Pythagorean Theorem and the converse, Pythagorean Theorem
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Hypotenuse
The longest side of a right triangle which is opposite the right angle.

5
a = 3, b = 4, c = ?
25
a = 7, b = 24, c = ?
10
a = 6, b = 8, c = ?
A triangle where one angle is 90 degrees.
Right Triangle
Yes
Does this forma right triangle? 8, 15, 17
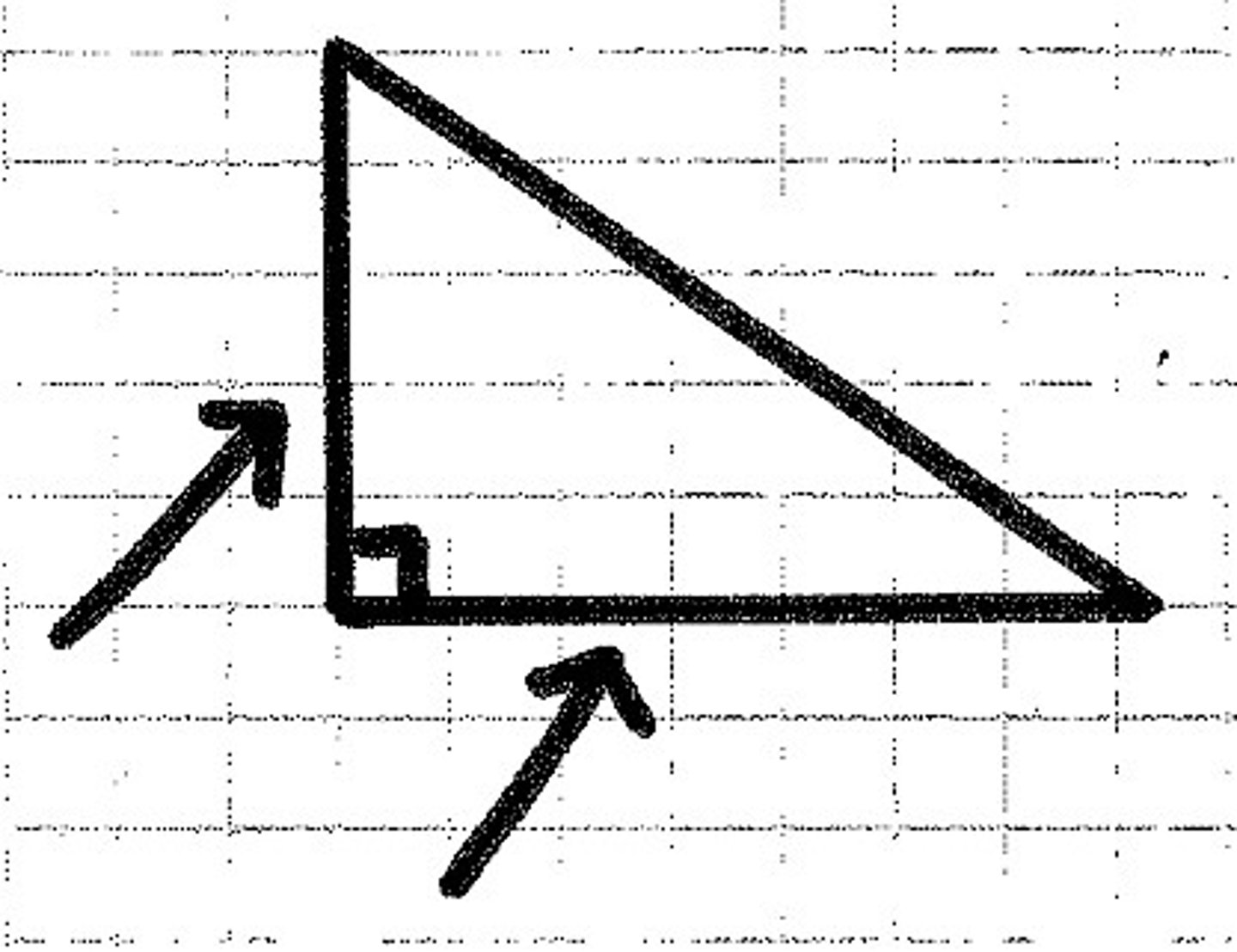
What part of the triangle is being shown?
