DNA Replication and Recombination | Quizlet Import
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
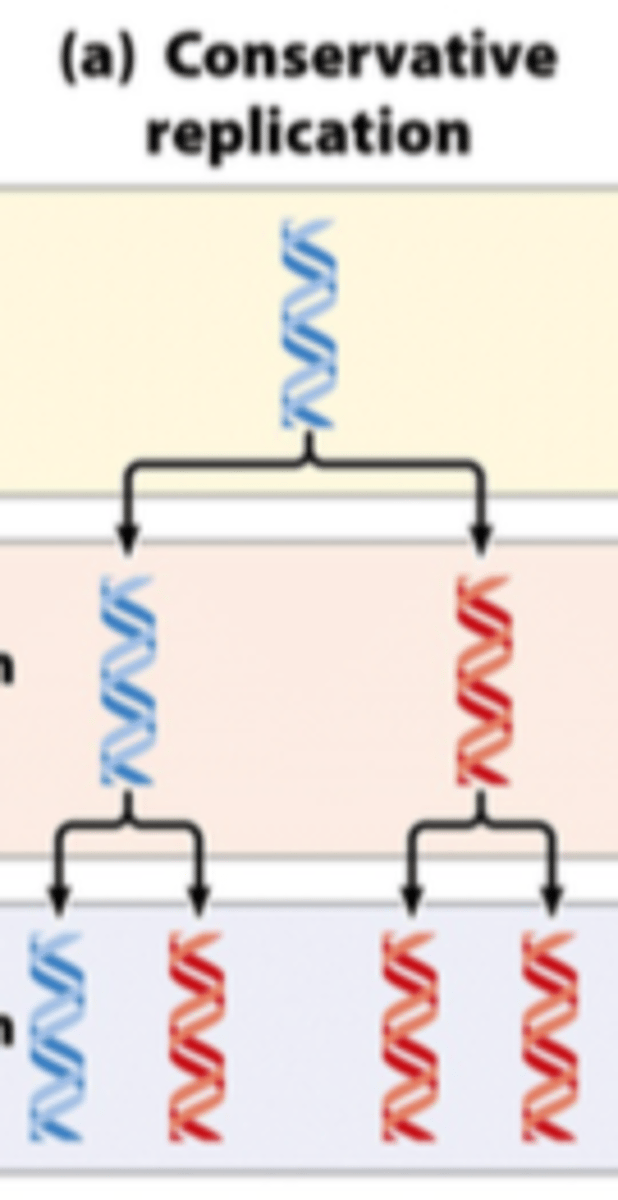
What are the three models of DNA replication
- conservative
- dispersive
- semiconservative
conservative replication
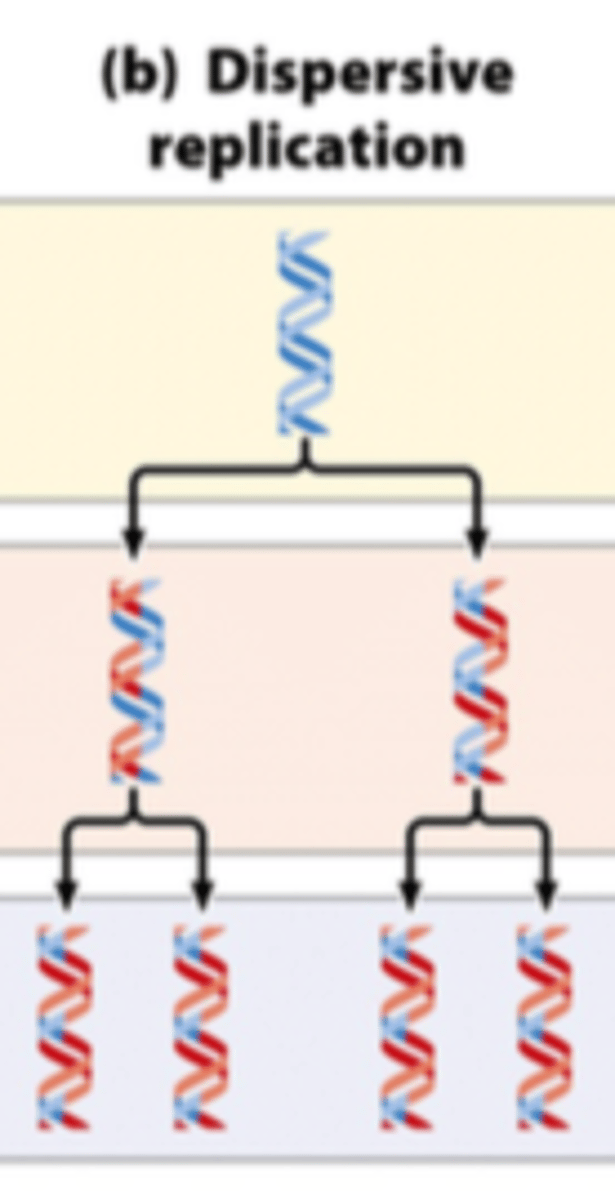
dispersive replication
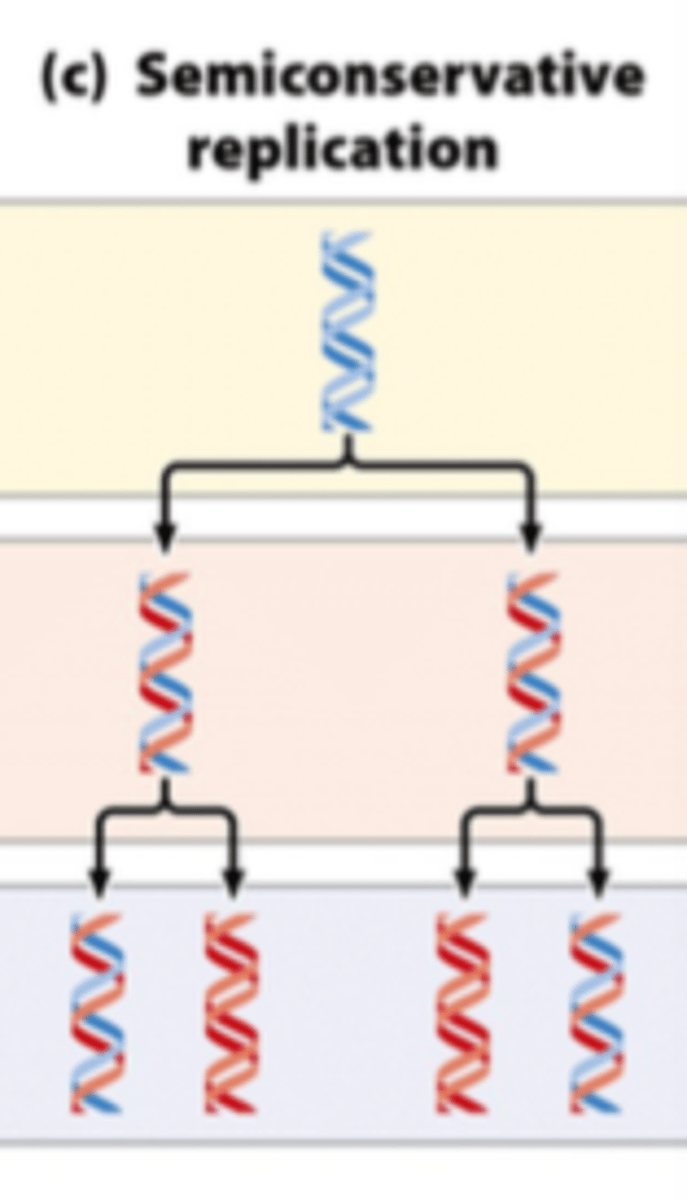
semiconservative replication
each strand serves as a template for a new strand during replication
describe the Meselson and Stahl experiment
-fill centrifuge with salt and DNA
- spin for days
