2-Histology of the Endocrine Organs
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Secretory Ducts
Endocrine glands don’t have any of THESE
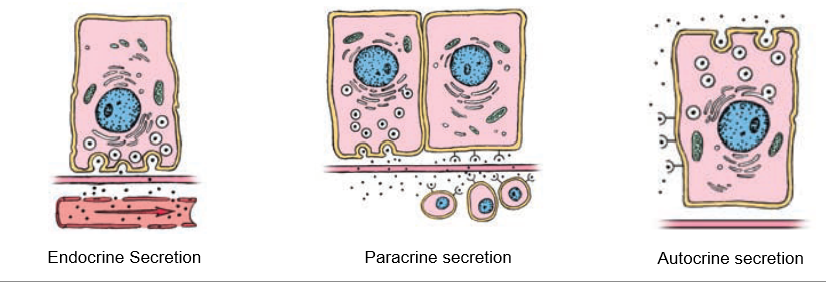
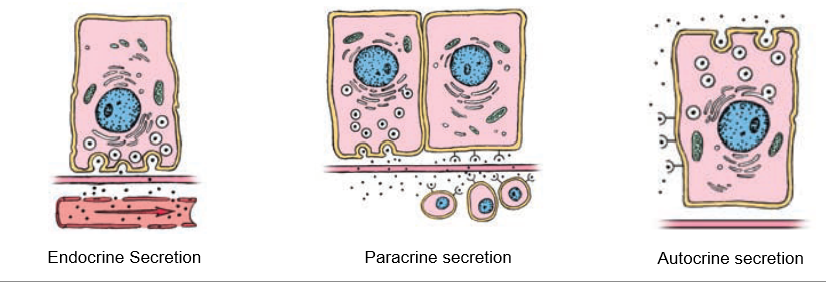
Paracrine Secretion
Localized secretion into interstitial fluid for action on nearby cells (ex. – somatostatin in pancreatic d-cells)
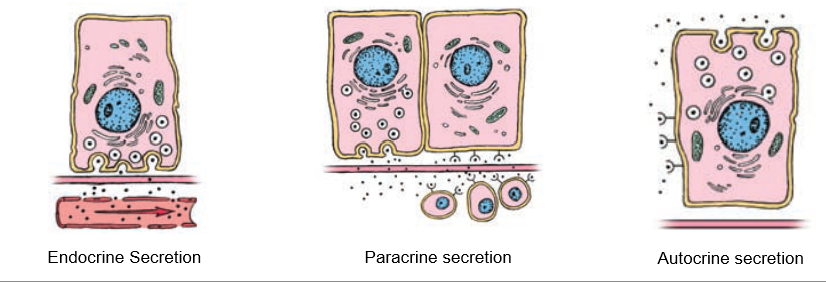
Autocrine Secretion
Cells produce molecules that act on themselves or cells of the same type (ex. – growth factors)
Juxtacrine Secretion
Substances anchored to cell membrane bind to receptors on adjacent cells (ex. – delta signaling in developing nervous system)
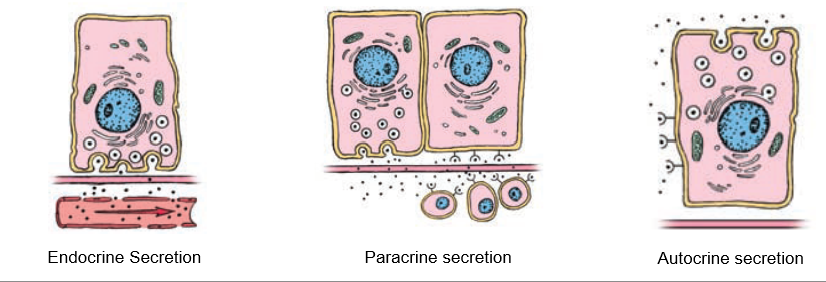
Endocrine Secretion
Substances released through interstitial space into bloodstream, communicates with far-away cells.
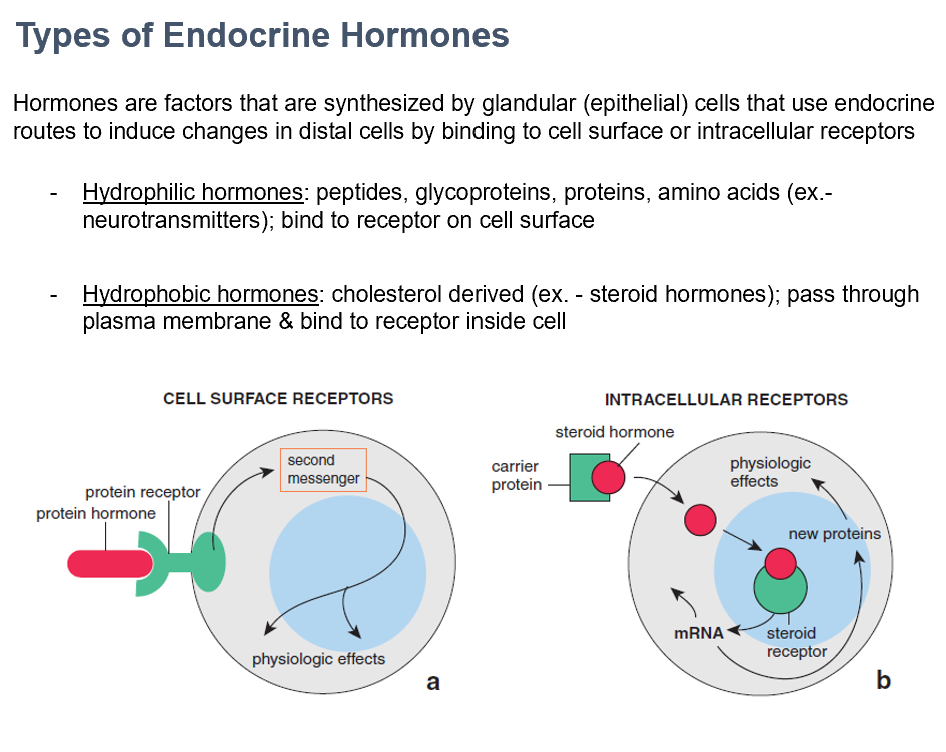
Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Hormones
The 2 types of endocrine hormones
Made by glandular (epithelial) cells, use endocrine routes via binding to cell surfaces or intracellular receptors
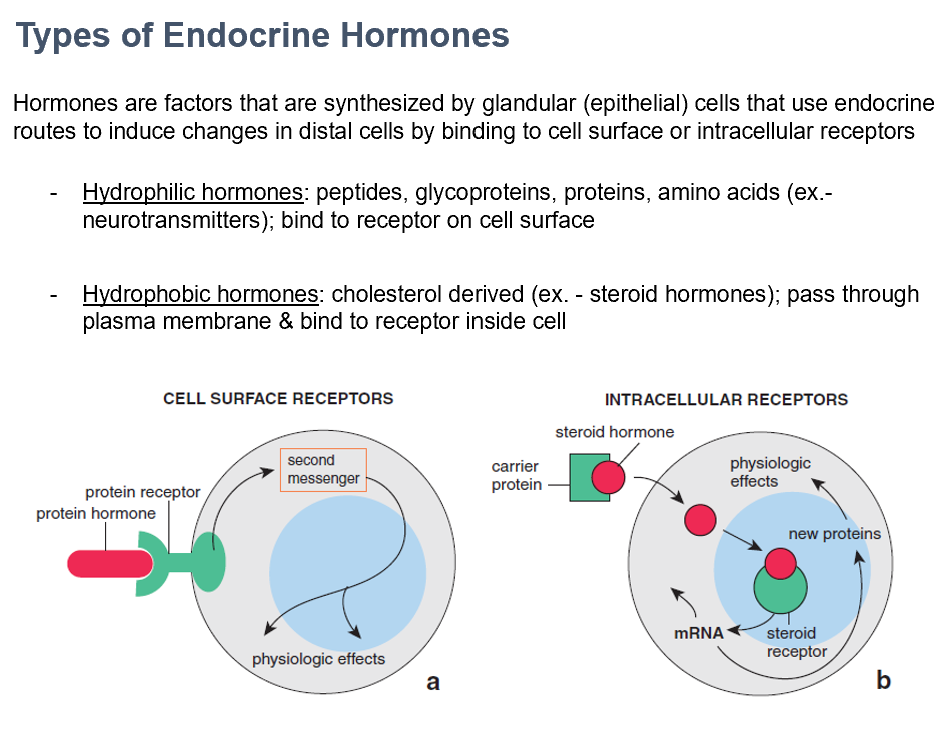
Hydrophilic Hormones
Peptides, glycoproteins, proteins, amino acids (ex.- neurotransmitters)
Bind to receptor on cell surface
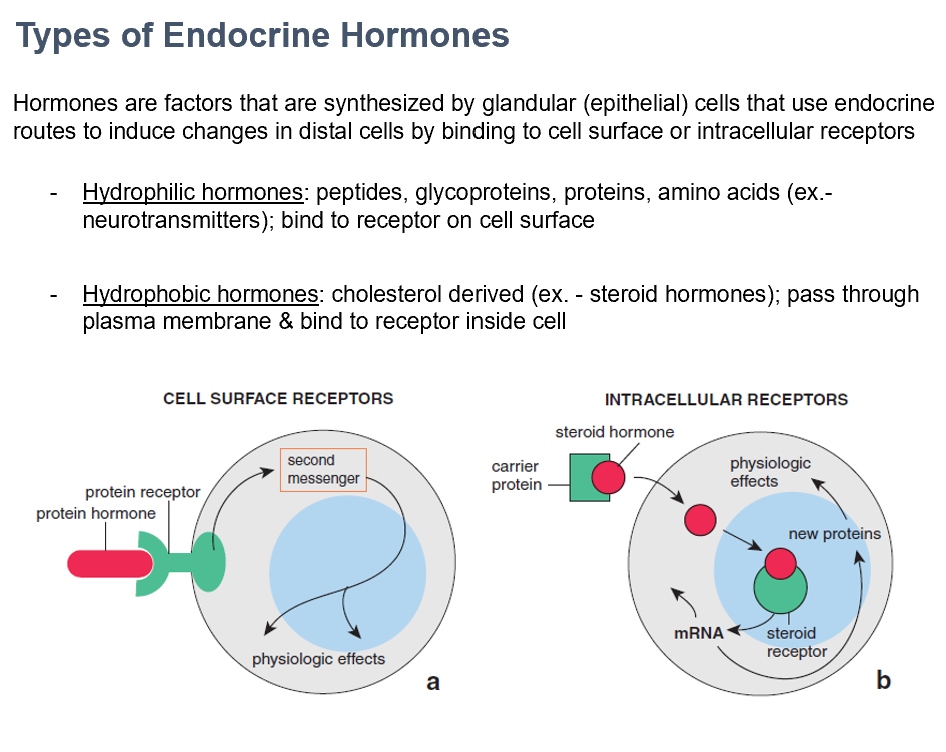
Hydrophobic Hormones
Cholesterol derived (ex. - steroid hormones)
Pass through plasma membrane & bind to receptor inside cell
Capilaries
The vascular system transports hormones to target cells/organs.
THIS is how hormones escape the vascular system.
Continuous
Fenestrated
Sinusoid (Discontinuous)
These are the 3 types of capillaries.
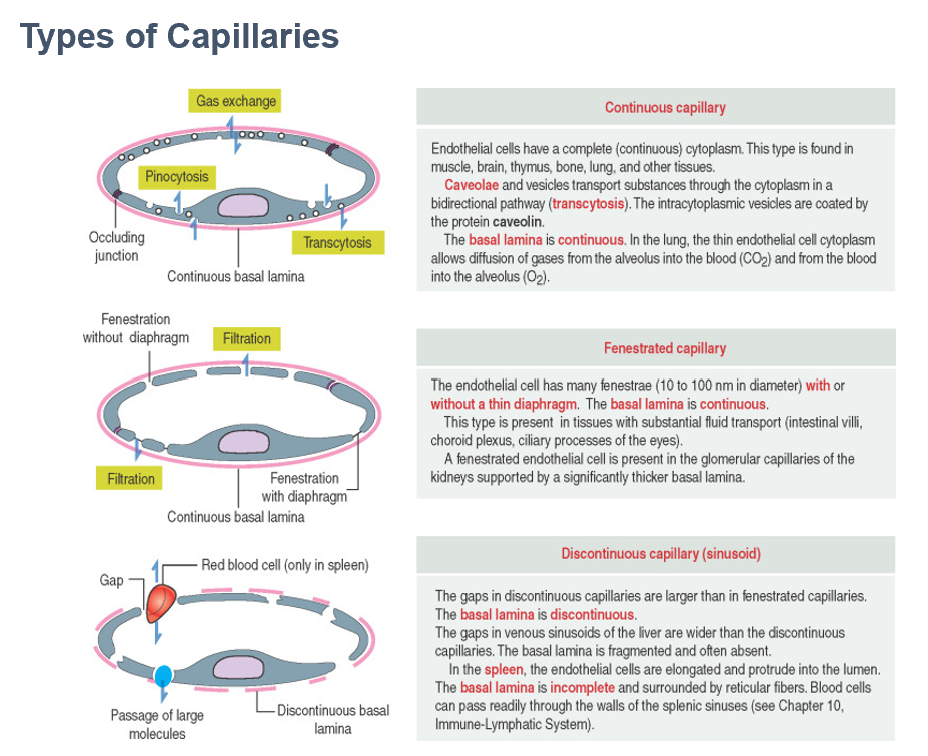
Continuous Capillary
Continuous basement membrane and endothelial layer
Allows diffusion of only small molecules & ions (ex. – lung & skeletal muscles)
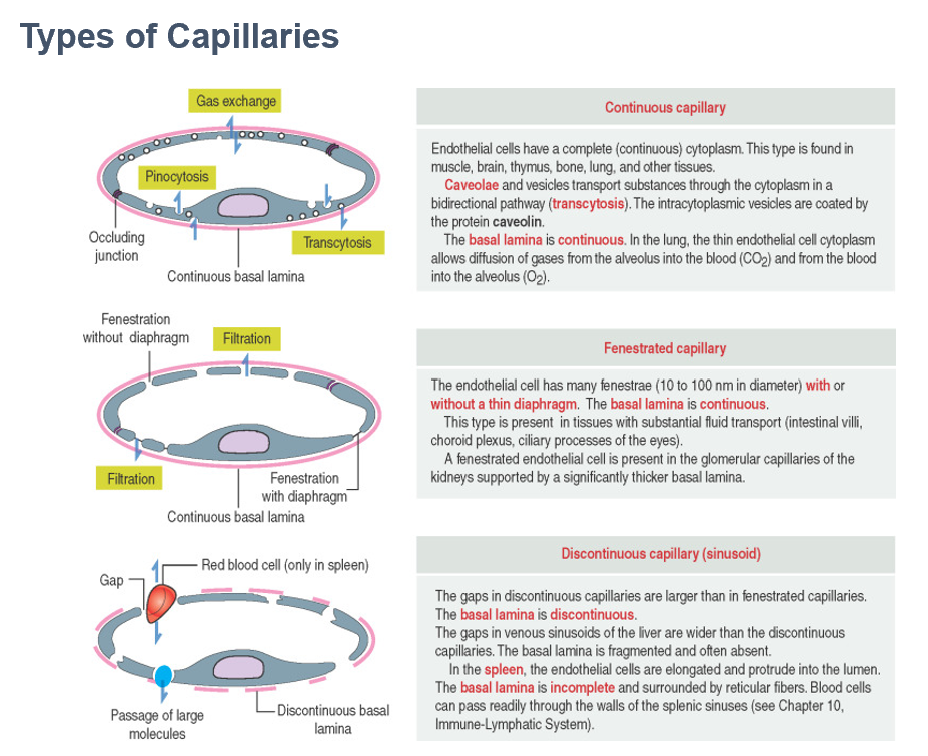
Fenestrated Capillary
Continuous basement membrane; endothelial cells contain small “fenestrae”
Allows diffusion of larger molecules and proteins (ex. – glomerulus of kidneys; most endocrine glands)
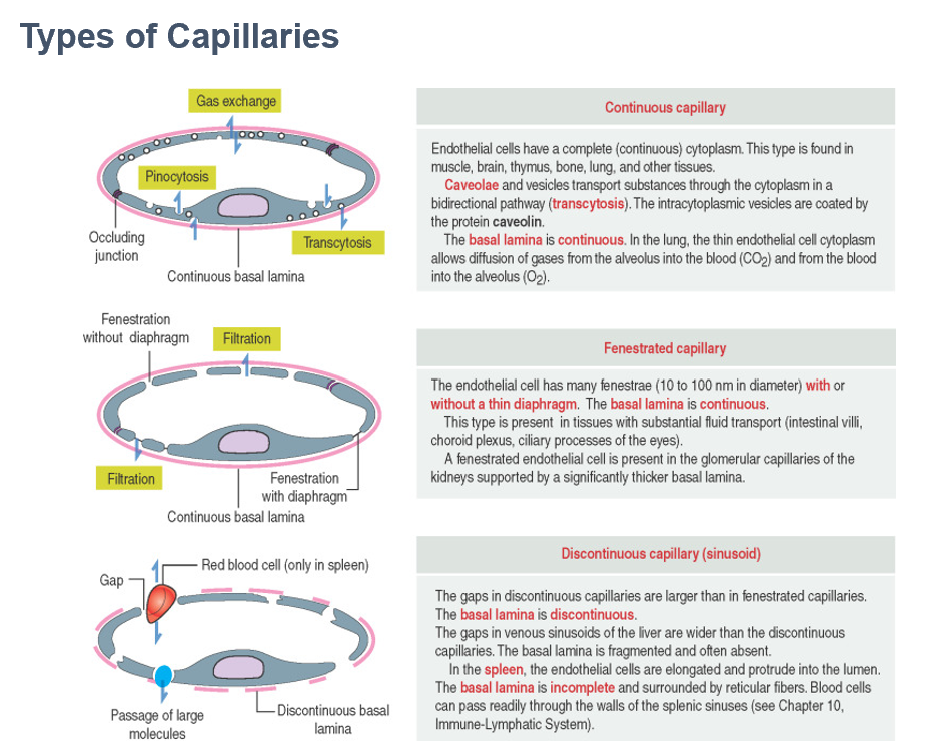
Sinusoid (Discontinuous) Capillary
Discontinuous basement membrane; endothelial cells have large gaps between them (sinusoids)
Allows diffusion of large molecules, cells & cell fragments (ex. – spleen & red bone marrow)
Endocrine Organs
Endocrine glands with a large portion of cells with endocrine functions.
Ex. gonads (testes/ovaries).
Hypothalamus
Secretes hormones that regulate the pituitary gland (anterior and posterior).
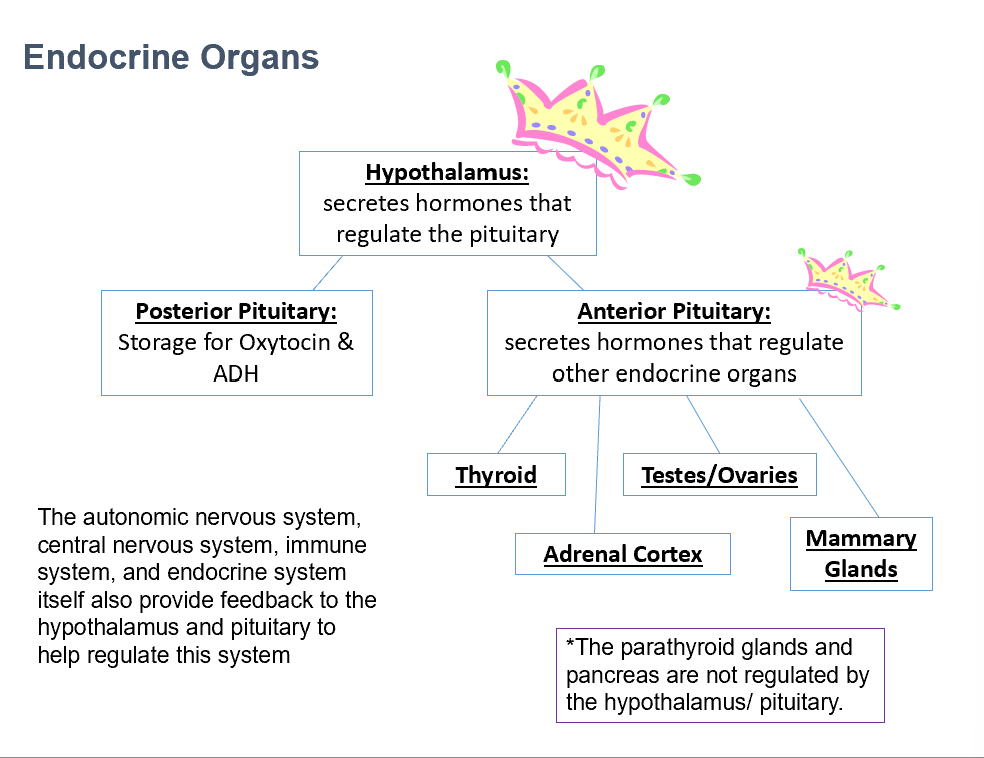
Posterior Pituitary
Stores Oxytocin and ADH.
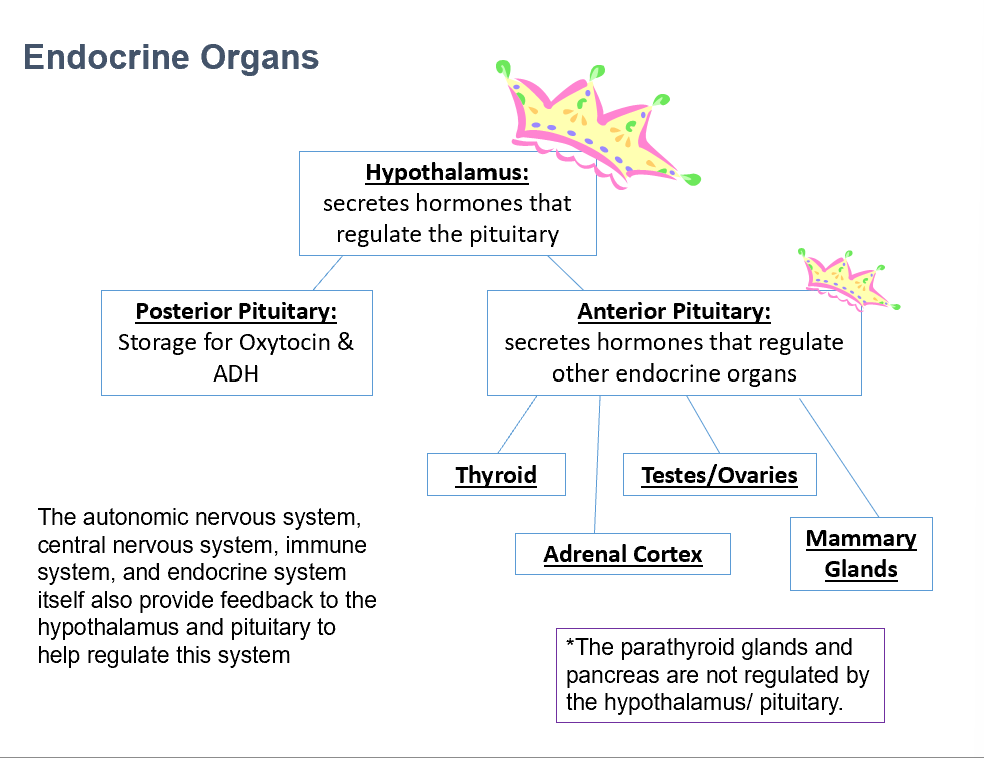
Anterior Pituitary
Secretes hormones that regulate other endocrine organs.
Thyroid
Adrenal Cortex
Testes/Ovaries
Mammary Glands
Parathyroid Glands
Pancreas
THESE 2 things that are NOT regulated by the hypothalamus/pituitary.
