DNA and RNA Viruses
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Characteriistics of Viruses
Obligate intracellular parasite
DNA viruses replicate and bud off the nucleus
RNA viruses replicate in and are released from the cytoplasm.
Some viruses are strictly human origin and others are zoonotic and transmitted by other means
Some cross the placenta to cause developmental distirbances
Evolutionary origin of viruses
Viruses may be derived from DNA or RNA nucleic acid components of host cells that become able to replicate autonomously
Viruses may be degerate forms of intracellular parasites
NB. Pox viruses may exhibit evolutionary product of some cellular ancestors (large and complex)
2 types of DNA viruses
Enveloped
ds genome( poxviruses, herpes
No enveloped
Consequences of HPB B19 replicating in immature erythroid cells
Fetal death
Severe anemia in immunocompromised patients
Aplastic crisis in sicklers
Polyomavirus
Induces tumour (JC and BK viruses)
BK- urinary complications
JC- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Latent after primary infection and reactivated in immunocompromised individuals
Adenovirus xtics
Naked icosahedral (70-90nm)
Linear ds DNA
Fibers protrude from each penton vertex of capsomere
Over 100 serotypes . 49 cause infection of the respiratory tract.
Others cause eye and gastrointestinal infections
Used to study viral oncogenesis by tumour induction into new born hamsters
Herpesviridae
Large (150-200)
Enveloped
Icosahedral
Ds circular DNA
Causes latent infections which may last the life span of the person
8 Herpesviridae that infect humans
HSV1
HSV2
HHV6
HHV7
HHV8
Epstein Barr virus
Cytomegalovirus
Varicella-zoster: causes chicken pox. Vesicular rash,spread by direct contact with pus/ aerosol, multiplies in lungs
Xtics of Herpesviridae
Envelope has glycoprotein spikes
Asymmetrical tegument
HSV1 and HSV2
HSV1: orofacial lesions, sore throat , fever and blisters.(gingostomatitis,keratoconjunctivitis sicca,infection in trigeminal nerve)
HSV2: lesions on genitalia (14-29). Reactivated by stress,UV,fever. (Genital herpes,infections in ganglia of sensory nerves, considered STD
Cytomegalovirus
Transmitted via saliva,mucus, milk, urine , semen
Asymptomatic
Latent in bone marrow stem cell, myeloid cells
Epstein Barr virus
Affects lymphoid tissue
Transmission by direct oral contact
Cause mononucleosis (sore throat,high fever ,cervical cancer, lymphadenopathy)30-50 day incubation
Burkitts lymphoma(malaria)
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
HHV 6
T lymphotropic virus
Transmitted by close contact
Causes roseola, an acute febrile disease
70% of multiple sclerosis patients
Can cause encephalitis,cancer
HHV7&8
HHV 7 - closely related to HHV6
HHV 8 - Kaposi’s sarcoma, common tumours of aids patients, multiple myeloma
Hepadnaviruses
Small (42-48nm)
Enveloped
Icosahedral
Causes acute and chronic hepatitis
4types infect mammals
Poxviruses characteristics
Largest (230-400nm)
Ds DNA
Unique as it replicates entirely in the cytoplasm
Pathogenic to humans( variola, vaccinia, mollusum contagiosum).
Cowpox and monkeypox can infect humans as well
Inhalation/contact
Fever malaise rash
Classification of RNA Viruses
Enveloped : ss segmented (orthomyxoviruses,Bunyaviruses,Arenaviruses) & ss non segmented ( paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses, Filoviruses, Togaviruses, Flaviviruses, coronaviruses) & ss encoded reverse transcriptase (retroviruses)
