AP Human Geography Ultimate Study Set for the National Exam
1/770
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab, practice problems, and models all relating to the entire AP Human Geography course.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
771 Terms
agriculture
The deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain.

crop
Grain or fruit gathered from a field as a harvest during a particular season.

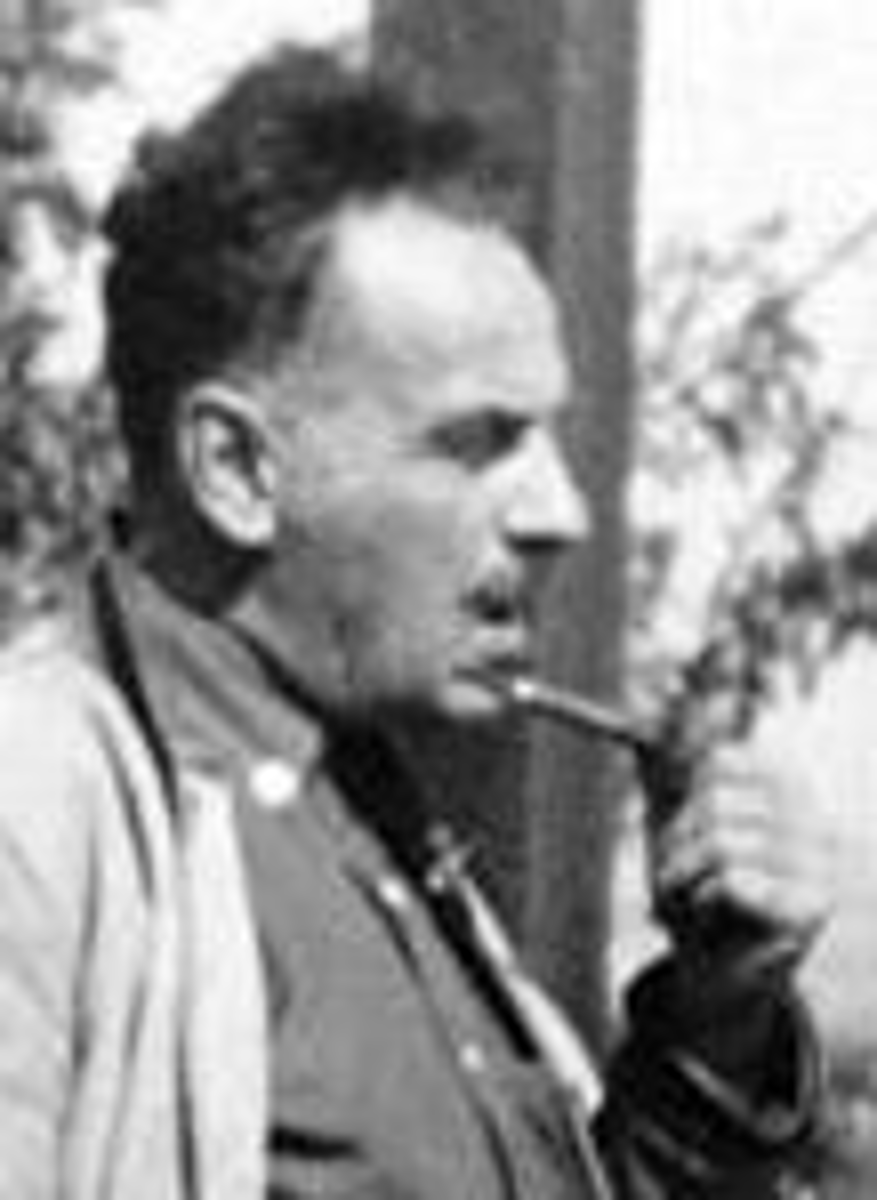
Carl Sauer
Conducted pioneering research on the origins and dispersal of plant and animal domestication. Suggested plants (taro, yam, banana, palm, etc.) in SE Asia were grown through vegetative planting. Was one of the first to propose that the process of domestication was independently invented at many different times and locations.

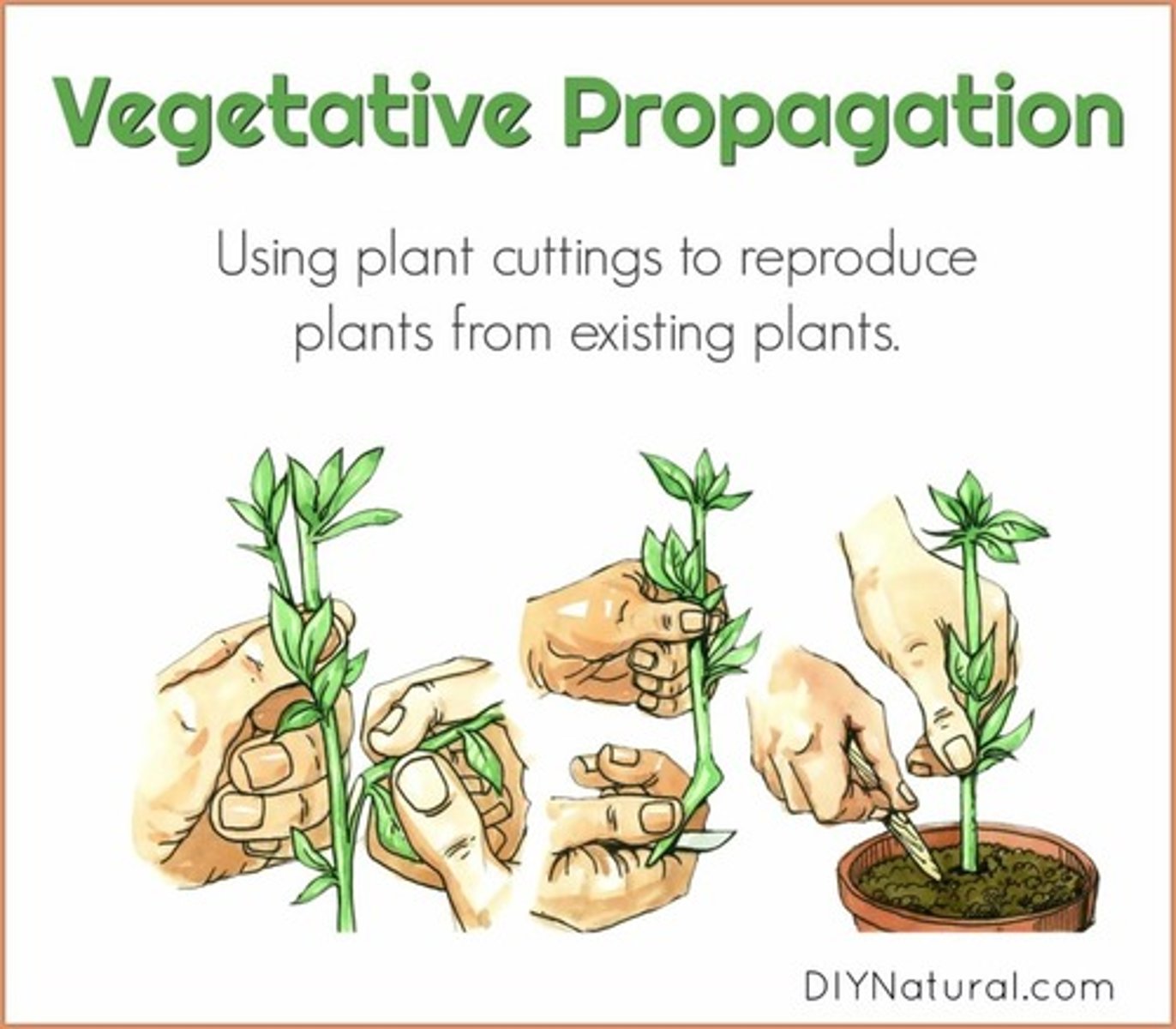
vegetative planting
earliest form of plant cultivation; reproduction of plants by direct cloning from existing plants, such as cutting stems and dividing roots
seed agriculture
the taking of seeds from existing plants and planting them to produce new plants

