unit 5: urinalysis
1/84
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
- What is the main function of the urinary system?
Remove waste from the body
- What organs are involved in the urinary system?
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
- What shape are dog/cat's kidneys?
Smooth, bean-shaped
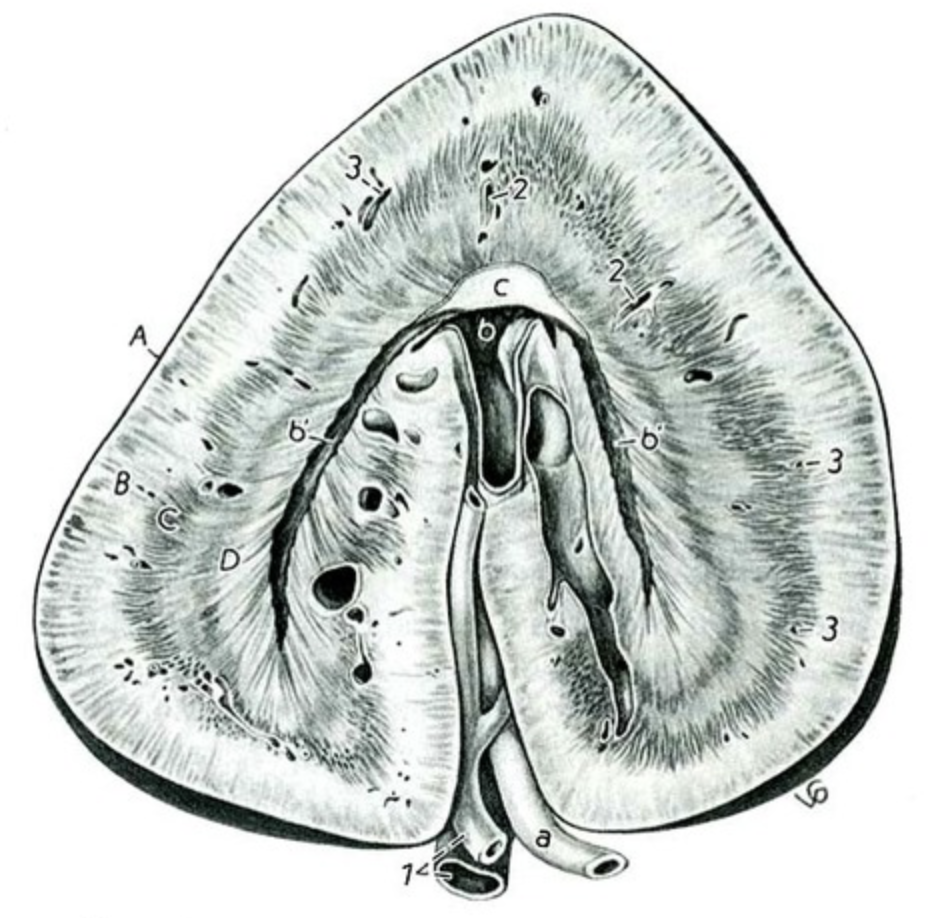
- What shape are a horse's kidneys?
The right kidney is heart shaped
- What are the purpose of the ureters?
transport urine from kidneys to urinary
bladder
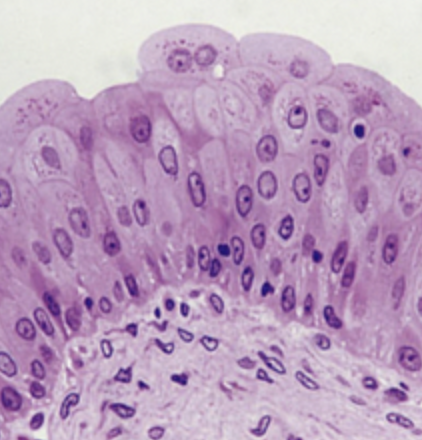
- What is the urinary bladder lined with?
Epithelial cells
- What are the characteristics of a female Urethra?
Short, fairly straight, wide,
strictly urine function
- What are some characteristics of a male urethra?
Relatively long, curved,
narrow, and is part of the urinary and reproductive systems
- What 2 hormones are related to the production of urine?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) - pituitary gland
Aldosterone - adrenal cortex
- What is oliguria?
decreased urine production
- What is Polyuria?
