Day 7 - Biosynthesis and Degradation of Nucleotides
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
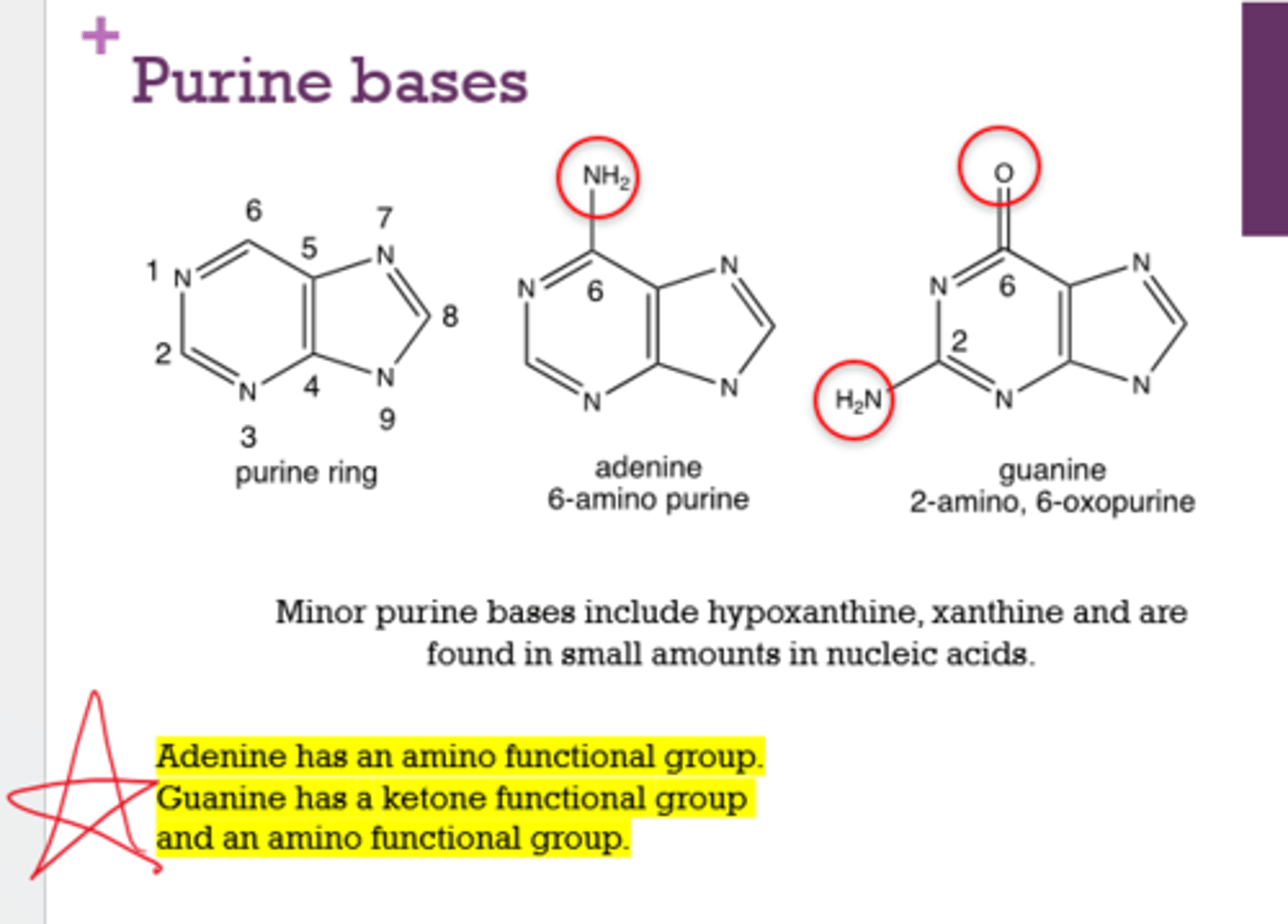
What function groups do adenine and guanine have?
Adenine: amino
Guanine: amino and ketone
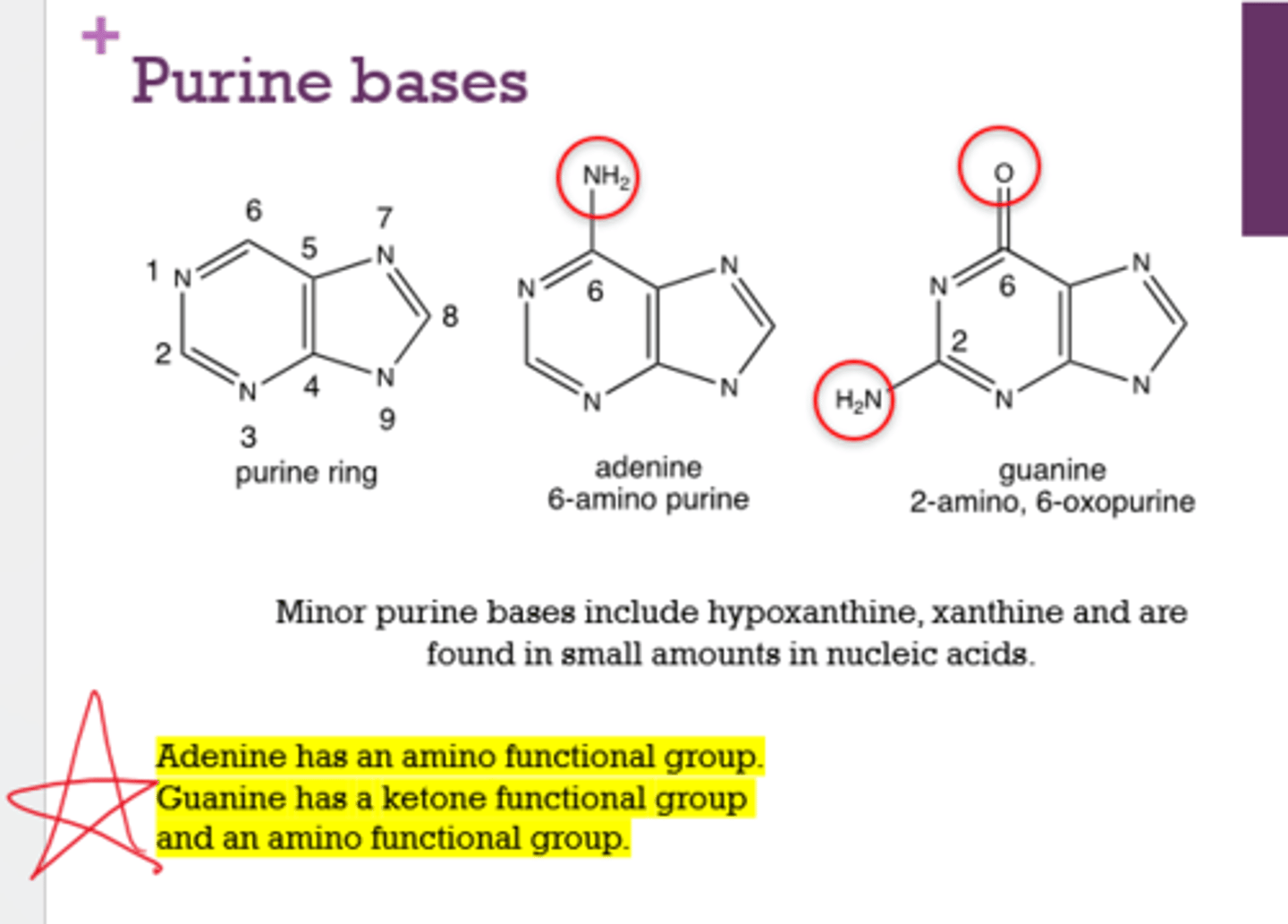
What are the purine bases?
