AP World Unit 5 - Age of Revolutions
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
The Enlightenment
movement that began in Europe in the late 1600s as people began examining the natural world, society, and government; also called the age of reason
Voltaire
French philosopher and writer whose works often attacked injustice and intolerance.

French Revolution of 1789
Period of radical social and political change in a major absolutist European power, ending with the execution of their King

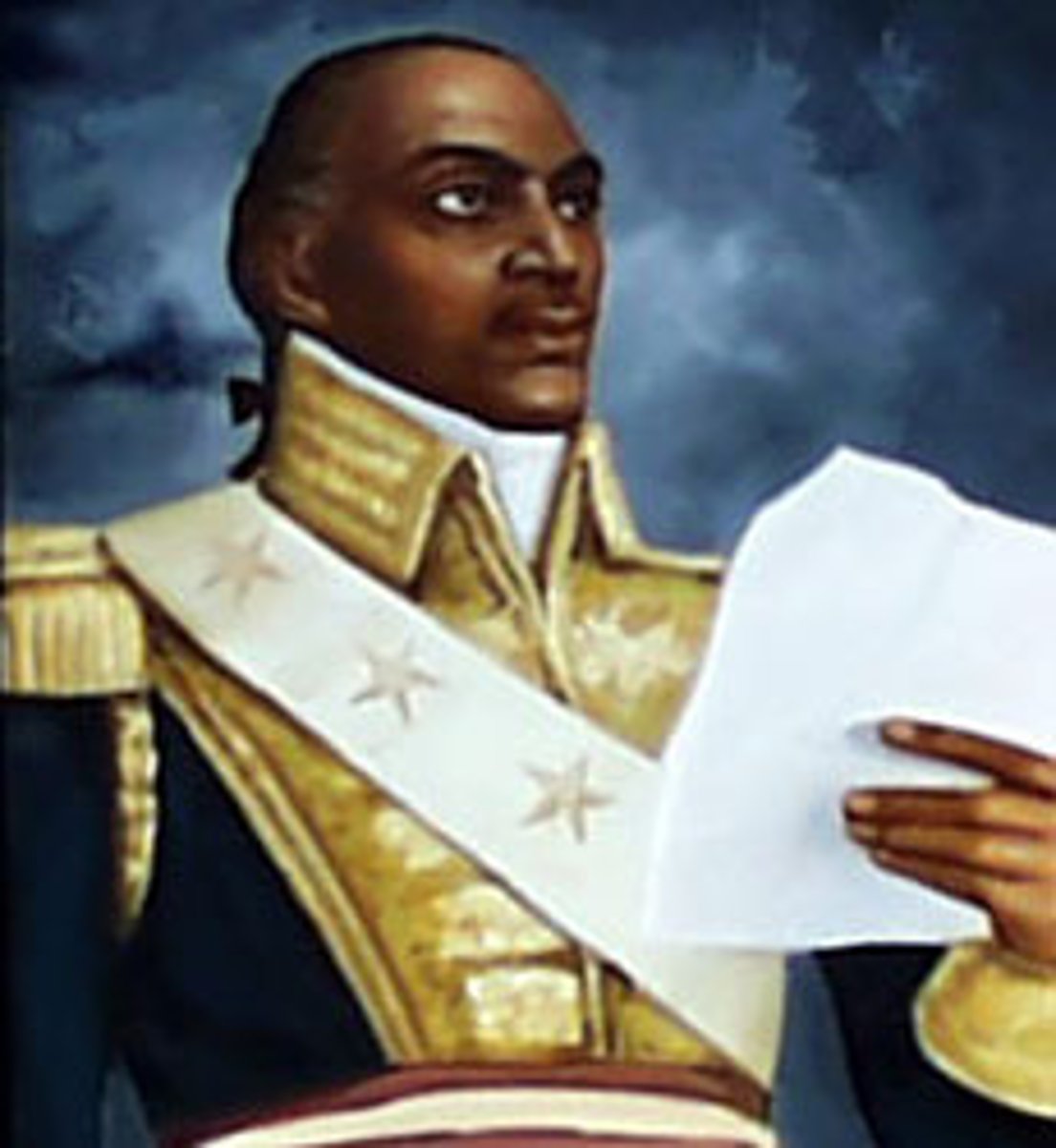
Haitian Revolution
A major influece of the Latin American revolutions because of its successfulness; the only successful slave revolt in history; it is led by Toussaint L'Ouverture.

