Biology 1408 Lab Practical 2
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Diffusion
Net passive movement of particles from a region in which they are in higher concentration to regions of lower concentration.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane
Isotonic
The concentrates of the solutes is equal.
Hypertonic
The solution has a higher solution concentration than the other.
Hypotonic
The solution has a lower solute concentration than the other.
Selective Permeability
Some particles, ions, or water can cross the membrane.
Diffusion increases as the temperature increases
What effect does temperature have on the diffusion of molecules?
37 C
Which will migrate faster: molecules at room temperature or 37 C?
Smaller molecules moves faster than larger ones
What effect does molecular size have on the diffusion of molecules?
511 Daltons
Which migrates slower: a molecule that weighs 294 Daltons or a molecule that weighs 511 Daltons?
Smaller Circle
If 2 circles of dye are shown on a plate, which had a higher molecular weight: the bigger circle or the smaller circle?
Refrigerator
If we wanted them to move slower, should I place them in an oven or refrigerator?
higher, lower
______ concentrations of water are associated with ____ concentrations of solutes.
Hypertonic
Out of the bag
out of the bag
When a bag of 10% solute is placed in a beaker of 45% solute, the solution in the beaker was called? Which directions did the water flow? If we then poured a spoonful of salt into the beaker, which direction would the water flow?
Isotonic
In and out at equal rates
out of the bag
When a bag of 30% solute was placed in a beaker of 30% solute, the solution in the beaker was called? Which direction did the water flow? If we then poured a spoonful of salt into the beaker, which direction would the water flow?
Hypotonic
When we weighed one of the bags, we saw that it gained weight after being placed in the beaker. This means that the beaker contained a __ solution.
Size and charge
What quality of the molecules determines if they pass through a semi-permeable membrane?
Sodium Chloride
What is salt called?
Silver Nitrate
Milky white precipitate
clear
Positive
We used ___ ___ to determine if the chloride ions were able to pass through the membrane. A positive result would be? A negative result would be? What was the result?
Barium Chloride
White Precipitate
Clear
Positive
Unable to determine from info
The bag also contained Sodium Sulfate. We sued __ __ to determine if the sulfate ions were able to pass through the membrane. A positive result was? A negative result was? What was the result? Does this mean the Chloride ions were bigger or smaller than sulfate ions?
reducing sugar
Benedict's reagent
Brown
Blue
Positive
The bag also contained glucose. Glucose is a ___ ___ and we can use ____ ____ to determine if the glucose was able to pass through the membrane. A positive result looked? A negative result looked? What was the result?
Larger
Starch and Protein are both formed by the chains of molecules. This means they are ___ than the other molecules tested.
Less
Starch and Protein are both formed by the chains of molecules. This means they are ____ likely to pass out of the bag.
Protein
purple
blue
negative
Biruet reagent was used to determine the presence of what?A positive result looked? A negative result looked? What was result?
Iodine
very dark blue/ black
Orange/ brown
Negative
We tested for the presence of starch using ___. A positive result looked? A negative result looked? What was the result?
Starch, Protein, Glucose, Sulfate ions, Chloride ions
Put these molecules in order from largest to smallest: glucose, sulfate ions, protein, chloride ions, starch
No, too big
Would you expect Sucrose to be able to cross out of the bag? why?
No, each was individual of others
Did having mixture of the molecules have any effect on their ability to diffuse or not diffuse through membrane? why?
Shriveled
hypertonic
When we mixed sheep blood with a solution that was 10% NaCl, the cells ____ because the solution was ____.
remained the same
isotonic
When we mixed sheep blood with a solution that was 0.9% NaCl, the cells ___ because the solution was ___.
Hypotonic
burst
We could not see any cells under the microscope after they were mixed with 0.45% NaCl because the solution was ___ causing the cells to ____
shriveled
Hypertonic solution
pressed against cell walls
Plant cells look ___ in isotonic solution?
Enzyme
protein that acts as a catalyst to lower the activation energy needed for reactions to progress in the cells
substrate
the reactants of the reaction that is/are bound by the enzyme
Activation energy
The min amount of energy needed for a chemical reaction to occur.
active site
a region of the enzyme where binding to substrate occurs.
Protein denaturation
process of forcing a protein to lose its structure and in most cases its functionality
Specificity
The ability of an enzyme to choose exact substrate from a group of similar chemical molecules
Cofactor
non-protein molecules or ions that bind to proteins
Chelate
a chemical compound that binds with metal ions
Lactas
Lactose
Glucose
Galactose
The main enzyme used in lab was ___ which breaks ____ into its products ___ and ____.
pH
temperature
The activity of every enzyme is affected by environmental factors such as ___ and ___.
denatures
What happens to proteins at high temperature?
No, not proteins
If we added a chemical that could break down Carbs would we expect to see a change in enzyme activity?
Enzyme Specificity
When the enzyme breaks down one substrate more than the other.
EDTA
Cofactors
____ was added to remove metal ions that may function as ___ for our enzyme.
decrease
If these metal ions were needed for lactase, we would have seen a ____ in the amount of glucose produced.
Aerobic
Has O2
Anaerobic
Has no O2
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
Qualitative
Measuring the color, appearance of something
Quantitative
Measuring the numerical value
Mitochondria
In eukaryotes, respiration is primarily carried out in a cellular organelle known as ___
decreases
As the size of the animal increases the metabolic rate ___.
mL of O2/ hr/ g
What is the unit used to calculate oxygen consumption?
