ANFS 240 - Muscles & Joints
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
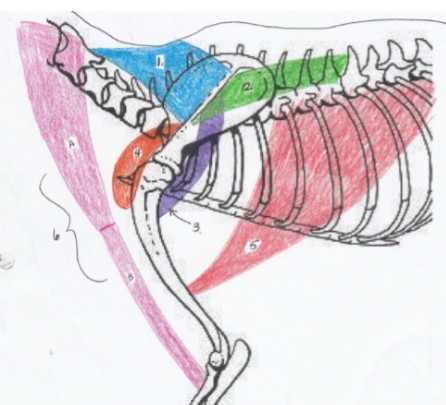
Pectoral muscle group
1-4
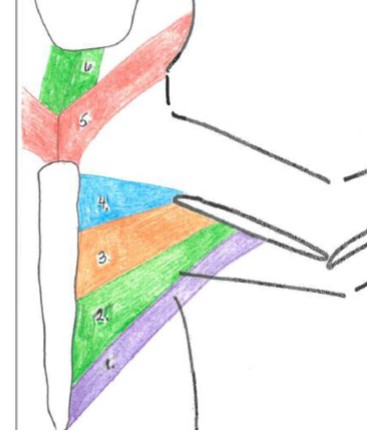
sternomastoid
5 red
origin: first costal cartilage and manubrium
Insertion: hyoid bone
Function: retracts the hyoid bone
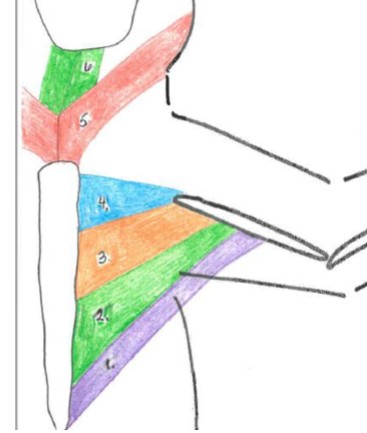
sternohyoid
6 green
Origin: cranial manubrium
Insertion: hyoid bone
Function: flex the head (pair) or turn the head (singly)
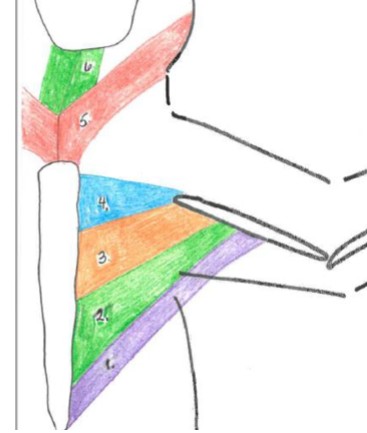
pectoantebrachialis
4 blue
Origin: manubrium
Insertion: humerus (just proximal to the elbow)
Function: adduction of the forelimb
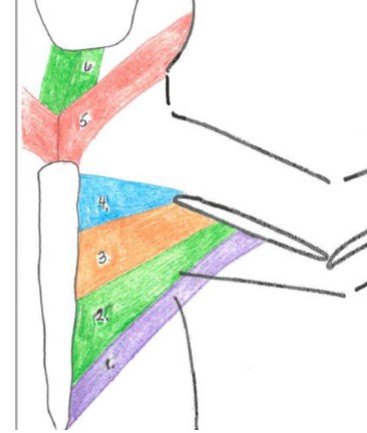
pectoralis major
3 orange
Origin: body of the sternum
Insertion: diaphysis of the humerus
Function: adduction of forelimb
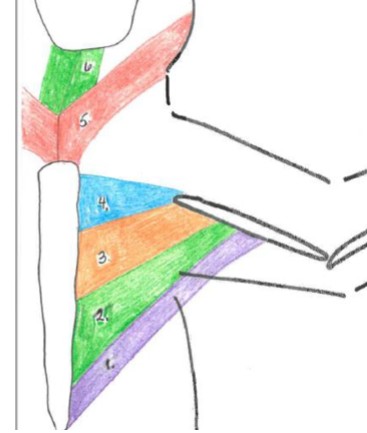
pectoralis minor
2 green
Origin: body of the sternum
Insertion: ventral humerus
Function: adduction of the forelimb
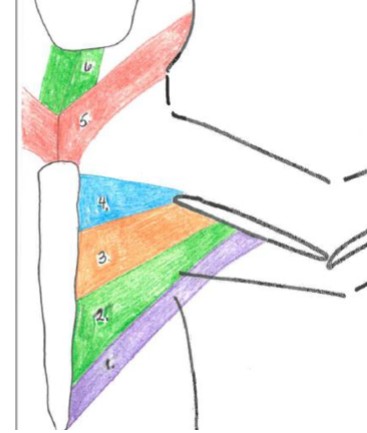
xiphihumeralis
1 purple
Origin: xiphoid of the sternum
Insertion: ventral humerus
