Unit WS-- PHSC
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Wave
is a disturbance that moves through a material, carrying energy with it as it
goes.
If the frequency remains the same, increasing the wave speed will __________ the wavelength, and decreasing the wave speed will ___________ the wavelength.
increase
decrease
As the longitudinal or transverse wave pulse moves along the spring does it transfer energy?
Yes it does, because it is showing a contact push/ pull interaction.
The medium for any wave is the material for which it moves.
For example: the oceans medium is simply the water
The back & forth movement of a persons hand got the wave pulse started and, as such, is called
the source of the wave
Do you think the amplitude and/or frequency of the wave will change its wavelength?
A. Changing the amplitude will change the wavelength but changing the frequency will not.
B. Changing the amplitude will not change the wavelength but changing the frequency will.
C. Changing either will change the wavelength.
D. Changing either will not change the wavelength.
The frequency of a wave depends only on the ________ of its source, and they are numerically equal. Increasing the source frequency will increase the __________ by the exact same amount.
frequency
wave frequency
The amplitude of a wave depends only on the _____ of its source, and they are equal. Increasing the source amplitude will increase the _________ by the same amount.
amplitude
wave amplitude
1. For waves moving along a string, the wave speed depends only on the tension. The greater the _________, the faster the waves move along the string.
tension
If the wave speed remains the same, increasing the frequency will _______ the wavelength, and decreasing the frequency will ___________ the wavelength.
decrease
increase
In order for a wave to exist, three conditions must be present:
i) a source to start
the disturbance; ii) a medium (material) for the wave to move through; and
iii) a
mechanism by which the disturbance can be transmitted from one part of the medium
to the next.
What are the type types of waves?
Transverse and longitudinal
If the child at the other end now pulls the rope tighter, but still moves her hand up and down the same frequency, what will happen to the speed at which the wave moves from the child to the other?
A. the wave speed will remain the same
B. the wave speed will increase
C. the wave speed will decrease
In the previous question, when the rope is pulled tighter, what will happen to the wavelength of the wave?
A. the wavelength will stay the same
B. the wavelength will become longer than 1.5m
C. the wavelength will become shorter than 1.5m
A transverse wave
is one
in which the individual
parts of the medium move
in a direction that is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the
wave (side-to-side).
Why does amplitude of the wavefront decrease with distance from source?
Each wavefront carries the same amount of energy from the source, but as it moves away the energy spread out over a larger and larger circle.
So each fixed part of the wavefront carries less energy
The energy carried by the wavefront is related to its amplitude, so if theres less energy carried by a part of the wavefront that means its amplitude would be less. Thus, the peaks become less bright and the valleys become less dark further from the sourc.e
What is an example of a transverse wave?
waves on a string, surface water waves, and some types of earthquake & spring waves
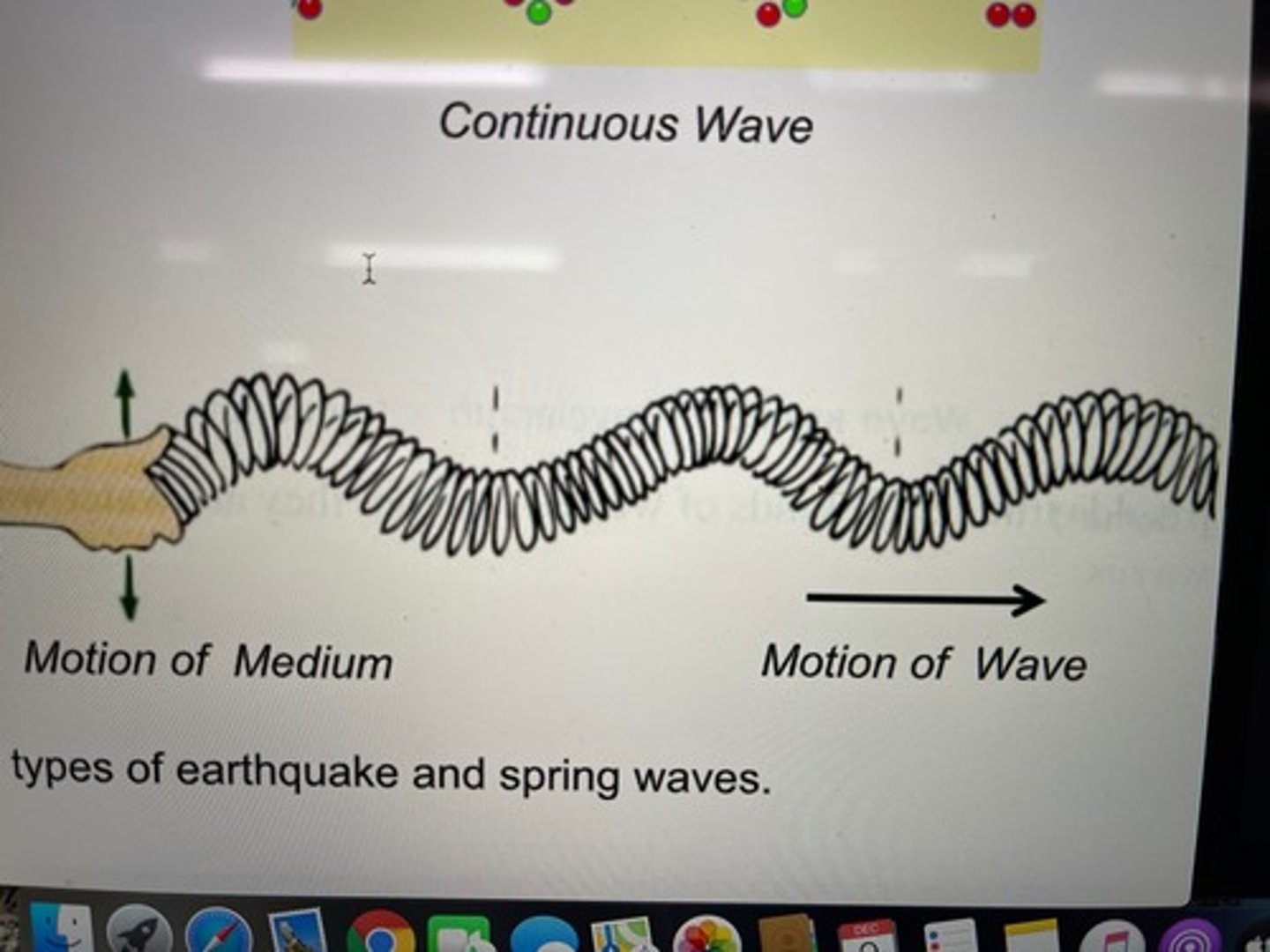
A longitudinal wave
is one in which the individual
parts of the medium move
in a direction that is aligned with the direction of motion of the wave (backward and forward).