Adenine and Guanine
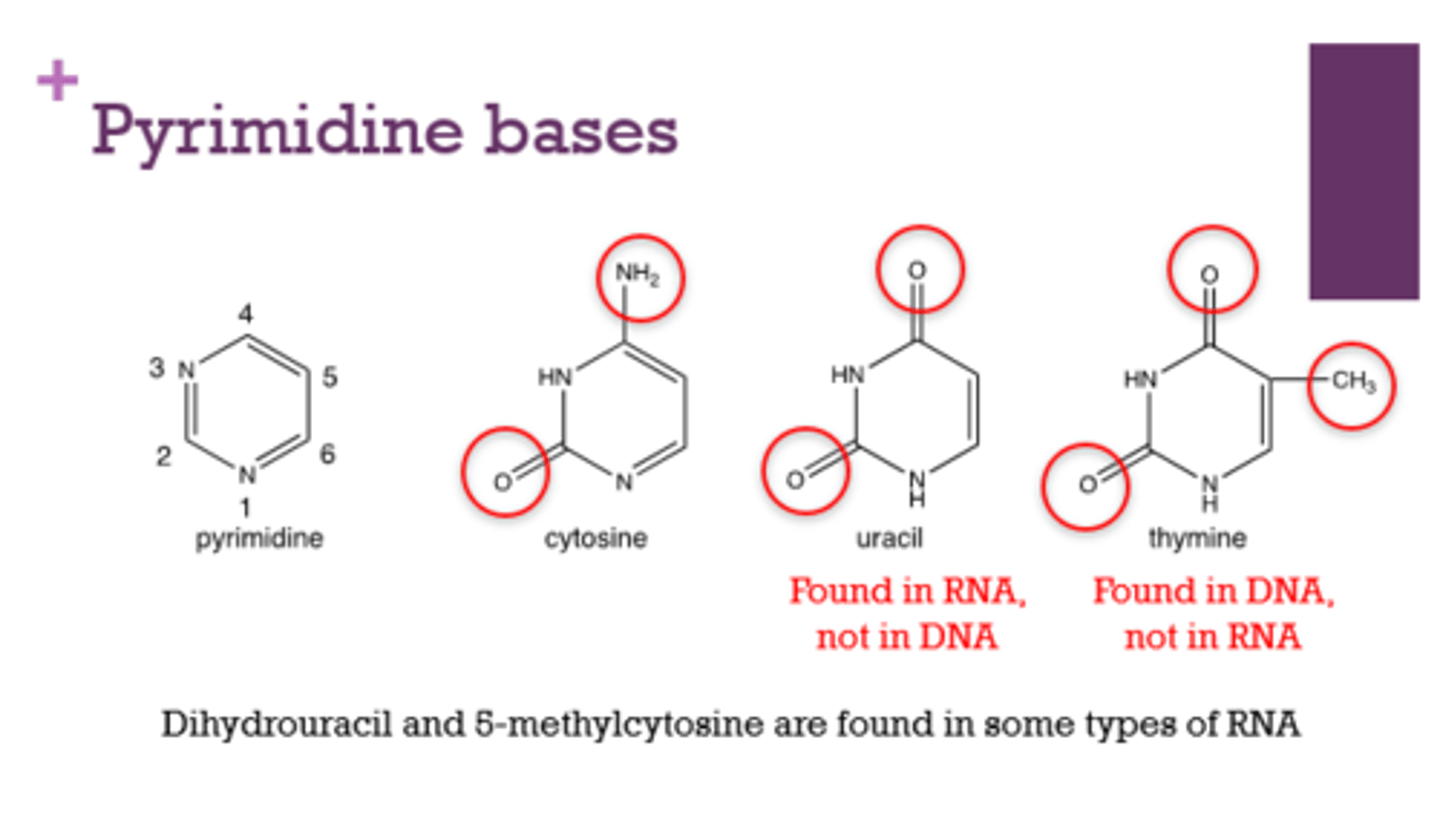
What are the pyrimidine bases?