Function: adduction of the forelimb
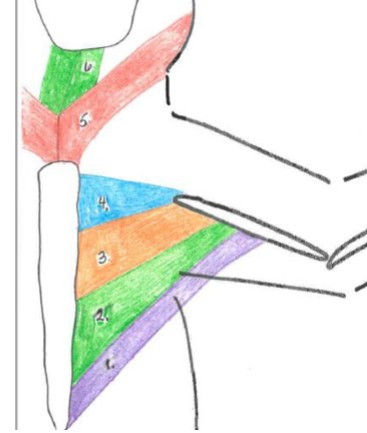
latissimus dorsi
5
Origin: spinous processes of 4th and/or 5th thoracic and 6th lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: the medial side of the proximal humerus shaft
Function: retracts the limb, drawing the forelimb dorsocaudally. If limb is fixed, it advances the trunk forward
atlanto-occipital
condylar joint between occipital bone in the skull and atlas bone
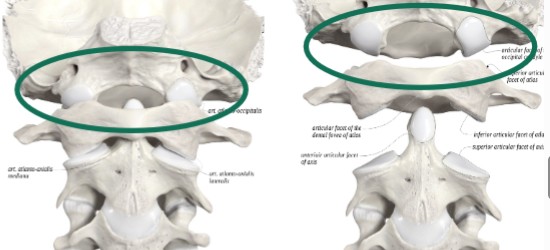
atlanto-axial
pivot joint between atlas bone and axis bone
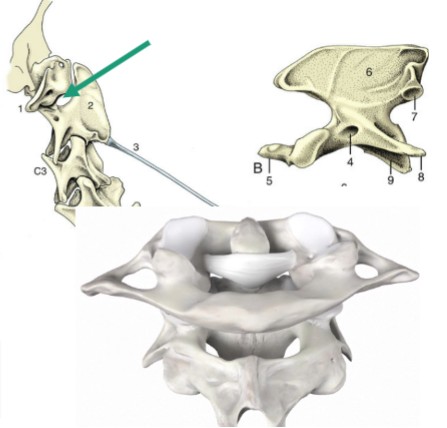
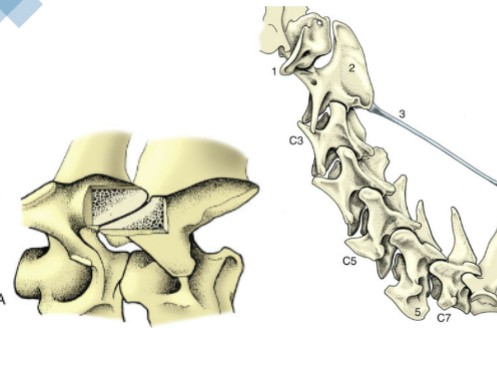
vertebral articulations
plane joint, small articular surfaces that are nearly flat, more of a sliding motion than a true flexion or rotation
glenohumeral
ball and socket joint, shoulder joint, head of humerus articulates with the supraglenoid cavity, capable of circumduction but prohibited due to excessive muscling
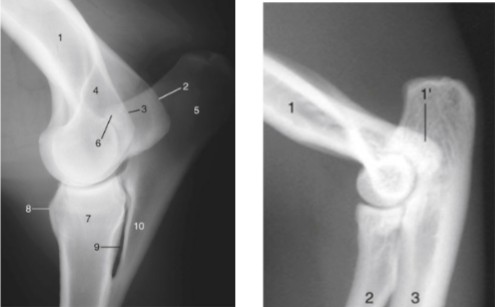
humeroradioulnar
hinger joint, elbow joint, flexion and extension only in one plane, no rotation or adduction/abduction