Non enveloped: ss(Picornavirus,Calcivirus) & ds (reovirus)
Picornavirus
Small(28-30nm)
Naked icosahedral
Ss (+) RNA
Enteroviruses and 100 rhinovirus (common cold ) affect humans
6 genera of Picornavirus
Parecho eg. Echo 22 & 23
Hepato eg. Hepatitis A virus
Entero eg. Polio
Aphtho eg. Foot and mouth viruses
Rhino eg. HRV A,B,C
Cardio eg. encephalegaly
Similar viruses to Picornavirus
Astroviruses: Associated with gastroenteritis
Caliciviruses: Norwalk virus and Hepatitis E virus
Reovirus
Ds nonenveloped
Medium (60 to 80)
Naked icosahedral
Segmented
Reclusion strain is used in head and neck cancer treatment
Arboviruses families infecting humans
Togavirus(rubella), flavivirus , bunyavirus
Others : rhabdovirus , arenavirus, reovirus
Corona virus
Longest genome RNA
7 human coronaviruses causing diseases in humans. 4mild causing 30% of common cold
Types of corona viruses
SARS-CoV-2(COVID 19)
SARS-CoV(severe acute respiratory sundrome)
MERS-CoV (Middle East respiratory syndrome
HCoV-NL63
HCoV-229E
HCoV-OC43(mild respiratory disease)
HKU1
Retroviruses
Replication is unique by reverse transcription of DNA copy from RNA genome
Lentivirus: HIV 1&2
Oncovirus:HTLV
Bunyavirus
3 segments : L,M,S
Arthropod vectors
Bunyavirus cause
Rift valley fever
California Serogroup
Sandfly fever virus
It’s a hantavirus
Secondary transmission of Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever
Cannot be transmitted from person to person except phlebovirus
Orthomyxoviruses (80-120nm)
All influenza viruses are orthomyxoviruses
Undergo a lot of mutation
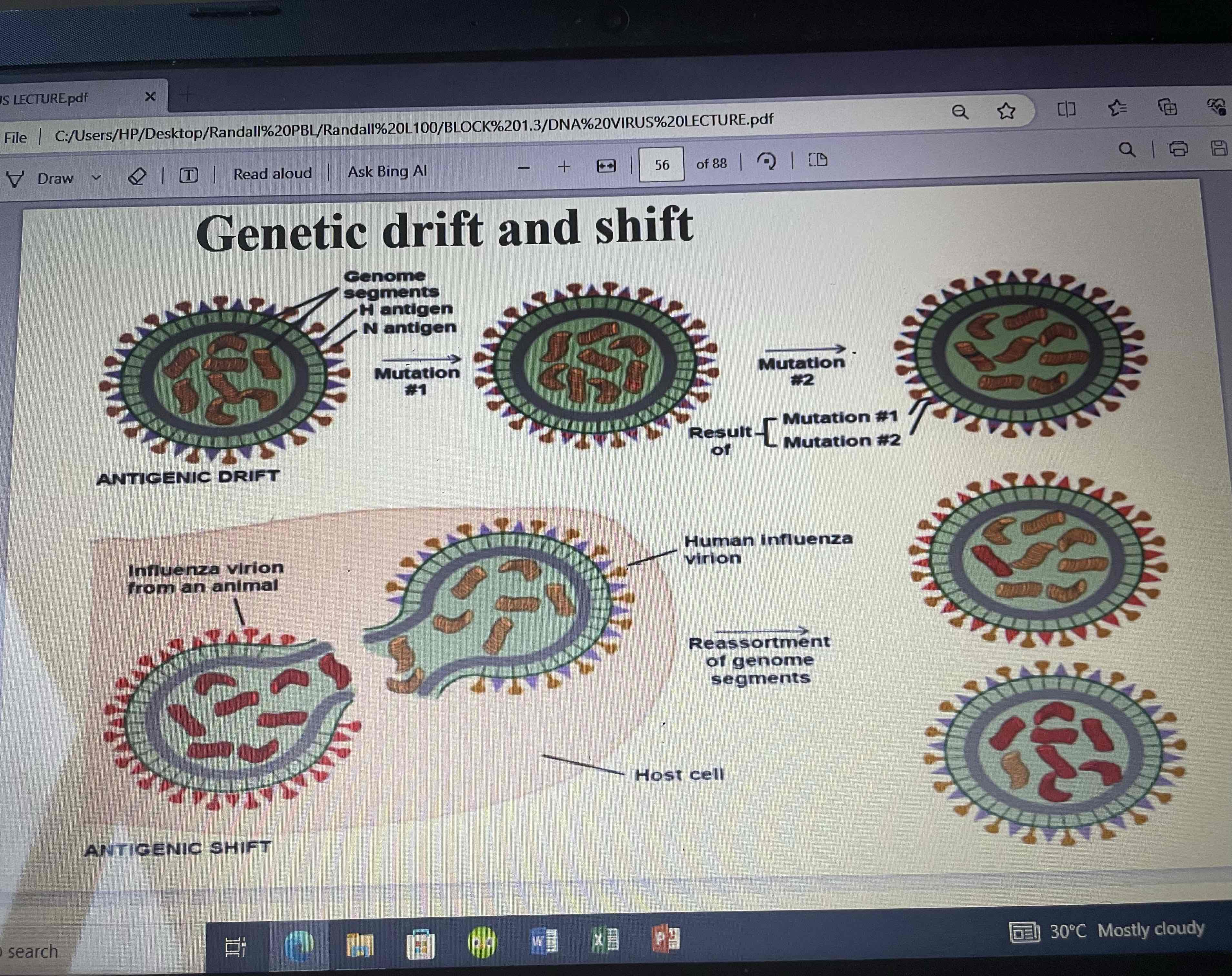
Antigenic shift and drift
Influenza Type A
Seasonal, epidemic
Acute contagious respiratory illness
Aerosols
Binds to ciliated cells of respiratory mucosa
Influenza Type A causes
Rapid cell shedding
Stripping the respiratory epithelium
Severe inflammation
Fever
Headache
Myalgia
Pharyngeal pain
Shortness of breath
Coughing
Paramyxovirus sub families and six of the seven genera that affect humans
paramyxovirinae
Repirovirus : parainfluenza 1,3
Rubulavirus: parainfluenza 2,4 and mumps
Mobillivirus:measles
Henipavirus: Hendra, nipah
Pneumovirinae
pneumovirus: RSV
Metapneumovirus: Human metapneumovirus
Mumps
Painful swelling of the parotid salivary glands
Measles
Also known as red measles / rubeola
Causes sore throat, conjunctivitis, lymphadenitis, fever , Koplik spots ,oral lesions , rash, dry cough, headache
Complications: Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis,progressive neurological degradation of cerebral cortex
RSV
Infects URT
Produces synctia
Infections in children 6months / younger
Replicates in nasopharynx
Rhinitis, otitis, wheezing, croup
Also called pneumovirus
Rhabdovirus
Resembling a bullet
Envelop has spikes
Genetic arrangement similar to paramyxovirus with 5 genes
Rabies virus
Filovirus
Pleomorphic
Cylindrical
Marburg and Ebola
Bornavirus
Neurotropic and may be associated with neuropsychiatric diseases in humans
Factors enabling viruses to produce diseases
Genetic changes
Growth in privileged sites of the immune system
Possession of enzymes that help in Pathogenesis(neurominidase)
Down regulation of MHC preventing destruction by T-cells.
Host factors determining resistance
Conjunctivae(cleansing action)
Interferon
Cellular and humoral immune response
Stomach acids
Mucus
Bile
Infections may be
Productive
Abortive
Restrictive