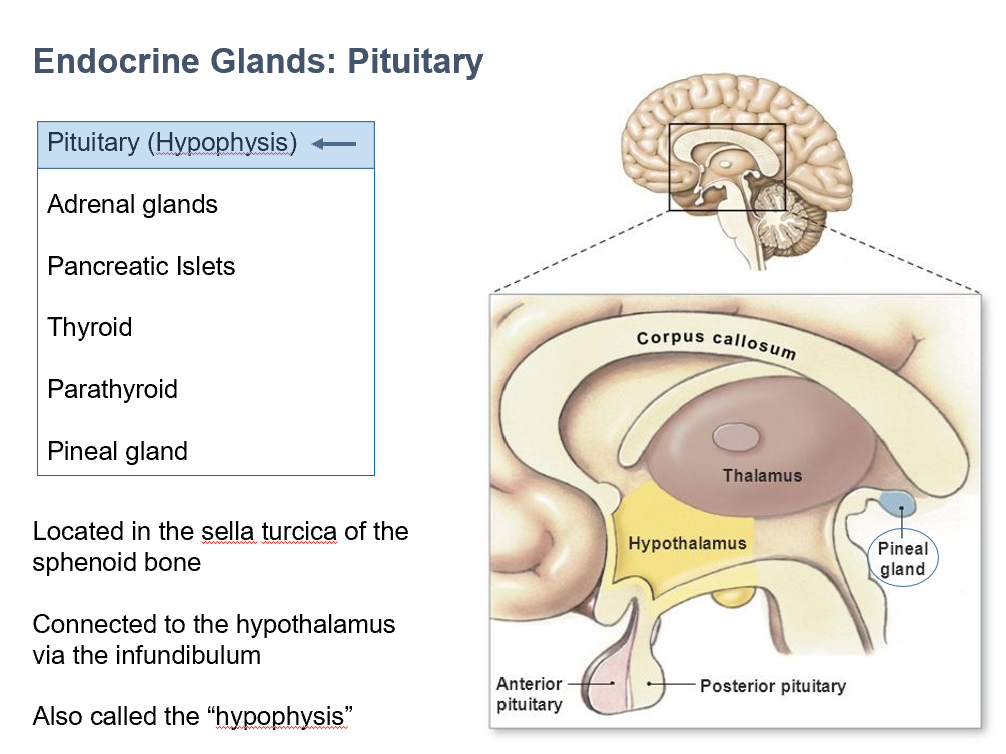
Pituitary (Hypophysis)
Location:
Sella Turcica of sphenoid bone
Connects to hypothalamus via infundibulum
Stalk is easily damaged with head trauma
Tumors:
Expand upward
Compress optic chiasm (peripheral blindness/tunnel vision)
Neuroectoderm
The embryonic origin of the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Part of diencephalon.
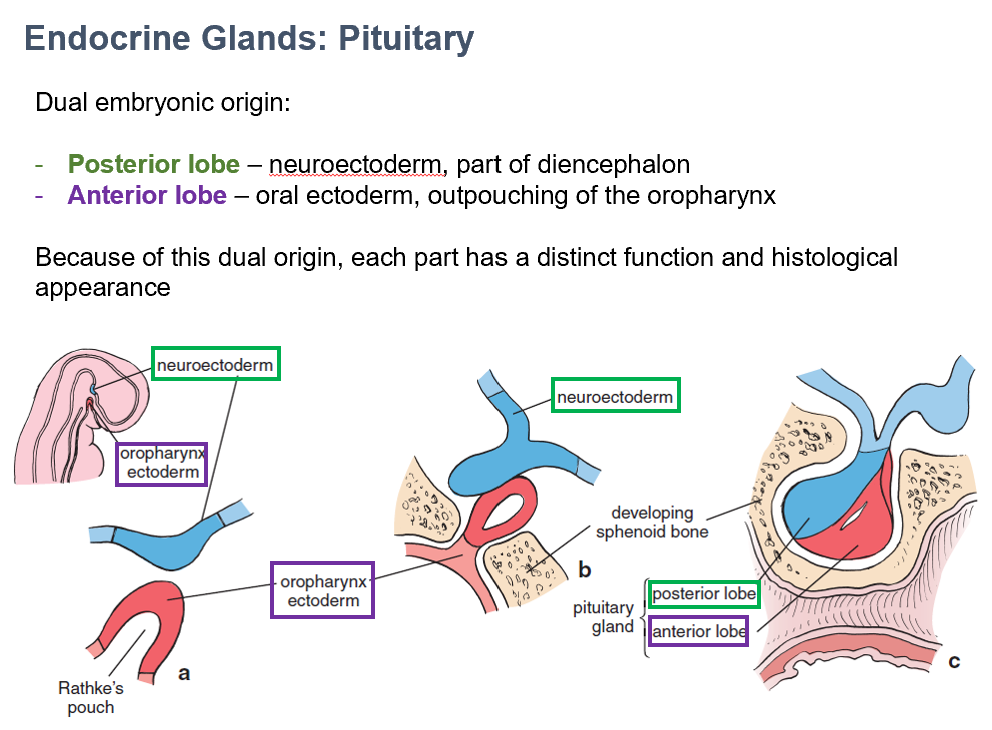
Oral ectoderm
The embryonic origin of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Outpouching of oropharynx.
Neurohypophysis
Histologically looks like brain tissue
Contains axons and neurons, cell bodies in hypothalamus
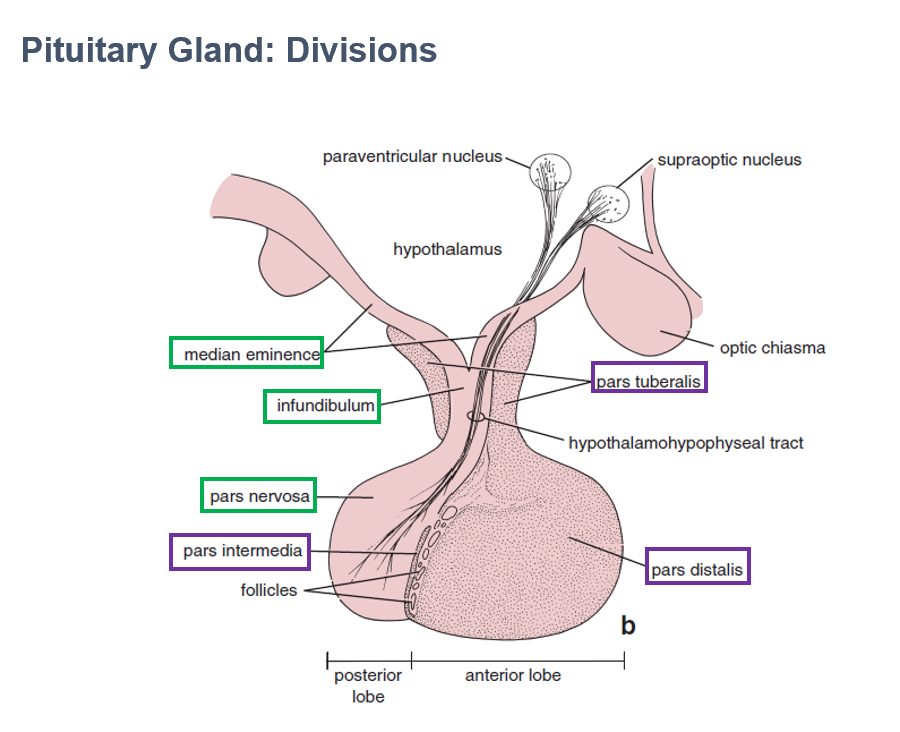
Parts:
Pars Nervosa
Infundibulum
Median Eminence
AKA Posterior lobe of pituitary
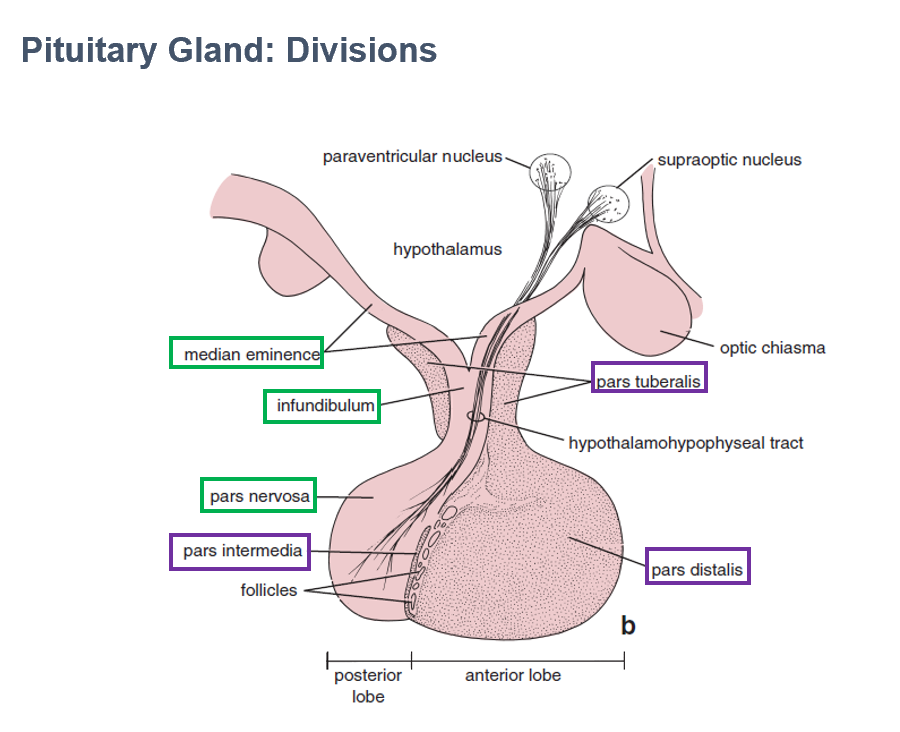
Pars Nervosa
Largest part of neurohypophysis
Contains neurosecretory axons
Infundibulum
Part of neurohypophysis
Continuous with median eminence
Connects pituitary to hypothalamus
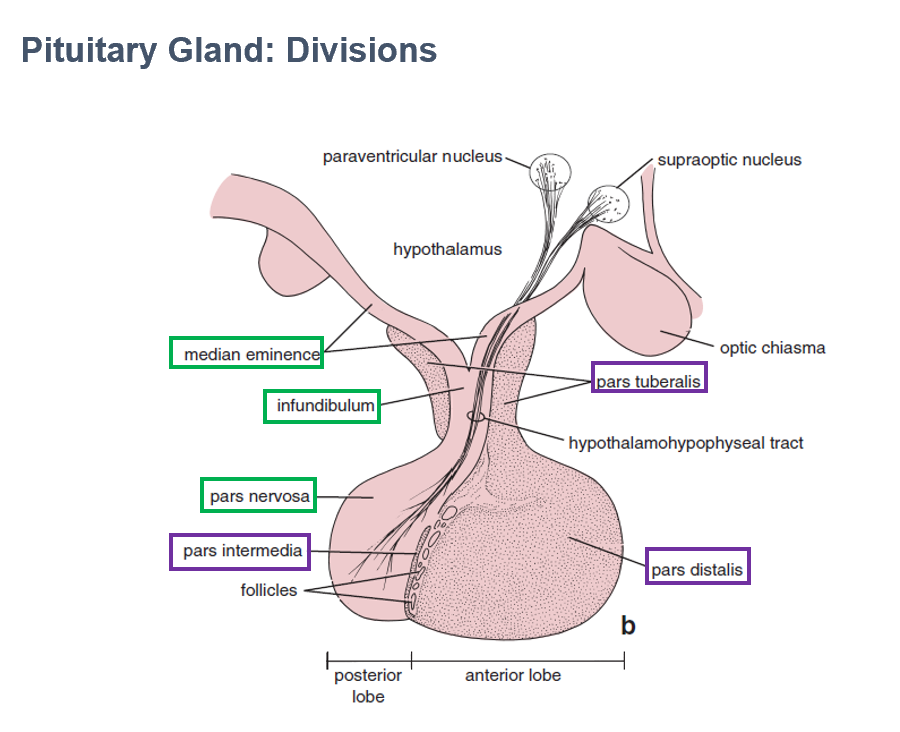
Median Eminence
Part of neurohypophysis
Contains hypothalamohypophyseal tracts
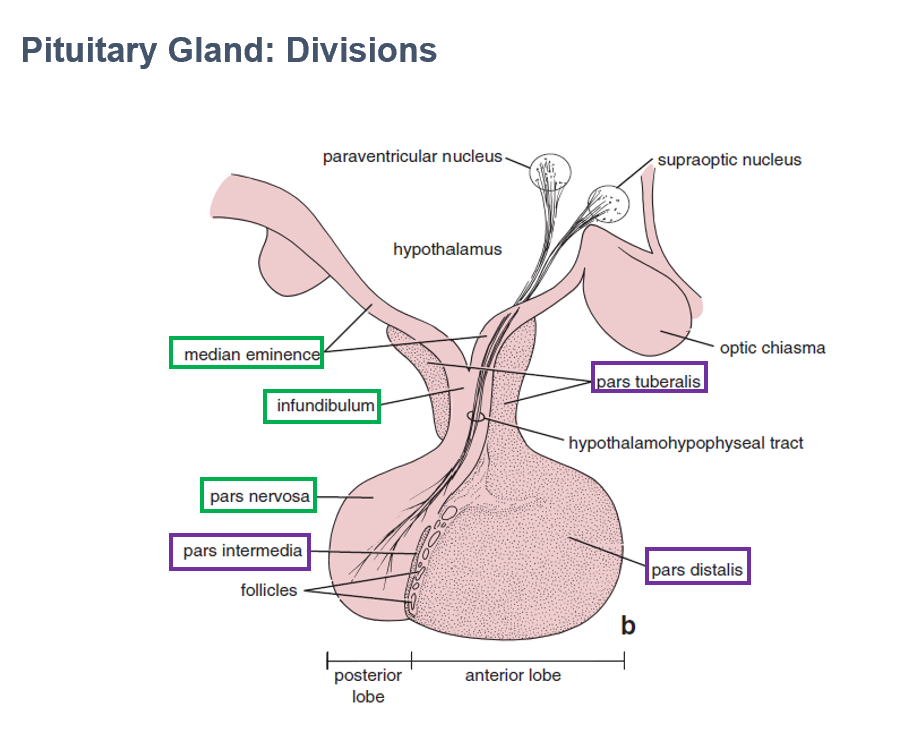
Adenohypophysis
Histologically looks dark, epithelial tissue
Ectodermal origin
Contains functional secretory epithelial cells
Parts:
Pars Distalis
Pars Intermedia
Pars Tuberalis
AKA Anterior lobe of pituitary
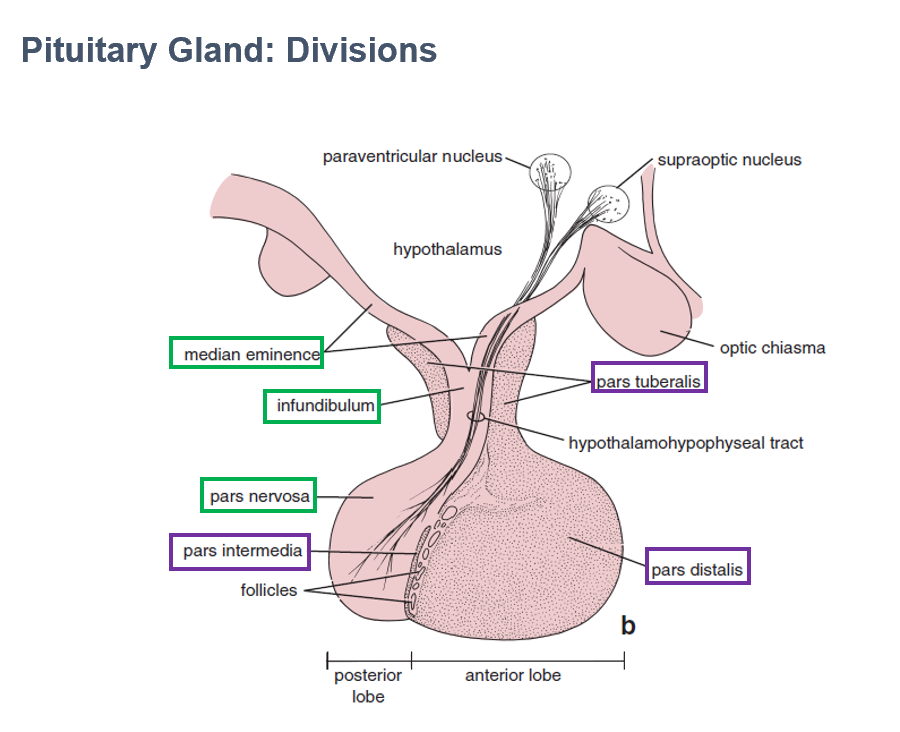
Pars Distalis
Part of adenohypophysis
Largest part
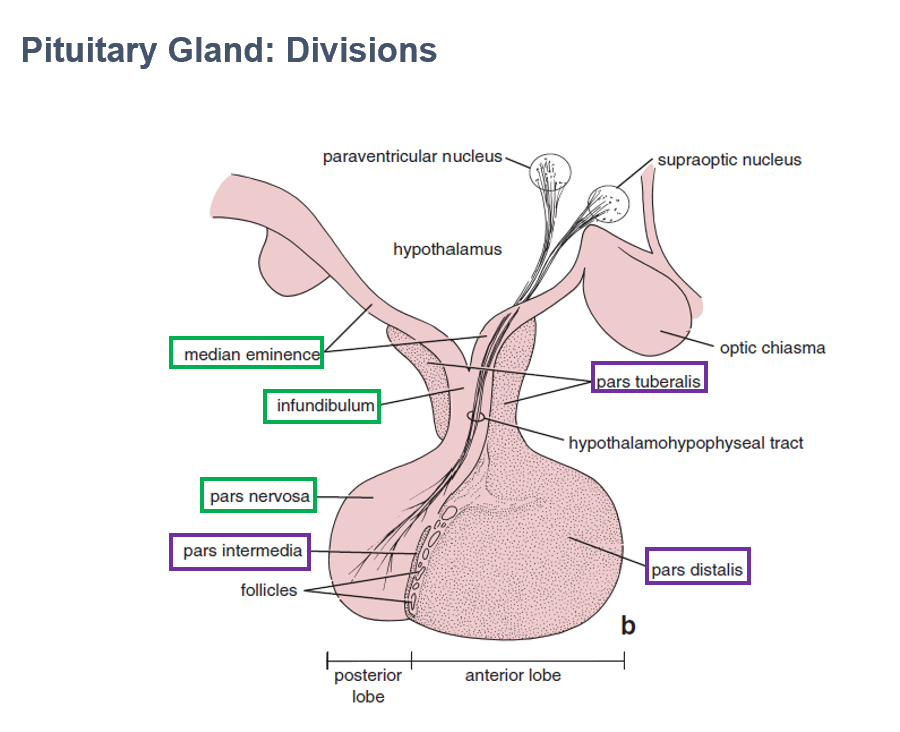
Pars Intermedia
Part of adenohypophysis
Thin wall between anterior/posterior pituitary lobes
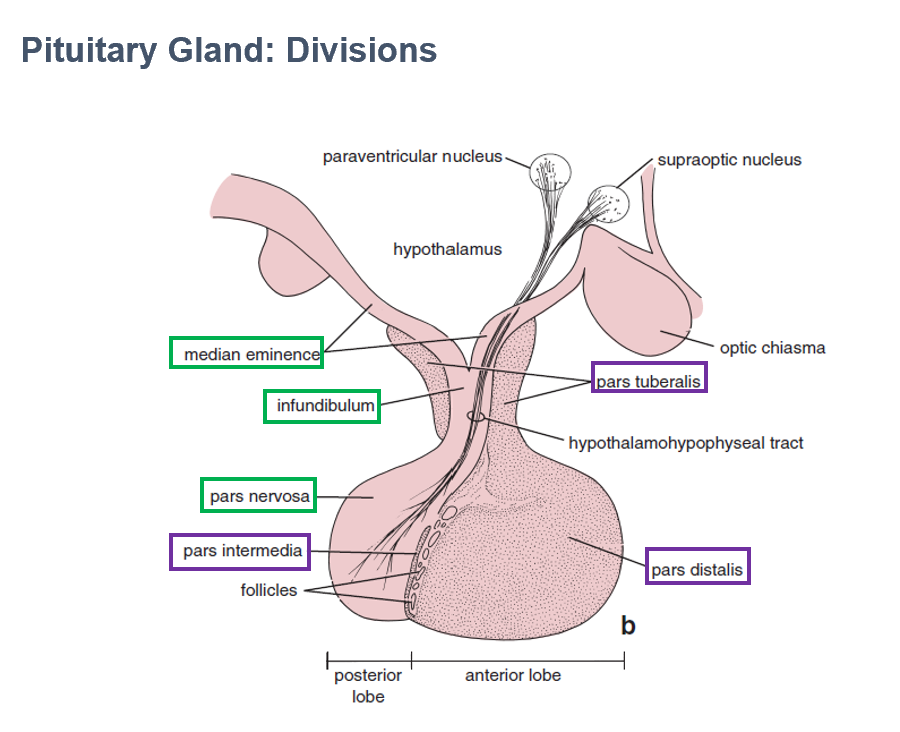
Pars Tuberalis
Part of adenohypophysis
Makes collar around infundibulum (part of neurohypophysis)
Anterior Lobe of Pituitary
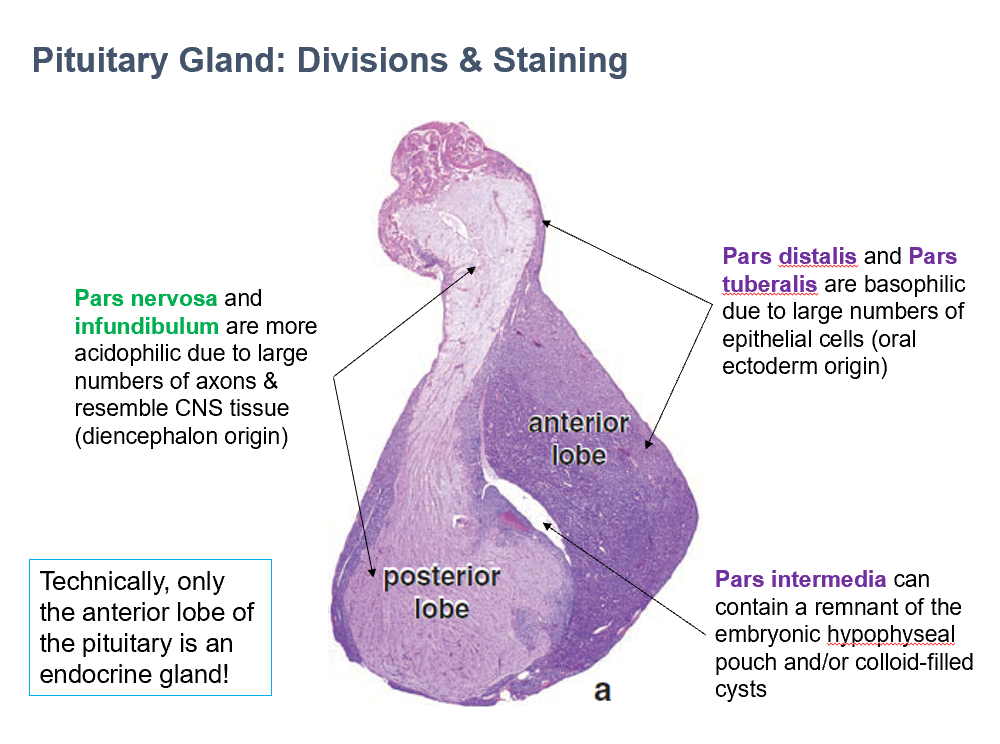
Technically only THIS portion of the pituitary is an endocrine gland.