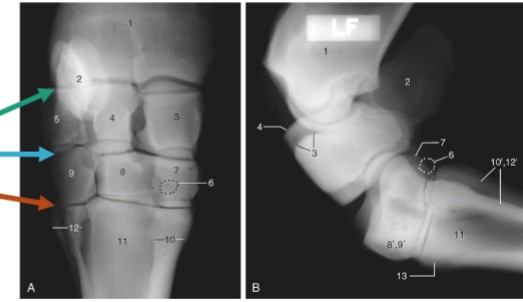
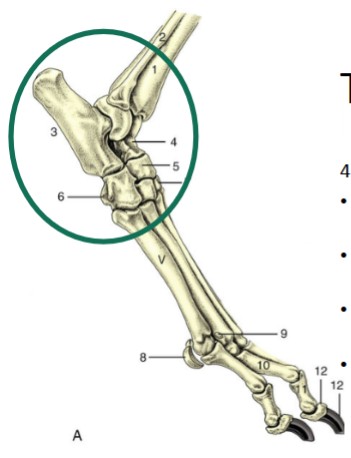
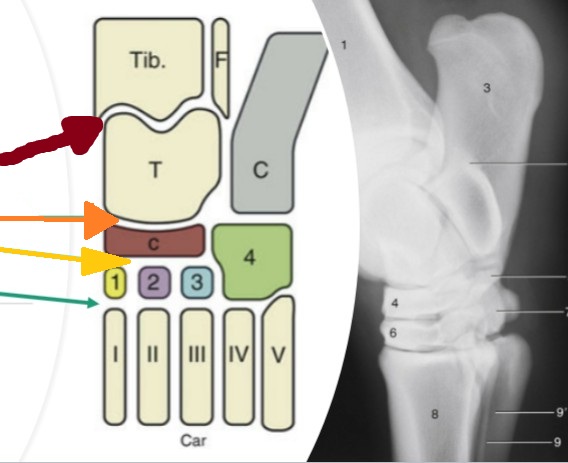
carpus
made up of 3 rows of joints
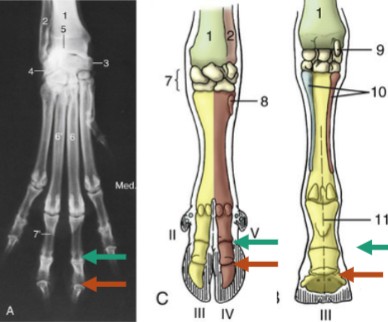
metacarpophalangeal
fetlock, hinge joint, between metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges, where the proximal sesamoid bones lie, on the palmar side
proximal interphalangeal/pastern
teal, where P1 articulates with P2
distal interphalangeal joint
orange, where P2 articulates with P3, where distal sesamoids lie
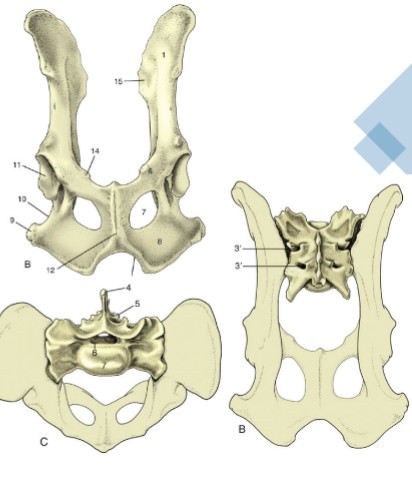
pelvic symphysis
cartilaginous joint, where two pubis bones and two ischium bones meet ventrally, ossifies as animals age, before giving birth the joint will soften to allow for the neonate to fit through the pelvic canal, “amphiarthrosis”
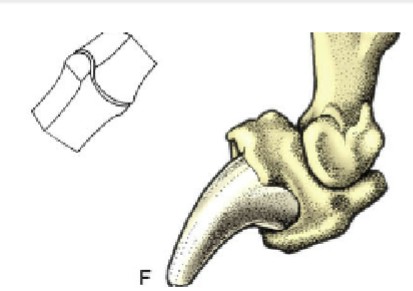
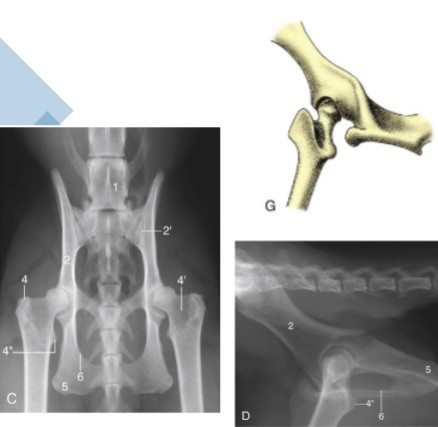
coxofemoral
ball and socket joint, head of femur articulates with the acetabulum of the os coxae, capable of circumduction, unless there is heavy musculature (horse)