Increased urine production
- What is Anuria?
No urine production
- What is pollakiuria?
frequent urination
- What are some collection methods for urine?
Bladder expression, Catheterization, cystocentesis, Void sample
- When is it best to collect a sample?
In the morning or after several hours of
water deprivation
- Is a void sample a good method?
It's the easiest method but has limited
diagnostic value. The distal genital tract can contaminate it
- Is bladder expression a good method?
It is not useful in bacteria culturing,
must be gentle, and should never be done with obstructed urethras.
- Is catheterization a good method?
Avoid the first portion of collected urine,
which may have increased RBCs and epithelial cells due to trauma to the bladder,
but it is a sterile sample!
- Is a cystocentesis a good method?
The sample is sterile, can be done on
calm patients, and may have RBCs present due to the use of a needle.
- What two sample collection methods are considered sterile?
Catheterization and Cystocentesis
When should you analyze a urine sample?
Why?
within 30 mins- 1 hour
crystals form when urine cools
- What happens to urine when left out?
Crystals form when cooled,
increased
pH, bacteria growth,
breakdown of RBCs, and
casts.
- What factors affect Urine volume?
Fluid intake, temperature, humidity, exter-
nal losses, type/amount of food, type/size of animal, activity level
- What may cause Polyuria?
Nephritis, diabetes mellitus and insipidis, Pyome-
tra, and liver disease
- What may cause Oliguria?
Restricted water access, environmental increase
temperature, acute nephritis, fever, shock, heart disease, dehydration.
- What may cause Anuria?
Urethral obstruction, urinary bladder rupture, renal
shutdown
- What is specific gravity?
Weight (density) of a liquid compared with that of an
equal amount of distilled water.
- How would you read 1.008, 1.010, and 1.012 on a refractometer?
-10 08,10 10, 10 12
physical properties of urine
volume
color
odor
transparency
specific gravity
- what is Isothenuria?
When the USG approaches that of the glomerular filtrate
(1.008 - 1.012)
- What does Isothenuria mean?
It means the kidneys aren't able to concen-
trate/dilute the urine. may hint at chronic kidney disease.
- What are the three things necessary to have a complete urinalysis?
Physical evaluation, Chemical evaluation, and microscopic evaluation
- If a P.H is above 7.0, what is it?
Alkline
- If a p.H is below 7.0, what is it?
Acidic
- What is Glycosuria/Glucosuria?
Presence of glucose in urine
- What is Ketonuria?
Presence of Ketones in urine
- What is Hematuria?
presence of intact rbcs in urine
darker yellow = more concentrated urine
higher specific gravity
lighter color = less concentrated urine
lower specific gravity
- What is Hemoglobinuria?
presence of free hemoglobins in urine
because of muscle cell lysis
equine normally cloud and rabbits and guinea pigs normally milky
high concentration of calcium carbonate crystals and mucus
- What are leukocytes?
white blood cells
- What can you find in the sediment of a urine sample?
Epithelial cells, mucus
threads, RBCs/WBCs, Hayaline Casts, and crystals
- What are the settings for the centrifuge for a urine sample at school?
