D1- Histology 1.5 Exam 1 Connective Tissue Types, Cells, and Fibers: Histology and Clinical Significance
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is the primary function of connective tissue?
To provide structure, mechanical strength, space filling, and support for specialized tissues.
____ is the most abundant and widely distributed of the basic tissues
Connective Tissue
What are the three primary components of connective tissue?
Cells, fibers, and ground substance.
What makes up the extracellular matrix in connective tissue?
Fibers and ground substance.
What are fibroblasts and their role in connective tissue?
Spindle-shaped cells that synthesize and maintain proteinaceous ground substance and connective tissue fibers like collagen and elastin.
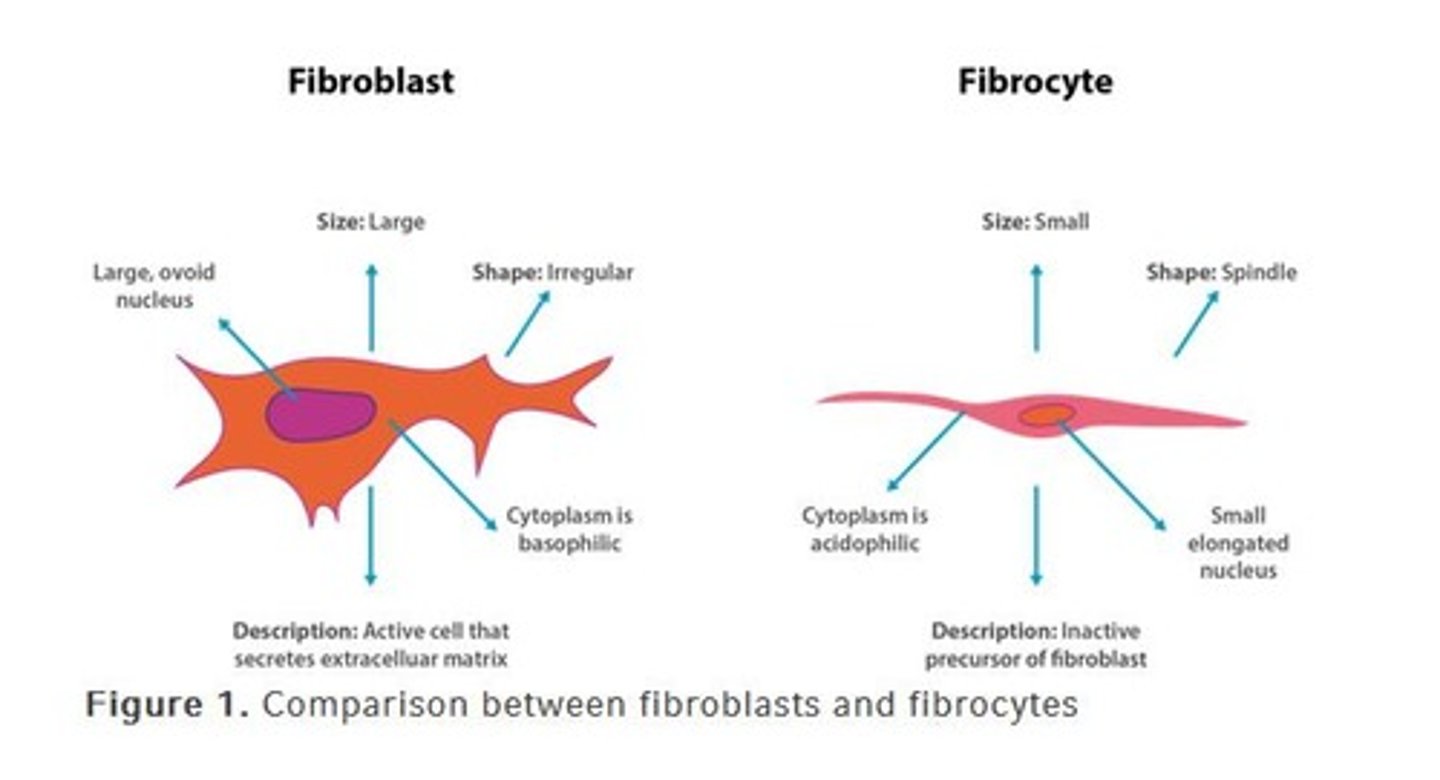
What are myofibroblasts?
