The Biological Basic of Behavior - Anatomy of the Brain
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
The Hindbrain
Location: is positioned at the back and lower part of the brainstem.
It contains structures that control basic functions, such as breathing and heart rate
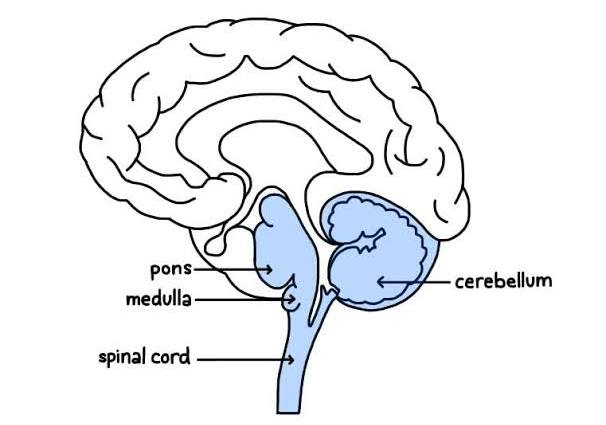
Medulla Oblongata
Pons
Brain Stem
Cerebellum
What are the main structures of the Hindbrain?
Medulla Oblongata
Controls autonomic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure
the lowest part of the brainstem, connecting the brain to the spinal cord
Pons
Relays signals between the cerebellum and the rest of the brain.
Involved in regulating sleep and arousal.
Brain stem
"stalk” the lower part of the brain the connects the spinal cord to higher region of the brain
Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary movements
Maintains balance and posture.
The Midbrain
Location: Central part of the brainstem, above the hindbrain.
Involved in auditory, visual processing, and eye movement
Tectum
Tegmentum
Cerebral Penducles
What are the main structures of the Midbrain?
Tectum
Processes visual and auditory information.
Includes the superior colliculus (visual processing) and the inferior colliculus (auditory processing).
Tegmentum
Contains the red nucleus and substantia nigra, which are involved in motor control.
Integrates sensory information and regulates motor responses.
Cerebral Peduncles
Large bundles of fibers at the front of the midbrain.
Pathways for motor signals from the cortex to the pons and spinal cord
Forebrain
The largest and most anterior part of the brain.
Function: Involves voluntary movement, reasoning, impulse control, language, and speech.
Diecephalon
Telecephalon
What are the main functions of the Forebrain?
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer that consists of cerebral hemispheres, which account for two-thirds of the brain’s total mass
Corpus Callosum
a network of nerve fibers that are connects the to right and left hemispheres of the brain
Cerebrum
Involved in higher cognitive functions: thought, reasoning, sensory processing, and voluntary motor activities
Frontal
Pariental
Temporal
Occipital
What are the lobes in the Cerebrum?
Frontal Lobe
Planning of movements, working memory--events that happened very recently
Executive Functions: Planning, decision-making, and problem- solving.
Personality and Behavior: Regulation of emotions and social behavior.
Pariental Lobe
Sensory
Integration of sensory information from the body through the primary somatosensory cortex.
Temporal Lobe
Auditory
Primary auditory cortex, responsible for processing sound.
Thalamus
Acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex.
Processes and transmits information to different parts of the brain.
Hypothalamus
Regulates homeostasis: helps manage your body temperature, hunger and thirst, mood, sex drive, blood pressure and sleep.
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Cingulate Gyrus
Pineal Gland
What are the components under the Hypothalamus?
Hippocampus
Function: Memory formation
Amygdala
Function: Emotion, particularly fear and pleasure
Cingulate Gyrus
an arch-shaped brain structure that is part of the limbic system
Function: Emotion, behavior, and cognitive processing
Pineal Gland
a pea-shaped gland that regulates sleep
Left Hemisphere
Typically associated with logical reasoning, language processing, and analytical tasks.
Right Hemisphere
Generally linked with creativity, spatial awareness, and holistic thinking
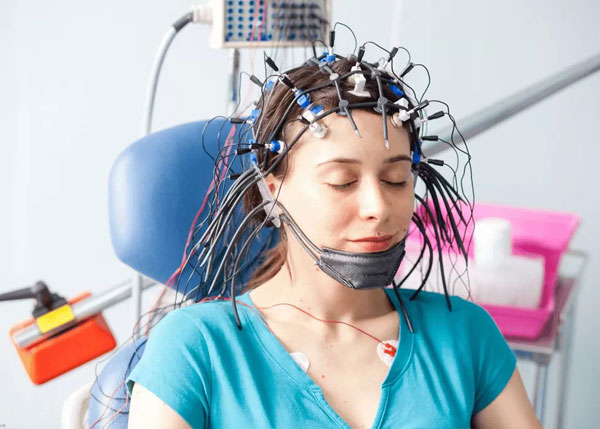
Electroencephalography (EEG)
measures electrical activity in the brain by placing electrodes on the scalp.
records the brain’s electrical signals in real-time, providing a continuous stream of data.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
What method of studying the brain is this?