American Revolution
This political revolution began with the Declaration of Independence in 1776 where American colonists sought to balance the power between government and the people and protect the rights of citizens in a democracy.
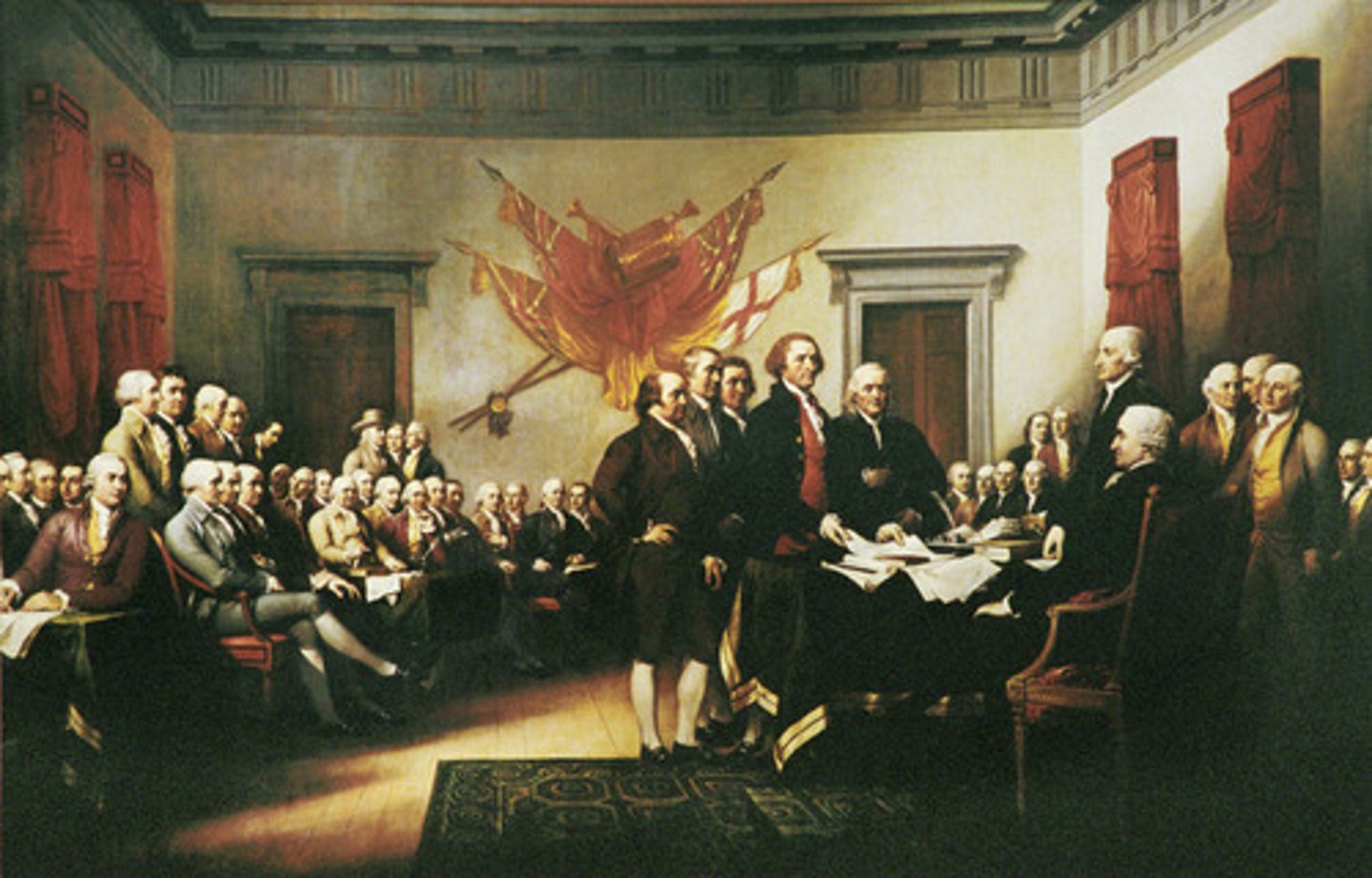

Latin American Revolutions
Political revolutions in various countries beginning in the late 18th century. These revolutions were sparked by political instability in their parent country, allowing for revolutionaries to take power.