legs
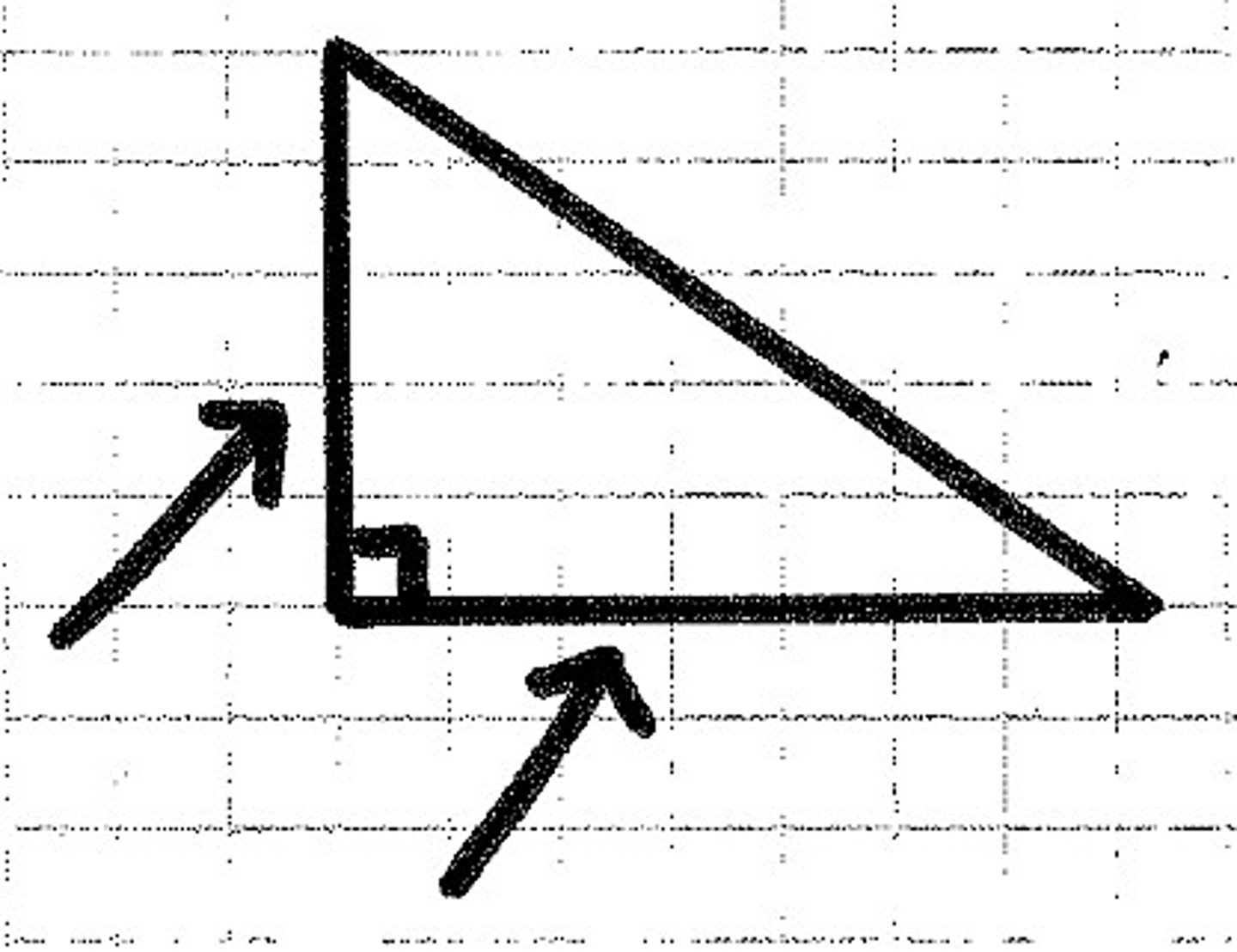
What part of the triangle is being shown?
