Let 2. Abstractions
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is programming?
Programming is the process of creating a program.
What do you represent a program?
We represent a program with a language(programming language)
What are high-level languages?
F#, Haskell, Skala
What are low-level languages?
Assembly language
What are the pros and cons of low-level programming languages?
Low-level programming languages provide a way to directly manipulate the computer hardware.
What are the pros and cons of low-level programming languages?
High-level programming languages provide a way to abstract our ideas about computations
Why abstraction matters?
1. Abstraction hides unnecessary details, making things easier to understand.
2. Abstraction allows us to focus on the important parts of a problem.
3. Abstraction allows us to build complex systems by combining simple ideas (because abstracted ideas can be easily combined to form more complex ideas).
What does good programming language do?
A good programming language should help developers abstract things away thereby making the code readable.
What does F# do?
#F is a functional first language.
F# is a multi-paradigm language that prioritizes functional programming.
F# code is concise and easy to read.
F# code is likely to be correct.
F# code requires less maintenance cost.
What is a program?
A program is a series of computations (functions) that eventually result in a value.
What do we use to represent computations?
Functions
What do we build abstractions and manipulate data with?
Functions
What is imperative programming?
Imperative programming is all about firing up commands: “do this, do that, etc.”
What is functional programming?
Functional programming is all about writing down functions denoting values.
What do we call functional programming as?
Value-oriented programming.
What is the basic building block for programs?
Expressions
What is expression?
An expression is abstraction that can be evaluated by the programming language interpreter to produce a value.
What is semantics?
Every expression has its own semantics, which describes what kind of computation the expression represents.
When do we say a program is well-typed?
When all expression in the program satisfy the type constraints.
What does expression have?
Each expression has its own type, which poses constrains on expression.
What does evaluation of an expression fail?
When the type checking fails.
What is a function?
A function is an expression that takes in an expression and returns an expression.
How do you call a function?
Give a name to call it. We say we apply a function f to an argument a, when we call f with a as a parameter
Does function application need parentheses?
Function applications typically do not require parentheses in F#.
What id REPL?
Read-Evaluate-Print Loop.
A REPL for F# is…
fsi (or fsharpi).
Where the result of evaluation is stored after printing it out?
In a special identifier, called “it”.
What do we use to indicate type of expression?
colon ()

How can we write a function that takes in two or more arguments without introducing a new syntax?
Function is an expression.
Therefore, we can return a function from a function.
What is currying?
The technique of translating the evaluation of a function takes multiple arguments into evaluating a sequence of functions, each with a single argument'.

What is function pipelining?
We can apply function in a reverse order by using the infix operator (|>). This operator allows function pipelining, which links a sequence of functions in an intuitive manner.

What is anonymous function?
We call a function without its name as an anonymous function, a.k.a., lambda expression (λ).

How to make function more readable if we take 2 arguments?
A function taking two arguments can often be more readable if we use infix notation.

Nested functions
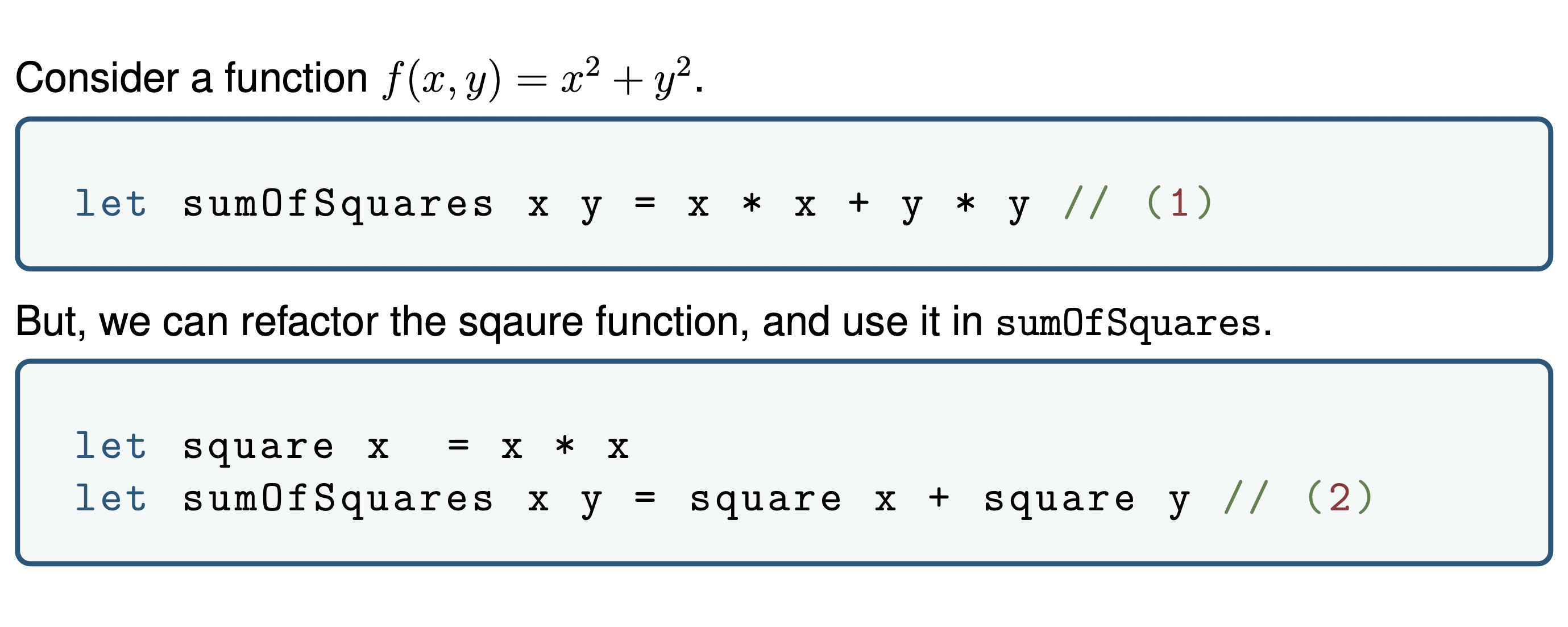
Evaluation rule?

What is evaluation?
Evaluation is a procedure, i.e., a function, that takes in an expression as input, and returns a value as output.
What is nested function?
A nested function is a named function that is defined within another function.
let sumOfSquares x y = x*x + y*y
let square x = x * x
let sumOfSquares x y = square x + square y