Evolutionary Mechanisms
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
The different processes that contribute to variation in a gene pool (need to be able to explain each):
Random assortment of chromosomes - occurs during meiosis. reuslts in gametes that have a huge number of possible combinations of the chromosomes that originally came from the male and female parent
Crossing over - occurs during meiosis and may result in pieces of chromatid being broken off and attaching to a different chromatid. Results in recombination of the alleles along the resulting chromosome.
Non-disjunction - where one or more members of a chromosome pair fail to separate during meiosis. Gametes then contain more or less than the correct number of chromosomes.
Mutations [most important source] - permanent changes in DNA of a chromosome and may result in totally new characteristics in an individual. Mutations in gametes can be passed from generation to generation
Random Fertilisation - Each person produces a huge number of different gametes with respect to the number of alleles each contains, and because any sperm can fertilise any egg there is an infinite number of possible combinations of alleles in the offspring.
What is evolution?
The gradual change of a species’ characteristics over time
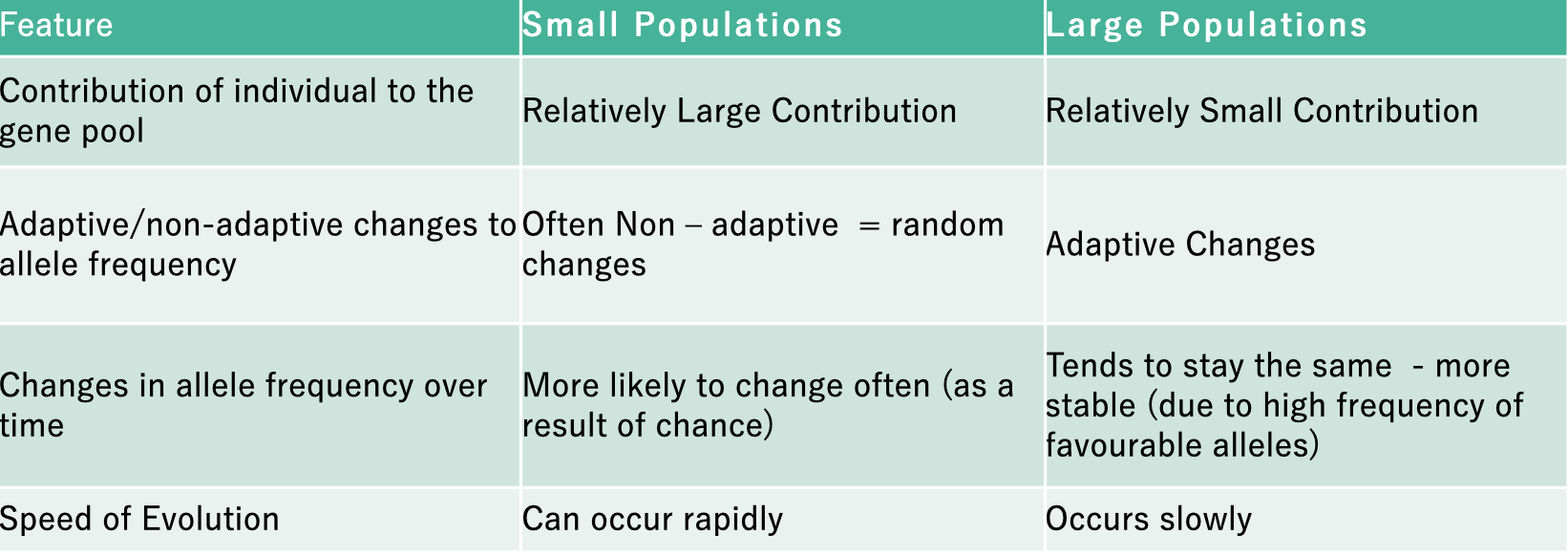
Gene pool & allele frequencies in different sized populations:
What is gene flow:
The movement of genetic material (alleles) from one population to another.
what brings about gene flow?
migration. Immigrants to a certain country can bring alleles that are not already in the population they immigrate to or they can alter existing allele frequencies
impact of barriers on gene flow:
populations are often kept apart by barriers that inhibit the amount of interbreeding between them and preventing gene flow. isolation leads to seperate gene pools forming. Different environmental pressures experienced by different populations → particular characteristics being favoured → altering the frequency of alleles in each gene pool. In extreme cases, can lead to speciation
What are the classifications of barriers to gene flow (particularly relevant for early human populations)? Provide examples.