- heavy/light DNA separate
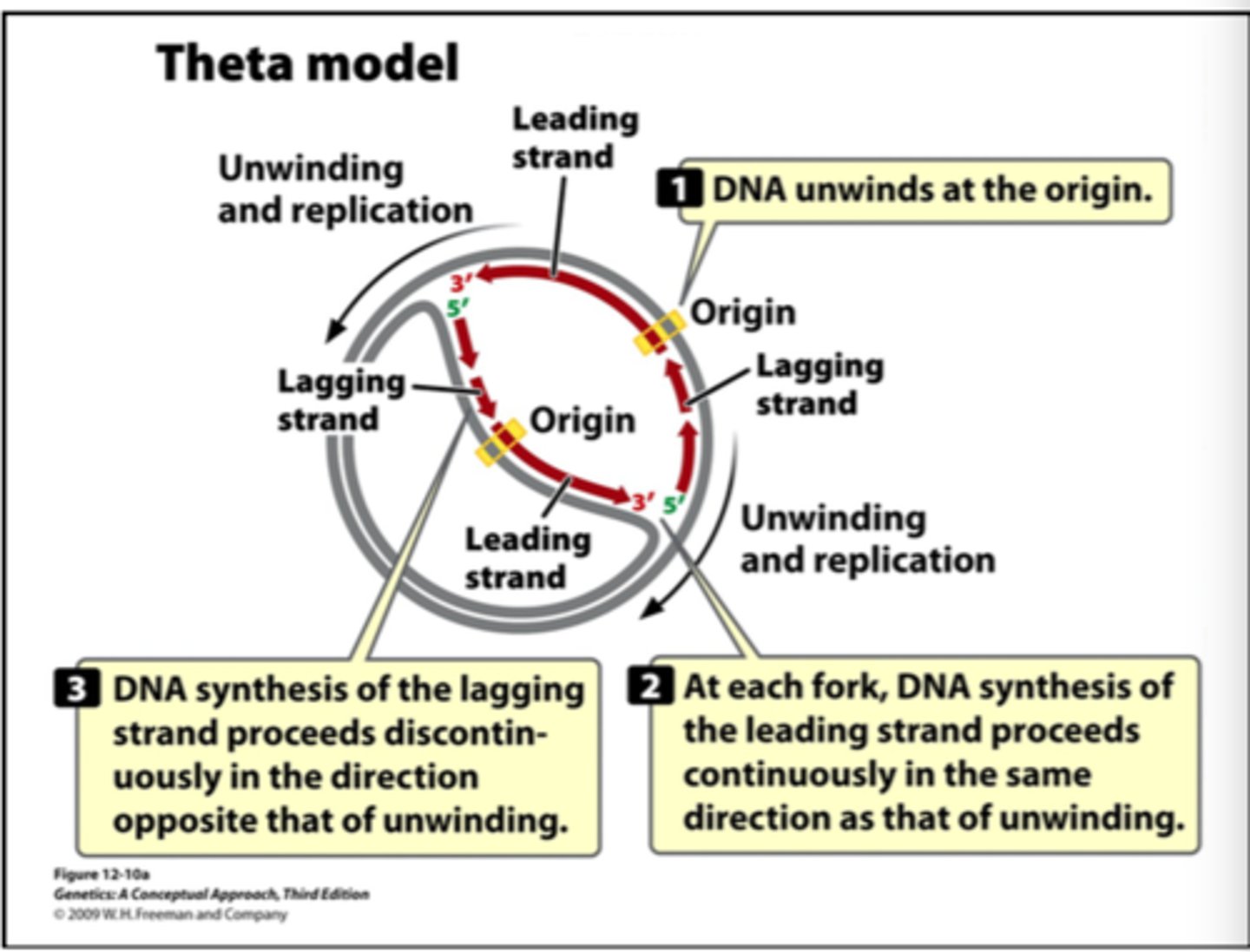
theta replication
replication of circular chromosomes. resembles greek later theta
what is the product of theta replication
two circular DNA molecules
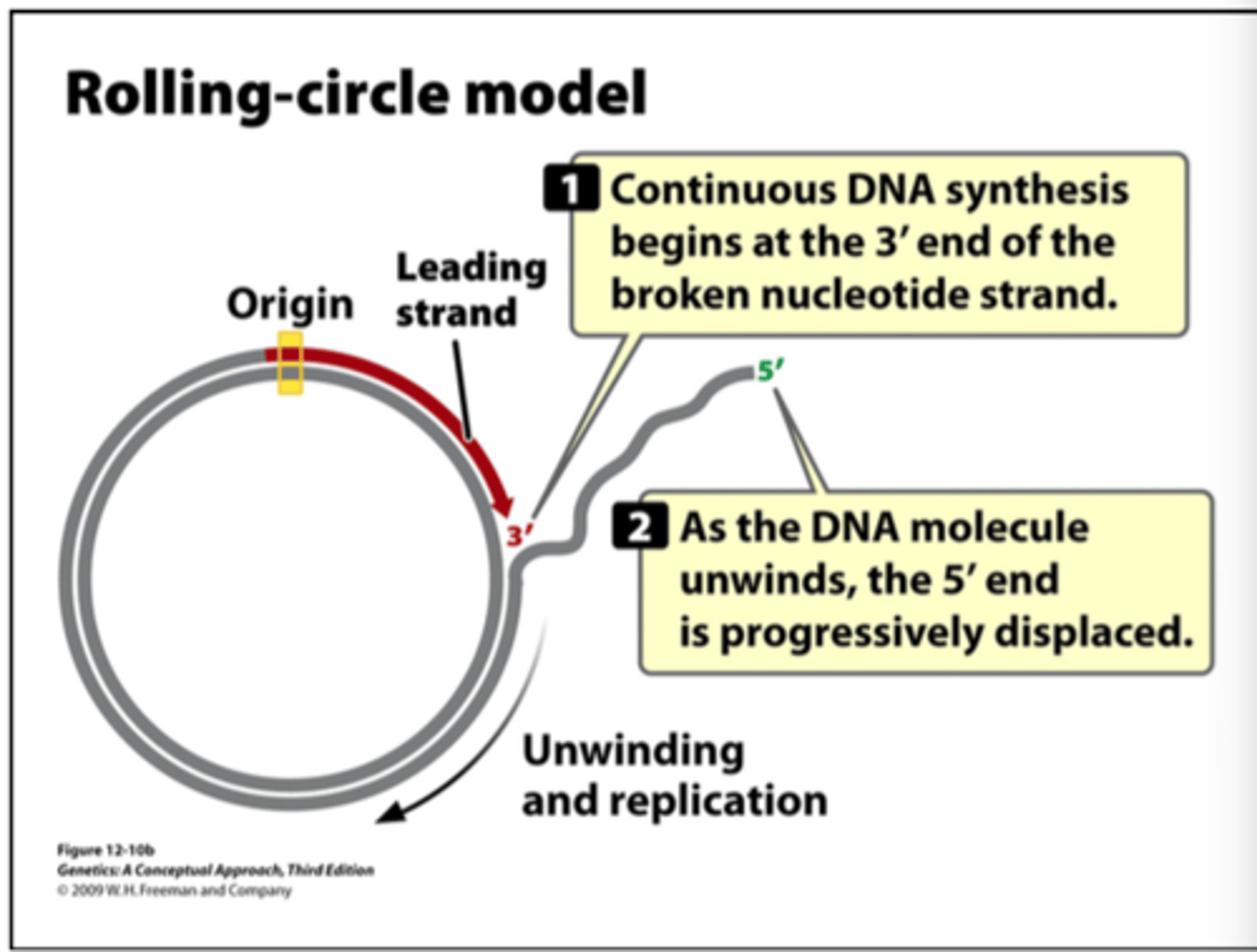
rolling circle replication
takes place in viruses and plasmids. circular DNA breaks and copies a strand starting with 3' end
what is the products of rolling circular replication
multiple circular DNA molecules
replicon
individual unit of replication. larger DNA molecules require more
