Nerve Anatomy - LCC
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Central Nervous System
A subdivision of the human nervous system comprising the brain and spinal cord. Transmits & receives messages to & from the PNS
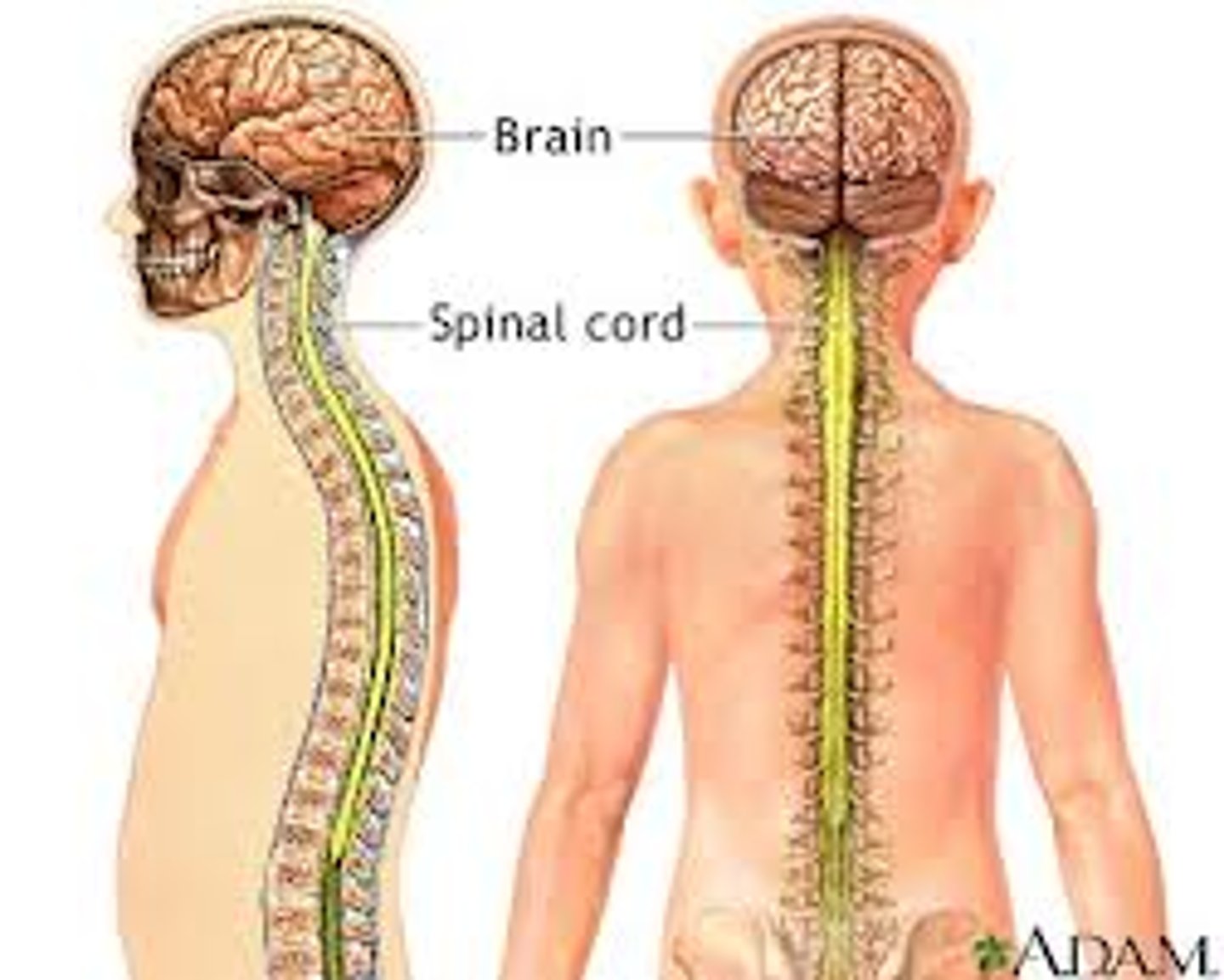
Peripheral Nervous System
A division of the nervous system consisting of all nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord.
Somatic Nervous System
The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
Autonomic Nervous System
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Controls involuntary activity of visceral muscles and internal organs and glands.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations.
Fight or flight
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy.
Feed and breed
Enteric Nervous System
Subdivision of the parasympathetic nervous system
The nervous system of the gastrointestinal tract. It controls secretion and motility within the Gi tract, and is linked to the central nervous system.