cytosine, thymine, uracil
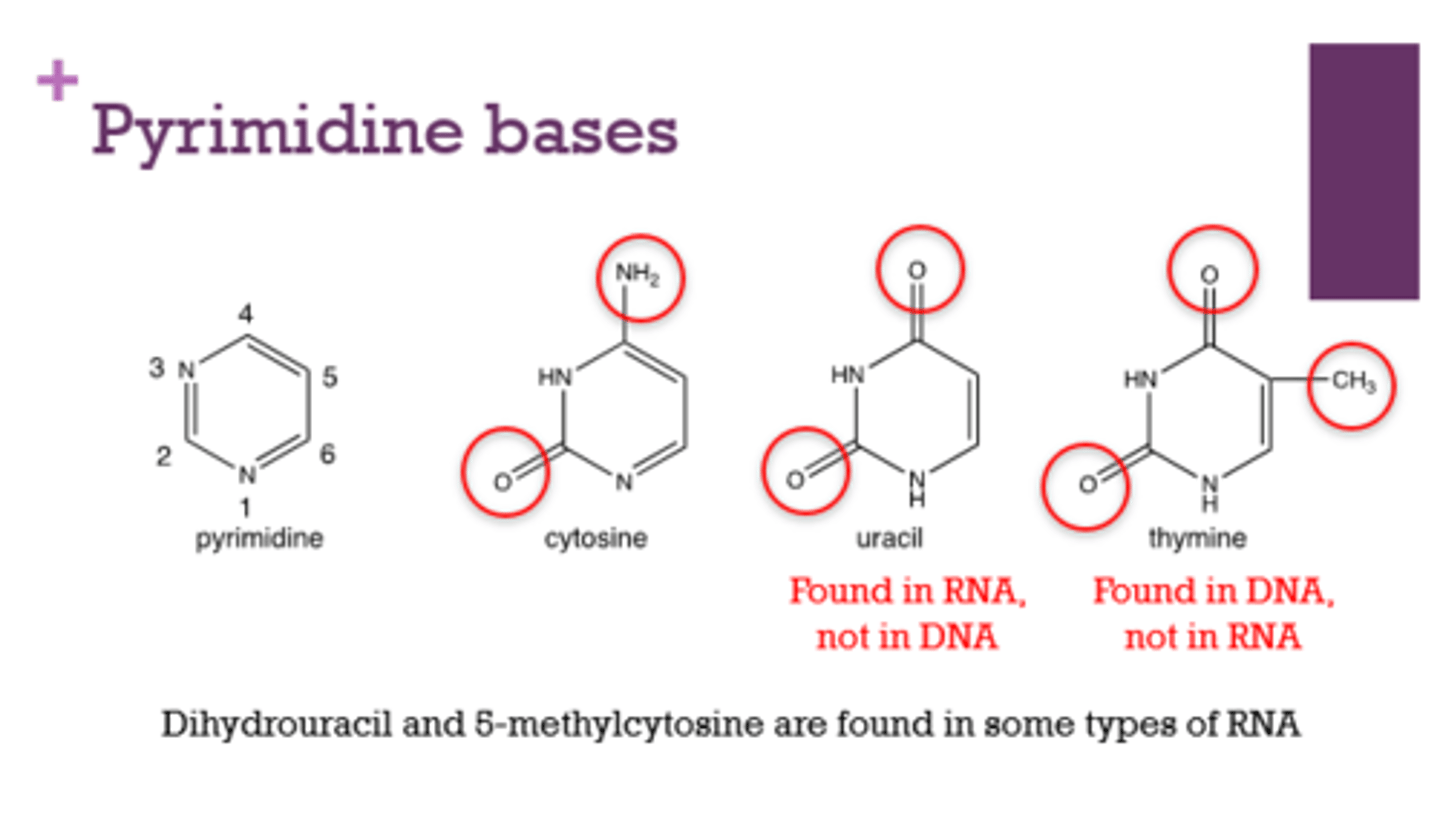
Which pyrimidine is found in RNA? DNA?
RNA: Uracil
DNA: Thymine
What do you add to get a nucleoside?
sugar
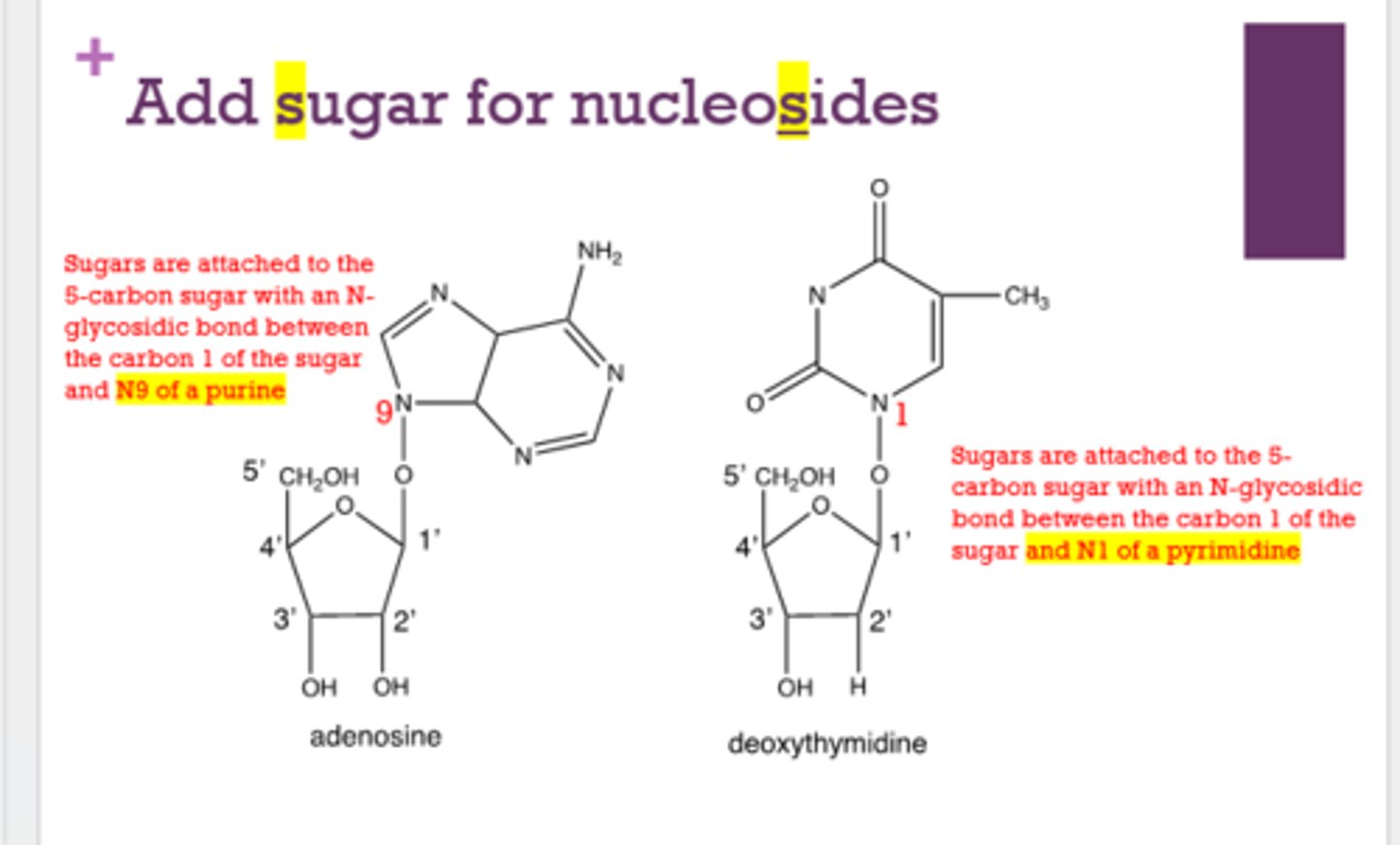
Where are sugars added on purines and pyrimidines?