subsistence agriculture
Self-sufficient agriculture that is small scale and low in technology. The food produced is for personal consumption by the farmer and his/her family.

commercial agriculture
The goal of this type of agriculture is to sell the product(s) and make a profit as a business. It can describe large scale farming and ranching operations, large mechanized equipment, expensive technologies, factory-type labor.

prime agricultural land
A designation assigned by U.S. Department of Agriculture defining land that has the best combination of physical and chemical characteristics for producing food, feed, forage, fiber, and oilseed crops and is also available for these land uses.

agribusiness
The business sector encompassing farming and farming-related commercial activities. It includes activities ranging from seed production, farms, processing plants, fertilizer companies, distributors, advertisers, etc.

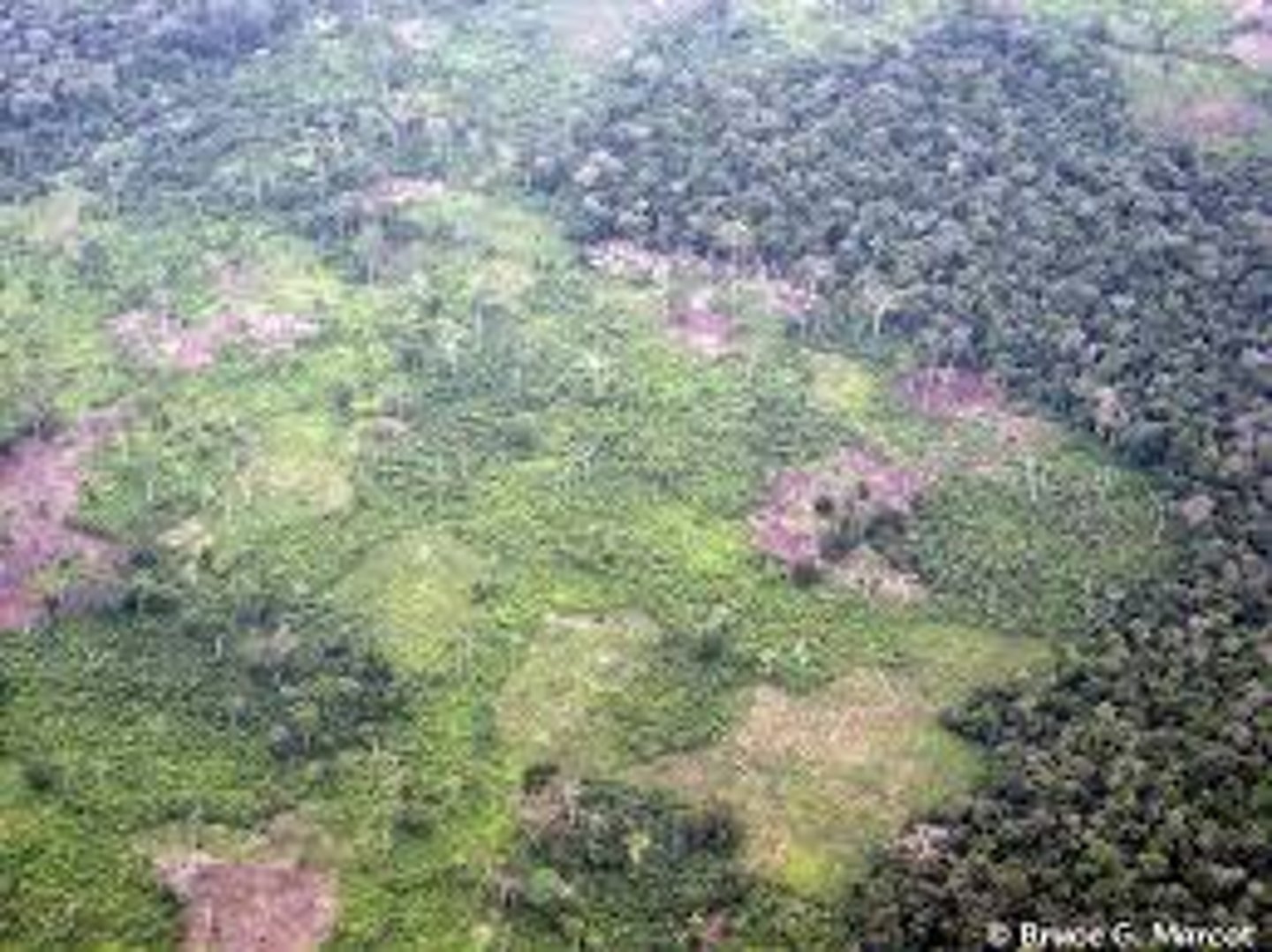
shifting cultivation
A form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift activity from one field to another; each field is used for crops for relatively few years and left fallow for a relatively long period.