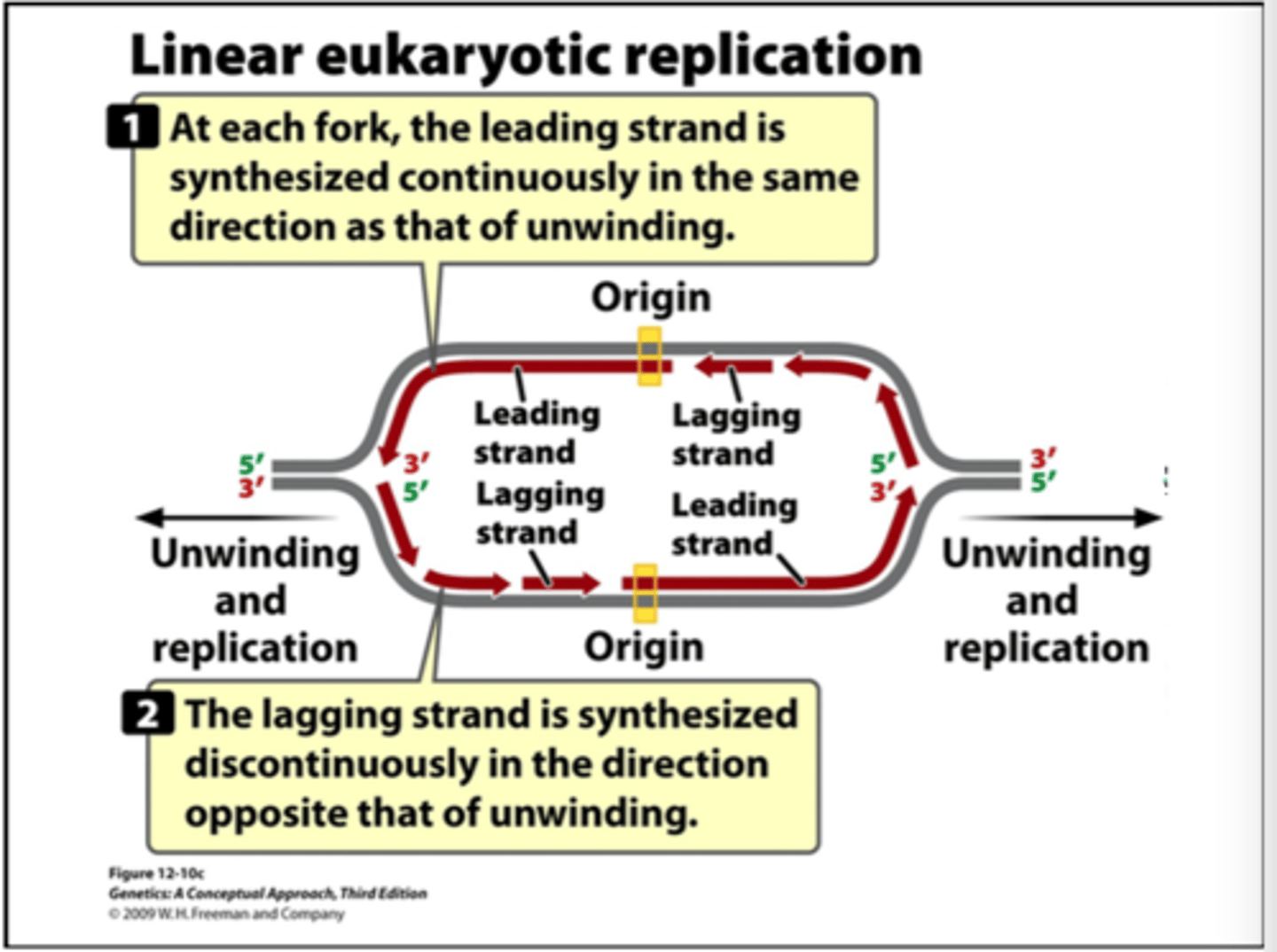
linear eukaryotic replication
large linear chromosomes are too large to replicate quickly from a single origin. they have many origins
products of eukaryotic DNA replication
two linear molecules
understand difference between theta, rolling-circle, and linear eukaryotic replication models

what is required for replication
- template strand
- raw materials/substrates
- enzymes/proteins to read template and assemble substrates
what is the raw material that synthesizes DNA
dNTP (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates).