stifle joint
the knee, made up of two separate joints
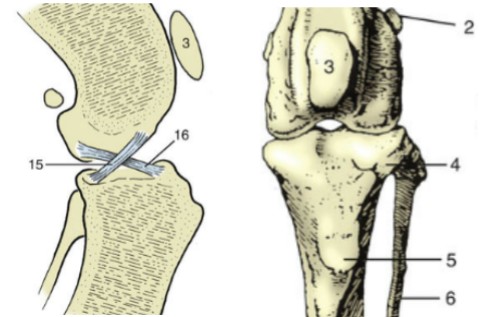
femoropatellar joint
makes up stifle joint, craniodistal aspect of the femur articulates with the sesamoid patella
femorotibial joint
makes up stifle joint, distal aspect of the femur articulates with the tibia (not fibula)
tarsus/hock
compound joint of 4 distinct joints
metatarsophalangeal/fetlock joint
metatarsal articulates with the proximal phalanx (P1), where proximal sesamoid bones lie
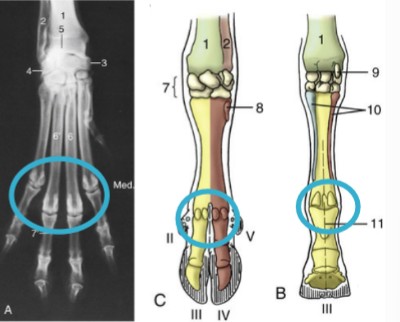
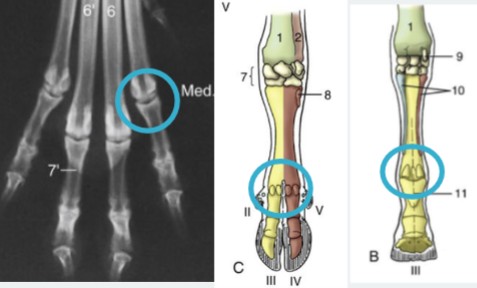
antebrachiocarpal joint
green, between radius and proximal row of carpal bones, capable of the most flexion
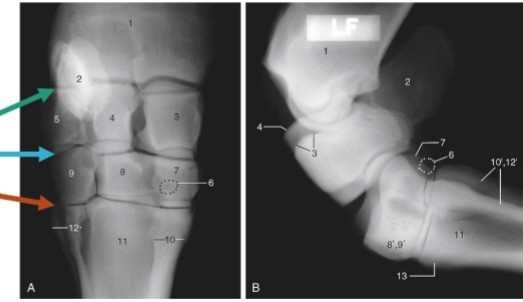
middle carpal joint
blue, between the proximal and distal rows of carpal bones, moderate flexion
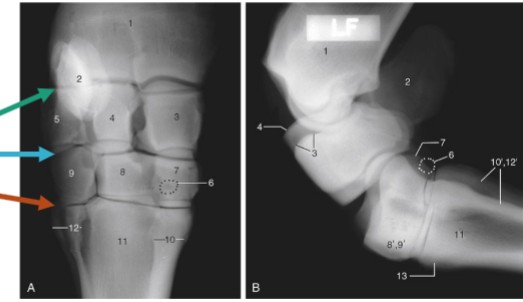
carpometacarpal
orange, between the distal row of carpal bones and the metatarsals, ver little motion
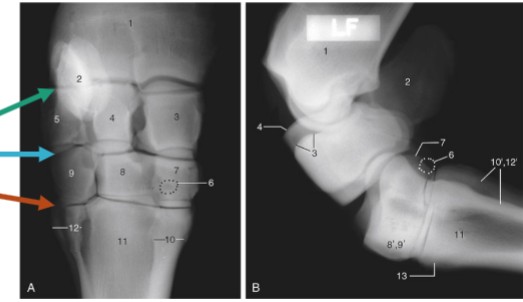
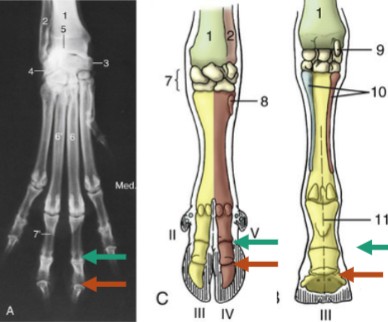
tarsocrural
