Alkenes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
How is the double bond formed?
The double bond results from the sideways overlap of a spare un-bonded singly filled p-orbital
Name and Angle of the C=C
Planar
120 degrees
Structural Isomerism
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
Stereoisomerism
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms in space
Why does stereoisomerism occur?
It occurs as a result of restricted rotation about the C=C double bond
Why do some molecules not show stereoisomerism?
On one of the carbon atoms of the C=C bond it has two of the same groups attached,
Z isomerism or Cis Isomerism
the priority groups are on the same side
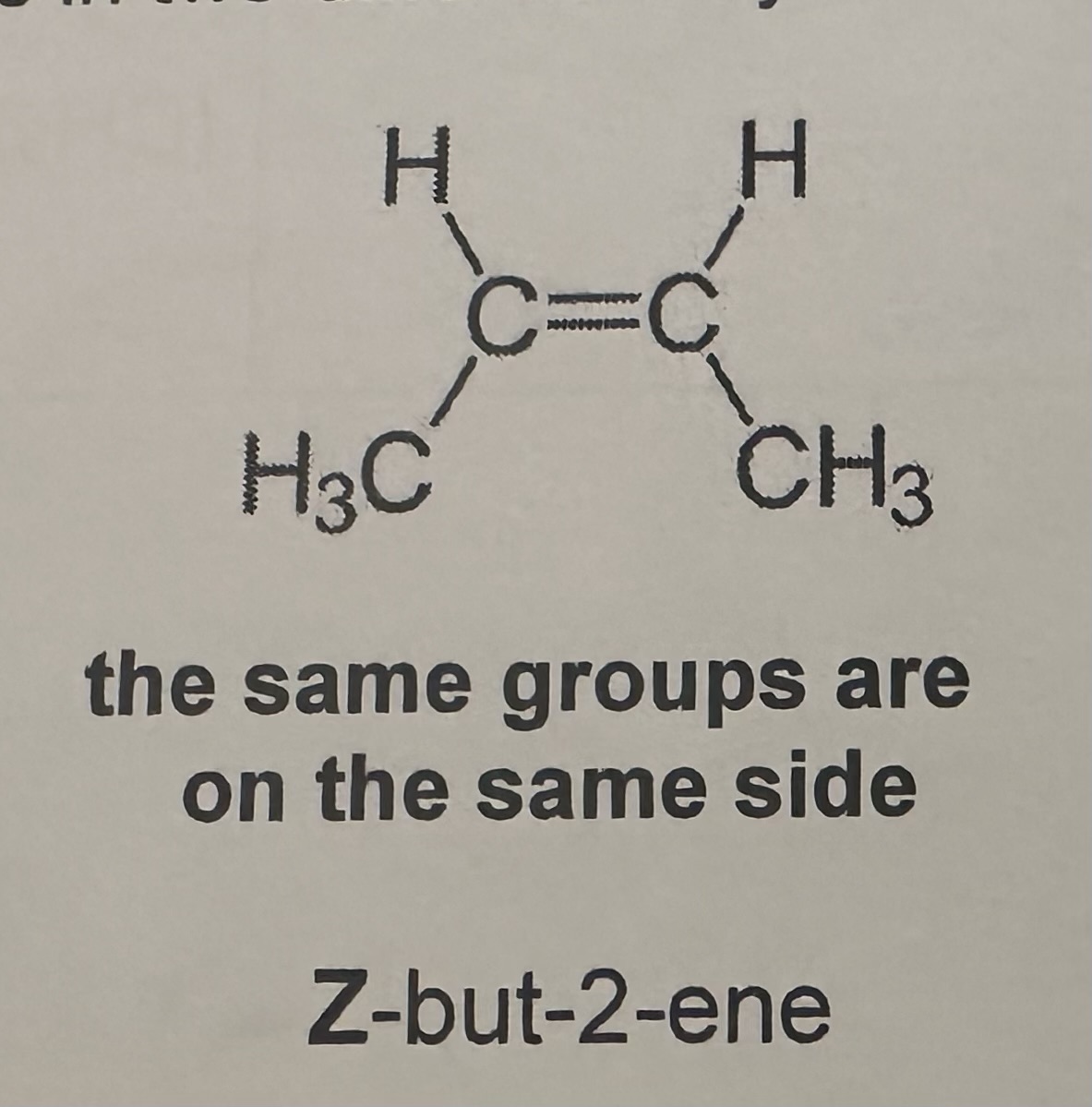
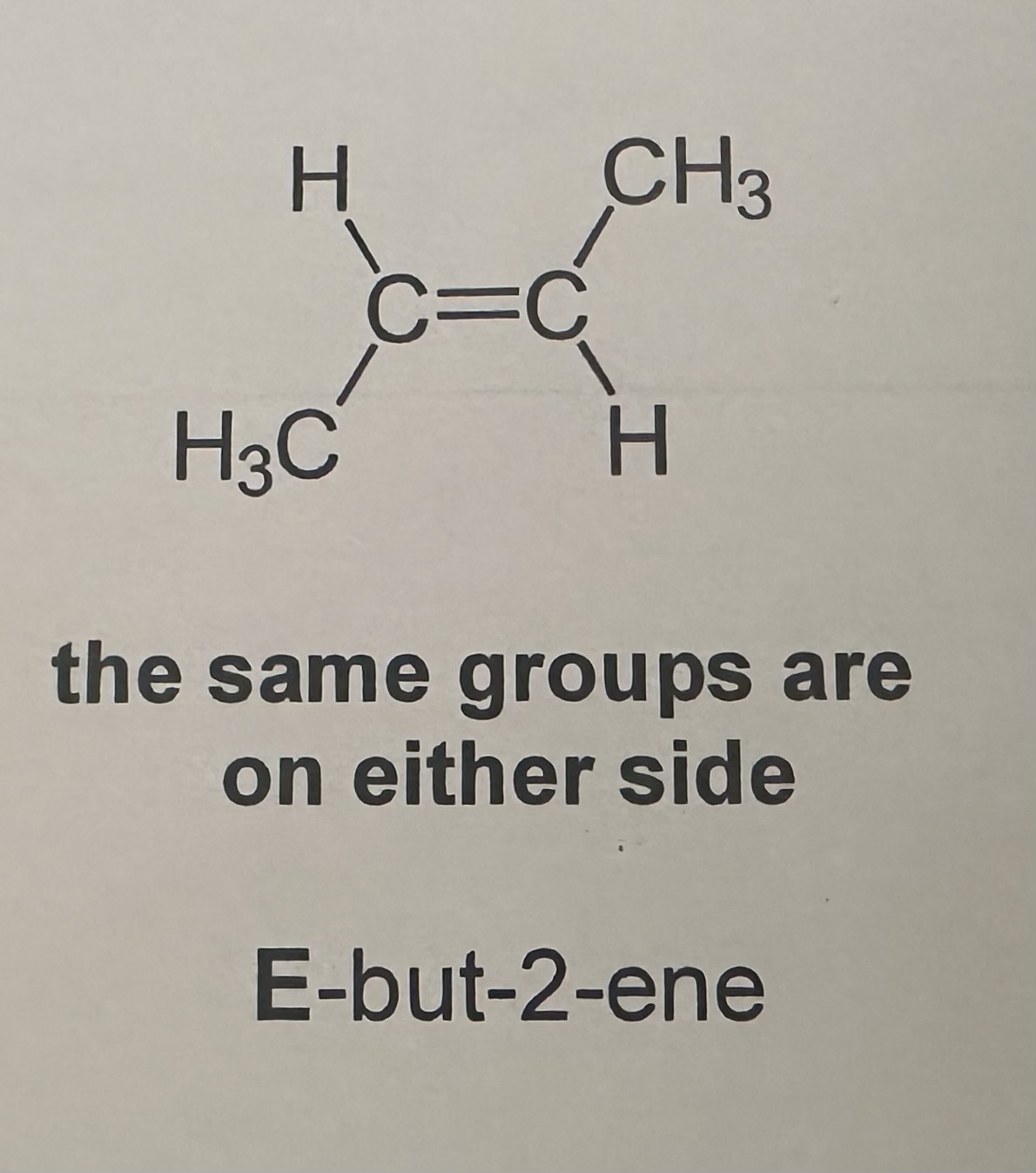
E isomerism or Trans Isomerism
the priority groups are on different sides
Reaction of Alkenes: Hydrogenation
Addition of hydrogen
Reagents: H2/Ni
Importance: used in the manufacture of margarine
Reaction of Alkenes: Halogenation
Addition of a halogen
Reagents: Br2 or Cl2