Geographical barriers - oceans, mountain ranges, large lake systems, deserts and expansive ice sheets
Socio-cultural barriers - economic status, educational background, social position, religion and language
When does natural selection occur & what impact does it have?
Occurs when nature favours one set of alleles over another. This causes major changes to the allele frequency in the gene pool of the population.
why does natural selection occur?
when allele provides a survival advantage, increased frequency of allele & non -favourable allele frequency decreases
what are the observations which lead to darwin’s theory of evolution through natural selection:
Variation {is reason why survival of the fittest is possible} - All members of a species show variation/differences. These traits were passed down through generations, where the characteristics of the parents were seen in their offspring.
Birth Rate - All living things reproduce at a rate that is greater than the rate at which their food supply and other resources increases. Normally, this would result in overcrowding.
Nature’s Balance - Even though brith rate was very high, the number of individuals of each speicies remained relatively constant in the population
how do darwin observations lead to darwin’s theory
observation lead to → a struggle for existence which leads to → survival of the fittest
Survival of the fittest & its impact on gene pool - regarding organisms with favourable characteristics:
organisms with favourable characteristics survive and pass this favourable characteristic on to their offspring. This increases the allele frequency of the favourable/adaptive allele in the gene pool of the population.
Survival of the fittest & its impact on gene pool - regarding organisms with unfavourable characteristics:
organisms with the unfavourable characteristic die and are unable to pass on this characteristic. This decreases the allele frequency of the unfavourable allele in the gene pool of the population.
what is the selective agent
The environmental factor that acts on a population and determines which characteristics are favourable.
Steps of how evolution occurs through natural selection
There is variation of characteristics within a species
More offspring of a species are produced that can possibly survive to maturity.
Because of excessive birth rate and limited resources, there is a struggle for existence - competition for survival.
Individuals with characteristics best suited to the environment have more chance of surviving and reproducing - survival of the fittest.
Favourable characteristics (those with survival value) are passed on to the next generation
In the gene pool, the proportion of alleles that produce favourable characteristics gradually increases