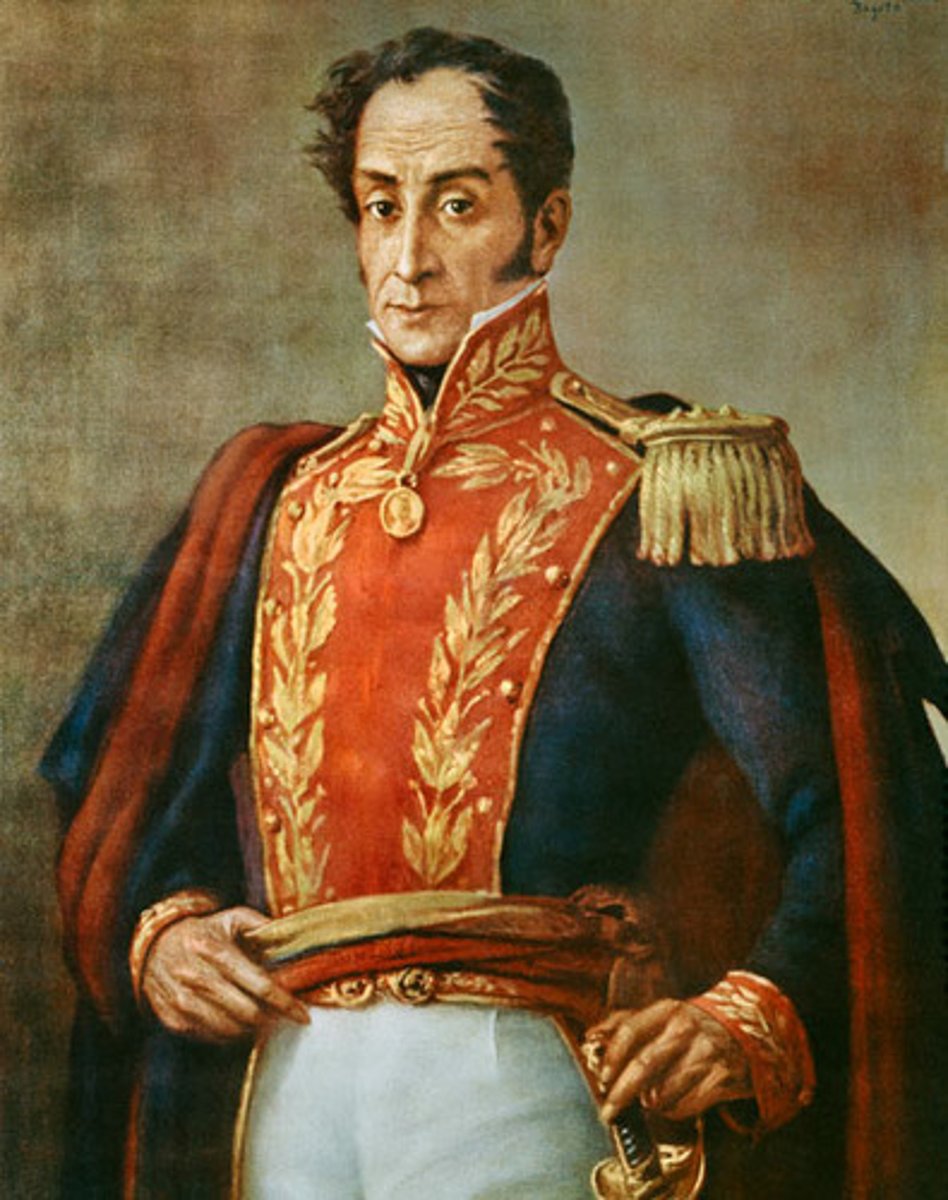
Simon Bolivar
The most important military leader in the struggle for independence in South America. Born in Venezuela, he led military forces there and in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia.

Gran Columbia
Bolivar's plan to unite Ecuador, Venezuela, Peru, Bolivia and Columbia. They united in 1822 but broke part in 1830 because of geography
Jamaica Letter
A was a document written in by Simon Bolivar where he famously expanded his views on thee independence movement

Thomas Jefferson
Author of the Declaration of Independence and 3rd President of the United States

Benjamin Franklin
Printer, author, inventor, diplomat, statesman, and Founding Father. One of the few Americans who was highly respected in Europe, primarily due to his discoveries in the field of electricity.