Can operate independantly of the CNS
Receptors
Special structures that allow living organisms to sense the conditions of their internal or external environment
Afferent Neurons
in-neurons, another name for sensory neurons
Effectors
Structures that respond to stimulus such as muscles or glands
Efferent Neurons
out-neurons, another name for motor neurons
Interneurons
Neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs.
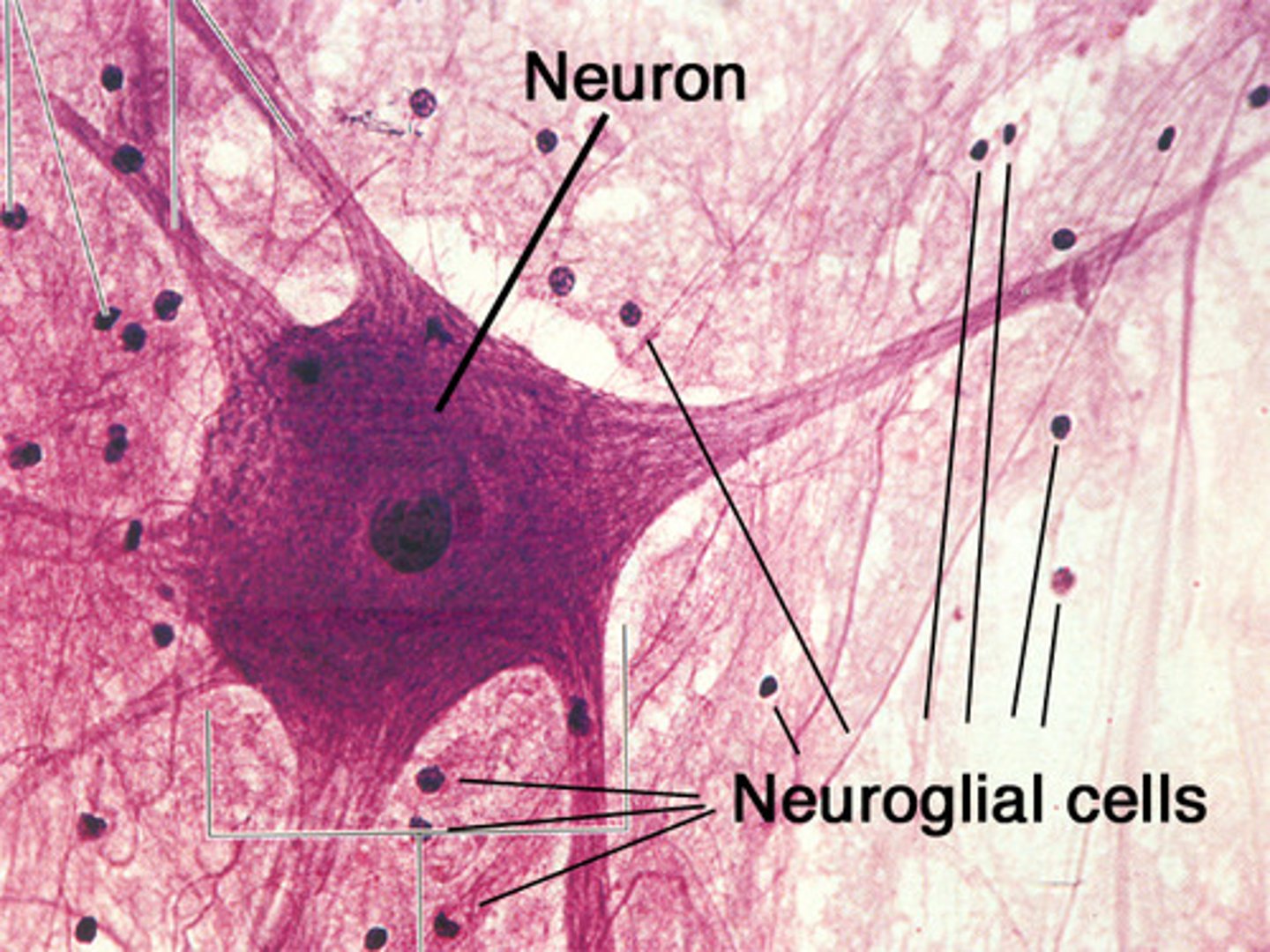
Neuron
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
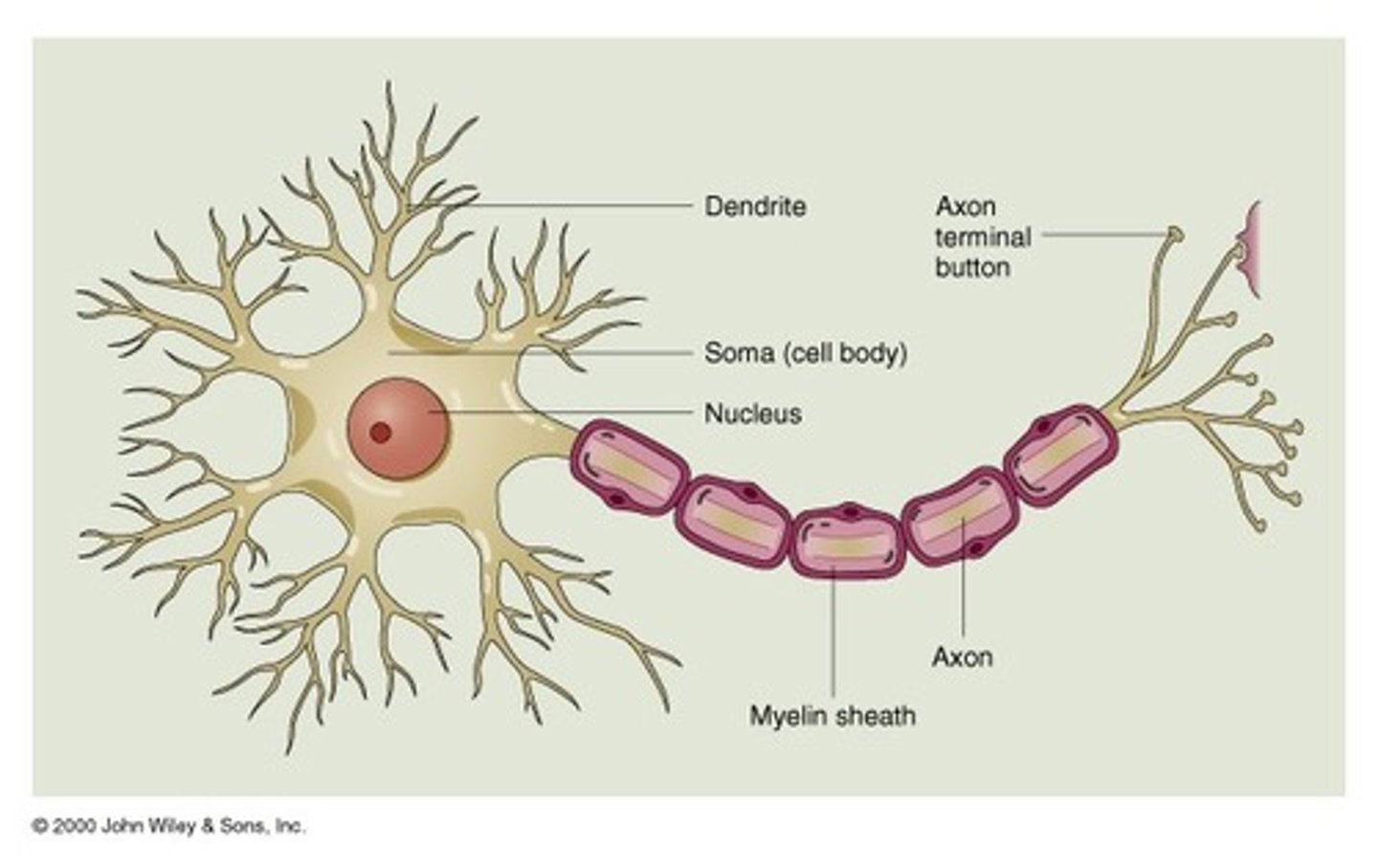
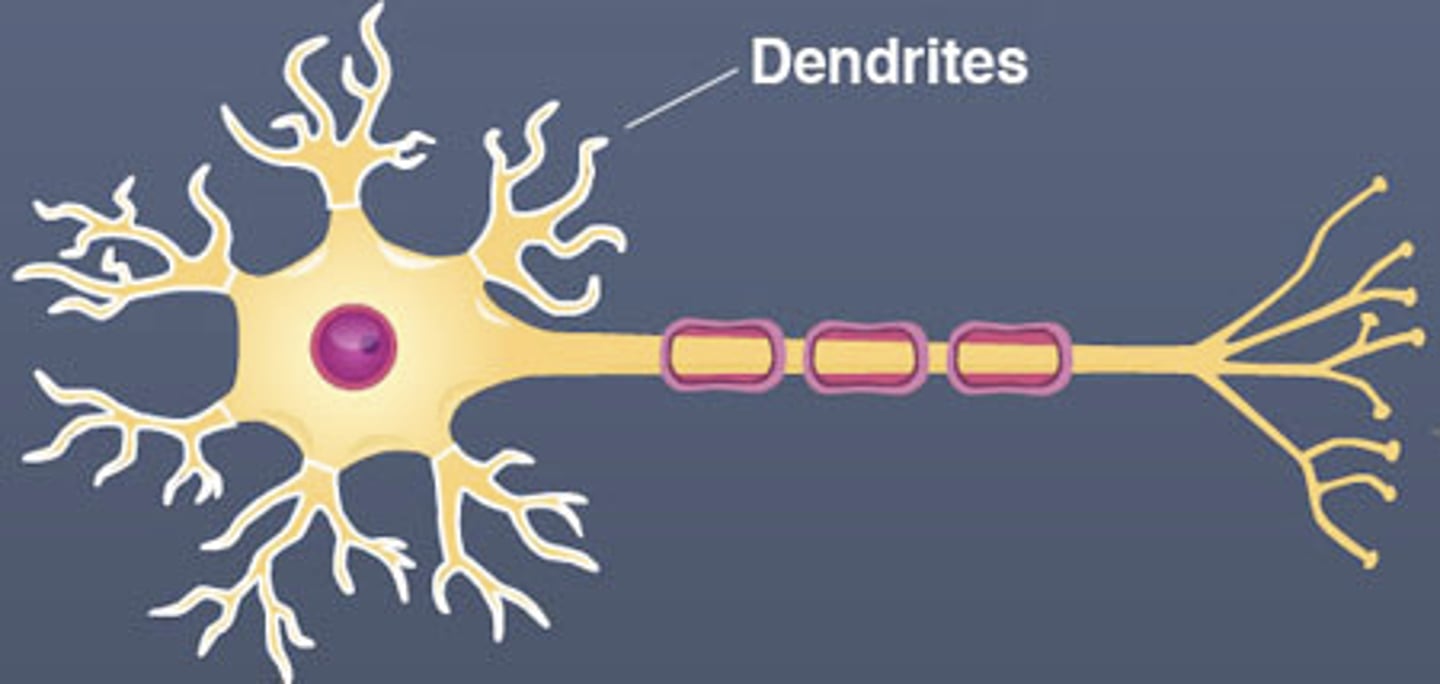
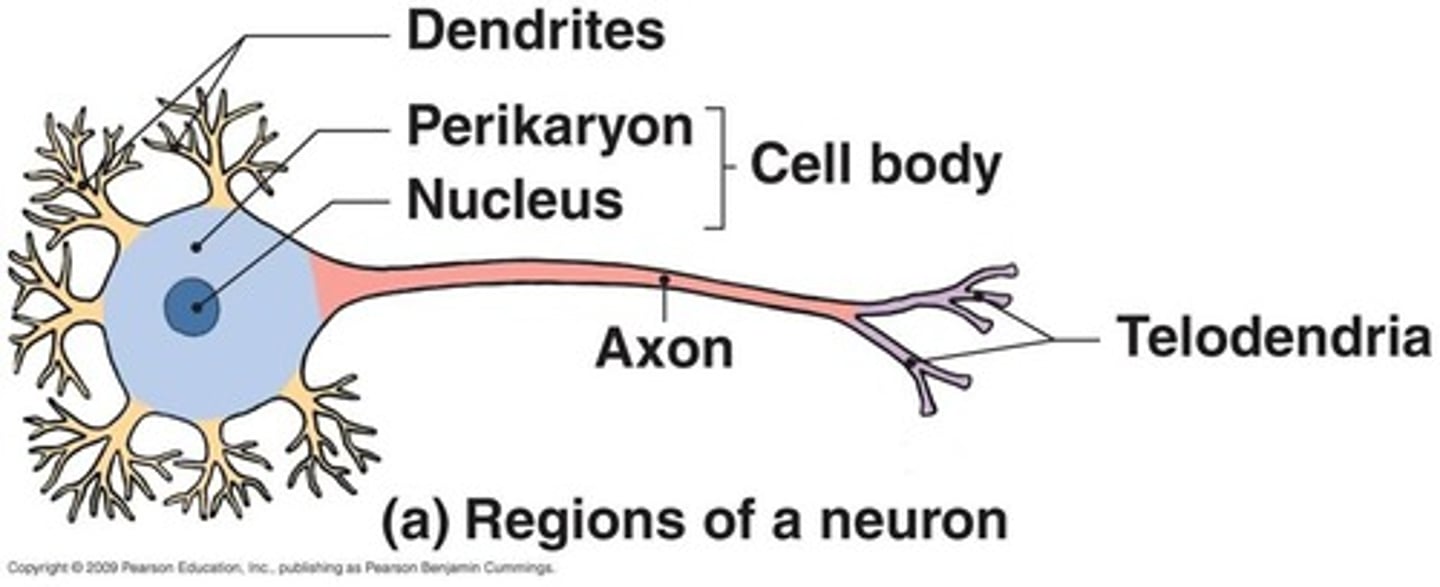
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
Cell Body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
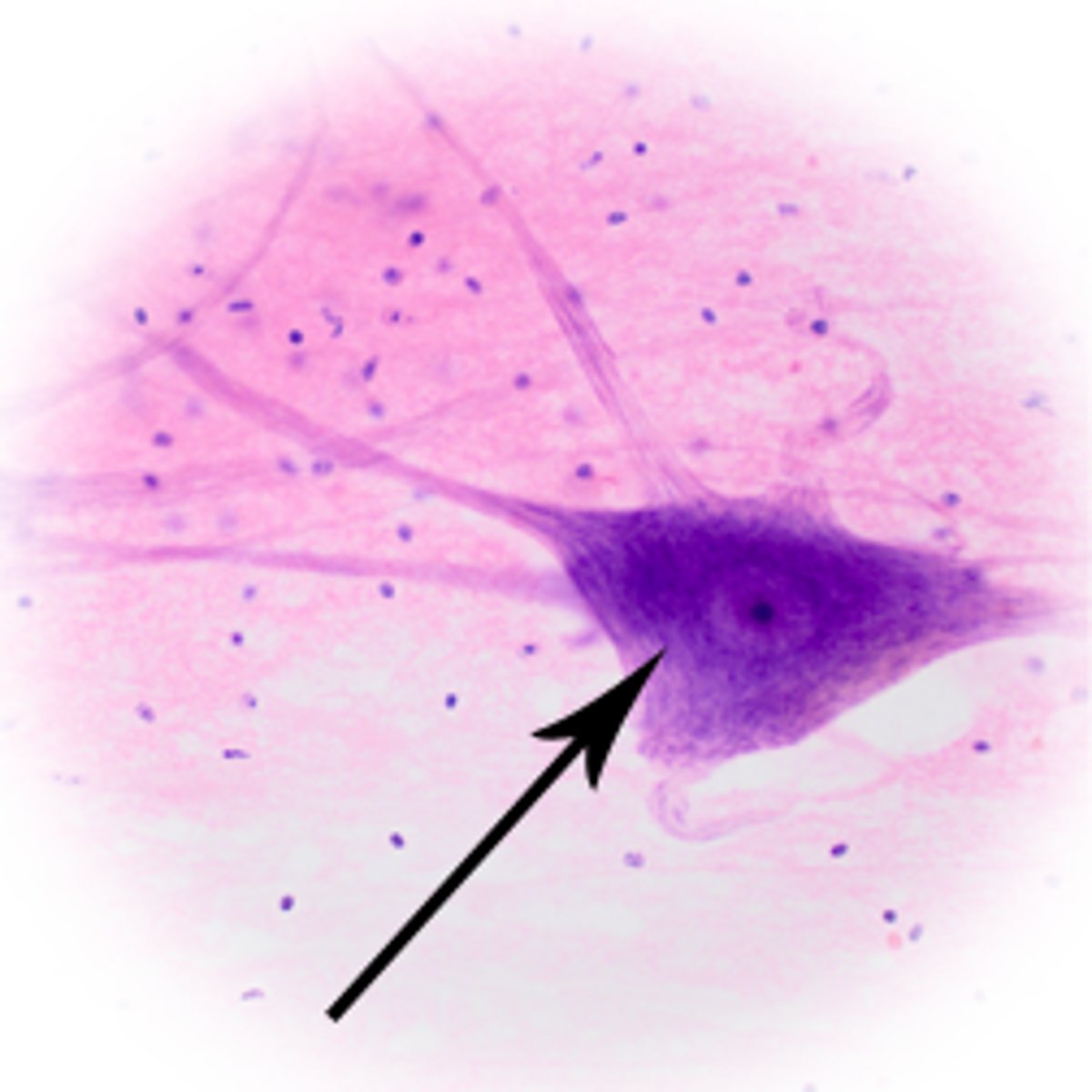
Axon Hillock
The conical region of a neuron's axon where it joins the cell body; typically the region where nerve signals is generated.