5 MIN @ 2500 RPMs
excessive amounts of protein can cause
acute and chronic renal disease
glycosuria - presence of glucose
indicative of diabetes mellitus
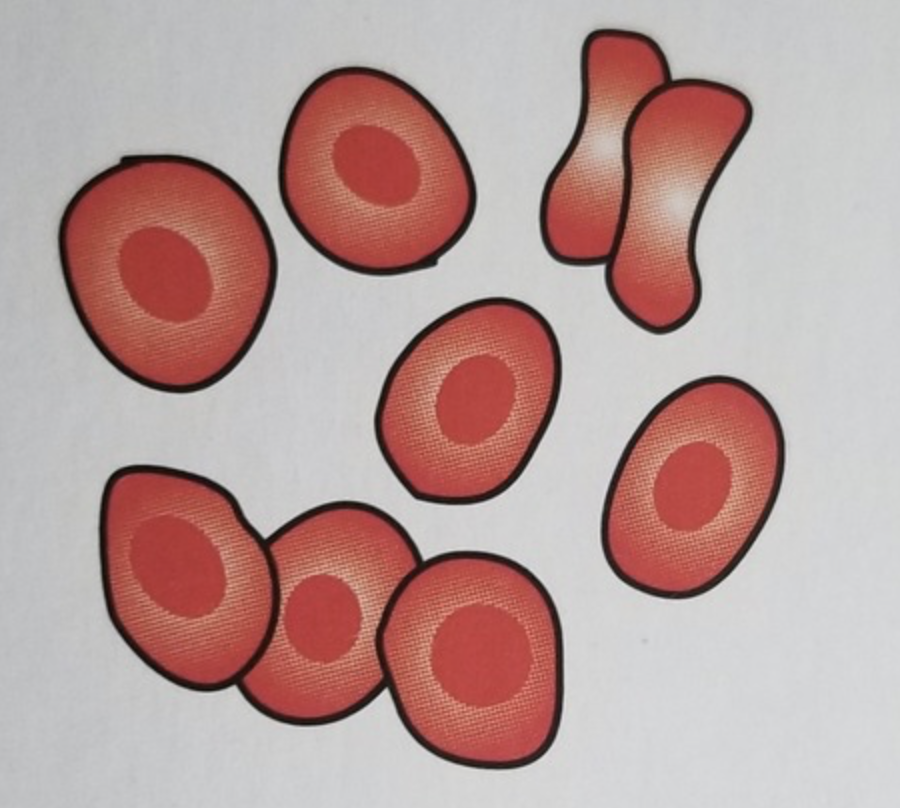
- What do intact RBCs look like?
Simple bright red typical cell
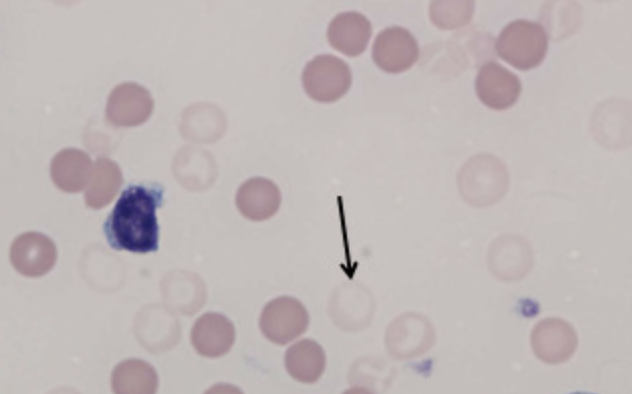
- What do Ghost RBCs look like?
Faded red blood cell
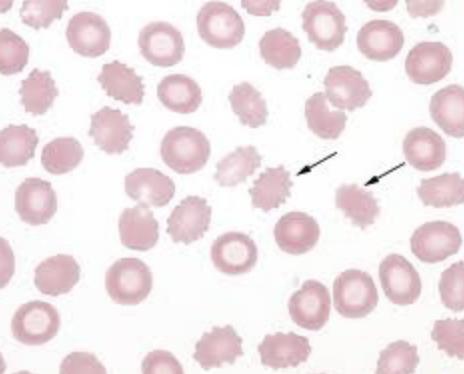
- What does a crenated rbc look like
Sharp projections on rbcs
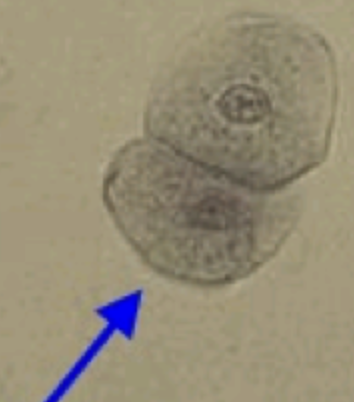
- What does a renal epithelial cell look like?
small pancakes
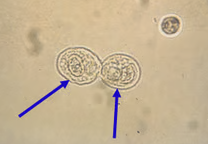
What does a squamous epithelial cell look like?
where are they derived?
a couple pancakes together
derived from the distal urethra, vagina, vulva, or prepuce
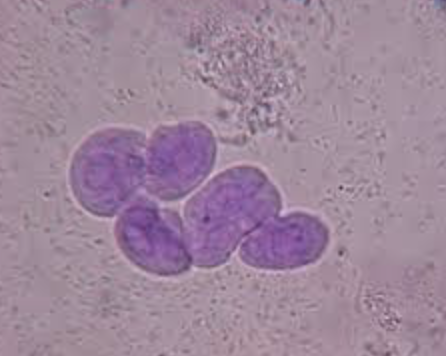
what does a Transitional epithelial cells look like?
where are they derived?