Pars Nervosa & Infundibulum
THESE are more acidophilic due to large numbers of axons & resemble CNS tissue (diencephalon origin)
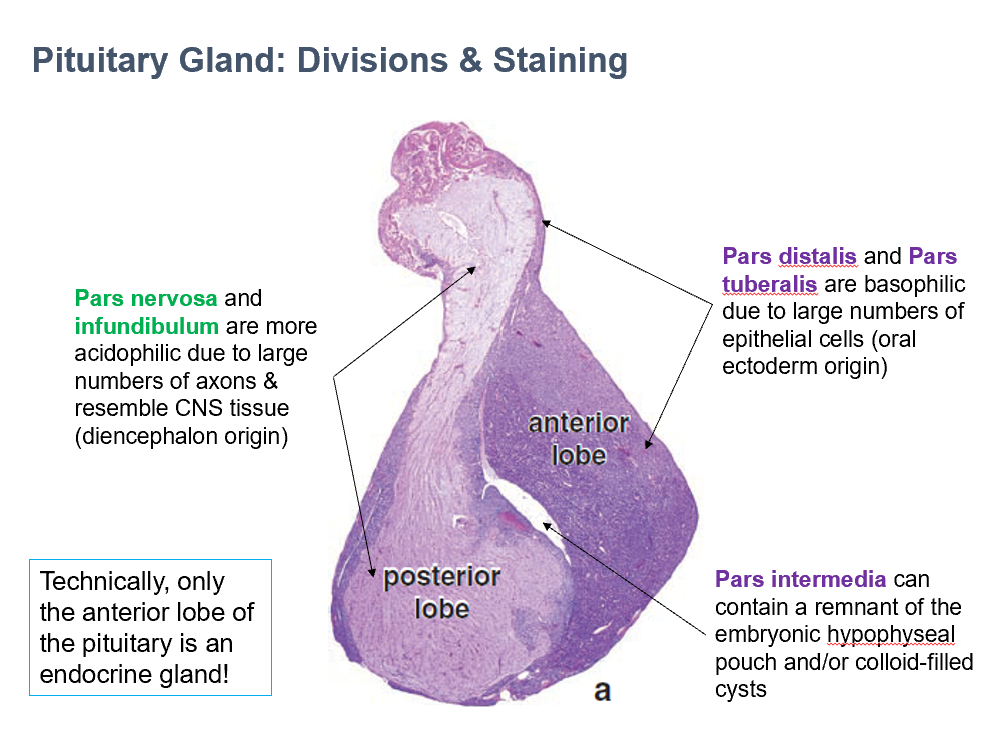
Pars Distalis & Pars Tuberalis
THESE are basophilic due to large numbers of epithelial cells (oral ectoderm origin)
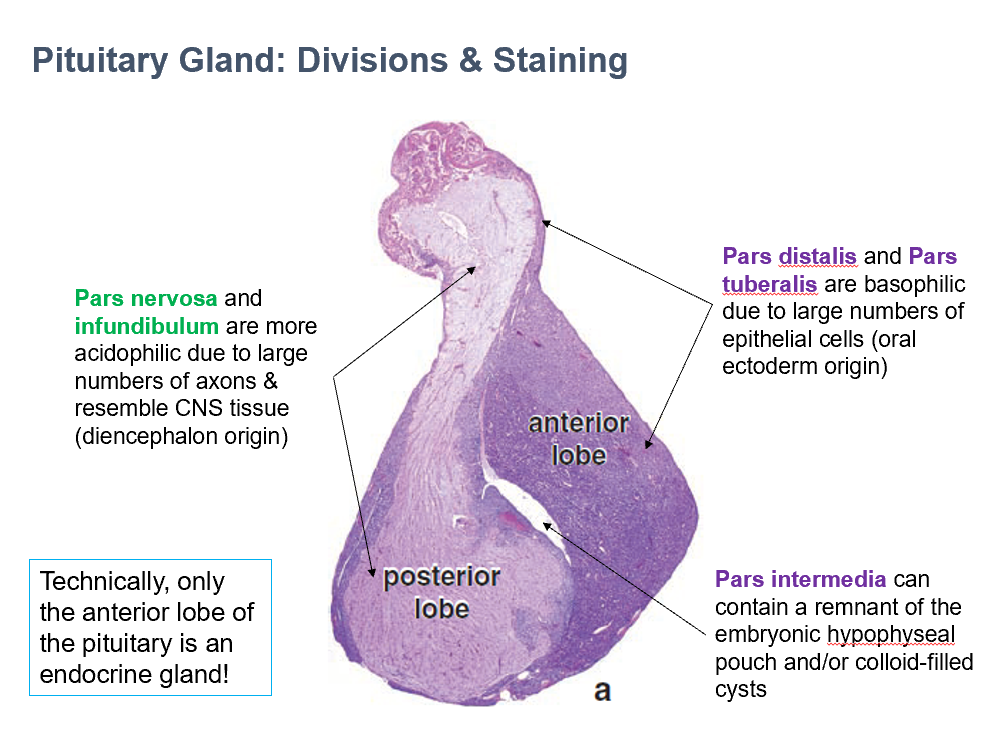
Pars Intermedia
THIS can contain a remnant of the embryonic hypophyseal pouch and/or colloid-filled cysts
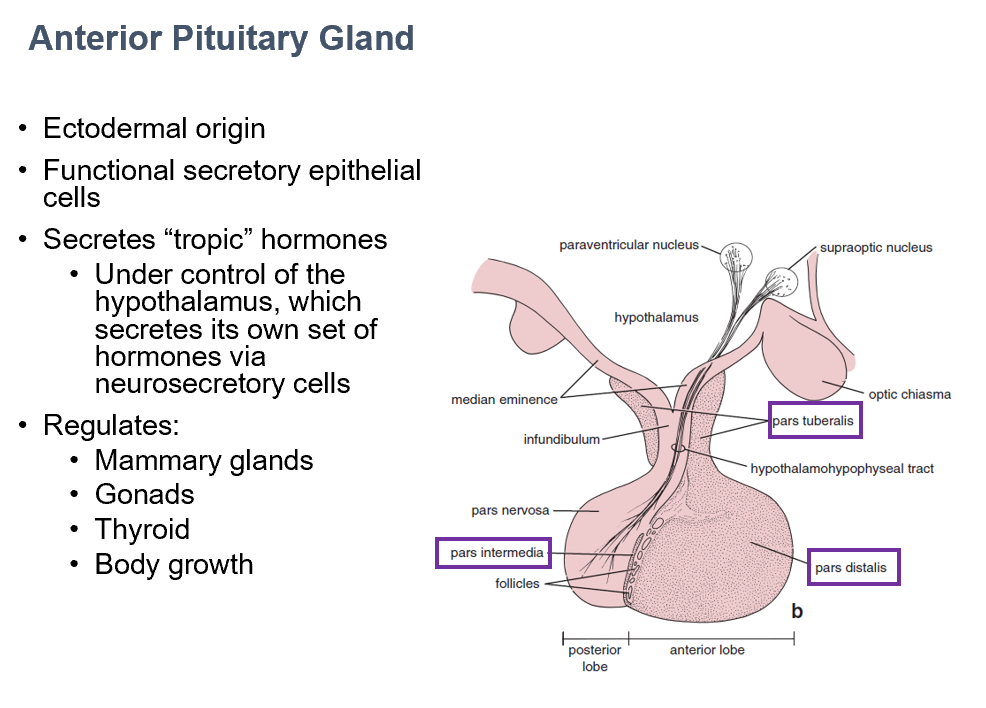
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Secretes tropic hormones
controlled by hypothalamus
Regulates:
Mammary glands
Gonads
Thyroid
Body growth
Ant. Pit. Tropic Hormones
GH
PRL
ACTH
FSH
LH
TSH
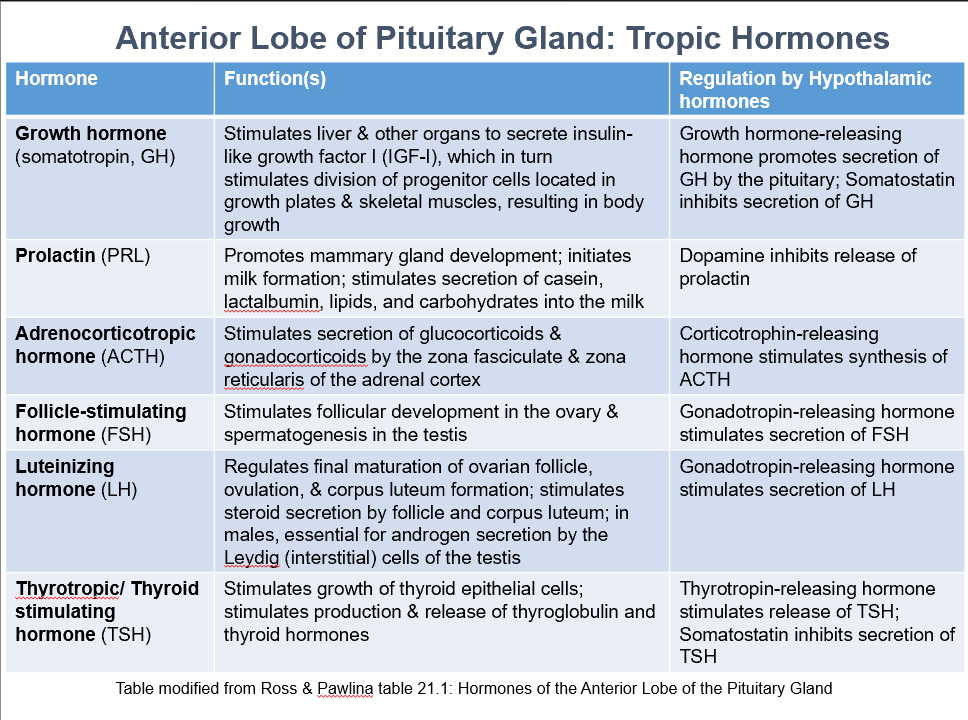
Growth Hormone (somatotropin, GH)
Function:
Stimulates liver & other organs to secrete insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), which stimulates division of progenitor cells located in growth plates & skeletal muscles, resulting in body growth.
Regulation by:
Growth hormone-releasing hormone promotes secretion of GH by the pituitary
Somatostatin inhibits secretion of GH
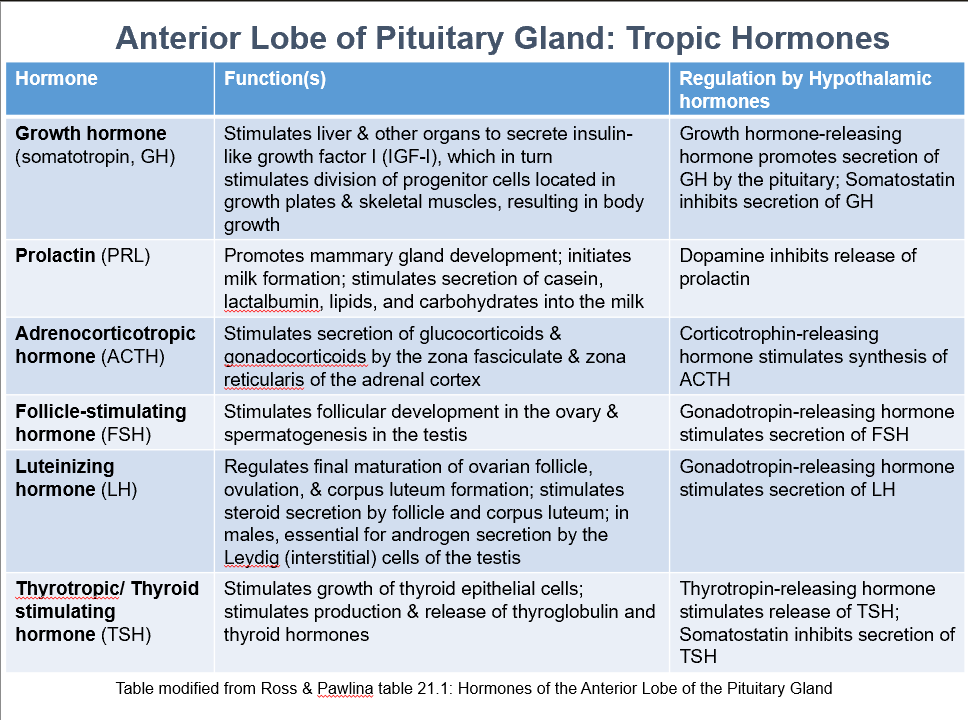
Prolactin (PRL)
Function:
Promotes mammary gland development
Initiates milk formation
Stimulates secretion of casein, lactalbumin, lipids, and carbohydrates into the milk
Regulated by:
Dopamine inhibits release of prolactin
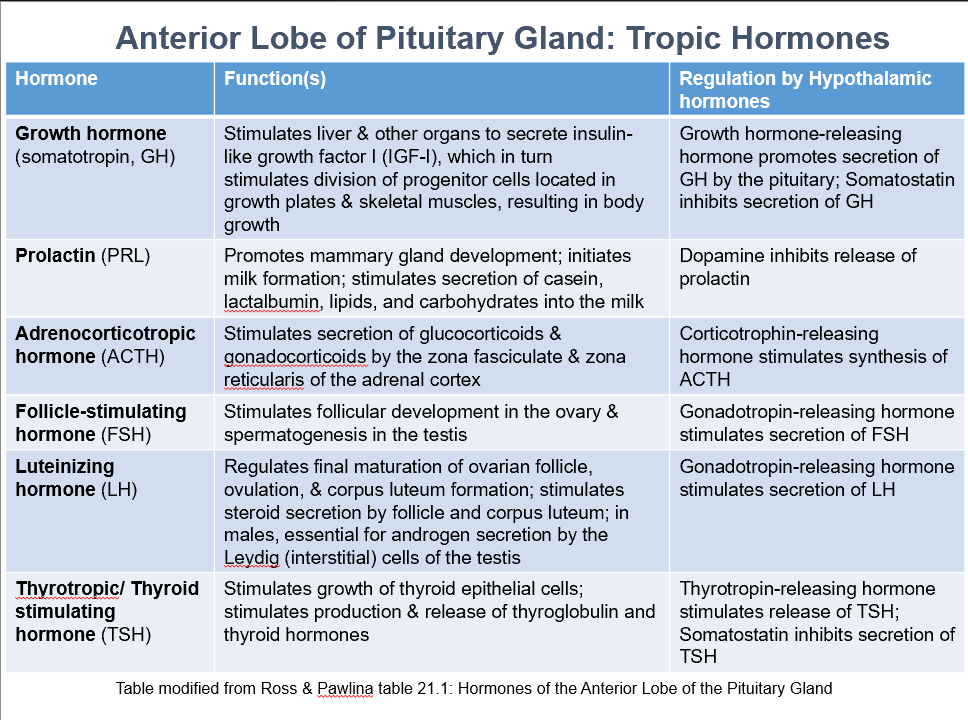
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Function:
Stimulates secretion of glucocorticoids & gonadocorticoids by the zona fasciculate & zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex
Regulated by:
Corticotrophin-releasing hormone stimulates synthesis of ACTH
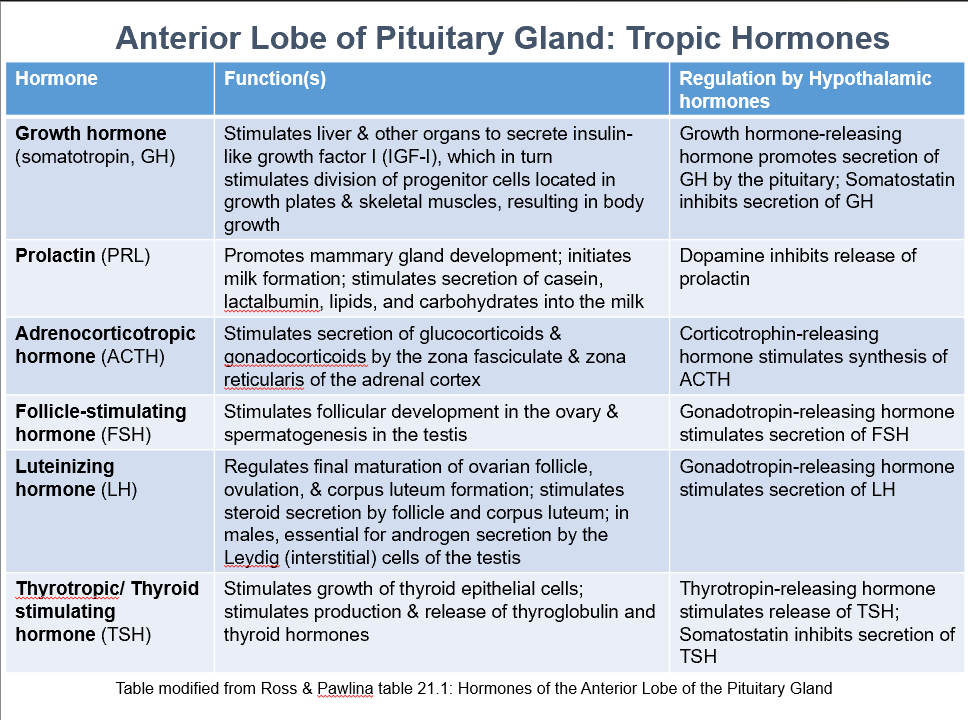
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Function:
Stimulates follicular development in the ovary & spermatogenesis in the testis
Regulated by:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone stimulates secretion of FSH
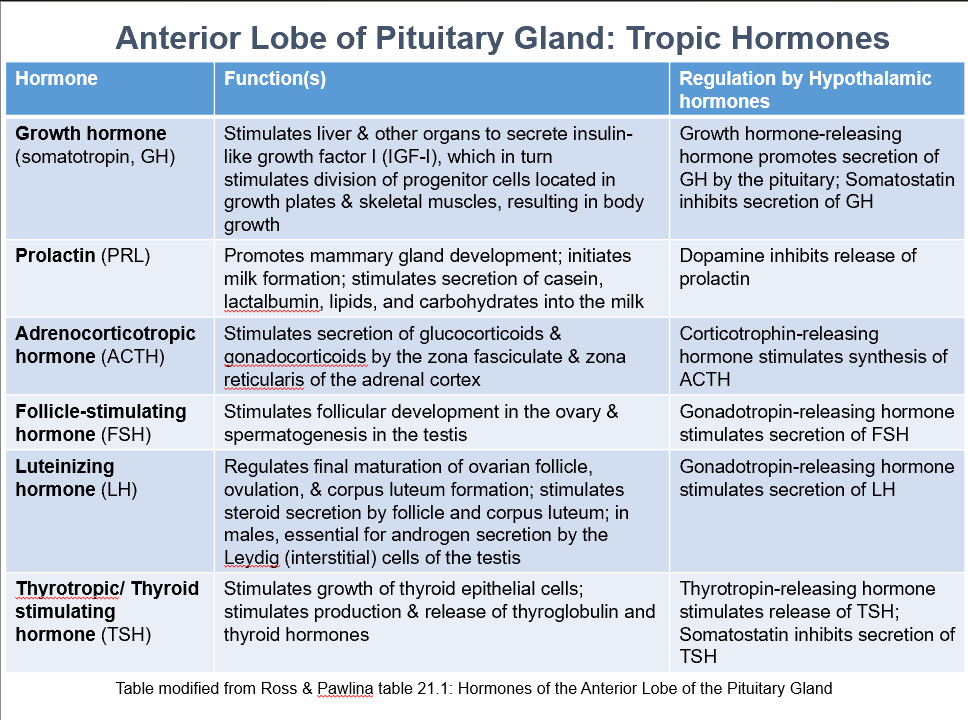
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Function:
Regulates final maturation of ovarian follicle, ovulation, & corpus luteum formation
Stimulates steroid secretion by follicle and corpus luteum
In males, essential for androgen secretion by the Leydig (interstitial) cells of the testis
Regulated by:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone stimulates secretion of LH
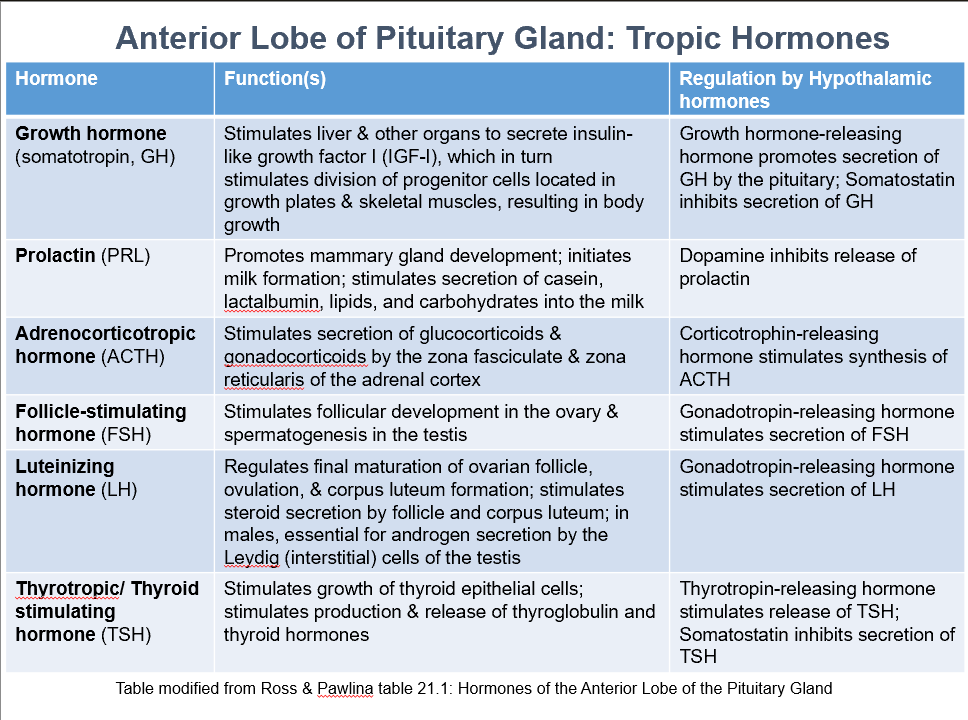
Thyrotropic/Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Function:
Stimulates growth of thyroid epithelial cells
Stimulates production & release of thyroglobulin and thyroid hormones
Regulated by:
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates release of TSH
Somatostatin inhibits secretion of TSH
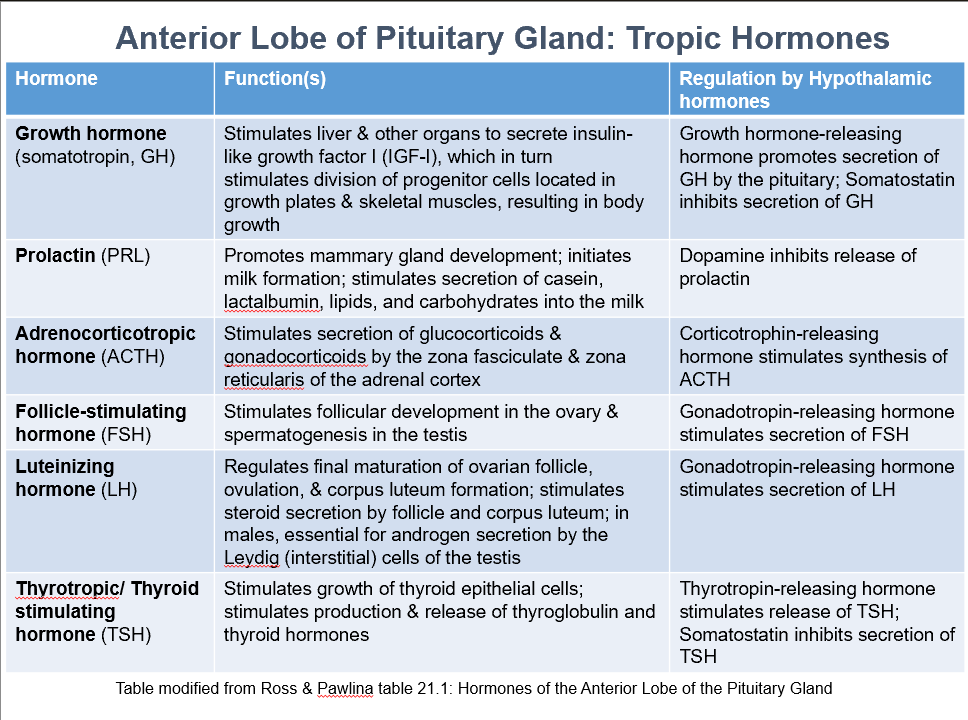
Classifications of ant. pit. cells in H & E
Acidophils (pink)
Basophils (blue)
Chromophobes (no stain)
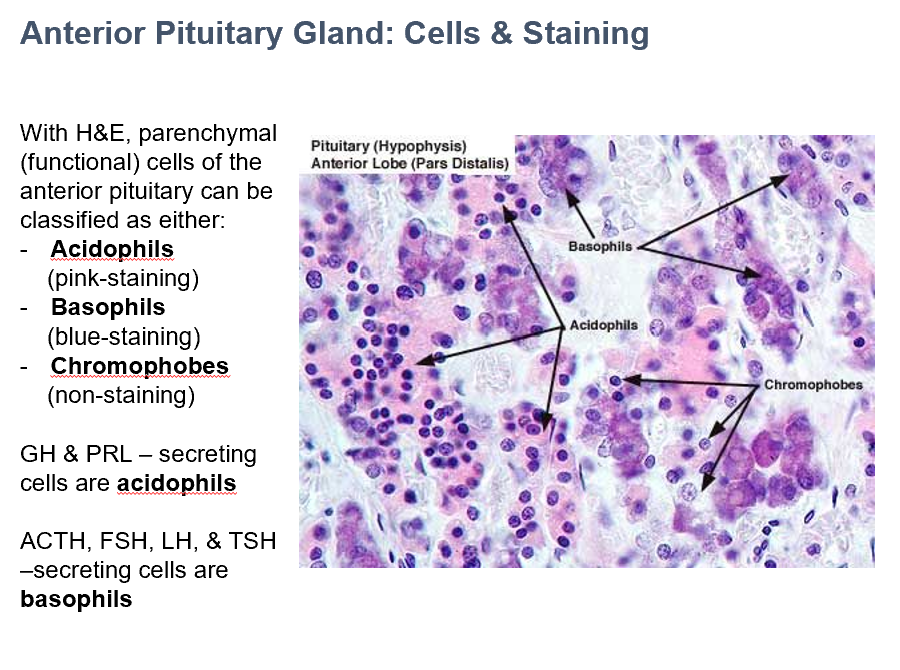
GH & PRL
In Ant. Pit., THESE secreting cells are acidophils.