hypotenuse
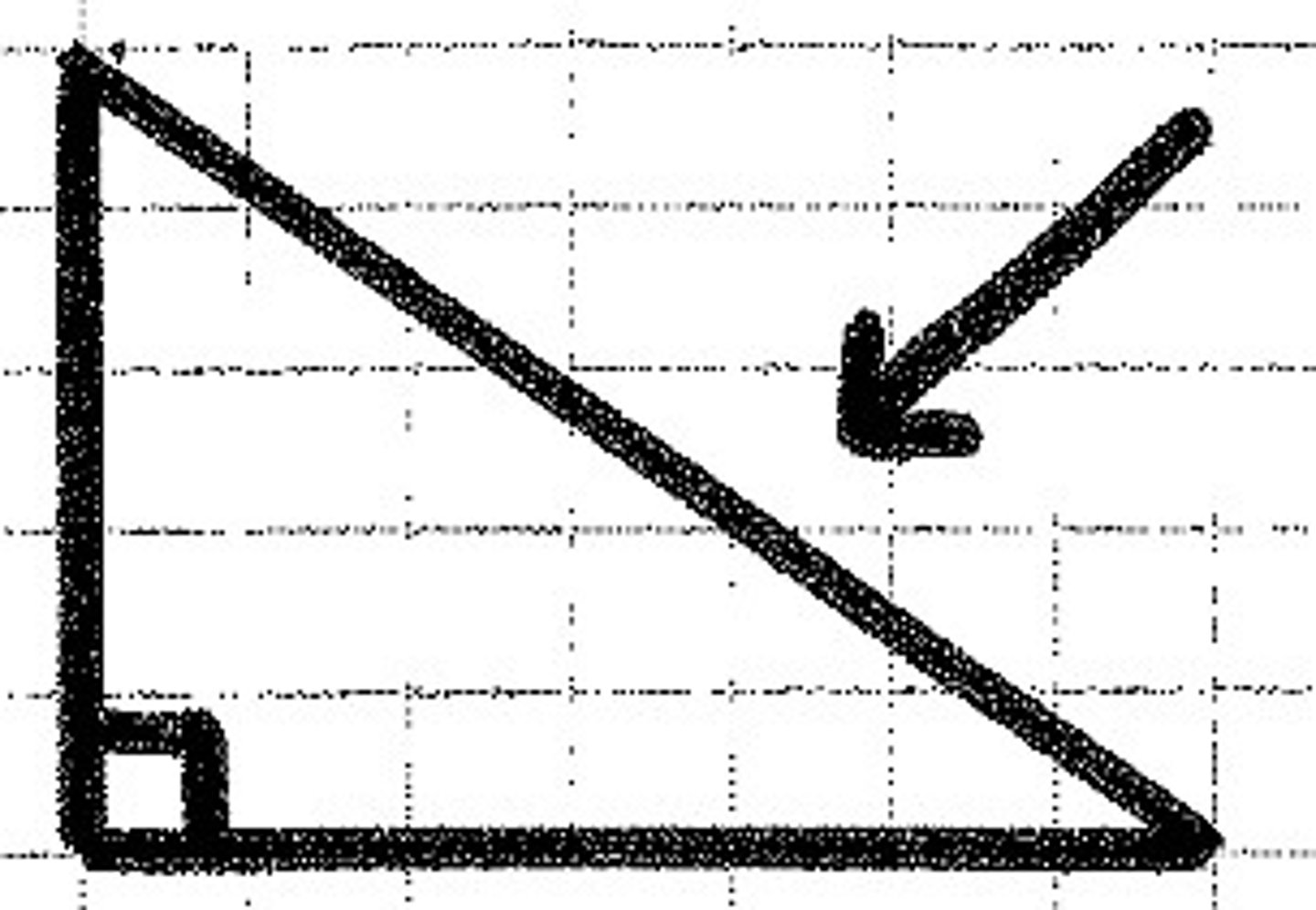
An angle of exactly 90 degrees.