SMALLER THAN SQUAMOUS
from bladder, ureters, renal pelvis, proximal urethra
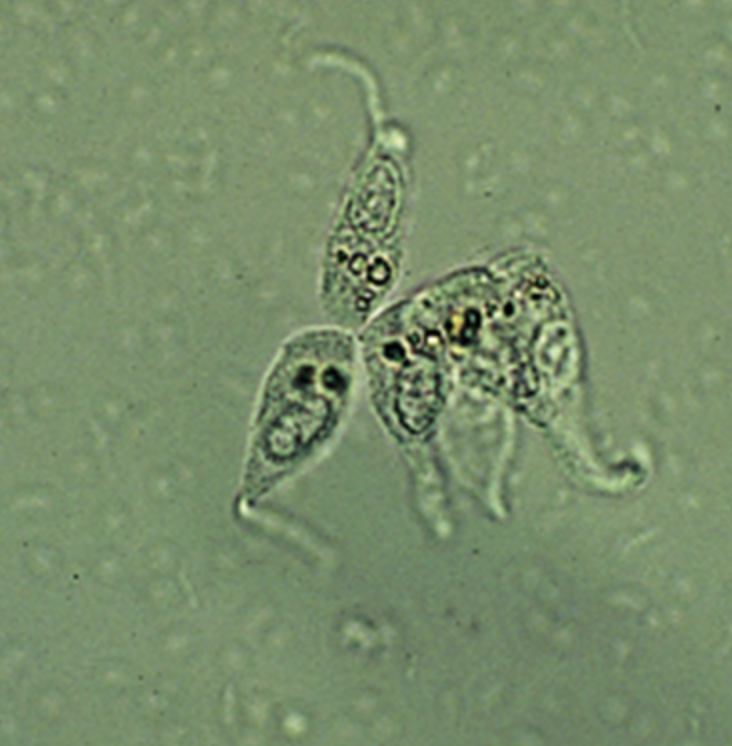
- What does a Caudate epithelial cell look like?
Has a point/tail
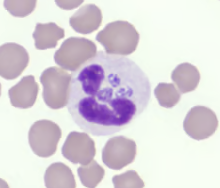
- What does wbcs look like?
have little beans in them
renal epithelial cells
originate in renal tubules
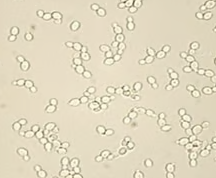
- What do yeast cells look like?
snowman
- What does an increased amount of epithelial cells mean?
Inflammation
- What are some types of casts?
Hyaline, epithelial, cellular, granular, waxy, fatty, and mixed casts

- Characteristics of Hyaline casts
Clear, colorless, composed of mainly protein,
effusion, exercise, and general anesthesia
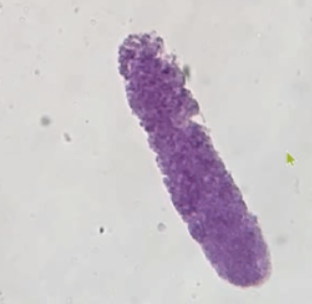
- Characteristics of Granular casts
Most commonly seen, look like hyaline
casts with granules, and are usually seen with acute nephritis
bacteria can proliferate if
left standing in room temperature
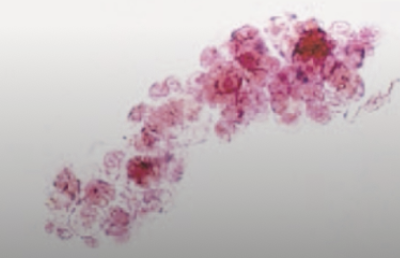
- Characteristics of epithelial casts
consists of epi. cells from renal tubules
embedded in hyaline matrix. Can be seen in acute nephritis and degeneration of
the renal tubules
- Characteristics of Leukocyte casts
Contain WBCs (mostly neutrophils), and
are seen in inflammation of renal tubules
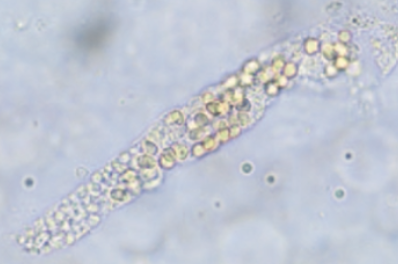
- Characteristics of erythrocyte casts
are a deep yellow-orange, contain
RBCs, and indicate renal bleeding
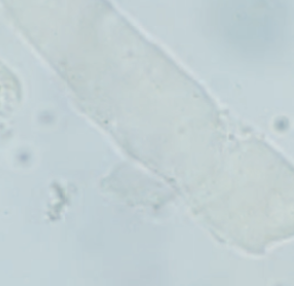
- Characteristics of Waxy Casts
Wider with square ends, dull, homogenous,
and a waxy appearance.