Purine: N9
Pyrimidine: N1
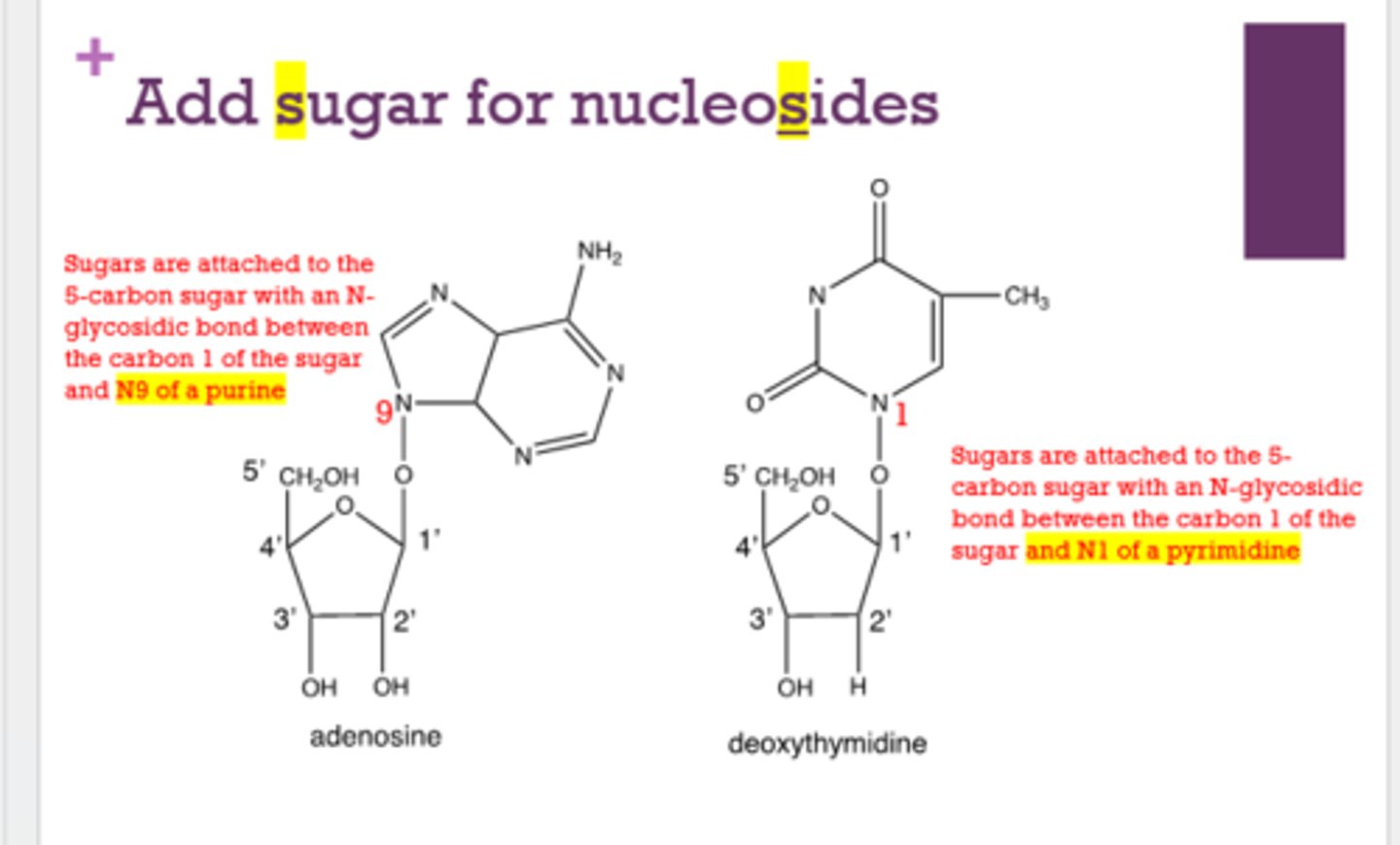
uracil + ribose = ?
uridine

cytosine + ribose = ?
cytidine

thymine + deoxyribose = ?
deoxythymidine

cytosine + deoxyribose = ?