Importance used in the test tube lab to test for the presence of an alkene
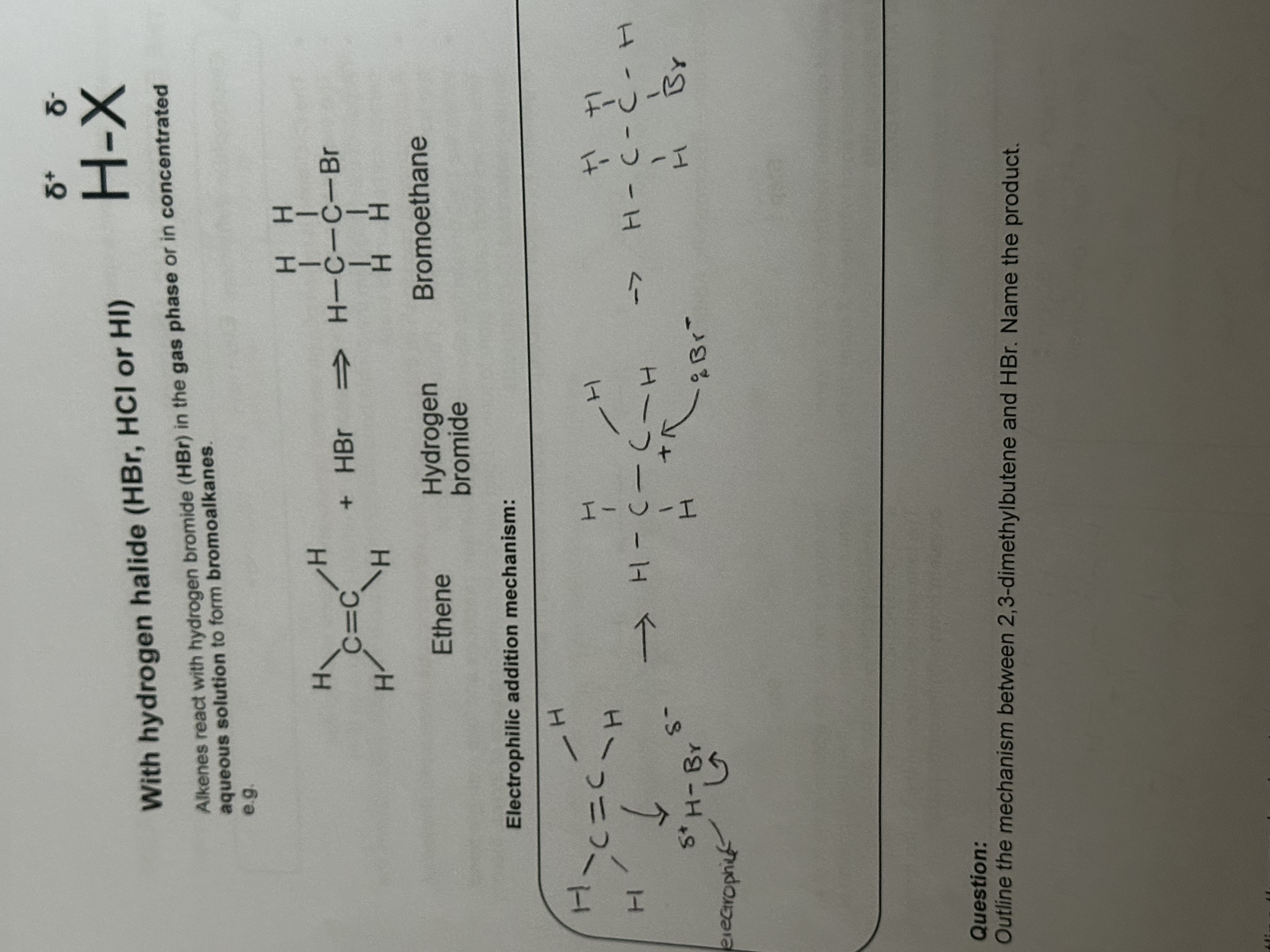
Reaction of Alkenes: Addition of an acid
Reagents: HBr or HCl
Importance: used in organic synthesis when making a haloalkane
Reaction of Alkenes: Hydration
Addition of water
Reagents: Steam, add a catalyst
Importance: used to make industrial ethanol for fuel and solvent purposes
Electrophile
Electron pair acceptor
Electrophilic addition
Why does hydrogen react more readily with alkenes than with alkanes?