Fibroblasts with contractile ability, similar to muscle cells, found in tendons and ligaments.
What are reticular cells and their function?
A type of fibroblast found in lymph nodes and bone marrow that synthesize reticular fibers and may have phagocytic function.
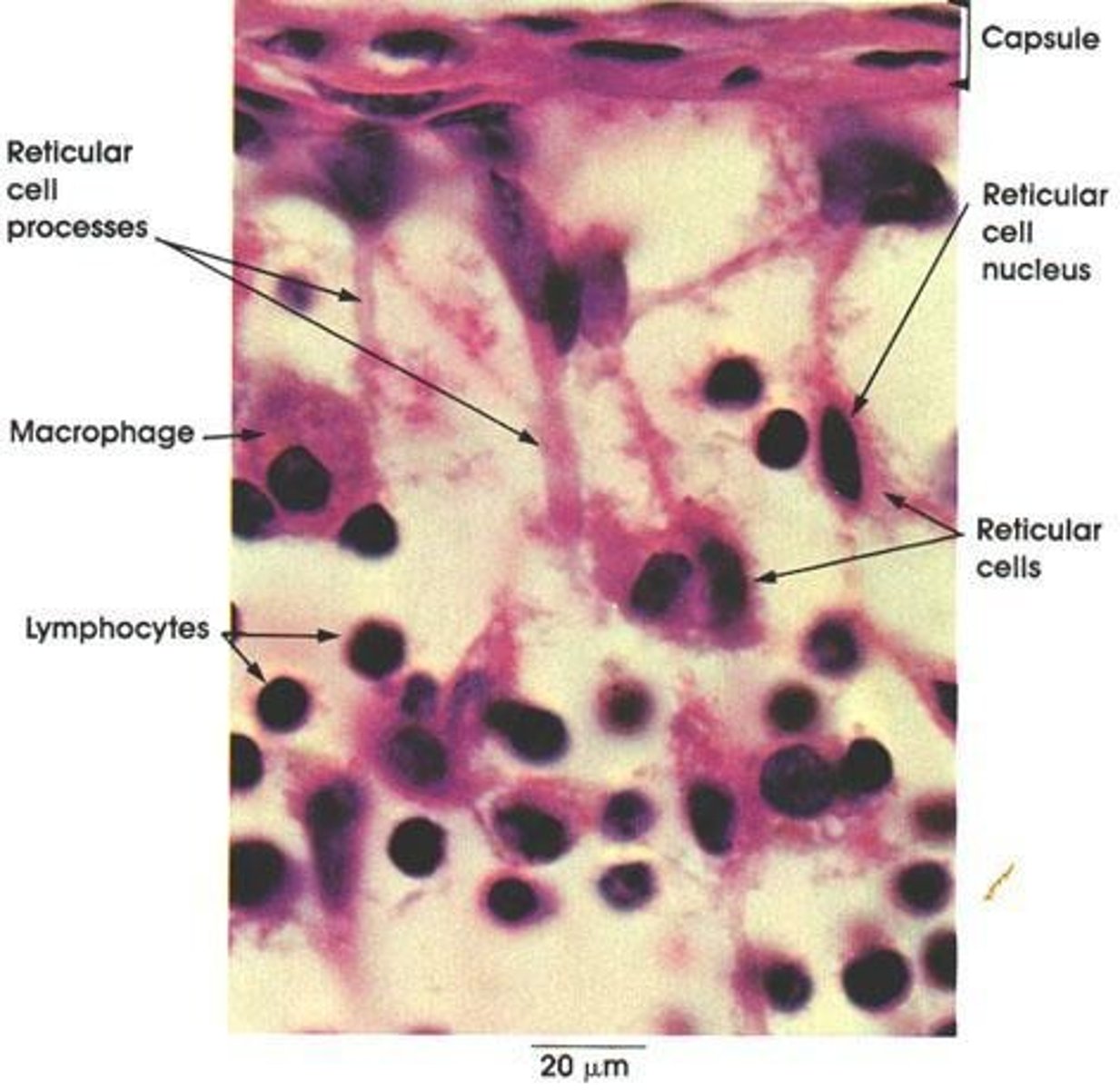
____ are morphologically similar to primitive mesenchymal cells; looks like branched fibroblasts
Reticular cells
_____ are also synthesized by regular fibroblasts in some tissues
Reticular fibers
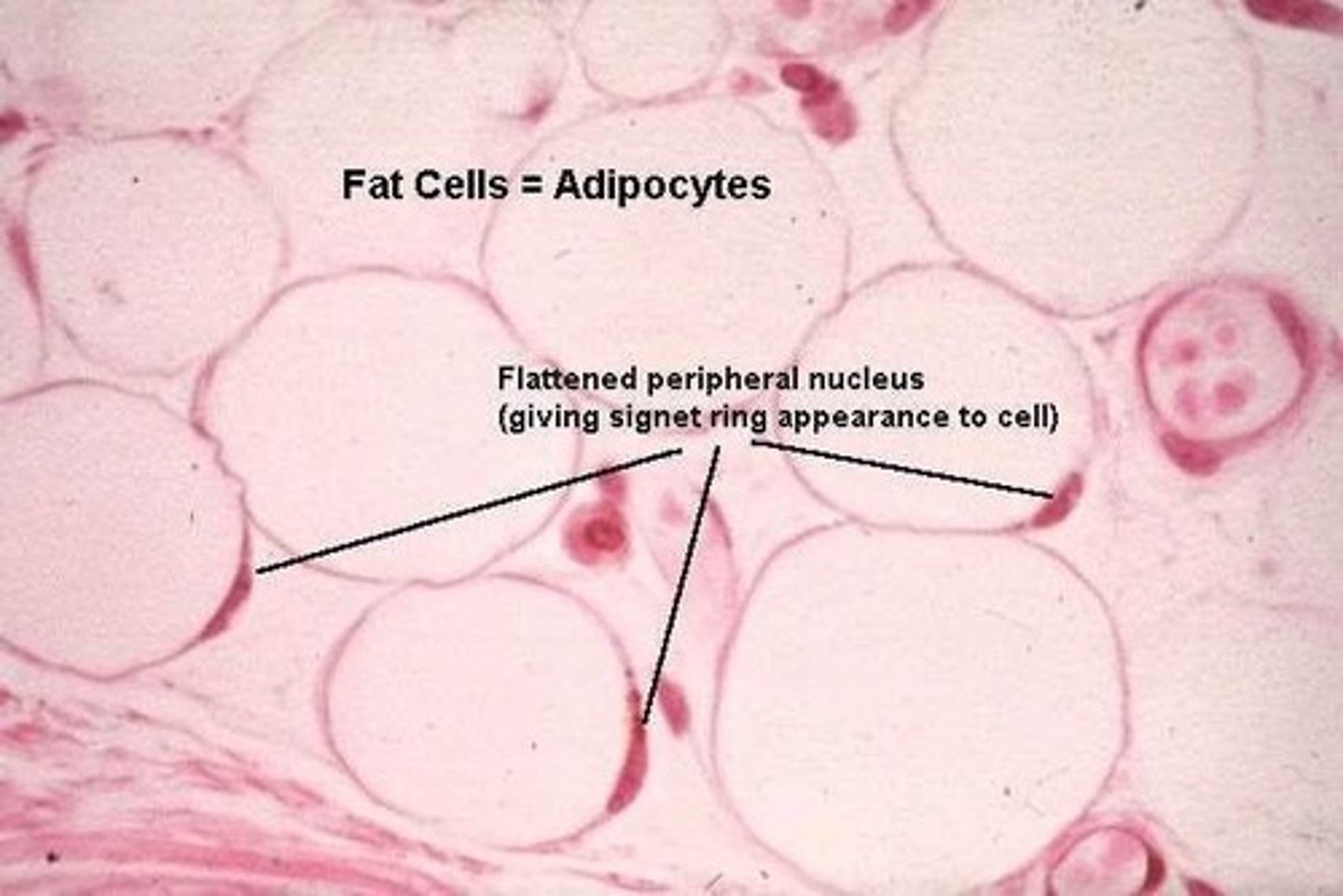
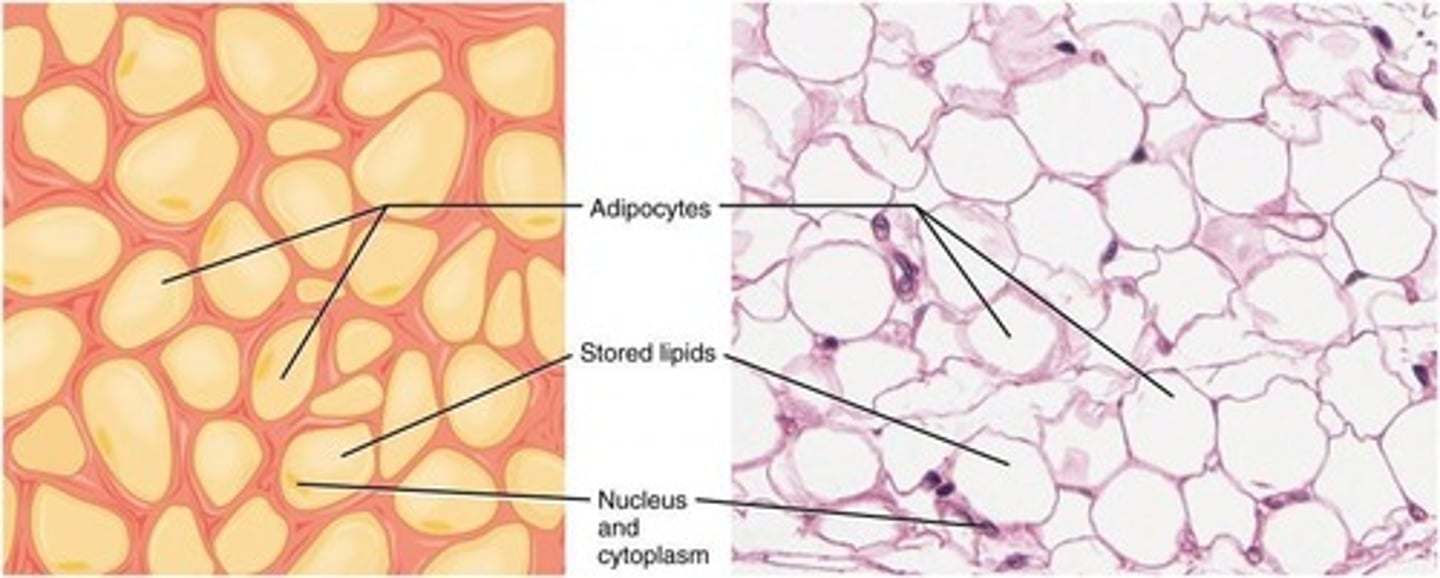
What are adipocytes and their primary function?
Large, balloon-shaped cells responsible for the storage and metabolism of lipids.
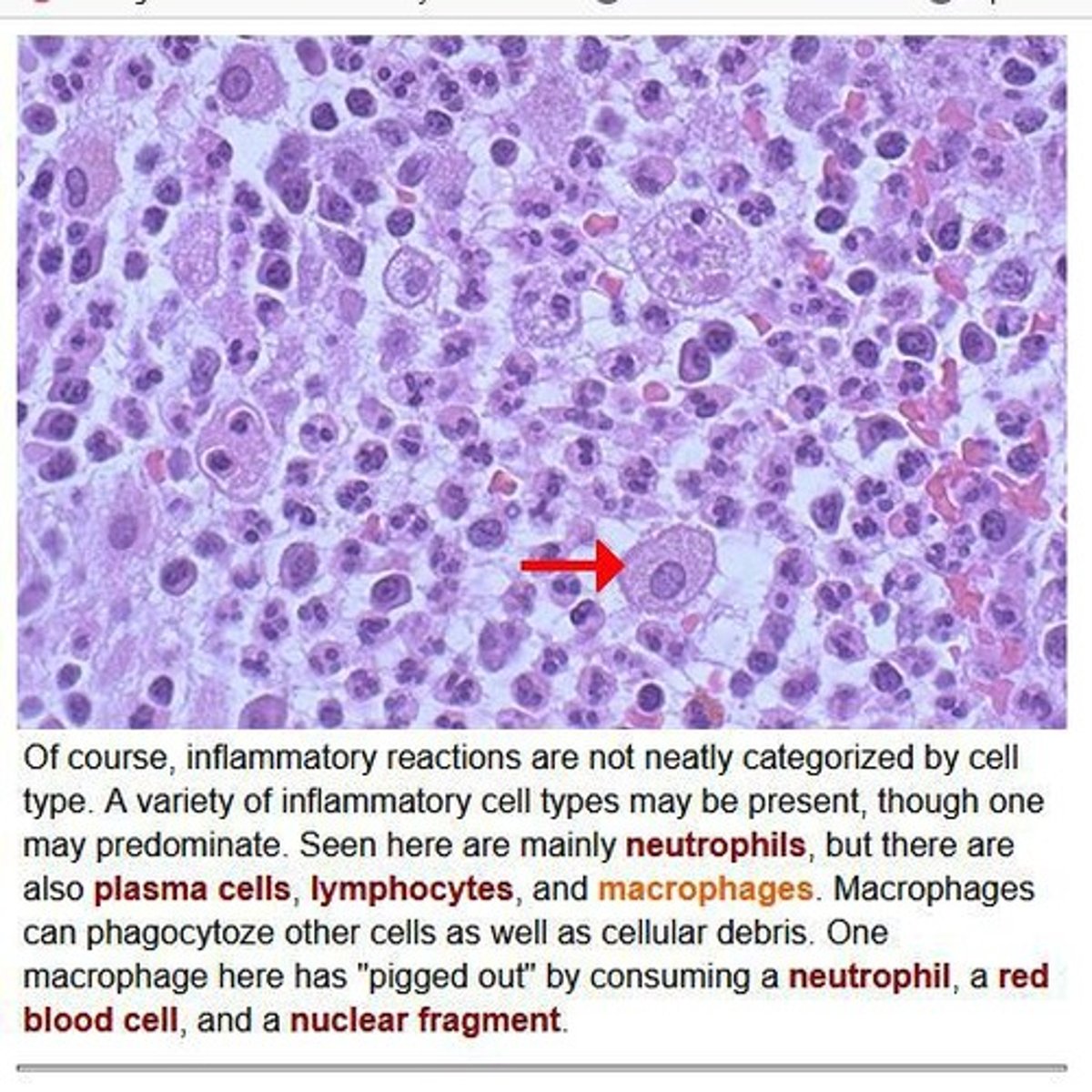