how is dNTP attached to DNA
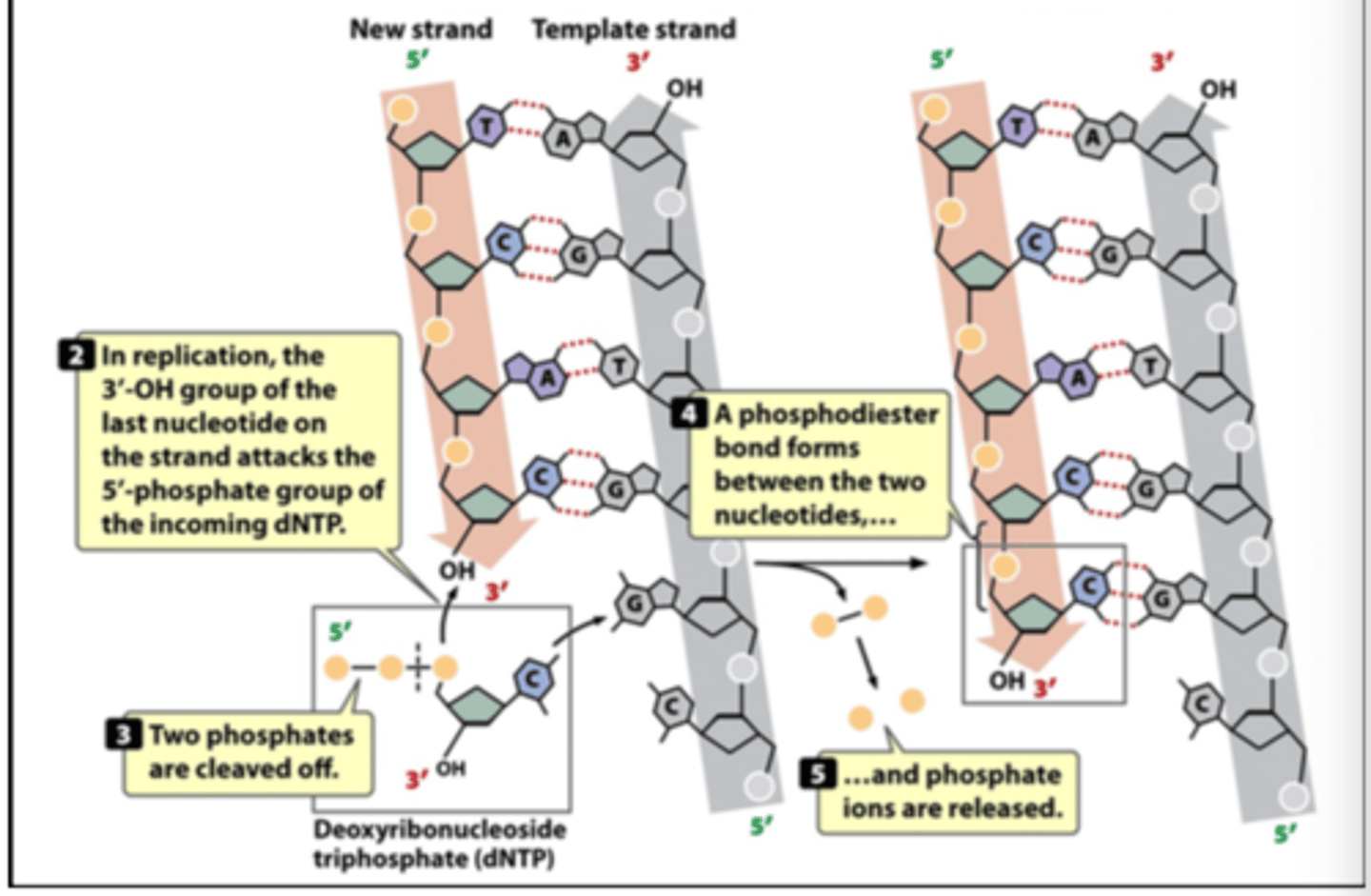
DNA polymerase
enzymes that synthesize DNA by adding nucleotides to 3' end
in which direction is DNA read and synthesized
read in 3' to 5' direction
SYNTHESIZED in 5' to 3' direction
okazaki fragments
short lengths of DNA produced by discontinuous replication
understand theta replication model
understand rolling-circle replication model
understand linear eukaryotic replication
