IBC Cheat Sheets
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
A. Occupancy Classification
Consult Chapter 3 of the IBC to determine the correct occupancy classification based on the Owner’s program criteria
Dependent on : Program Requirements
B. Sprinkler System
Given the occupancy classification and additional secondary criteria, consult Chapter 9 of the IBC to determine the required sprinkler system
Dependent on : Occupancy Classification, Occupant Load, Floor Area, Floor Height
C. Type of Construction
Consult Chapter 6 of the IBC to determine the construction type based on the fire-resistance ratings of building elements
Fire resistance ratings of : Structural frame, Bearing Walls, Non bearing walls (int. and ext.), Floor construction, Roof construction
D. Allowable Floor Area
Consult Chapter 5 of the IBC to determine the allowable floor area. Refer to Table 506.2
Dependent on : Occupancy Classification, Sprinkler Type, Types of Construction
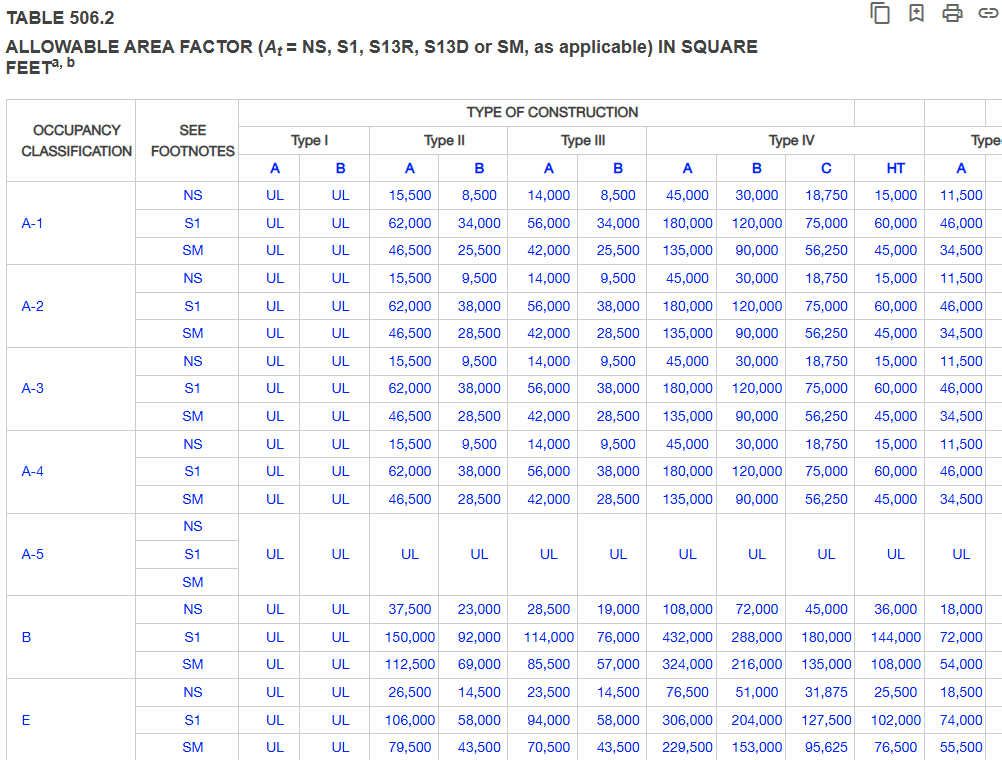
E. Allowable Height and No. of Stories
Consult Chapter 5 of the IBC to determine the allowable floor area. Refer to Table 504.3
Dependent on : Occupancy Classification, Sprinkler Type, Types of Construction
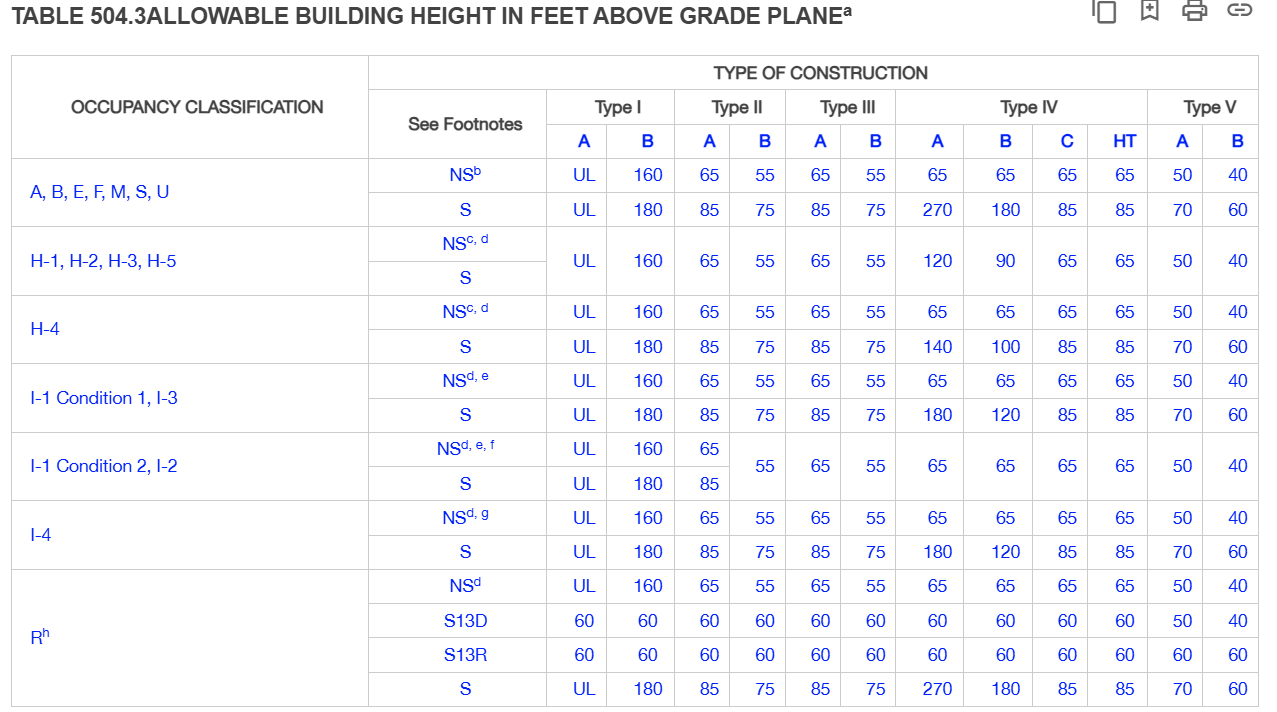
F. Location of Property
Consult Chapter 7 to site the project practically within the lot, taking into account the effect of fire separation distance on allowable openings and projections
Dependent on : Zoning, easements, Program Requirements
F. Means of Egress
Consult Chapter 10 to ensure provided means of egress is suitable for the given space planning, space function, occupant load, and sprinkler system. Table 1004.1.2 is especially useful for determining occupant load given the space function.
Dependent on : Space planning, Function of space, Occupant load, Occupancy classification, Sprinkler system
Chapter 2
Definitions
Chapter 3
Use and Occupancy
Chapter 4
Special Detailed Requirements based on Use and Occupancy (less important)
Chapter 5
Building Heights and Areas
Chapter 6
Types of Construction
Chapter 7
Fire and Smoke Protection Features
Chapter 8
Interior Finishes (less important)
Chapter 9
Fire Protection Sytems
Chapter 10
Means of egress
Chapter 11
Accessibility
Chapter 12-35
Appendix A-M: be generally familiar with their contents, but no need to memorize
Chapter 3: A: Assembly
Civic, social, or religious places of congregation
A.1
Fixed seating: movie theaters, concert halls, theaters
A. 2
Food or Drink consumption: Restaurants, bars, clubs
A. 3
Other: places of worship, community spaces, libraries, art museums, bowling alleys, gyms
A. 4
Indoor Sport: Arenas, stadiums, swimming pools
A. 5
Outdoor Activity: stadiums, amusement partks
Chapter 3: B: Business
Office or professional service (i.e. banks, car washes, labs, post offices, barber shops)
Chapter 3: E: Education
Educational spaces used by 6 or more people for classes up to 12th grade
If within a place of worship and less than 100 people, then considered A.3 occupancy group
Chapter 3: F: Factory
Fabrication, finishing, manufacturing
F. 1
Moderate Hazard
F. 2
Low Hazard : manufacturing materials are noncombustible
Chapter 3: H: High Hazard