deoxycytidine

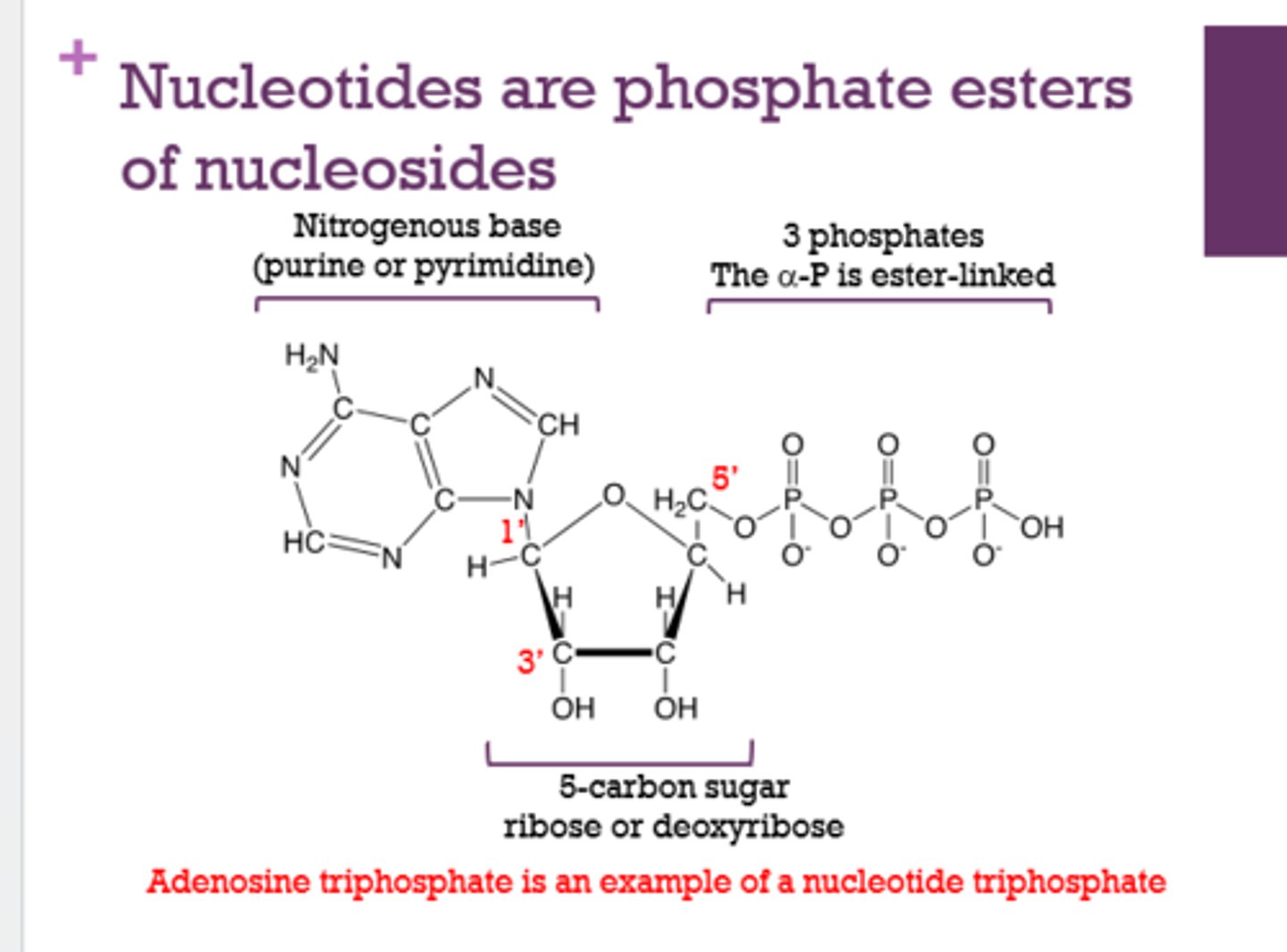
ATP is an example of a _________ triphosphate.
nucleotide
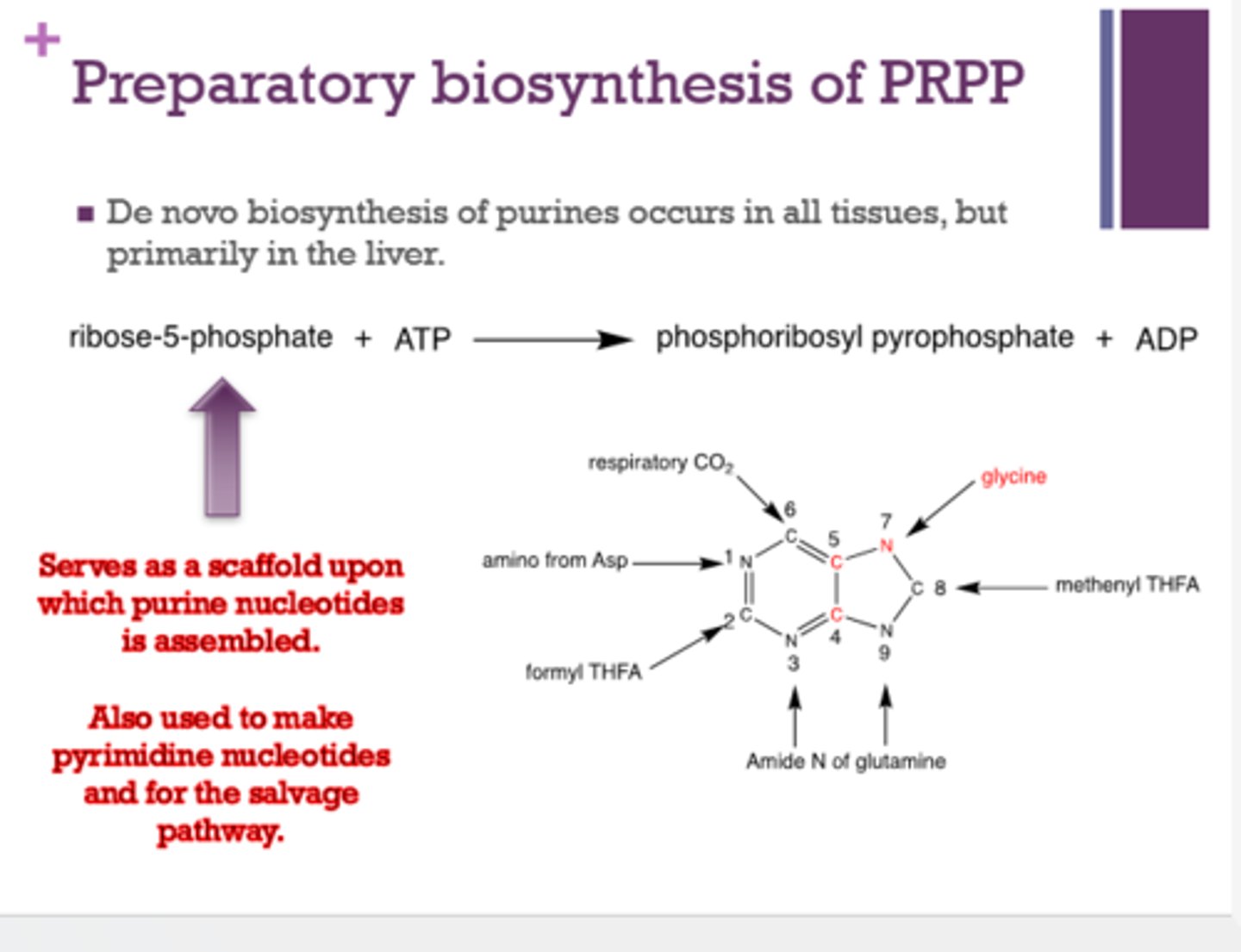
What molecule serves as a scaffold upon which purine nucleotides are assembled and also used to make pyrimidine nucleotides and the salvage pathway?