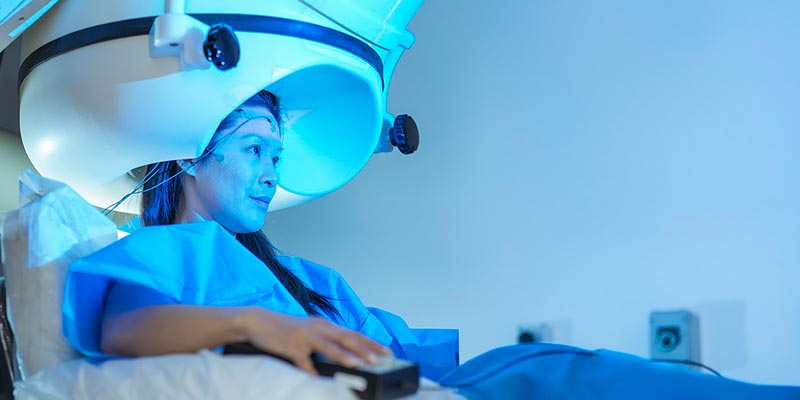
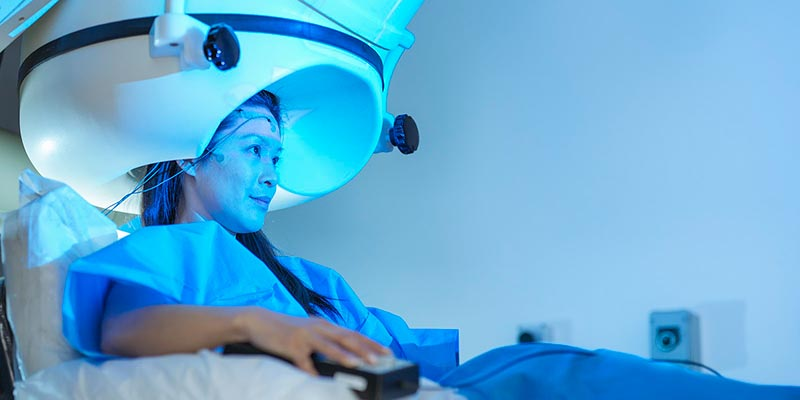
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
What method of studying the brain is this?
What method of studying the brain is this?
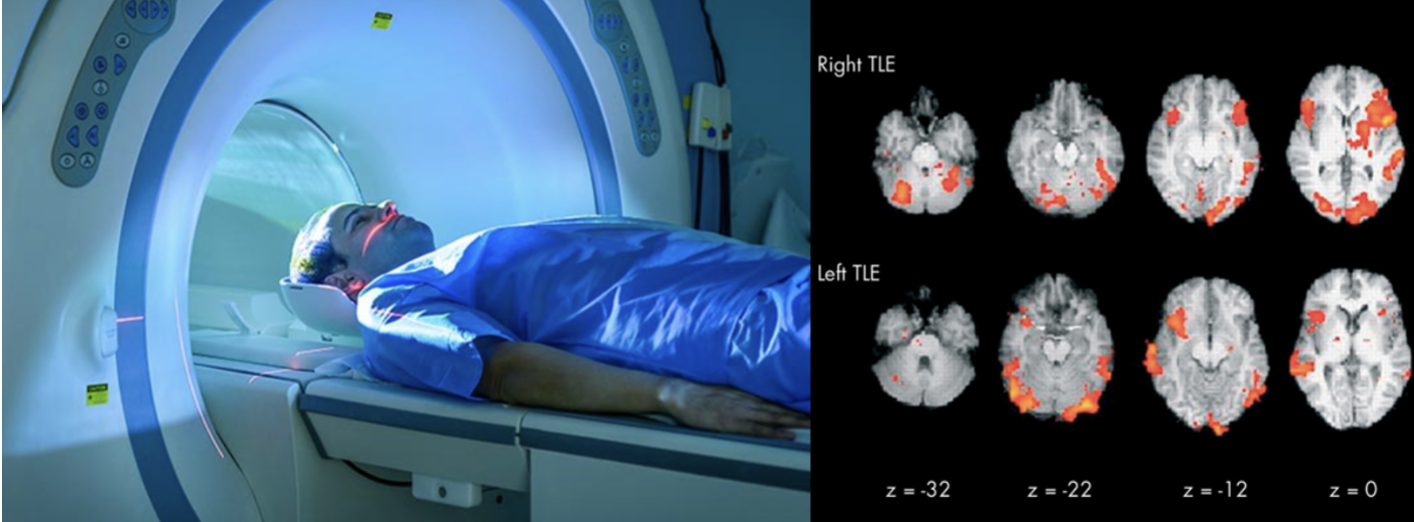
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
What method of studying the brain is this?
