D3.2 Homeostasis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis is the maintenence of the internal environment — keeping it in a small range of conditions. some examples of this are glucose concentration, blood water levels, and body temperature.
Regulation of blood glucose as an example of the role of hormones in homeostasis
Glucose is needed for respiration for ATP production, however if glucose levels exceeds, cells can be damaged, therefore blood glucose levels must be regulated and in a stable range. However, glucose fluctuates throughout the day— when we eat and when we don’t eat
Hormones regulating blood glucose
Hormones are secreted from 2 types of cells in the pancreas; alpha cells and beta cells in a small part called the islets of langerham which effects the liver.
These hormones are antagonisitc meaning they have the opposite effect to each other.
These hormones are called insulin and glucogen.
role of insulin:
high glucose levels ( for example after a meal), insulin tells adipose tissue to store glucose in the form glycogen
insulin from the beta cells are secreted from the pancreas and stimulate the liver to produce glycogen which means glucose decreases and the rate of glucose breakdown increases (by increaseing cell respiration rates)
role of glucogen
low glucose levels( for example, excercise)
glucogen is released from alpha cells of the pancreas and cause an increase in blood glucose concentration by stimulating glycogen to breakdown to glucose which gets released into the blood stream and increasing hte glucose levels
Glucose vs Glycogen vs Glucagon
glucose is usable energy (ATP)
glcyogen is the stored form of glucose
glucagon is the hormone that increase glucose levels
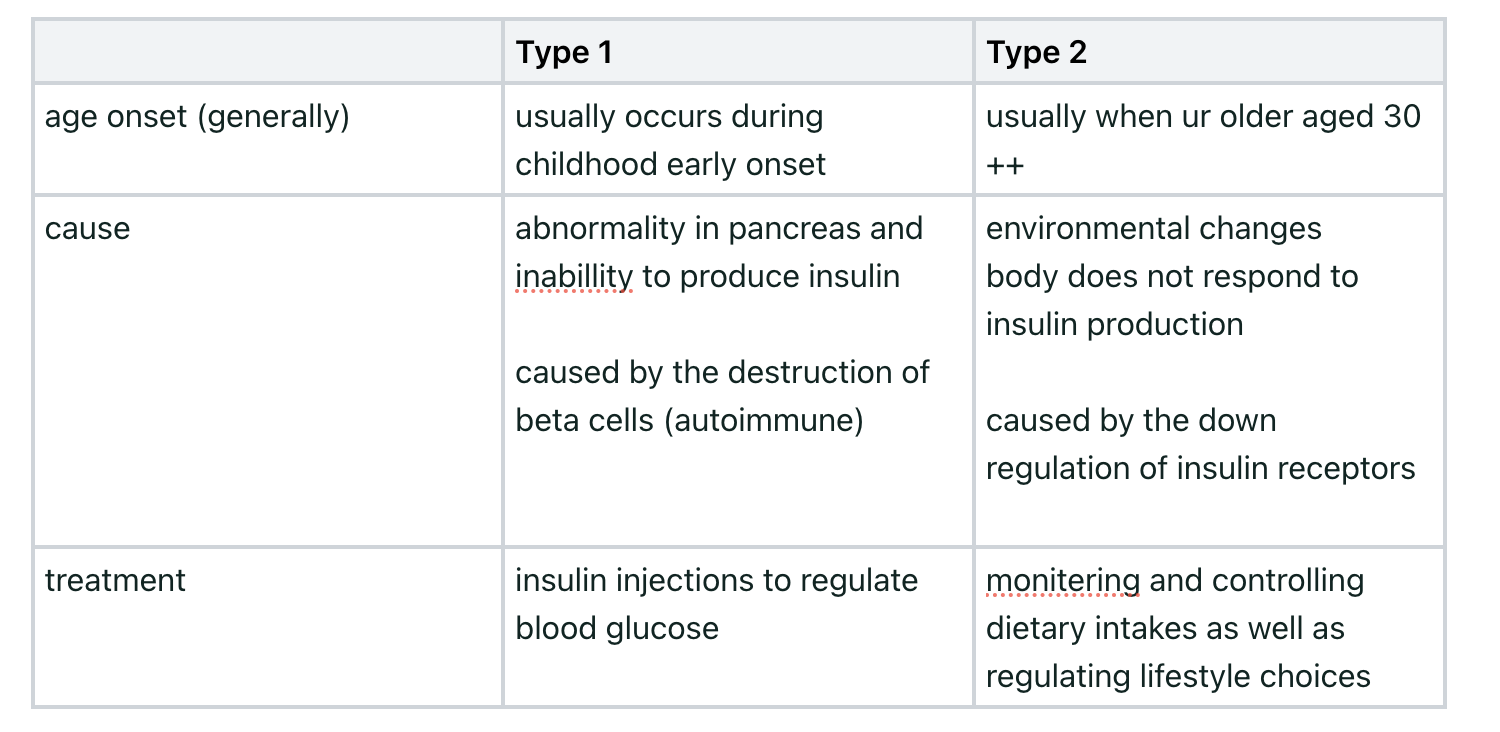
physiological changes that form the basis of type 1 and type 2 diabetes
diabetes is the metabolic disorder that results from a high blood glucose concentration over a prolonged period is diabetes.