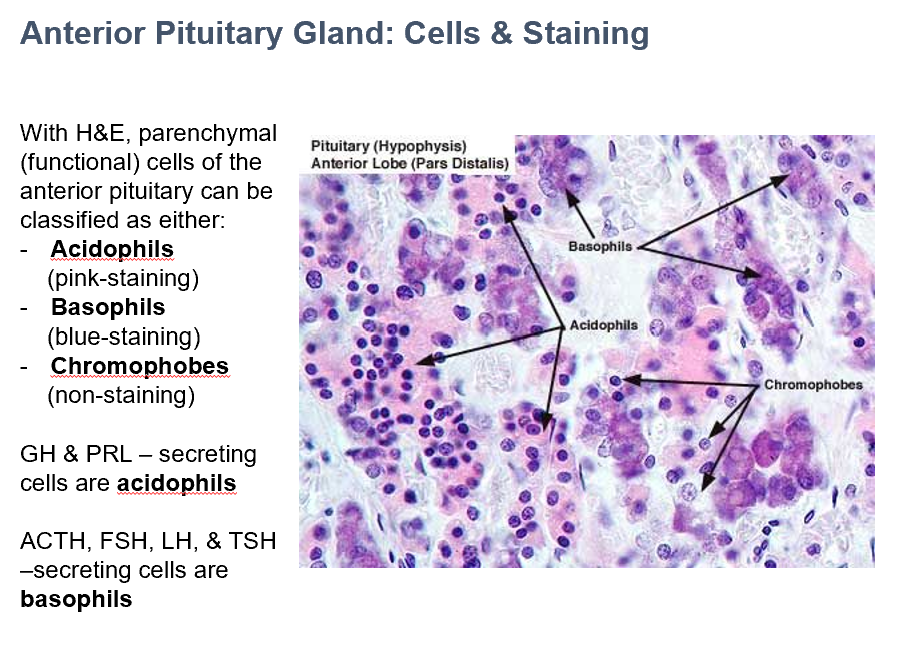
ACTH, FSH, LH, & TSH
In Ant. Pit., THESE secreting cells are basophils.
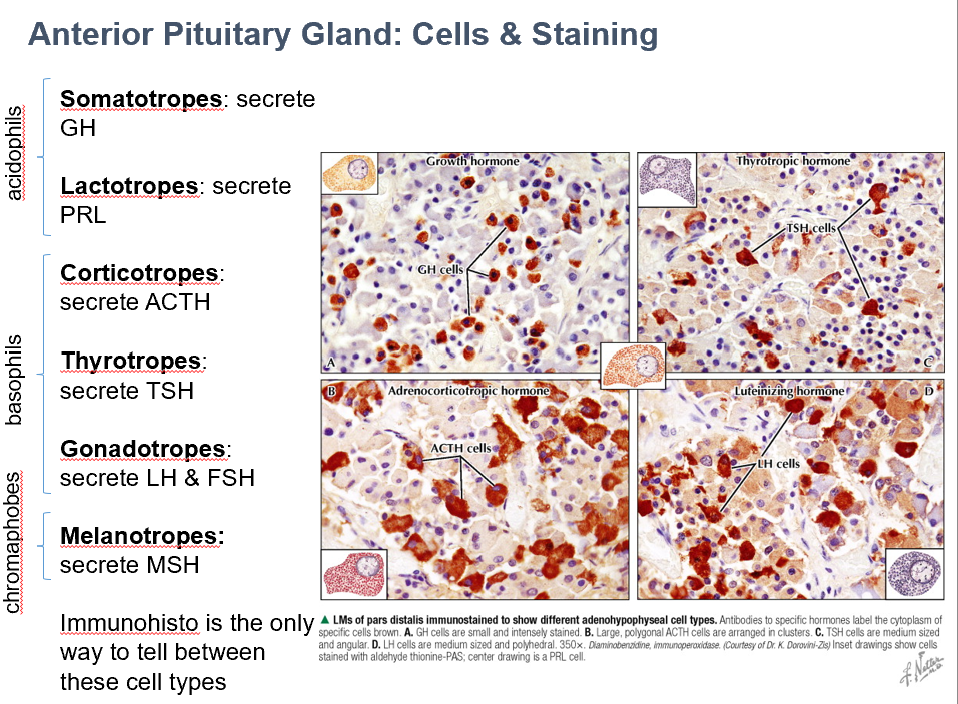
Somatotropes
Secrete GH
Acidophils
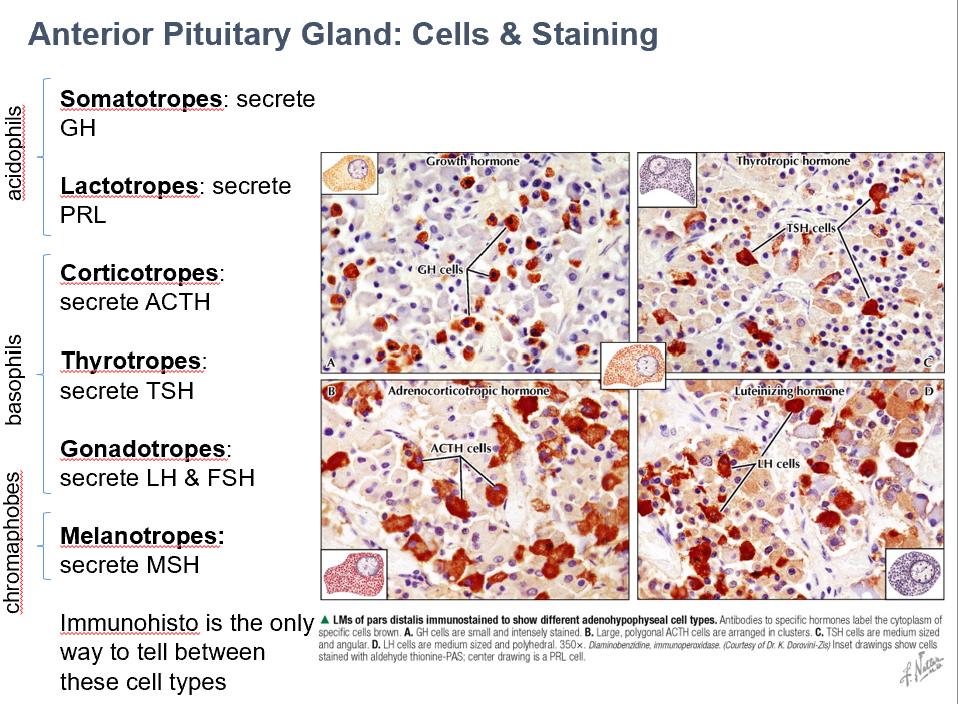
Lactotropes
Secrete PRL
Acidophils
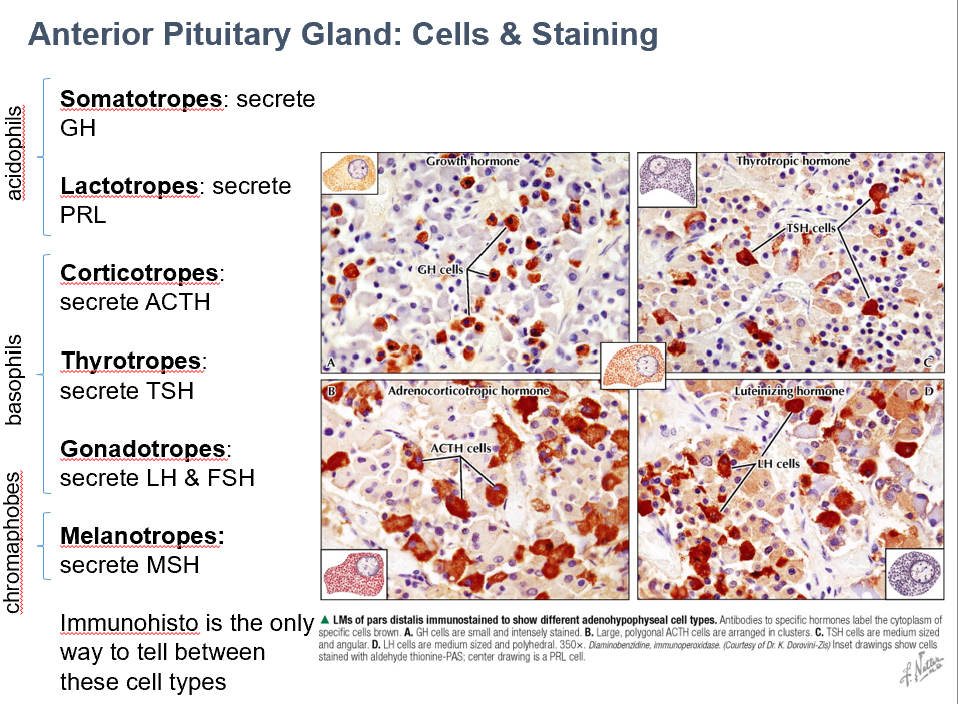
Thyrotropes
Secrete TSH
Basophils
Gonadotropes
Secrete LH & FSH
Basophils
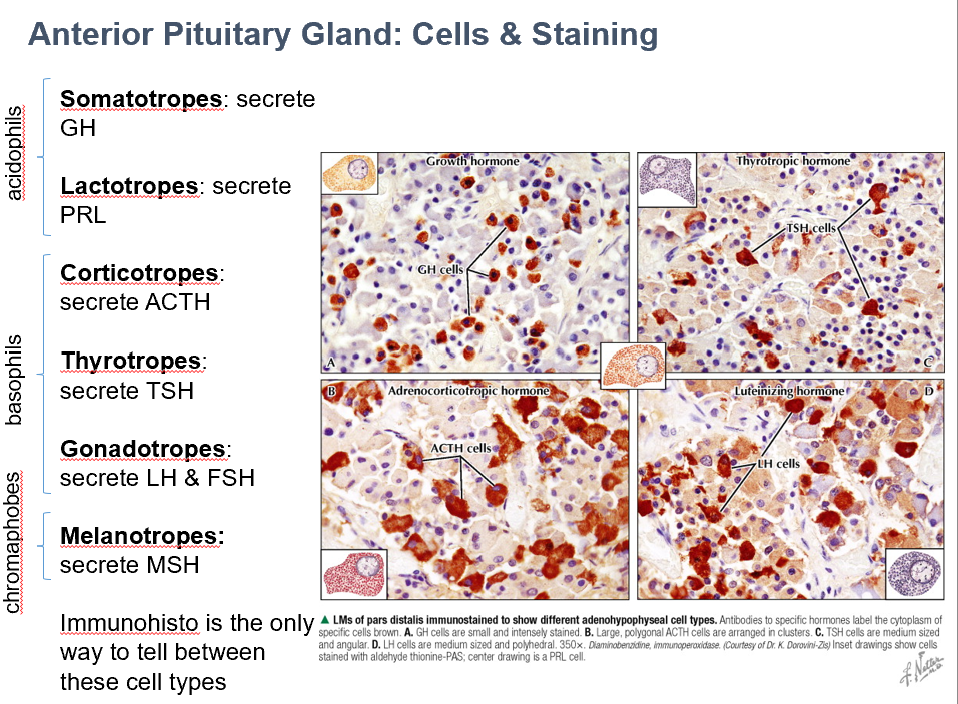
Melanotropes
Secrete MSH
Chromaphobes
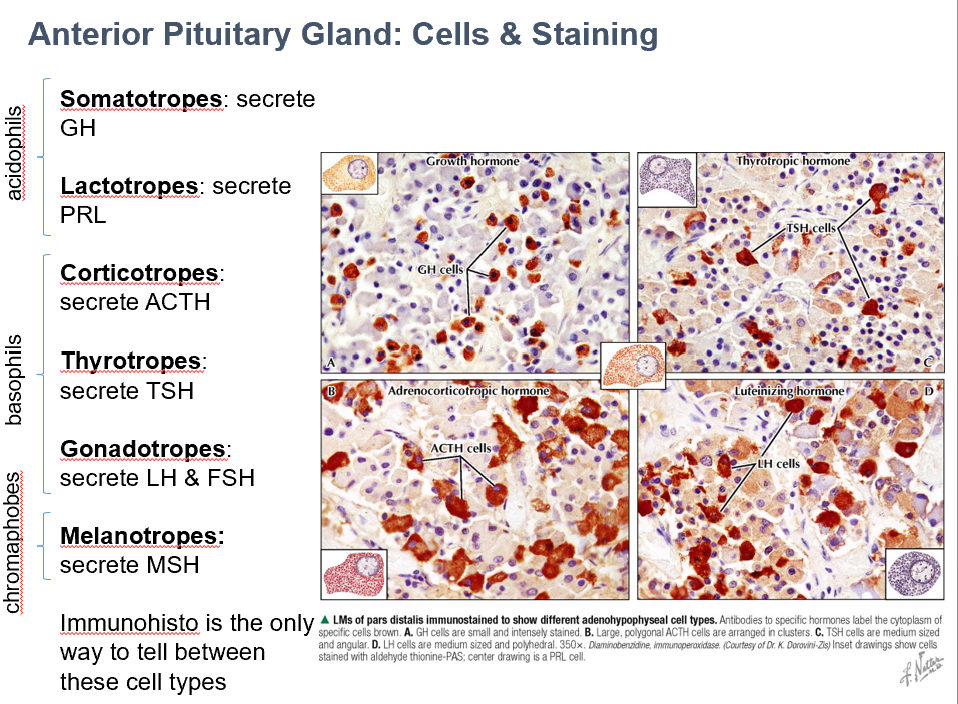
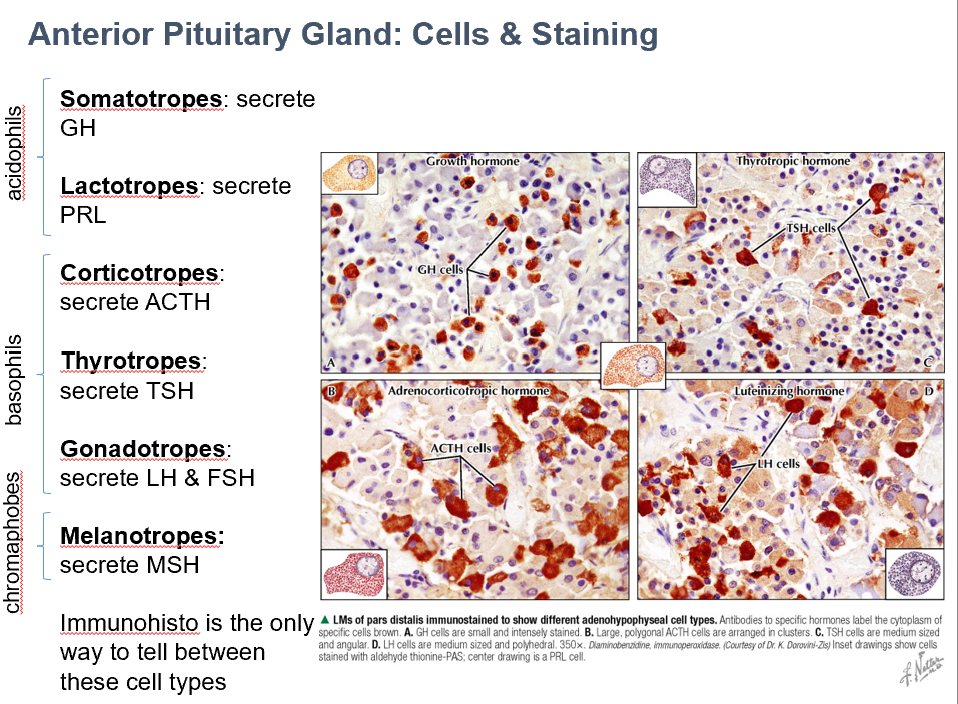
Corticotropes
Secrete ADH
Basophils
Oxytocin
ADH
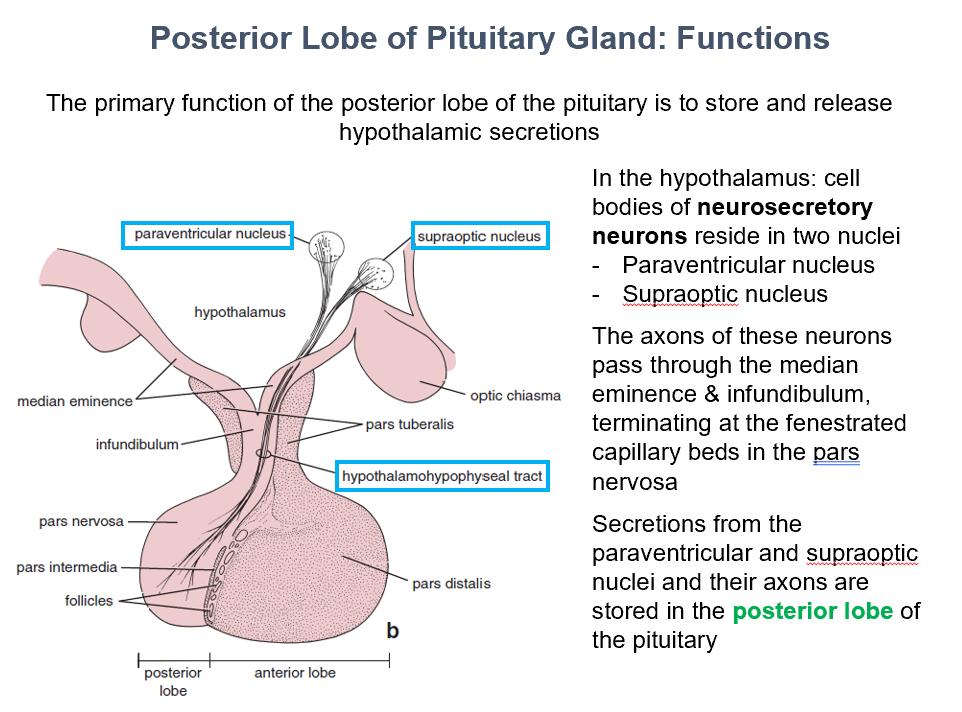
2 things the post. pit. stores:
_ in paraventricular nucleus
_ in supraoptic nucleus
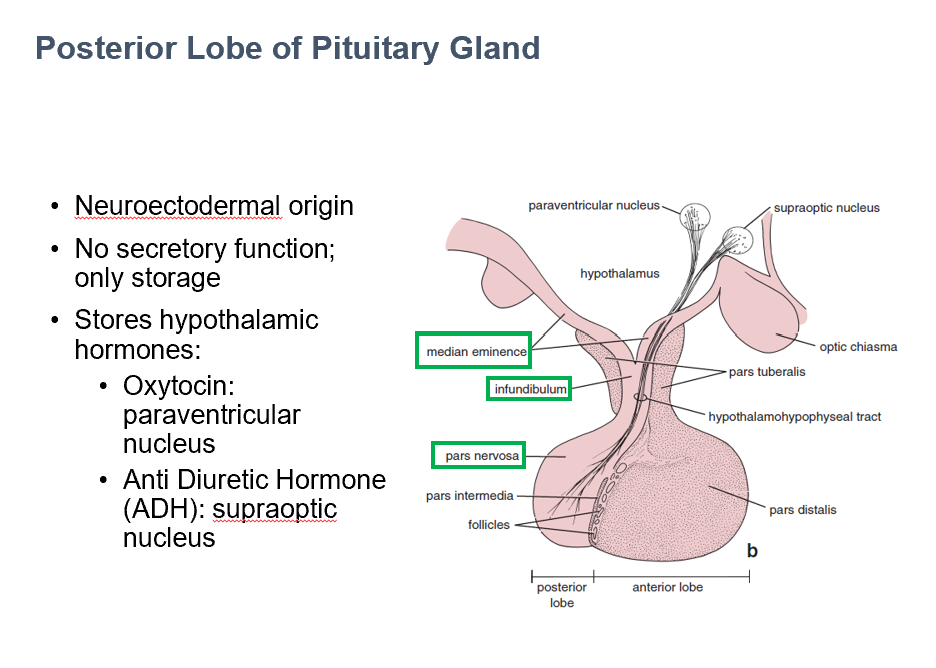
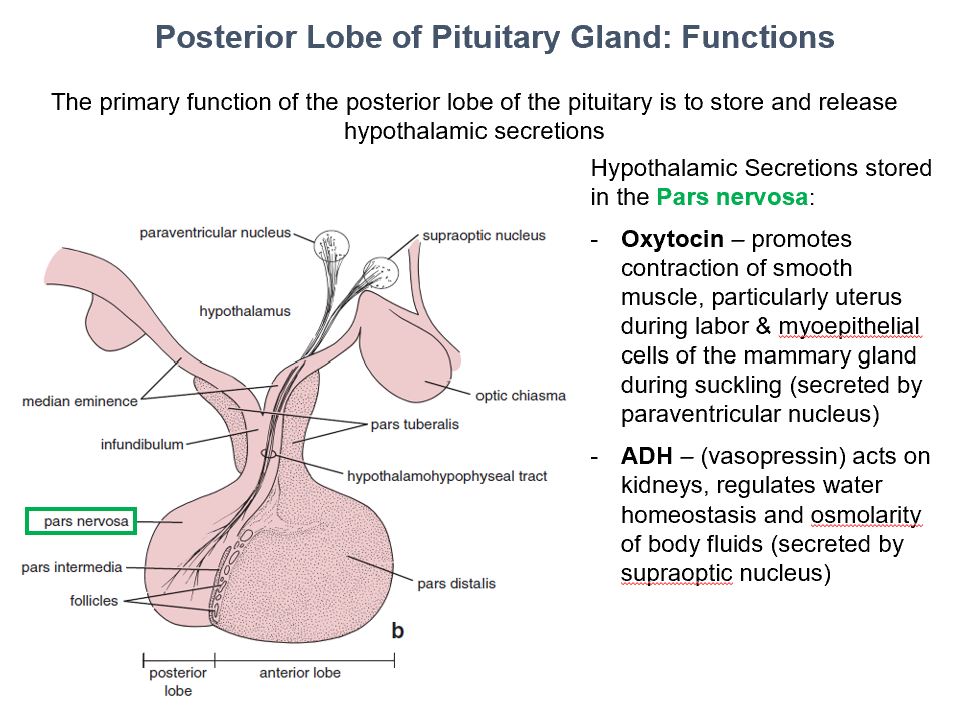
Store & Release Hypothalamic Secretions
The main function of the post. pit. gland is to_
Paraventricular & Supraoptic Nuclei
In the hypothalamus, THIS is where cell bodies of neurosecretory neurons can be found.
