Overview of the U.S. Supreme Court and Judiciary System
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is the highest court in the United States?
The Supreme Court.
How many justices serve on the Supreme Court?
Nine justices.
Who is the current Chief Justice of the United States?
John Roberts.
What is the term length for a Supreme Court justice?
Lifelong term.
Who nominates Supreme Court justices?
The President of the United States.
Who approves the nomination of Supreme Court justices?
The Senate.
What is the acceptance rate of cases by the Supreme Court?
1% acceptance rate (80 out of 8,000 cases).
What are the three layers of the US Federal Court system?
1. Supreme Court 2. Circuit Courts 3. District Courts.
What is a Writ of Certiorari?
A written request asking the Supreme Court to hear a case.
What are the categories for case selection by the Supreme Court?
1. Case of national importance 2. Lower court invalidates federal law 3. Resolve split decision.
What is a Majority Opinion in the Supreme Court?
The written decision that represents the majority view of the justices.
What is a Concurrent Opinion?
An optional opinion that agrees with the majority but for different reasons.
What is a Dissenting Opinion?
An opinion that disagrees with the majority decision.
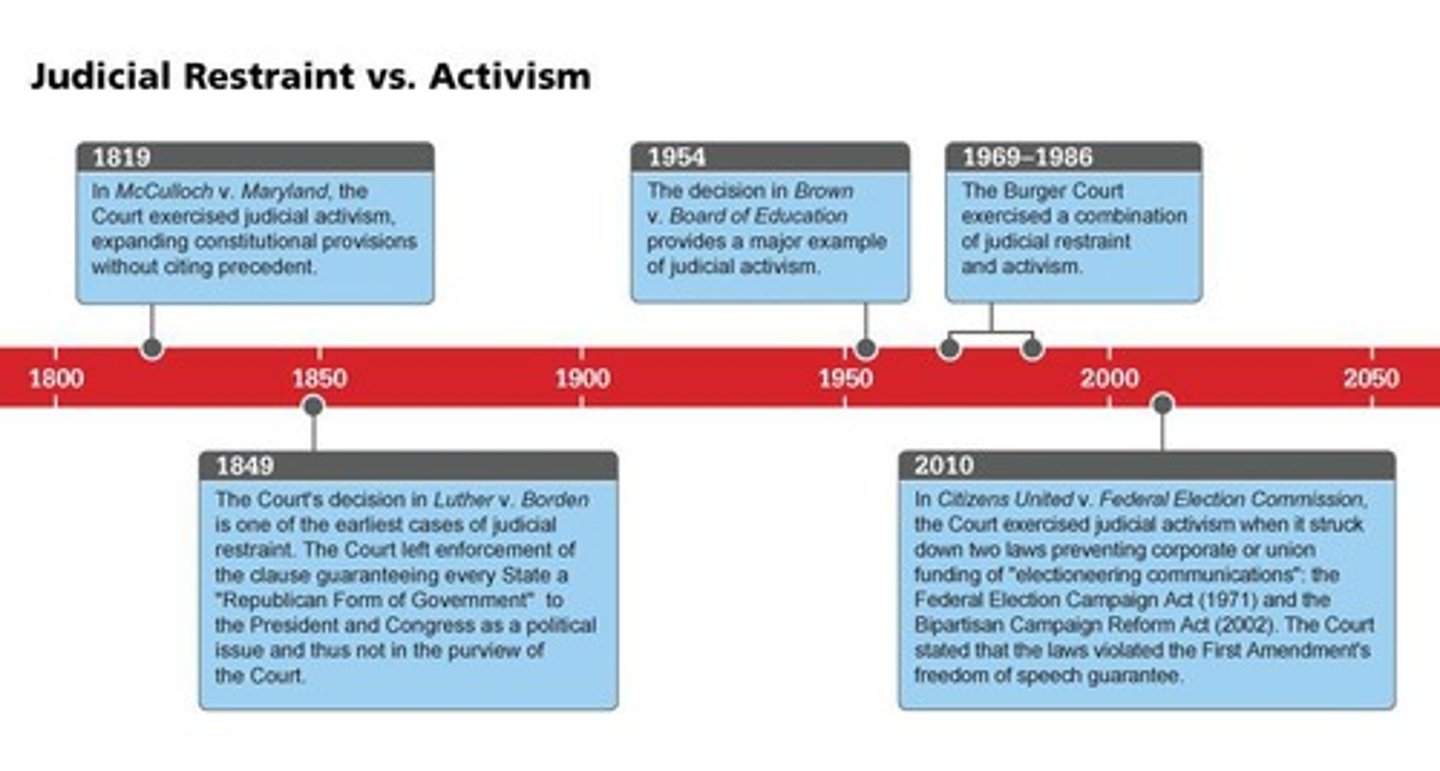
What is judicial restraint?