George Washington
1st President of the United States; commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution

Declaration of Independence
the document recording the proclamation of the second Continental Congress (4 July 1776) asserting the independence of the colonies from Great Britain

Constitution
a body of fundamental principles or established precedents according to which a state or other organization is acknowledged to be governed.

German Revolution of 1848
Liberals called for Frankfurt Assembly- first call for unification and Frederick William IV of Prussia refused title of emperor

Hungarian Revolution of 1848
Led by Lajos Kossuth, goal was autonomous Hungarian state with liberal government

Franz Joesph
new Austrian emperor, used Russian military assistance and loyal Austrian troops to reestablish his authority

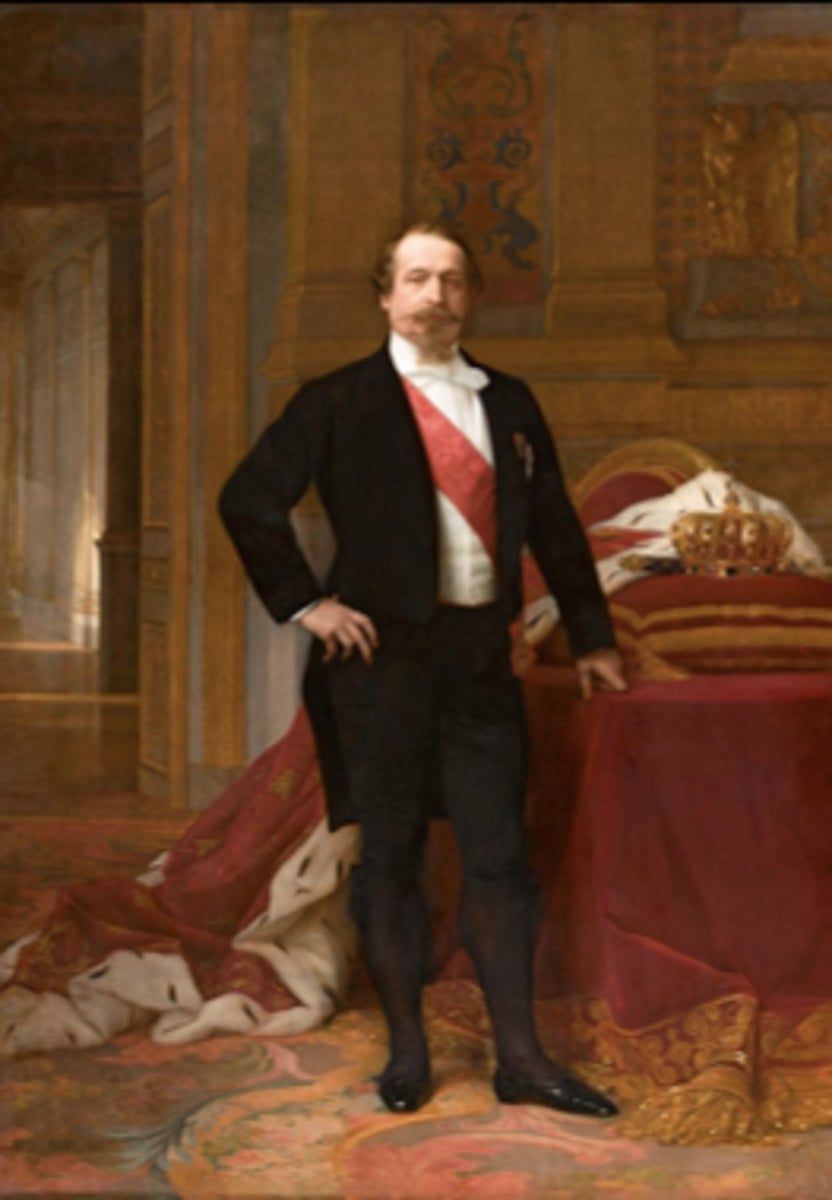
Napolean III
nephew of Napolean Bonaparte; became president of France in December 1848; seized power in coup d'état, ruled France as emperor until 1870; attempted to liberalize the empire