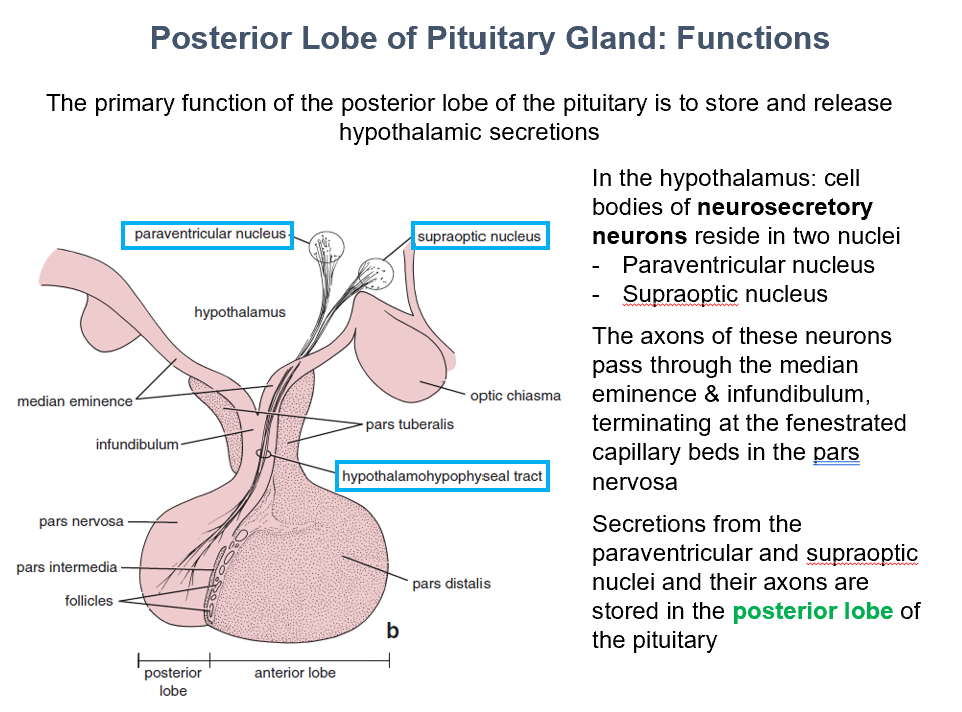
Posterior Lobe of the Pituitary
THIS is where secretions from the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei and their axons are stored.
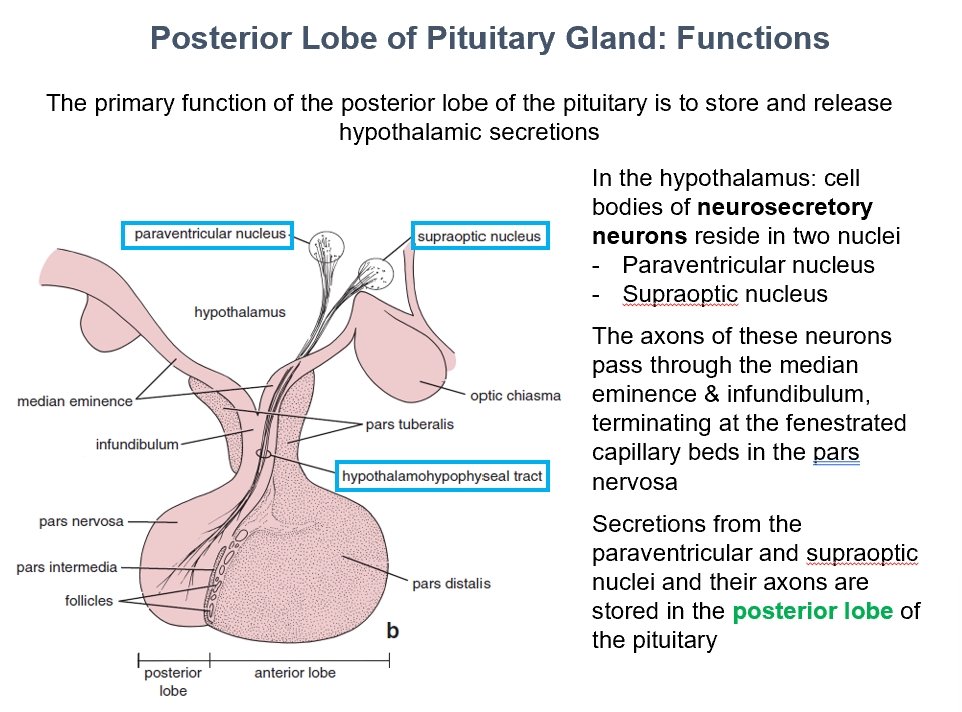
Pars Nervosa
Axons of the neurosecretory neurons pass through median eminence & infundibulum, they terminate at the fenestrated capillary beds found in THIS.
Oxytocin & ADH
THESE hypothalamic secretions are stored in the pars nervosa.
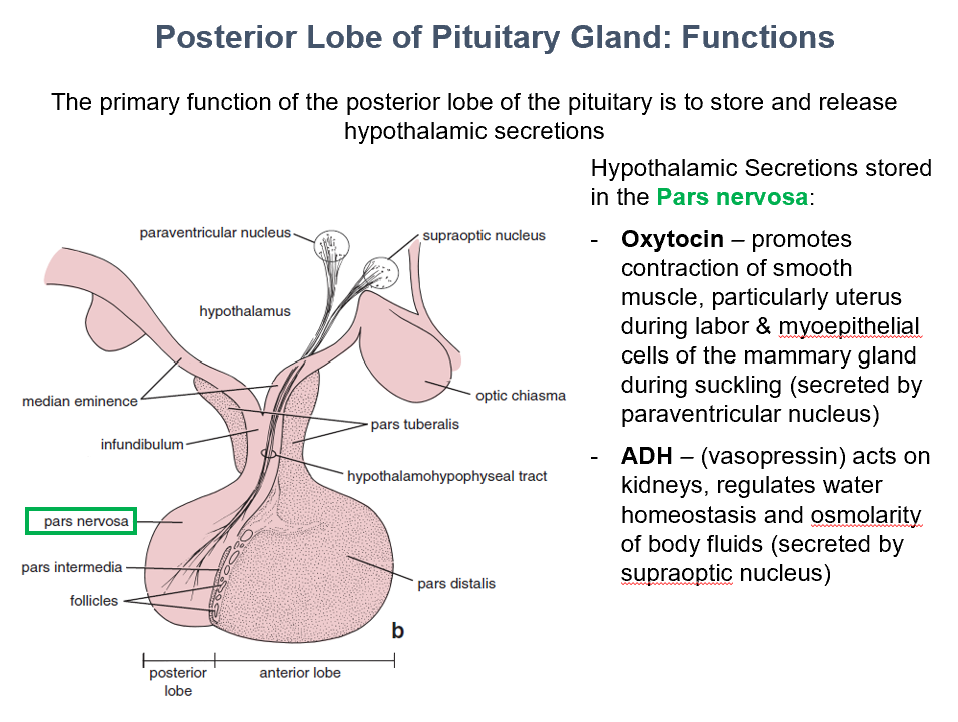
Oxytocin
Promotes contraction of smooth muscle, particularly uterus during labor & myoepithelial cells of the mammary gland during suckling (secreted by paraventricular nucleus)
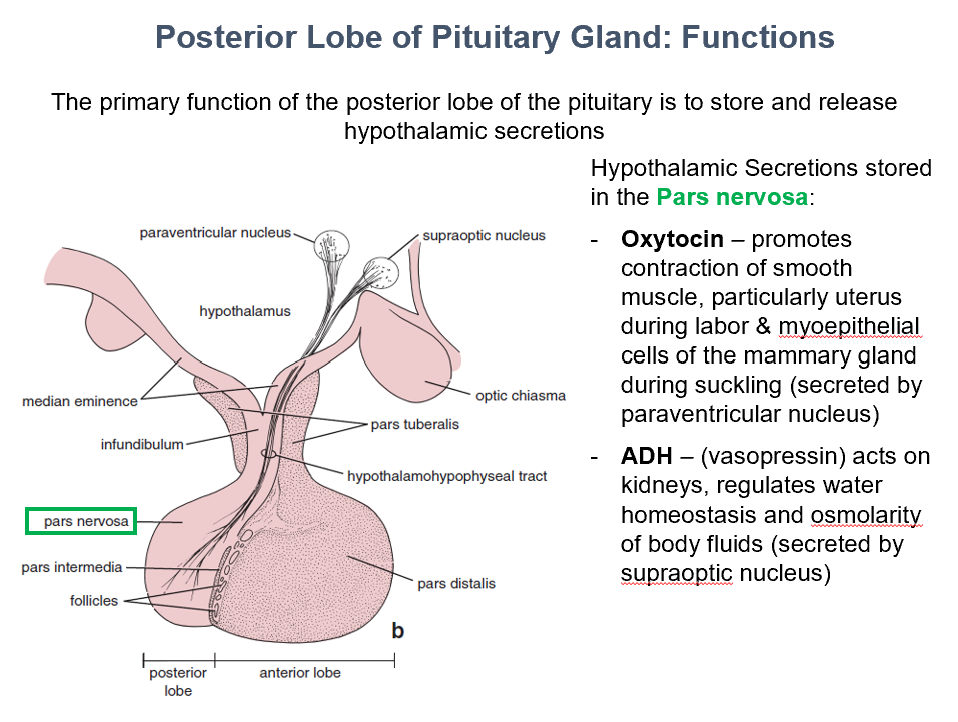
ADH
Acts on kidneys, regulates water homeostasis and osmolarity of body fluids (secreted by supraoptic nucleus)
AKA vasopressin
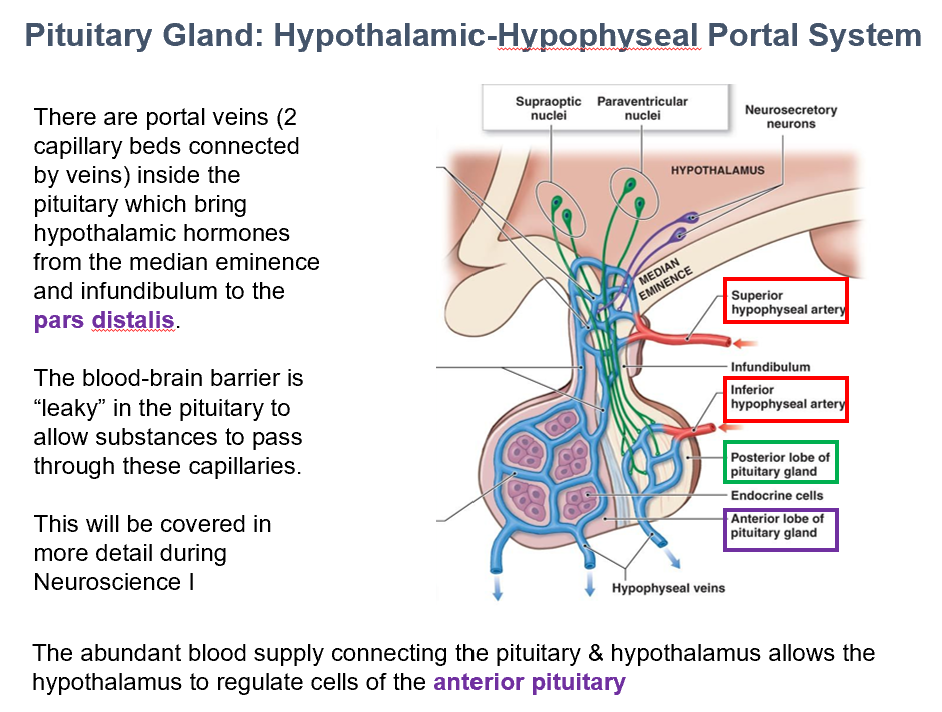
Superior Hypophyseal Artery
The Ant. Pit. is supplied by THIS.
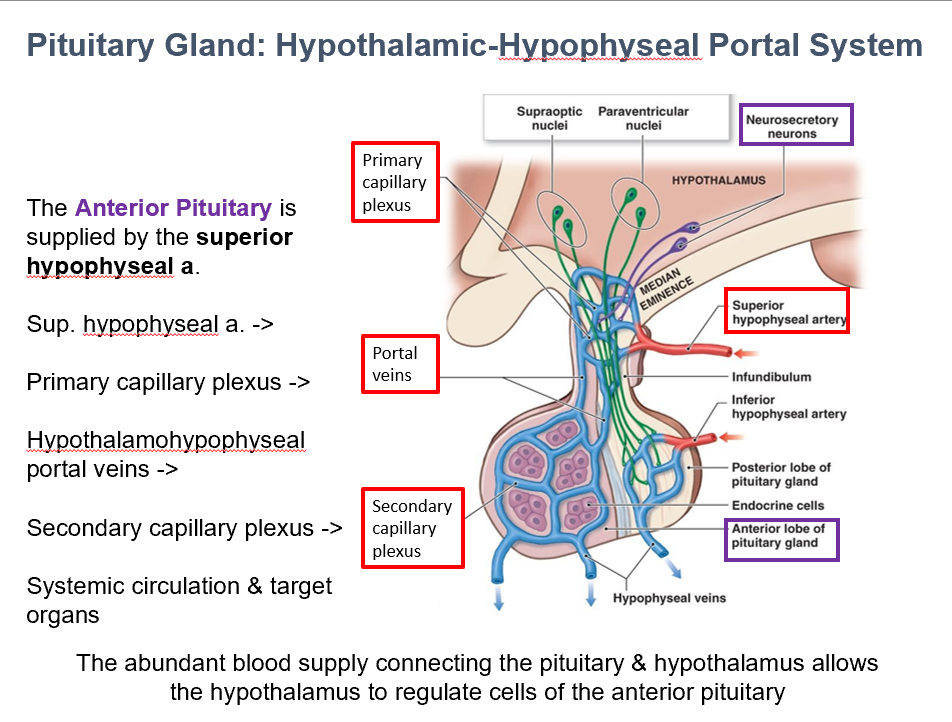
Hypothalamohypophyseal portal vv.
Superior hypophyseal a. → Primary capillary plexus → THIS→ Secondary capillary plexus → Systemic Circulation/Target Organs
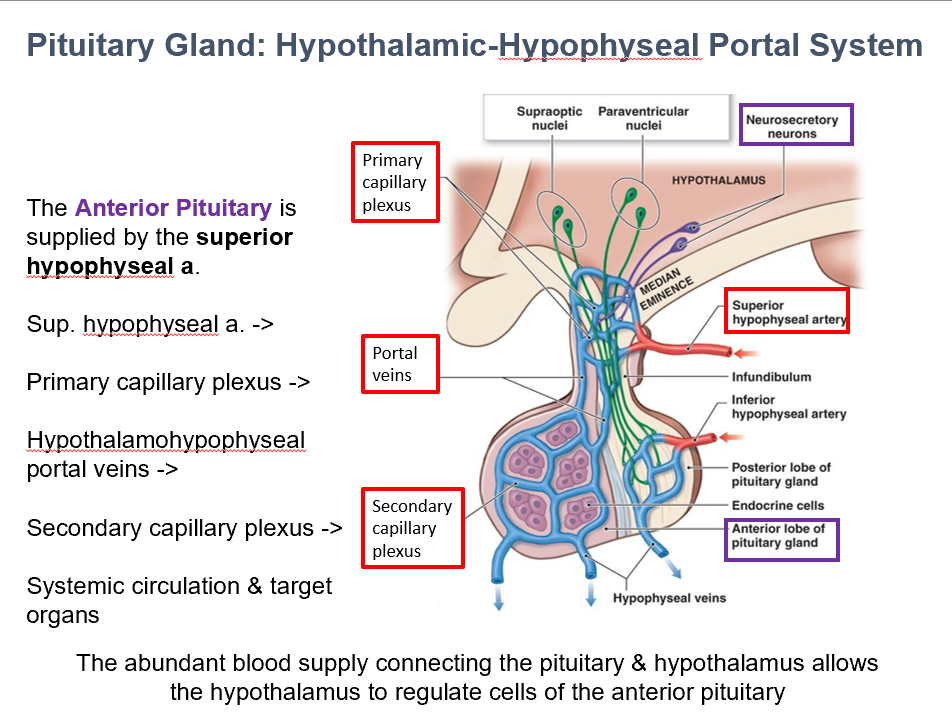
Abundant blood supply
THIS allows the hypothalamus to regulate cells of the anterior pituitary.
It does so via connecting the pituitary to the hypothalamus.
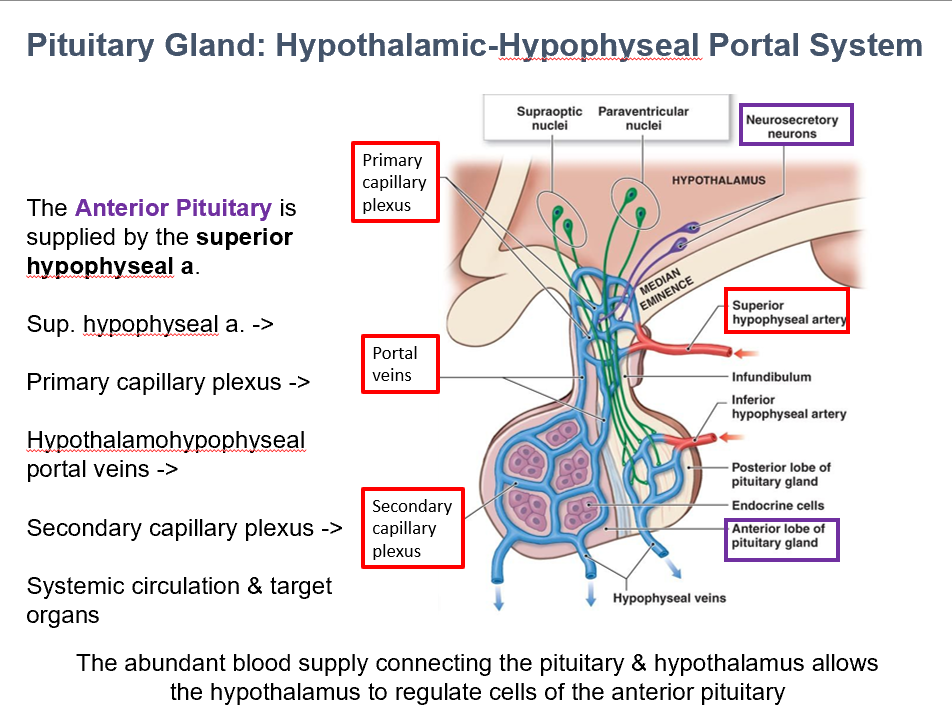
Portal Veins (Capillaries/Capillary Beds)
THESE are inside the pituitary, brining hypothalamic hormones from the median eminence & infundibulum → pars distalis.
The leaky BBB in the pituitary allows things to pass through these.
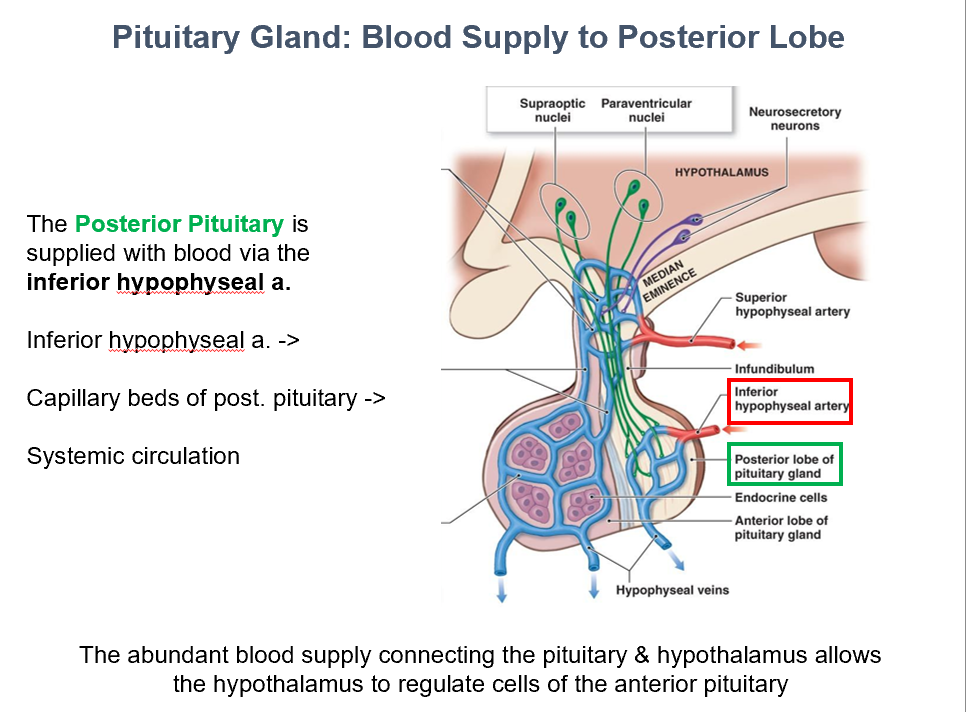
Inferior Hypophyseal Artery
The Post. Pit. is supplied with blood via THIS.
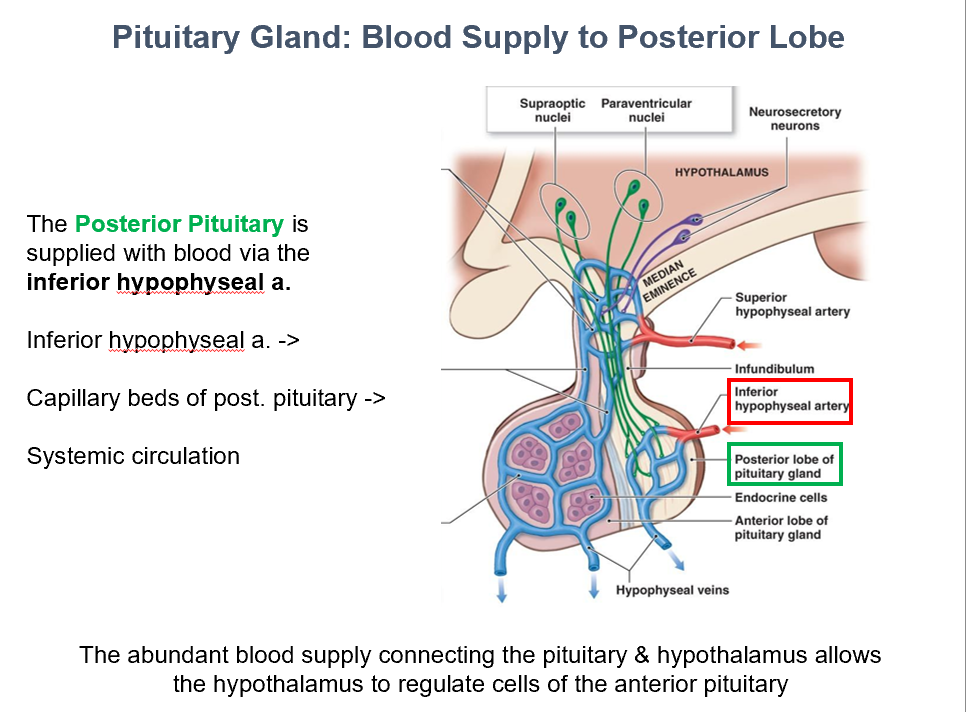
Capillary beds of post. pit.
Inferior hypophyseal a. → THIS → Systemic Circulation
Hypothalamic Hormones
THESE reach the post. pit. via neurons, where they are then stored.
Hypothalamic-Hypophysiotropic Hormones
THESE reach the ant. pit. via the hypothalamohypophyseal portal system.
They regulate synthesis & secretion of ant. pit. hormones.