A philosophy where judges limit their own power by adhering closely to precedent.
What is judicial activism?
A philosophy where judges are more willing to decide constitutional issues and invalidate legislative or executive actions.
Who was the first female Supreme Court Justice?
Sandra Day O'Connor.
Who was the first African American Supreme Court Justice?
Thurgood Marshall.
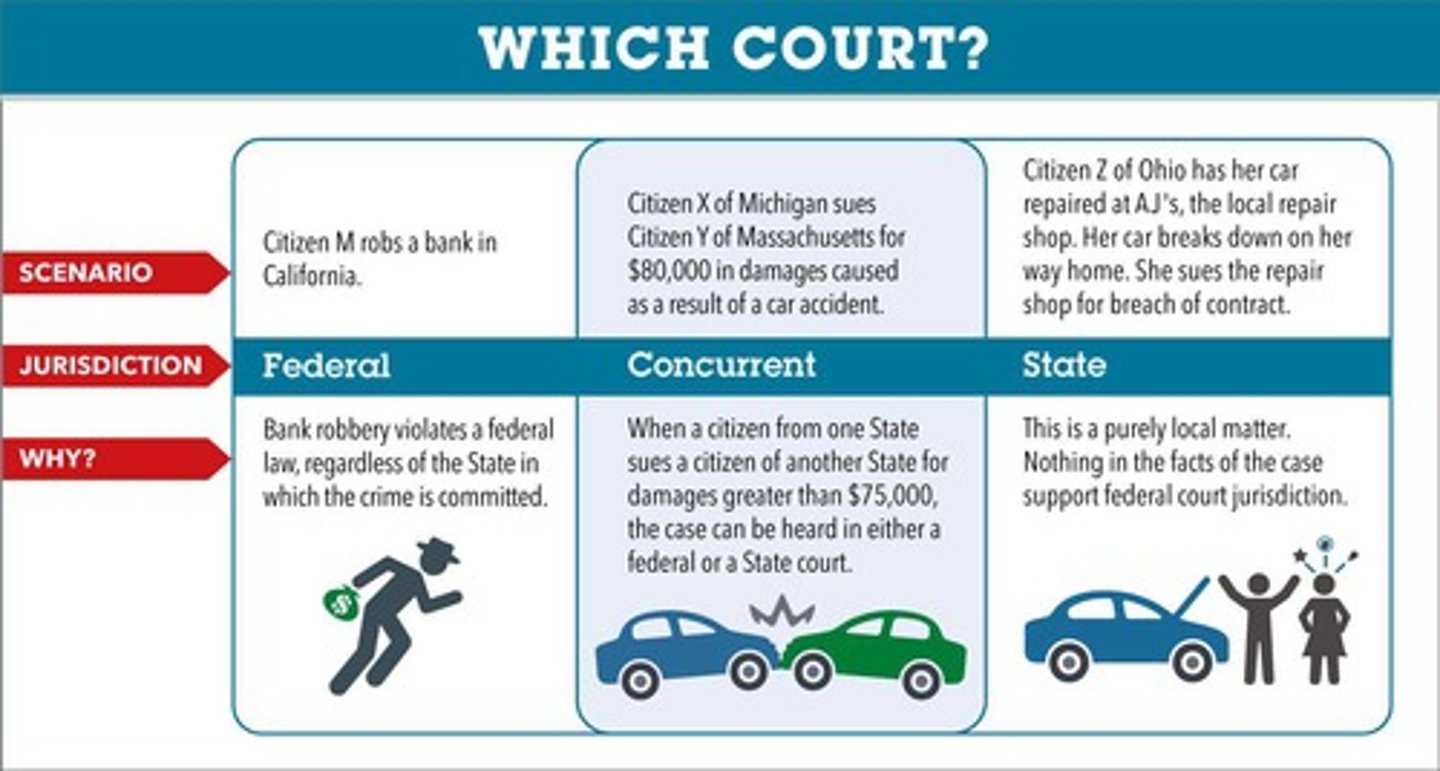
What is jurisdiction in the context of federal courts?
The authority of a court to hear and decide a case.
What is original jurisdiction?
The power of a court to hear a case for the first time.