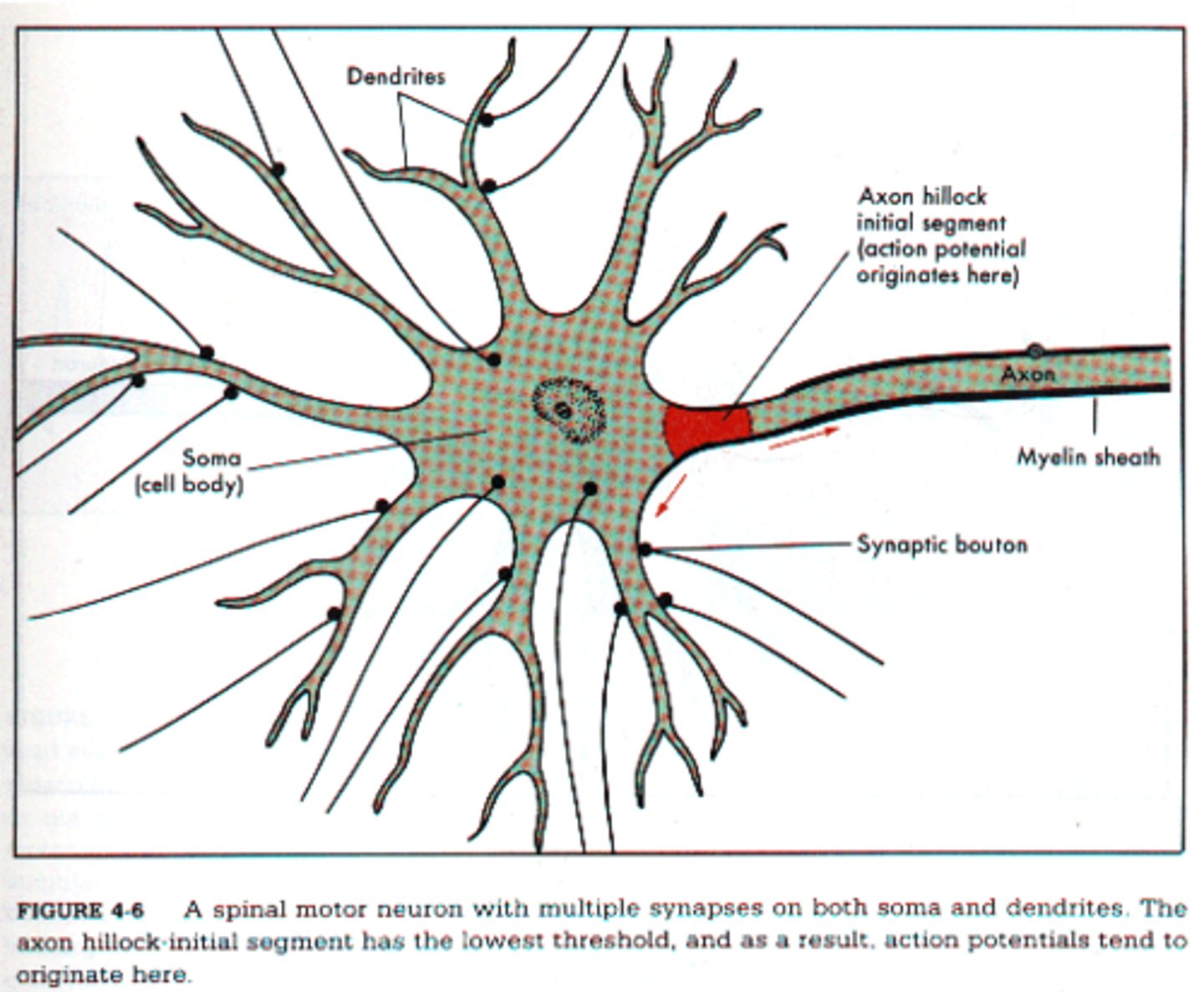
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
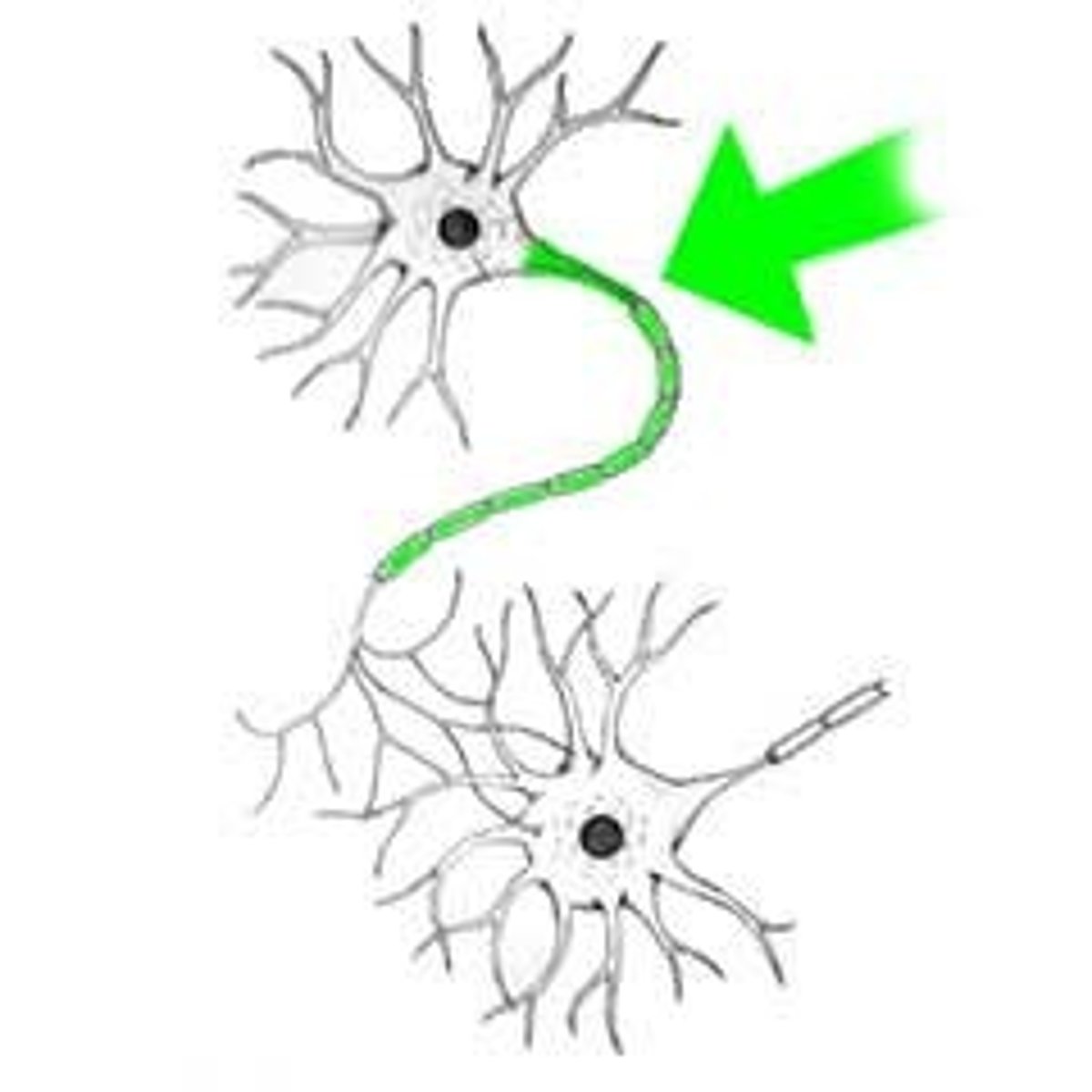
Telodendria
Series of fine, terminal extensions branching from the axon tip.
Terminal Buds
Ends of the telodendria where neurotransmitters are stored and released.
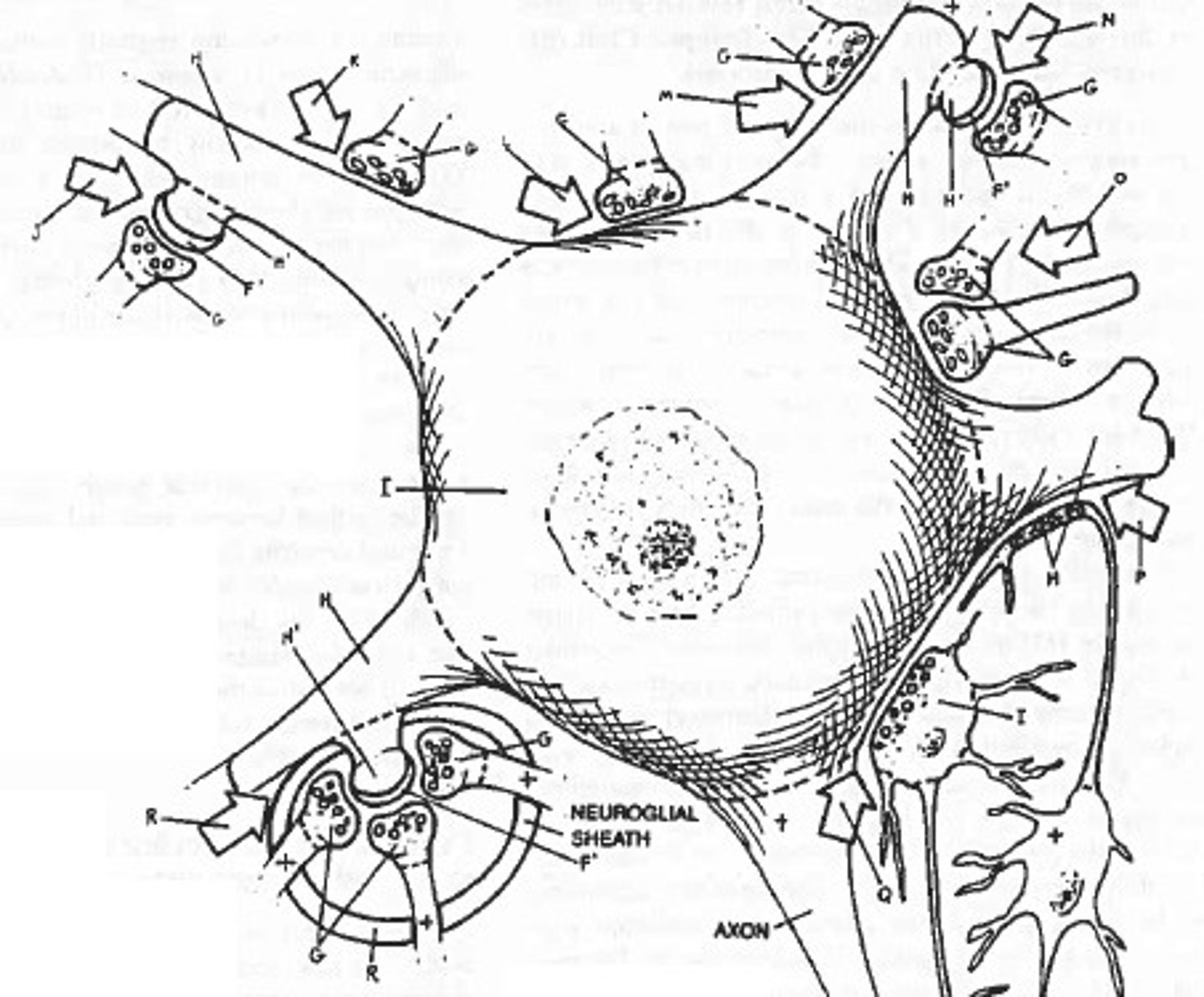
Synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
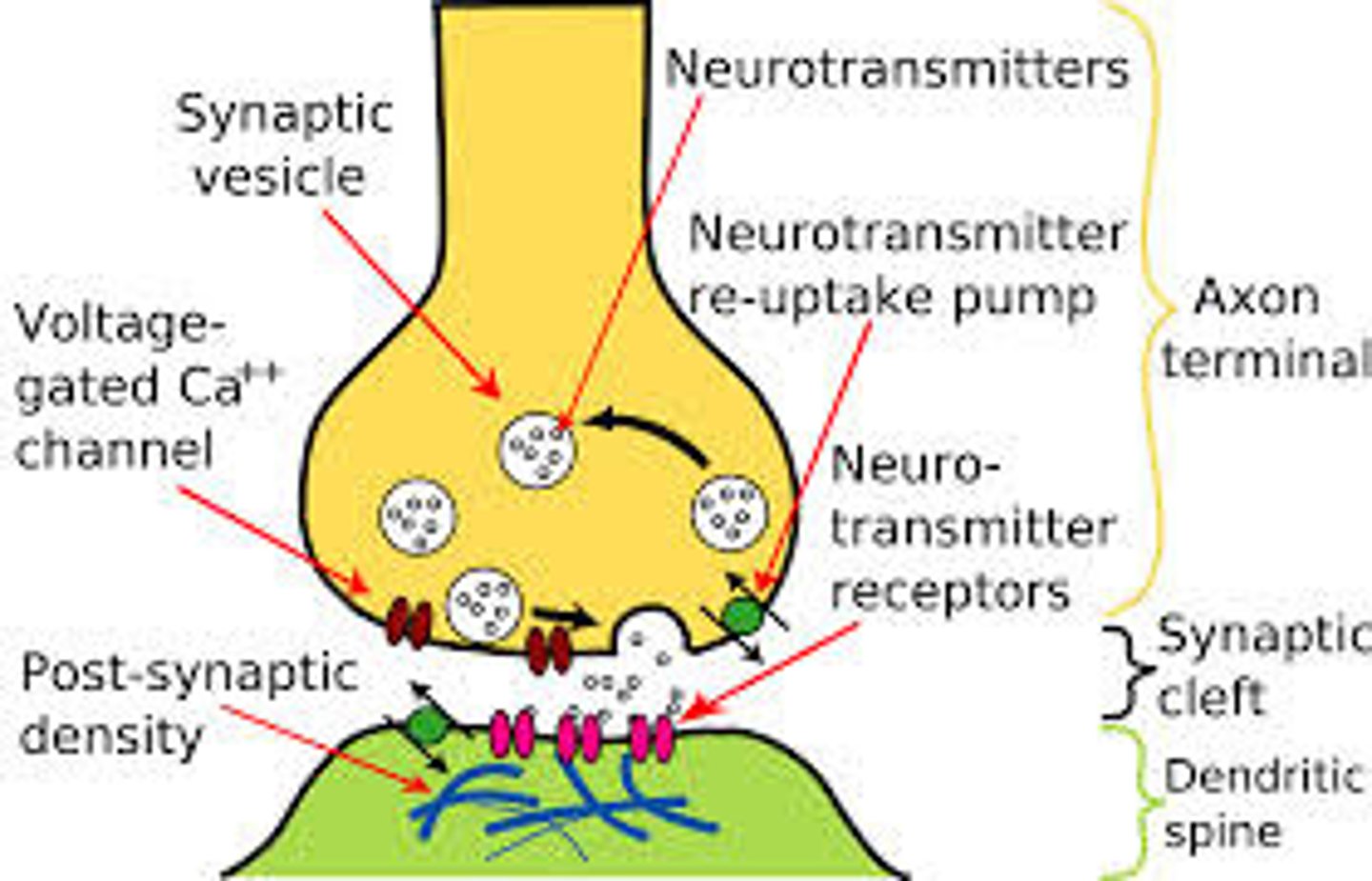
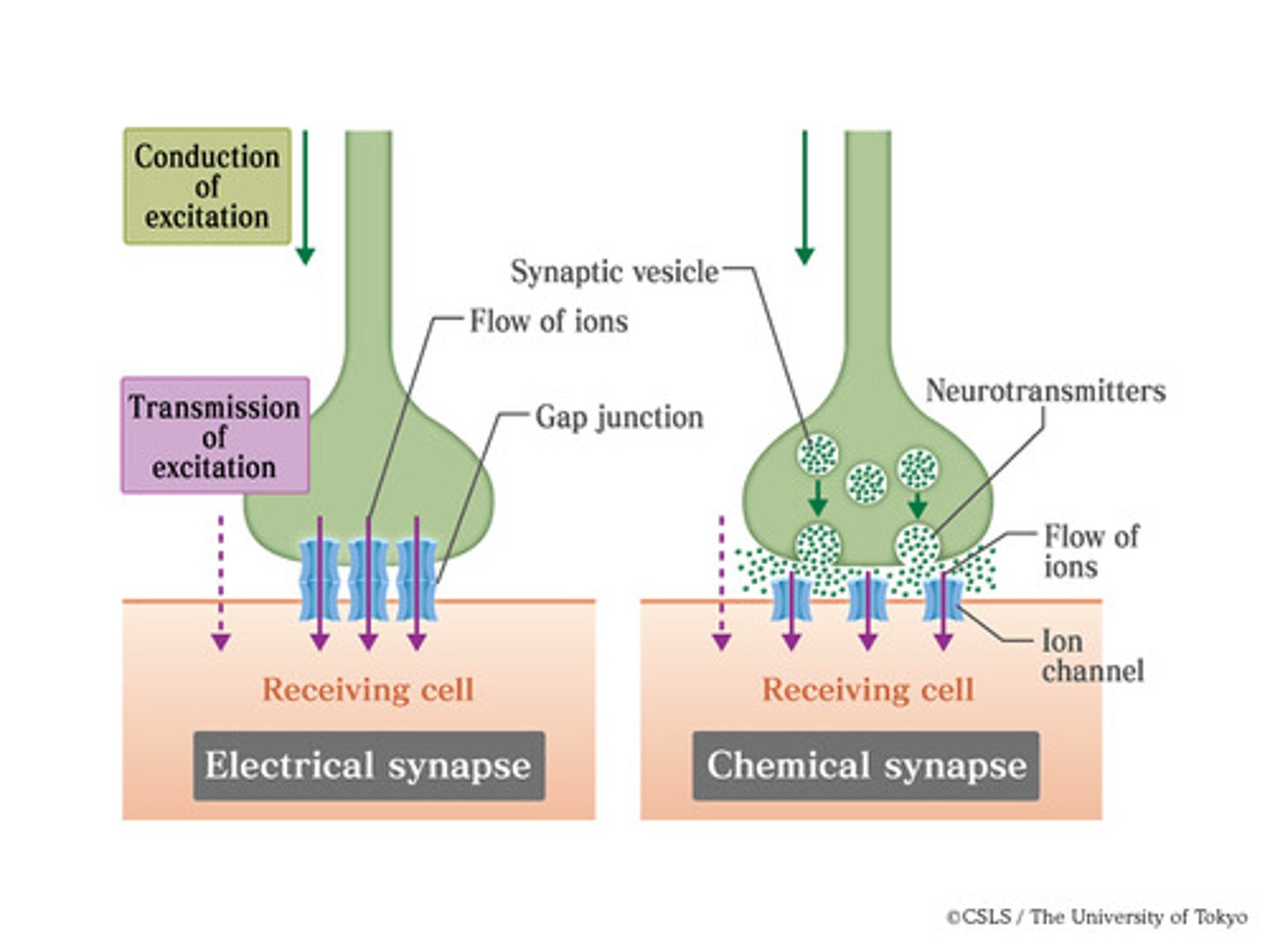
Chemical Synapse
A type of synapse at which a chemical (a neurotransmitter) is released from the axon of a neuron into the synaptic cleft where it binds to receptors on the next structure in sequence, either another neuron or an organ.
