Chem 1C Chapter 19
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Coordination Compound
a compound that contains a central metal atom or ion bonded to a group of molecules or ions (ligands)
ex. [Co(NH3)6]Cl3, where cobalt is the central metal ion, and ammonia (NH₃) acts as the ligand.
Complex Ion
an ion composed of a central metal ion bonded to one or more ligands
ex. [Cu(NH3)4]2+
complex ions and coordination compounds both have
coordination covalent bonds
counter ions
Counter ions are ions that balance the charge of a complex ion in a coordination compound. They don’t participate directly in bonding to the central metal ion.
ex. [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 vs [Co(NH3)6]3+
Coordination number
the number of ligand donor atoms directly bonded to the central metal atom or ion in a complex.
ex. [Co(NH3)6]3+, the coordination number of cobalt is 6
Ligand
a molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to a central metal atom or ion, can be neutral molecules (NH₃) or anions (Cl⁻). Ligands may be monodentate (donating a single pair of electrons) or polydentate (donating multiple pairs of electrons).
Chelate
a complex in which a ligand forms more than one bond with the central metal ion
Chelating ligands
also known as polydentate ligands, have multiple donor atoms that allow them to "wrap around" the metal ion, creating a stable ring structure.
ex. ethylenediamine (en), which can bond through two nitrogen atoms
Bidentate
a type of ligand that has two donor atoms
ex. ethylenediamine (en), which can bond through two nitrogen atoms
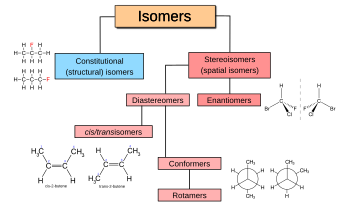
Isomers
compounds that have the same chemical formula but differ in the arrangement or connectivity of atoms within the molecule.
ex. Ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) and dimethyl ether (CH₃OCH₃) have the same molecular formula (C₂H₆O)
structural isomers
the same molecular formula but different connectivity.
ex. [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Br and [Cr(NH3)5Br]Cl
stereoisomers
compounds that differ in the arrangement, geometric isomers and optical isomers.
ex. PtCl2(NH3)2], can have cis and trans isomers (geometric)
ex. [Co(en)3]3+, can exist as two enantiomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other (optical)
![<p>compounds that differ in the arrangement, <strong>geometric isomers</strong> and <strong>optical isomers</strong>.</p><p>ex. PtCl2(NH3)2], can have <strong>cis</strong> and <strong>trans</strong> isomers (geometric)</p><p>ex. [Co(en)3]3+, can exist as two enantiomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other (optical)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c78d6dfe-d540-4d24-a191-71c07ac3c39b.jpg)
diastereomers and ____
enantiomers
coordination isomers
a type of structural isomer where the composition of the complex ions is interchanged between the cation and the anion
ex. [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] and [Cr(NH3)6][Co(CN)6]
Linkage Isomers
a structural isomer where a ligand can coordinate through different atoms
ex. nitrite (NO2-) can bond to a metal ion through the nitrogen atom (as -NO2, nitro) or the oxygen atom (as -ONO, nitrito)
weak field ligand
produce small splittings between the d orbitals and form high spin complexes
ex. Halides (Cl−, F−), water (H2O), and ammonia (NH3)
strong field ligand
produce large splittings between the d orbitals and form low spin complexes
ex. Cyanide (CN−), carbon monoxide (CO), and ethylenediamine (en)
low-spin complex
contains the lesser number of unpaired electrons
typically occur with: strong-field ligands, where the splitting energy (Δ) is larger
high-spin complex
compound with the greatest number of unpaired electrons
typical with: weak-field ligands, where the splitting energy (Δ) is smaller