ribulose-5-phosphate
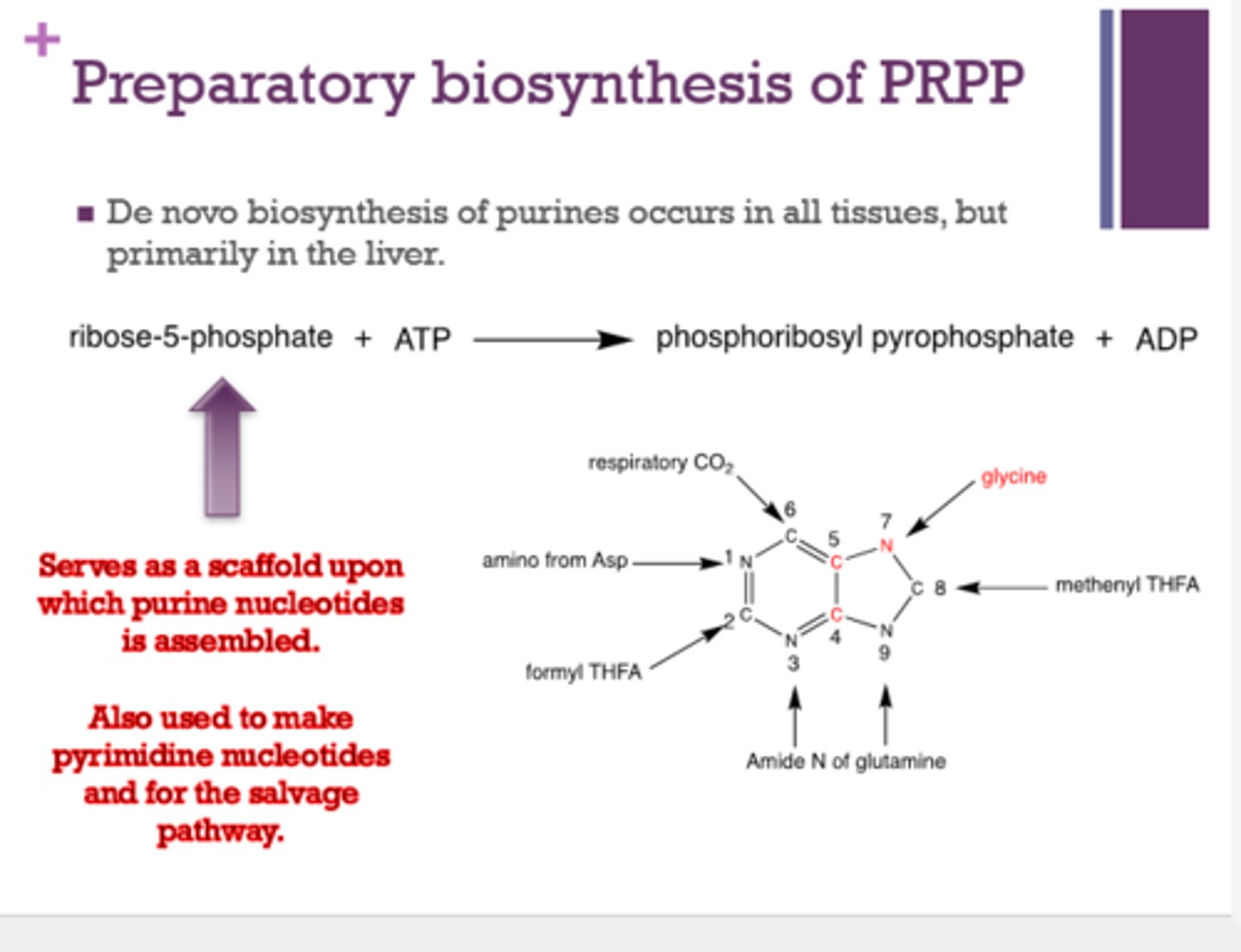
Where does de novo biosynthesis of purines occur?
all tissues, but primarily the liver
What is the Amidotransferase committed step (rate-limiting step) of purine biosynthesis?
