Understanding Cleft Lip and Palate Care and Impact
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Cleft Lip and Palate
A congenital condition where structures in the face do not fuse properly during fetal development, resulting in openings in the lip, palate, or both.
Submucous Cleft
A type of cleft palate where the soft palate is affected but is covered by a layer of skin.
Bifid Uvula
A condition characterized by a cleft or split in the uvula.
Cleft Lip (CLO)
A cleft that affects the lip, ranging from a slight notch to complete separation extending into the nose.
Cleft Palate (CPO)
A cleft that occurs when the roof of the mouth, including the soft and hard palate, has not joined completely.
Unilateral (UCL / UCLP)
A cleft that affects one side of the lip or palate.
Bilateral (BCL / BCLP)
A cleft that affects both sides of the lip or palate.
Antenatal Identification of CLP
The process of diagnosing cleft lip and palate before birth, which can be challenging, with cleft palate and submucous cleft being particularly difficult to locate on antenatal scans.
Threshold Theory
A concept explaining the development of cleft lip and palate as a result of a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental factors exceeding a certain threshold.
Orthognathic Surgery
Surgical procedures performed in adulthood to correct jaw and facial deformities, often necessary for individuals with cleft lip and palate. Serves to fix class 111 malocclusion
lots of screws involved
Cleft Lip Repair
3 -6 months target
Cleft Palate repair
9 - 13 months, predominantly for speech feeding and hearing
designed to seal gap between oral and nasal cavities
Alveolar Bonegraft
A surgical procedure typically done around 9-10 years of age to repair the alveolar ridge affected by cleft palate.
Pharyngeal Flap
A surgical technique used to improve velopharyngeal competency in individuals with cleft palate.
Pharyngoplasty
Acts as a speed bump. Secondary palatal surgical procedure in which a muscular flap is cut from the posterior pharyngeal wall, raised, and attached to the velum