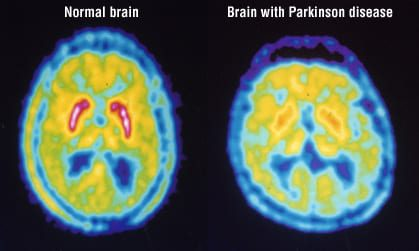
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
What method of studying the brain is this?
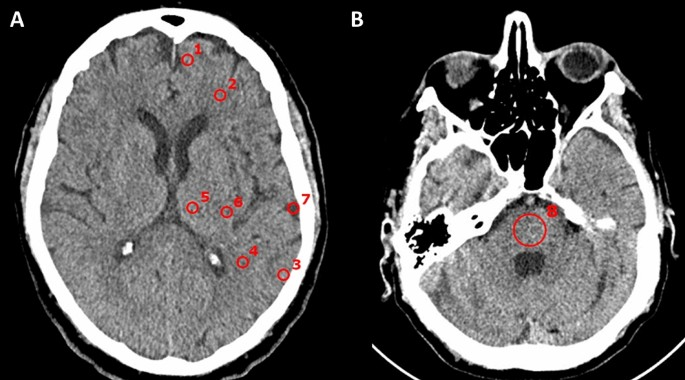
Computed Tomography (CT)
What method of studying the brain is this?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
What method of studying the brain is this?
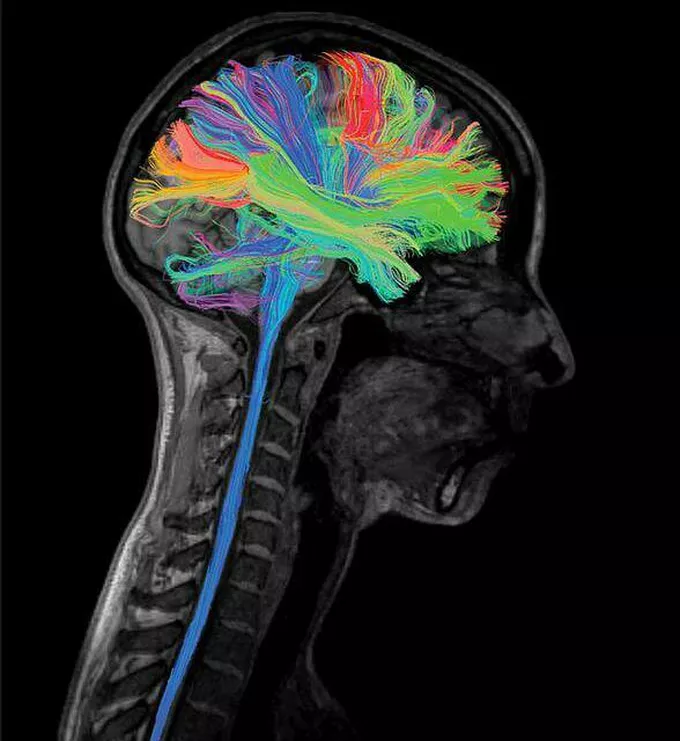
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
What method of studying the brain is this?