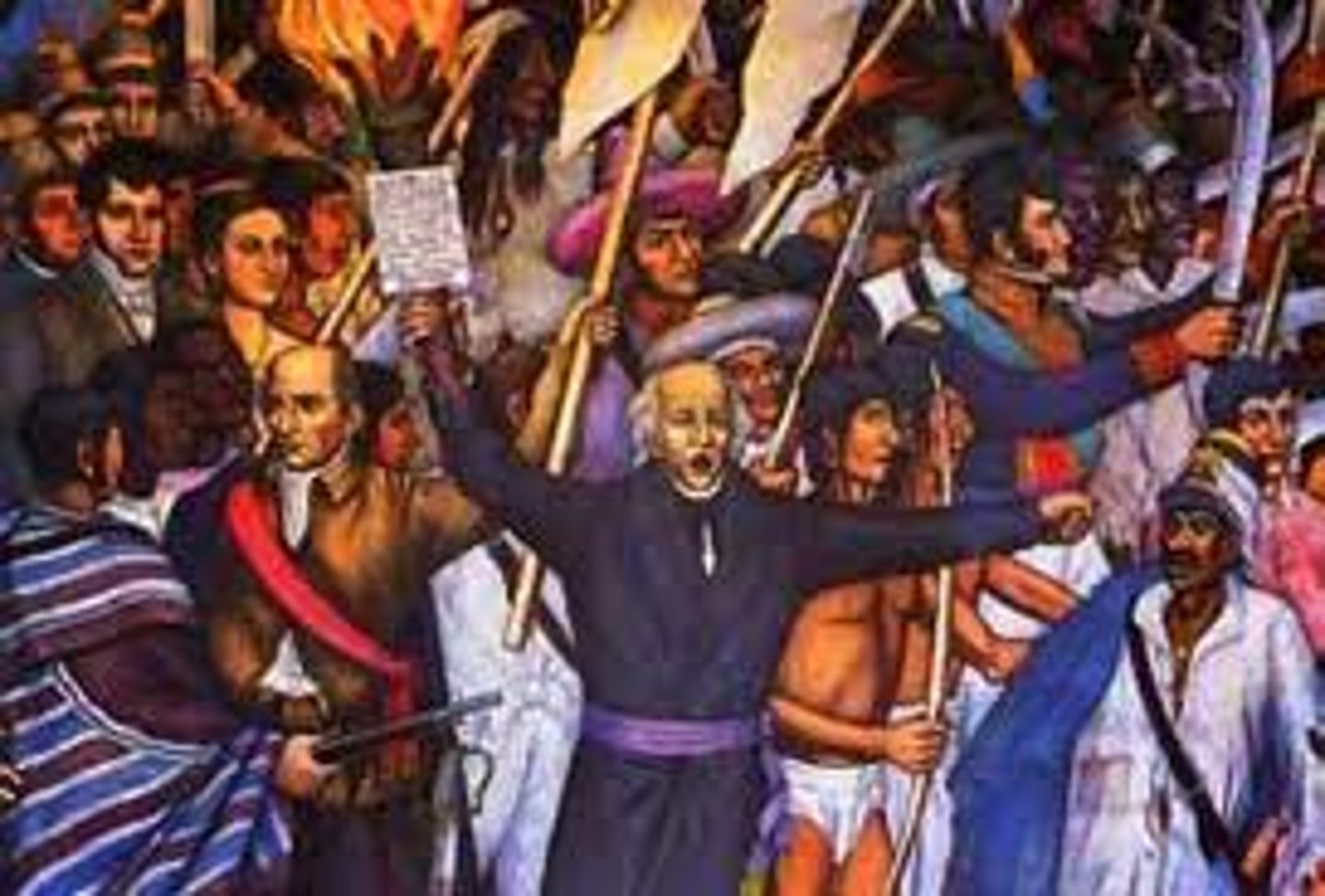
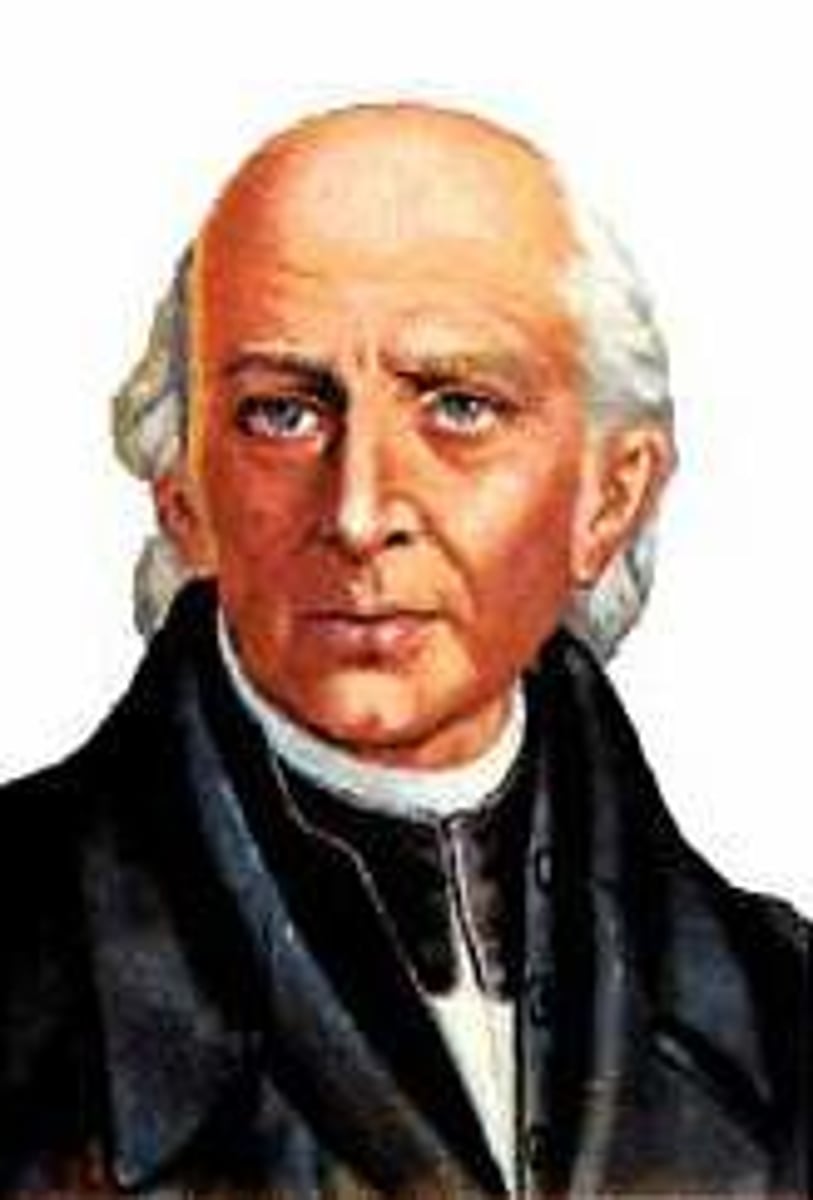
Miguel Hidalgo
Mexican priest who led peasants in call for independence and improved conditions