What is appellate jurisdiction?
The power of a court to review decisions made by lower courts.
What is concurrent jurisdiction?
When two different courts have the authority to hear the same case.
What is the role of federal judges?
To preside over court proceedings and make legal decisions.
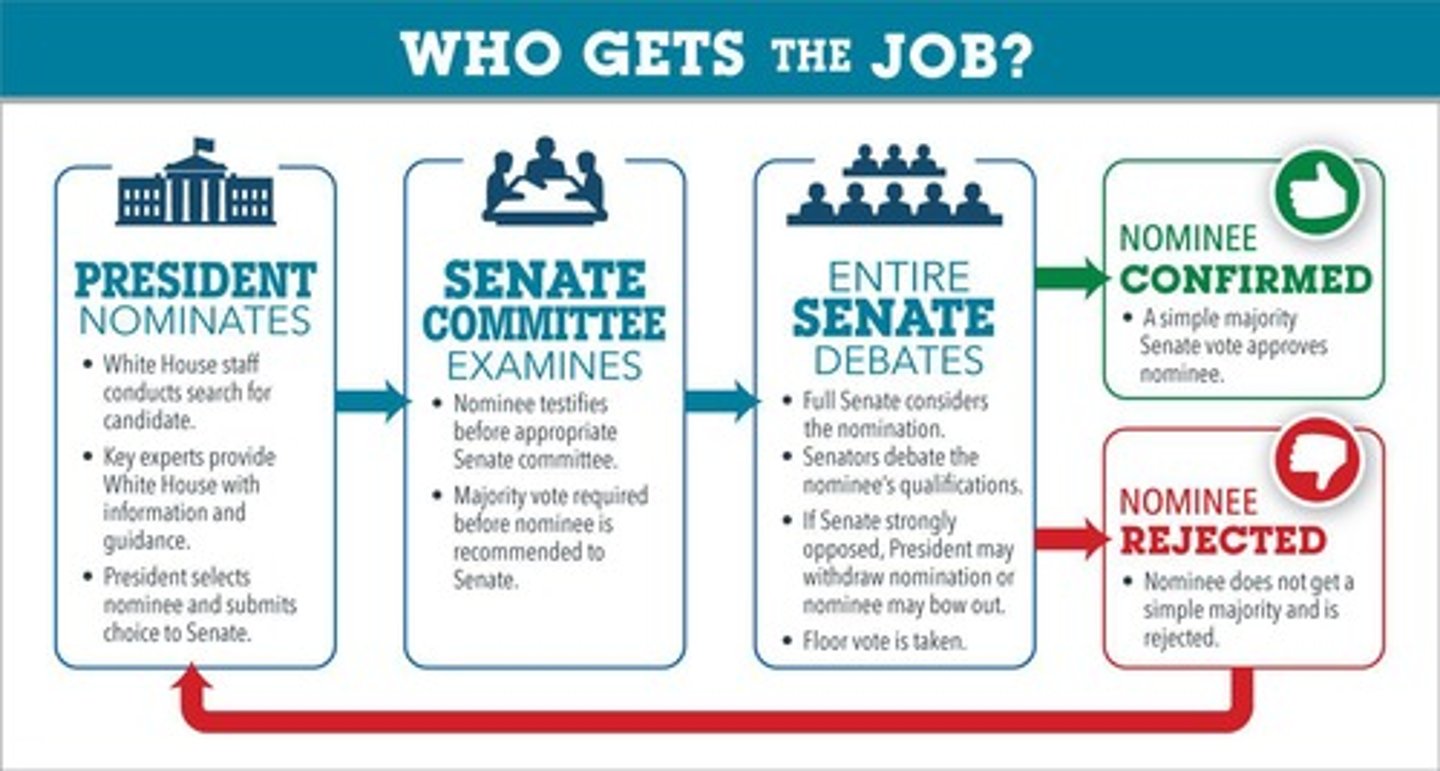
What is the process for appointing federal judges?
Nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate.
What is the significance of the Articles of Confederation regarding the judiciary?
There were no national courts or judiciary, leading to inconsistent law application.
Why did Alexander Hamilton advocate for a federal judiciary?
To settle state disputes and override state laws.
What is the difference between exclusive and concurrent jurisdiction?
Exclusive jurisdiction means only one court can hear a case, while concurrent jurisdiction means multiple courts can hear it.
What is the impact of judicial philosophy on court decisions?
It influences how judges interpret laws and the Constitution, affecting the outcomes of cases.