What is an example of a longitudinal wave?
sound waves & some other types of earthquake & spring waves

Characteristics of a continuous wave
A continuous wave consits of a regular series of identical peaks & valleys
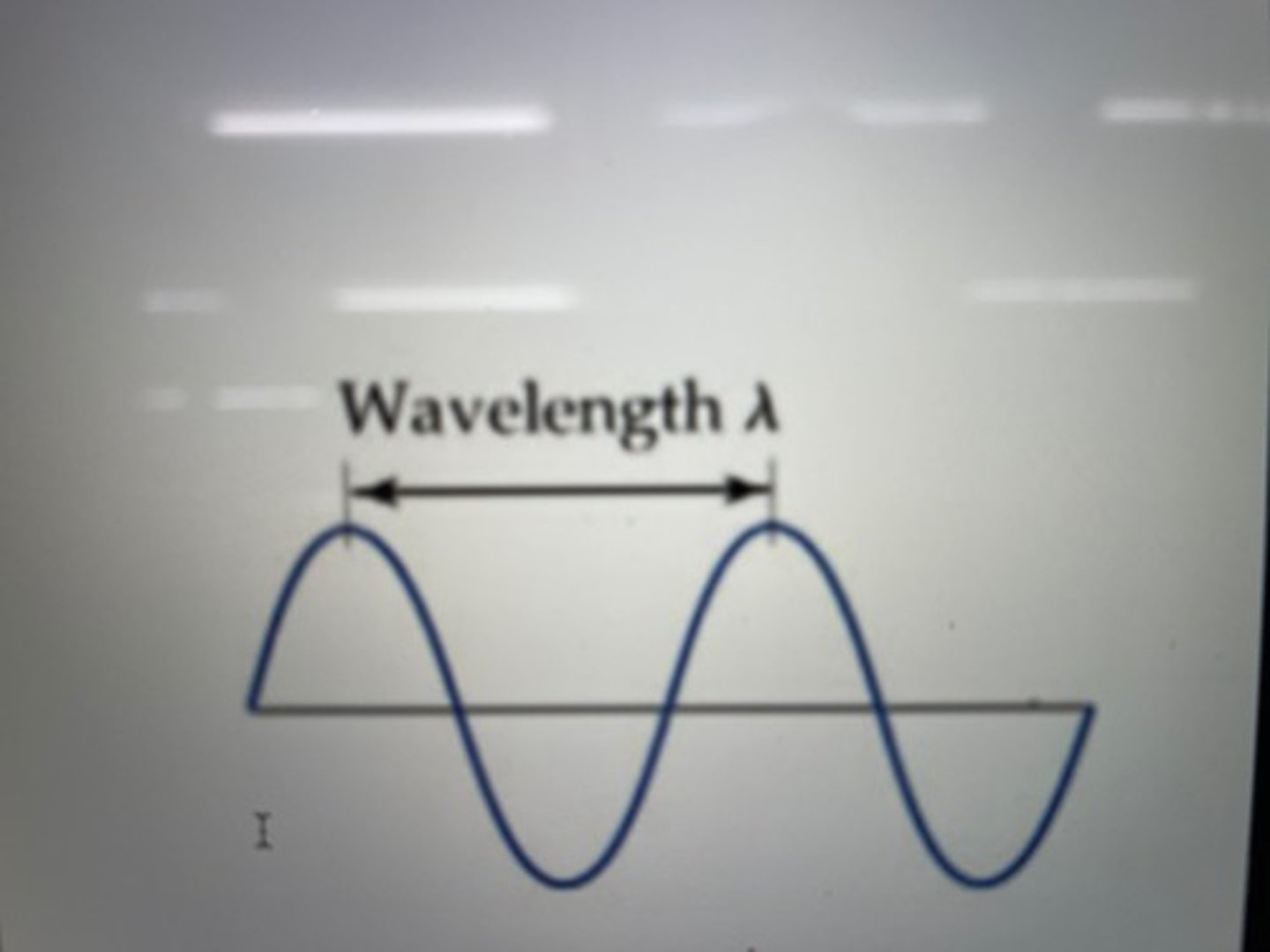
Wavelength
is the distance between neighboring peaks & valleys.