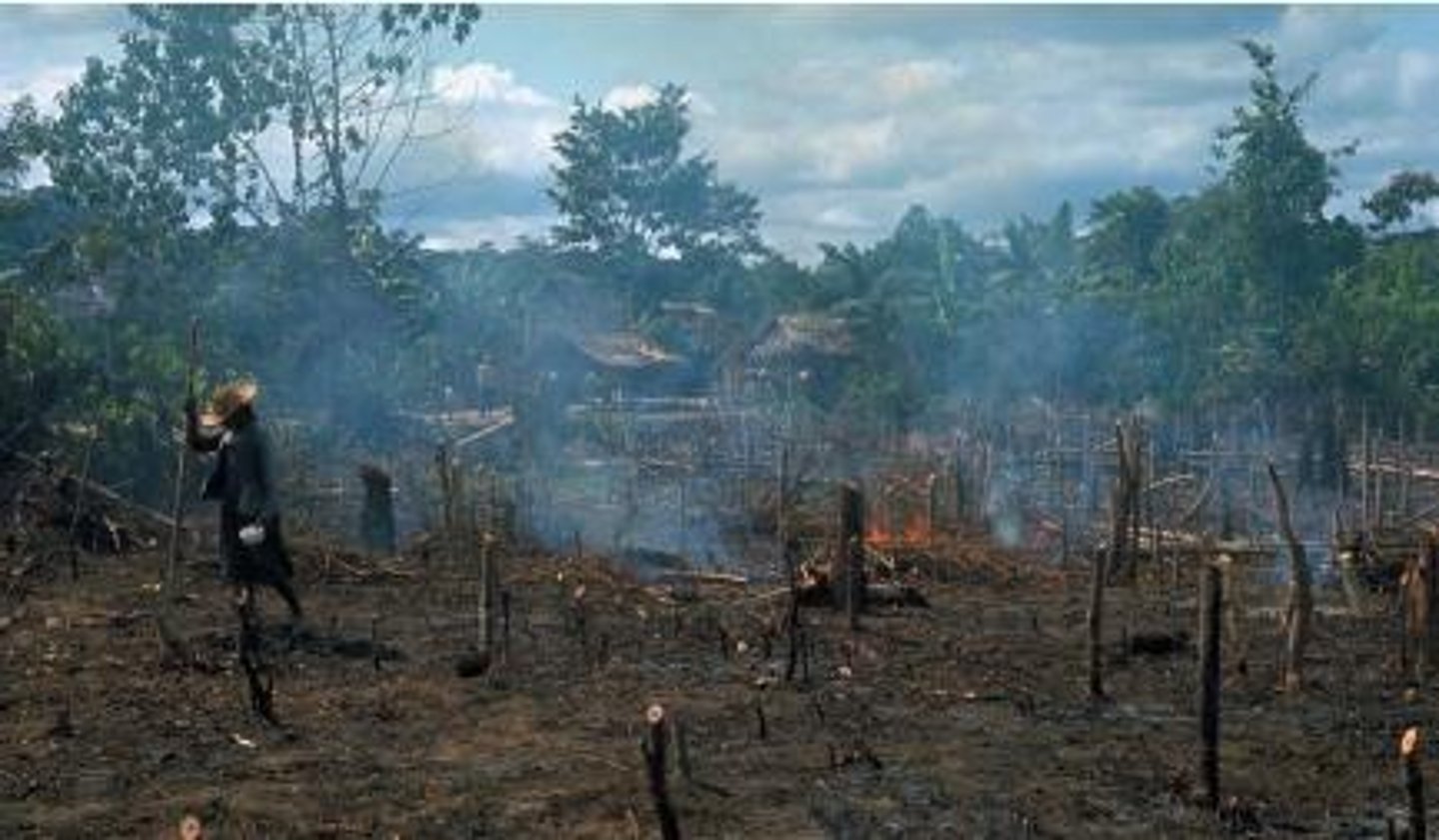
slash-and-burn
another name for shifting cultivation, so named because fields are cleared by slashing the vegetation and burning the debris

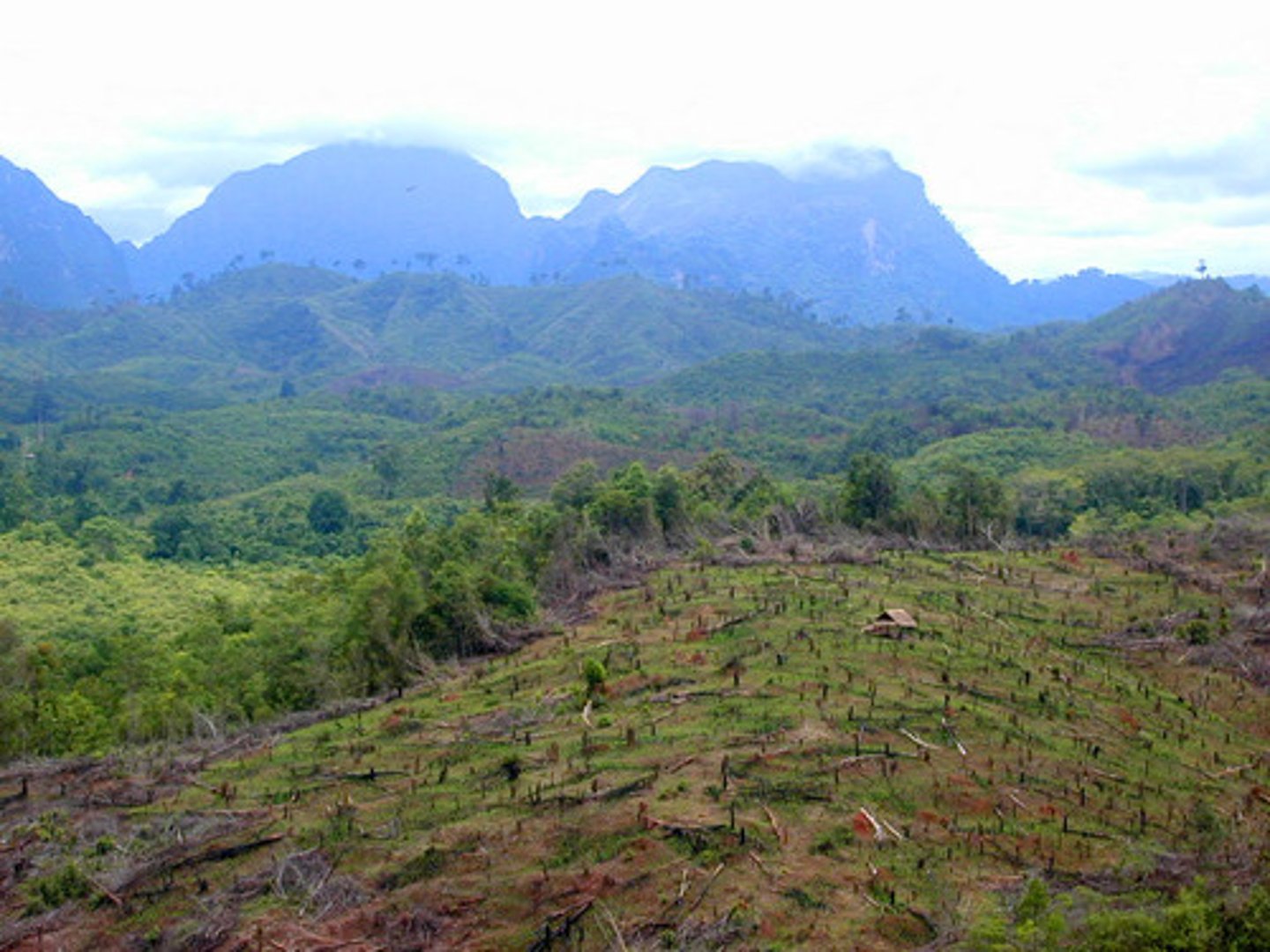
swidden
Land that is prepared for agriculture by using the slash-and-burn method.