- Characteristics Of fatty casts
Contain droplets of fat, seen in cats with renal
disease and dogs with diabetes mellitus
- What does Crystalluria mean?
presence of crystals in urine
- What factors do crystals depend on?
Urine pH, Concentration, temp., ele-
ments
- How do report crystals?
as occasional, moderate, many, or 1+ or 4+

- What are Struvites?
The most common crystal is seen. A.K.A. Triple Phos-
phate crystal. Found in alkaline to slightly acidic urine.
It is an eight-sided prism with tapered edges.
- What are the two groups of Calcium Oxalate crystals?
Dihydrate and Monohydrate
- Characteristics of Dihydrate Calcium Oxalate?
Small square with an X in the
middle. Found in acidic to neutral urine, common in small dogs, horses, and rabbits.
- Characteristics of Monohydrate Calcium Oxalate?
Small dumbbell shape,
and are from Ethylene Glycol posioning
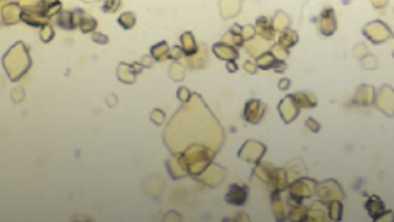
- What are uric acid crystals
Variety of shapes but mainly diamonds, can be
yellow-yellow/brown, and are not common in dogs/cats except Dalmatians.
- What are Amorphous Crystaline material?
Common in alkaline urine, and
has a granular precipitate look
- What are the two types of Amorphous Crystaline?
Amorphous Urates
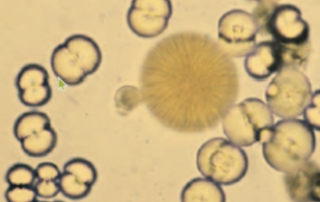
- What are Calcium Carbonates?
Common in horses and rabbits, they are
round with lines radiating from the center, and have no clinical significance
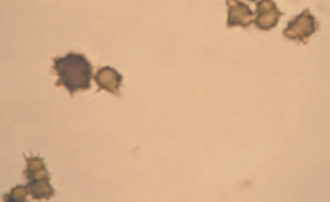
- What is ammonium Biurate?
seen in slightly acidic, neutral, or slightly alkaline
urine. They are brown with irregular spicules. Common in animals with severe liver
disease
- What are sulfonamides?
Seen in animals treated with sulfonamide drugs.
They are round, dark, with a radiating center.
- What are some microbes we can see in urine?
Bacteria, yeast, and fungi
- What are some parasites of urinary tact?
Pearsonema Plica- Canine Bladder
worm
Dictophyma Renale- Giant canine kidney worm
Dirofilaria Immitis- Heartworm
- What are Mucus threads?
are confused with casts, are twisted ribbon-like, and
indicate contamination with genital secretions
- What are Calculi?
Stones
- What does Urolithiasis mean?
presence of stone
urate uroliths = Dalmatians
Dalmatians are predisposed to developing urate stones, also known as urate urolithiasis, due to a genetic condition called hyperuricosuria