Openings on either side of the flap allow for nasal breathing, nasal drainage, and production of nasal sounds.
Helps close the VP port and reduces hypernasality.
Grommets
Tubes inserted into the eardrum to alleviate middle ear infections, a common issue in individuals with cleft palate.
Hypodontia
Can be missing teeth
Hyperdontia
Can be extra teeth, may be in palate rather than alveolar gum area
Malocclusion
Teeth in bottom jaw may approximate to unusual positions to accommodate upper jaw teeth position
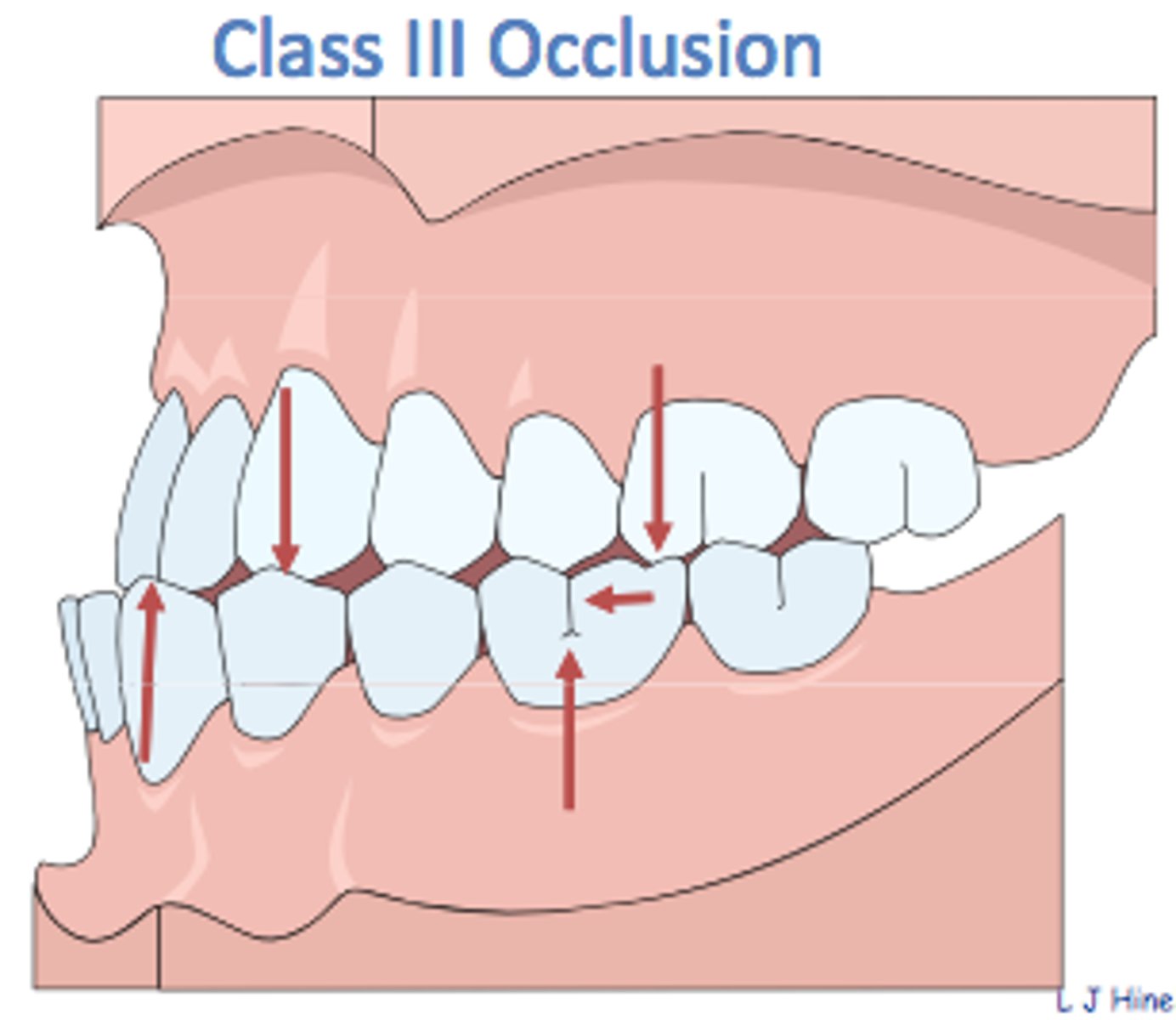
Class III malocclusion
Retracted maxilla in cleft palate cases, may require orthognathic surgery to correct
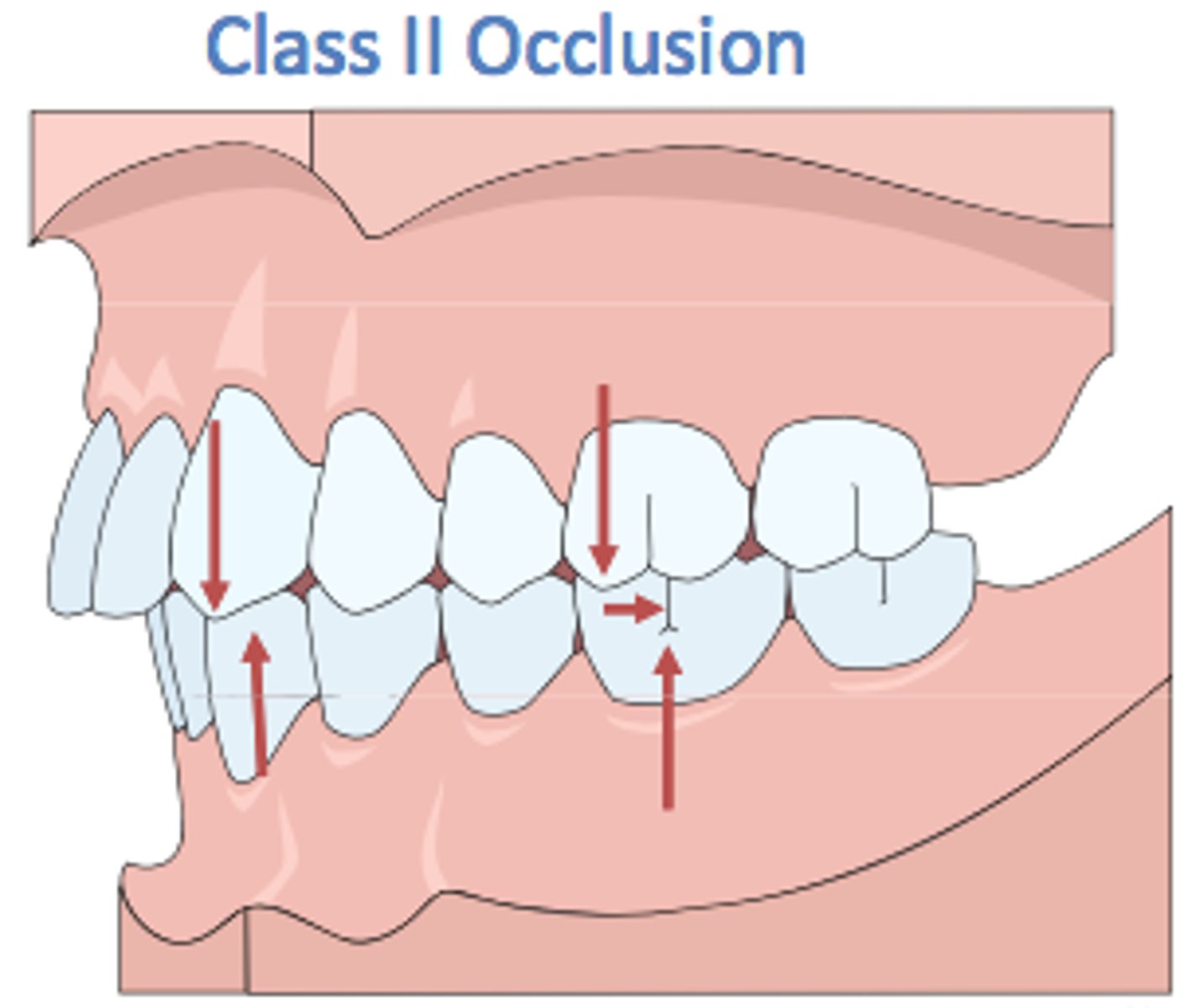
Class II malocclusion
Retracted mandible in Pierre Robin cases
Otitis media
More common for children with cleft palate due to exposure of Eustachian tube
Considerations for Aotearoa
New Zealand has high rates of CLP; Māori have highest rate of isolated Cleft Palate; no routine Clinical Psychology provision for cleft in Aotearoa
Cleft lip Speech
Normal incidence of articulation errors once lip repair complete, unless hearing difficulties remain
Cleft palate speech
incomplete articulation surface - passive (obligatory) errors
vowels don't tend to be affected as they are nasal
Non-pneumatic velopharyngeal closure
closure is high up and dramatic - swallowing, gagging and vomiting
Pneumatic velopharyngeal Closure
+ve pressure: blowing whistling and speech
-ve pressure: Sucking and kissing
Hypernasality
Increased or excessive nasal resonance heard on vowels and voiced consonants
Hyponasality
Decreased or reduced nasal resonance heard on vowels and nasal consonants
blocked nose
Mixed Resonance
Combination of hypernasality on oral consonants and hyponasality on nasal consonants
Abnormal Nasal Airflow - VPI
Nasal air emission and/or nasal turbulence that distorts oral high-pressure consonants
accompanied with and distorts any of all oral high-pressure consonants in a language