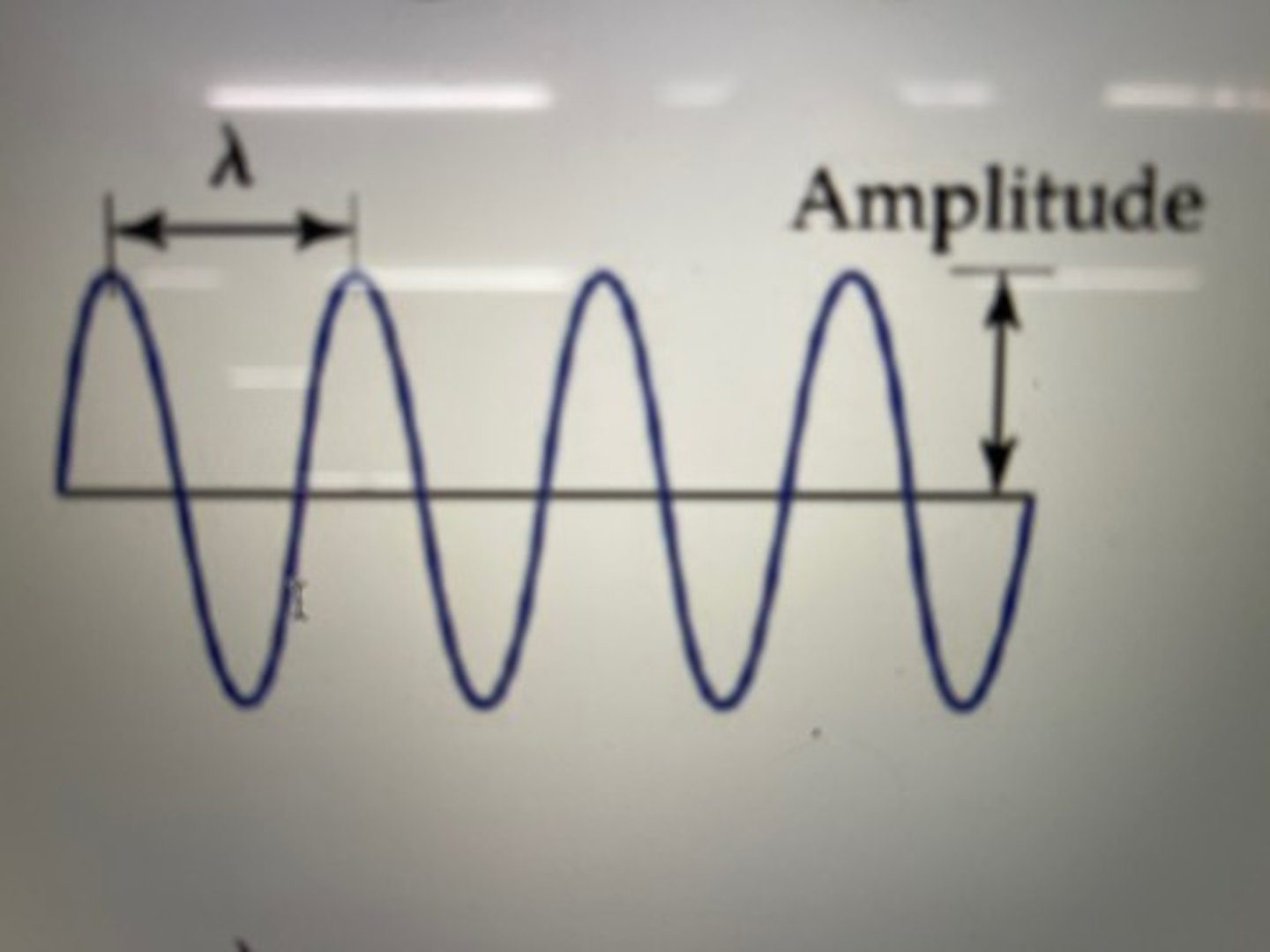
Amplitude
is the maximum distance any part of the medium moves away from its equilibrium (undisturbed) position
Frequency
is a measure of how often the medium moves up and down *or back & forth for a longitudinal wave).
Both the amplitude and frequency of a wave are equal to the amplitude and frequency of the source that is creating it:
Thus, it is only the motion of the source that determines a wave's amplitude and frequency
The speed with which waves move through is determined solely by the
characteristics of the medium itself
For waves that move along a string, the speed of the wave depends on the
tautness of the string--- the more taut the string, the faster the wave moves.
The wavelength of a continuous wave is realated to the
speed and frequency

If peaks are being created more often (at a higher frequency), each peak will not have time to get as far through the medium by the time the next peak is created, therefore there will be
less distance between peaks.
If the peaks are moving more quickly (higher seed),
each peak will be able to move further before the next peak is created
2D & 3D waves
Some waves move through their medium in two dimensions (surface water waves) or even in 3D (sound waves).
Wavefront
a representation in which lines are drawn to show the position of the peaks. We sometimes draw arrows to show the direction they are moving.
