AP Psychology: Unit 1
1/305
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
306 Terms
Nature
Genetics and biological factors influencing behavior.
Nurture
Environmental influences on learning and behavior.
Language Acquisition
Process of learning language through exposure.
Noam Chomsky's Theory
Genetic predisposition for language learning.
Universal Grammar Theory
Innate ability to understand language structure.
Behavior Conditioning
Behavior shaped by rewards and punishments.
Epigenetics
Environmental impact on gene expression without DNA change.
Mother Rat Studies
Research showing environment affects nurturing behaviors.
Long-Term Potentiation (LTP)
Increase in synaptic efficacy from high-frequency stimulation.
Enriched Environments
Settings that enhance learning and memory in rats.
Identical Twins
Monozygotic twins sharing the same genetic material.
Fraternal Twins
Dizygotic twins from two separate eggs.
Minnesota Twin Study
Research on twins raised apart over 35 years.
Heritability
Genetic contribution to variation in traits.
Highly Heritable Traits
Traits more common in identical twins than fraternal.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord controlling survival functions.
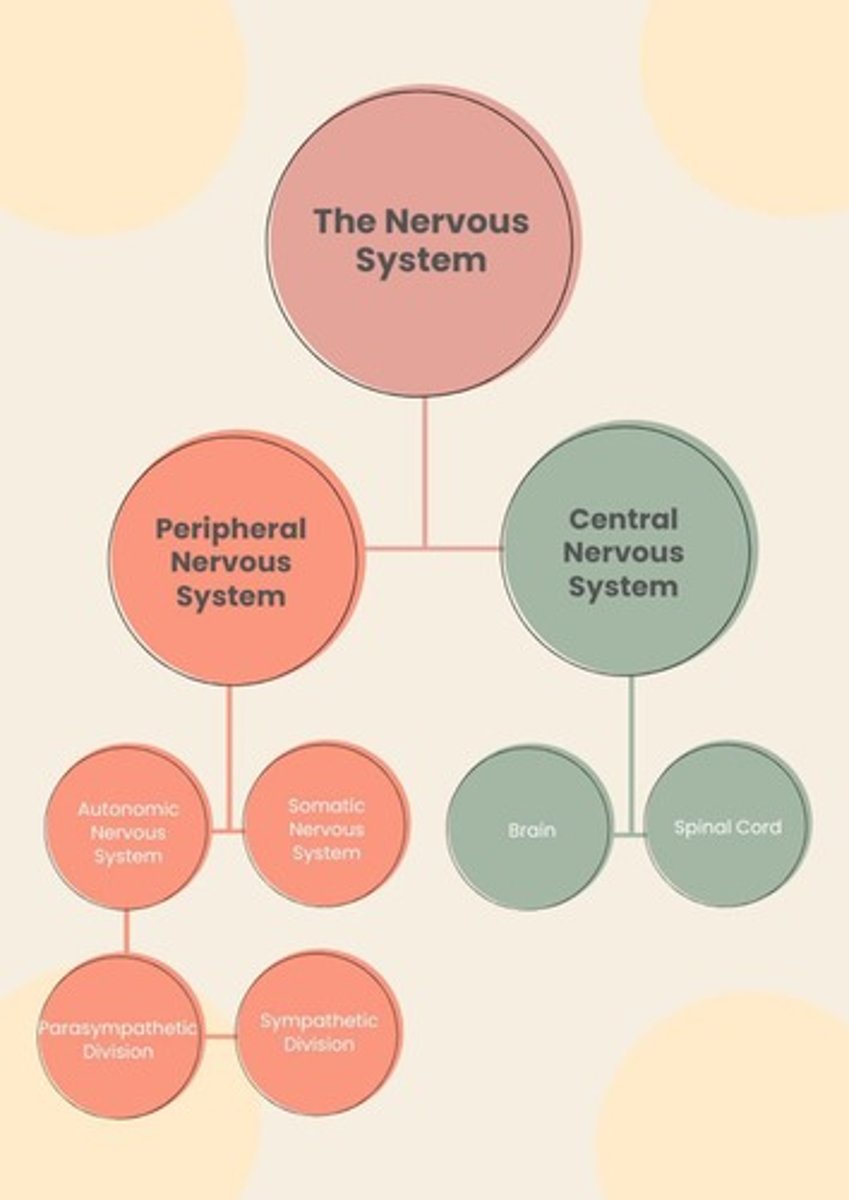
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nervous system excluding brain and spinal cord.
