Hematology/oncology
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
what increases total number RBC
dehydration
cardiac dx
polycythemia
hemoglobin
Reflects the capacity to carry oxygen
hematocrit
Proportion of RBC volume vs plasm
MCV
mean corpuscular volume → average size of RBC
MCH
mean corpuscular hemoglobin → how much hemoglobin per cell
RDW
red cell distribution width → variance of RBC size
what is included in indices
MCV
MCH
MCH concentration
RDW
reticulocyte count
most predominant WBC
neutrophils → 40-60%
“partner” of neutrophils
monocytes → 2-8%
primary allergic response WBC
eosinophils → 1-4%
WBC in early infection and wound healing
basophils → 2-8%
purpose of peripheral smear and findings
differentiate viral from bacterial,
classify anemia,
malaria (can see parasites inside RBC),
jaundice,
sickle cell disease,
coagulopathies,
malignancies
Assess for nucleated RBCs, platelets, and RBC/WBC morphology

What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
spherocytes - round, small, no nucleus
hereditary spherocytosis
autoimmune hemolytic anemia
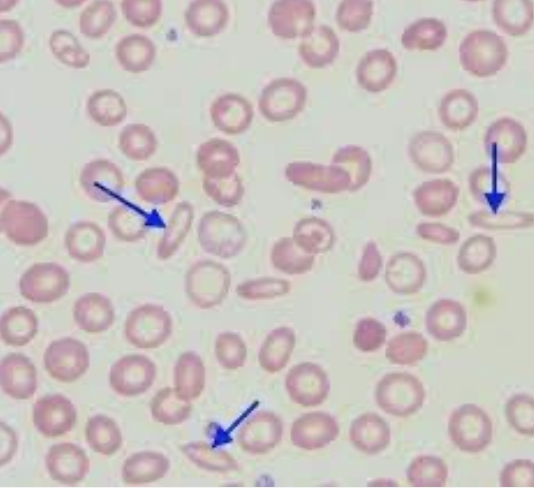
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
ovalocyte
megaloblastic anemias (vit B12 and folate deficiency)
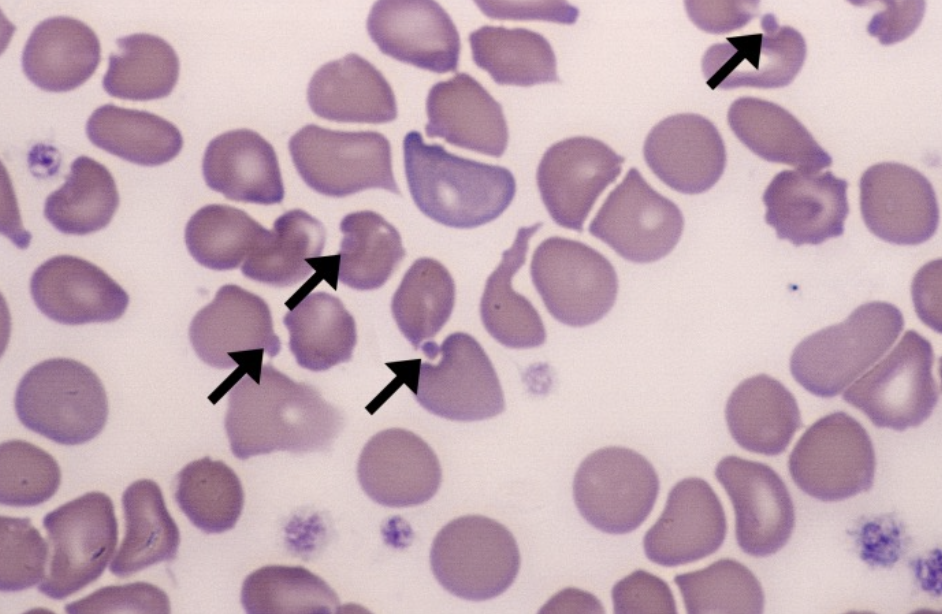
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
heinz bodies “bite cells”
G6PD
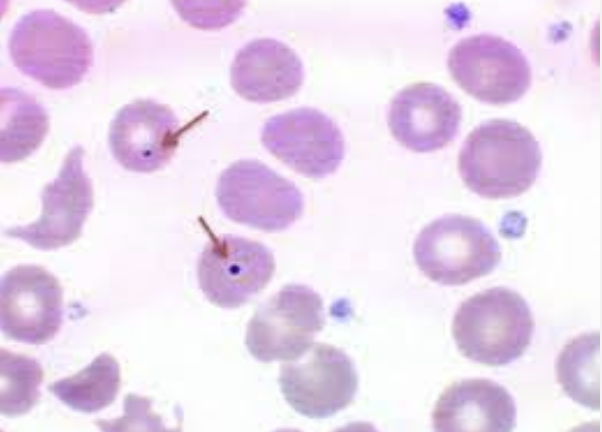
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
howell-jolly bodies - remnant purple DNA
surgical/functionally asplenic persons
autoimmune
ETOH dependency
congenital heart dx.