High hazard manufacturing and storage
Uses in this category require consultation with building officials early in the design process
Classification H-1 through H-4 varies by type of material and specific risks posed
Chapter 3: I: Institutional
Occupancies where individuals have special restrictions that influence their ability to take care of themselves in an emergency
I - 1
16 + people living under 24 hour custodial care (i.e. assisted living, rehab facilities). Individuals do no require assistance to respond to emergencies
I - 2
5 + people living under 24 hour medical care (i.e. hospitals, nursing homes). Individuals require assistance to respond to emergencies
I - 3
5 + people living under 24 restraint or security (i.e. prisons)
I - 4
5 + people living under less than 24 hour custodial care (i.e. daycare)
Chapter 3: M: Mercantile
Retail spaces for the display and sale of merchandise
Chapter 3: R: Residential
Spaces for sleeping:
R-1: 2+ dwelling units, transient occupants, staying 30 days or less (i.e. hotels, motels)
R-2: 2+ dwelling units, permanent occupants (i.e. apartments, dorms)
R-3: less than 2 dwelling units, permanent occupants (i.e. single family homes, duplexes)
R-4: 5-16 people living under 24 hour custodial care (i.e. assisted living or rehab facilities that are too small to qualify as I - 1)
Chapter 3: S: Storage
Storage spaces that are not classified as hazardous
S - 1 Moderate Hazard
S - 2 Low Hazard: Non-combustible (i.e. enclosed parking)
Accessory storage spaces (less than 100 sq ft) are classified as part of the larger adjacent occupancy
Chapter 3: U: Utility and Miscellaneous
Include building of accessory nature, typically unoccupied and separate
Not to be used as catch-all occupancy, but rather for specific items (i.e. fences and retaining walls)
Special Uses and Occupancies
Includes additional criteria for a variety of specific uses.
A few to be familiar with are covered and open malls (402), High rise building (403) [Considered a high rise if occupied floor is above 75 feet tall, equivalent to the height of a fire ladder; Considered a “super high rise'“ if over 420’ tall], Atriums (404), Underground buildings (405) , Motor vehicle related occupancies (406), Group I-1 hospitals (407), Group I-3 Prisons (408), Childern’s play structures (424)
Building Area
Exclusive of exterior walls, Exclusive of shaft areas and shaft walls, Inclusive of areas under building overhangs
Gross Area
Measured from exterior face of walls
Building Height
Measure to average hight of the highest roof (i.e. mid-slope)
Grade Plane
Reference plane representing average grade level along the exterior edge of the building
Basement
Cannot be greater than 12’ above the grade plane at any point
Mezzanine
Intermediate floor level inserted between larger floor plates.
Open and unobstructed access to floor area below; 42” wall allowable
Limited to 1/3 the are of the larger floor plate area below. Floor area does not contribute to Floor area, Building area, or Number of stories
When a floor contains a mezzanine and an equipment platform, the aggregate area of both raised levels must be less than or equal to 2/3 of the room area
Types of Construction : Type I (A+B)