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary muscle movements.
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates involuntary bodily functions.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Activates 'fight or flight' response.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Promotes 'rest and digest' functions.
Behavioral Genetics
Study of genetic and environmental influences on behavior.
Twin Studies Purpose
Assess nature vs. nurture in traits.
Influence of Culture
Culture shapes personality and social behavior.
Environmental Factors
External conditions affecting genetic expression.
Gene-Environment Interaction
How genes and environment influence each other.
Psychological Traits
Characteristics shaped by both genetics and environment.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Prepares body for fight-or-flight response.
Epinephrine
Hormone released during stress; increases heart rate.
Cortisol
Stress hormone that regulates metabolism and immune response.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Calms body after stress, promotes rest and digestion.
Neurogenesis
Process of growing new neurons in the brain.
Sensory Neurons
Detect stimuli; send afferent signals to brain.
Motor Neurons
Control muscle movements; send efferent signals from brain.
Interneurons
Connect sensory and motor neurons; facilitate reflexes.
Reflex Arc
Pathway that bypasses the brain for quick responses.
Neurons
Primary communication cells of the nervous system.
Glial Cells
Support neurons and facilitate chemical signaling.
Neural Impulse Speed
Neural messages travel at 330 mph.
Nature vs. Nurture
Both influence human development and behavior.
Epigenetics
Environmental factors can modify genetic expression.
Twin Studies
Research method to explore genetic vs. environmental influences.
Afferent Signals
Signals that arrive at the brain from sensory neurons.
Efferent Signals
Signals that exit the brain to control body actions.