The bond enthalpy of C-C sigma bonds is higher than that of pi bonds
What happens when an unsymmetrical alkene is added to HBr or HCl
A major product and minor product is form
The major product is formed via the more stable carbocation
Carbocations
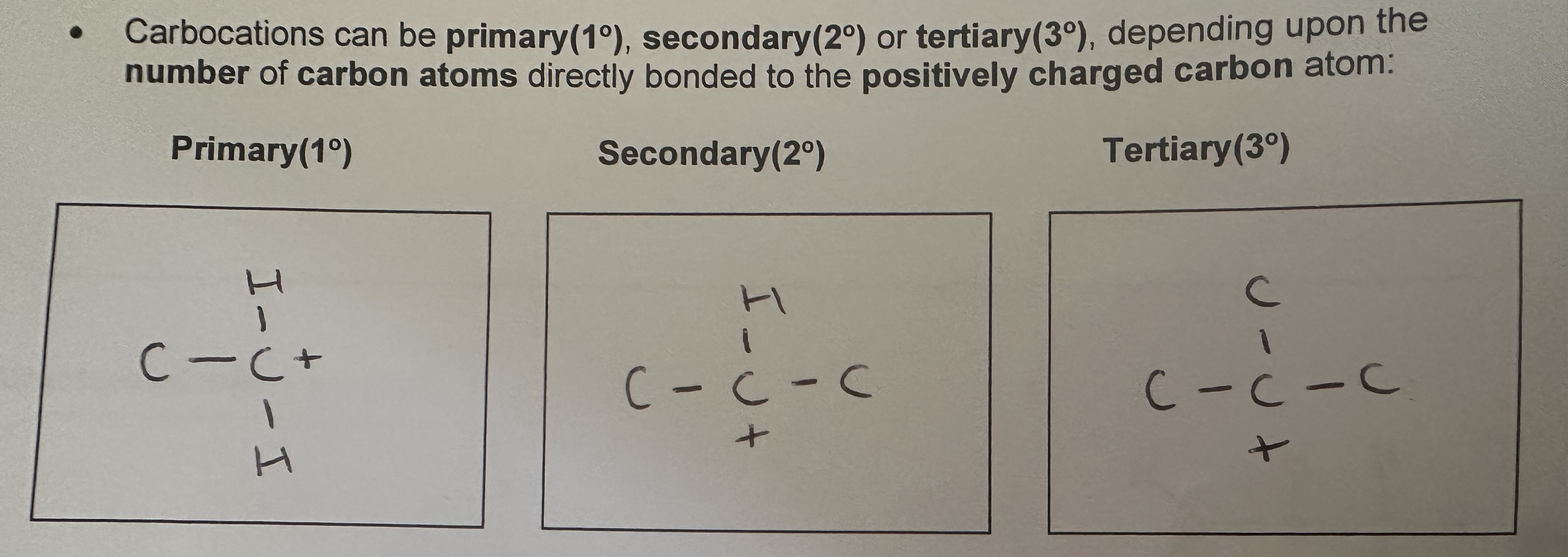
What increases the stability of carbocations?