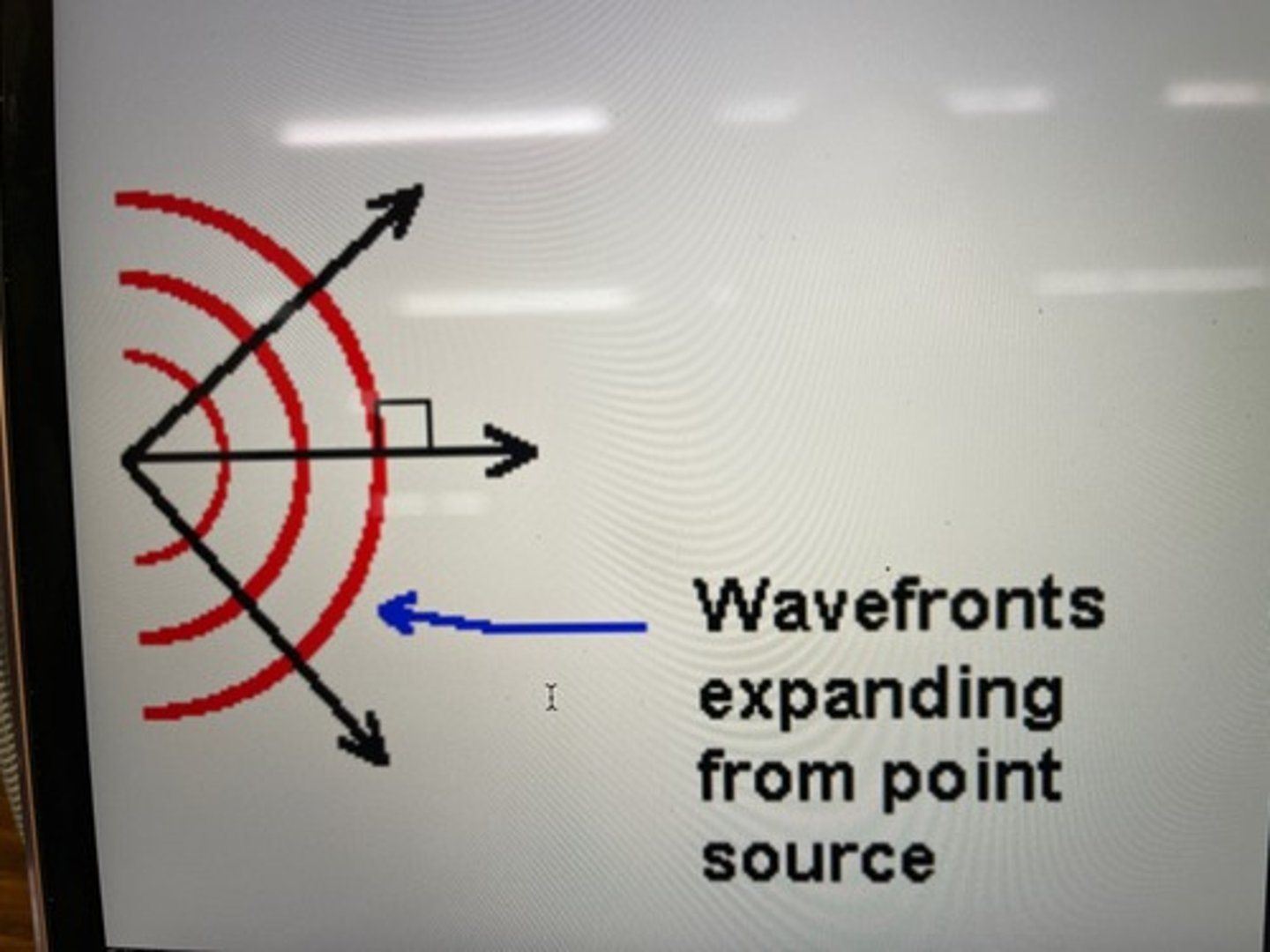
Reflection
when waves meet a barrier in the medium, they reflect from it.
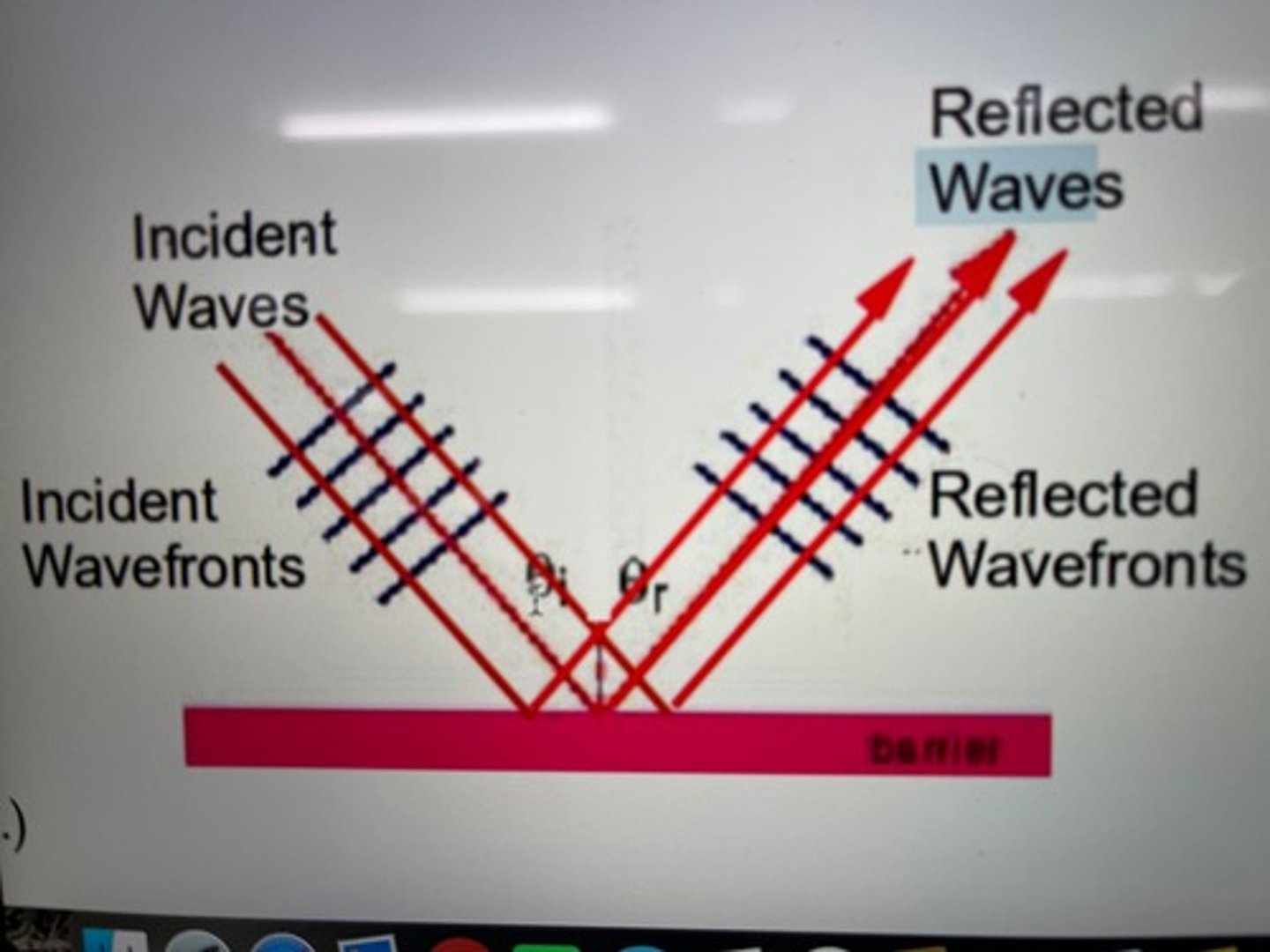
For 2D and 3D waves the Law of Reflection tells us that the reflected wave will leave the boundary at the ..
same angle as the incoming wave. (For 1D waves, the reflected wave simple travels back along the string/spring in opposite direction)
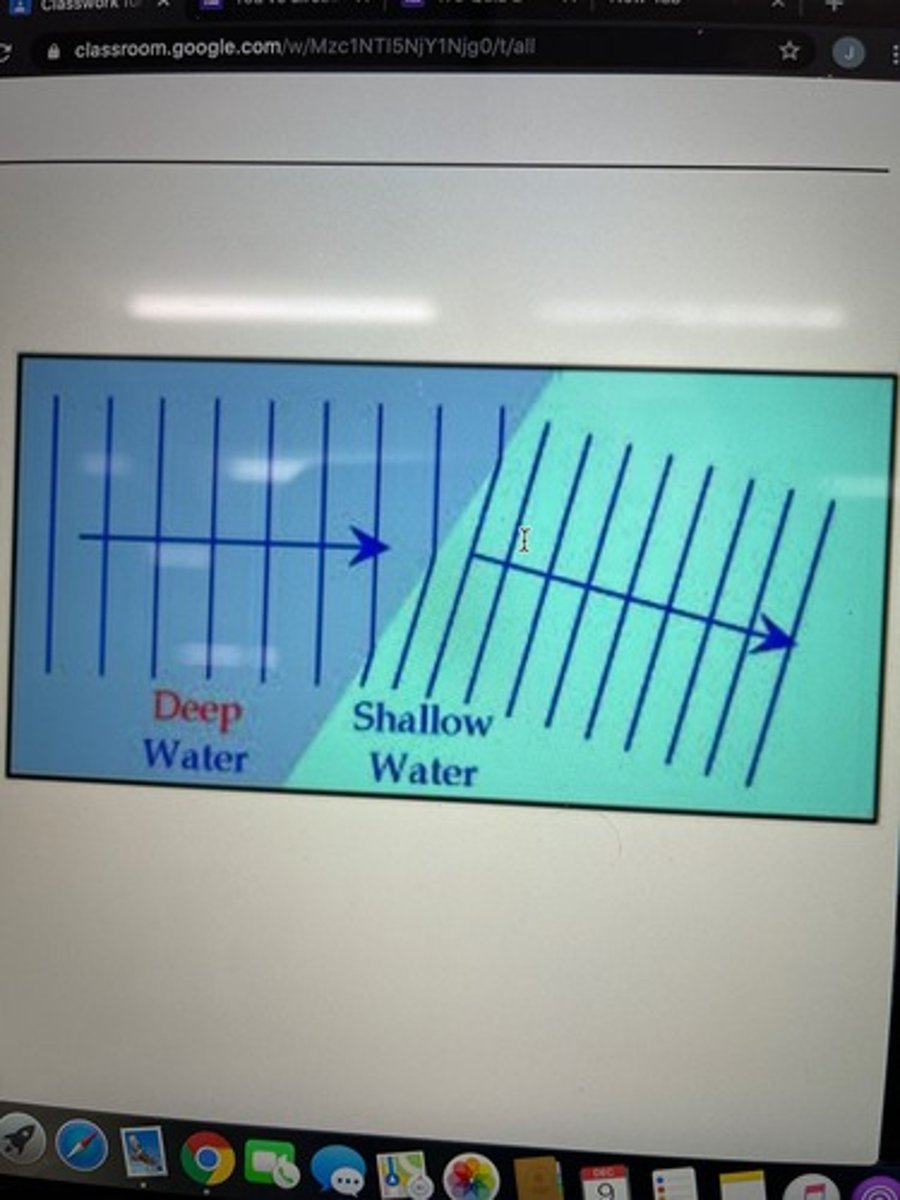
Refraction