KOH Pellats
absorb CO2
Quantitative
When measuring the oxygen consumption of the rat on the computer program, what was the white substance on the bottom of the cage? Why was it there? Was the experiment qualitative or quantitative?
CO2
became acidic turned yellow
denature proteins
The gas produced from black eyed peas is ____. When the gas was released through phenol red, what happened? What was purpose of boiling peas?
If peas were boiled
CO2
Qualitative
What was the independent variable in the black eyed pea experiment? Dependent? Qualitative or Quantitative?
Ethanol and CO2
CO2
What are the products of fermentation? Which one did we measure in yeast?
No
No
Solution
CO2
Quantitative
Can yeast breakdown starch directly into glucose? did we see the products produced in the tube with 1% starch? Independent variable? Dependent? Qualitative or Quantitative?
Photosynthesis
process by which plants acquire energy and convert it into chemical energy
Chloroplasts
The entire process of photosynthesis is carried out in the?
Stored glucose from starch
Where do the plant cells get energy at night?
Iodine
no color change due to no starch
amount of light
starch present
Qualitative
What chemical did we use to determine which leaves were covered from light? what happened? independent variable? dependent variable? Qualitative or Quantitative?
Glycogen in liver or fat throughout body
Where do humans store extra additional nutrients and carbs in their bodies?
transmitted
absorbed
The colors perceived are the wavelengths of light ___ by an object instead of ____.
less, longer
Red wavelengths travel with ____ energy, their wavelengths are _____ than purple.
Chromatography
What process did we use in the lab to separate the pigments on spinach?
least
top
higher
slow
(Spinach) The pigments that are ____ soluble move up the paper fastest. The more hydrophobic ones will end up at the ___ of the paper. Hydrophilic molecules have ____ affinity for the paper so their movement is ____.
Carotene
Xanthophyll
Chlorophyl a
Chlorophyl b
Chromotography results pigment colors from top to bottom:
Metaphase plate
mitotic spindles
During metaphase, the chromosomes line up along a region of the cell called the ____ before being pulled apart by ___ during anaphase.
Cytokensis
Special process during Tellophase
clevage furrow
structure during telophase
body, 2, identical, diploid
Mitosis of a (body or gamete), a diploid cell becomes (1, 2, 3, 4) (unique or identical) (haploid or diploid) cells.
gamete, 4, unique, haploid
Meiosis of (body or gamete) cell, a diploid cell becomes (1, 2, 3, 4) (unique or identical) (haploid or diploid) cells.
Interphase
At what part of the cell cycle are we likely to see the first set?
S phase or interphase
When does replication step occur?
Metaphase I
At what stage would the pair on the right split apart?
Metaphase II
At what point would the 2 sides of the X split?
24
48 chromosomes, how many are in gamete cell?
transcription
producing RNA from DNA template?
translation
creating protein from RNA template?
Banana
meat tenderizer
soap solution
Ethanol
For the DNA extraction experiment what were the combined ingredients?
Meat Tenderizer
DNA extraction experiment: A protease that breaks down proteins?
Soap Solution
DNA extraction experiment: The emulsifier that disrupts the lipid membrane
Banana
DNA extraction experiment: cells that provided the DNA
Ethanol
DNA extraction experiment: Gives a way to visualize the DNA
White strands mixed with small bubbles
DNA extraction experiment: what did the DNA look like?
fragments of DNA
What do the bands on the gel represent?
0-
What blood type can be a universal donor?
AB+
What blood type is able to accept transfusion from any blood type?
Binary Fission
A method of asexual reproduction in which a single organism divides into two identical daughter cells.
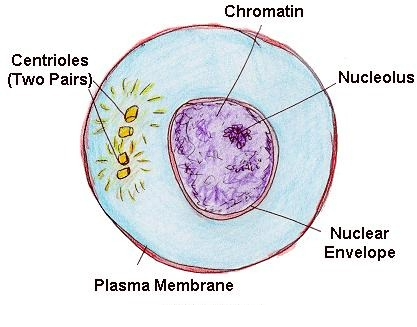
Interphase
What phase of cell division is shown
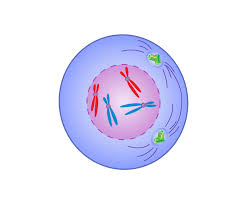
Prophase
What phase of cell division is shown
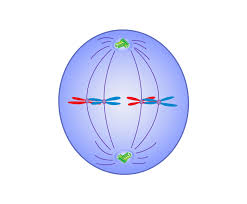
Metaphase
What phase of cell division is shown
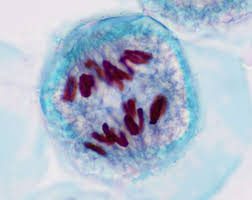
Anaphase
What phase of cell division is shown
Telophase
What phase of cell division is shown
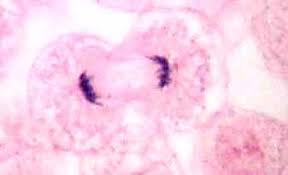
Cytokinesis
What phase of cell division is shown
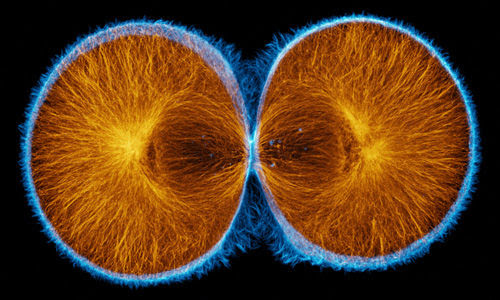
Glucose and oxygen
Products of photosynthesis