Music Production Test 1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is a transducer
A device that converts one form of energy to another; sound into electric energy.
What's the "Good" Rule in recording
Good music
Good instruments
Good room
Good mics
Good (mic) placement
What are the types of microphones
Dynamic, condenser, and ribbon
Ribbon Microphone
- most human and warm sounding mic
- incredibly fragile
Dynamic Microphone
- most durable & affordable
- can handle loud sources with little distortion
- Stiff mylar diaphragm attached to finely wrapped wire coil/voice coil, which is suspended by magnetic thingy
Condenser Microphone
- considered to have the highest fidelity/most accurate sound quality
- needs 48v phantom power
A ribbon microphone is made up of...
A thin aluminum ribbon diaphragm suspended with a magnetic flux
A condenser microphone is made up of...
2 plates one thin movable diaphragm and one fixed backplate which together form a capacitor
A dynamic microphone is made up of...
Stiff mylar diaphragm attached to finely wrapped wire coil/voice coil, which is suspended by magnetic flux(?)
Which microphone needs phantom power?
Condensor
What is amplitude on a waveform
The vertical distance between the center line and wave
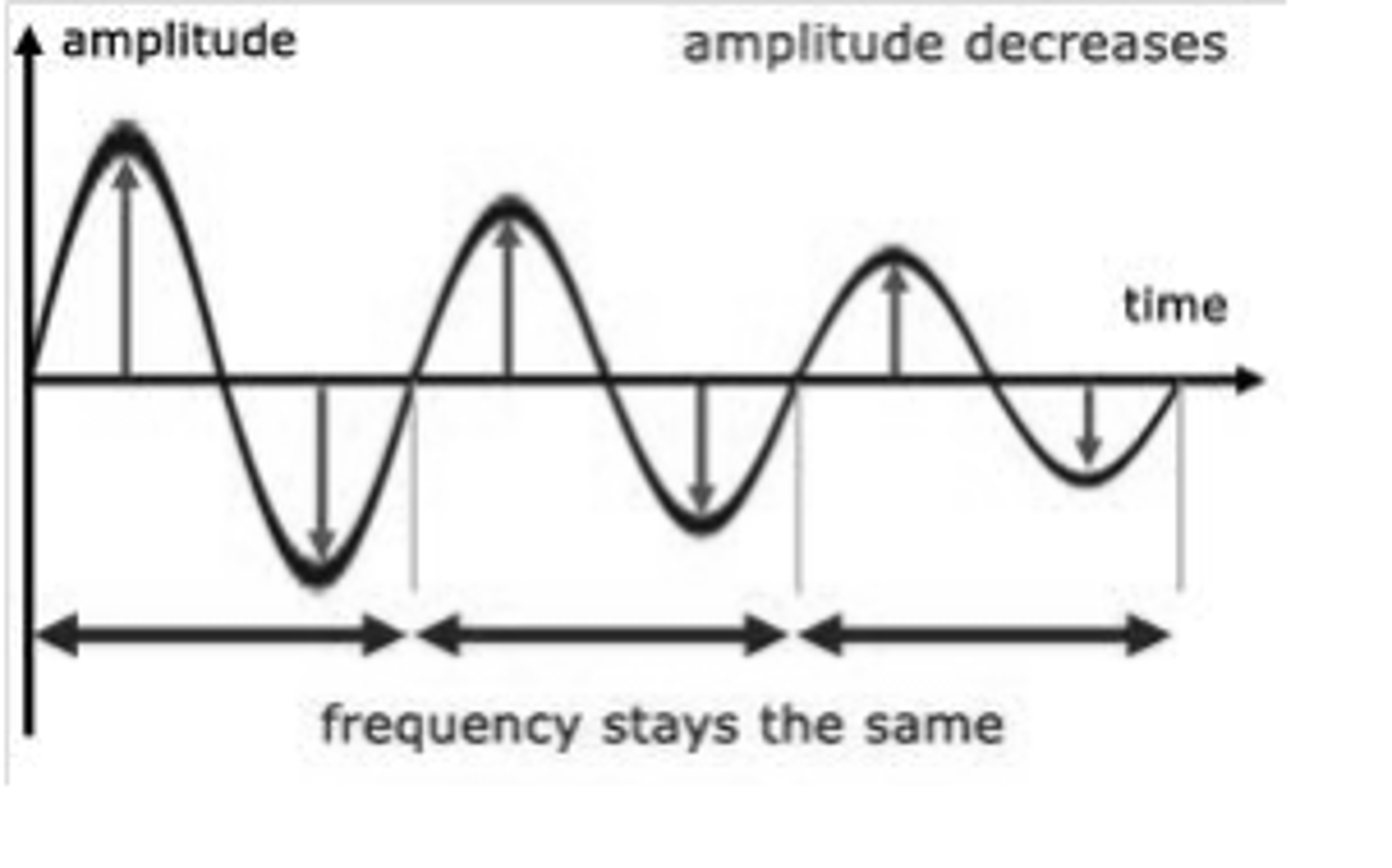
What is frequency on a waveform
The rate of vibration, how fast the wave makes a circle
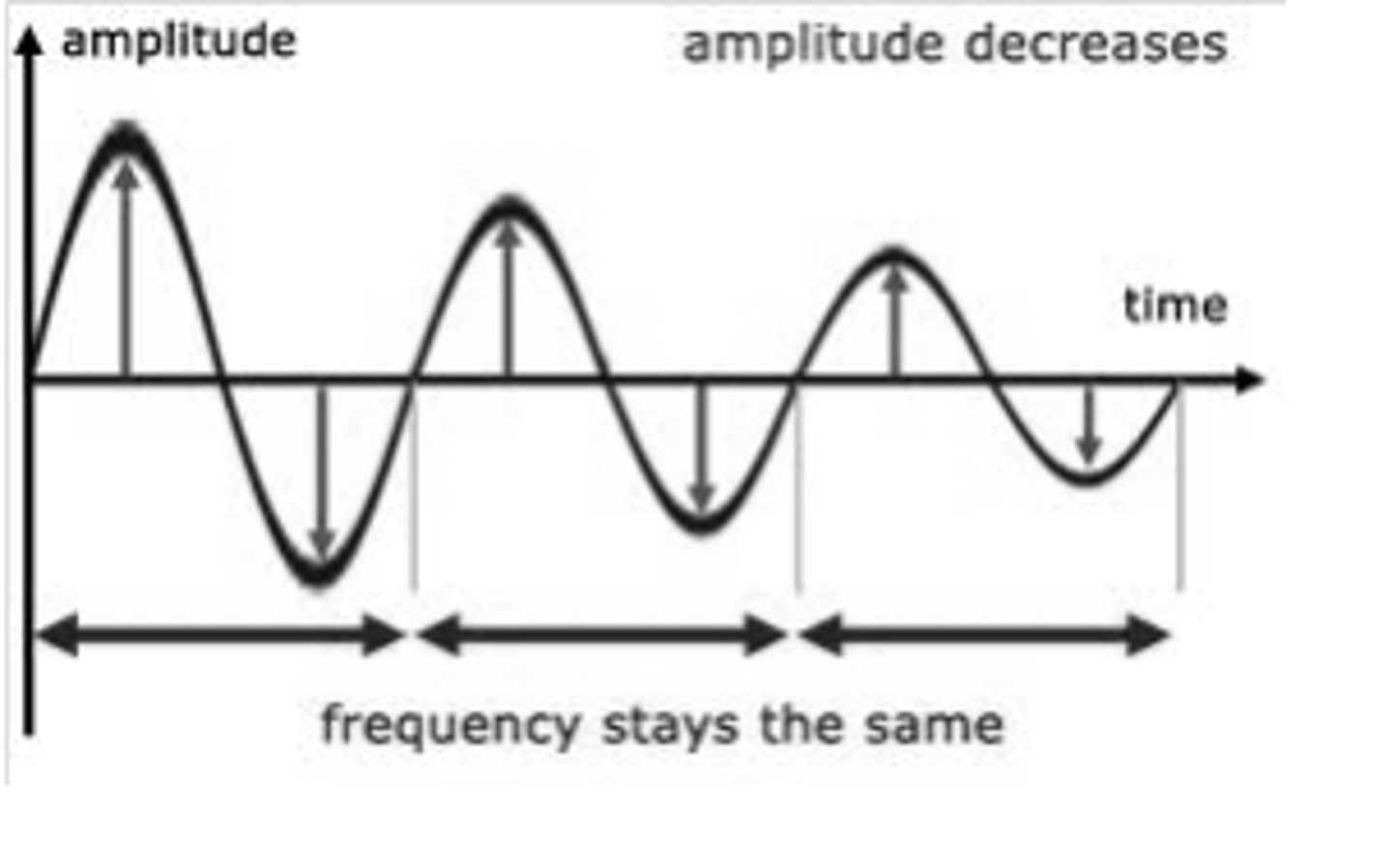
What is Frequency measured in?