Anterior Pituitary Adenomas
Sx: (compression related)
Headaches
Visual field defects
Increase in skin tags from increased GH production
Common:
Lactotropes
Somatropes
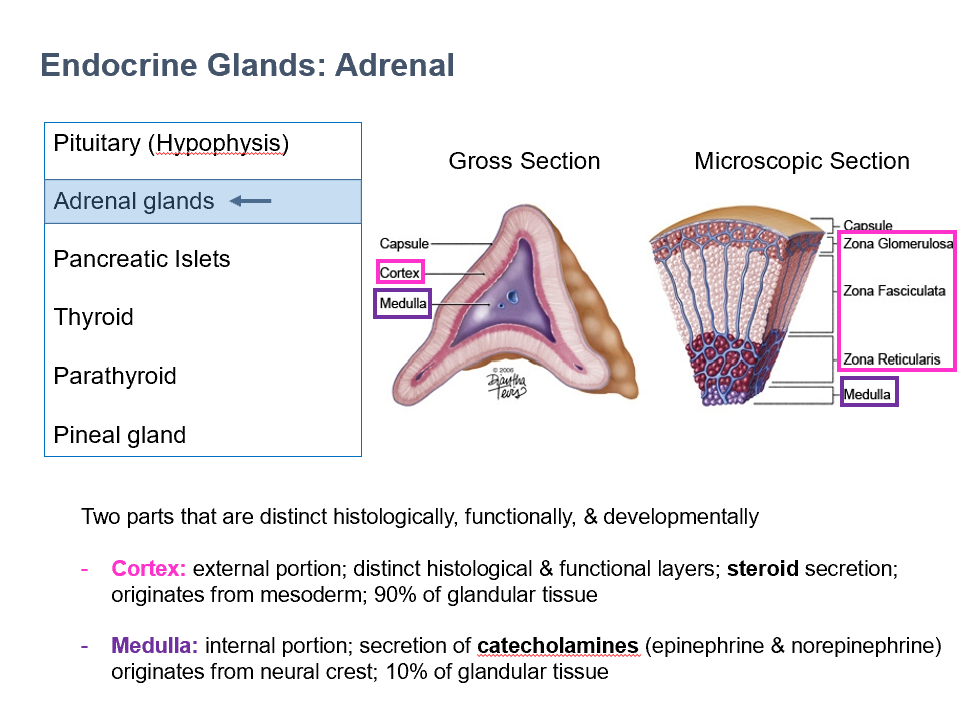
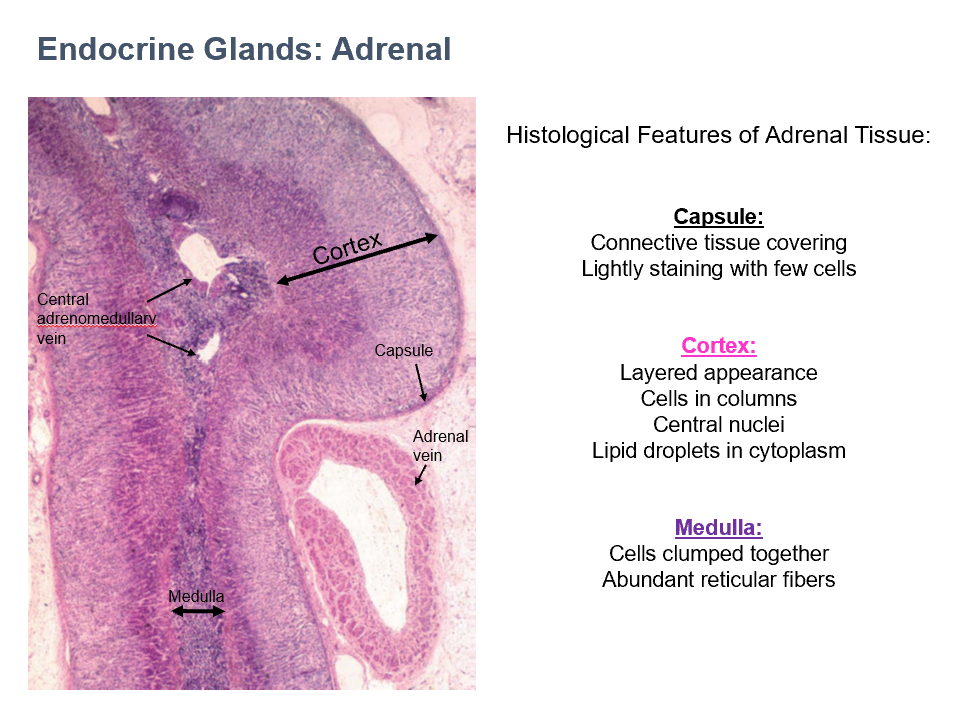
Cortex & Medulla
THESE are 2 parts of the adrenal glands that are distinct histologically, functionally, and developmentally.
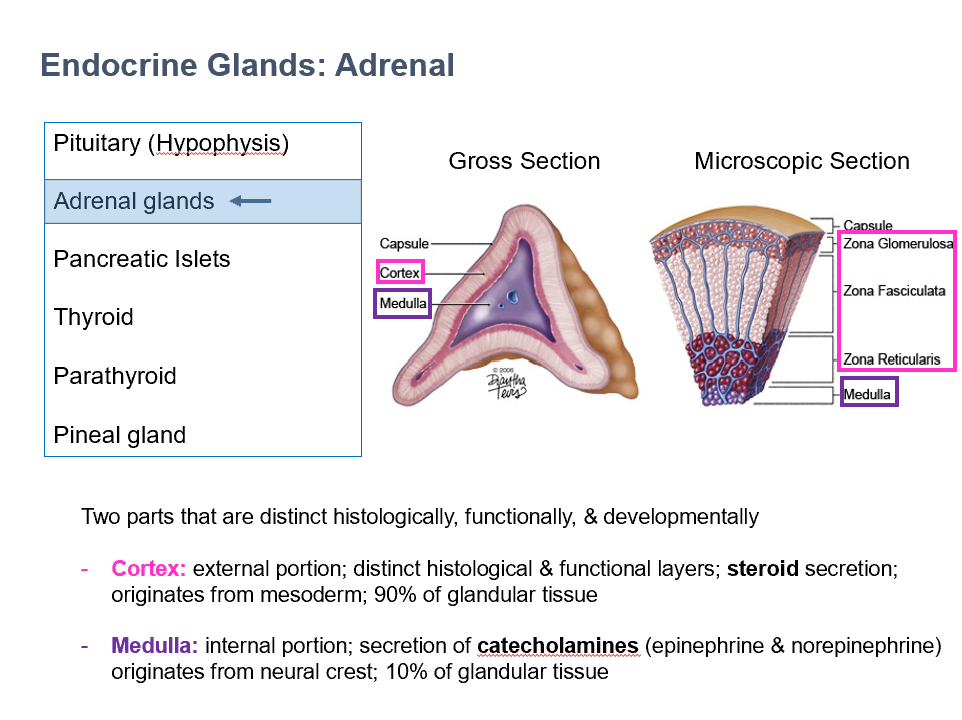
Cortex
External portion of adrenal gland
Distinct histological & functional layers
Steroid secretion
Originates from mesoderm
90% of glandular tissue
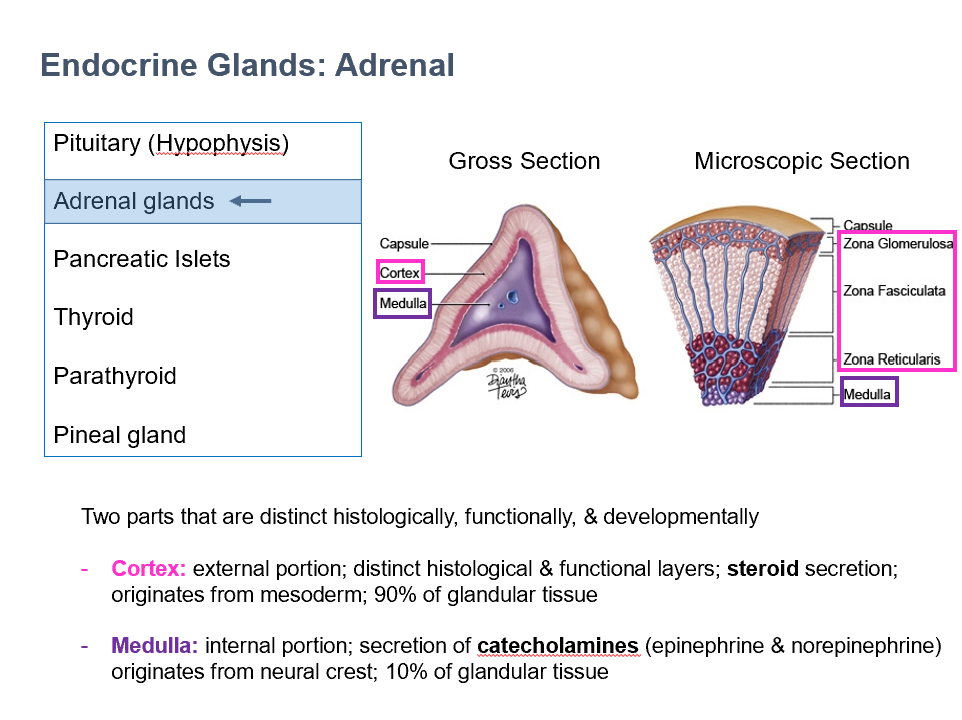
Medulla
Internal portion of adrenal gland
Secretion of catecholamines (epinephrine & norepinephrine)
Originates from neural crest
10% of glandular tissue
Capsule Histology
CT covering
Lightly staining
Few cells
Adrenal
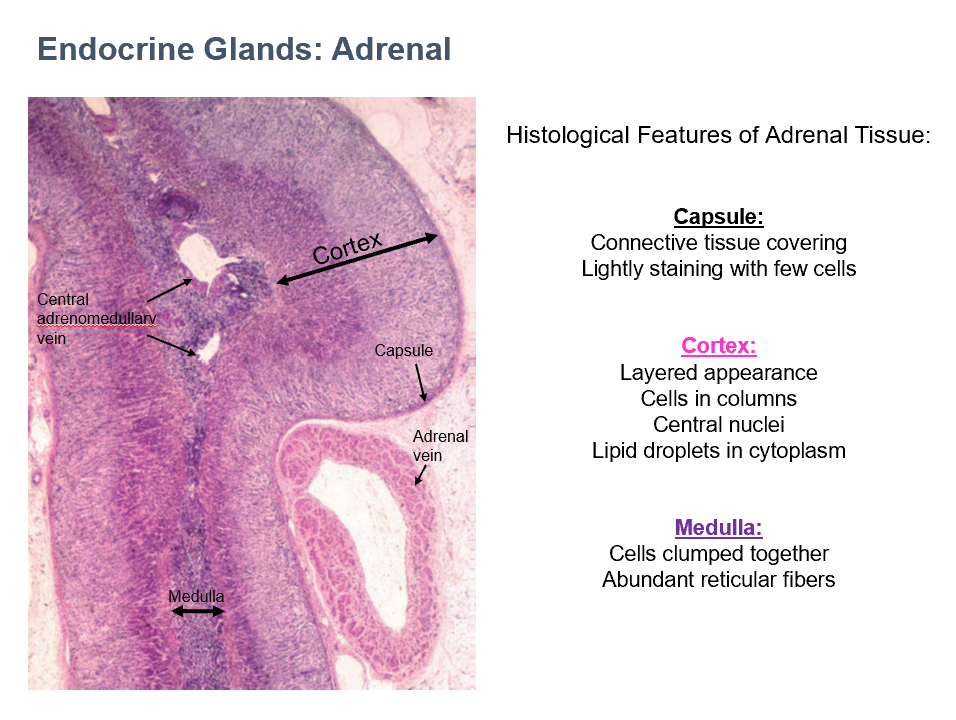
Cortex Histology
layered appearance
cells in columns
central nuclei
lipid droplets in cytoplasm
Adrenal
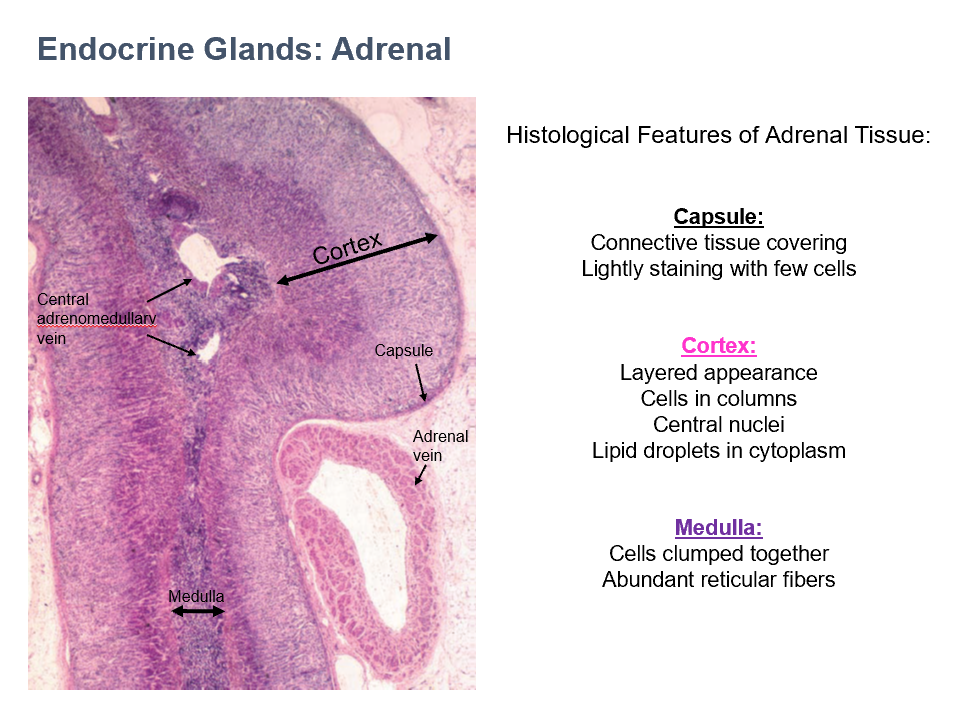
Medulla Histology
cells clumped together
abundant reticular fibers
Adrenal
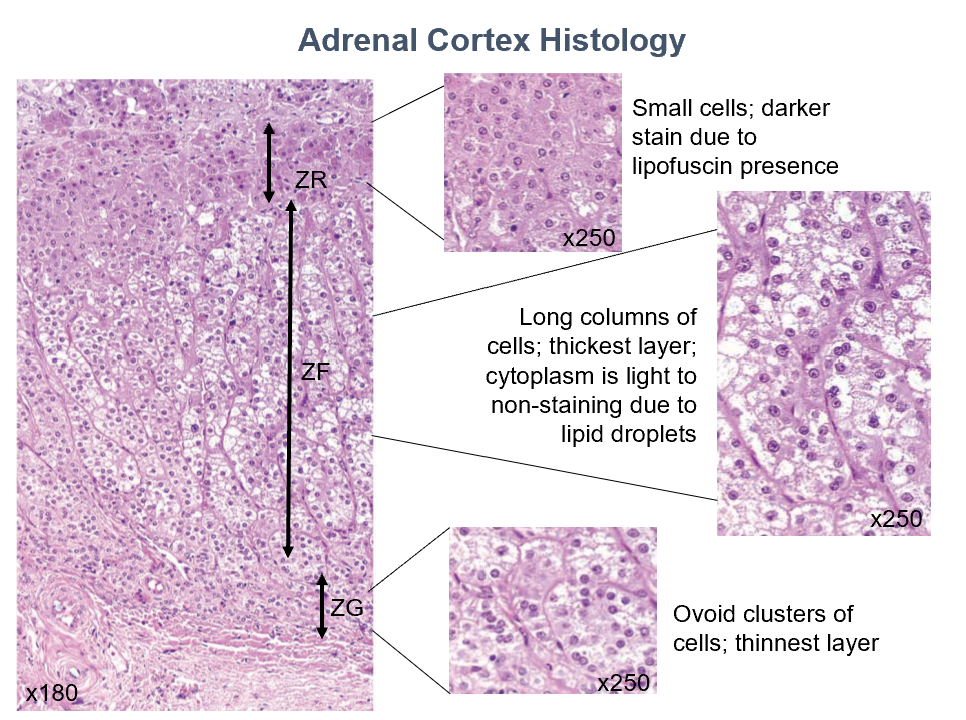
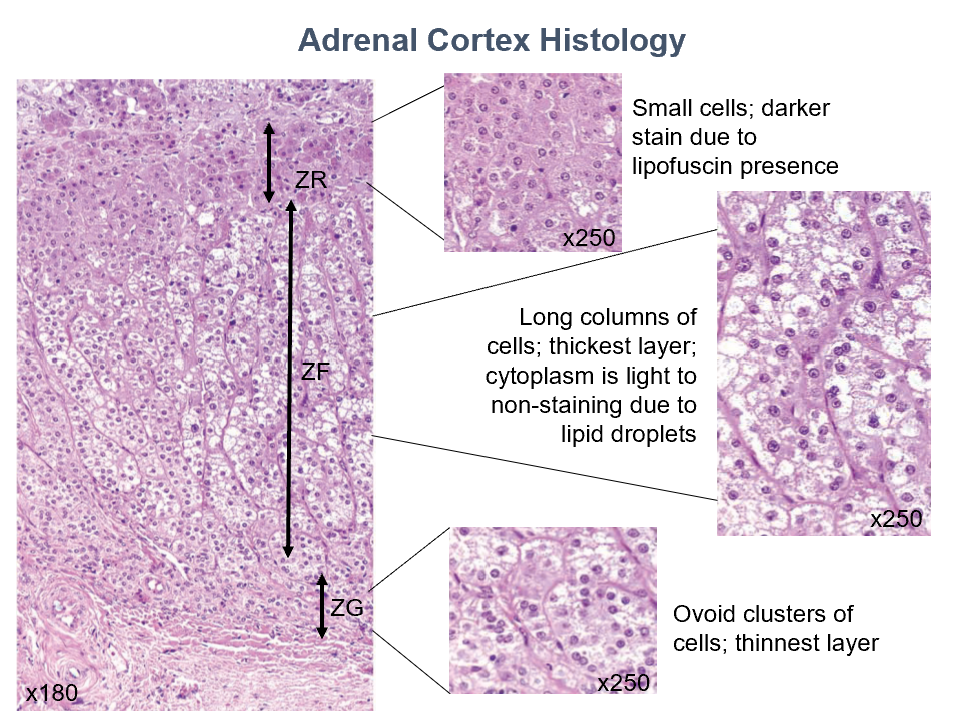
Adrenal Cortex Layers (superficial to deep)
Zona Glomerulosa
Zona Fasiculata
Zona Reticularis
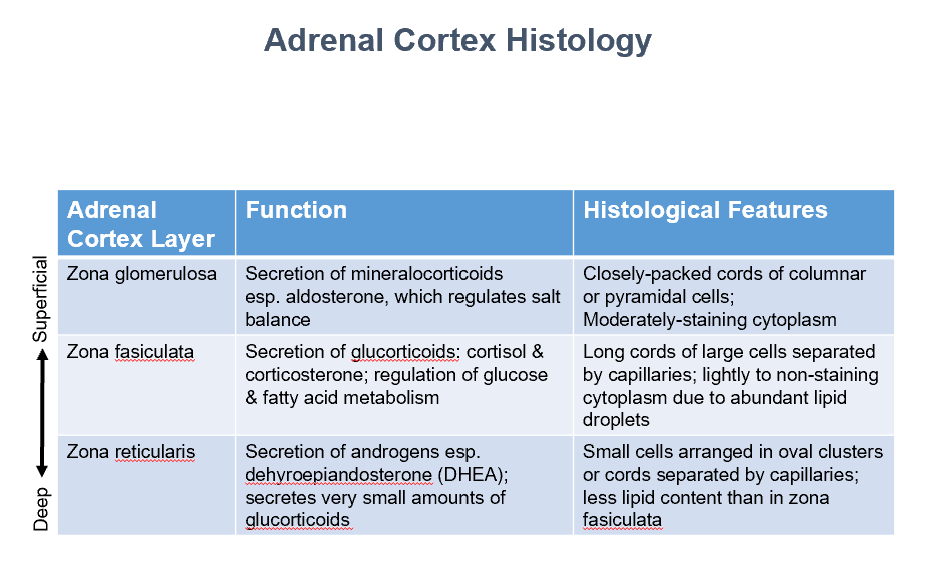
Zona Glomerulosa
Function:
Secretion of mineralocorticoids
esp. aldosterone, which regulates salt balance
Histo:
Closely-packed cords of columnar or pyramidal cells
Moderately-staining cytoplasm
Zona Fasiculata
Function:
Secretion of glucorticoids: cortisol & corticosterone
Regulation of glucose & fatty acid metabolism
Histo:
Long cords of large cells separated by capillaries
Lightly to non-staining cytoplasm due to abundant lipid droplets
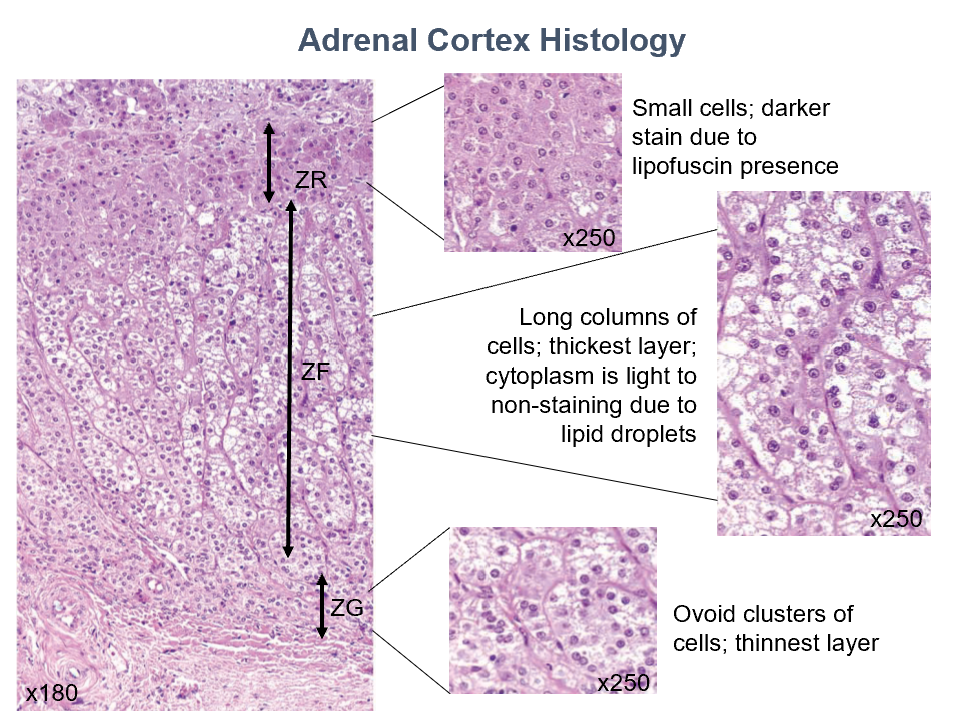
Zona Reticularis
Function:
Secretion of androgens esp. dehyroepiandosterone (DHEA)
Secretes very small amounts of glucorticoids
Histo:
Small cells arranged in oval clusters or cords separated by capillaries
Less lipid content than in zona fasiculata
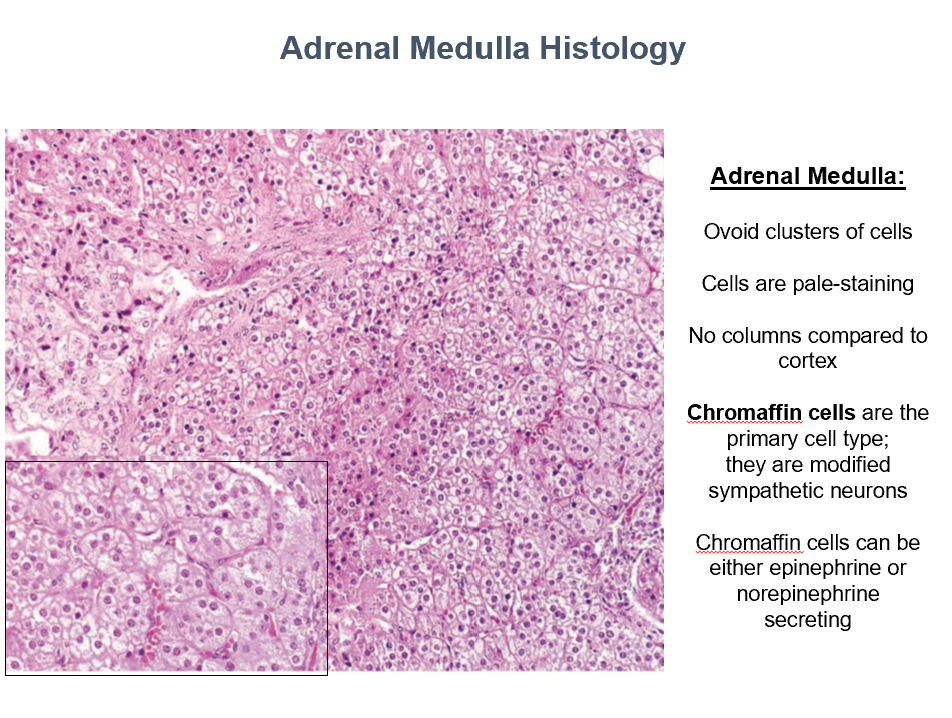
Adrenal Medulla Histology
Ovoid clusters of cells
Pale-staining
No columns
Chromaffin cells!