The presence of alkyl groups
Addition polymerisation
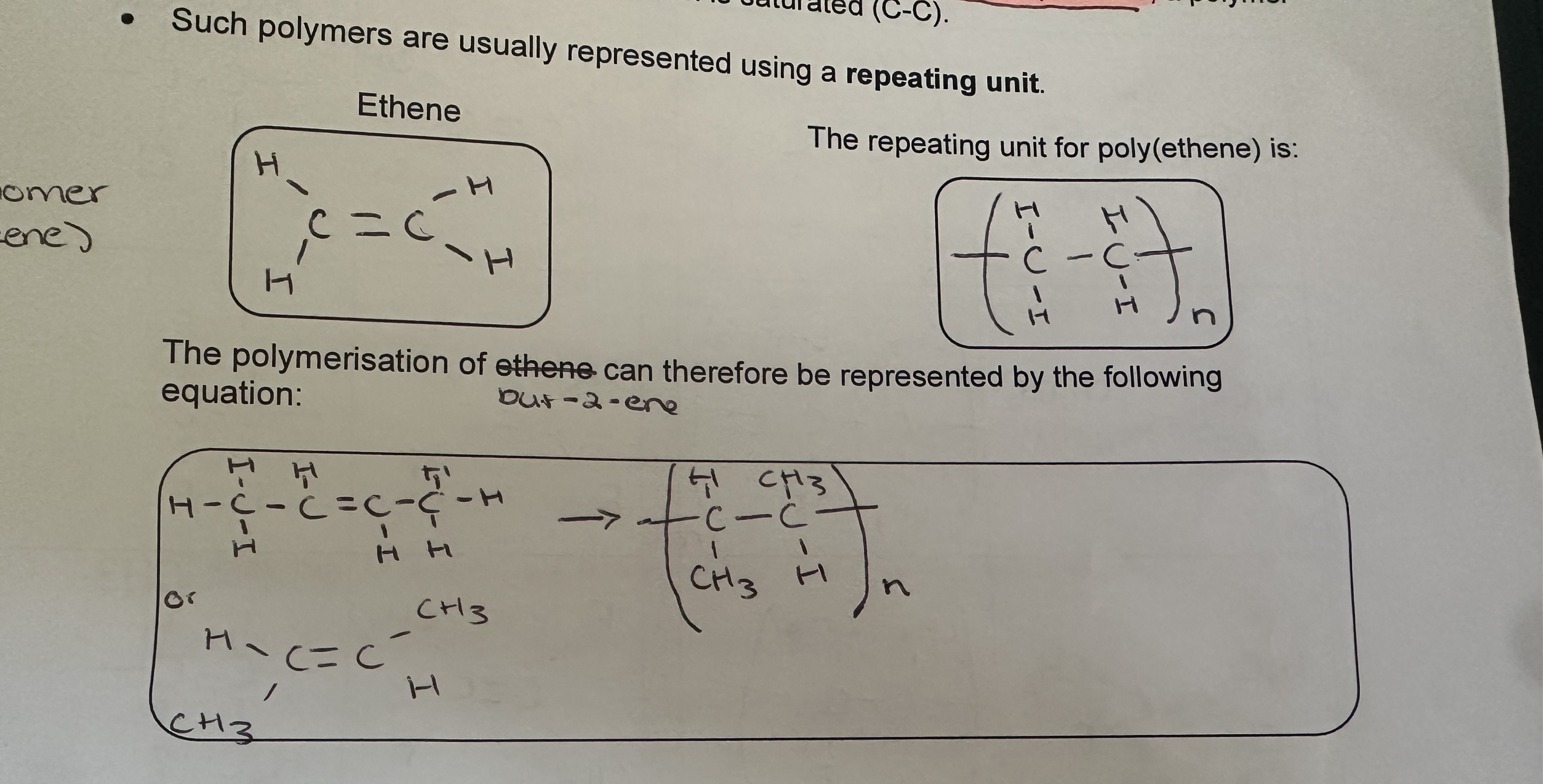
Uses of Polymers
Poly(ethene) - washing up bowls, plastic bags
Poly(propene) - Rope
Poly(chlororethene) PVC
Hard and rigid as there is PDD, Plasticisers are added to make the plastic more flexible
Waste polymers and alternatives: Combustion for energy production
Polymers can be burned to release heat energy for generating electricity
Adv/Disadv of using combustion for energy production
Advantage - Reduces the need for combusting fossil fuels
Disadvantage - Produces HCl gas which is toxic. Can be prevented from entering atmosphere by reacting with bases e.g. CaCO3 and CaO
- Releases CO2
- Releases CO. Ensure there is plenty of oxygen to avoid incomplete combustion.
Waste polymers and Alternatives: Organic Feedstock
Waste polymers can be converted into other chemicals such as alkenes, that can be used in manufacturing processes
Advantage of Organic Feedstock
Reduces the need for cracking crude oil
Biodegradable and Photodegradable Polymers
Plastics can be made from renewable food sources - corn starch - this reduces the dependency on crude oil
Biodegradable - naturally broken down by bacteria
Photodegradable - naturally broken down by sunlight