here are 2 types
type 1- body cannot produce insluin
type 2- body fails to respond to insulin production (insulin resistance)— environmental changes, non-communicable disease
it is treated with either insulin injections (type 1 only) or by carefully monitoring and controlling dietary intake (type 2)
Type 1 vs Type 2 diabetes (age, cause, treatment)
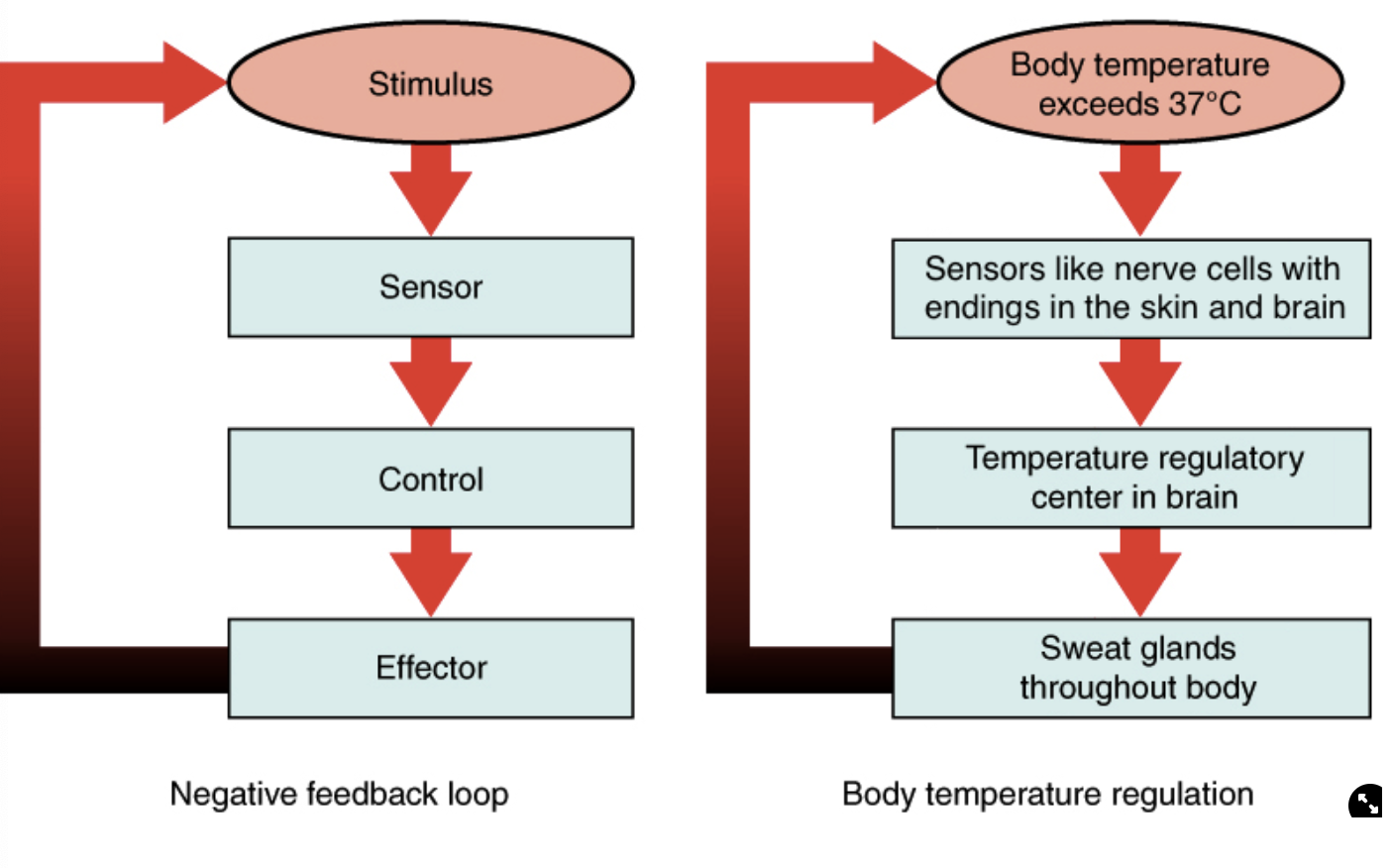
Thermoregulation as an example of a negative feedback loop
negative feedback loop - put into a set level

Diagram of negative feedback loop and body temp reg as an example