N9 added to glutamine
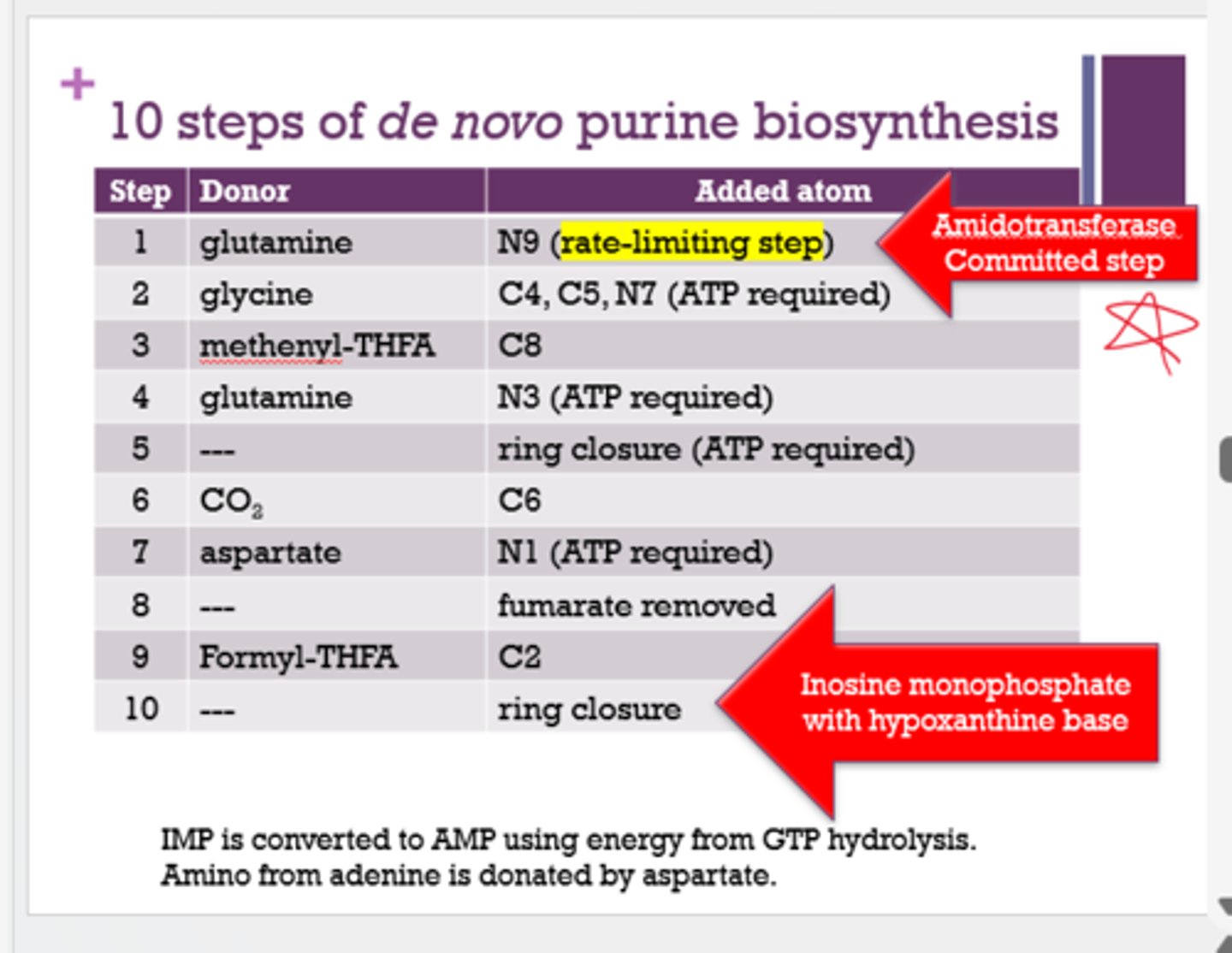
What is inosine monophosphate with hypoxanthine base associated with?
(could also be worded as "what is the last step in de novo purine biosynthesis?")
Ring closure
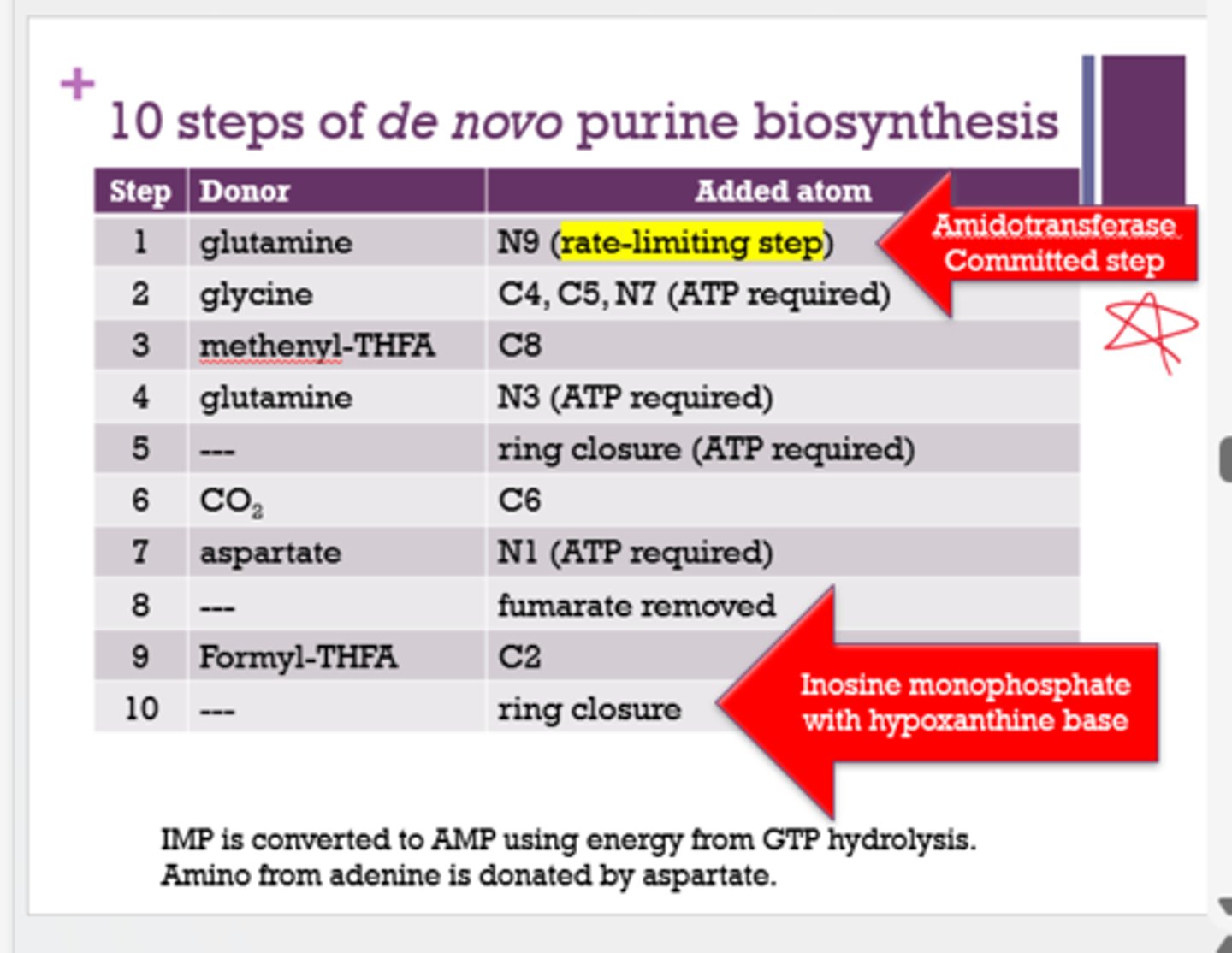
What 3 amino acids are used in the de novo purine biosynthesis? (for sure on test)
glutamine
glycine
aspartate
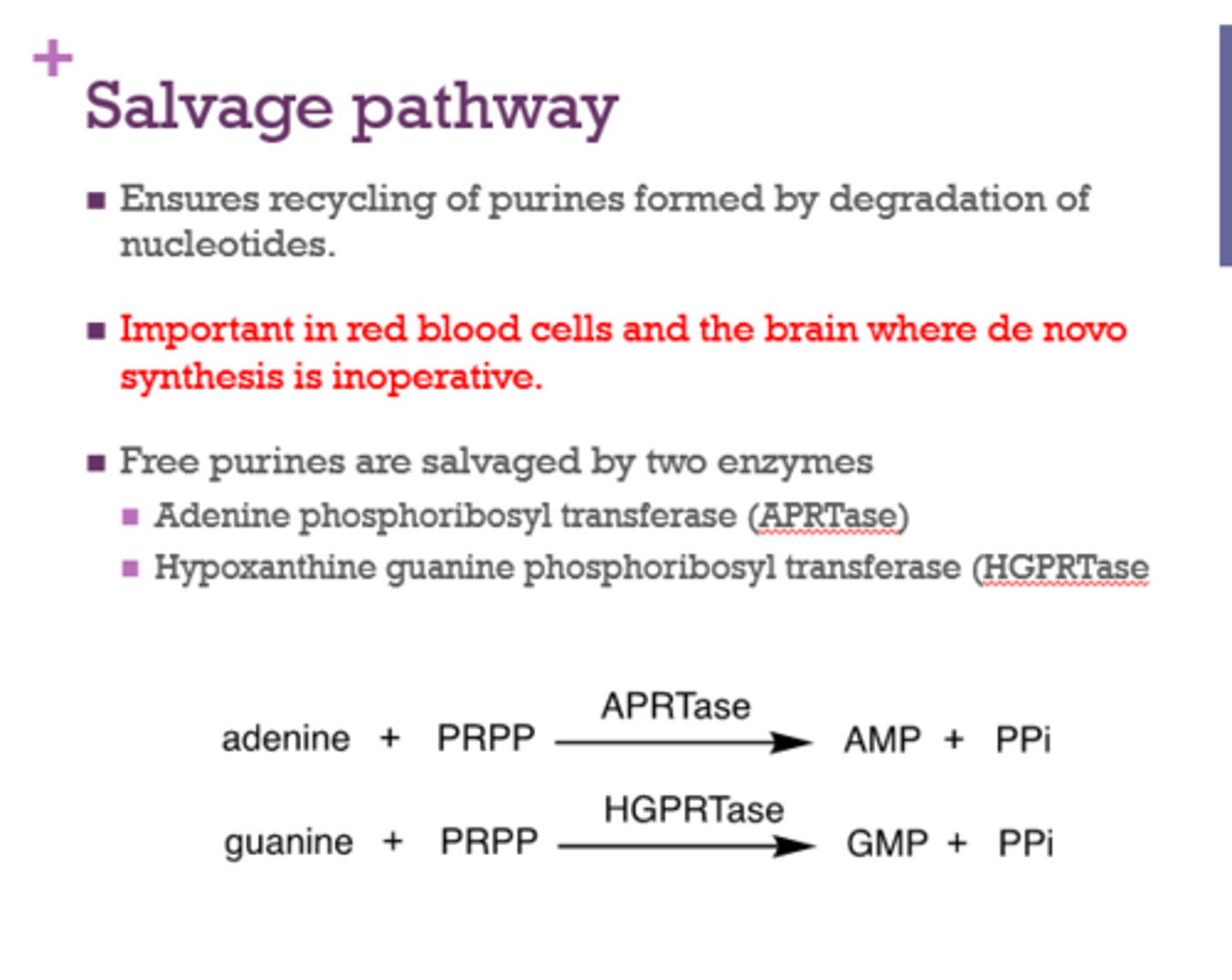
Where is de novo synthesis inoperative? (2) (for sure on test)
RBCs and the brain
What is the rate limiting step in purine biosynthesis?
Amidotransferase (step 1)

What is the end product of purine base metabolism?
uric acid (2,6 - dioxopurine)
Where does degradation of purine nucleotides mainly occur?
liver
Xanthine oxidase contains FAD, molybdenum, and iron, and produces ______________________.
reactive oxygen species (ROS)
What are some disorders of purine metabolism? (5)
- hyperuricemia
- uricosuria
- gout
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
- Hypouricemia
Note: "Be familiar with these disorders related to purine, but don't need to know the details"