Hertz, Hz
What is the wavelength formula
λ = V/hz
wavelength = Velocity/frequency
What's the velocity of sound
1,130 ft/sec at 68 degrees F
What is phase
The timed relationship between 2 waveforms
What does it mean when two waveforms are "in phase"
It means they share the same shape, peak, amplitude, and frequency: they look identical
What does it mean when two waveforms are "out of phase"
it means 2 waveforms, identical frequency and amplitude, start at different points
What is the distance of phase measured in?
Degrees
What is phase shift?
Describes one waveforms lead or lag in time compared to another
What is an envelope?
It's how you describe the variations in amplitude that occur over the duration of a played note.
What are sections that an envelope consist of?
Attack
Decay
Sustain
Release
What is the A of ADSR
Attack - Time taken for a sound/note to reach its highest volume once it's initially played
What is the D of ADSR
Decay - how quickly a sound levels off to its sustain volume, after the attack
What is the S of ADSR
Sustain - the consistent ongoing sound after the initial Attack and Delay
What is the R of ADSR
Release - how quickly the sound depletes after the note is released/sustain ends
How is loudness measured?
Measured in decibels (dB)
What is loudness?
Changes in the sound pressure level
What's the "best" decibel level to mix?
85 dB/SPL
What are Fletcher Munson curves?
These indicate the range of different ranges one can perceive/sensitivity to loudness different at various levels
What is the theoretical range of human hearing?
20hz to 20,000hz
What unit is used to measure the range of hearing?
Hertz (hz)
What happens when two wavelengths are 180 degrees out of phase
The will cancel each other out and there'll be no sound
If there are two microphones placed at different distances from a singer what will happen?
They'll be out of phase and quality will be diminished
What type of microphone should you use at a live show?
A dynamic microphone
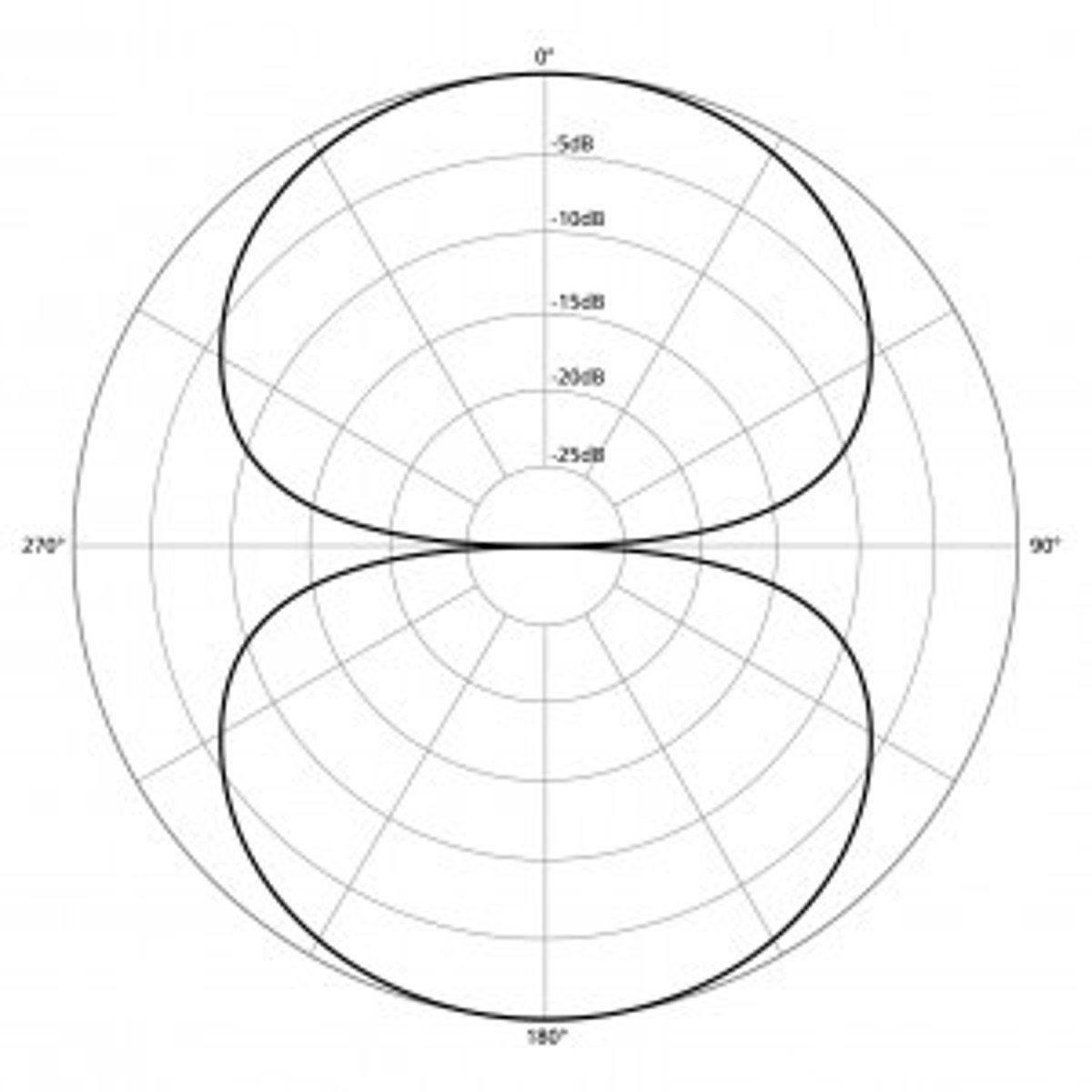
What is the figure 8 polar pattern?
