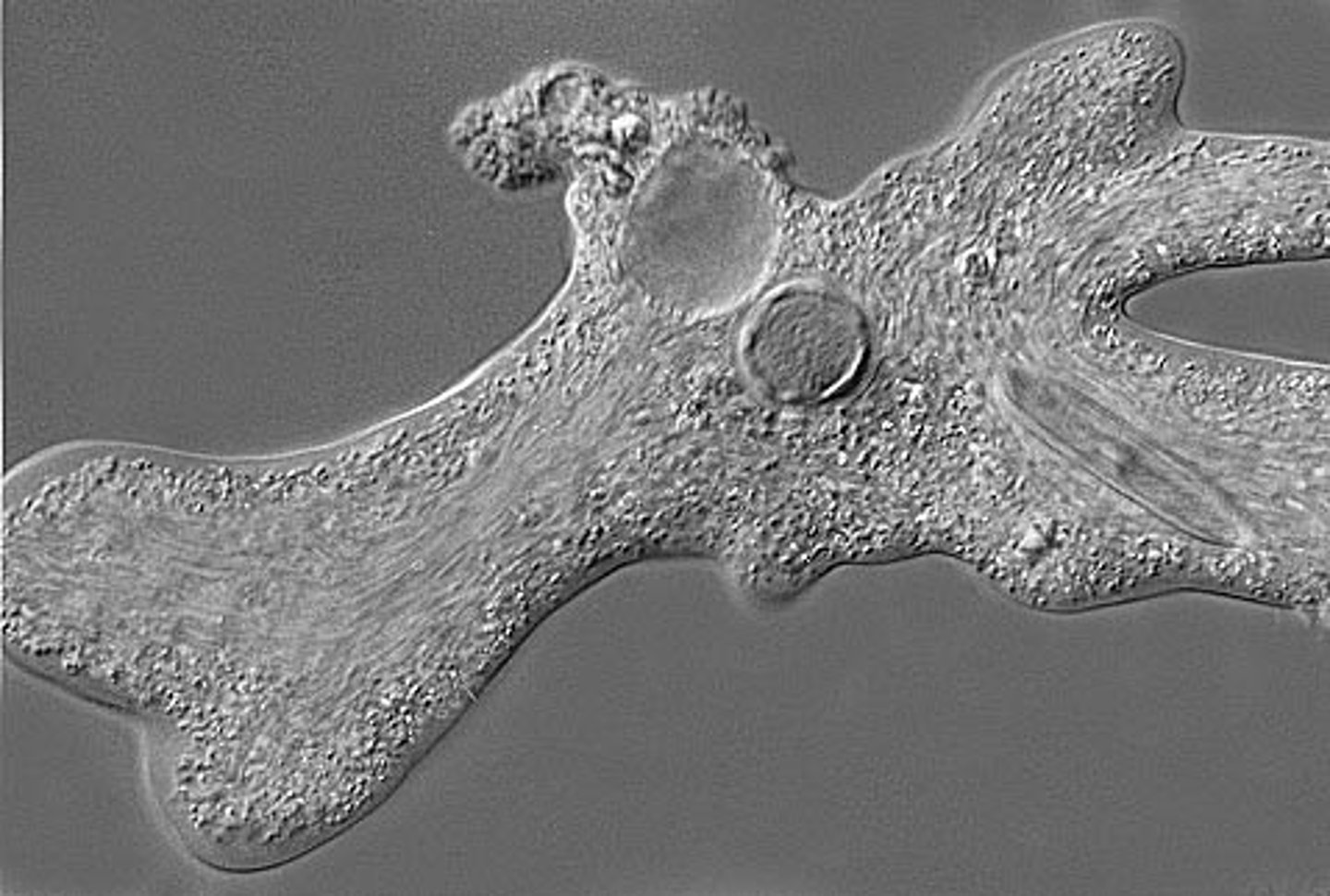
Ciliates
Protozoa that move by cilia arranged in rows
Balantidium coli
The only human parasite among ciliates, causing dysentery
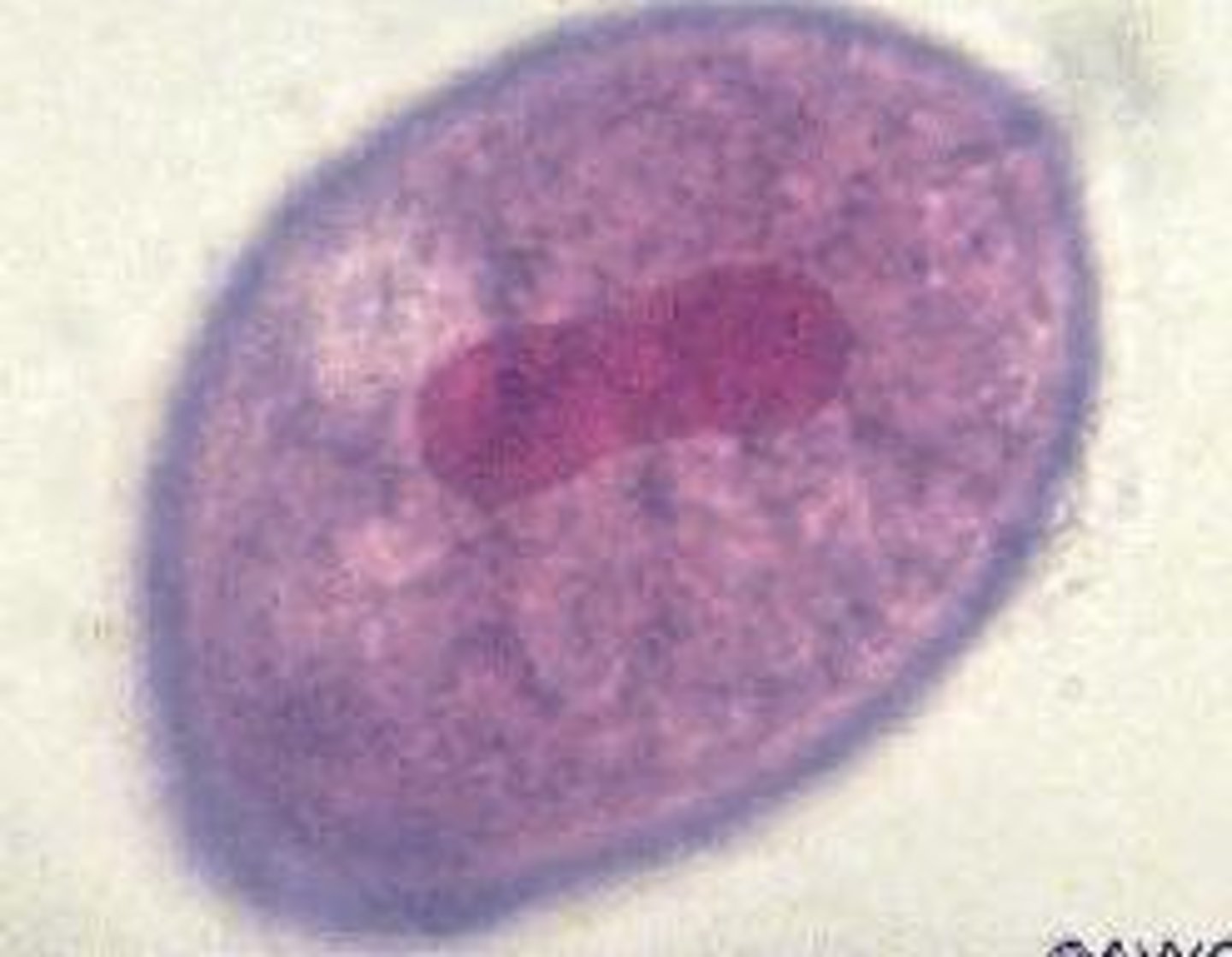
Helminths
Multicellular eukaryotic animals specialized to live in hosts
Platyhelminthes
Flatworms, including trematodes and cestodes
Trematodes
Flat, leaf-shaped flukes that absorb food through a cuticle
Schistosoma
Blood fluke causing schistosomiasis
Cestodes
Tapeworms with a scolex for attachment and proglottids for reproduction
Taenia solium
Pork tapeworm causing intestinal and neurocysticercosis
Nematodes
Roundworms with a complete digestive system
Ascaris lumbricoides
Roundworm infecting human intestines
Enterobius vermicularis
Pinworm
Arthropods
Animals with segmented bodies, hard exoskeletons, and jointed legs
Vectors
Arthropods that carry pathogenic microorganisms
Mechanical transmission
Pathogens carried on the body of a vector
Biological transmission
Pathogens multiply in the vector