B2.2 Organelles and Compartmentalisation
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Organelles
Discrete structures in cells that are adapted to perform a specific function
Advantage of separation of the nucleus & cytoplasm into separate compartments
(in eukaryotes) keeping chromosomes in nucleus protects DNA
Gene expression is regulated by controlling what enters and exits the cell
Cell cycle control increases
Post-transcriptional modification of RNA
Process of changing & improving RNA molecules
Compartmentalisation
Organisation and separation of different functions/processes within specific areas within cells
Lysosomes contain:
High concentrations of enzymes
Phagocytosis
Plasma membrane engulfs a large particle
Phagocyte
Cells that perform phagocytosis
What does mitochondria produce?
ATP
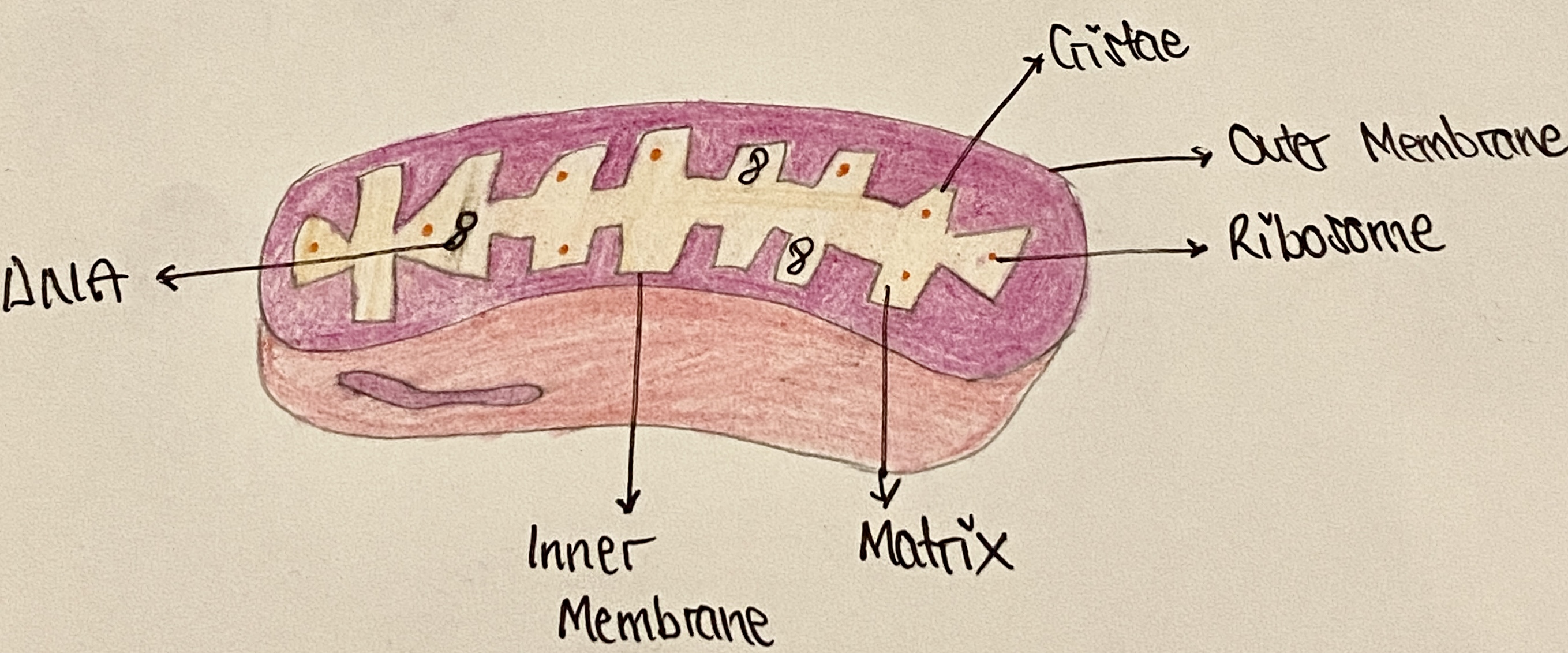
Adaptations of mitochondria
Double membrane with a small volume of intermembrane space
Large surface area of cristae
Compartmentalisation of enzymes and substrates of Krebs cycle in the matrix
Adaptations of chloroplast
Outer membrane- Exchange sions and metabolites
Inner membrane- Allows specific directions for molecules to go in and out of chloroplast
Stroma
Matrix- Citric Acid Cycle happens