looks like an 8, recording in front of and behind the microphone
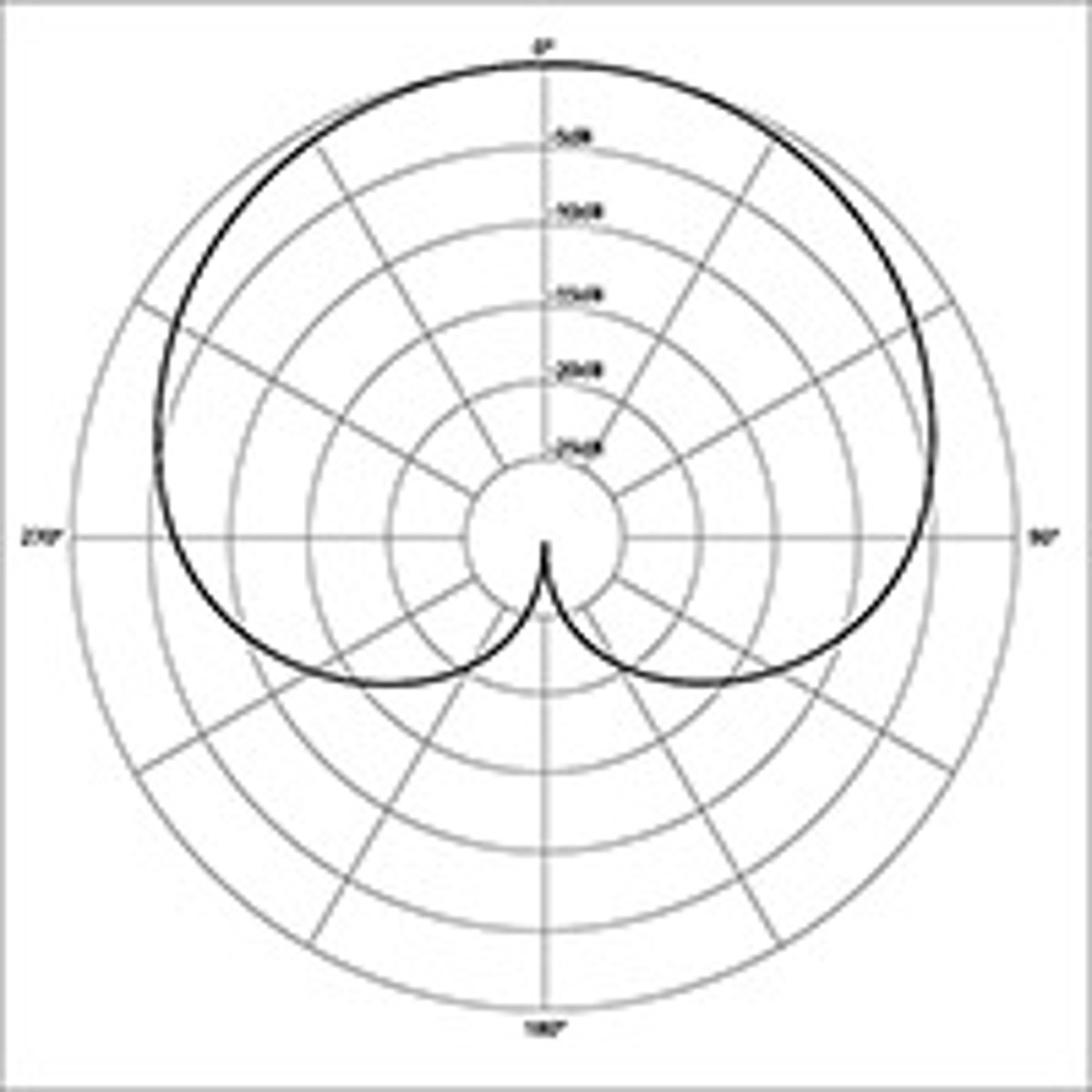
What is the cardiod polar pattern?