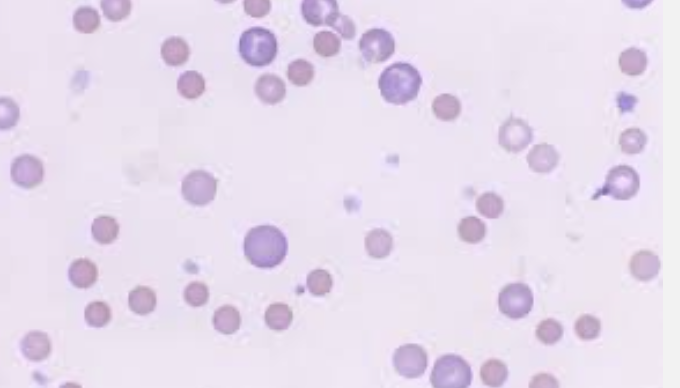
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
anisocytosis - non-uniform cell size
anemia
myelodysplasia
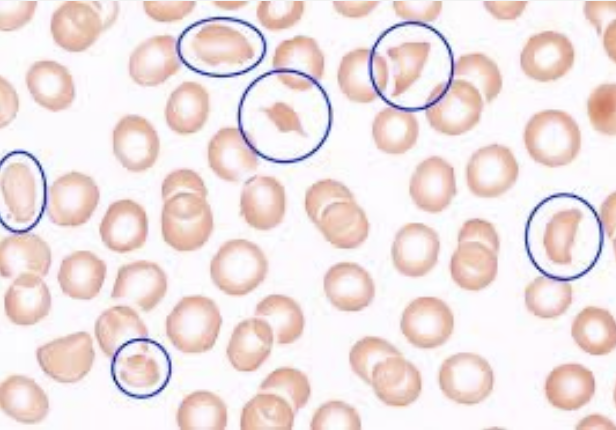
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
schistocyte
hemolytic anemias
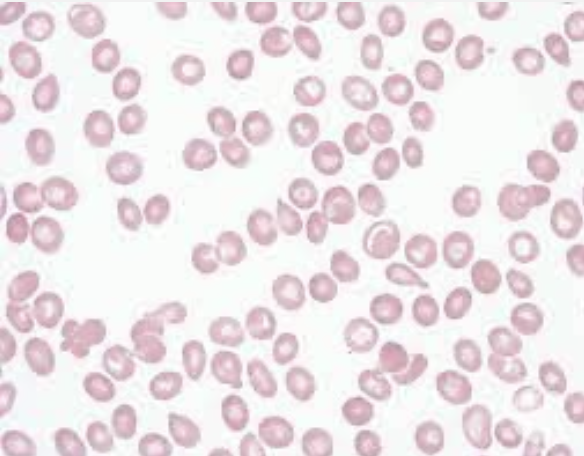
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
teardrop
Splenic disorders,
bone marrow disease,
anemia,
malignancy
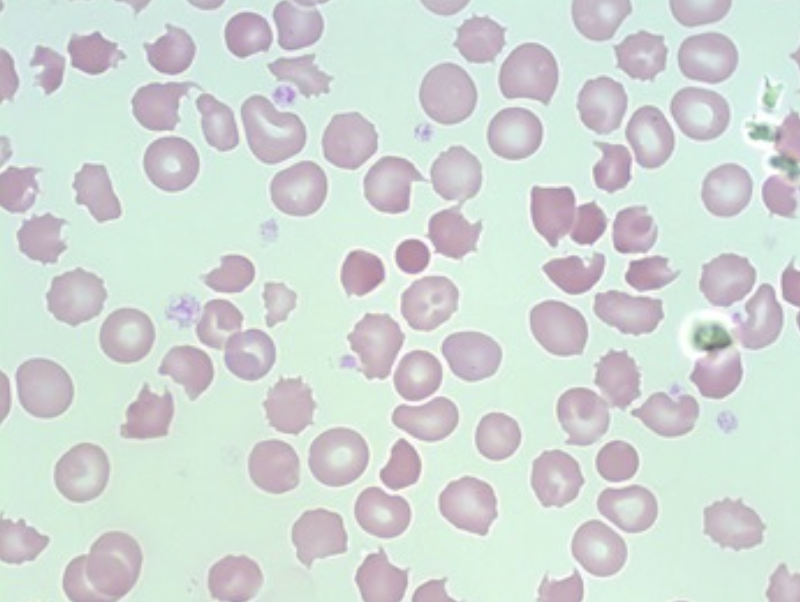
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
poikilocytosis (abnormal shape in >10% cells)
anemia
renal dx
hepatic dx
Cancer
what is required to be seen on peripheral smear in order to call the smear poikilocytosis
abnormal cell shape of >10% of all cells on the smear
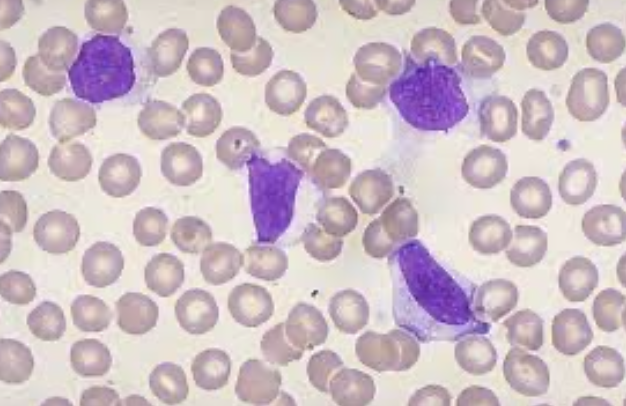
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
atypical lymphs
Immunogenic reactions
Transplant
autoimmune,
EBV and other viruses,
malignancies
drug therapies
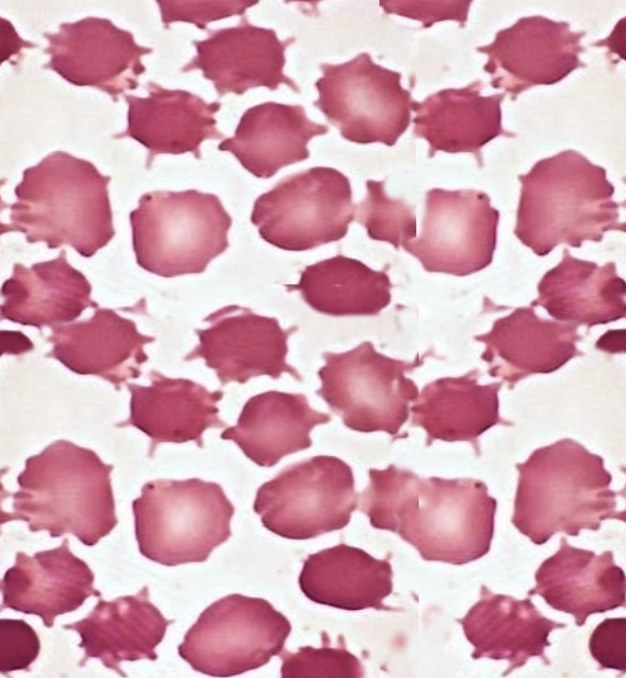

What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
acanthocyte
Hepatic dx,
malnutrition,
hypothyroid,
splenectomy
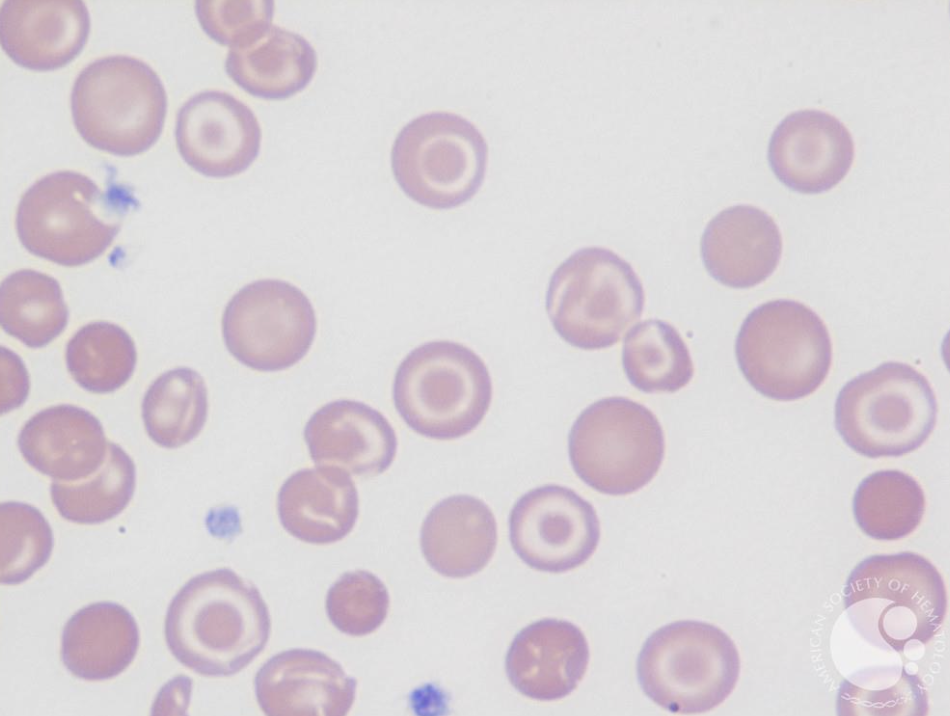
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
