ecology - trophic levels in an ecosystem
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
trophic levels
feeding levels within an ecosystem - can be represented by numbers
apex predators
carnivores with no predator
carne
meat
herb
plant
omni
plant and meat
vore
eater
lvl 1
plants and alga make their own food and are known as producers
lvl 2
herbivores that eat plant and alga = primary consumer
lvl 3
carnivores that eat herbivores = secondary consumers
lvl 4
carnivores that eat other carnivores = tertiary consumers
important role of decomposers in carbon cycle
break down dead plant and animal matter by secreting enzymes into environment. small soluble food molecules then diffuse into the microorganism
what are decomposers usually?
bacteria or fungi
key factors for creating optimum conditions for decay:
presence of oxygen
water
warmth
presence of microorganisms
biomass
amount of living material at each trophic level
what do pyramids of biomass show?
the relative amount of biomass in each level of a food chain
what is always at the bottom of a pyramid of biomass?
plant or alga
pyramid of biomass
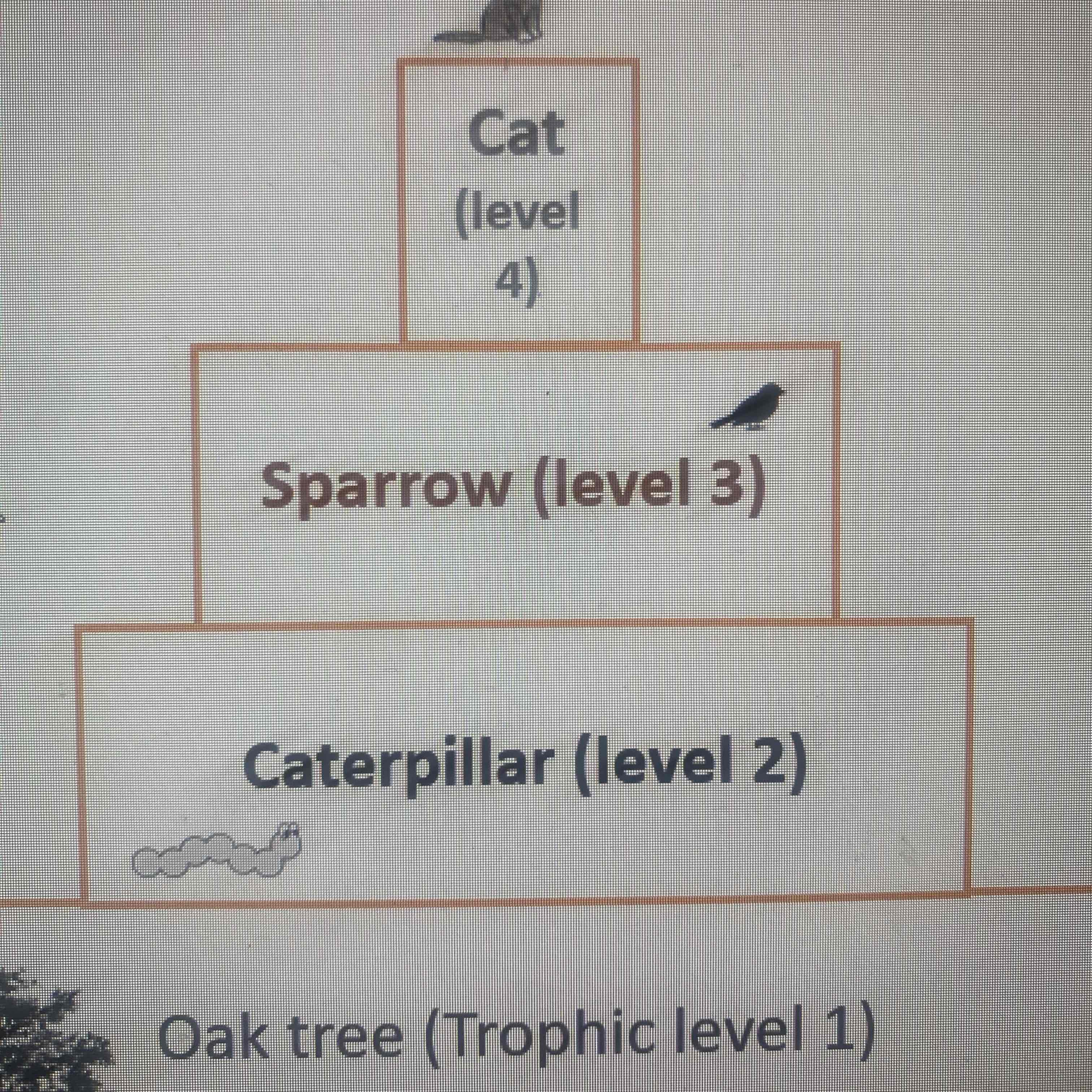
why is the diagram a pyramid shape?
because the amount of biomass and energy available at each trophic level decreases
incident light
the light which shines in the producer
what are producers mostly?
plants and algae
how much incident energy do producers transfer from light for photosynthesis?
1%
what percentage of biomass from each trophic level is transferred to the level above it?
10%
reasons for loss of biomass: (3)
not all ingested material is absorbed into the body some is egested as faeces
not all the absorbed material is used to make new biomass some is lost as waste like Co2 and water in respiration and water and urea in urine
large amounts of glucose are used up in respiration and provide energy for movement, growth and keeping a constant body temp.
use of glucose
used up in respiration
provides energy for:
movement
growth
keeping body at constant temp
waste products
carbon dioxide and water in respiration
water and urea in urine
equation for efficiency of biomass:
effciency of biomass = (biomass transferred to the next level / biomass available at the previous level ) x 100