These are defensive cells of connective tissues
Macrophages
How do macrophages develop and what is their role?
Form from monocytes, which migrate from the blood into tissues, where they play a critical role in innate immunity and antigen presentation.
Monocytes become _____ or ____ after migrating into tissues
Macrophages or dendritic cells
What is the role of mast cells in connective tissue?
Involved in allergic responses and release histamine.
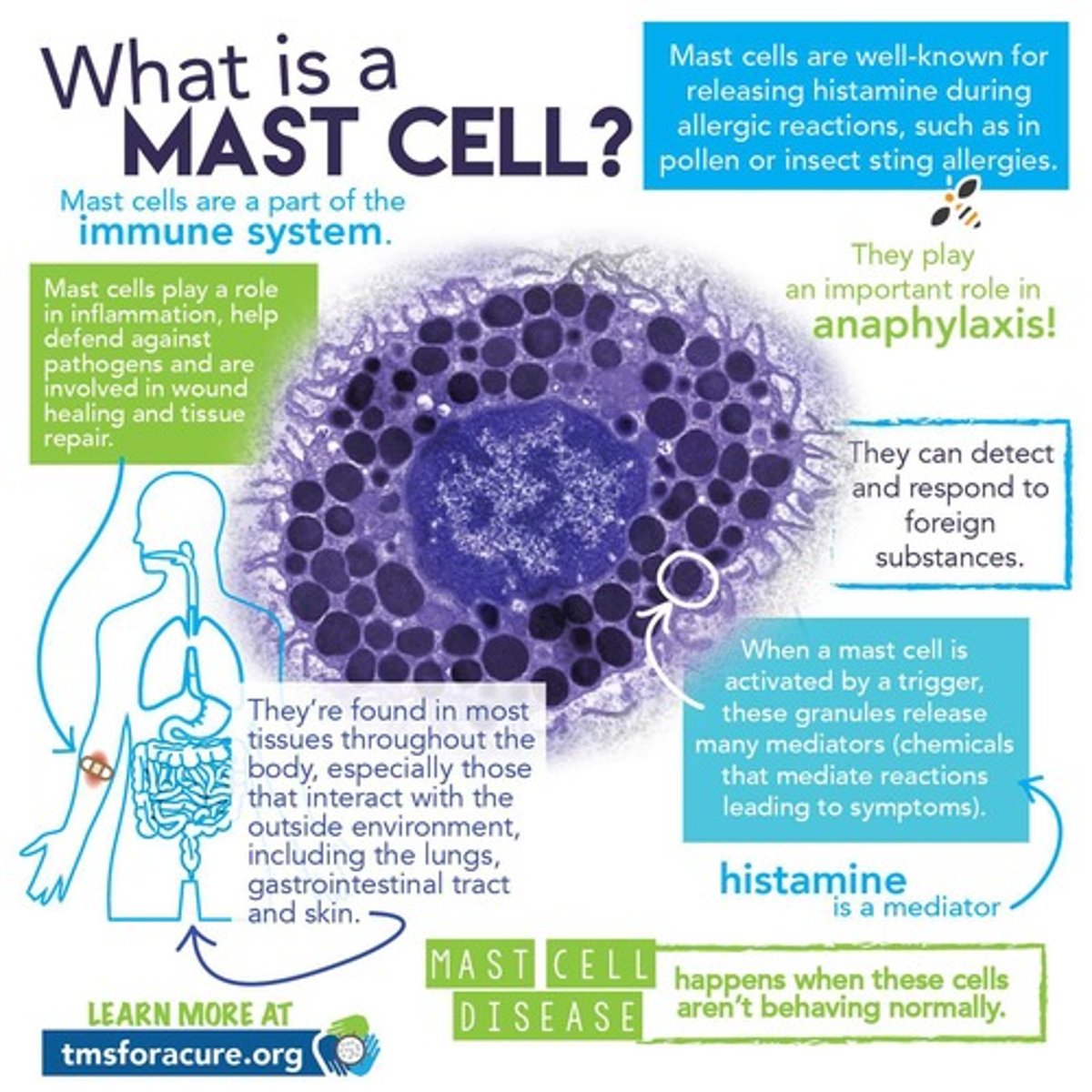
Mast cells are found in most tissues throughout the body, especially those that interact with the outside environment including _____,______ and ______
Lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and skin
Mast cells plays an important role in ______
Anaphylaxis