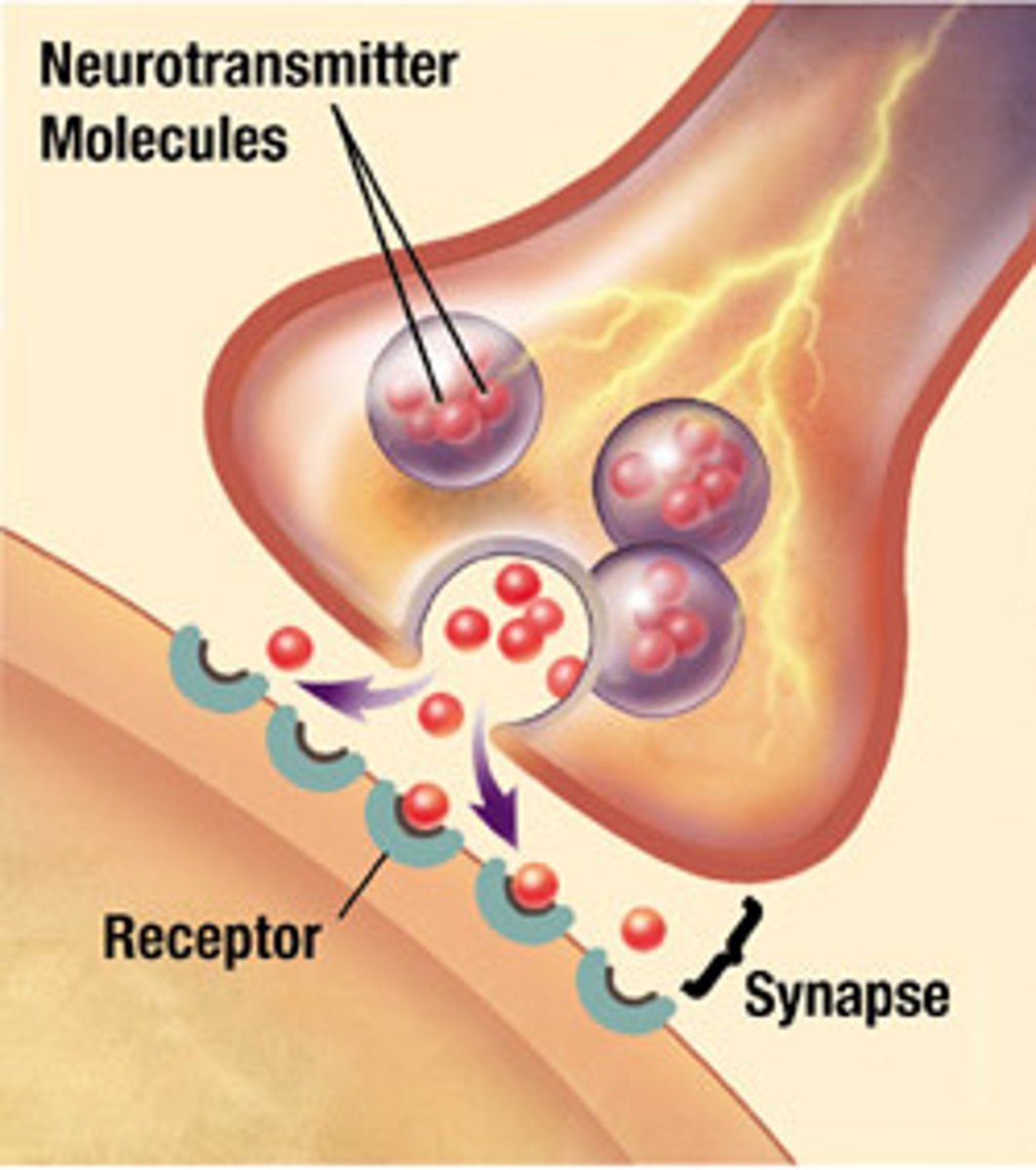
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse.
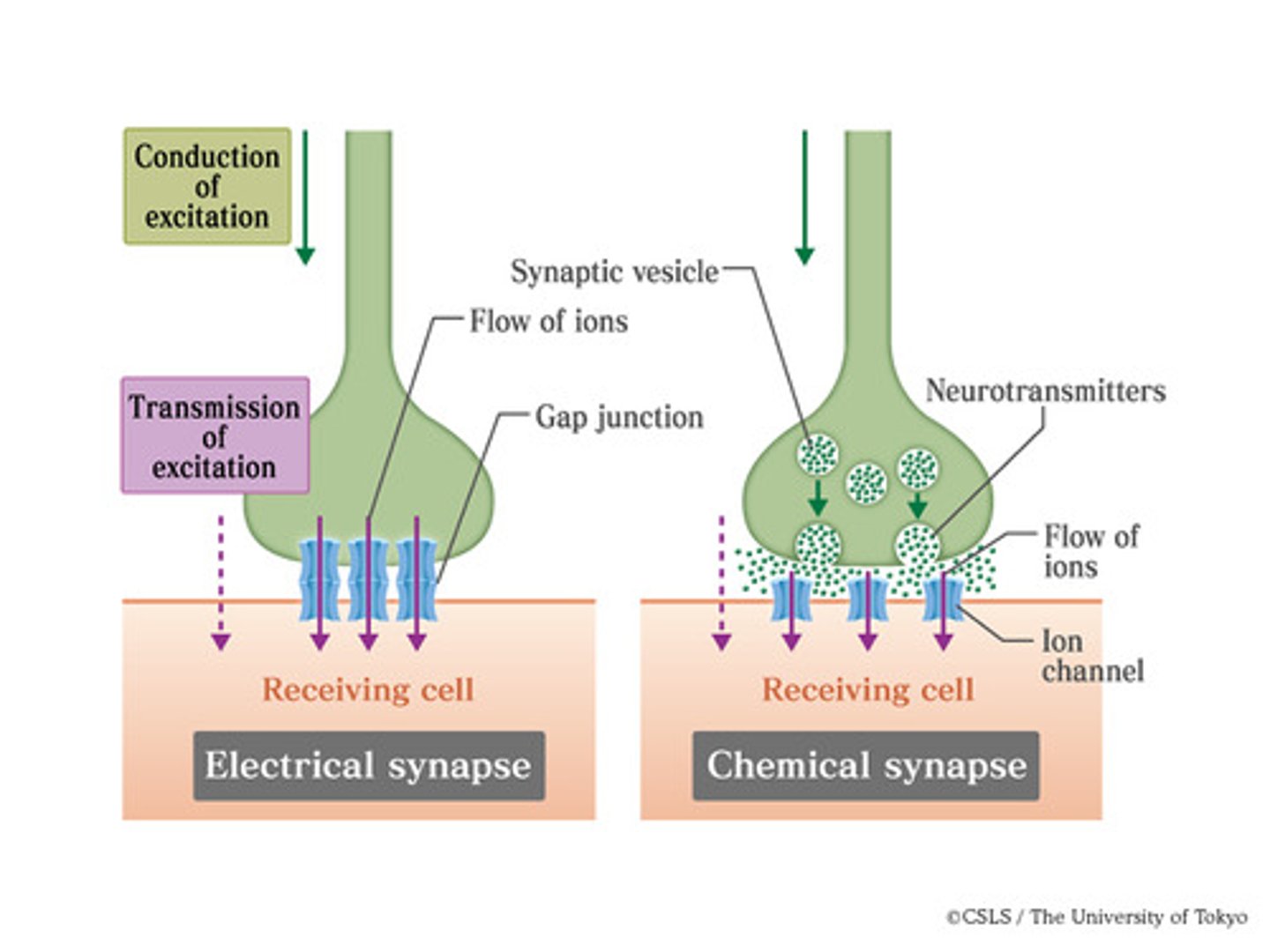
Electrical Synapse
A type of synapse in which the cells are connected by gap junctions, allowing ions (and therefore an action potential) to spread easily from cell to cell, usually in smooth and cardiac muscle.