how does initiation (start of replication) begin
1) initiator proteins bind to the origin of replication
2) this causes DNA to unwind
3) unwinding allows helices to attach
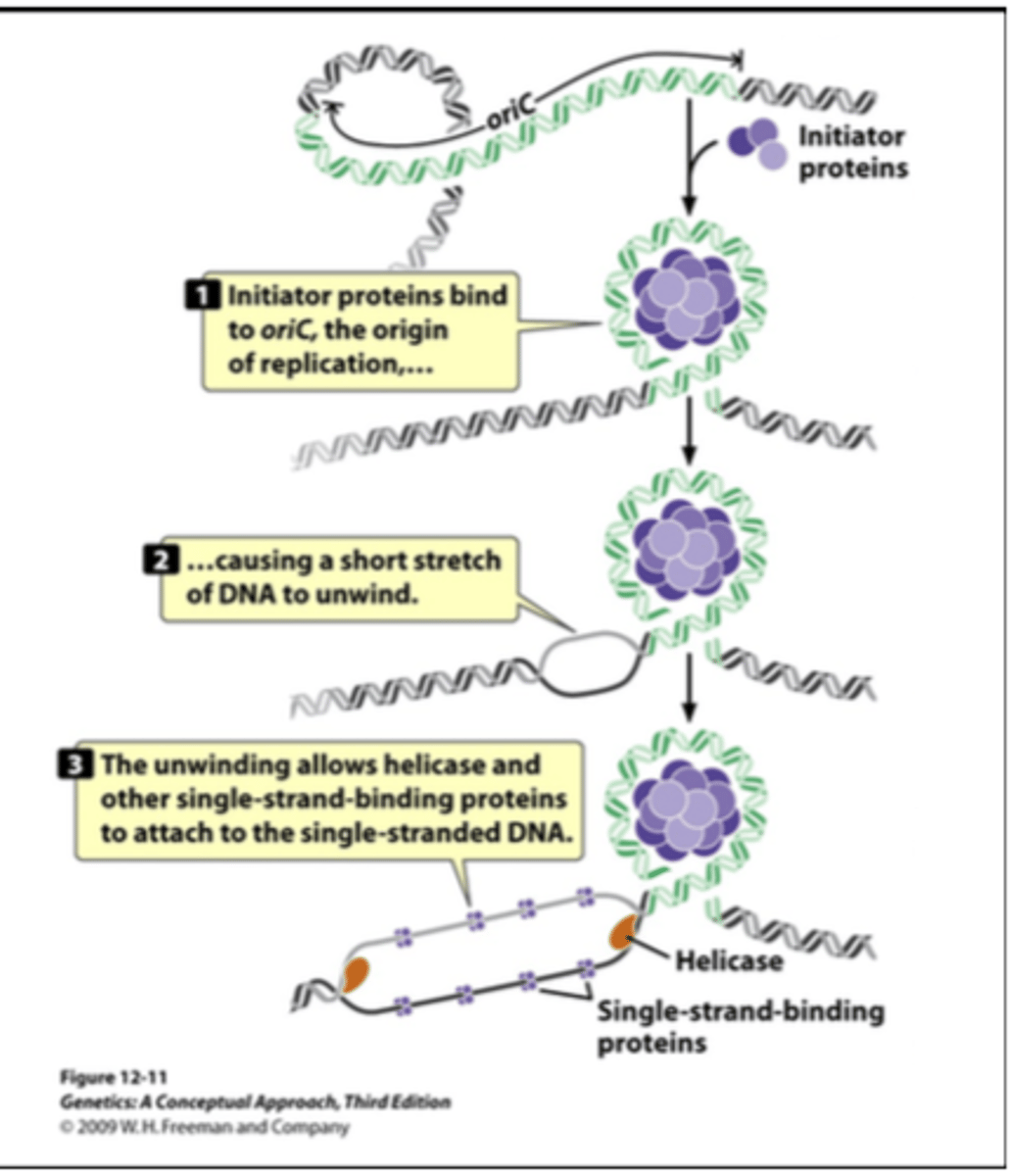
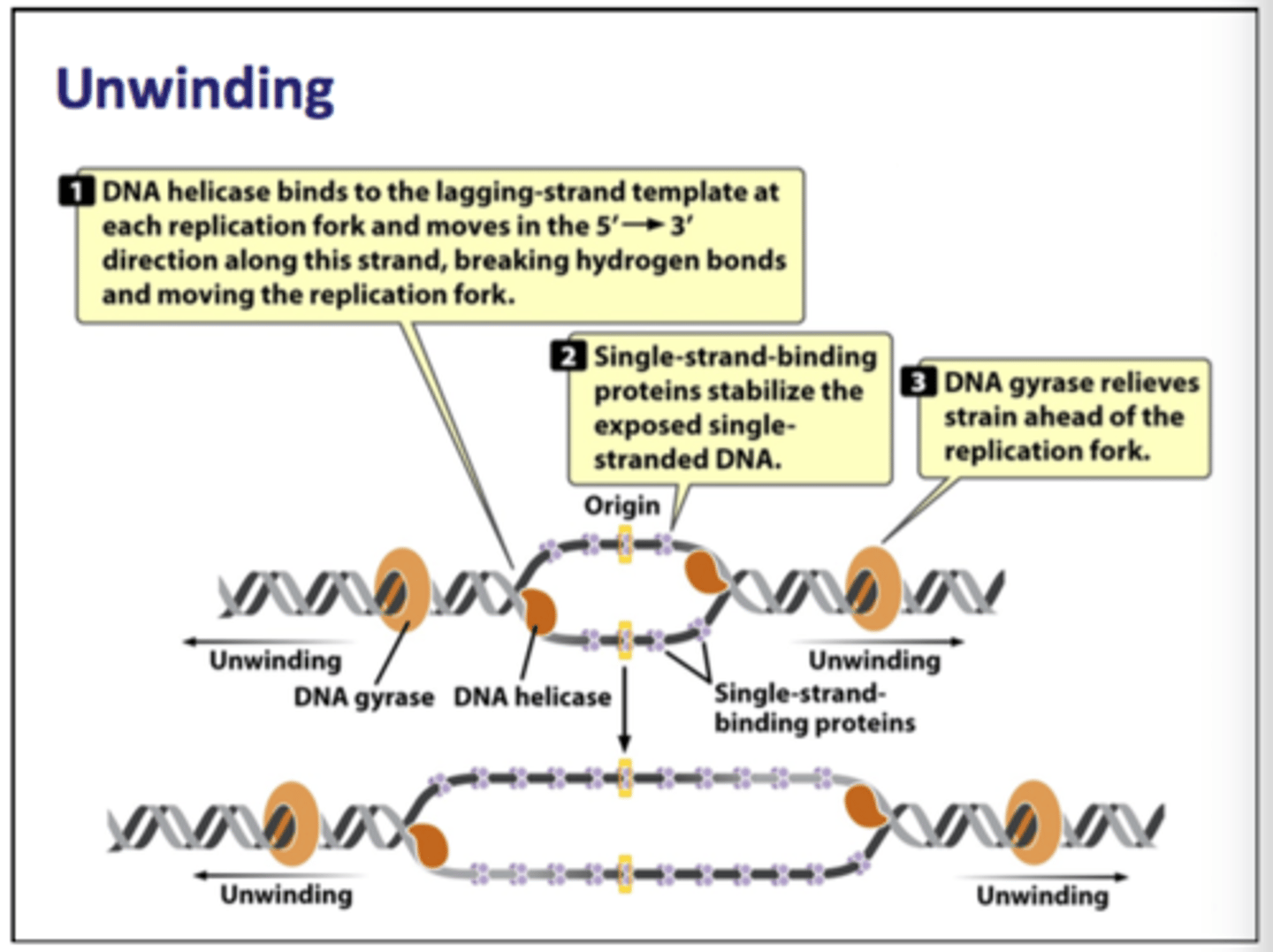
how does the unwinding process work
1) helicase unwinds DNA at replication fork
2) single-strand binding proteins prevent secondary strands from forming