pastoralism
A type of agricultural activity based on nomadic animal husbandry or the raising of livestock to provide food, clothing, and shelter.
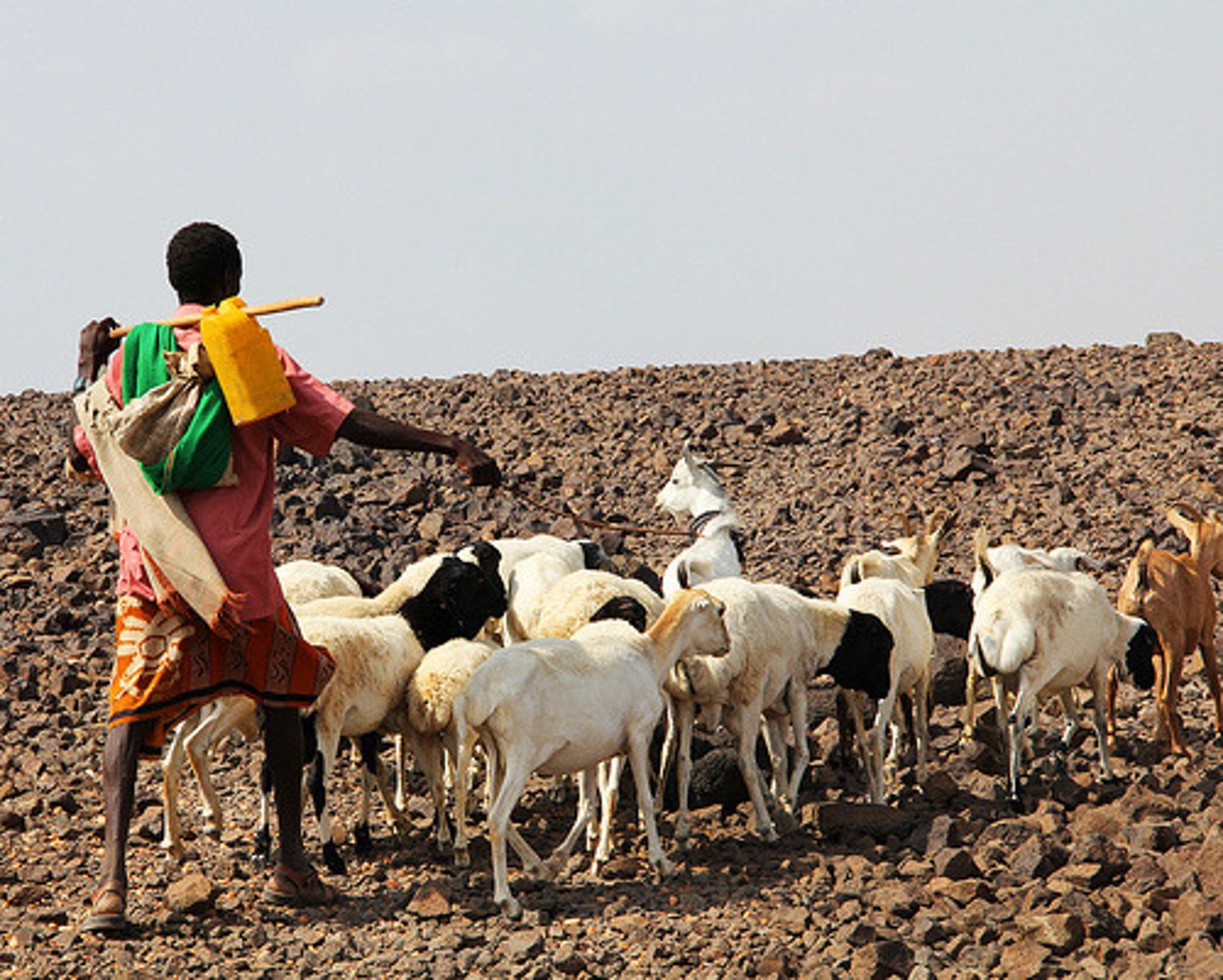

nomadism
A way of life in which groups of people continually migrate to find pastures and water for their animals, including cattle, goats, sheep, etc..
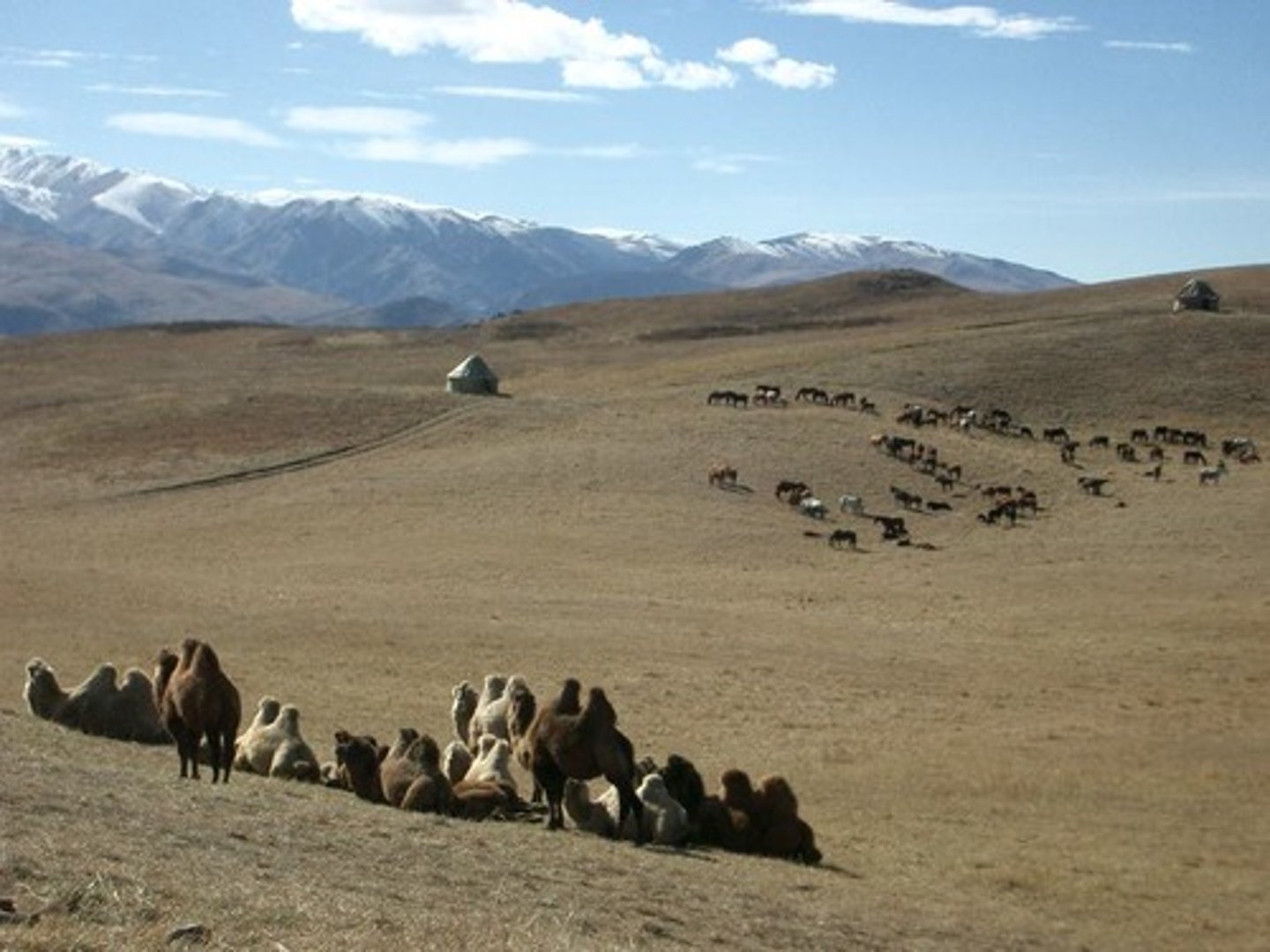