right angle
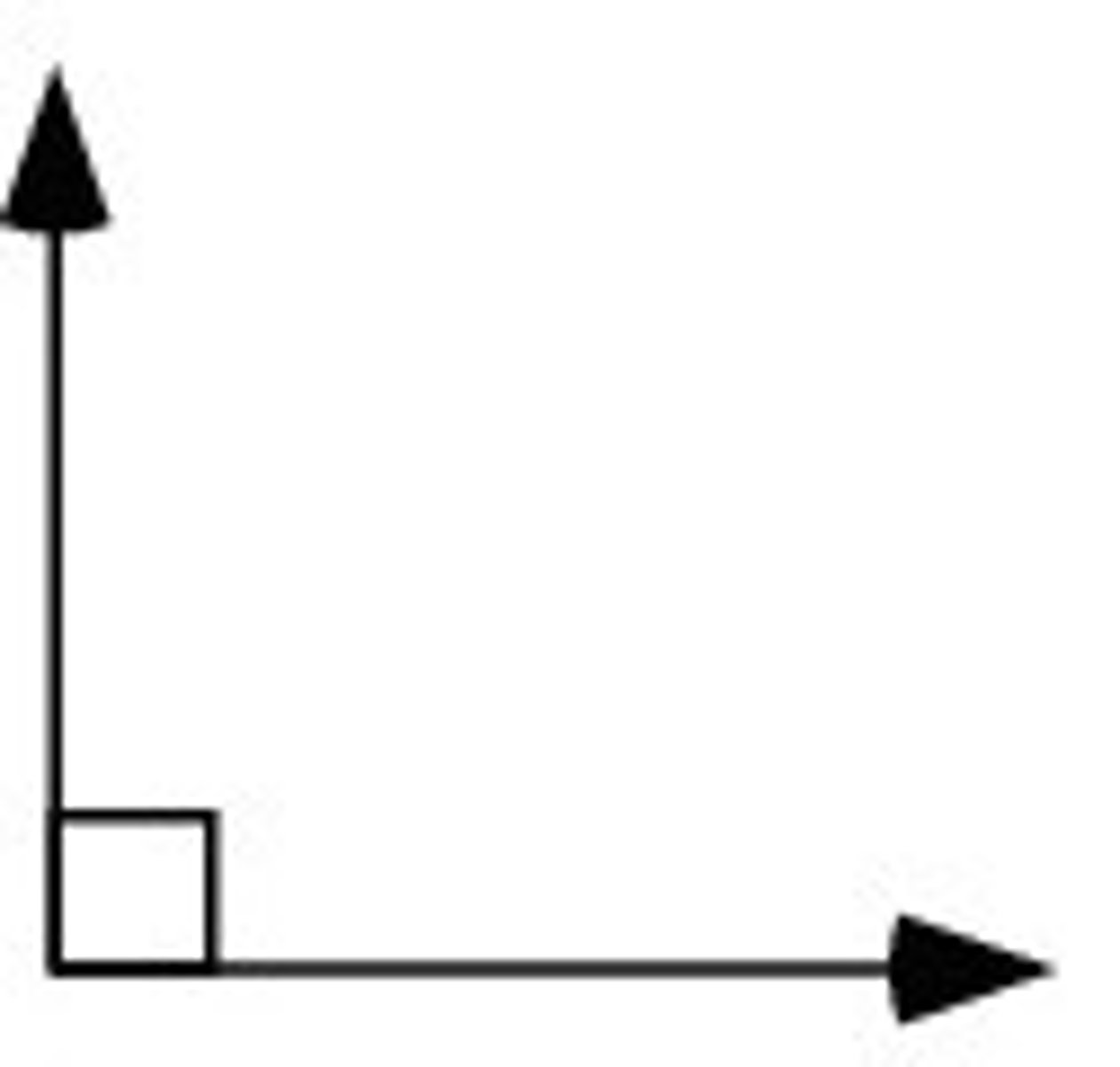
23.4
a = 18, b = 15, c = ?