_____ play a role in inflammation , help defend against pathogens, and are involved in wound healing and tissue repair
Mast cells
______ are fibrous proteins and are secreted into the extracellular space, they provide high tensile strength to the matrix. This is the principle fiber in extracellular matrix
Collagen fibers
_____ are long, thin fibers that form branching network in the extracellular matrix. They help the connective tissue to stretch and recoil
Elastic fibers
_____ are short, fine collagenous fibers that can branch extensively to form a delicate network
Reticular fibers
What type of collagen is most abundant in the body?
Type I collagen, which constitutes 90% of collagen in the body and is found in loose and dense connective tissues.
What is Type II collagen and where is it primarily found?
It is the main structural collagen in hyaline and elastic cartilage, composed of thin fibrils arranged in a meshwork.
This type of collagen are usually not readily visible by light microscopic methods
Type II collagen
What are reticulin fibers and their function?
Thin, branching fibers that provide structural support in organs such as the liver and spleen.
Reticulin fibers are ______ collagen
Type III
What is Type IV collagen and its role in connective tissue?
It is found in basement membranes, providing a dense, sheet-like form of extracellular matrix that separates and protects tissues.
This type of collagen does not form fibers
Type IV collagen
________ is a dense, sheet-line form of ECM that underlie epithelia and endothelia, surrounds muscles, fat, and schwann cells. It separates tissues and protect them from mechanical stress
Basement membrane
Type V collagen is found where?
Cornea, placenta, and dermo-epidermal junctions
________ collagen are special anchoring fibrils that link extracellular matrix to basement membrane
Type VII collage
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is best known as
Collagenopathy
What is the clinical significance of understanding connective tissue?
It helps in recognizing diseases and disorders related to connective tissue and their histopathological findings.
What is the histologic organization of connective tissue?
It refers to the arrangement and structure of cells, fibers, and ground substance within connective tissue.
