Comparative Digestive Systems
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
actions in digestion
mechanical, chemical, microbial
digestion
continuous process along alimentary canal, breaking down of food
alimentary canal
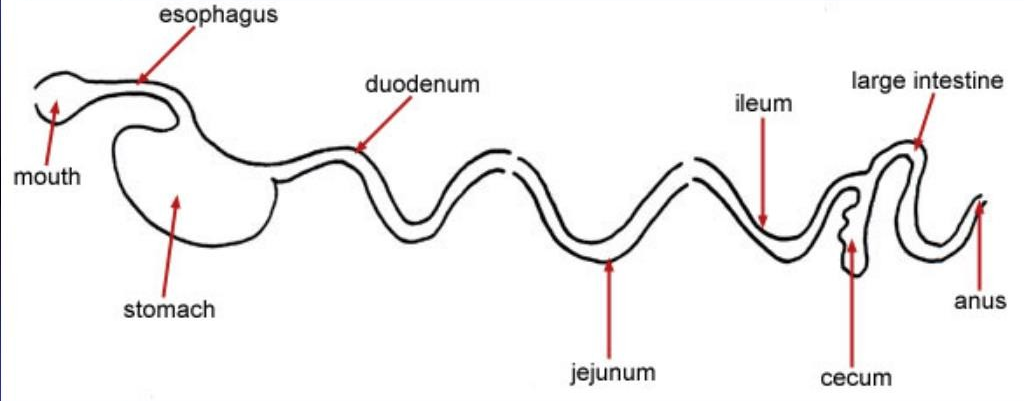
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
monogastric
one stomach, humans and pigs
modified monogastric
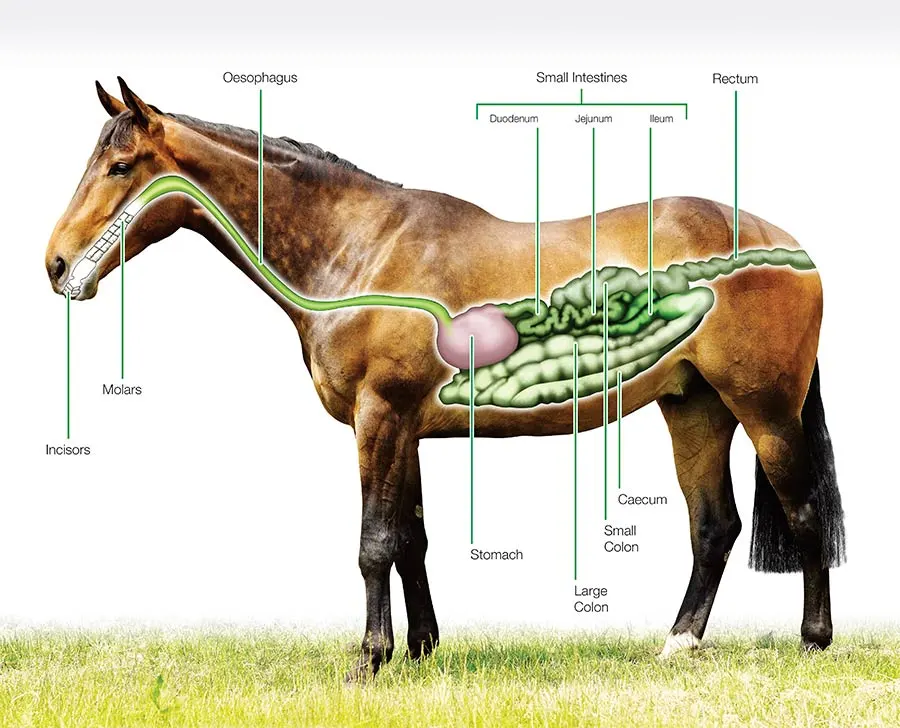
single stomach with specialized compartments that aid in digestion, horses and birds
ruminant
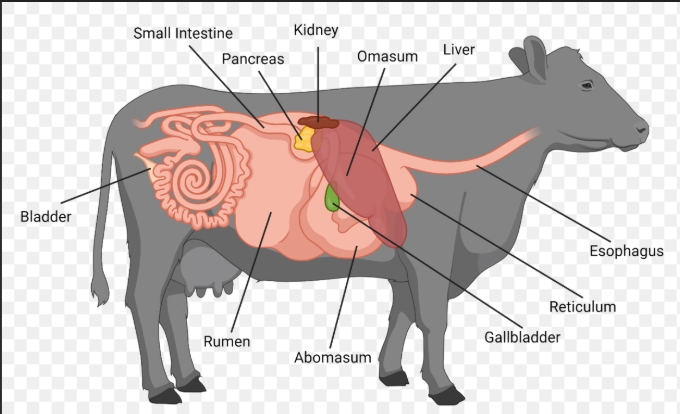
more than one stomach compartment, sheep cattle goats and llamas
monogastric diagram
ruminant diagram
specialized monogastric diagram
monogastric passage rate
8-12 hrs
ruminant passage rate
96-120 hrs, 6-8 hrs per day
salivary gland secretions
water, mucin, bicarbonate salts
mucin
lubrication aid for swallowing
bicarbonate salts
acts as a buffer to regulate stomach pH
swine mouth secretion
salivary amylase
ruminant mouth secretions
no enzymes
no ruminant mouth enzymes
provides source of N, P, and K
esophagus
ingested material moves via muscular contractions known as peristaltic waves
horse esophagus
only one way peristaltic waves
ruminant esophagus
two way peristaltic waves, allows chewing of cud
esophageal groove
prevents milk from entering the rumen of suckling animal by bypassing the reticulo-rumen and becoming fermented
reticulum volume
5%
rumen volume
80%
omasum volume
7-8%
abomasum volume
8-9%
reticulum
not completely separated from rumen, walls lined with intersecting ridges resembling a honeycomb
rumen
large, hollow, muscular compartment with papillae lining walls that secrete no enzymes and fills most of the left side of the abdominal cavity
rumen functions
storage, soaking, mixing, breakdown, fermentation chamber
fermentation chamber (rumen)
provides ideal environment for microbes to synthesize water soluble vitamins and vitamin K as well as deamination reactions
rumen provides bacteria
warm, moist, dark, anerobic conditions with 6.8 pH and substrate
bacteria provide rumen
VFAs, CP, vitamin K, B vitamins, body protein
Volatile fatty acids (VFAs)
three main energy sources in ruminant diet: propionate, acetate, butyrate, and horses and swine don’t use these well
proprionate
energy like glucose, higher in grain fed animals
Acetate
high in grazing animals
butyrate
VFA energy source with no change in concentration depending on feed
eructation
burping to prevent fatal bloat
urea cycle
takes nitrogen across the rumen wall back to the salivary glands in order to preserve nitrogen in the system
omasum (manyplies)
spherical organ filled with muscular laminae studded with short papillae
omasum functions
reduction of particle size and absorption of water
colostrum
milk produced up until 30 hrs after birth to provide nutrients and antibodies for developing the immune system
abomasum
essentially the same as the stomach in non-ruminants
monogastric features