No
Does it form a right triangle? 24, 25, 17
Pythagorean Theorem
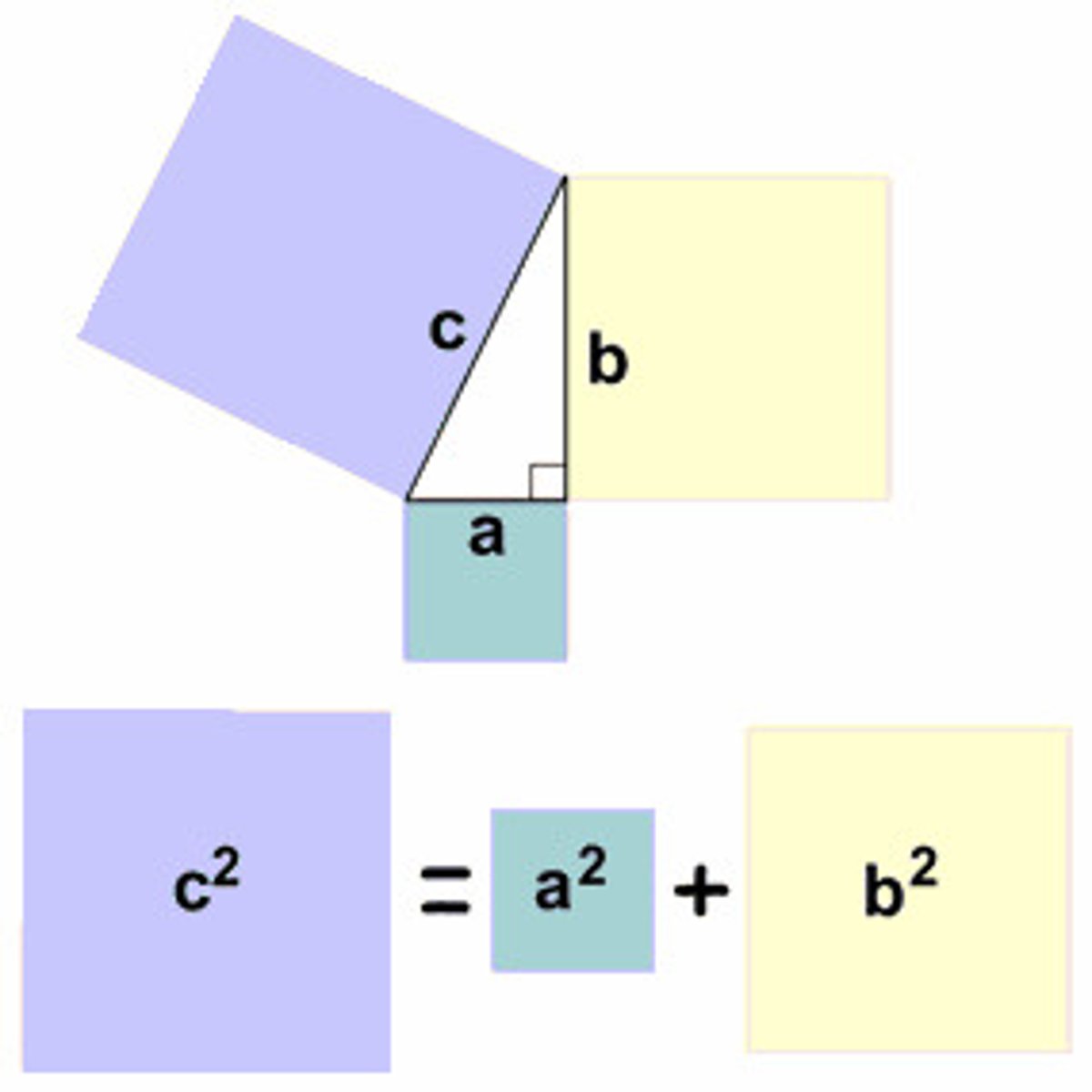
Legs
Sides that are adjacent (same vertex, share a common side) the right angle. There are two.
Hypotenuse
The side opposite the right angle
Right Triangle
A triangle that has one right angle (90 degrees) with 2 legs, and one hypotenuse.
leg
Either of the two shortest sides of a right triangle, they meet at a common vertex to form a right angle.