target cells
Thalassemias
hemoglobinopathy
asplenia
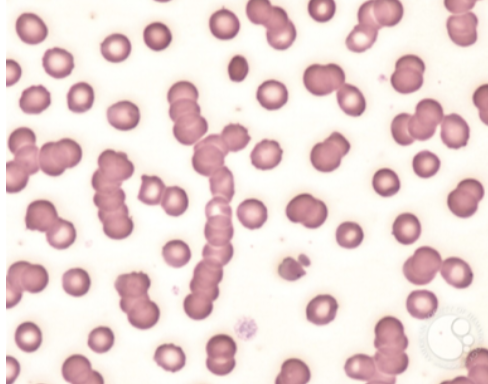
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
rouleaux formation
Infections,
DM,
CA,
Inflammatory disorders
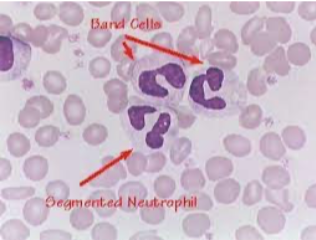
What type of smear cell and what conditions is it seen in
bands
infection
which smear cells associated with infection
atypical lymphs (virus/EBV)
rouleaux formation
bands
which smear cells associated with malignancies
teardrop
poikilocytosis
atypical lymphs
rouleaux formation
which smear cells are associated with autoimmune confitions
howell jolly bodies
atypical lymphs
which smear cells are associated with splenic disorders
howell-jolly bodies
teardrop cell
acanthocyte
target cells
which smear cells are associated with hepatic disease
poikilocytosis
acanthosis
which peripheral smear cell would you see in vitamin B deficiency
ovalocytes
which peripheral smear cell would you see in myelodysplasia
anisocytes
which peripheral smear cell associated with malnutrition and hypothyroidism
acanthocytes
which peripheral smear cell would you see in thalassemia
target cells
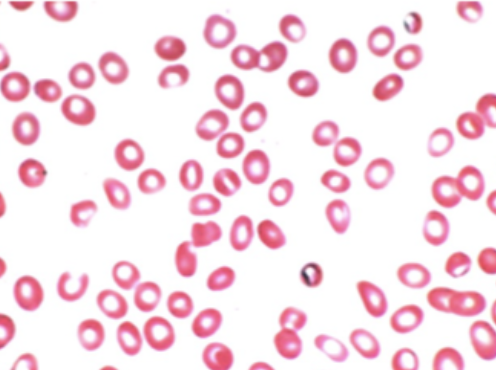
what type of anemia
microcytic → small pale RBC