What are the two main types of connective tissue fibers?
Collagen fibers and elastic fibers.
What is the role of ground substance in connective tissue?
Ground substance fills the space between cells and fibers, providing support and facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste.
What is the significance of collagen's banding pattern?
The distinct 67-68 nm banding pattern helps in identifying different types of collagen.
What is the function of macrophages in the immune response?
Macrophages engage in phagocytosis and help initiate specific defense mechanisms by recruiting lymphocytes.
What is the function of elastic fibers in connective tissue?
Provide elasticity and resilience, allowing tissues to return to their original shape after stretching.
Elastic fibers are synthesized by fibroblast as _____ precursor; polymerizes in ECM to form elastin
Tropoelastin
What type of collagen is affected in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
Type V collagen
What are the main characteristics of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
Hyperextension of joints, skin fragility, and poor wound healing.
What is the initial form of collagen synthesized by fibroblasts?
Procollagen, composed of three α polypeptide chains forming a triple helix.
What is the process that follows collagen synthesis in the extracellular space?
Extracellular enzymatic modification to form tropocollagen monomers.
How are collagen microfibrils formed?
By the polymerization of tropocollagen into larger bundles.
What are the two main components of elastic fibers?
Elastin and fibrillin.
What is the role of fibrillin in elastic fibers?
It is a structural glycoprotein that surrounds the elastin core.
What are glycoproteins, and give an example?
Large polypeptides with branched polysaccharide side chains; examples include fibrillin and fibronectin.
What is the function of fibronectin?
adhesion between the cell membrane and extracellular matrix
What is laminin, and where is it found?
A sulfated glycoprotein and major component of the basement membrane, produced by most epithelial and endothelial cells.
______,______, and _______ are non-filamentous molecules
Laminin, entactin, and tenascin
_______ is a sulfated glycoprotein that binds with laminin
Entactin
_____ binds cells to extracellular matrix; thought to be important in cell migration in developing nervous system
Tenascin
What are glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)?
Negatively-charged polysaccharide compounds composed of repeating disaccharide units present in mammalian tissues.
What is hyaluronic acid, and where is it predominantly found?
The predominant GAG in loose connective tissue, lacking sulfated side groups.
What is the primary function of ground substance in connective tissue?