Nationalism
Loyalty and devotion to a particular nationality

Social Contract
A voluntary agreement among individuals to secure their rights and welfare by creating a government and abiding by its rules.

Montesquieu
French political philosopher who advocated the separation of executive and legislative and judicial powers

Jean-Jacques Rousseau
A French man who said humans are natural good and free. He said Government should exist to protect common good, and be a democracy

Mary Wollstonecraft
English writer and early feminist who denied male supremacy and advocated equal education for women

Thomas Paine
Author of Common Sense

Suffrage
the right to vote in political elections

Abolition of Slavery
Gradually abolished in most countries, except Haiti and America, saw a push from this form of exploitation towards wage based employment

Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods.
Free Markets
Markets that are allowed to operate without undue interference from the government

Socialism
A system in which the workers own and control the means of production.

Karl Marx
Co-Founder of Communism; wrote Das Kapital

Fredrich Engels
A German, co-wrote the Communist Manifesto, came from a wealthy background

Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation
prominent bank established and based in a Chinese city, that does a lot of banking in East Asia

Meiji Restoration
Followed the destruction of the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1868, set Japan on the path of centralization, industrialization, and imperialism.

Commodore Perry's Expedition
Japanese ports were opened to world trade as a result of an American Naval Commander showing up ships and guns

Sick Man of Europe
A Nickname based in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, a name based on the Ottoman sultans' inability to prevent Western takeover of many regions

Tanzimat Reforms
A set of reforms in the Ottoman Empire set to revise Ottoman law to help lift the capitulations put on the Ottomans by European powers.