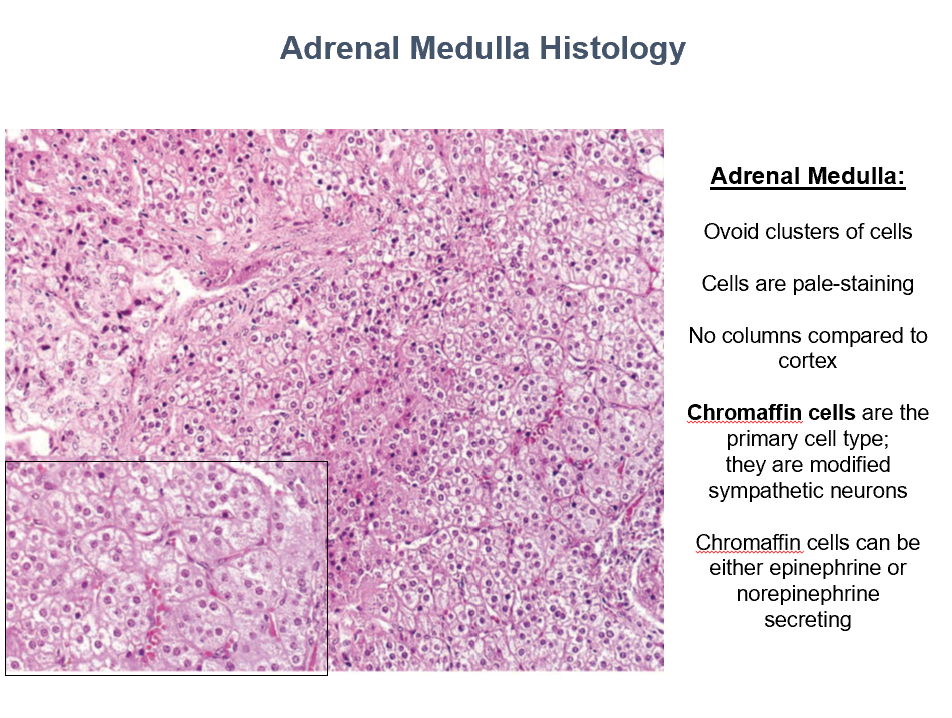
Chromaffin Cells
Main cell type in adrenal medulla
Modified sympathetic neurons
Can secrete Epi or NE!
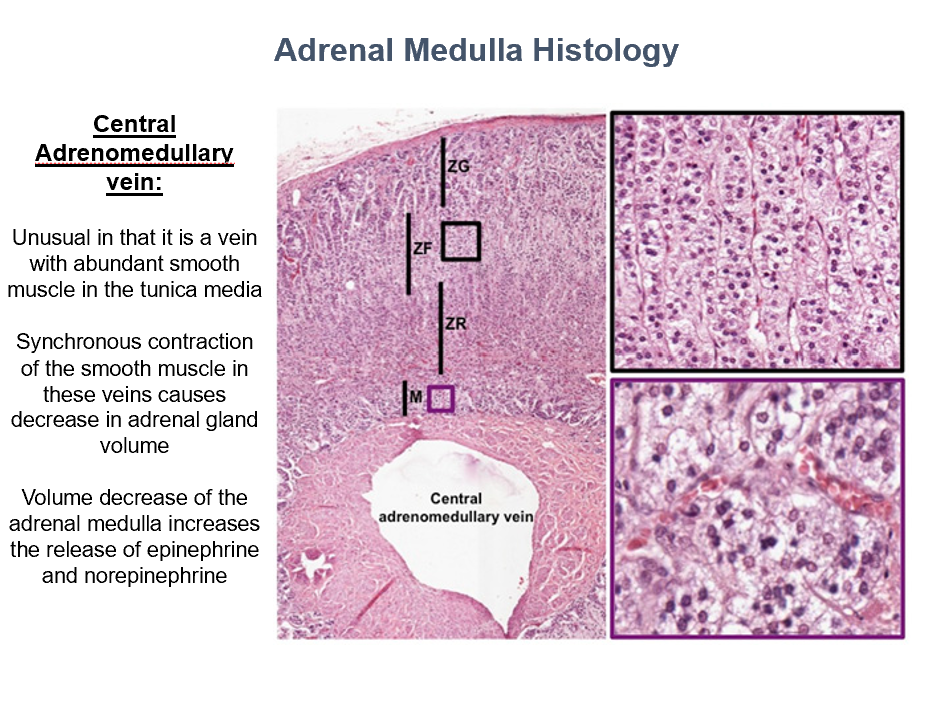
Central Adrenomedullary Vein
Abundant smooth muscle in tunica media! (unique)
Synchronous contraction of the sm in THIS decreases adrenal gland volume (increasing Epi and NE release)
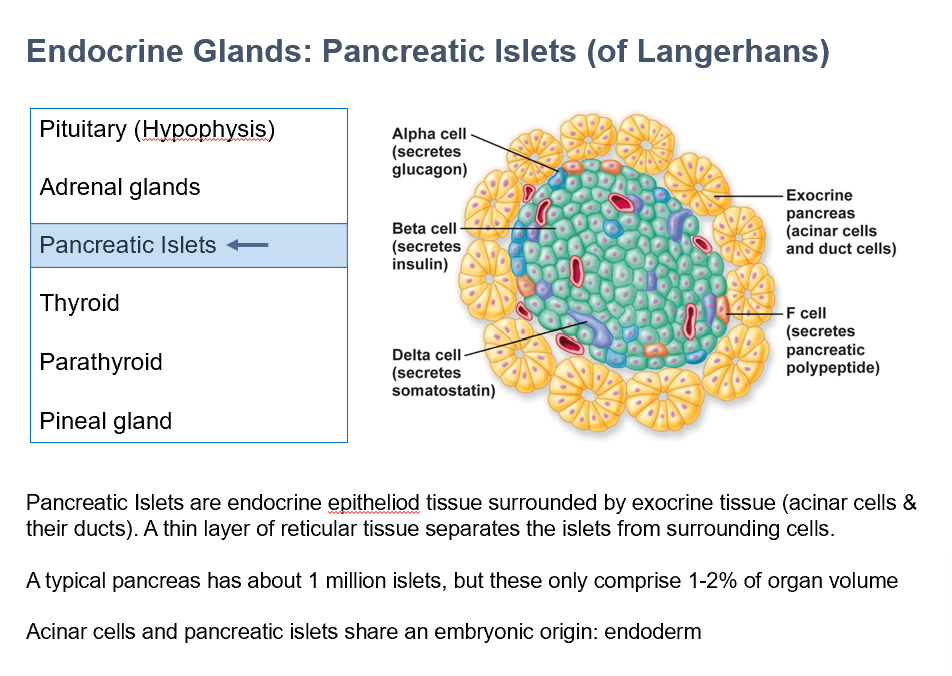
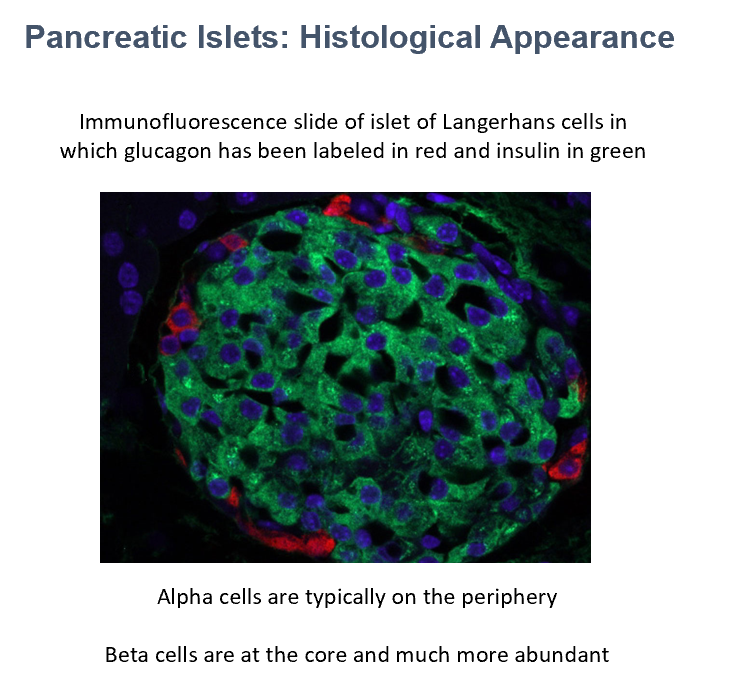
Pancreatic Islets (of Langerhans)
Endocrine epithelioid tissue
Surrounded by exocrine tissue (acinar cells/ducts)
Thin layer reticular tissue separates THESE from the surrounding cells
Shares embryo origin with acinar cells = Endoderm
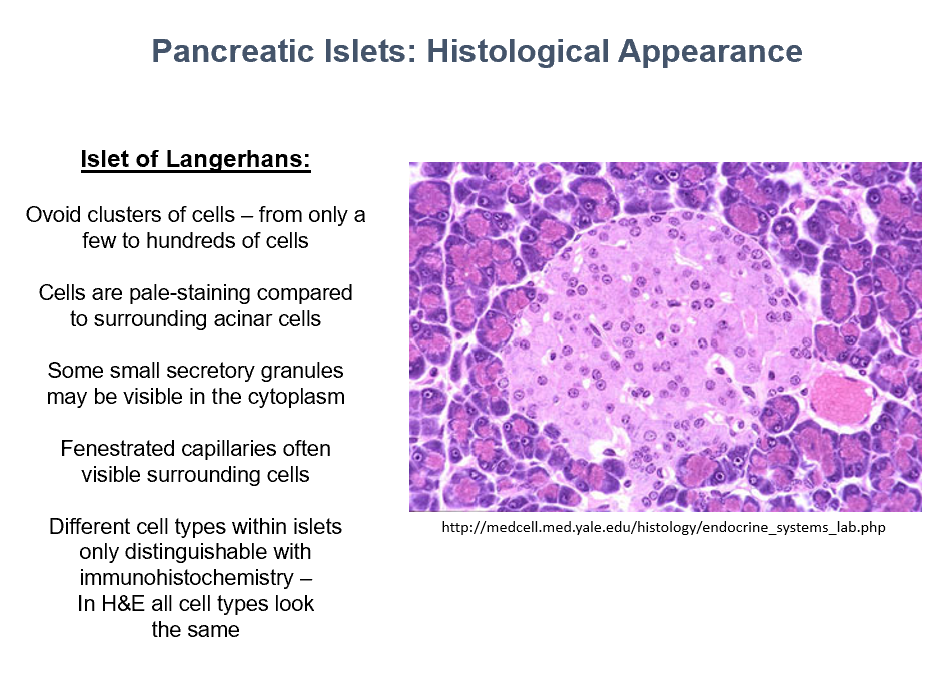
Islets of Langerhans Histology
ovoid clusters of cells
pale-staining (compared to surrounding acinar cells)
small secretory granules in cytoplasm
fenestrated capillaries around the cells!
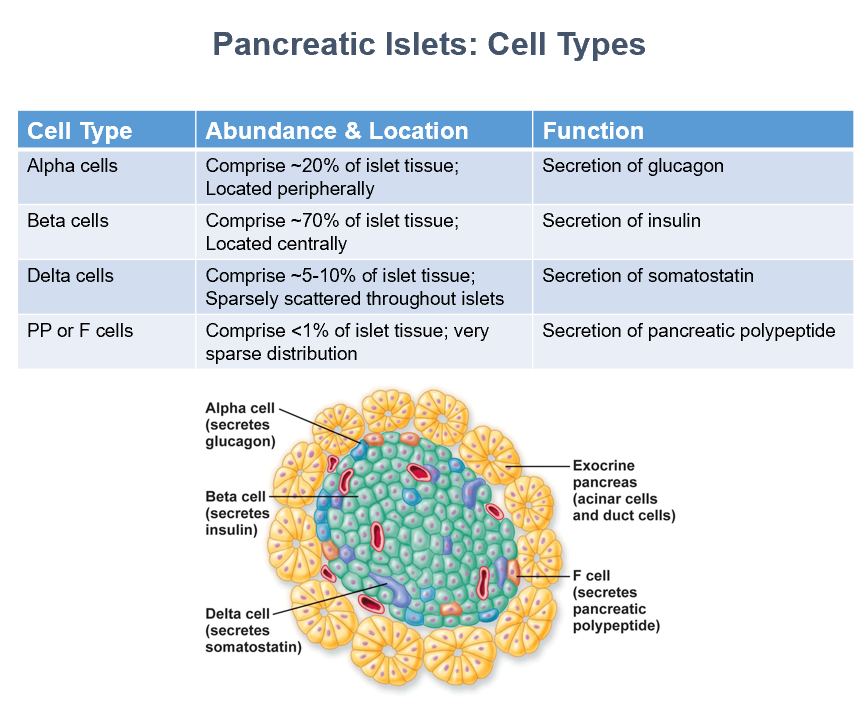
Pancreatic Islets Cell Types
Alpha (secrete glucagon) (peripheral)
Beta (secrete insulin) (central)
Delta (secrete somatostatin) (sparse)
PP or F (secrete pancreatic polypeptide) (very sparse)
Glucagon
Insulin
Immunofluorescence of islets!
The cells in red are THIS.
The cells in green are THIS.
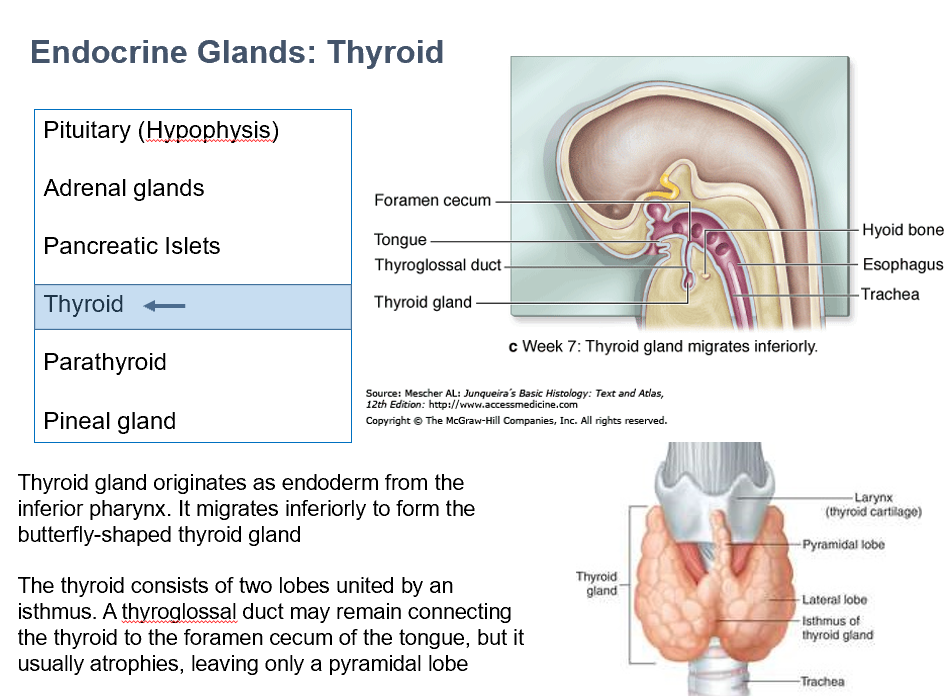
Thyroid
origin is endoderm (from inferior pharynx)
Migrates inferiorly
made of 2 lobes, connected via isthmus
thyroglossal duct may remain (connects THIS to foramen cecum of tongue)
if it atrophies, it leaves pyramidal lobe
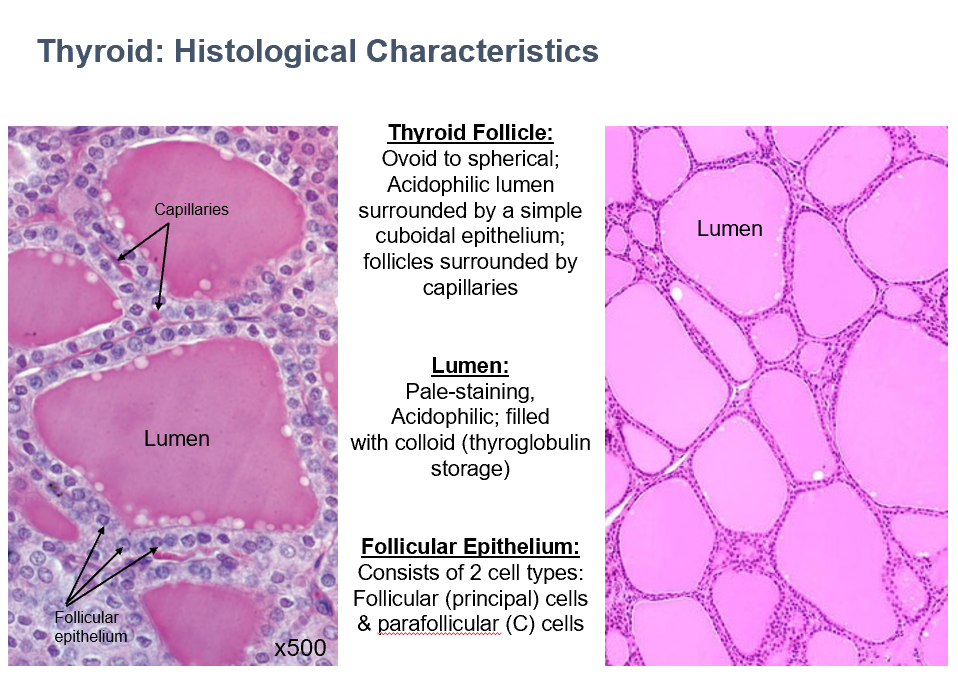
Thyroid Follicle Histology
Ovoid/spherical
Acidophilic
Surrounded by simple cuboidal epithelium
Capillaries surround
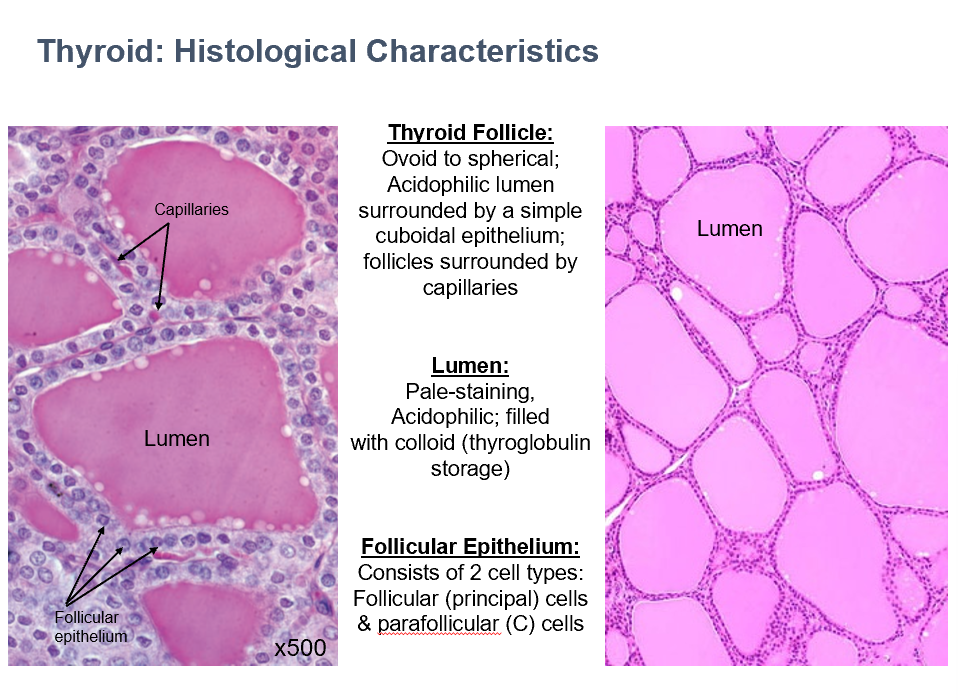
Thyroid Lumen Histology
Pale-staining
Acidophilic
Filled with colloid (thyroglobulin storage)
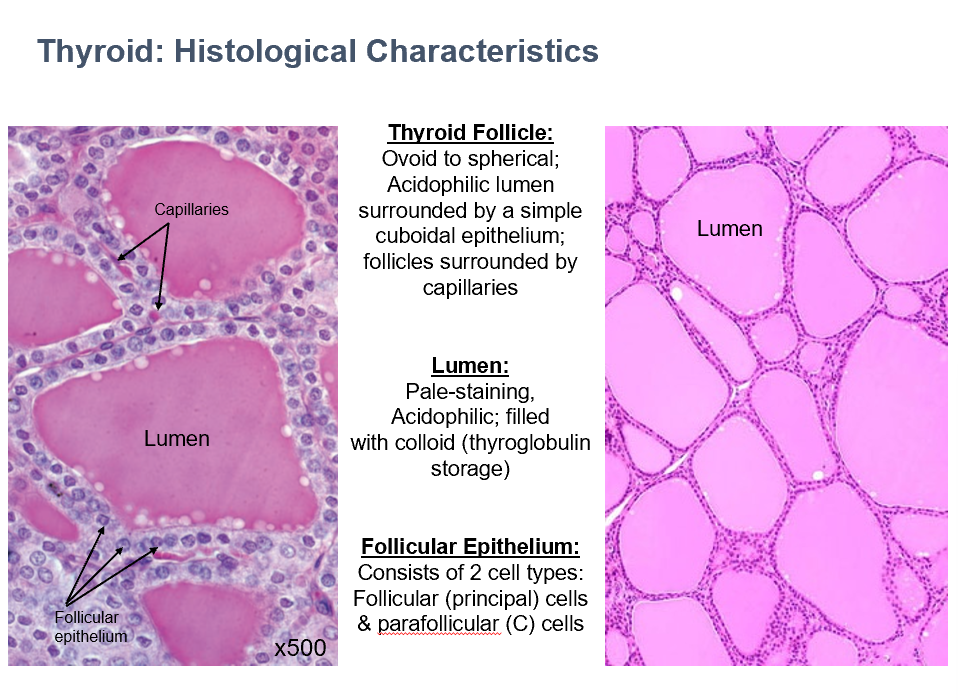
Thyroid Follicular Epithelium
2 cell types:
Follicular (principle) cells
Parafollicular cells
Stores its own product
The thyroid gland is unique in terms of endocrine glands because it _ in an inactive form (thyroglobulin).