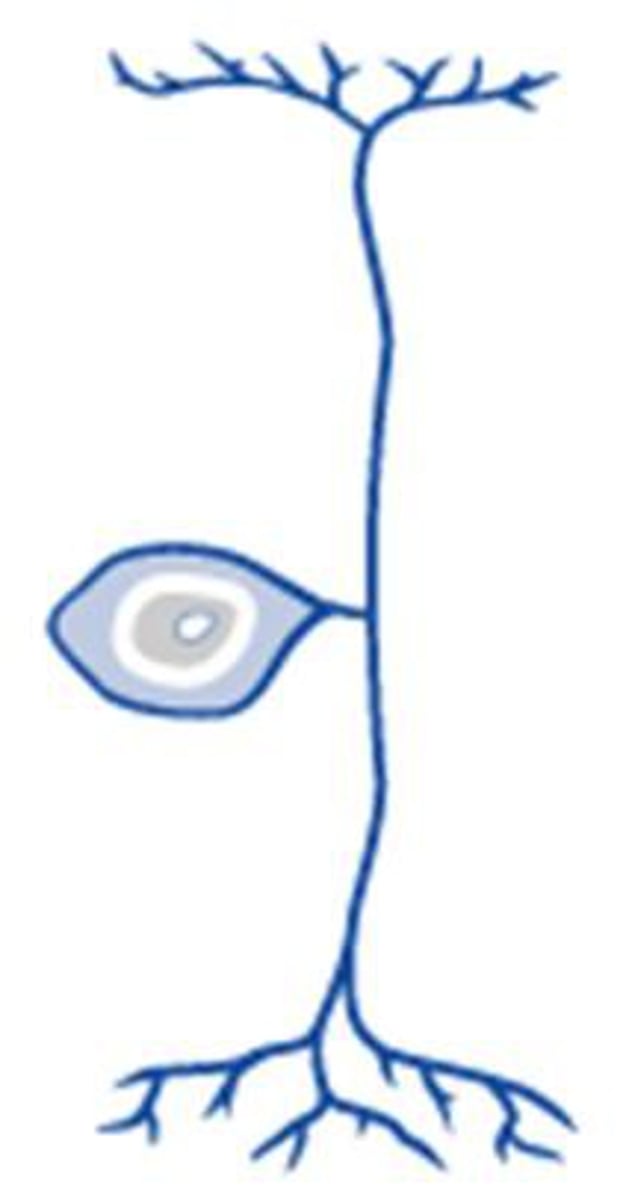
Unipolar Neurons
Single process that has two branches but functions as a single axon; first branch, peripheral process, is associated with dendrites near peripheral body part and other enters the brain or spinal cord
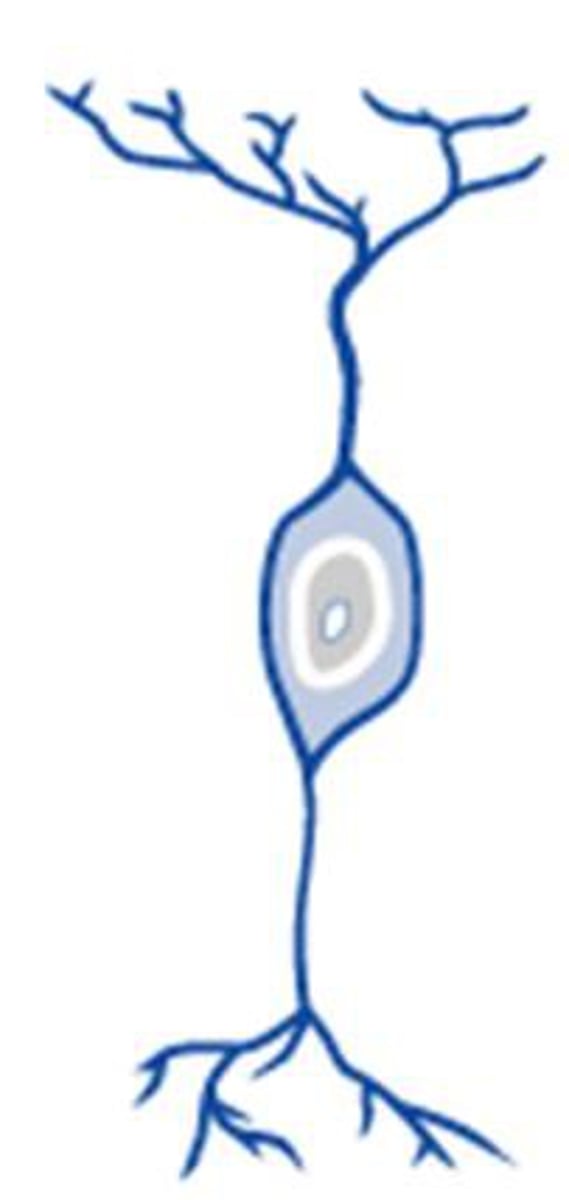
Bipolar Neurons
Have 2 processes, 1 axon, 1 dendrite. These are rare, found in the retina and olfactory mucosa.
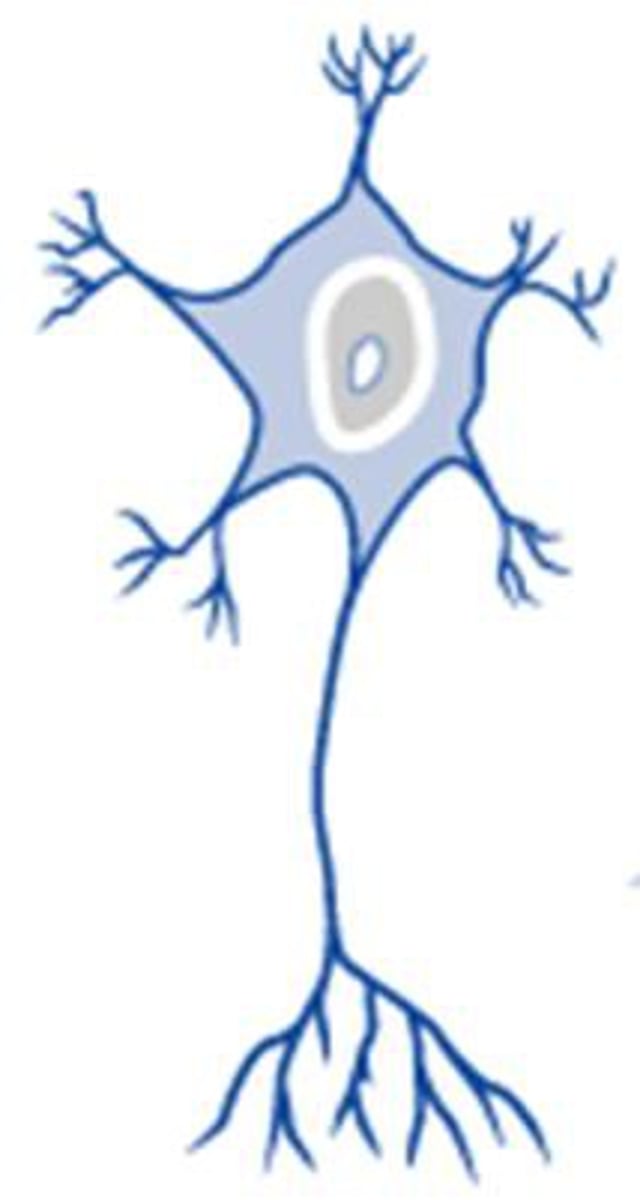
Multipolar Neurons
Have one axon and two or more dendrites. These are the most common neurons of the CNS and all motor neurons that control skeletal muscles are multipolar neurons
Neuroglia
Cells that support the neurons and help communicate with one another.
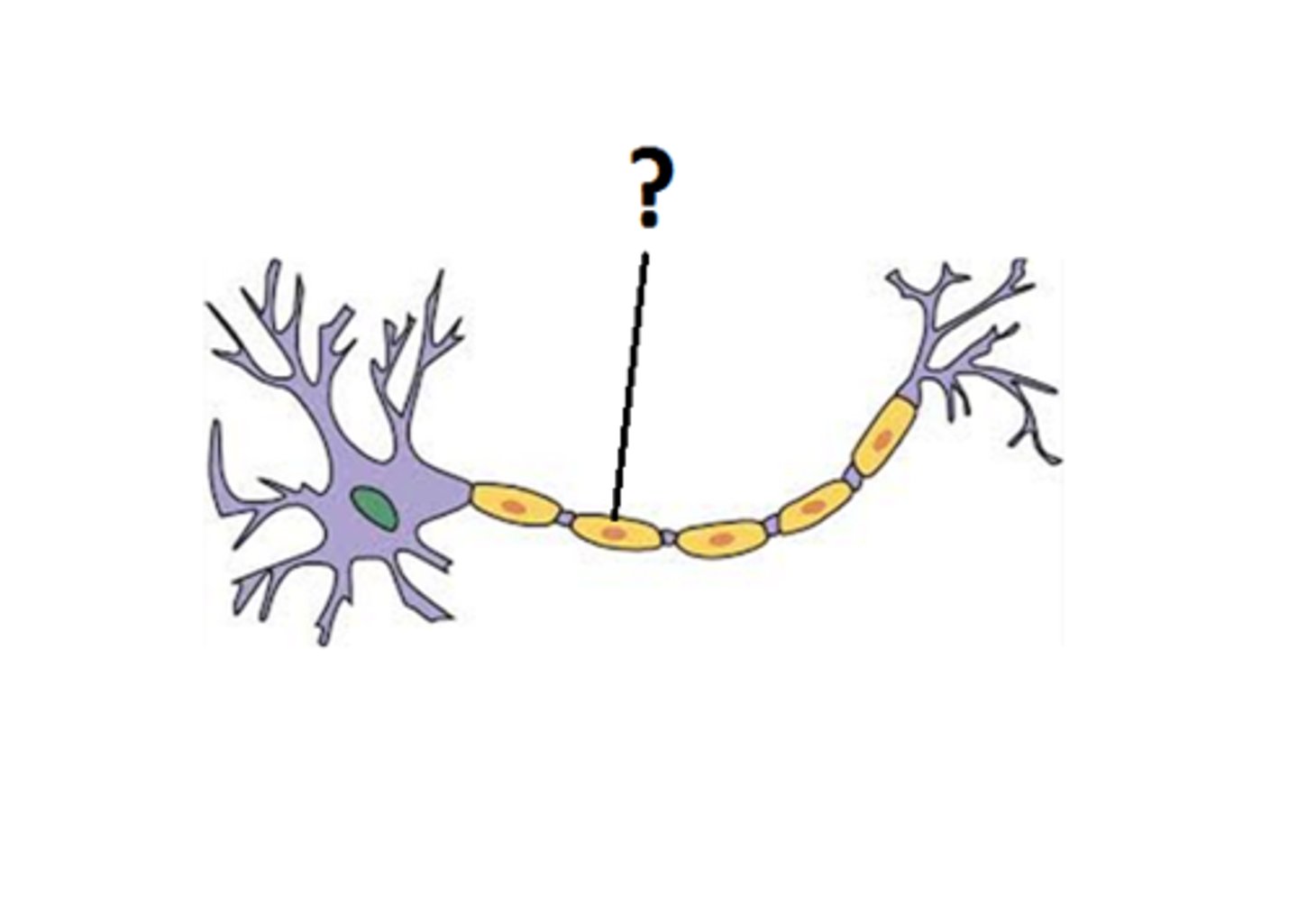
Myelin
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
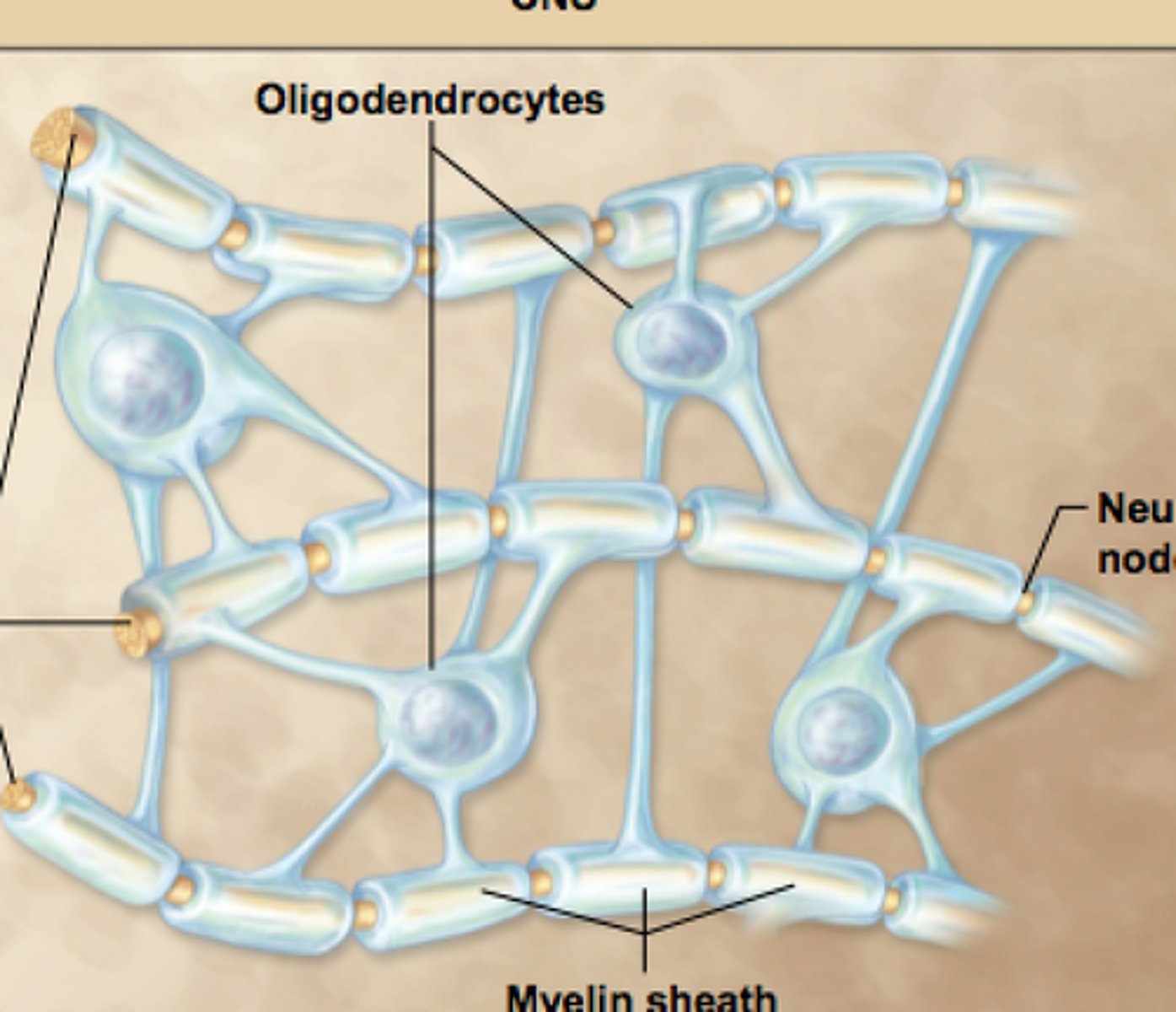
Oligodendrocyte
Glial cells responsible for insulating neurons of the central nervous system.