Stroma in chloroplast
Colourless fluid around thylakoids
Nucleus
Info-processing organelle of cell
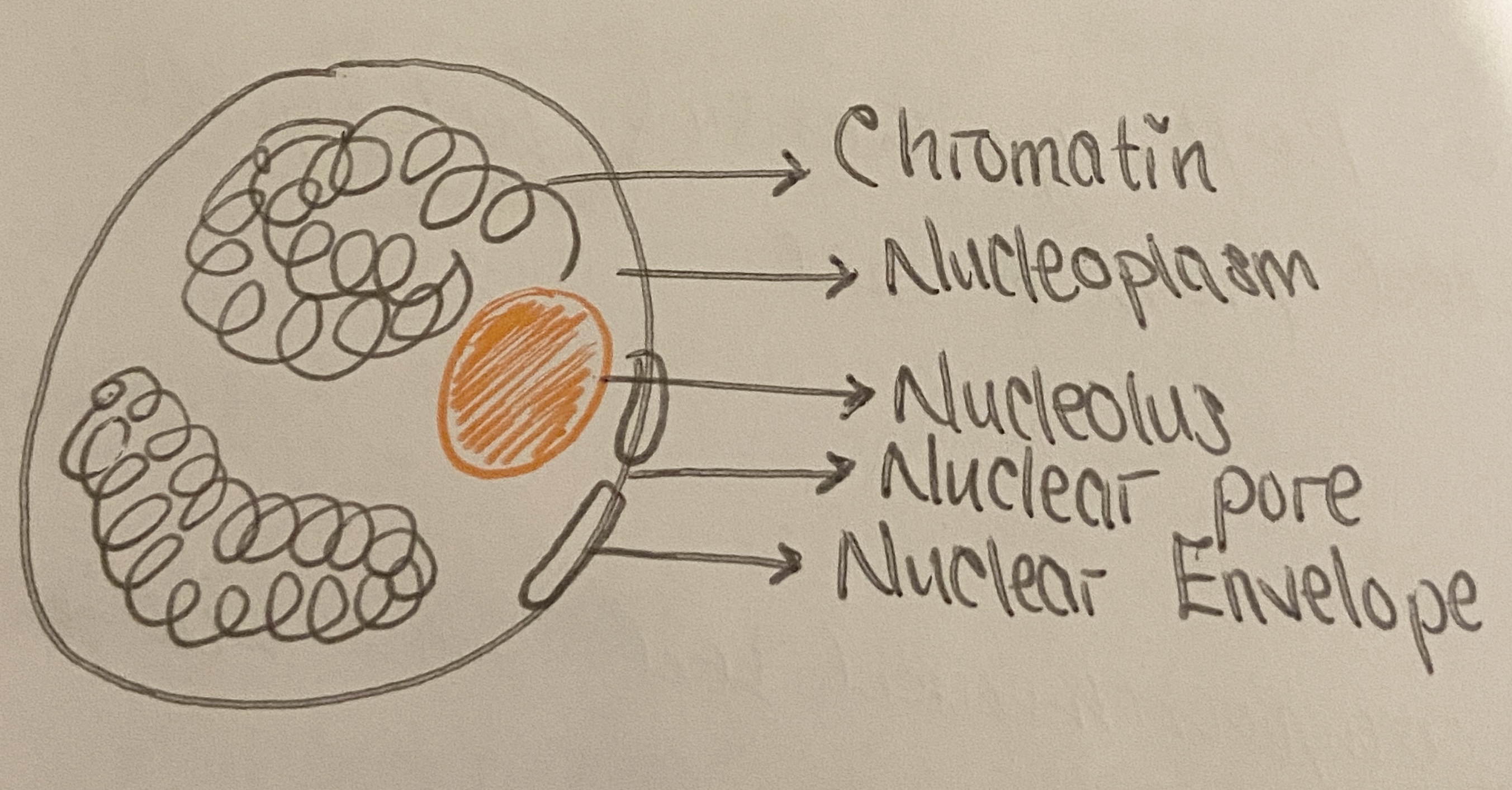
Parts of nucleus
Chromatin
Nucleus
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear pore
Nucleoplasm
Nucleus _________ and _________ each time most cells divide
disassembles, re-forms
rRNA
ribosomal RNA
Function of ribosomes
In eukaryotes
“Free ribosomes” In cytoplasm, synthesis proteins used within cell
“Bound ribosomes“ Attached to rER, synthesis proteins secreted from cell
Endomembrane System
System of compartmentalised sacs within eukaryotic cells
Cisternae
Flattened membrane-enclosed sacs in Golgi Apparatus
Role of Golgi Apparatus
Modifications of proteins & lipids
Name of entry face of Golgi Apparatus
Cis face
Name of exit face of Golgi Apparatus
Trans face
Clathrin
Protein that plays an important role in the formation of vesicles in cells
Function of Transport Vesicles
Transports proteins & lipids from one location to another in cell
Function of Secretory Vesicles
Transports proteins & lipids inside the cell to the plasma membrane
Endocytic Vesicles
Formed by invagination of the plasma membrane
Vesicle Fusion
Merging of vesicle and another organelle