Records everything to the side and infront of the mic, but not behind
What is the omni directional polar pattern?
Gets all of it, everything around the microphone
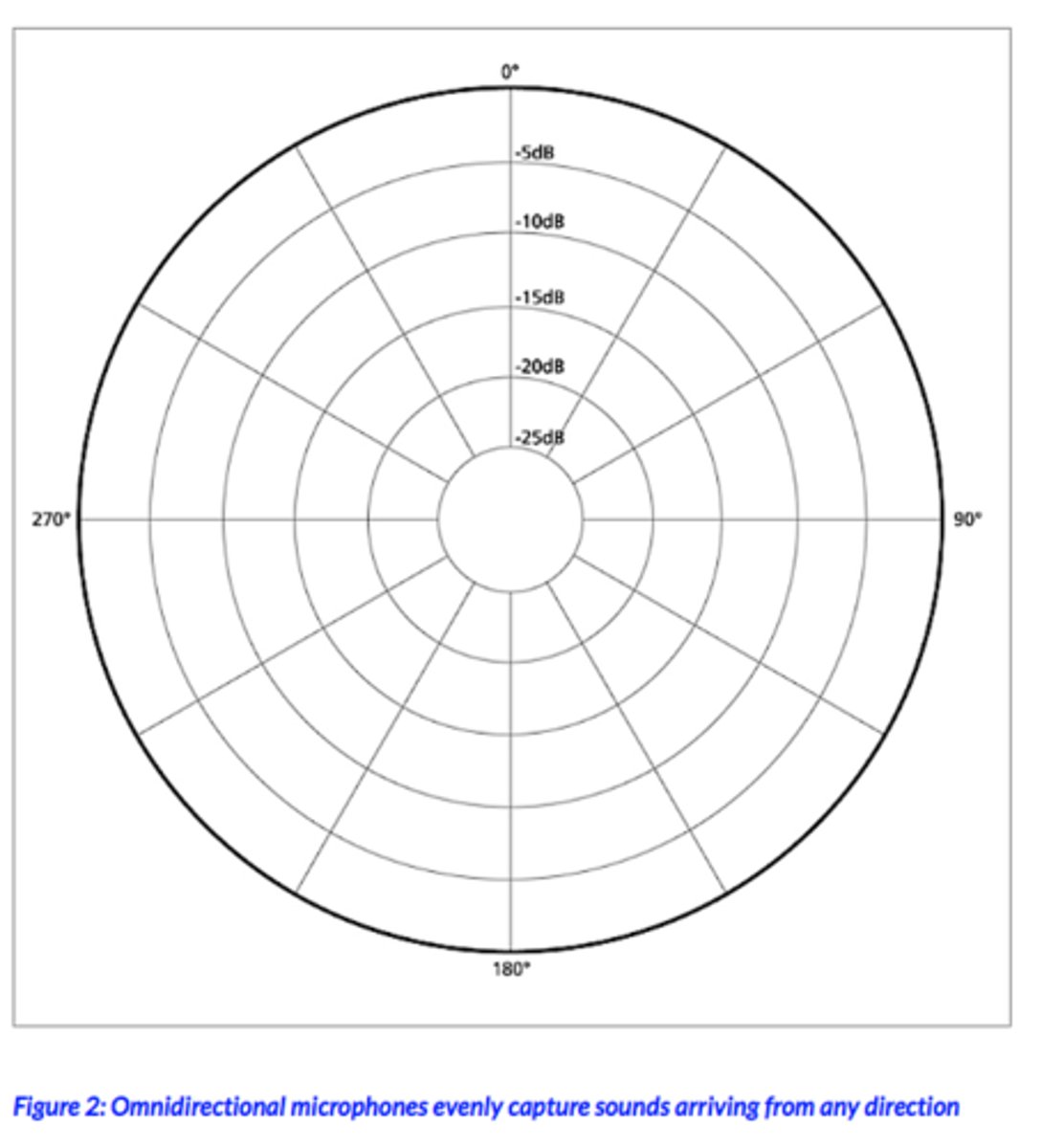
What is the "proximity effect"?