One oligodendrocyte can insulate many axons.
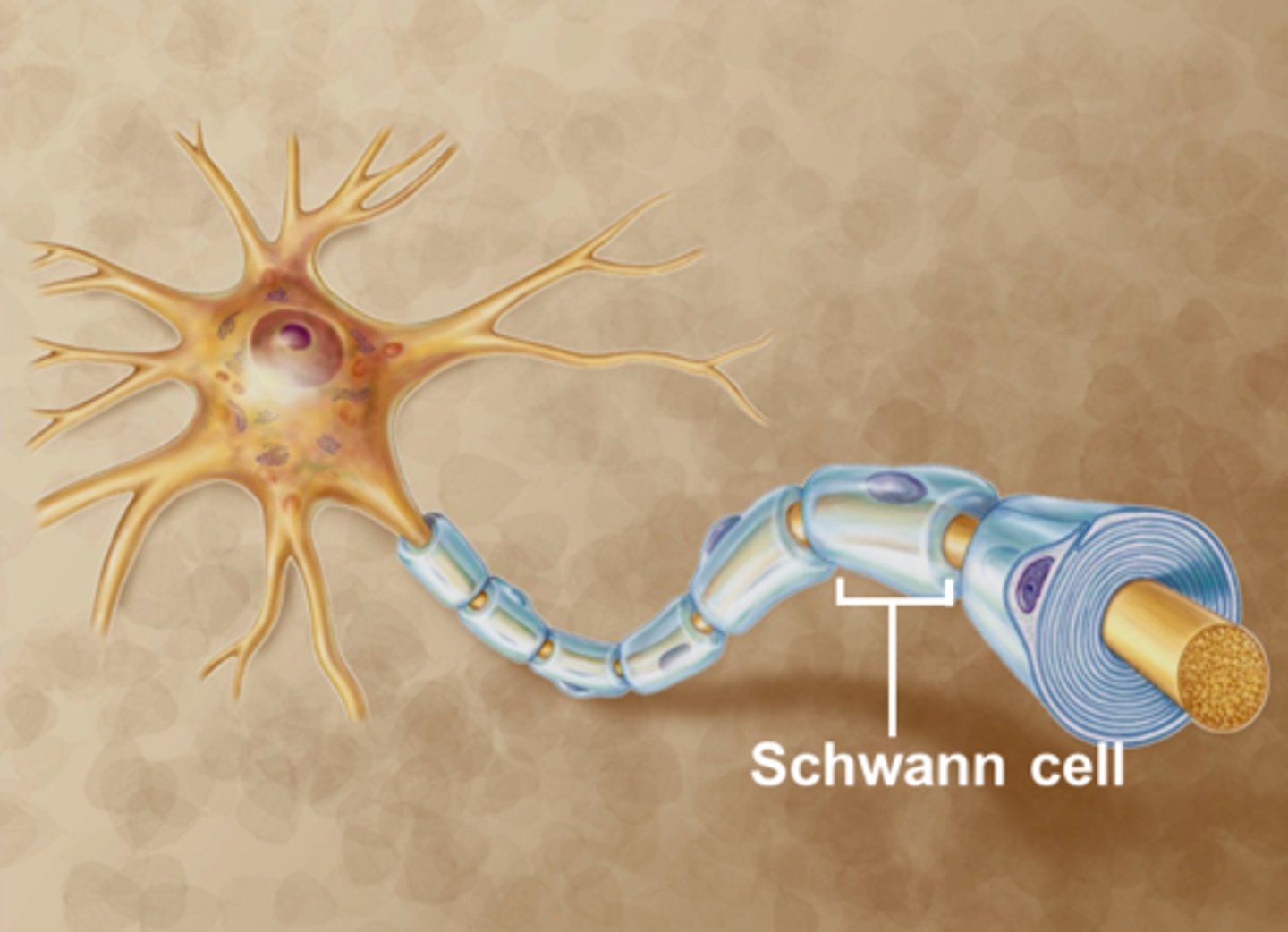
Schwann Cells
Glial cells that are located in the peripheral nervous system and that form the myelin sheath around the axon of a neuron.
One Schwann cell can insulate only a single axon.
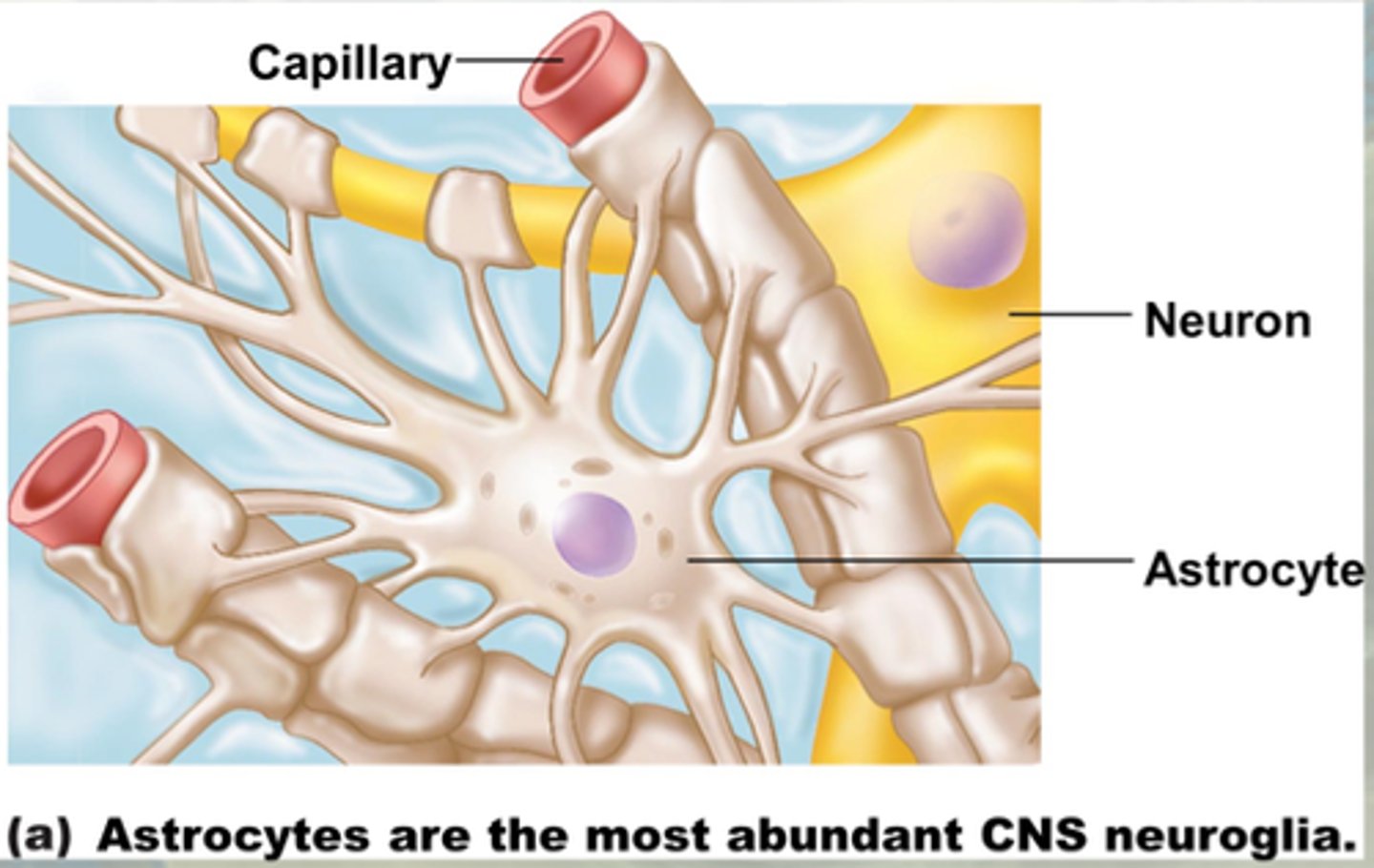
Astrocytes
Glial cells of the CNS responsible for physical support and maintaining blood brain barrier.