when waves pass a boundary and move into a region of the medium in which the wave speed is different, their wavelength will change accordingly. (the frequency doe NOT change)
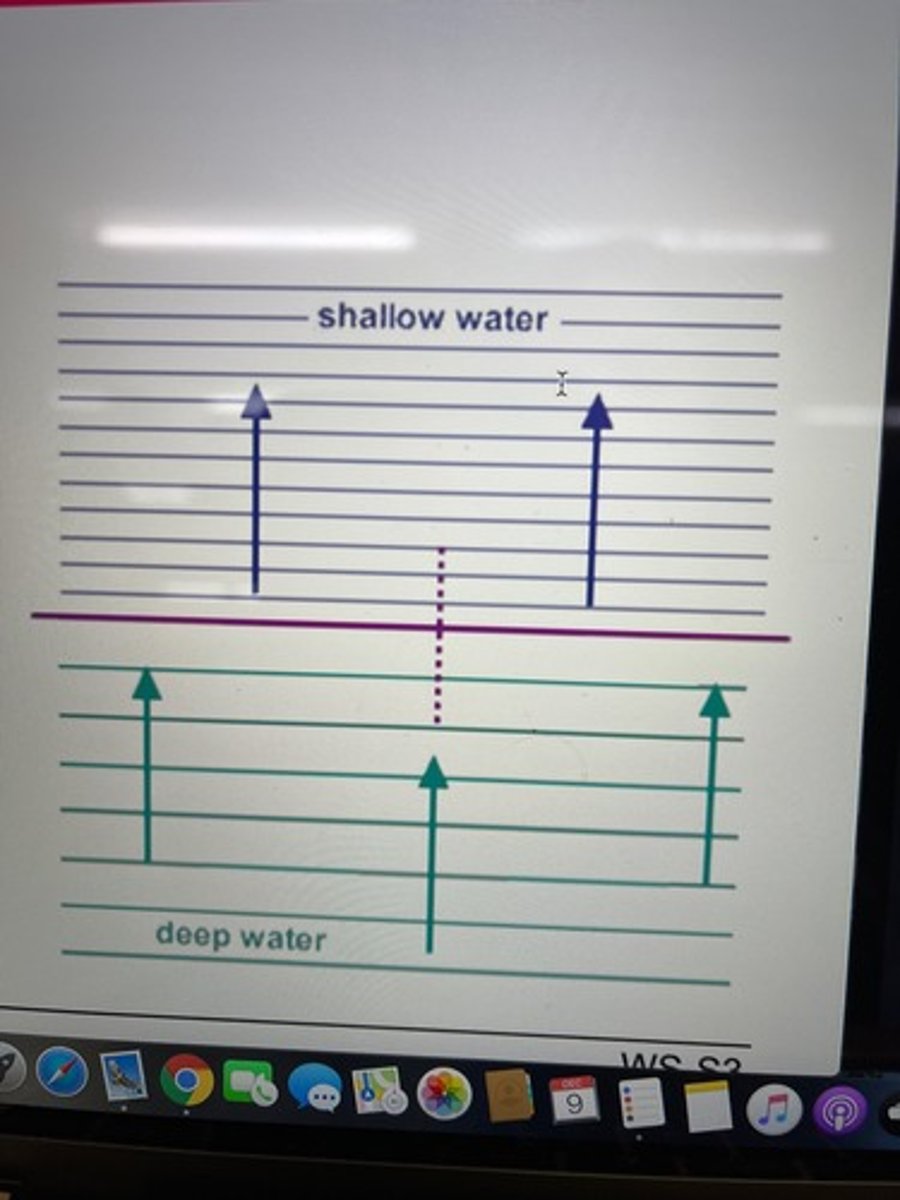
Water travels faster when the water is
deeper
Differenation of point, line, & ideal line sources:
Insert Image
If the water waves were to change their speed as they enter a region where the depth of the water changes, what would then happen to the wavelength of the waves (distance between peaks or valleys)?
A. The wavelength will not change.
B. The wavelength will become shorter when they slow down and longer when they speed up.
C. The wavelength will become longer when they slow down and shorter when they speed up.
A swimming pool has a gradually changing depth from one end to the other. To divide the pool into two areas, a lifeguard throws a rope across it at exactly halfway along its length. This creates some straight waterfronts that travel toward each end of the pool.
Which end of the pool will the wavefronts reach first?