red, between the tibia/fibula and the proximal row of tarsal bones (high motion)
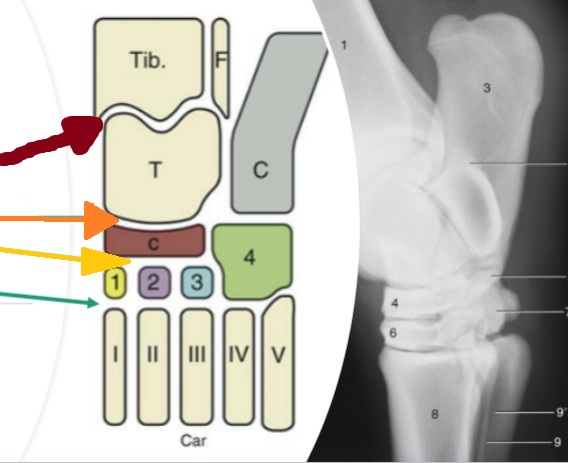
proximal intertarsal
orange, between the proximal row of tarsal bones and the central/4th tarsal bones (low motion)
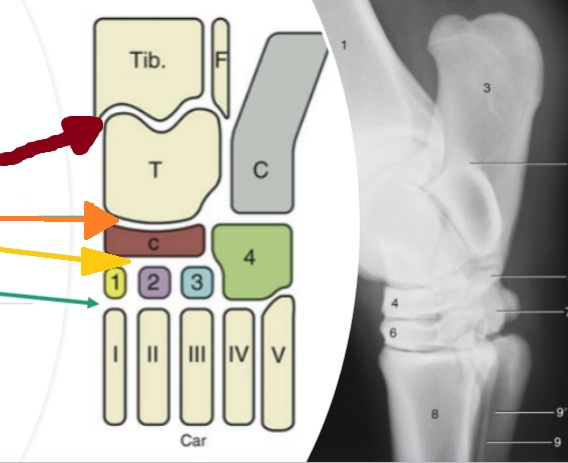
distal intertarsal
yellow, between the cental tarsal bone and tarsal bones I, II, and III (low motion)
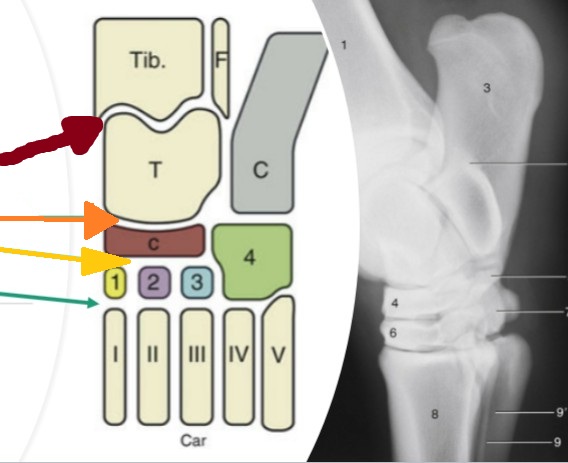
tarsometatarsal
teal, between the distal row of tarsal bones and the metatarsal bone (low motion)
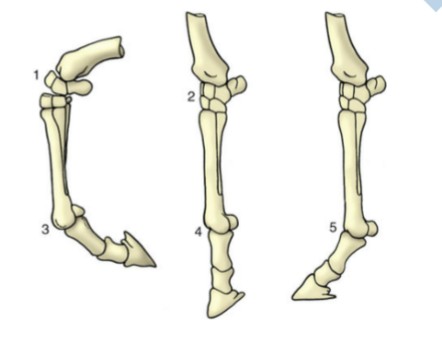
flexion
1, reduction in the angle between two segments of the limb
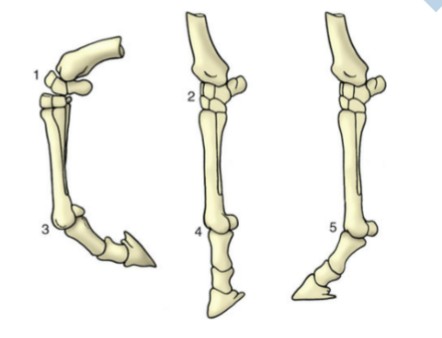
extension & alignment
2, opening of the angle between two segments of a limb, aligning those segments
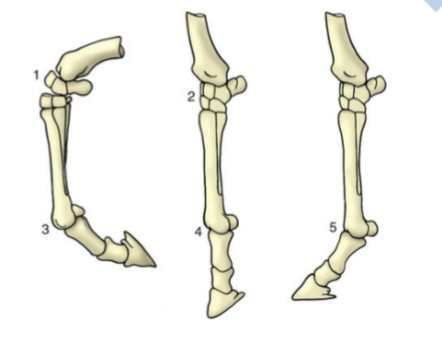
overextension
3, normal extension past straight alignment, mainly seen in distal limb
abduction
carrying moving part away from the median plane
adduction
carrying the moving part towards the median plane
rotation
a moving bone turning/spinning about the axis perpendicular to the articular surface
