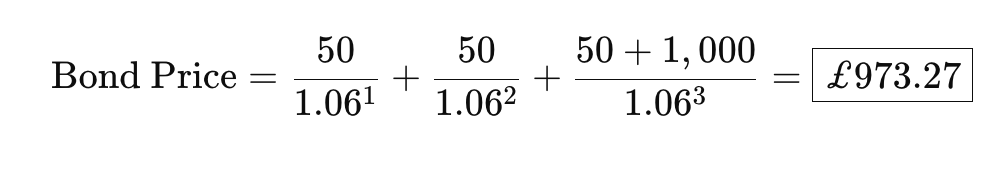1 Money, Banking and Financial Markets
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Money
Any generally accepted means of payment
Medium of exchange
What are the functions of money?
Medium of exchange
Unit of account
Unit in which prices are quoted and accounts kept.
Store of value
Token Money
How cost of making $100, is a lot less than its value
IOU Money “I owe you”
Acknowledgement of debt
What is clearing in the banking system
Process of settling transactions between banks within and between countries.
Liquidity
Cheapness, speed and certainty that assets can be converted to cash.
Bank Reserves
Money that bank has available to meet withdrawals by depositors.
Liabilities of Commercial Banks
Sight Deposits
Money that be drawn right away
Time Deposits
Require notice before withdrawal (So pay higher interest)
Liquidity of Time vs Sight deposits
Sight deposits are more liquid than time deposits.
How do banks make profit
By lending and borrowing
Banks 3 Main Assets in their Portfolio of Investments
Low amount of Reserves
Liquid Assets in case in need of immediate cash
Illiquid Assets that earn higher Interest Rates
What is a Financial intermediary
A bank
It specialises in bringing lenders and borrowers together.
Insurance Companies
Pension Fund
Building Societies
Reserve Ratio
Ratio of banks reserves to deposits
Ratio of 10% means 10:90 reserves to deposits
Money Supply
Currency in circulation outside banking system + deposits of commercial banks.
Types of Financial Assets
contract entitling earning to stream of income for a specific period
Commercial Banks Raise money by selling them
e.g. Bonds, Stocks, Treasury Bills
Treasury Bills vs Corporate Bills
Long-term of short term?
Do they pay direct interest?
Types of Bonds
Treasury: GOV
Corporate: From Companies
Short-term e.g. 1 year
Don’t pay direct interest but with a known date of repurchase by the original original borrower at a known price.
Bonds
Way for borrowers to raise money by promising to repay with interest. Investors buy bonds to earn steady income and get their money back at maturity.
Owners are payed a coupon (Fixed Dividend) each year
When it expires (Reaches Maturity), Gov Repurchases it
Bonds vs Bills Liquidity
Bonds are less liquid than bills due to uncertainty of price it can be sold and cash it will generate.
Money Multiplier and what it measures
The Ratio of Broad Money (Liquid and Near Liquid Assets) to the Monetary Base (Currency in circulation +Bank reserves)
Measures how much money supply can increase for each unit of reserves held by banks
M/MB
Broad Money (M)
All Liquid and Near liquid assets in economy
M = Currency in circulation + deposits + savings accounts
Monetary Base (MB)
All Currency in Circulation + Banks reserves
MB = Currency in Circulation + Reserves
What happens to Money Multiplier (M/MB) if there’s a
Disproportionate increase in M
Disproportionate increase in MB
Disproportionate increase in M increases Multiplier
Happens when Banks lend more aggressively, creating new deposits and increasing supply of Money
Disproportionate increase in MB Decreases Multiplier
Happens when banks hold Excess Reserves, instead of lending, or if people prefer to hold cash instead of deposits
What causes a Disproportionate increase in Broad Money (M)
Happens when Banks lend more aggressively, creating new deposits and increasing supply of Money.
What causes a Disproportionate increase in Monetary Base (MB)
Happens when banks hold Excess Reserves, instead of lending, or if people prefer to hold cash instead of deposits.
Factors that affect the Money Multiplier
Reserve Ratio
If there is a greater share of reserves there will be more MB, decreasing Multiplier
Cash holding
If more cash is hold than depositing there will be higher MB, decreasing multiplier
Confidence in the banking system
Means people will deposit more, increasing M which increases the multiplier
Fractional Reserves Banking
How banks only keep of fraction of total deposits as reserves and loan the rest out.
Formula for Money Multiplier
1/Reserve Ratio
e.g. 1/10% = 10
Narrow vs Broad Money
Narrow only includes most liquid assets
Cash + Demand deposits
Broad Includes Liquid and near liquid assets
Cash + Demand deposits + Savings Accounts
Factors that Make Banks Less willing to lend
Economic Downturns
e.g. 2008 crisis
Low interest
Less profitable
High Interest
Less incentives for borrowing as its expensive, reducing demand
Higher risk tos supply loans
Role of Central Banks
Why are they under public control
Set/mange monetary policy in economy
Act as Lender of Last Resort (LOLR)
Provide emergency liquidity to banks during short-term crises.
Because politicians would use them for short-term gains in their best interest
What is monetary policy
Monetary policy is the process by which a central bank manages the money supply and interest rates to achieve specific economic objectives such as controlling inflation and stabilizing currency.
Traditional Means of Monetary Control
Central Banks
Open Market Operations (OMO)
Buying and selling government bonds in the open market
Buying—> Increases Money Supply
Selling—> Decreases Money Supply
Sets Reserve Requirements
High Reserve Ratio —> Less lending and money creation
Low Reserve Ratio —> More lending and money creation
Discount Rate / Bank Rate
Charges Commercial Banks higher or lower rates for borrowing
Higher —> discourages borrowing, tightening money supply
Lower —> encourages borrowing, expanding money supply
Why are Bond Prices and Interest Rates Inversely Related
Bonds pay a fixed coupon (interest), so if new bonds offer higher rates, old bonds become less attractive unless sold at a lower price.
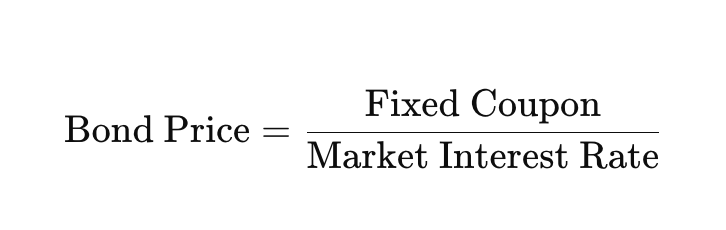
Calculating Bond Price