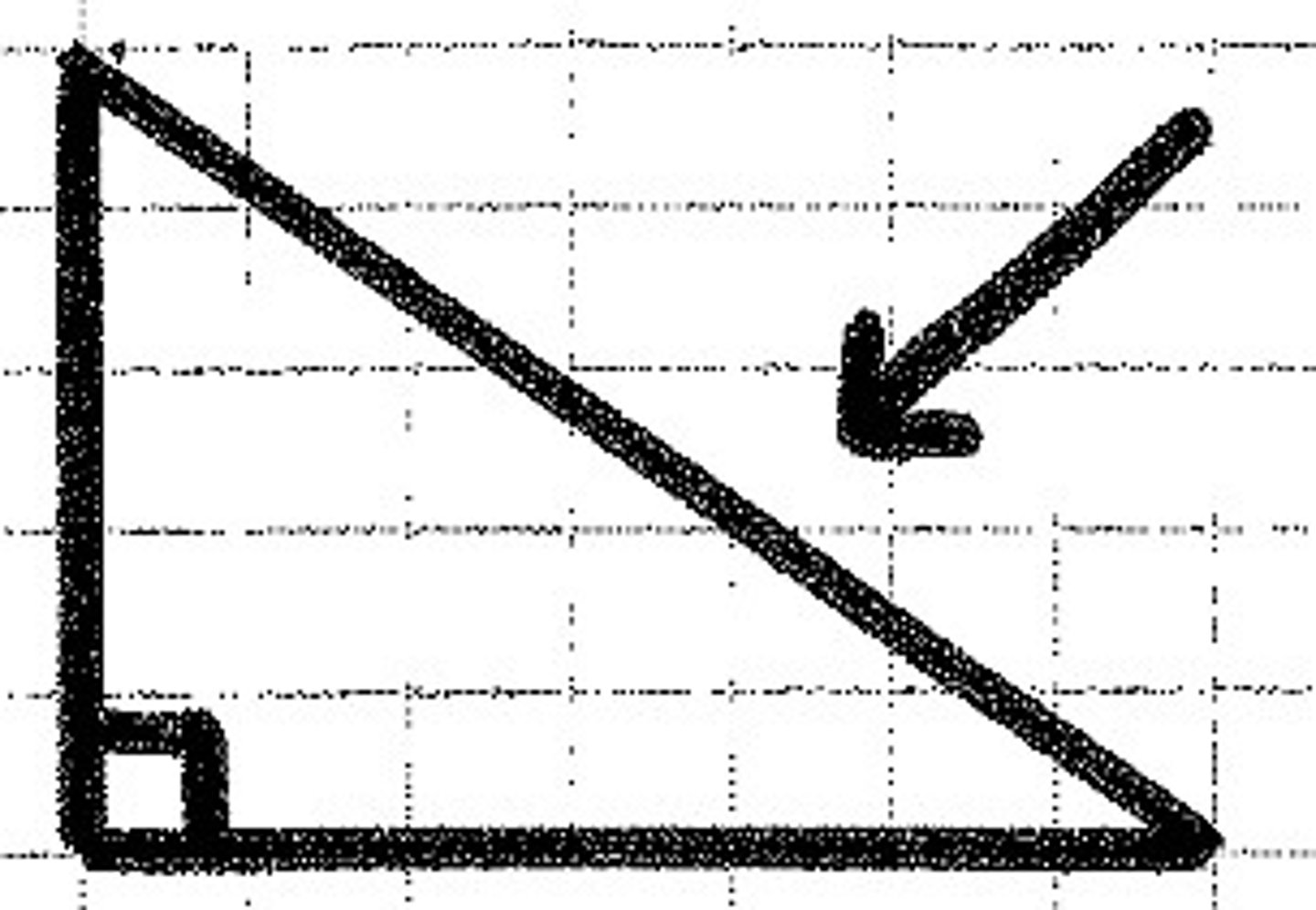
hypotenuse
The longest side of a right triangle. It is always opposite of, and never is a part of, the right angle.