As you get closer to a microphone the more low frequencies you'll hear (gets more bass-y)
Describe the AB or Spaced pair technique
2 mics of the same make and model space them equidistant from your source; from a few to 30 feet
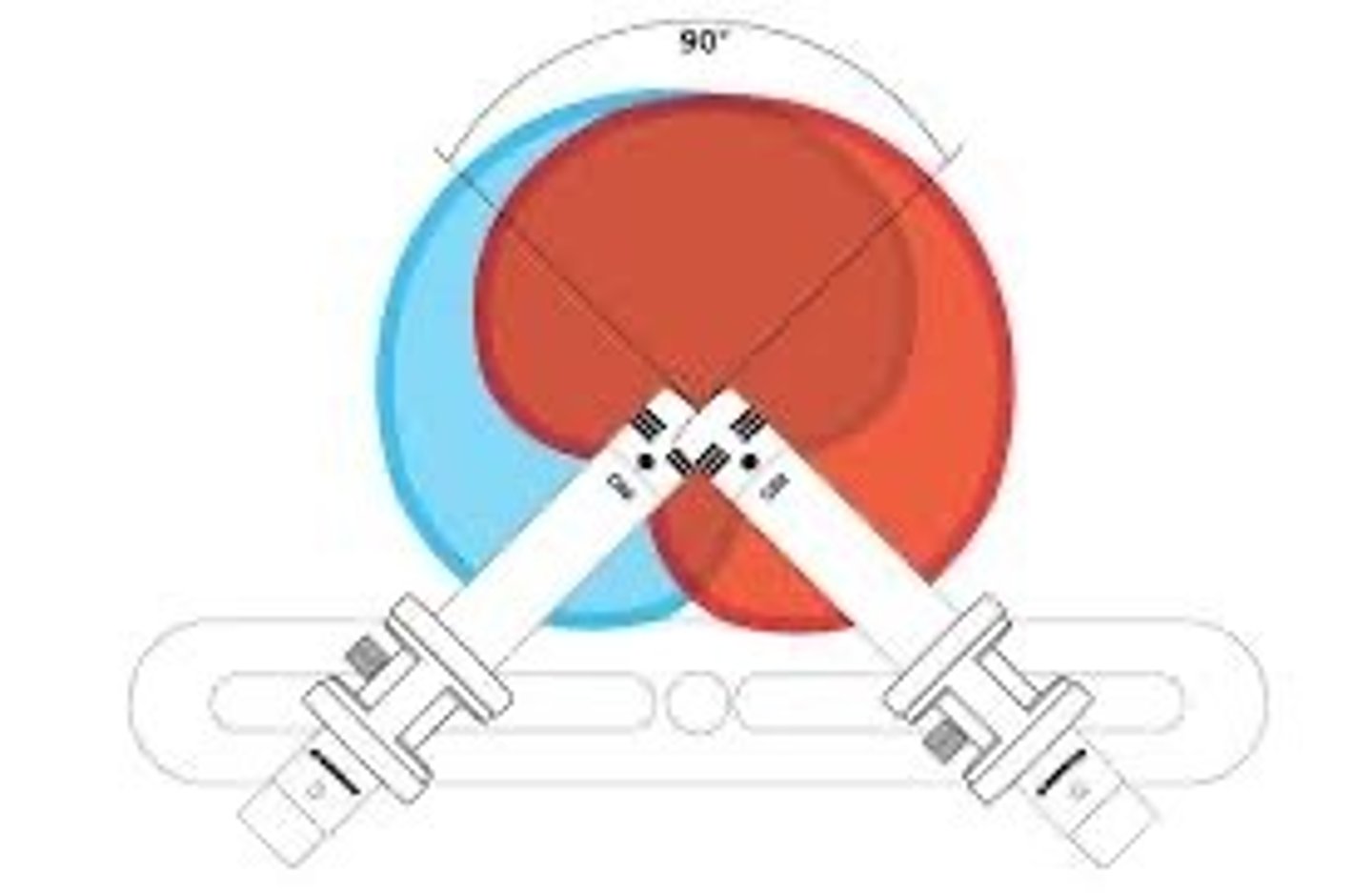
Describe the XY technique
Micing technique with 2 mics where the grills are placed as close as possible to each other without touching and make a 90 degree angle
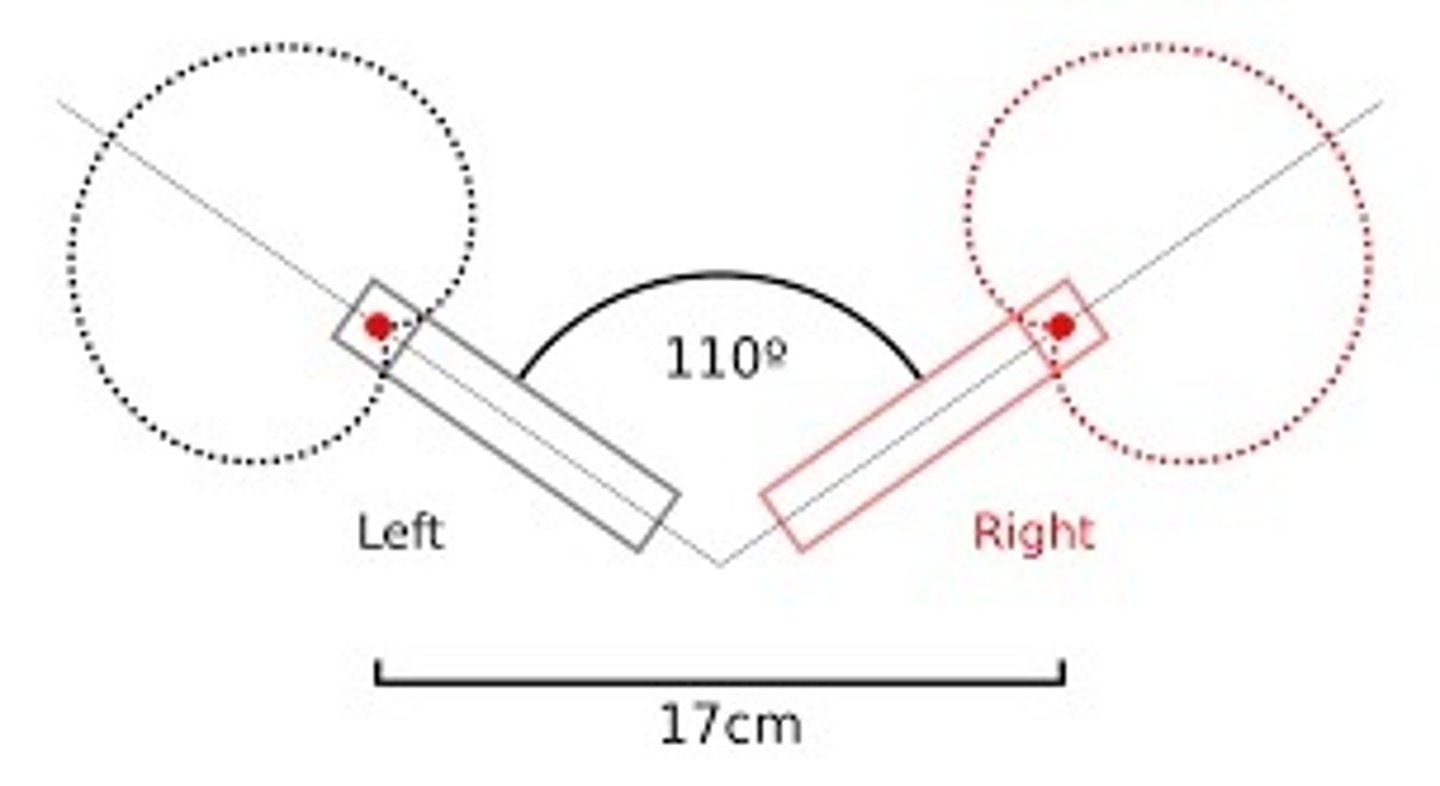
Describe the ORTF technique
Micing technique with two mics making a 110 degree angle facing away from each other
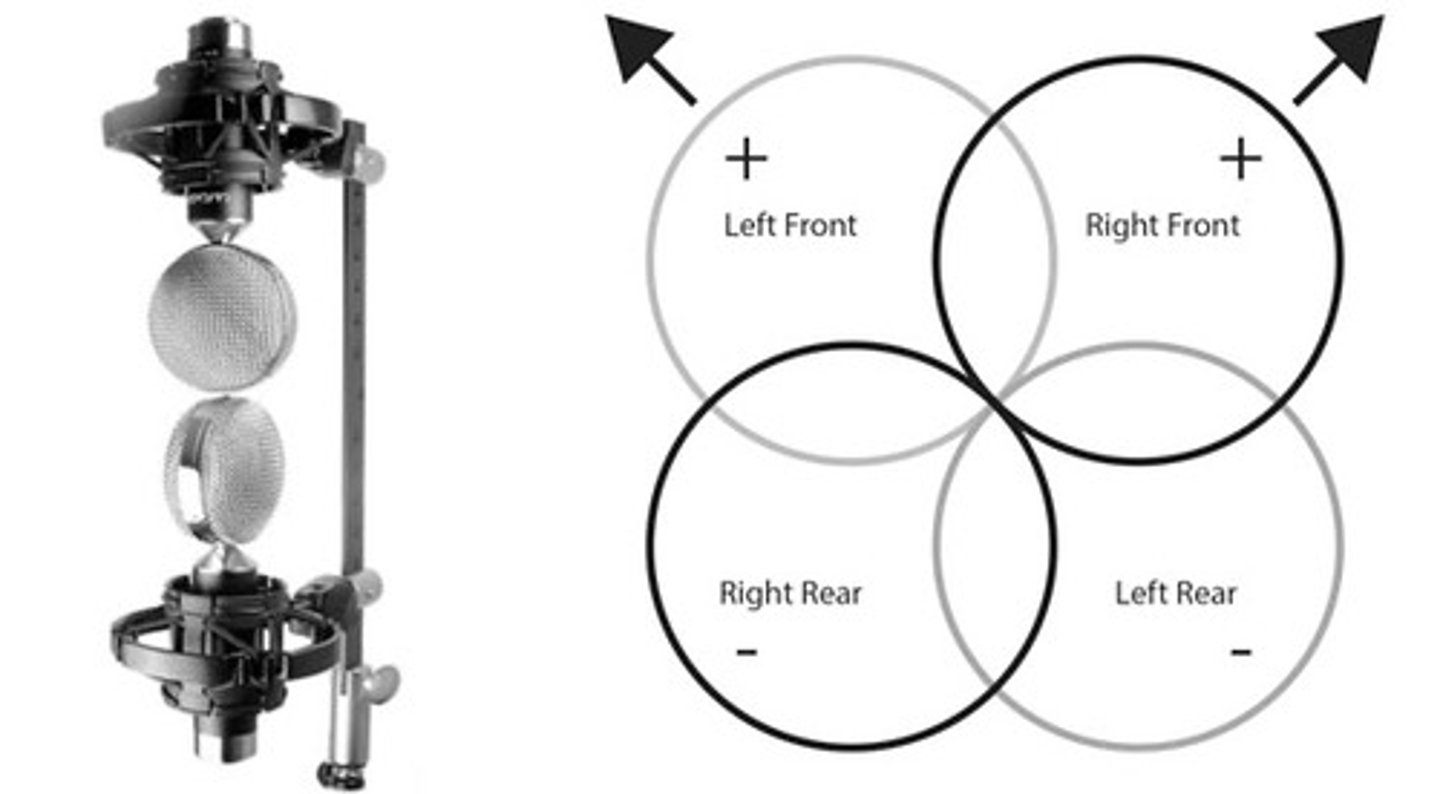
Describe the Blumlein technique
2 figure 8 mics one straight up and the other straight down and on top (barely not touching) and turned 90 degrees, making an x if you saw it from above
Where should place a mic in front of a guitar amp
slightly off center; the further from center, the darker the sound
What does it mean for a mic to be "on axis"
this means its directly facing the sound source
Describe the mid-side technique?
Micing technique using one cardiod mic on axis and one figure 8 mic, perpendicular
what is the rate of speed that sound travels through the air at 68 F?
1130 ft per second.
knowing the velocity and speed what else can you deduce about sound
wavelength in feet. velocity/frequency
AB or spaced pair technique
placed infront of center of an instrument or ensemble. same height and position just placed apart.
XY technique
two mics of same type placed with their grills as close as possible without touching and facing 90 degrees of eachother. midpoint of the mics are facing sound source.
ORTF technique
two cardioid mics placed at a 110 degree angle from each other and 17cm apart.
blumlein technique
relative to xy technique but instead of cardioid mics it is 2 figure 8 mics placed diagonally so you get a 4 way polar pattern
decca tree technique
uses 3 omni mics on a t shaped bar pointed left right and center. used for orchestral recording.
mid side technique
one mic is designated the the mid position, typically cardioid pointed to sound source. there is a diff mic pointed sideways in figure 8 pattern for the "side". used for recording drums/piano. most phase coherent