A. The deep end.
B. The shallow end.
C. The wavefronts will reach both ends at the same time.
Waves traveling in water:
1. Do waves travel faster in the deeper or shallower water?
a. Deeper water: the wavelength is bigger
2. In the situation where the wave crosses a boundary into a region of deeper water, do the waves speed up, slow down, or stay at the same speed?
a. Deeper water=speed up
3. In the situation where the waves cross a boundary into a region of shallow water, do the waves speed up, slow down, or stay the same speed?
a. Shallower water= slow down
4. In the situation where the waves speed up, does the wavelength increase, decrease, or remain the same?
a. Waves speed up= wavelength Increases
5. In the situation where the waves slow down, does the wavelength increase, decrease, or remain the same?
a. Waves slow down= wavelength decrease
When the wavefronts cross the boundary at an angle, they will change direction in a phenomenon known as refraction:
This occurs because different parts of the wavefronts change speed at different times
Consider a line of people, like the line you considered earlier, but closely packed, like particles in a solid.
What actions could cause an involuntary wave through this line, and what kind of wave would it start? The answer below should both describe involuntary wave and describe the type of wave pulse accurately.
A. The person at the front of the line stretches her body to the side. It would start a transverse wave pulse.
B. Somebody runs into the last person in line, and bumps him accidentally. It would start a transverse wave pulse.
C. The person at the front of the line falls backward into the person behind him. It would start a longitudinal wave pulse.
D. The person at the front of the line stretches her arms out while yawning. It would start a longitudinal wave.
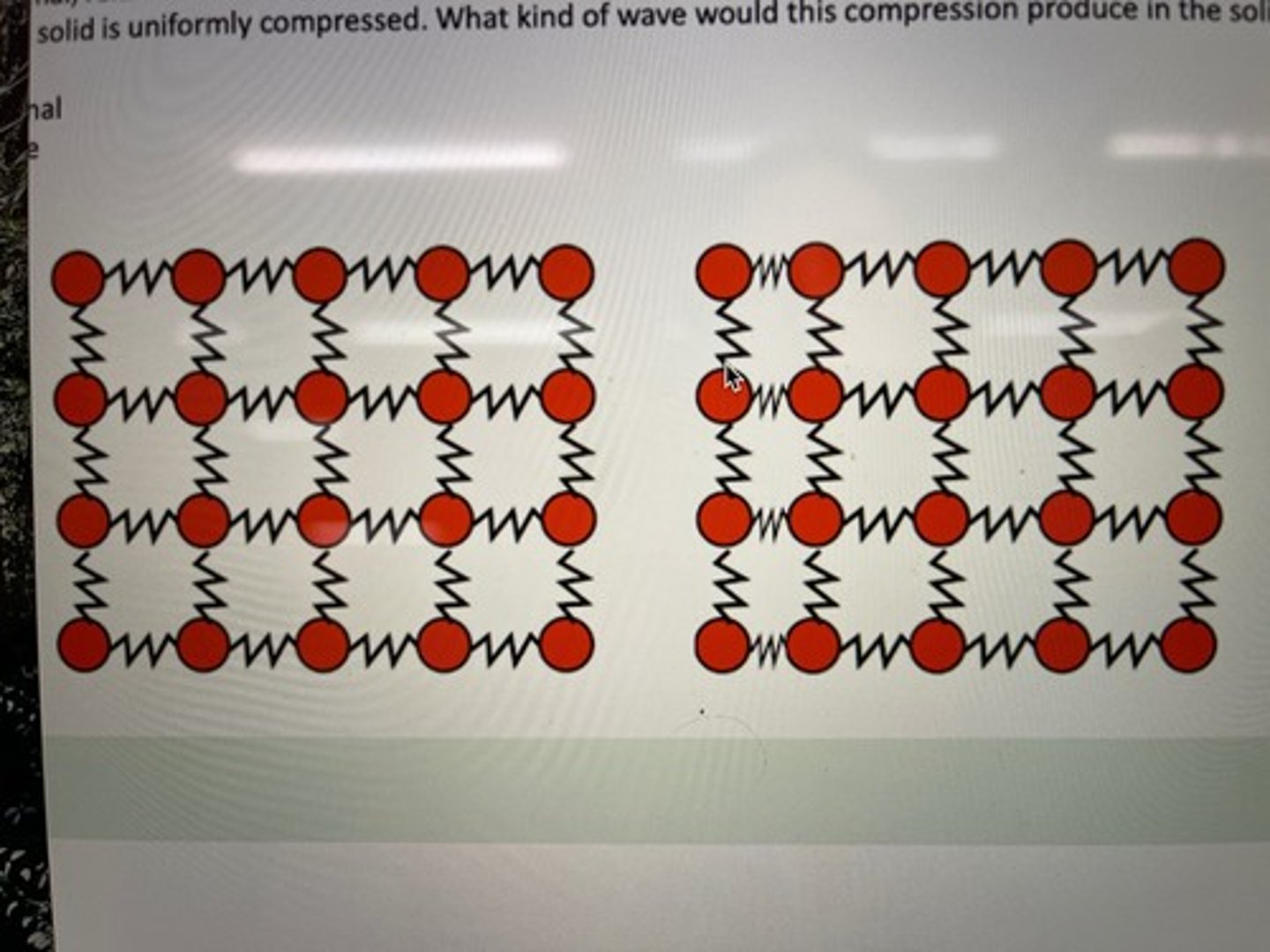
Consider a two-dimensional model of a solid like the one shown below. The left picture represents the solid in its normal, relaxed state. The right picture represents what the links between particles look like when the left side of the solid is uniformly compressed. What kind of wave would this compression produce in the solid?
A: Longitudinal
B: Transverse
C: Neither
D: Both
In general, why does a toy car change direction when crossing a boundary between two surfaces, such as hard plastic and carpet, on which its speed is different?