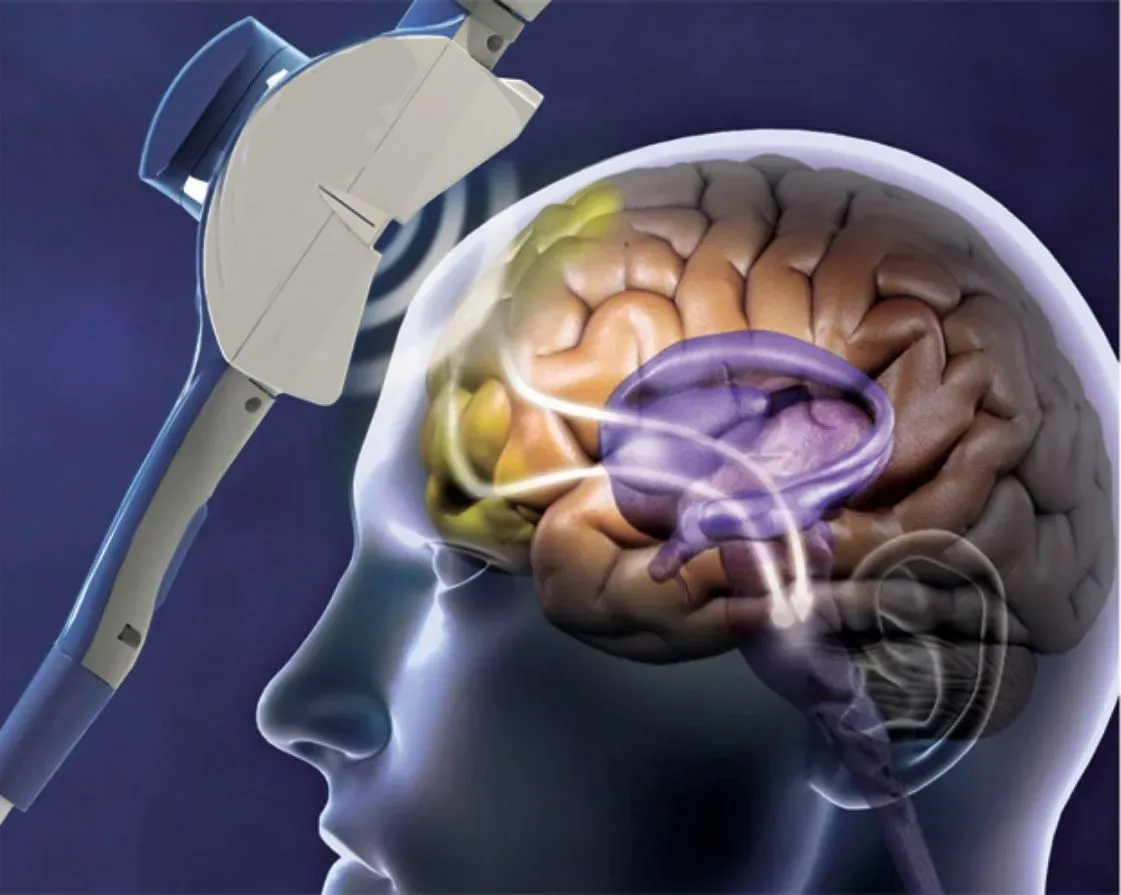
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
What method of studying the brain is this?
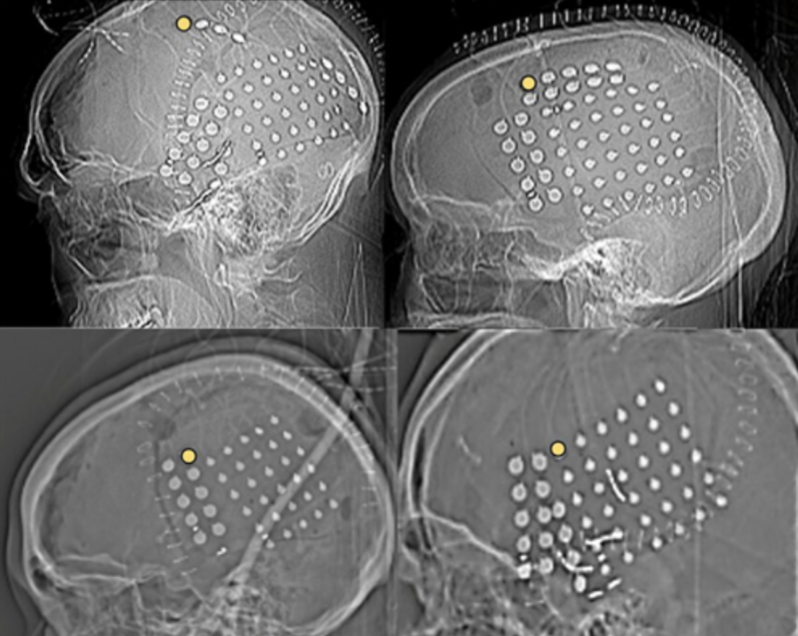
Invasive Techniques
What method of studying the brain is this?
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
measures the magnetic fields generated by neuronal activity using highly sensitive magnetometers.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
detects changes in blood flow and oxygenation levels in the brain, which are associated with neuronal activity.
It provides detailed images of brain activity over time.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
involves injecting a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream, which emits positrons.
detected to create images of brain activity based on glucose metabolism or other markers.
Computed Tomography (CT)
uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the brain.
often used to identify structural abnormalities such as tumors or bleeding
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of brain structures.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
A type of MRI that maps the diffusion of water molecules in the brain, allowing visualization of white matter tracts and connectivity.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
involves using magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain.
can temporarily disrupt normal brain activity and is used to study brain function and causality.
Invasive Techniques
involve placing electrodes directly on the brain or within it to record neuronal activity.
They are used in research and clinical settings, particularly in epilepsy treatment.
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
What are the main components of the Limbic System?