Young Turks
A coalition starting in the late 1870s of various groups favoring modernist liberal reform of the Ottoman Empire. It was against monarchy of Ottoman Sultan and instead favored a constitution.

1905 Revolution
The revolution that began January 1905 with Bloody Sunday and ended with Nicholas II creating the October Manifesto.

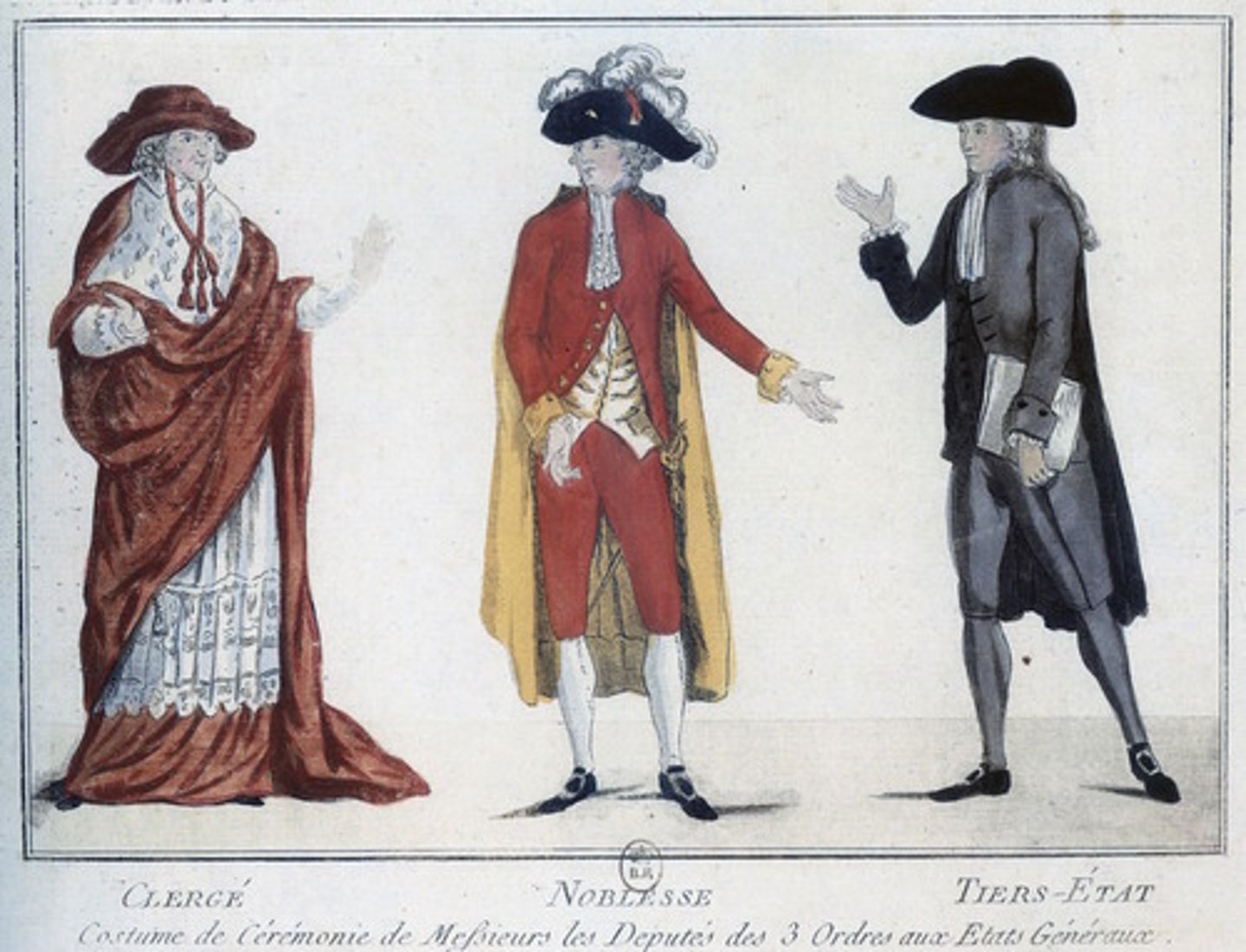
The Three Estates
1st (Clergy, 1%), 2nd (Nobility 2%), 3rd (Everyone else 97%)