provide human examples of natural selection:
pigmentation of skin - adaptive feature, allowing person to suvive in their natural environment
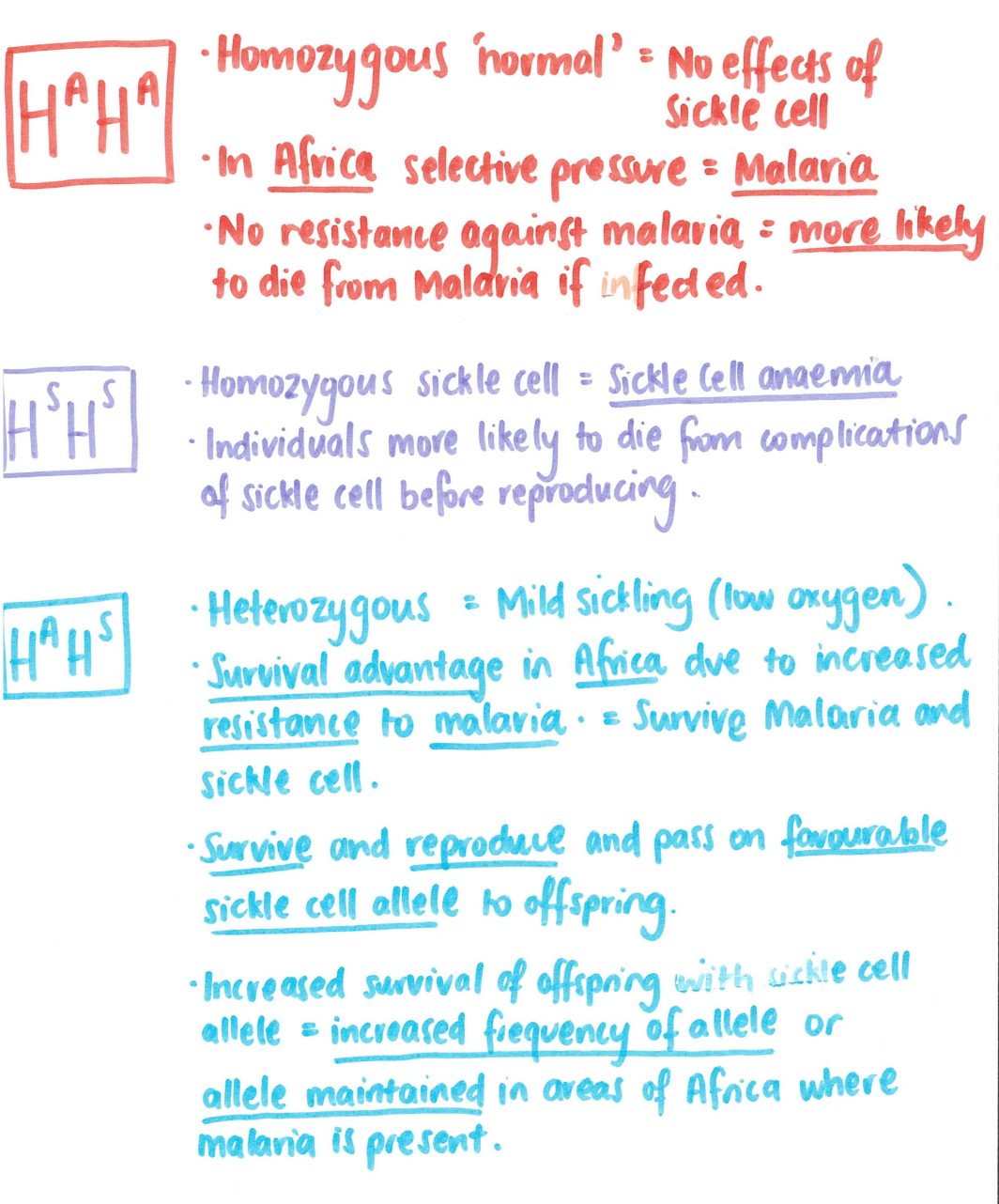
sickle-cell anaemia (heterozygotic advantage in africa)
explain the heterozygotic advantage of sickle cell anaemia by explaining the result of all possible genotypes.
(write as in table drawn in class)
what is random genetic drift?
a random, non-directional (doesn’t deliberately change because there is an advantage) variation in allele frequency.
when does random genetic drift occur + causes ?
when variant forms of a gene (alleles) increase or decreases by chance over time. occurs in small populations.
Cause: random mating or other random events (chance - eg car crash).
Effects of random genetic drift:
traits being lost from small populations
unusual traits, not normally found in the parent populations, and that are often non-adaptive become more frequent
what amplifies impacts of random genetic drift:
differences in the number of children raised by couples
high incidence of premature deaths (before they reproduce)
types of random genetic drift:
founder effect
bottleneck effect
define founder effect
Founder effect occurs when a small number of people migrate away from their homeland and settle in a new area to establish a new community.
describe founder effect
Founder effect occurs when a small number of people migrate away from their homeland and settle in a new area to establish a new community. (This population is called founding population) This population then reproduces and members of the population increase.
The migrant group, being only a small sample of the original population, is usually not genetically representative of them and generally show less variation. The new community, therefore generally shows features that are not typical with the original population.
describe bottleneck effect
Situations which can cause a sudden drop in population size and reduces mating possibilities. The alleles that remain after the event are non-adaptive and are not genetically representative of the original population.
examples of situations causing bottleneck effect
•Natural Disasters
•Wars
•Migration
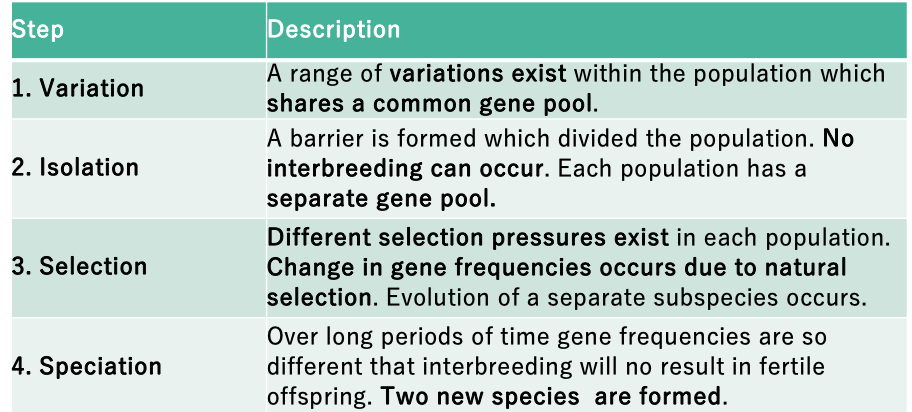
Explain Speciation
isolation: If two populations are isolated for a very long period of time, and the environmental influences on each are different enough, major changes in the allele frequencies within each population could occur.
Members of the two populations can become so different that, even if the barriers to reproduction are removed, interbreeding would no longer be possible à new species has formed!
process of speciation