Also involved in generating neural connections
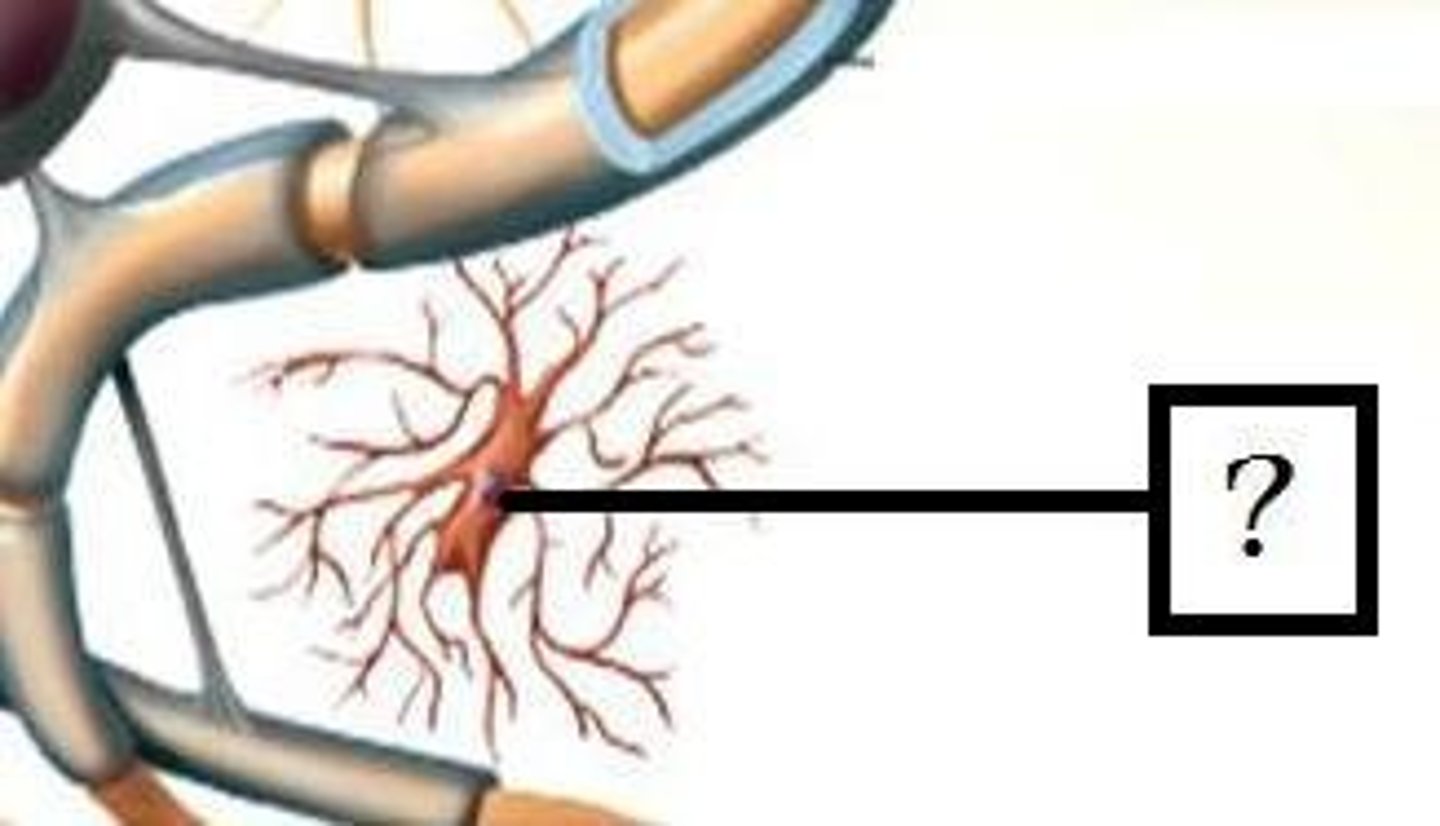
Microglia
Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system
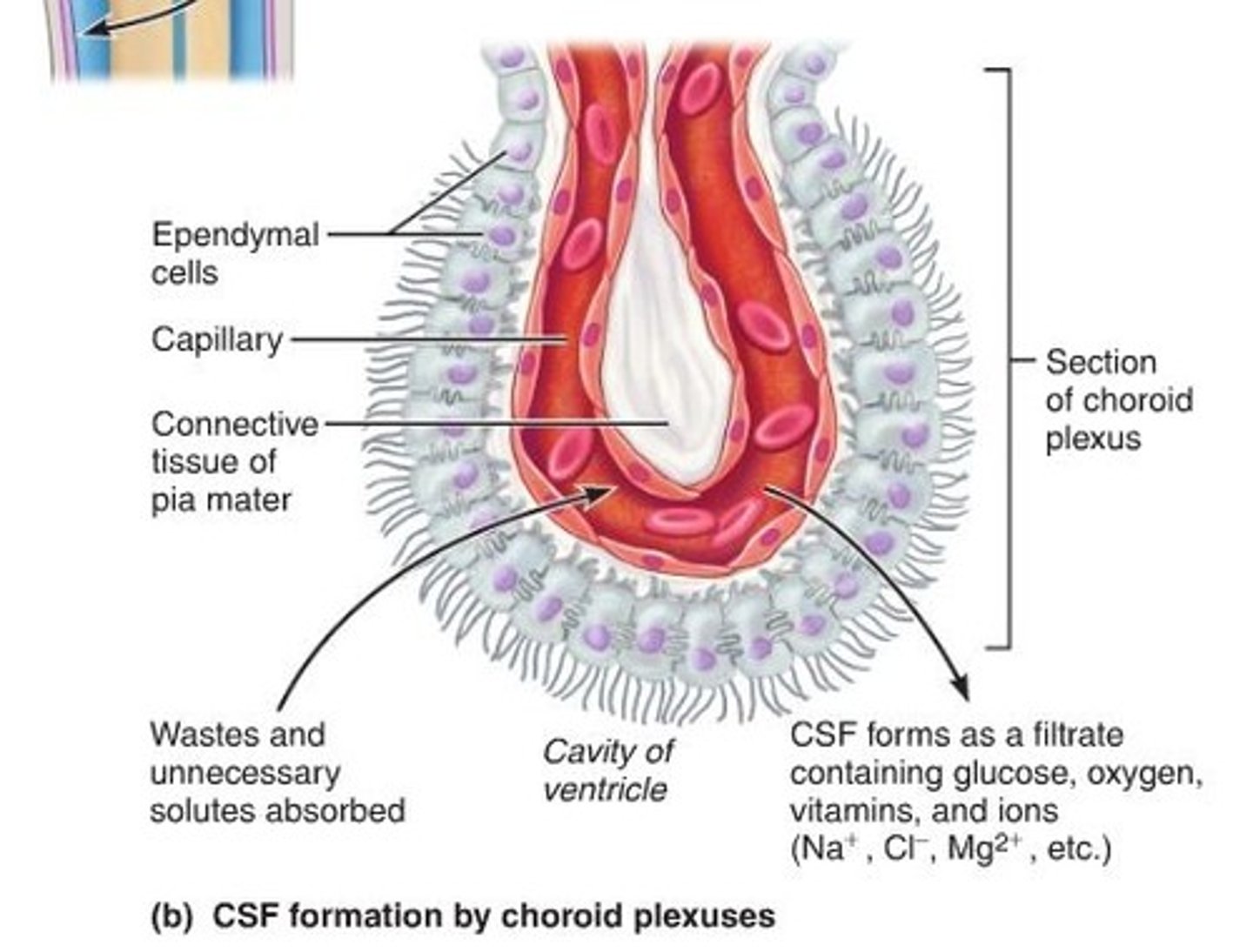
Ependymal cells
Neuroglia in choroid plexuses
Line brain ventricles and spinal cord central canal. Secrete spinal fluid (cilia move it)
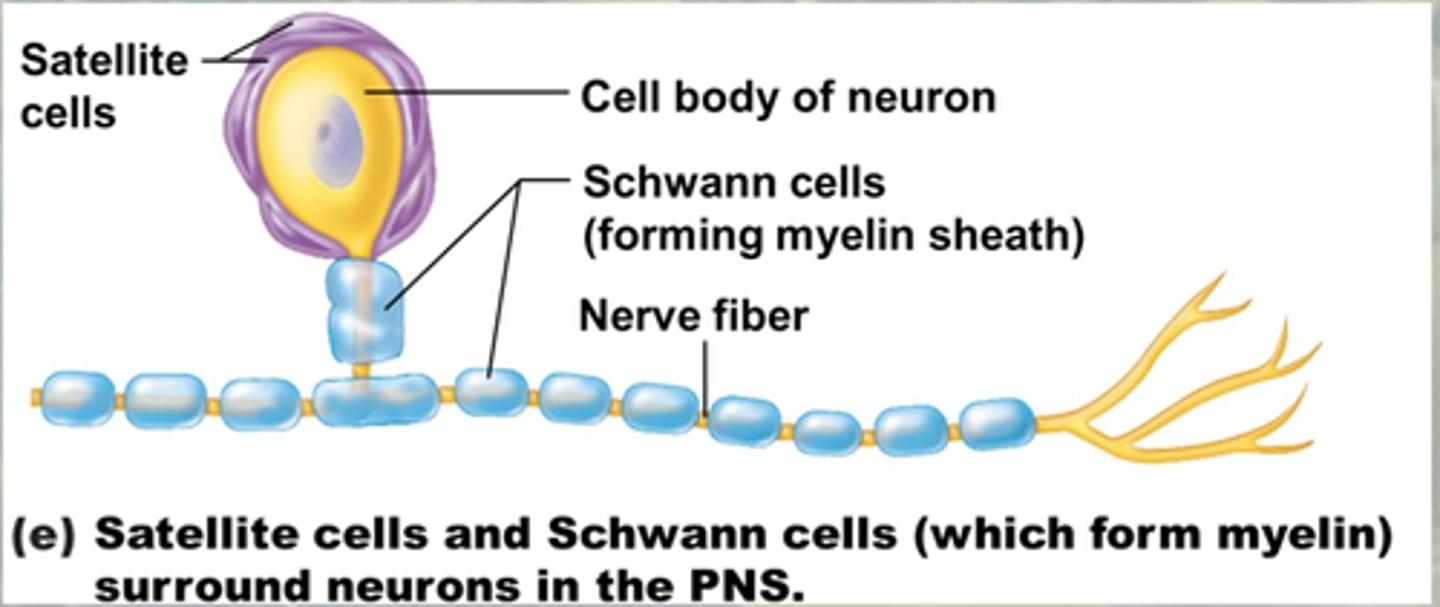
Satellite cells
Glial cells that surround the neurons in ganglia of the PNS
Regulate and exchange fluid between interstitial fluid and neuronal cell bodies.
Nerves
Bundled axons that form neural "cables" connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs.
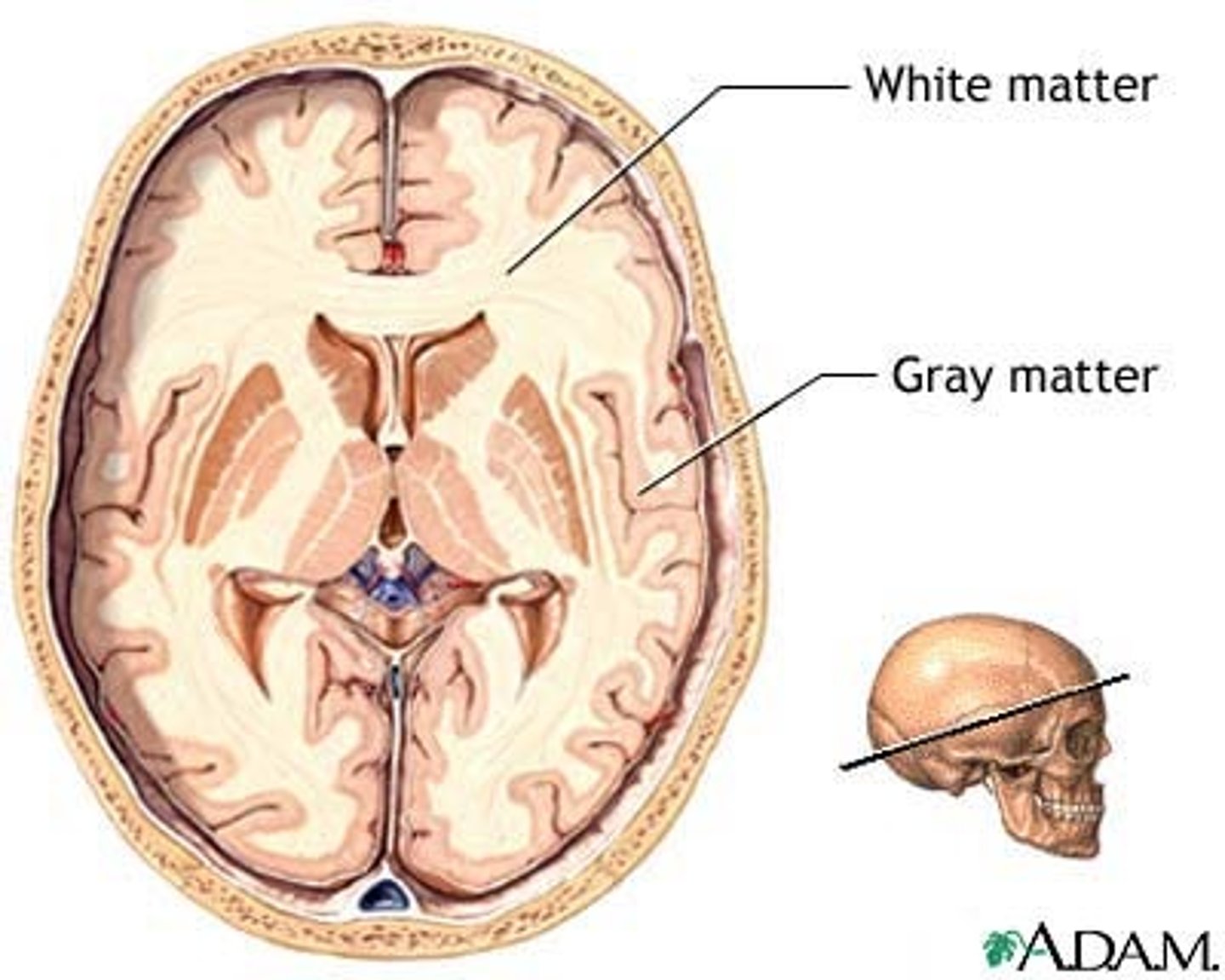
Gray matter
a portion of the CNS consisting of neuronal cell bodies, their dendrites and synaptic connections.
Processing of information
White matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of axons and their myelin sheaths.
Conducting signals.