A. The wheels of the car move at a different speeds on each surface, so the direction they move in is different.
B. Between the time the first wheel crosses the boundary and the last wheel of the car does so, the car wheels are moving at different speeds. This causes the car to turn left or right.
C. Between the time the first wheel of each axle of the car crosses the boundary and last wheel of each axel does so, the wheels on the same axle are moving at different speeds. This causes the car to turn left or right.
D. The car turns slightly crossing the boundary because the amount of friction the car experiences on each surface is different, so the interaction between the car and the surface changes, which pushes the car slightly to the left or right.
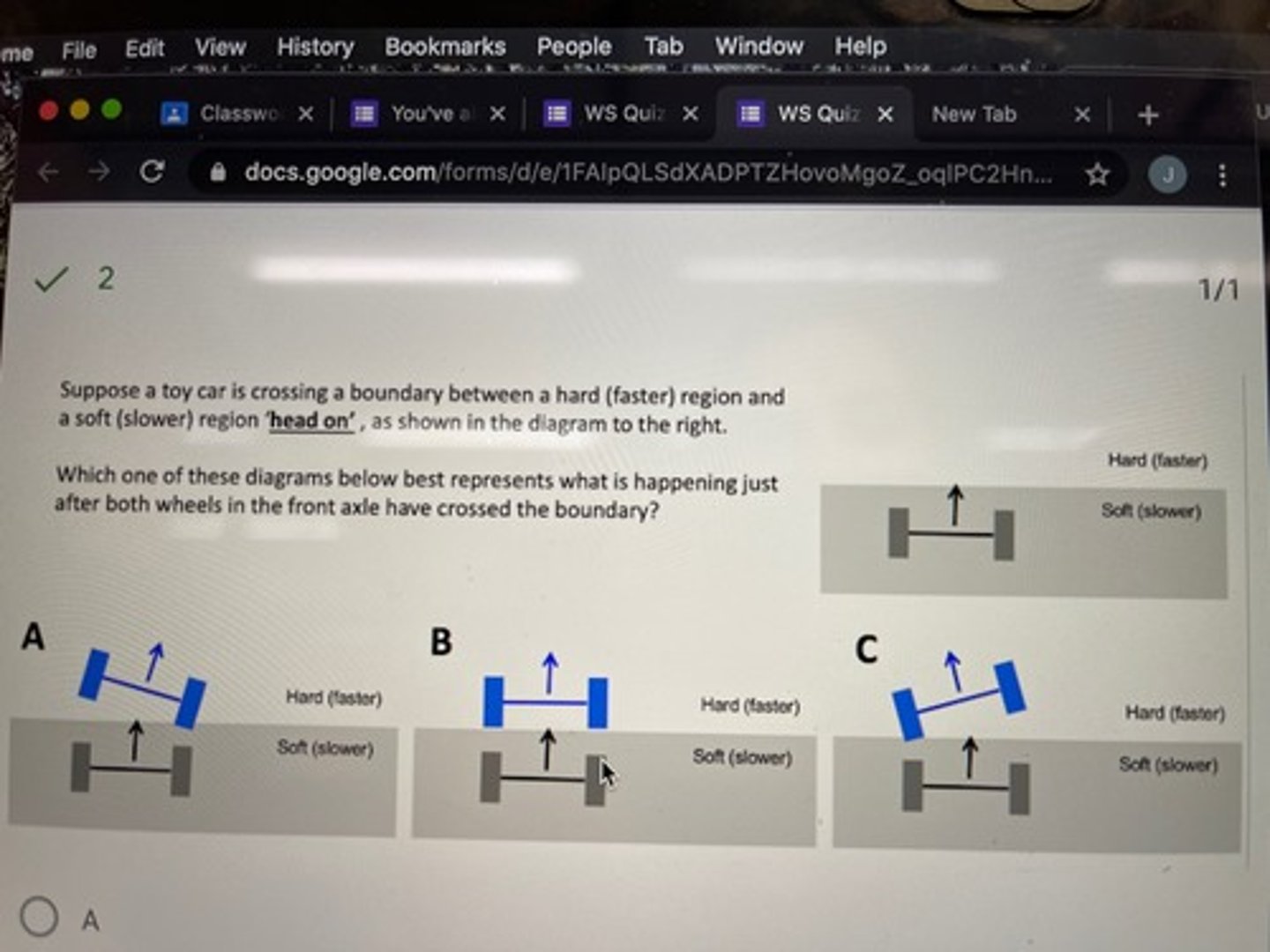
Suppose a toy car is crossing a boundary between a hard (faster) region and a soft (slower) region "head on", as shown in the diagram.
Which one of these diagrams below best represents what is happening just after both wheels in front axle have crossed the boundary?
A: slightly turning to the right
B: Not turning at all (Because neither wheel will cross the boundary sooner than the other so there will be no turn)
C: slightly turning to the left
Suppose water waves are moving from the deep end to the shallow end of the pool. That is, the waves are moving into a medium of shallow water, where they slow down. In what direction will the waves turn slightly and why? Choose the best explanation below.
I
A. The waves will turn slightly to the left, because the left side of each wave front hits the boundary first and slows down, moving more slowly than the right side until the right side of the wave front reaches the boundary. This causes the wave to veer slightly to the left.
WRONG answer: The waves will turn slightly to the left, bc the right side of each wave front hits the boundary first and slows down, moving more slowly than the left side until the left side of the wave front reaches the boundary. This causes the wave to veer slightly to the left