3) DNA gyrase relieves strain
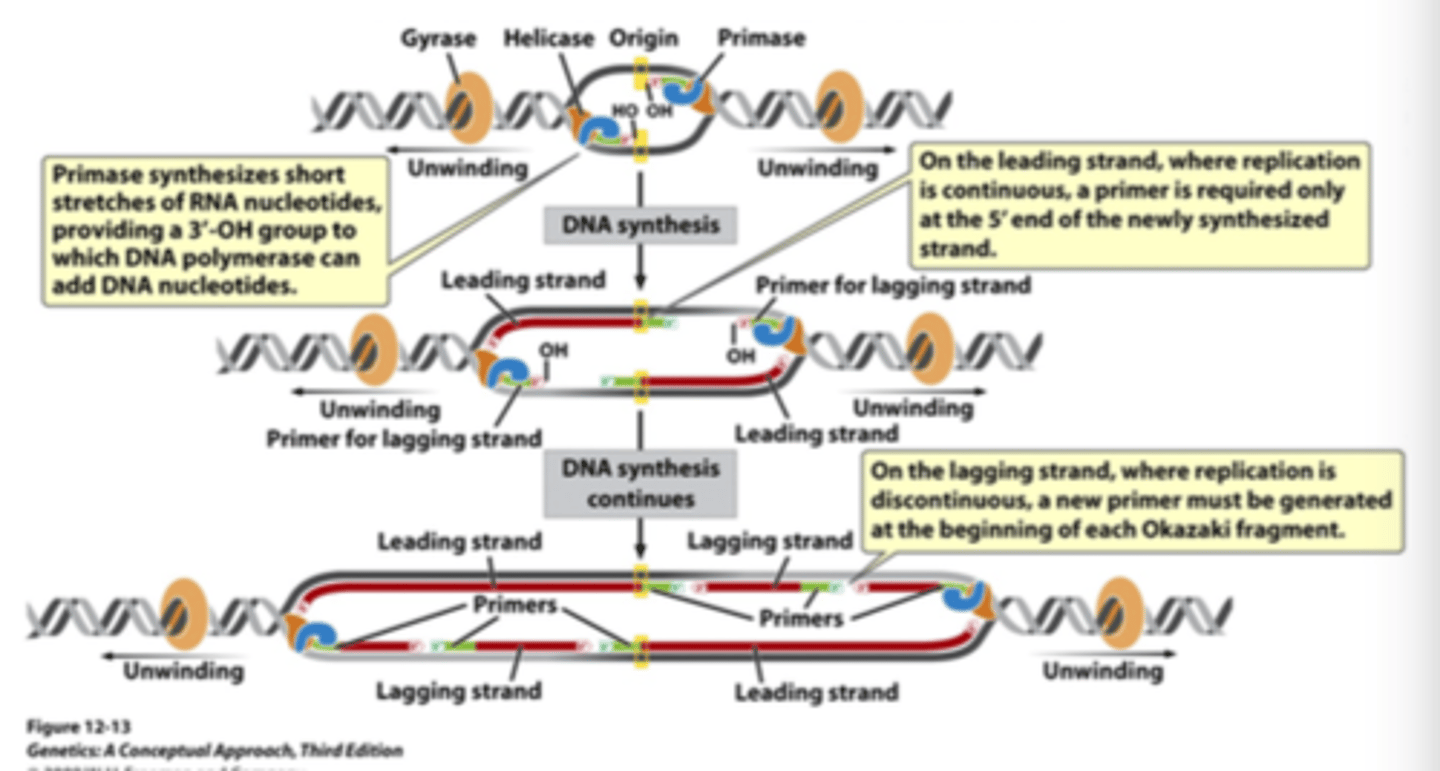
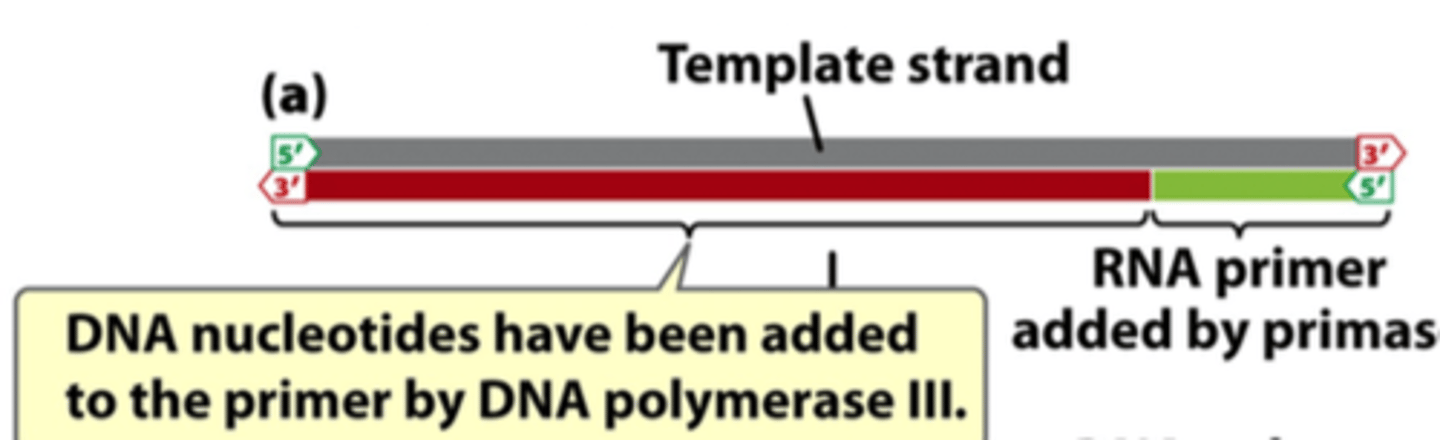
what do DNA polymerases require? what provides this?
- they require a nucleotide with a 3'-OH group
- primase synthesizes short stretches of RNA with a 3'-OH group
understand how primers operate
what is the function of DNA polymerase
elongate the polynucleotide strand. DNA polymerase III is the main workhorse of replication.