MCV in order to be considered microcytic anemia
<83
most common cause of microcytic anemia
iron deficiency
MCV in order to be macrocytic anemia
>99
define normocytsic anemia
normal MCV (80-100) but hemoglobin and hematocrit are low (normal size, just less RBC)
what would be seen in peripheral smear of hemolytic anemia
low HgB and HCT
spherocytes
schistocytes
heinz bodies
target cells
(SSHT the cell burst)
G6PD deficiency
deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrigenase makes RBC susceptible to hemolysis after exposure to certain drugs/chemicals, foods, infections, stress
ASA, some NSAIDs
sulfa antibiotics
infection
fava beans
how is G6PD treated
supportive and remove trigger
normal bleeding time
1-8 minutes
at what point does thrombocytopenia require therapy
once platelets are <50,000 (normal is 150,000-324,000)
causes of thrombocytopenia
inadequate production
abnormal destruction
medication
difference between PT and APTT
PT → assess extrinsic pathway; monitor warfarin; normal 11-13 sec
APTT → assess intrinsic pathway; monitor heparin; normal is 30-40 sec
sickle cell anemia aggravated by
temperature
altitude
stress
dehydration
which lab value is important for sickle cell anemia
reticulocyte (expected to be high bc marrow responding)
Direct vs indirect coombs test
direct → autoimmune hemolytic anemia
detects antibodies/complement proteins bound to RBC
indirect → screen pregnant women and prior to blood transfusions
detects free-floating antibodies that COULD bind to RBC
electrophoresis role
identify types of hemoglobins → F,S,C,E
alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
pregnancy → part of triple or quad screen to assess defects
adults → elevated in liver, ovarian, and testicular cancer and hodgkin’s lymphoma
CA 19-9
pancreatic cancer
can also rise in
cirrhosis
cholelithiasis
pancreatitis
CF
CA 15-3 and CA 27-29
diagnose and monitor breast cancer
can also rise in
Hepatitis
cirrhosis
TB
PID
endometriosis
SLE
lactation
CA 125
ovarian cancer
falsely elevated in
IBS
diverticulitis
menses
pregnancy
ovarian cysts
calcitonin
medullary thyroid carcinoma
insuloma
lung cancer
bony metastasis
also elevated in goiter
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
used as screening for prostate cancer
false elevation
BPH
prostatitis
age
ejaculation
bike riding
testosterone therapy.
normal hemoglobin lvl
M: 13.6-16.9
F: 11.9-14.8
normal MCV
80-100
normal platelet
M: 150-320
F: 150-360
normal WBC
3.8-10.4