transhumance
The movements of livestock according to seasonal patterns, generally lowland areas in the winter, and highland areas in the summer.
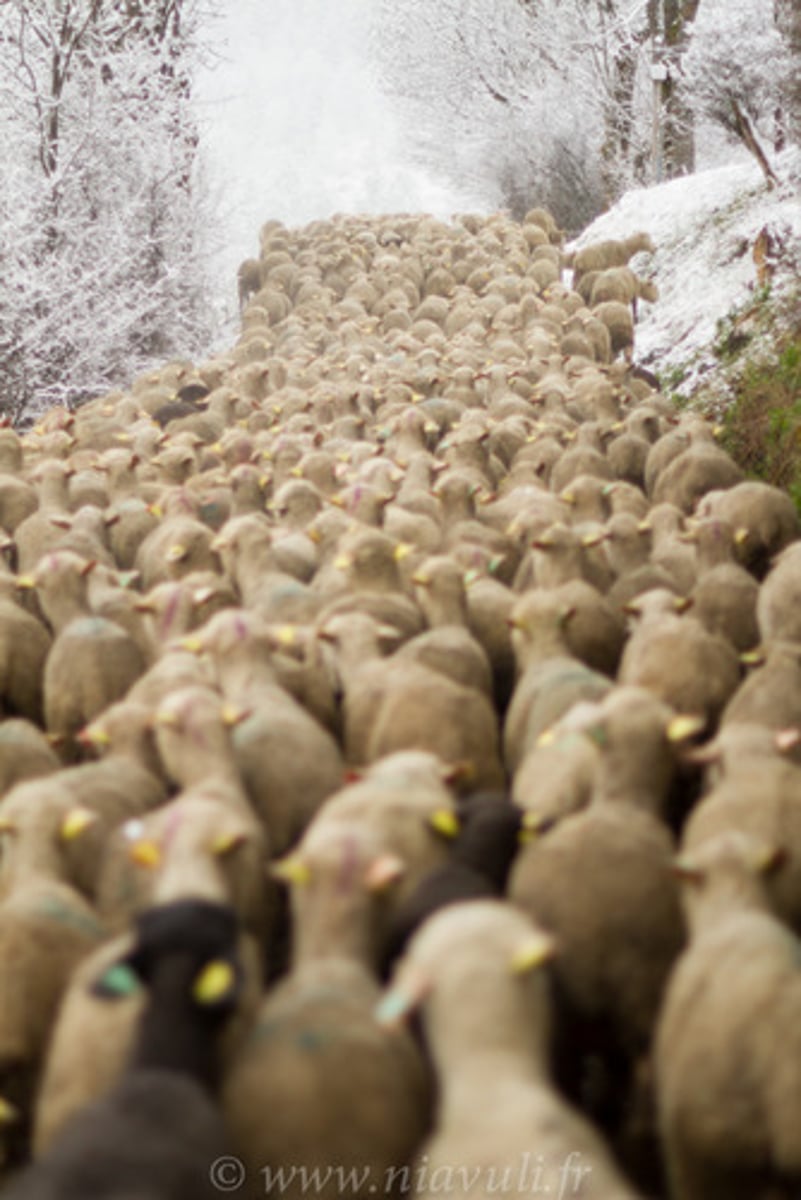

pasture
Grazing land for animals

intensive subsistence agriculture
form of subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a small parcel of land; practiced in densely populated areas such as East, South, and Southeast Asia

double cropping
growing more than one crop a year on the same land

crop rotation
the practice of alternating the crops grown on a piece of land each year in order to retain soil fertility and reduce soil erosion - for example, corn one year, legumes for two years, and then back to corn.
cereal grain
A grass yielding grain for food. ex. oats, wheat, rye, or barley

milkshed
The ring surrounding a city from which milk can be supplied without spoiling.

grain
the seeds of plants (such as wheat, corn, and rice) that are used for food

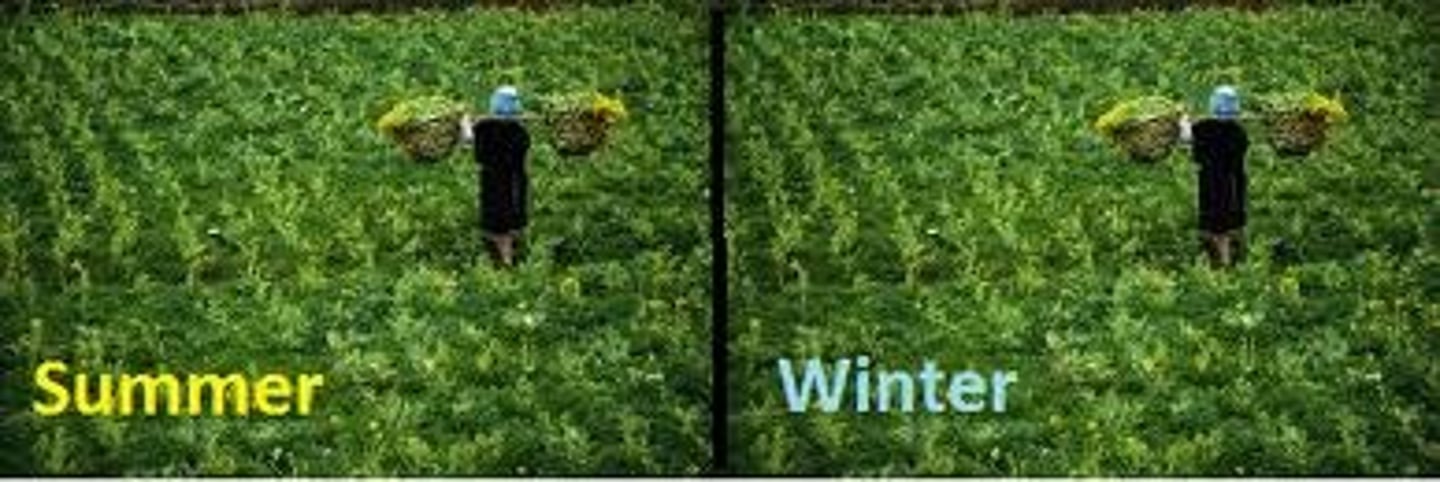
winter wheat
wheat planted in the fall and harvested in the early summer

spring wheat
Wheat planted in the spring and harvested in the late summer.