All noncombustible materials (masonry, concrete, steel)
Passive fire protection of all elements
Type A: 3 hr fire rating for structural system and bearing walls
Type B: 2 hr fire rating for structural system and bearing walls
Types of Construction : Type II (A+B)
All noncombustible materials (masonry, concrete, steel)
Active or Passive fire protection of all elements
Type A: 1 hr fire rating for structural system and bearing walls
Type B: 0 hr fire rating for structural system and bearing walls
Types of Construction : Type III (A+B)
Exterior walls are noncombustible materials, interior materials can be anything code approved
Types of Construction : Type IV (HT)
Exterior wall are noncombustible, structural frame is heavy timber construction, interior building elements are solid or laminated wood
Types of Construction : Type V
Exterior walls, structural frame, and interior materials can be anything code approved
Type A: 1 hr fire rating for structural systems and bearing walls
Type B: 0 hr fire rating for structural systems and bearing walls
Fire Wall
Produces complete fire separation between building and construction types. Required firewall resistance rating vary by occupancy (refer to Table 706.4), but 3 hours is a good rule of thumb
Fire Barrier
A less restrictive fire separation of usually 2 hours. Used in many different instances, including to:
Separate different occupancies
Divide single occupancy into fire areas
Separate interior exit stairs from remainder of egress
Surround shaft enclosures
Fire Partition
The least restrictive type of fire separation, of generally 1 hour. Used primarily to separate dwelling units and corridors
Smoke Barriers
A continuous vertical or horizontal membrane, such as a wall, floor, or ceiling assembly, that is designed to resist the passage of smoke. A 1 hr fire resistance rating is required
Smoke Partition
Similar to a smoke barrier, but no fire resistance rating is required
Interior Finishes
The IBC’s primary concern is with the flame-spread and smoke generation characteristics of materials
Flame Spread Index and Smoke-Developed Index
Used to determine “Class” of material:
Class A : Least combustible
Class B
Class C: Most combustible
Fire Protection Systems
IBC allows for trade-offs between “active” and “passive” fire protection systems. The best designs include both for redundancy
Active Systems
Sprinklers used for fire protection
Passive Systems
Materials with inherent fire protection used
Egress
Continuous and unobstructed path of exit travel from occupied space to public way
Exit Access
Leads from occupied portion of a building to the exit. Can include aisles, passages, corridors, and rooms. The length and geometry of this path is limited by code requirements
Refer to table 1017.2 “exit access travel distance” to determine the maximum travel distance by occupancy type and sprinkler system
Exit
A means of exiting the building that has fire separation from the rest of the building. Can include indoor or outdoor fire stairs, ramps or passageways. This length and geometry of the path taken while in the “exit” is not restricted.
Exit Discharge