circumduction
combination of flexion/extension and adduction/abduction, allows for an ellipsoidal or circular movement, typically ball and socket joints
synarthrosis
immovable, ex: sutures between two skull bones
amphiarthrosis
slightly movable, ex: pelvic symphysis
diarthrosis
freely movable
plane joint
one flat surface slides over another
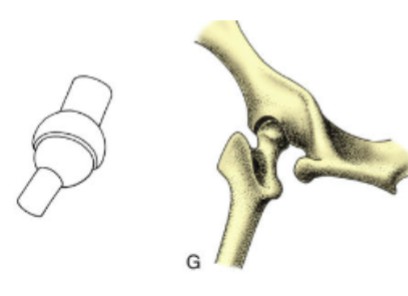
ball and socket joint
most versatile movement, multi-axial
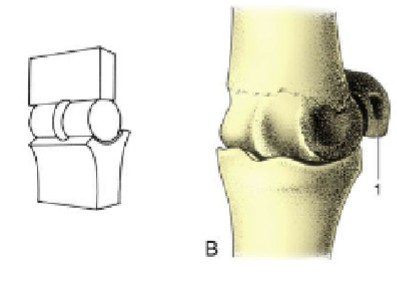
hinge joint
move in only one phase, one bone is cylindrical & other is shaped to receive it, elbow
pivot joint
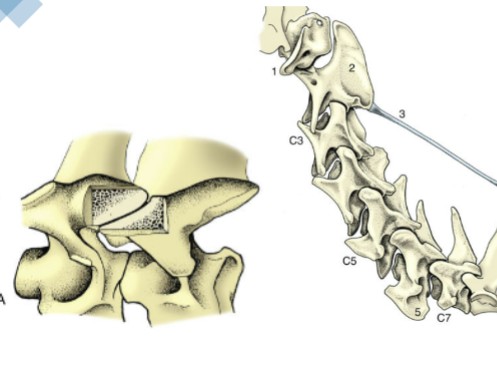
one bone is peg-shaped & the other forms a ring around it, atlantoaxial
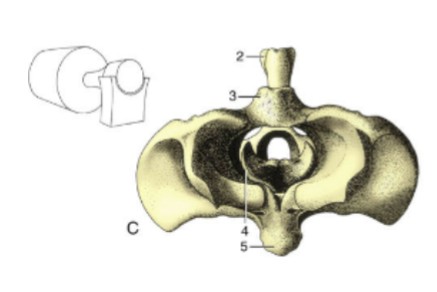
condylar joint
two knuckle-shaped condylar surfaces correspond with other bones’ concave surfaces
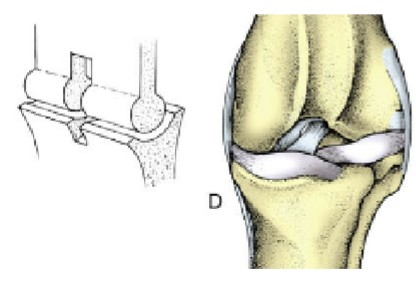
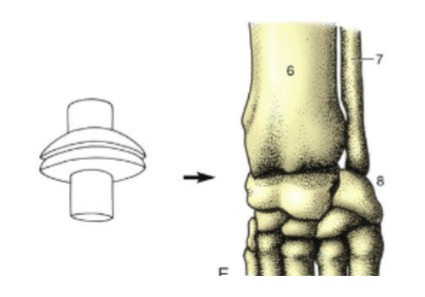
ellipsoidal joint
oval-shaped convex surface fits over a concave one
saddle joint
one convex surface articulates with a 90 degree rotated concave second surface