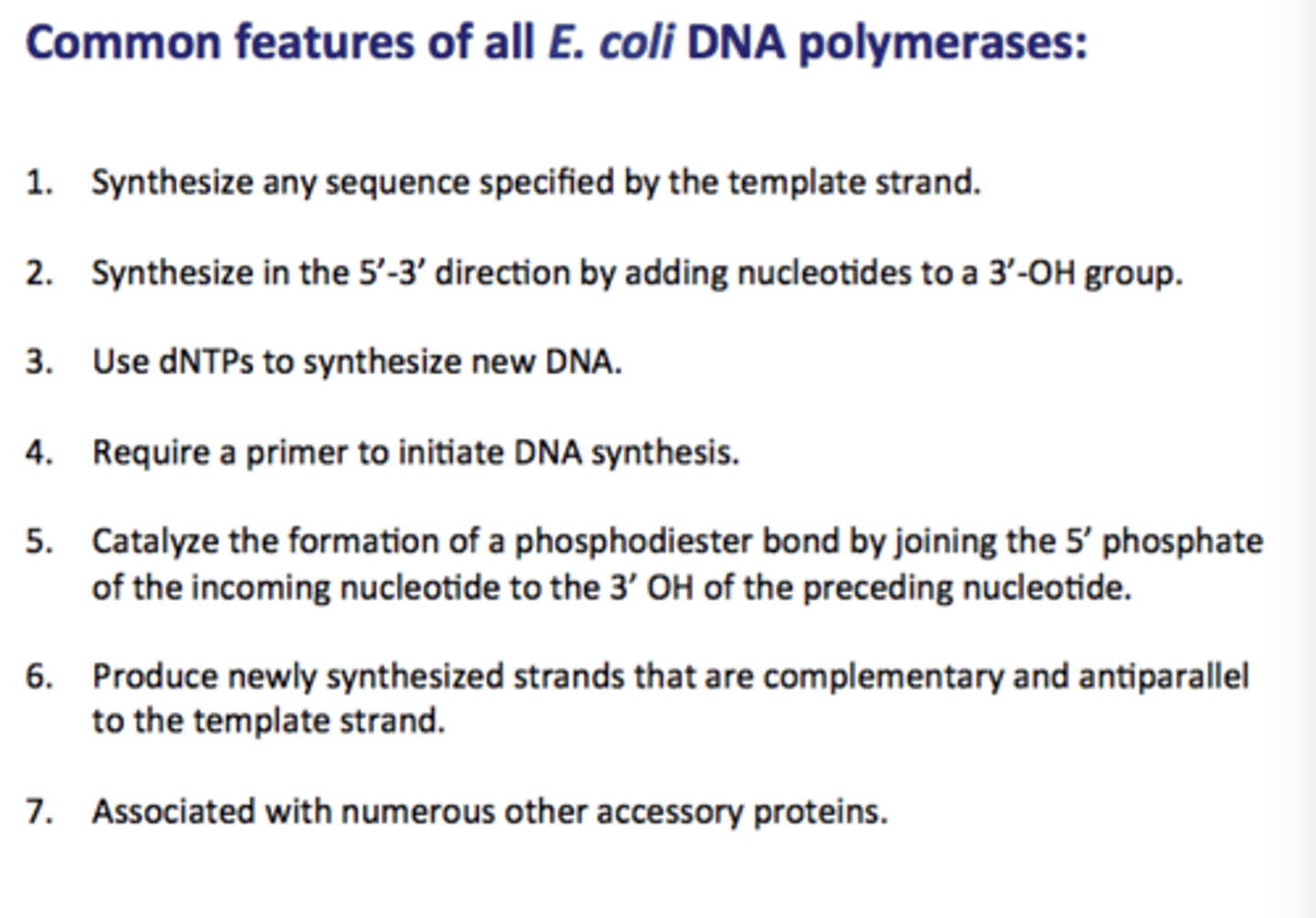
common features of all E. coli DNA polymerases
function of DNA polymerase III
adds nucleotides to primer
function of DNA polymerase I
replace RNA nucleotides of primer with DNA nucleotides
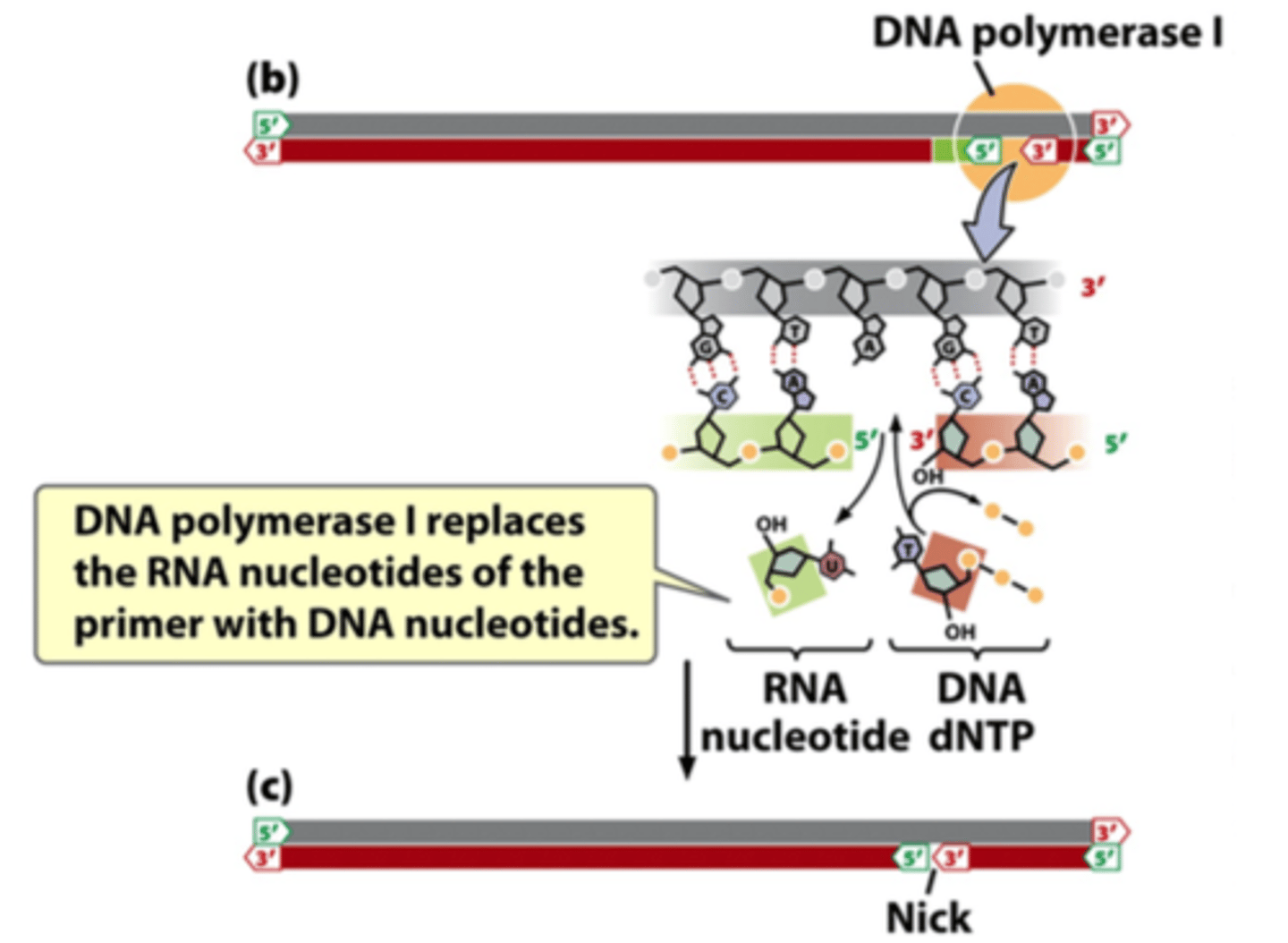
function of DNA ligase
seals the "nick" between 5' group in initial nucleotide and 3'-OH group of final nucleotide added by DNA polymerase I
understand components required for replication in bacterial cells
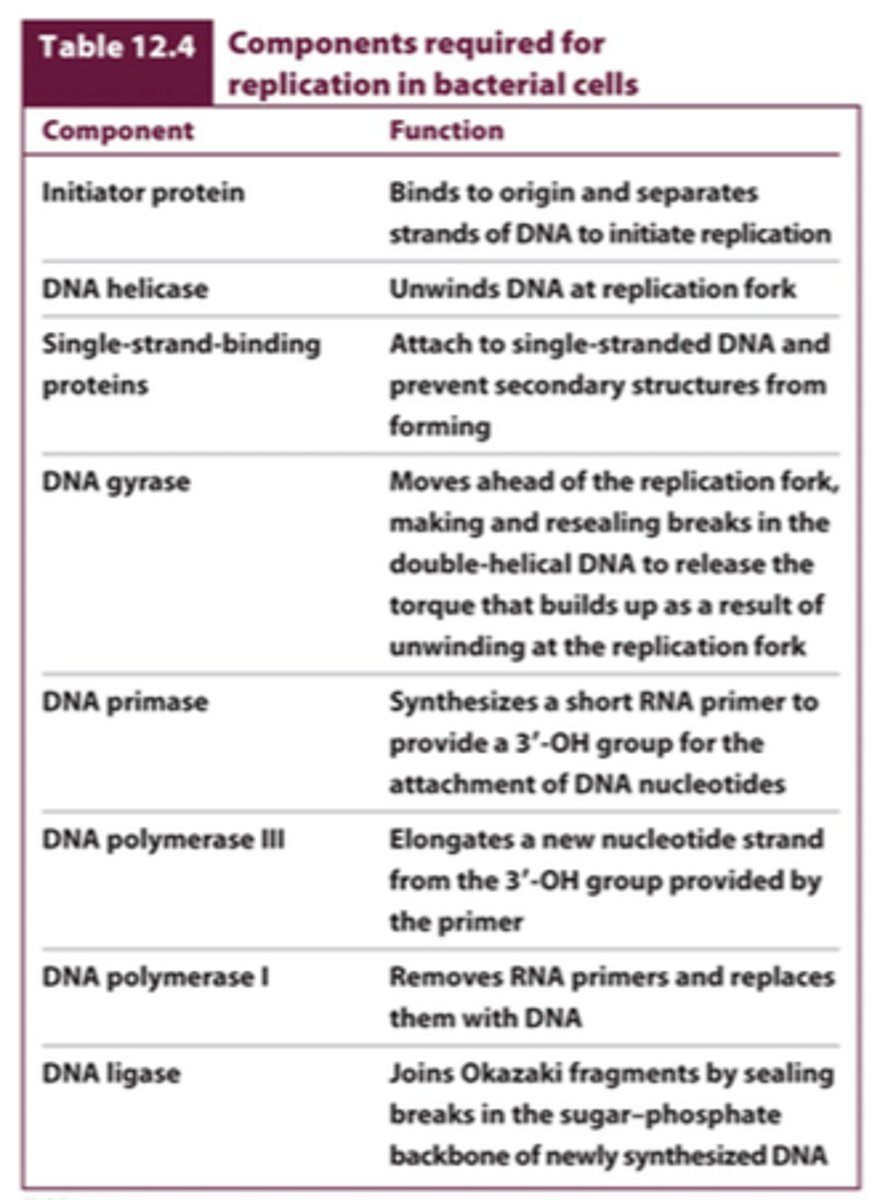
basic components of replication fork
- helicase
- single stranded binding proteins
- gyrase
- primase
- DNA polymerase
what adjustments does DNA make in order to replicate both strands at the same time
- lagging strand loops around by leading strand so they replicate simultaneously
- when lagging strand ends, it shifts to new position
what are two ways that errors are corrected
- proofreading
- mismatch repair
rules of replication
- always semiconservative
- begins at origins
- fast and accurate
what is unique to eukaryotic DNA replication
- multiple origins of replication
- linear chromosomes
- presence of histones and nucleosomes
what are autonomous replication sequences in eukaryotic DNA replication
these sequences can enable replication in any DNA sequence to which they are attached. contains A-T base pairs.
what are the two steps for initiation in eukaryotic DNA replication
1) origins are marked by replication licensing factor
2) replication machinery starts only at origins licensed by RLS
*after replication begins, replication licensing factor leaves so as not to begin again during that cell cycle
MCM complex
mini chromosome maintenance. DNA helicase unwinds DNA after binding of MCM to DNA
Geminin
prevents MCM from binding again and reinitiating. degraded at end of mitosis, allowing a relicensing of the origin.
what would happen if there were no special mechanisms to fill the gap after the removal of a primer
DNA replication would leave gaps
in DNA replication in eukaryotes, what fills the gap let by RNA primer
telomerase extends the DNA filling the gap