ranching
commercial grazing of livestock over an extensive area

range wars
Typically fought over water rights or grazing rights to unfenced/unowned land. It could pit competing farmers or ranchers against each other

horticulture
The growing of fruits, vegetables, and flowers.

truck farming
Commercial gardening and fruit farming--larger scale and tends to be monocropping. So named because truck was a Middle English word meaning bartering or the exchange of commodities.
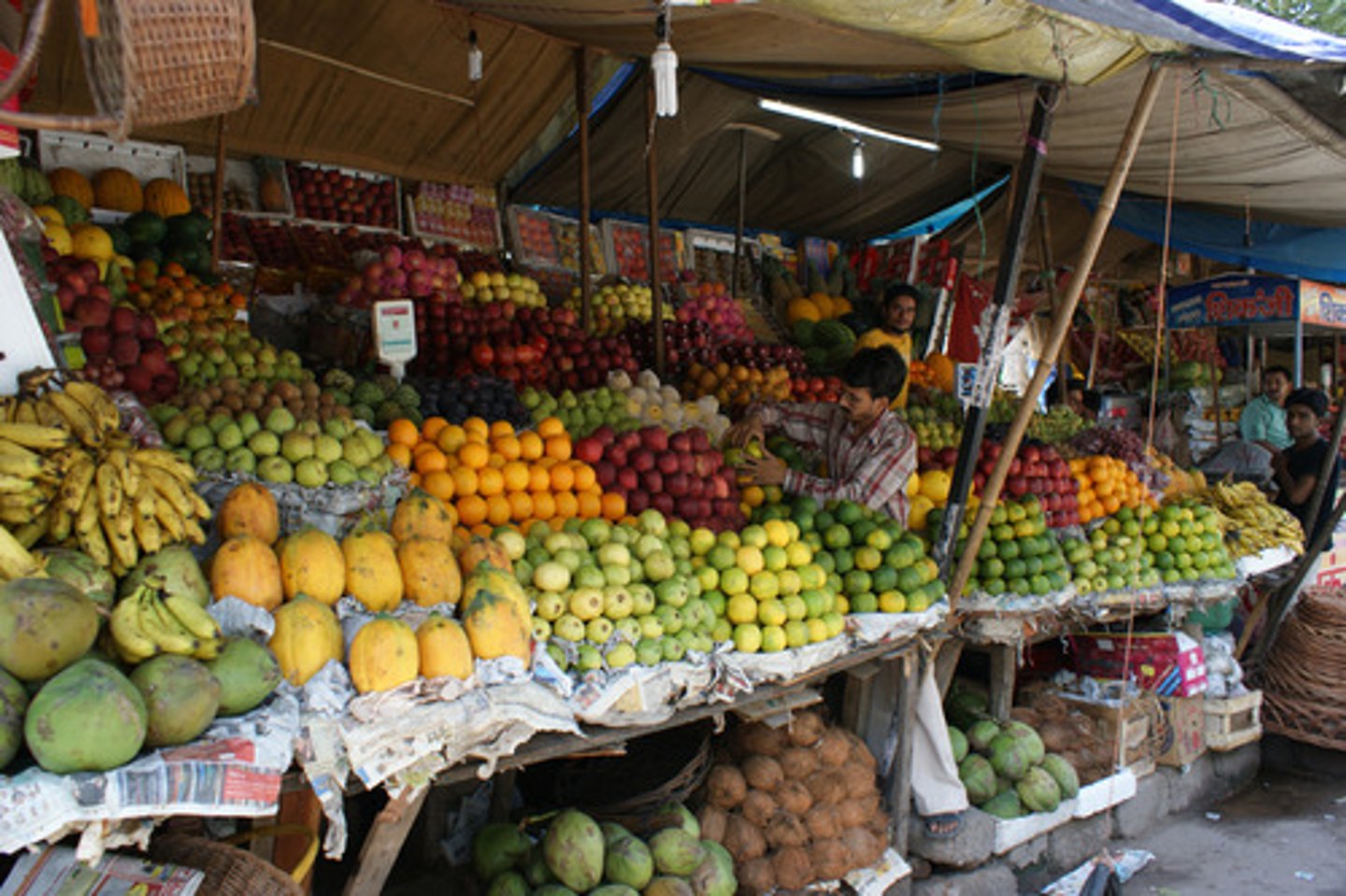

market gardening
The small scale production of fruits, vegetables, and flowers as cash crops sold directly to local consumers. Distinguishable by the large diversity of crops grown on a small area of land, during a single growing season. Labor is done manually.

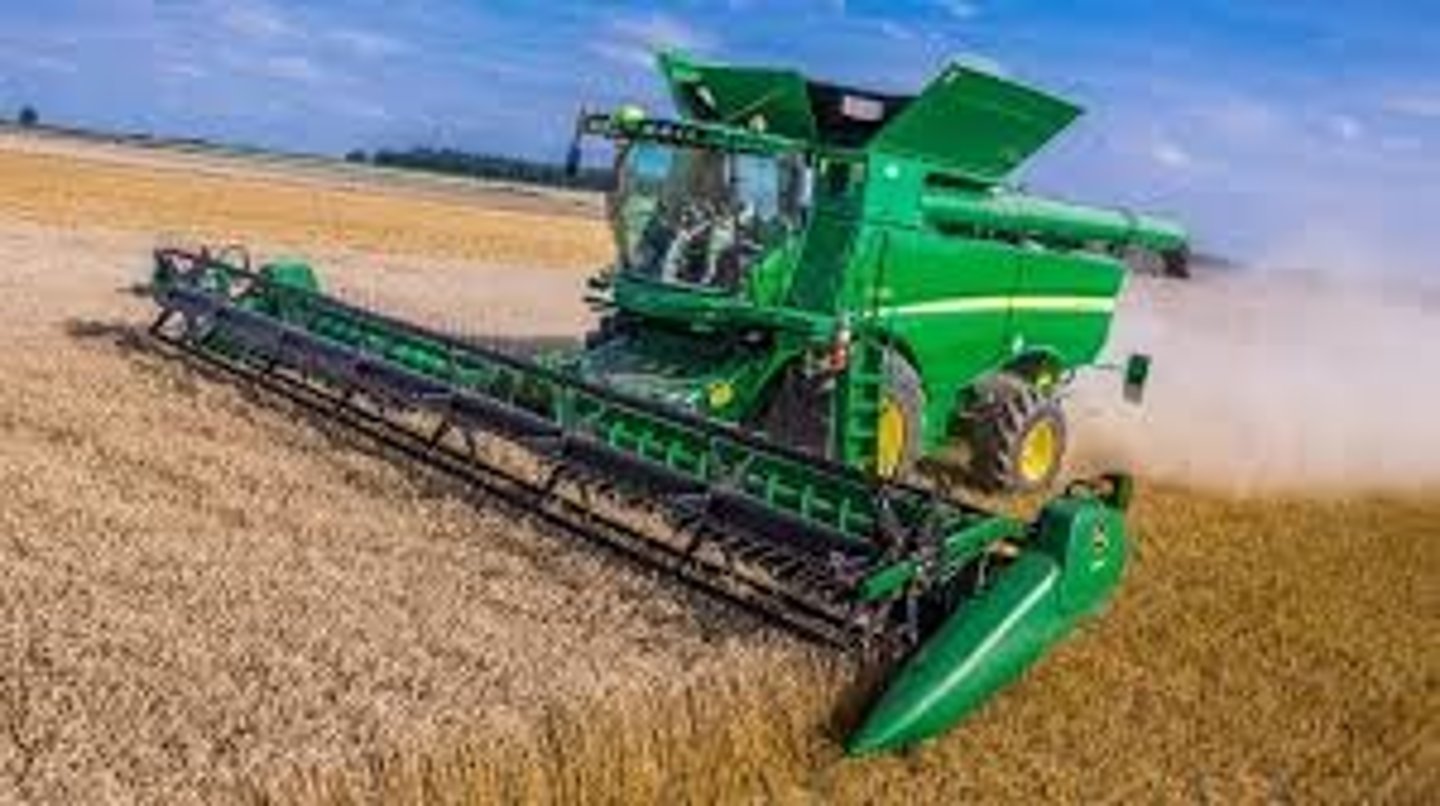
McCormick reaper
Mechanized the harvest of grains such as wheat, allowing farmers to cultivate larger plots. Started commercial agriculture in the Midwest.