Pupil Dilation
Sympathetic response that enhances vision.
Digestion Suppression
Sympathetic response that slows down digestive processes.
Mnemonic: S.A.M.E.
Sensory = Afferent, Motor = Efferent.
Neural Communication
Process of transmitting signals between neurons.
Reflex Example
Pulling hand away from a hot surface.
Neural Firing
Rapid transmission of signals in the nervous system.
Final Summary
Nervous system functions are critical for survival.
Soma
Cell body containing nucleus, maintains neuron health.
Dendrites
Branch-like structures receiving messages for soma.
Axon
Tube transmitting electrical impulses from soma.
Myelin Sheath
Fatty layer insulating axons, speeding transmission.
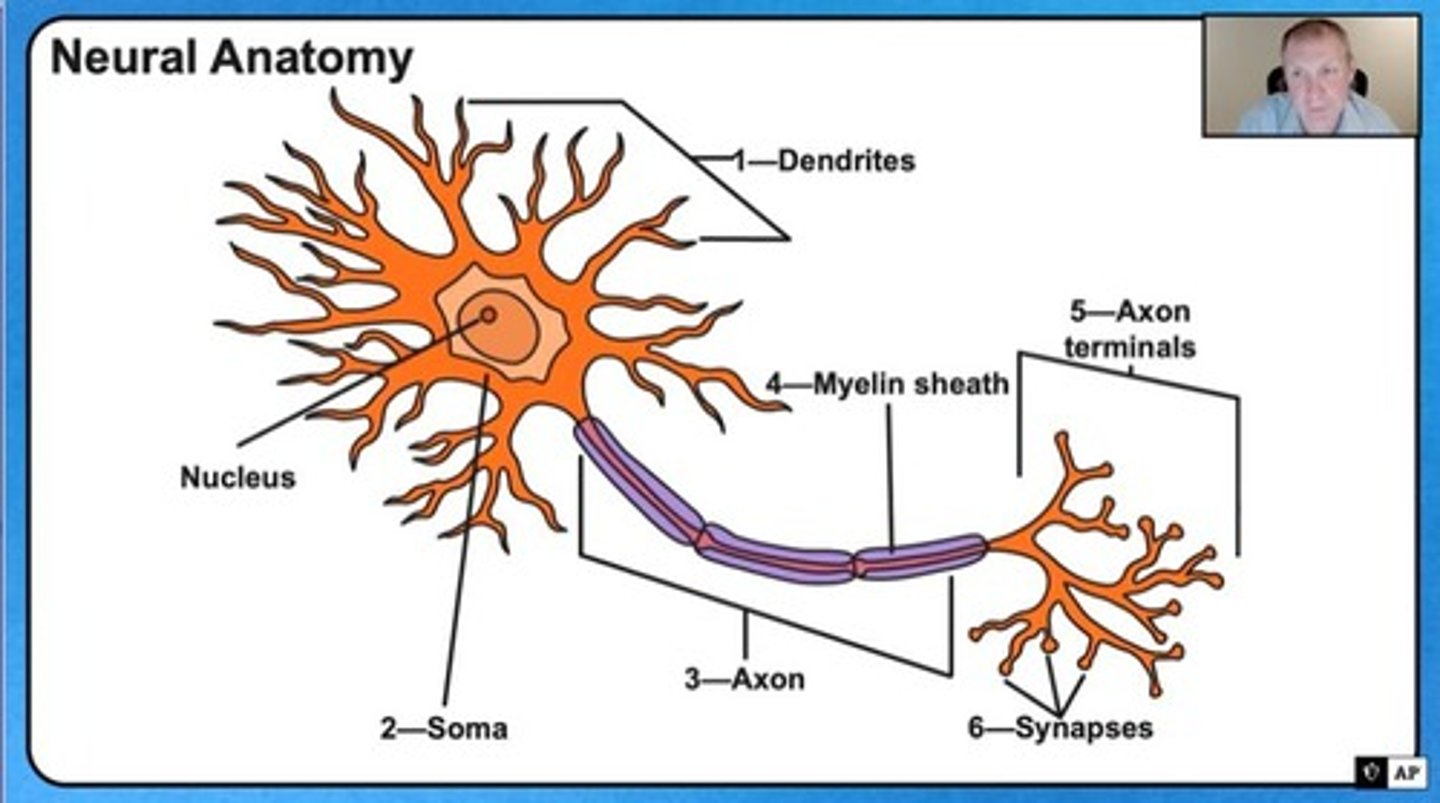
Axon Terminal
End of axon where neurotransmitters are released.
Terminal Buttons
Bubbles at axon terminals connecting to other neurons.
Synapse
Gap between neurons for neurotransmitter transmission.
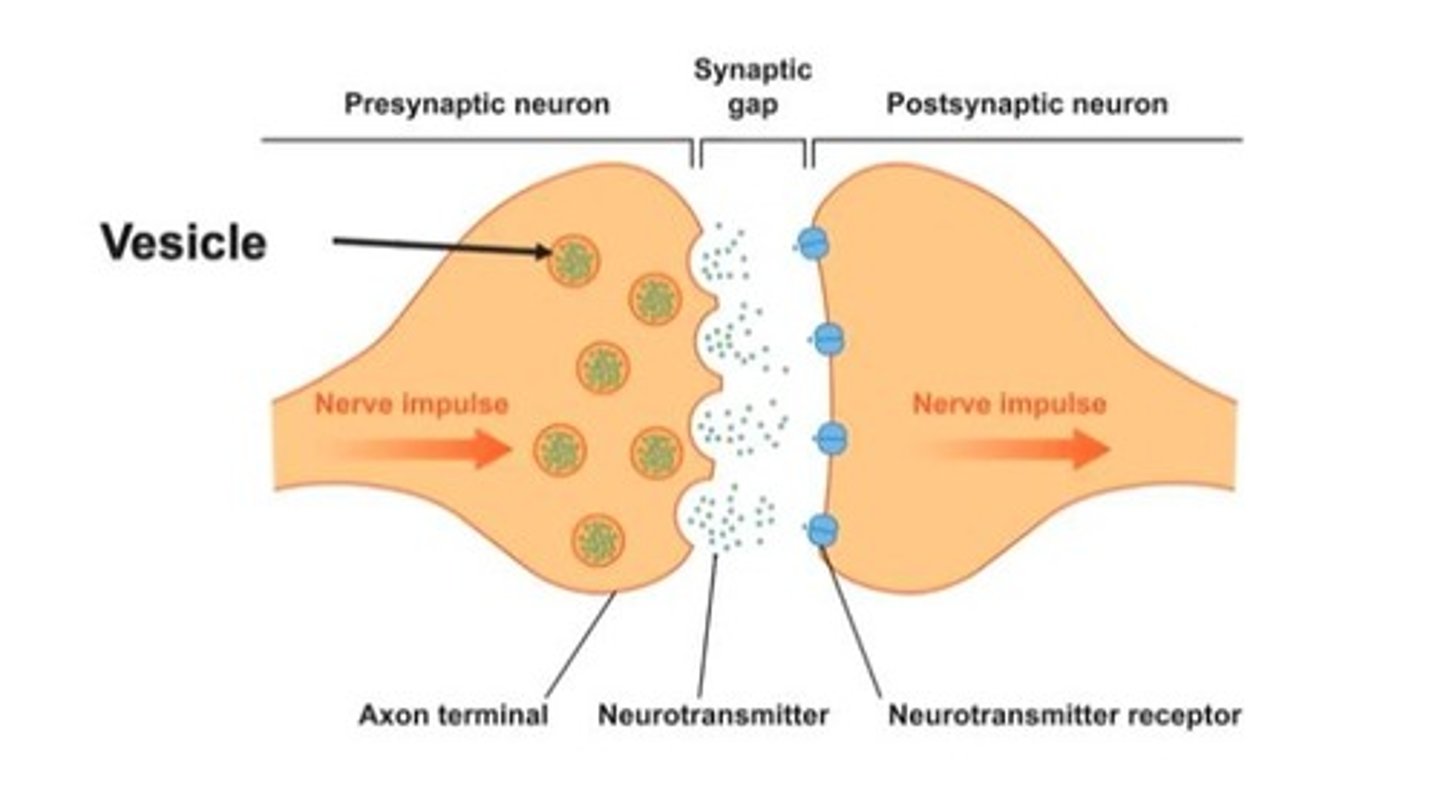
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals transmitting signals across synapses.
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Increase likelihood of next neuron firing.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Decrease likelihood of next neuron firing.
Resting Potential
Inactive state of neuron at -70 millivolts.
Firing Threshold
Minimum stimulation required for neuron to fire.
Action Potential
Electrical impulse traveling down the axon.
Depolarization
Positive charge inside neuron during action potential.
Refractory Period
Brief recovery time after neuron fires.
Reuptake
Process of neurotransmitters being reabsorbed by neurons.
Synaptic Vesicles
Contain neurotransmitters, release them into synapse.
Neural Firing
Shift in electrical energy triggering neuron activation.
Neural Networks
Interconnected neurons communicating efficiently.
DSATS
Acronym for neuron firing sequence: Dendrite, Soma, Axon, Terminal.
Polarization