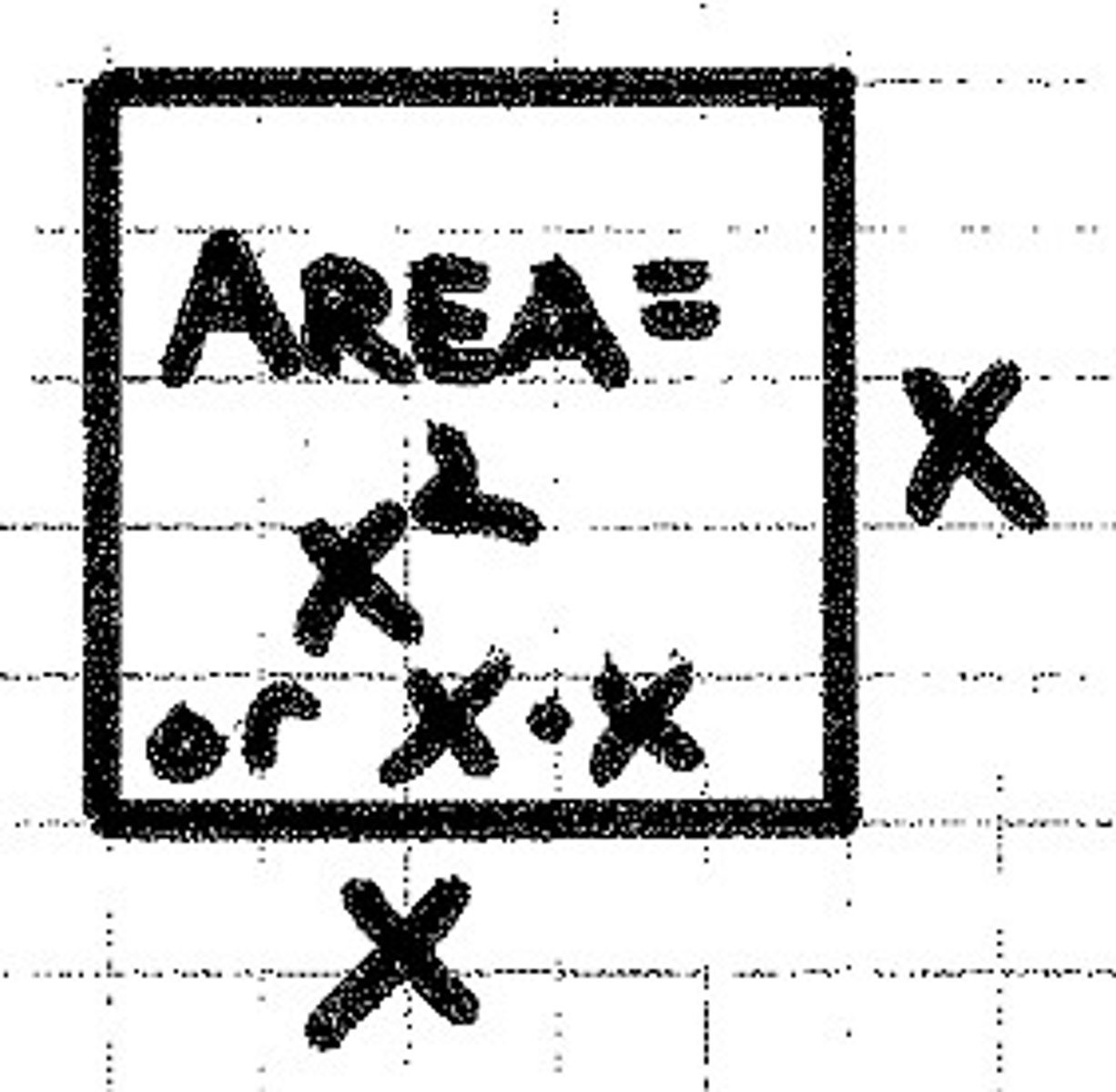
square
The result of multiplying a number by itself.
perfect square
A square with a whole number root.

Pythagoras
Greek philosopher, 570-495 BC. There is no evidence that Pythagoras himself worked on or proved the Pythagorean Theorem, which was used previously by Babylonians and Indians.

inverse operations
Math operations that reverse the effect of each other.