combine machine
A machine that reaps, threshes, and cleans grain while moving over a field.

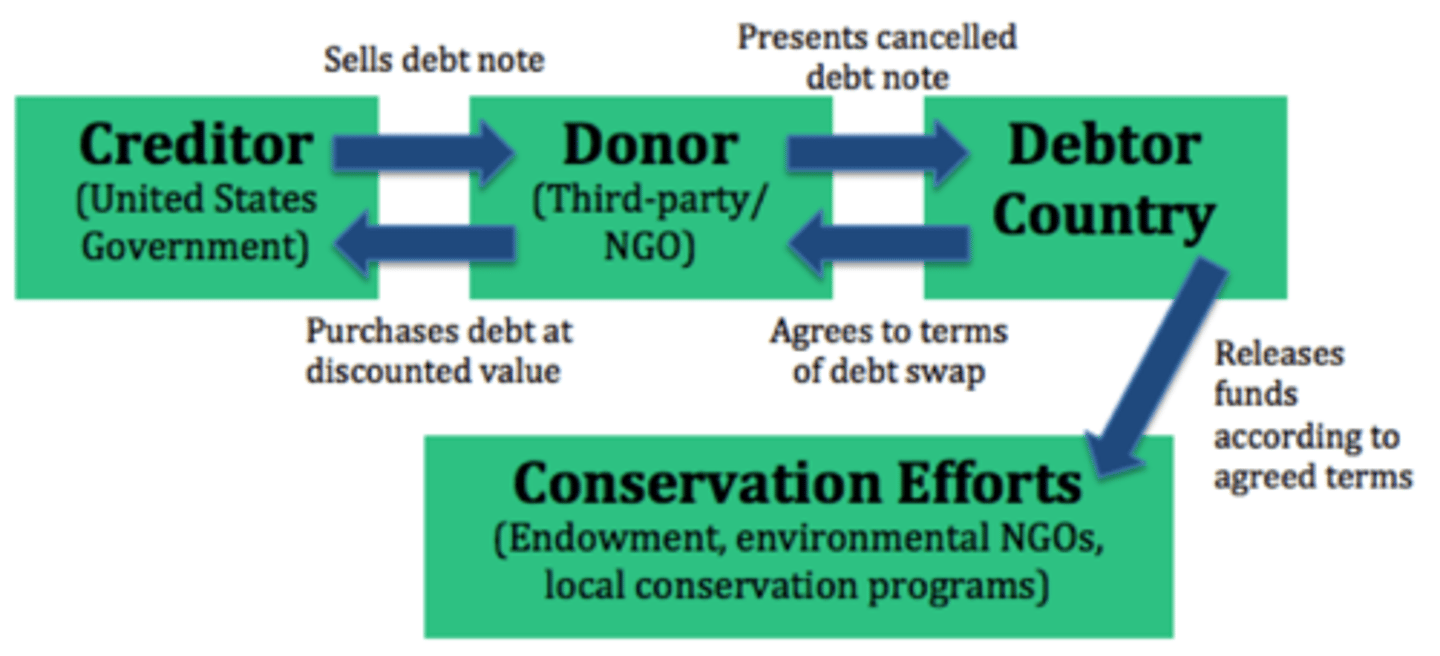
debt for nature swap
when agencies such as the World Bank make a deal with developing countries that they will cancel their debt if the country will set aside a certain amount of their natural resources for conservation
Aquaculture
The cultivation or farming (in controlled conditions) of aquatic species, such as fish or shrimp, raised in ponds and underwater cages. This contrasts with commercial fishing, which involves catching wild fish.

collective farm
a farm or group of farms run by the government, as in a communist state

pesticide
A chemical intended to kill insects and other organisms that damage crops.

herbicide
A substance used to destroy plants, especially weeds

soil erosion
Movement of soil components, especially topsoil, from one place to another, usually by wind, flowing water, or both. This natural process can be greatly accelerated by human activities that remove vegetation from soil.

growing season
The average number of days between the last frost of spring and the first frost of fall, the season during which a crop grows best. Varies from region to region.
extractive industry
Industries involved in the activities of prospecting, exploring, developing, and producing for non-regenerative natural resources from the Earth