Weak or omitted consonants, short utterance length due to nasal air emission
Passive Speech Errors
Weak or omitted consonants
Short utterance length
Nasalized Phonemes
Active (compensatory) errors in speech
generally the manner of articulation is preserved but place of articulation is moved backwards
What is VPI
Velopharyngeal insufficiency resulting in nasal emission, nasal turbulence, hypernasality, hyponasality, and mixed resonance
places of articulation compromised
Palate, alveolar ridge, velum, uvula
Abnormal airflow
Nasal Emission, nasal turbulence
PROMs
Patient Reported Outcome Measures used to understand patient priorities and evaluate treatment efficacy
Biofeedback
Using techniques like a nasal mirror or teaching stethoscope to provide feedback for reducing nasality in speech
Treatment for hypernasality
exaggerated articulation, decreasing speaking rate, auditory training (increase patient awareness of excessive nasal emissions)
UK Adult Services Project
A project (2018-2021) studying the needs of adults with cleft, aiming to develop support interventions
Interpersonal Relationships
Reflects positive family and friend relationships, experiences of bullying/discrimination, and social competence in individuals with cleft
Treatment Experiences
Concerns, surgeries, and outcomes related to dental visits, entitlement to treatment, and surgical decisions in individuals with cleft, 1/3 were concerned about visiting the dentist
Face development during Utero
structures move towards the midline and fuse together starting at the lip (6 weeks) and progressing to the soft palate which will be sealed by around the 16th week
global average of cleft
1/700 live births
New Zealand average of cleft
1/550
Māori population and Cleft
highest incidence of isolated cleft Palate in the world - 1/460
Cause of CLAP
multifactorial - a combination of genes and environment
Syndromic link
something else if happening, for example genes
nonsyndromic
happening in isolation
Chances of CLAP if one parent has cleft
1 in 50
Chances of CLAP if both parents have cleft
1 in 10