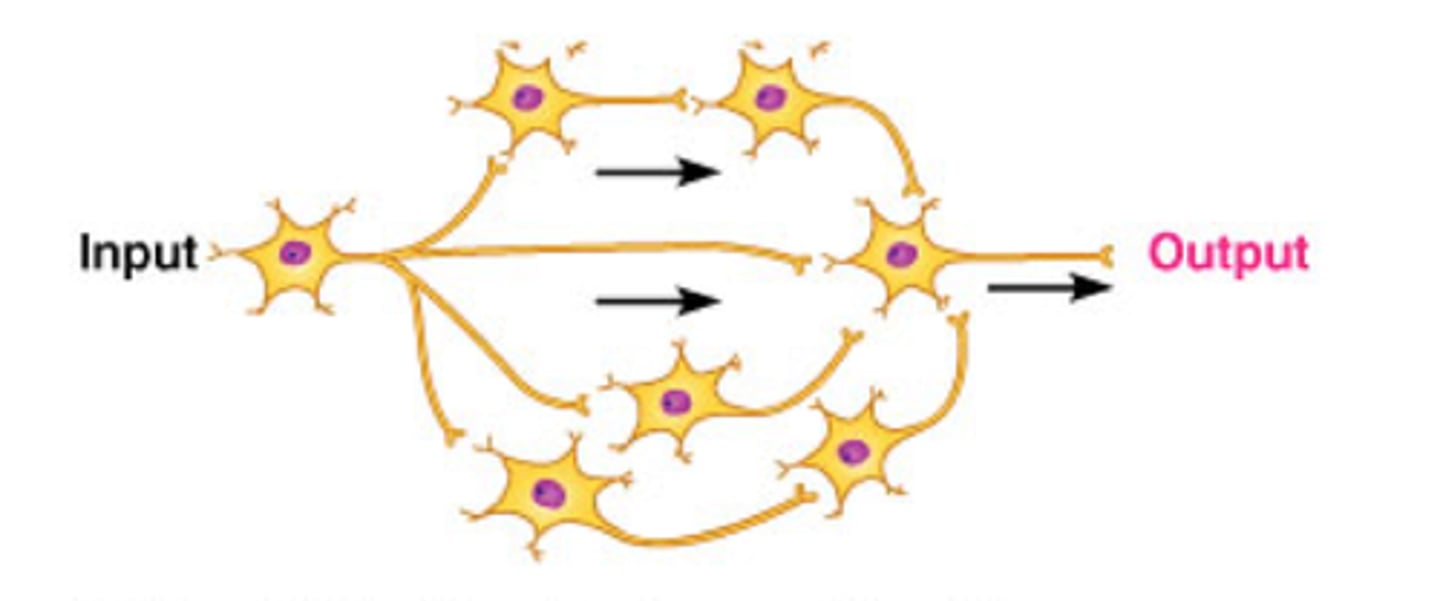
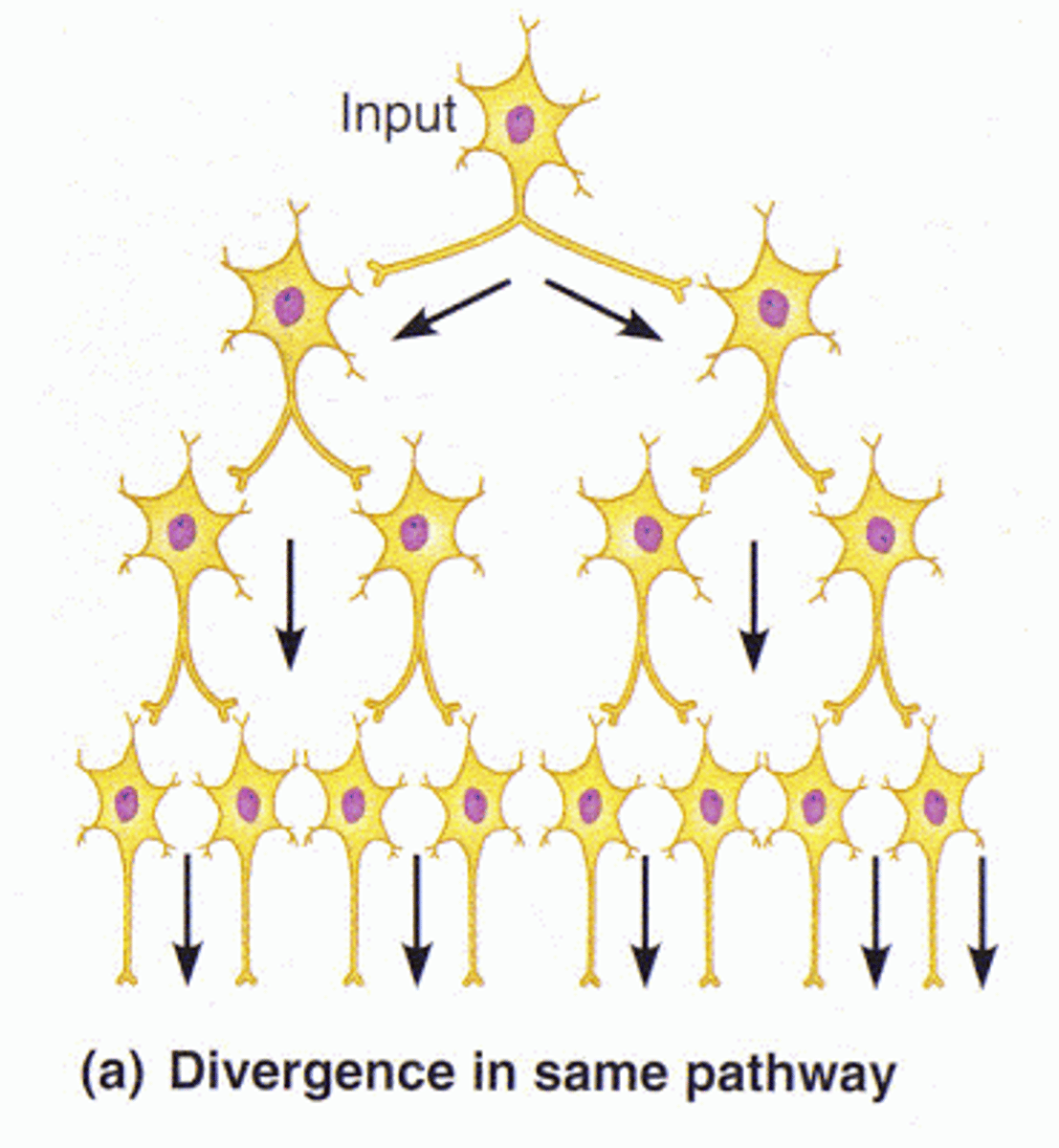
Diverging circuit
one presynaptic neuron producing output in multiple postsynaptic neurons
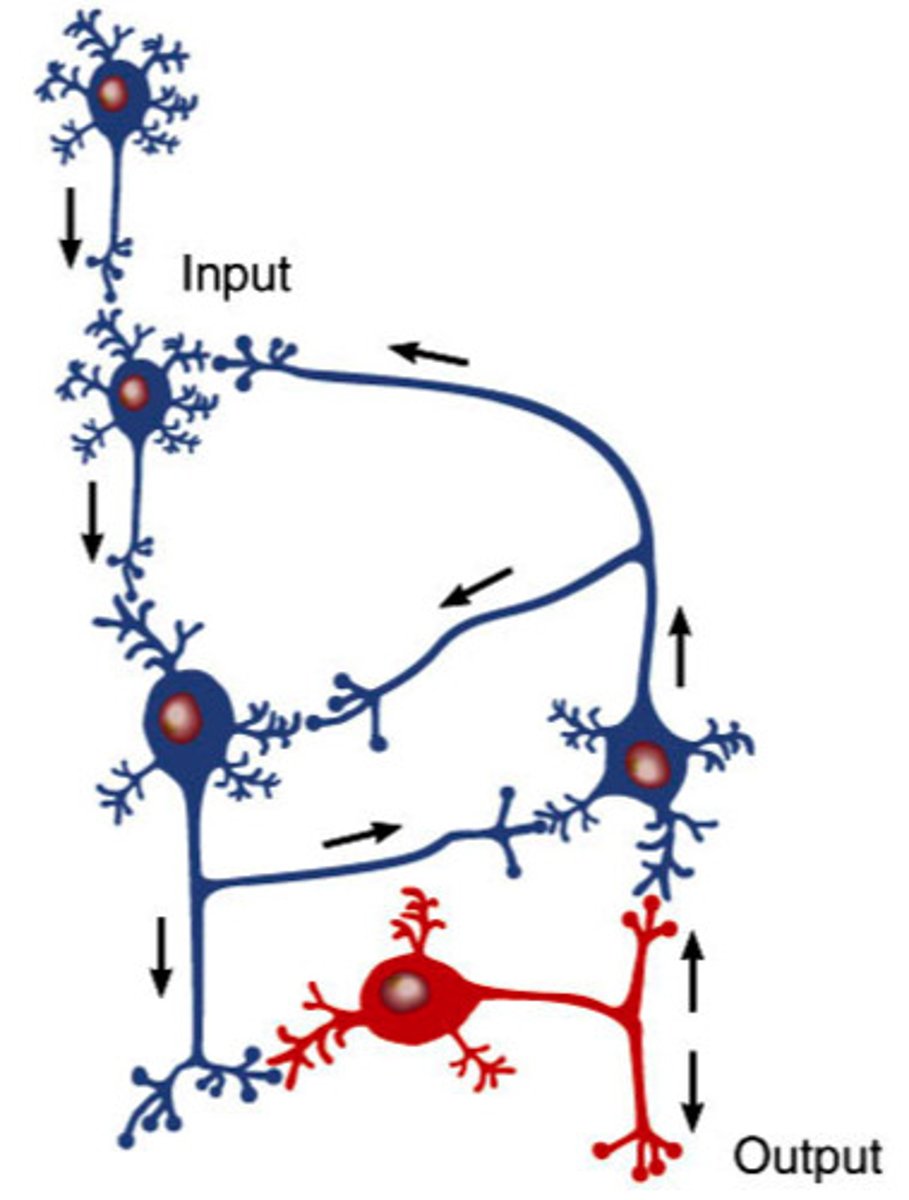
Reverberating circuit
Circuit with feedback loops
Converging circuit
postsynaptic neuron receives nerve impulses from several different sources
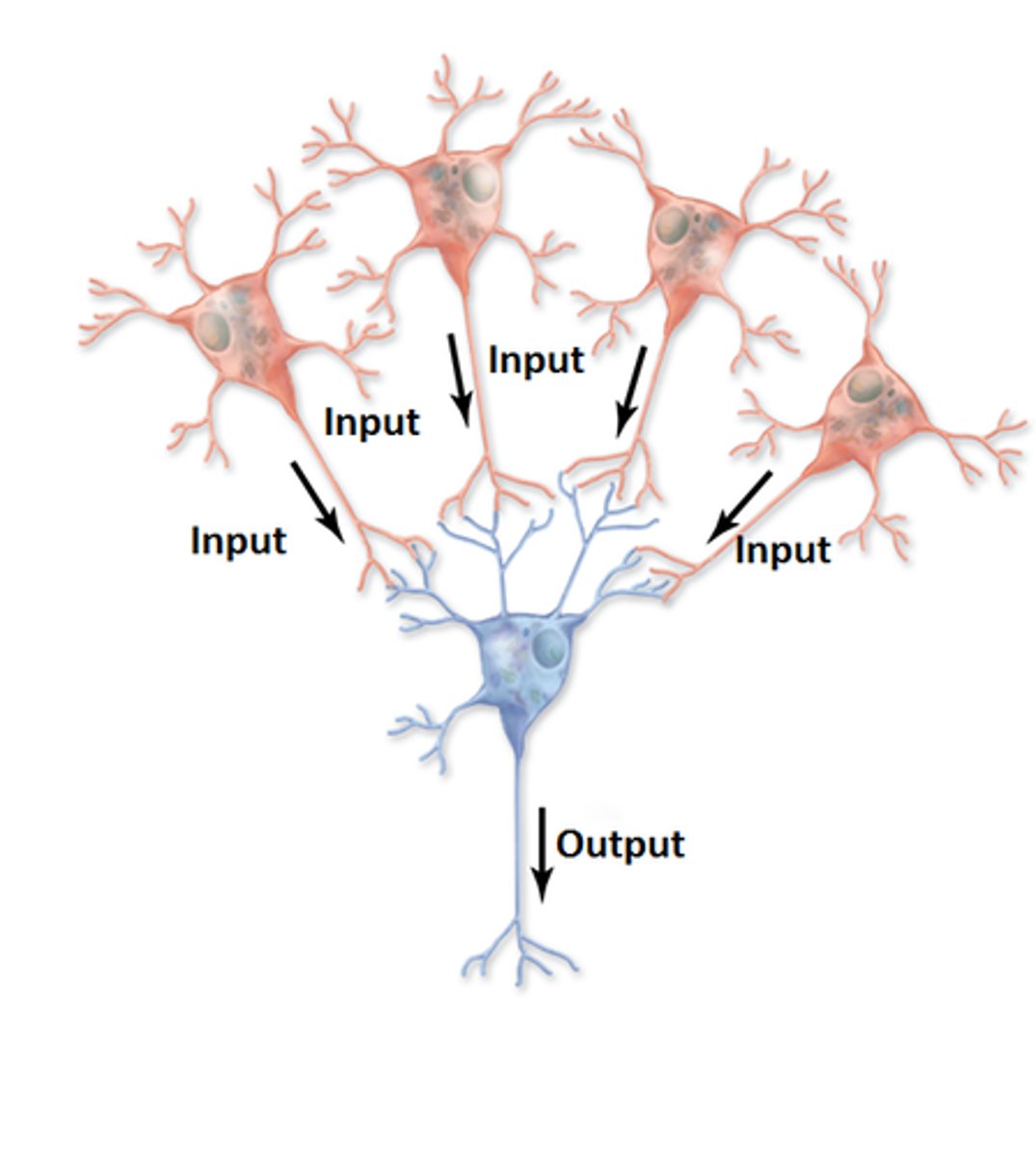
Parallel circuit
Contains two or more branches for current to move through