State of neuron at resting potential.
Neural Messages
Signals transmitted through electrical impulses.
Neural Disorders
Conditions linked to myelin issues, like MS.
Microscopic Axons
Tiny axons requiring microscope for visibility.
Sciatic Nerve
Long axon running from lower back to toes.
All-or-None Law
Neuron fires fully or not at all.
Threshold Reached
Sufficient neurotransmitters trigger neuron firing.
Neural chain
Sequence of events in neuron firing.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers in the nervous system.
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Stimulate neural activity and increase firing.
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
Reduce neural activity and decrease firing.
Glutamate
Abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain.
GABA
Inhibitory neurotransmitter, acts as CNS brakes.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Involved in movement, learning, and memory.
Dopamine
Linked to pleasure, movement, attention, and learning.
Endorphins
Natural painkillers, reduce pain and induce reward.
Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
Boosts energy, involved in fight or flight.
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline)
Enhances arousal, alertness, and vigilance.
Serotonin
Regulates mood, appetite, sleep, and dreams.
Alzheimer's disease
Associated with diminished acetylcholine functioning.
Parkinson's disease
Linked to lack of dopamine in the brain.
Schizophrenia
Excess dopamine thought to contribute to symptoms.
Reuptake process
Reabsorption of neurotransmitters into presynaptic neuron.
Agonists
Mimic neurotransmitters, enhance their effects.
Antagonists
Block neurotransmitter effects at receptor sites.
Direct agonists
Mimic neurotransmitters, bind to receptors.
Indirect agonists
Block reuptake, increasing neurotransmitter availability.
Heroin
Agonist for endorphins, mimics natural painkillers.
Nicotine
Agonist that enhances acetylcholine activity.