Portion of means of egress between termination of Exit and the Public Way. Can include exit courts, yards, stairways, ramps. It is assumed to be open air. The width must be larger than the minimum width of all exits served.
Required Means of Egress
Is dependent on the occupant load of a given space, the travel distance required, and the common path of travel
Occupant Load
Number of people allowed to occupy a spaced according to code.
Maximum Floor Area Allowance Per Occupant
Refer to Table 1004.1.2
To determine the Occupant Load by dividing the sqft of a space by the area required per occupancy for a given use. Occupants from an accessory area who pass through primary area are to be added to the occupant load
Spaces with One Exit or Exit Access Doorway
Refer to Table 1006.2.1
To determine if a single means of egress is acceptable from a space with a given occupancy and occupancy load. Maximum path of egress travel to qualify for a single means of egress is also given
Minimum Number of Exits or Access to Exits per story
Refer 1006.3.1
To determine the number of exits required per story based on occupant load
Travel Distance
Distance from the most remote point on a story along the unobstructed path of egress to the exit
Common Path of Egress
The portion of the exit access which occupants must travel before two separate and distinct path of egress are available. So, the common Path of Egress may be equal to the Travel Distance, but it will never exceed the Travel Distance
The egress path may NOT go through…
a kitchen, storeroom, closet, sleeping area, or bathroom
Egress Sizing
Width Factors, Stairs
Not Sprinklered : 0.3 X Occupant Load = width required (inches)
Sprinklered : 0.2 X Occupant Load = width required (inches)
Stair Requirements
Width: determined by stair width factor, with minimum widths required. When Occupant Load < 50 people, 36” minimum. When occupant load > 50 People, 44” minimum. If stair is part of an ADA accessible means of egress, 48” minimum.
Clear Height: 6’8” minimum
Risers: minimum 4”, maximum 7” (7-3/4” in R3 or inside an apartment unit)
Treads: minimum 11” (10” in R3 or inside an apartment unit)
Nosings: maximum 1-1/4”
Handrails: 34”-38” above finished floor
Guardrail Requirements
42” minimum above finished floor
Door Requirements
Minimum 32” wide
When the occupant load is over 50 people, exit doors must swing with the direction of egress travel
Panic hardware required in Assembly, Educational, and High Hazard occupancies with an occupant load of over 50 people
Corridor Requirements
20’ maximum length for a dead end corridor in a building that is not sprinklered
50’ maximum length for a dead end corridor in a building a sprinklered building
If a plenum for heating, cooling, and/or ventilation is used, it must be fire rated or the air handler unit must shut down when it detects smoke
Generally, a 1 hr fire rating is required in corridors
Horizontal Exit
An exit in a means of egress system to another area or building on the same floor
2 hour fire separation required (fire wall or fire barrier)
All duct or air transfers must be rated
Fire doors must be self or automated closing
The refuge area that the horizontal exit serves must accommodate its own occupant load and the occupant load from the adjoining space