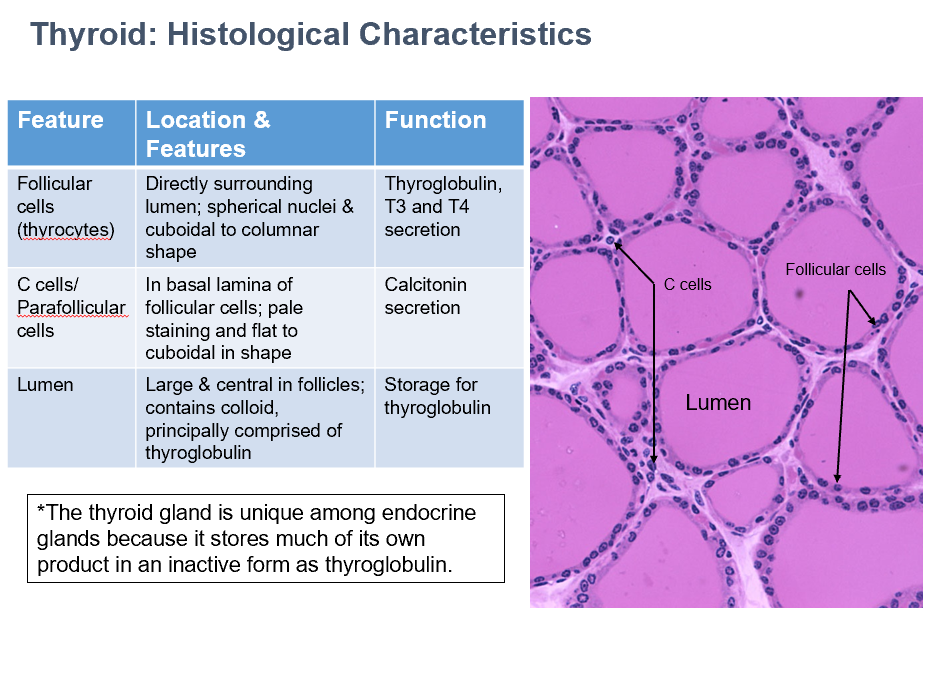
Follicular cells (thyrocytes)
Location/Features:
Directly surrounding lumen; spherical nuclei & cuboidal to columnar shape
Location:
Thyroglobulin, T3 and T4 secretion
Thyroid
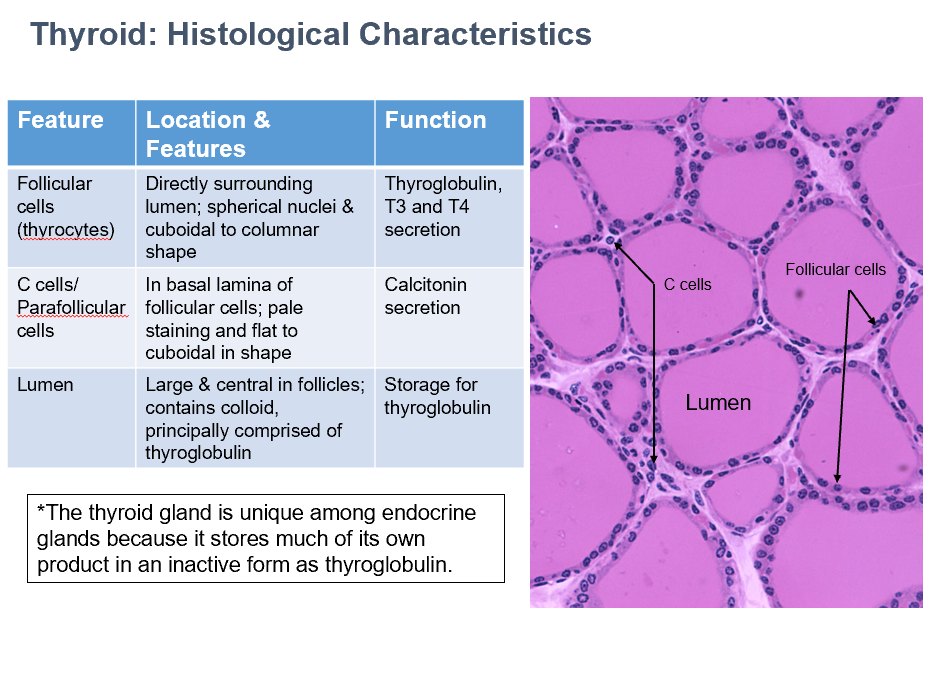
C Cells/Parafollicular Cells
Location/Features:
In basal lamina of follicular cells
Pale staining and flat to cuboidal in shape
Do NOT contact colloid
Small clusters
Fenestrated capillaries between follicles
Function:
Calcitonin secretion
Thyroid
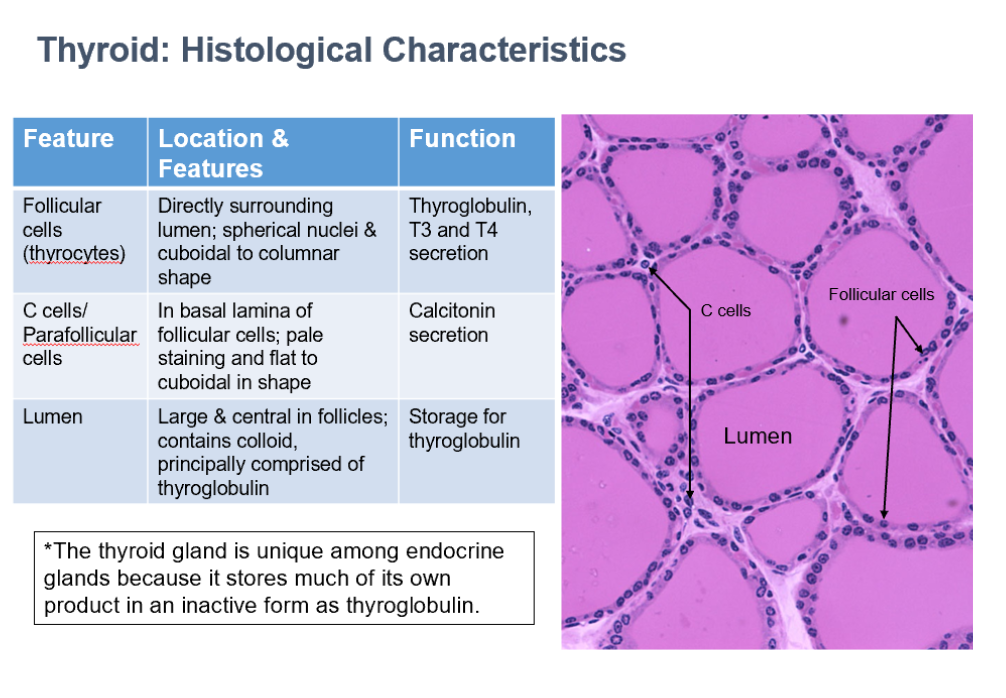
Thyroid Lumen
Location/Features:
Large & central in follicles; contains colloid, principally comprised of thyroglobulin
Function:
Storage for thyroglobulin
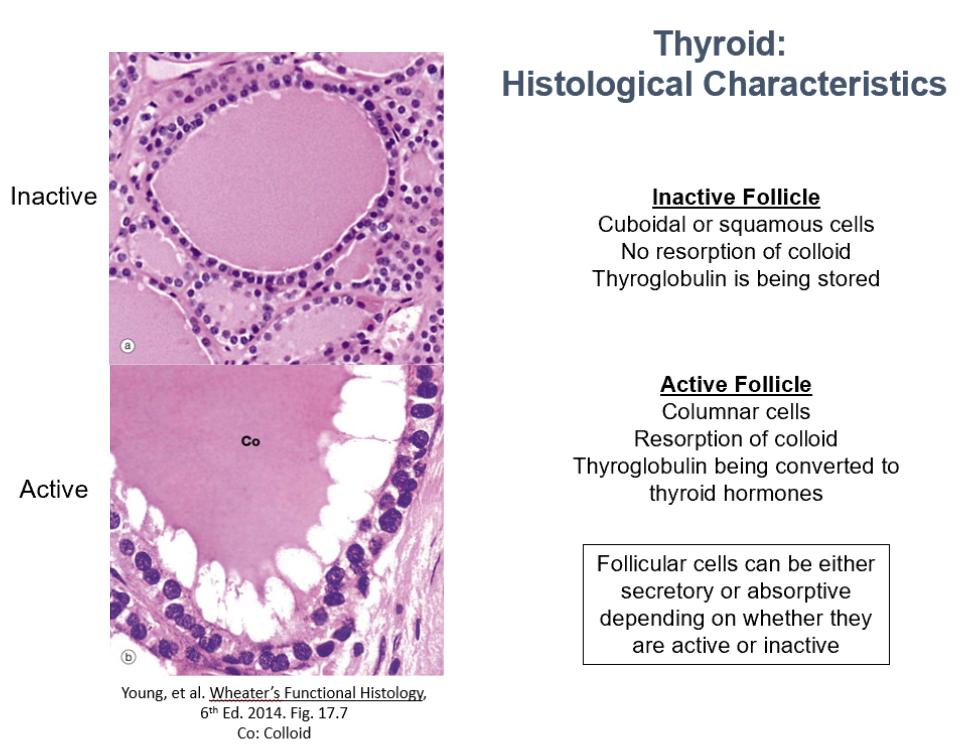
Thyroid Histological Characteristics (2 things)
Inactive Follicle:
Cuboidal or squamous cells
No resorption of colloid
Thyroglobulin is being stored
Active Follicle:
Columnar cells
Resorption of colloid
Thyroglobulin being converted to thyroid hormones
Follicular cells can be either secretory or absorptive depending on whether they are active or inactive
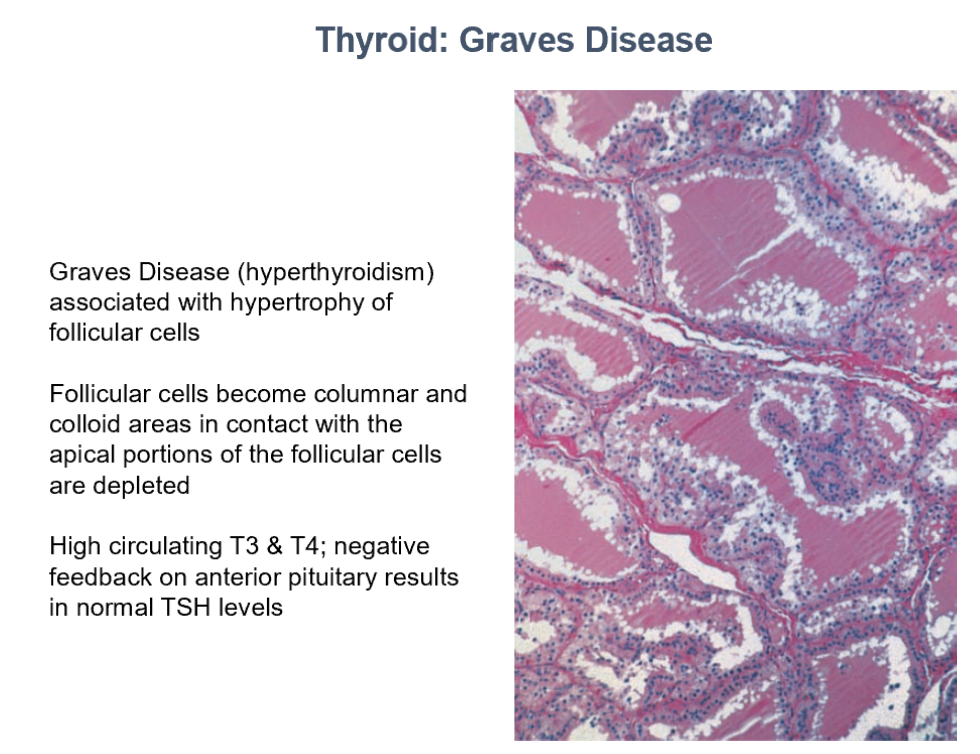
Thyroid: Graves Disease
Hyperthyroidism
Hypertrophy of follicular cells
Follicular cells become columnar
Colloid areas in contact with apical portions of follicular cells decrease
High circulating T3 and T4
Negative feedback on Ant. Pit. = Normal TSH Levels
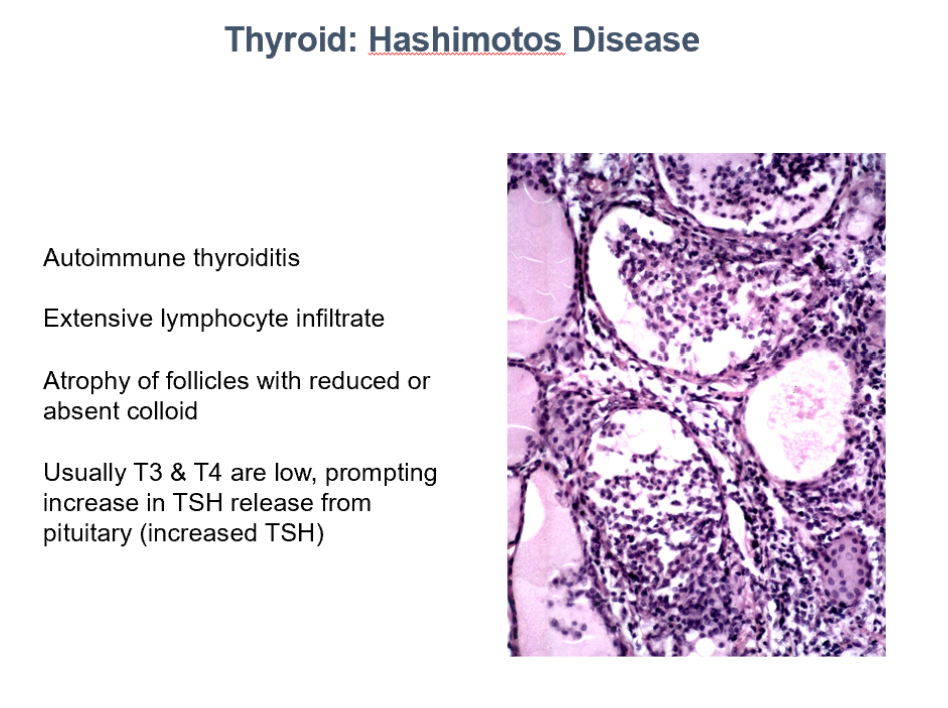
Thyroid: Hashimoto’s Disase
Autoimmune thyroiditis
Extensive lymphocyte infiltrate
Atrophy of follicles with reduced or absent colloid
Usually T3 & T4 are low, prompting increase in TSH release from pituitary (increased TSH)
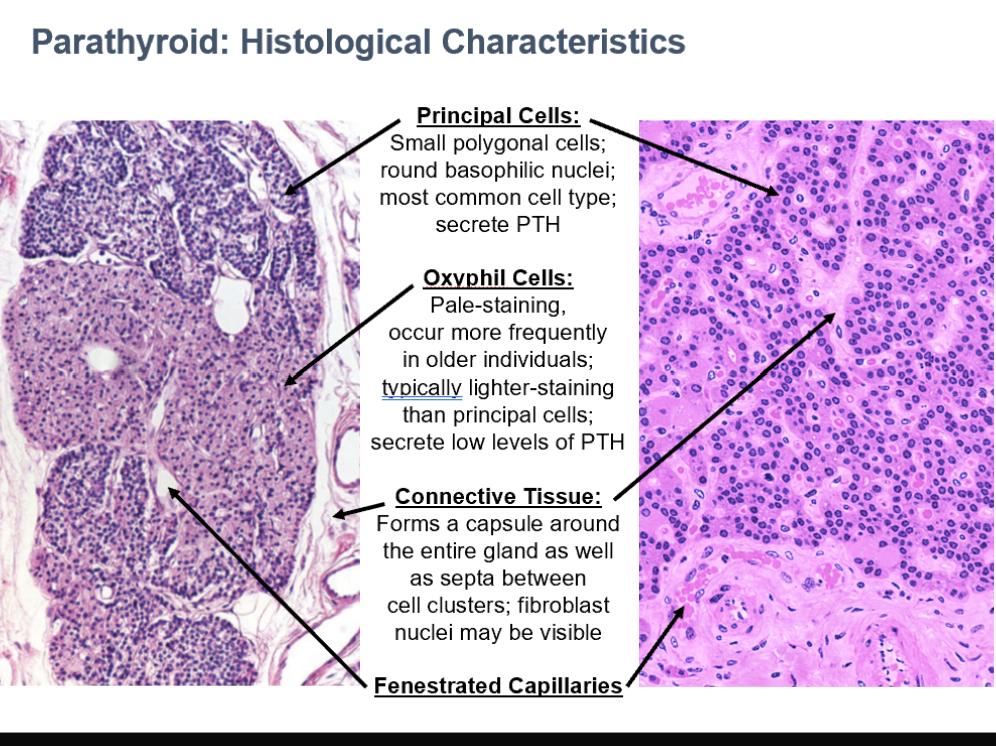
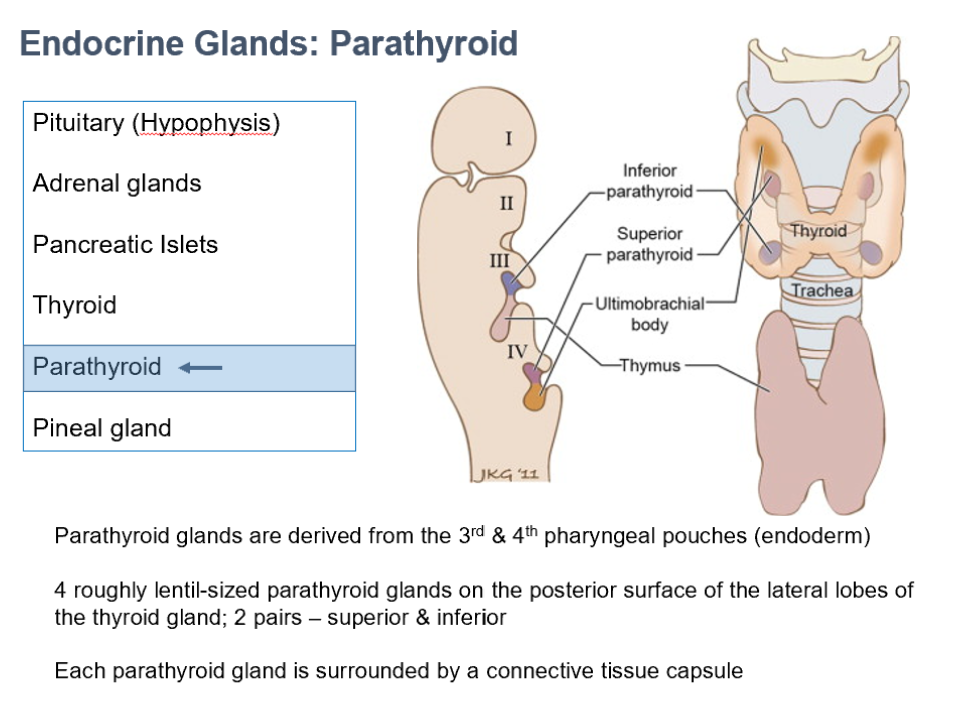
Parathyroid Glands
Originate from 3rd & 4th pharyngeal pouches (endoderm)
4 lentil-sized glands on posterior surface of lateral thyroid lobes (2 pairs, superior/inferior)
Each is surrounded by a CT capsule
Parathyroid Cell Types
Principal Cells
Oxyphil Cells
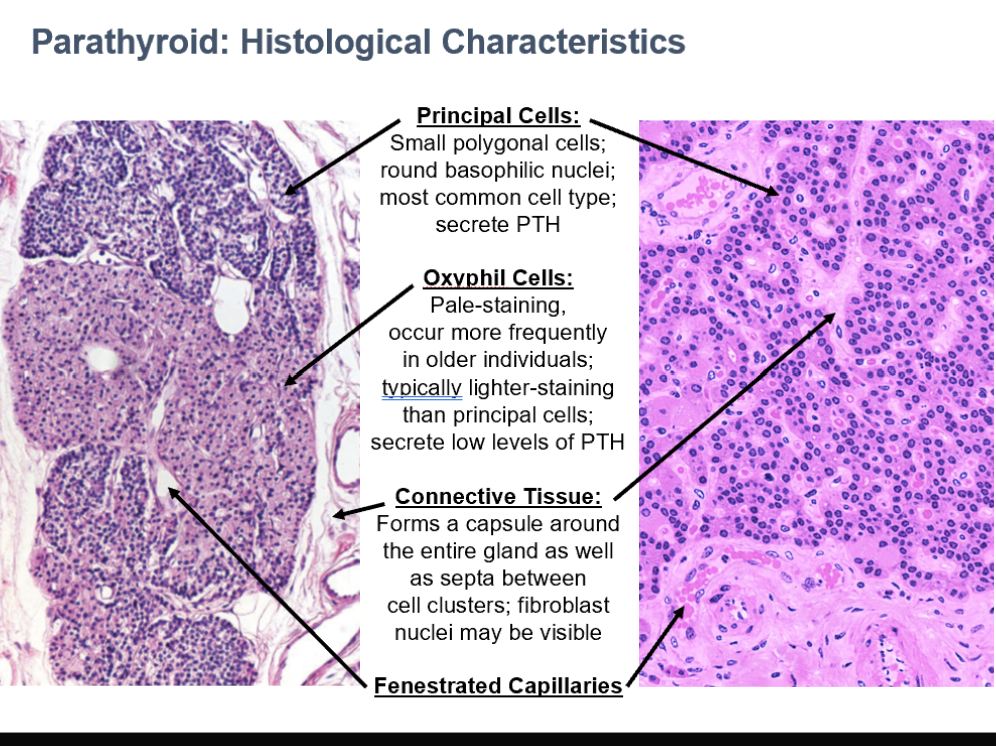
Principal Cells
Small polygonal cells
Round basophilic nuclei
Most common cell type
Secrete PTH
Parathyroid
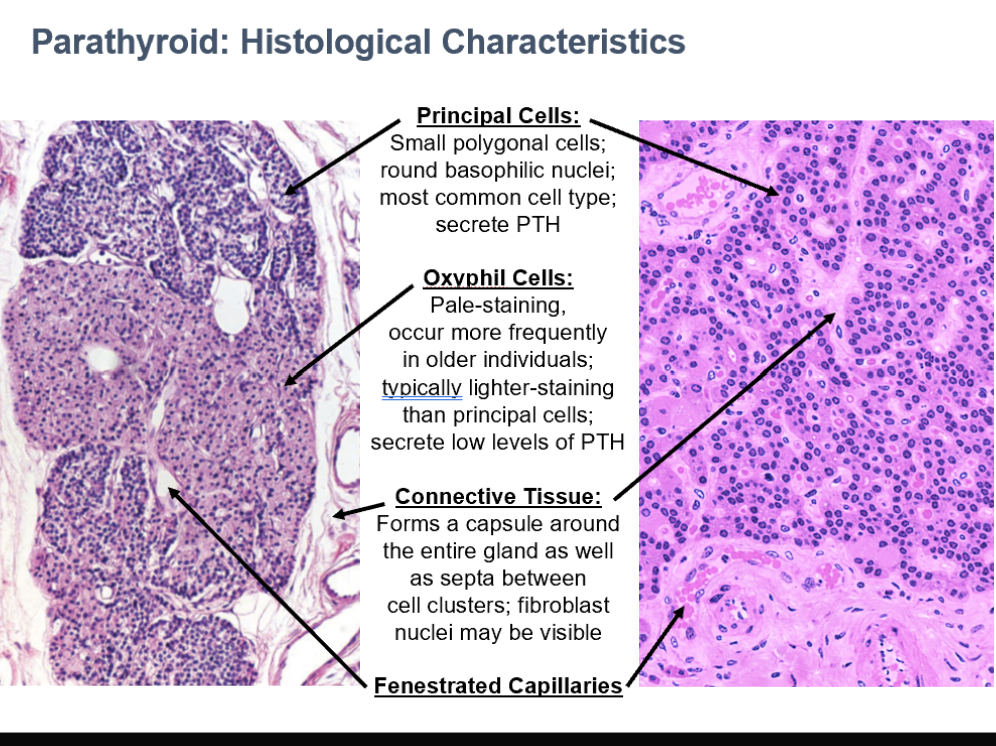
Oxyphil Cells
Pale-staining
occur more frequently in older individuals
typically lighter-staining than principal cells
secrete low levels of PTH
Parathyroid
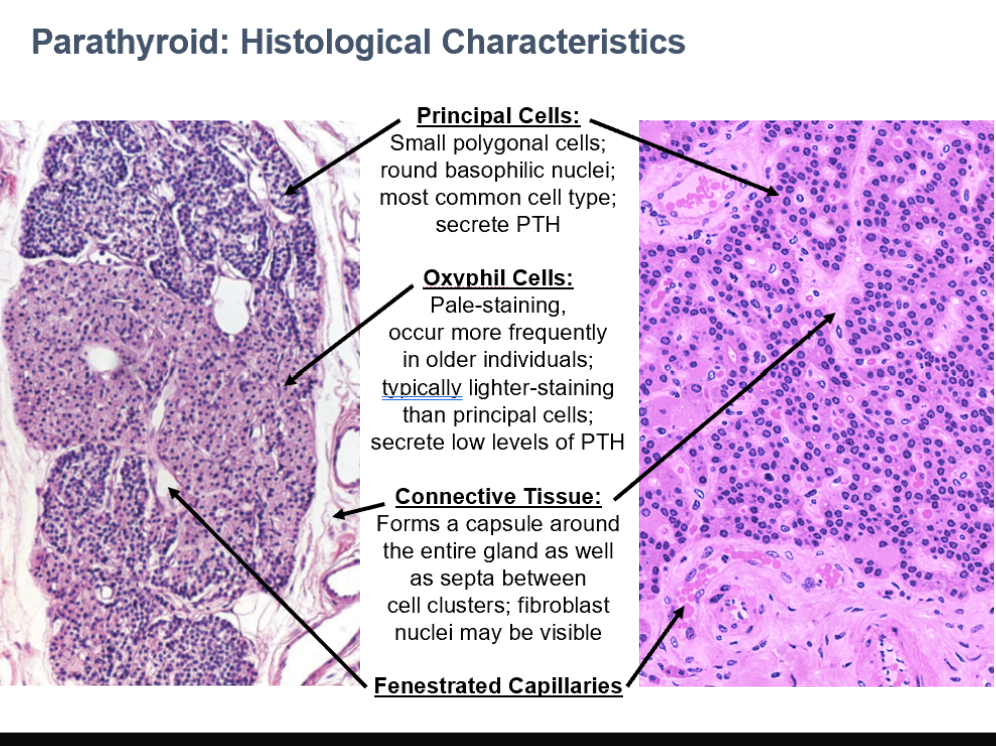
CT in Parathyroid
Forms a capsule around the entire gland as well as septa between cell clusters
fibroblast nuclei may be visible
Can see fenestrated capillaries in parathyroid histo too!