To provide a semi-fluid gel-like consistency that supports cells and fibers.
What are the two types of dense connective tissue?
Regular and irregular dense connective tissue.
What characterizes regular dense regular connective tissue?
Collagen fibers oriented parallel to each other, densely packed in fascicles.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
Energy storage, thermoregulation, and acting as a shock absorber.
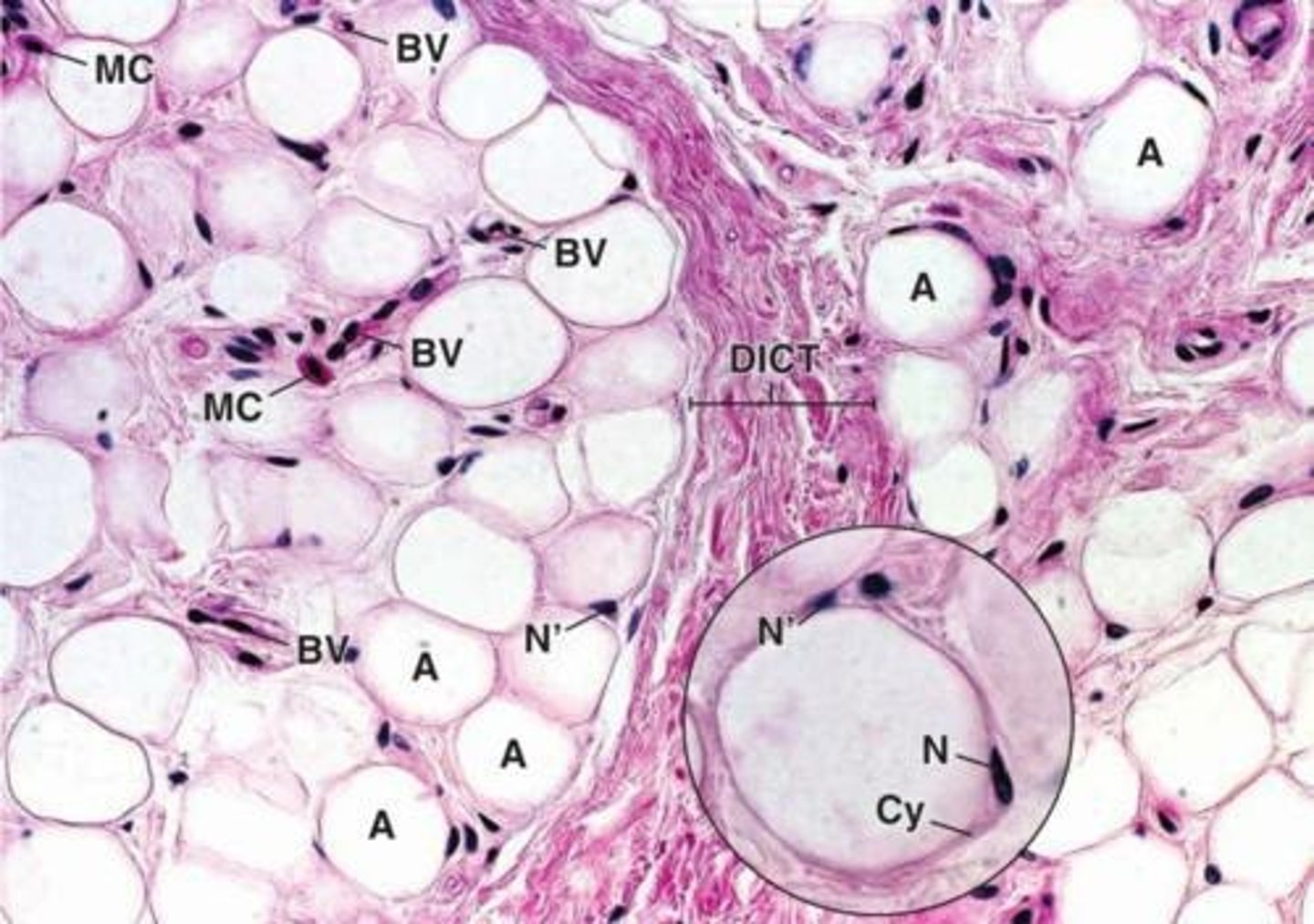
What distinguishes white fat from brown fat?
White fat is unilocular and stores energy, while brown fat is multilocular and specialized for thermoregulation.
What is Marfan's syndrome?
An autosomal dominant condition resulting in abnormal elastic fibers, characterized by tall stature, long limbs, and long, thin fingers. And risk of aortic dissection.
What are the functions of glycosaminoglycans?
They contribute to gel formation and provide structural support in connective tissues.
What is the significance of the negatively charged nature of GAGs?
It makes them hydrophilic, aiding in gel formation and providing turgor pressure.
What happens in lysosomal storage diseases related to GAGs?
Non-functional lysosomal enzymes lead to the accumulation of GAGs.
What is another name for lysosomal storage disease?
Mucopolysaccharidoses
What is the composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
It consists of fibers (collagen, elastin), ground substance (GAGs, proteoglycans), and various cells.
_____ are found in most connective tissue
Hyaluronic acid
______ are found in cartilage and bone
Chondroitin sulfate
______ are found in cartilage, bone, cornea, and intervertebral disk
Keratan sulfate
_____ are found in dermis of skin, blood vessels, and heart valves
Dermatan sulfate
______ are found in the basement membrane, lung, liver
Heparan sulfate
Hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate, dematan sulfate, and heparatan sulfate are all types of ______
GAGs
________ connective tissue are sparse fibers and abundant ground substance. It has supportive function, and is located beneath epithelia
Loose (areolar) connective tissue
______ connective tissue provides structural support. Abundant fibers, lesser ground substance.
Dense connective tissue
_____ connective tissue are collagen fibers oriented randomly, have moderate numbers of fibers and few cells
Dense irregular
Bone, blood, cartilage, adipose tissue, hematopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue are all what type of connective tissue?
Specialized
_____ are distributed in dermis and around intraperitoneal organs. 20% of body weight in male and 25% in female
White fat
_______ are highly specialized, present in infants and hibernating animals
Brown fat
Brown fat is used in _________
Thermoregulation to maintain body temperature