pH around 2-3, stores ingested food, muscular movements cause physical breakdown, secretes digestive juices
digestive juices
gastrin, hydrochloric acid, pepsin, rennin
horse stomach
larger than other species, glandular plus non-glandular regions divided by margo plicatus, ulcers
gastrin
hormone that causes release of digestive enzymes
gastrin stimuli
stomach distension, presence of partially digested proteins, hypercalcemia
gastrin inhibitors
presence of acid in stomach, somatostatin
hydrochloric acid
activates pepsin, constitutes majority of gastric acid
parietal cells
secrete HCl
pepsinogens
proteolytic enzyme that begins protein digestion, degrades food proteins into peptides
chief cells
release pepsinogens
rennin
complex of enzymes produced in all mammals to digest milk
small intestine
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Duodenum secretion providers
Brunner’s gland, pancreas
Brunner’s gland
Alkaline secretion for duodenum
Pancreas
Secretes majority of digestive juices with hormone secretin for duodenum
Enzyme for peptides
Peptidase
Enzyme for lactose
Lactase
Enzyme for sucrose
Sucrase
Enzyme for maltose
Maltase
Enzymes for protein
Chymotrypsin, trypsin
Enzyme for lipids
Lipase
Enzyme for carbohydrates
Amylase
Jejunum
Active site of nutrient absorption of AAs, sugar, fatty acids, glycerol with villi to increase absorptive area
Illeum
Second active site of nutrient absorption, mainly absorbing vitamin B12 and bile salts
Liver
Has bile salts and cholesterol
Bile salts
Emulsify fats, activate lipase, stored in the gall bladder
Large intestine parts
cecum, colon, rectum
large intestine function
microbial digestion of VFAs and MCPs, absorption of water, synthesis of B vitamins
Horse large intestine
60% of GIT
Horse cecum
bacterial fermentation, synthesis of water soluble vitamins and vitamin K, proteins considered of limited value to horse
health issues in the digestive system
founder, colic, acidosis, ketosis, milk fever, urinary calculi, thiamine deficiency
Lignin
undigestible plant fiber
old tall plant
high in lignin
bolus
ball of food that goes back and forth between rumen and mouth for remastication
rumen volume
40-50 gal
essential amino acids
A.A.s essential for life that must be ingested
lysine
essential AA for swine
CHONS
protein atoms
CHO 1:2:1
carbohydrate atoms
CHO not 1:2:1
lipid atoms
CHONPS
nucleic acid atoms
microbial crude protein
primary protein source for ruminants
copraphagy
animal with spiral colon that poops pellets and will eat shit to regain CP and B-vitamins
Founder cause
overload of carbonaceous concentrates (too many simple carbohydrates)
Horse cecum volume
25 qts
rennin
clot milk for digestion
Digestibility
how fast food moves through the GI tract
Urea
non-protean nitrogen source, makes up 1-3% of diet
founder
coffin bone points down as a consequence of severe laminitis from overfeeding
colic
twisted gut
urinary calculi
Ca:P ratio off
transfonation
move bacteria from one animal’s rumen to another