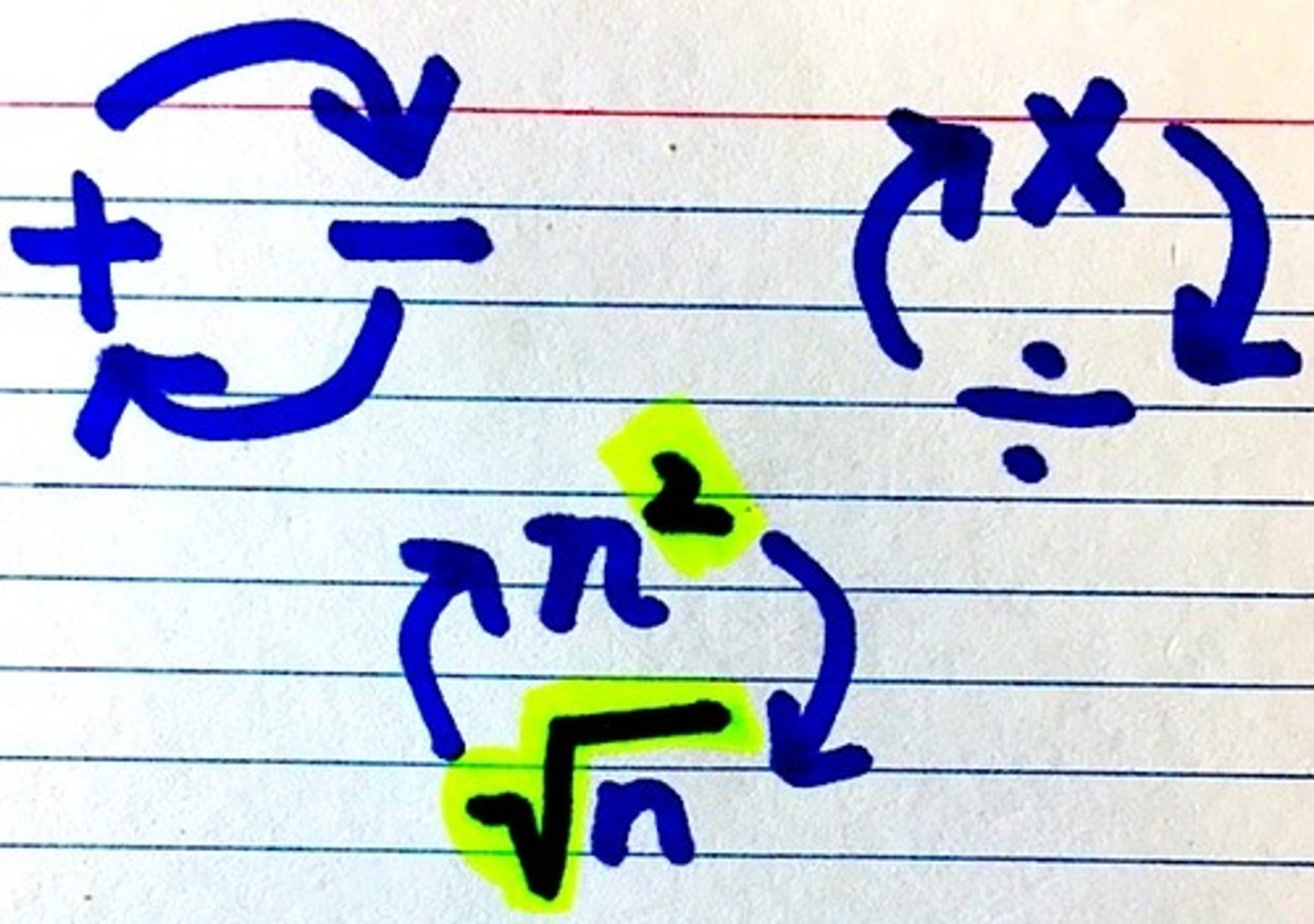
32
Leg a- 20 Leg b- 25
15.2
Leg a- 6 Leg b- 14
right triangle
a triangle with a 90 degree angle
Right
The Pythagorean theorem can only be used with ___________ triangles.
25
If the legs of a right triangle are 7 and 24, what is the hypotenuse?