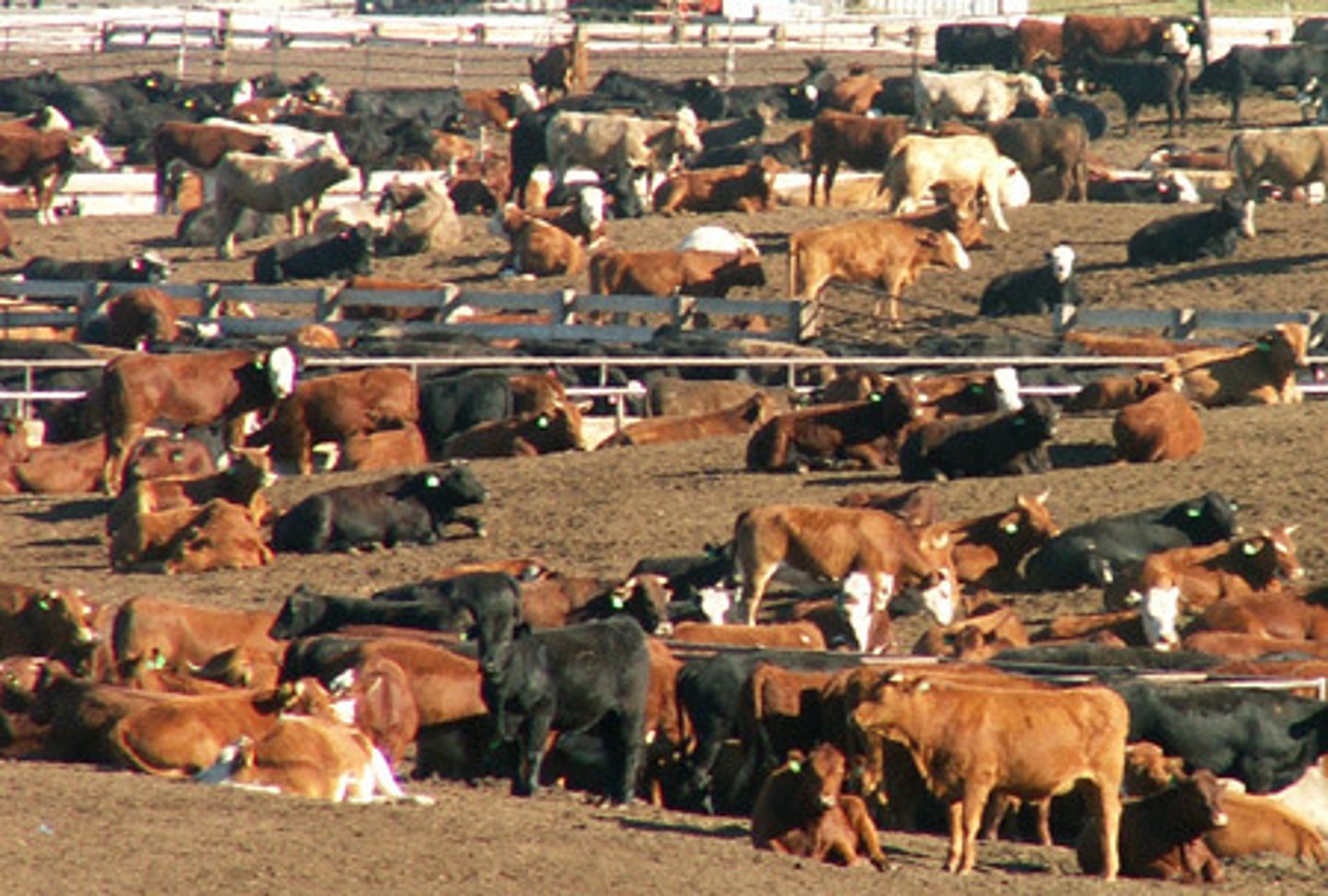
feedlot
a plot of land on which livestock are fattened for market

staple grains
basic dietary items, such as wheat, rice, or corn. harvested and stored to be eaten all year

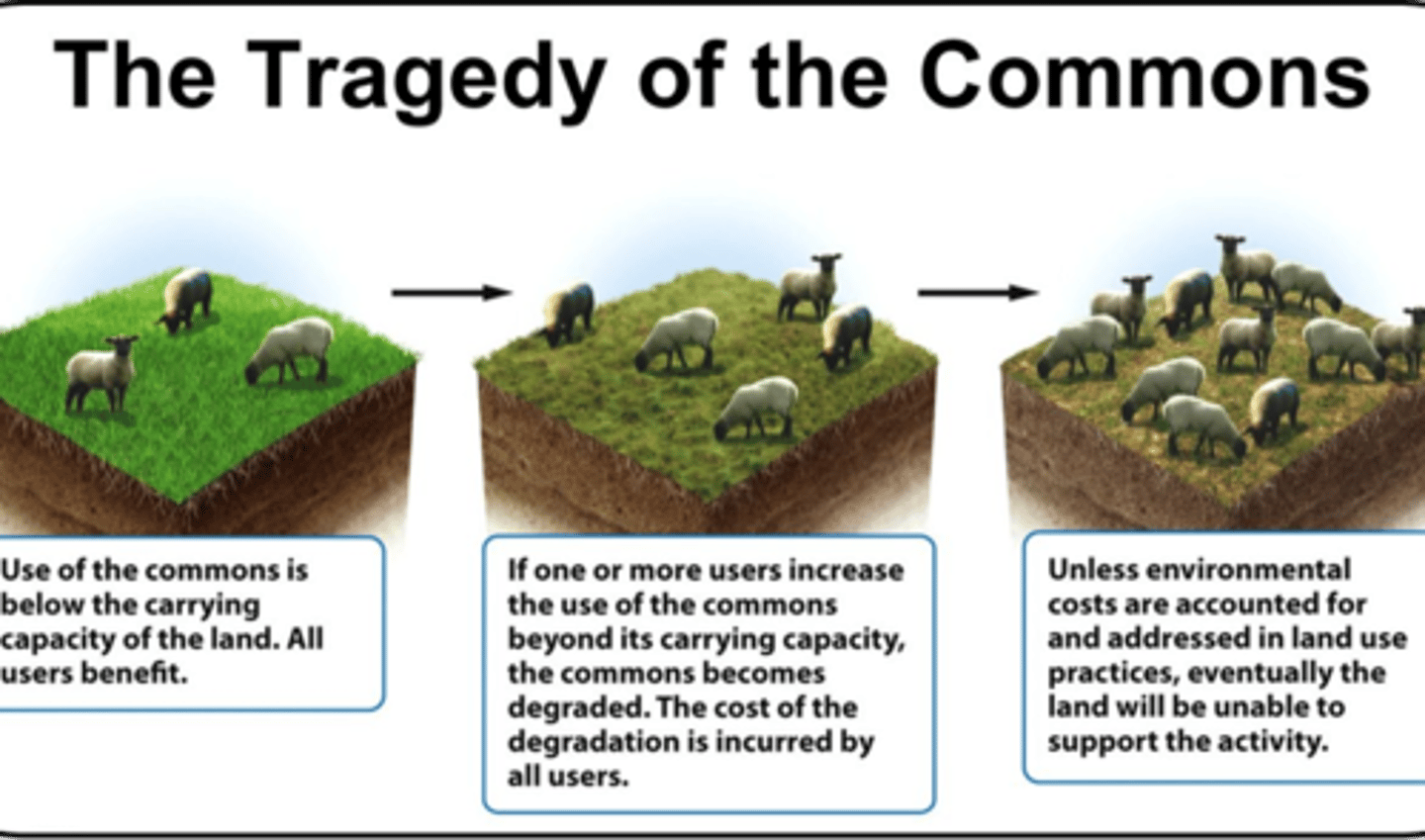
tragedy of the commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community
plantation
A large farm in tropical and subtropical climates that specializes in the production of one or two crops for sale, usually to a more developed country.

Ester Boserup
said population density creates more agricultural output and humans will figure out ways of producing more food on the same amount of land rather than starve to death (non-Malthusian)

cash cropping/export crops
the raising of crops for market sale rather than domestic consumption
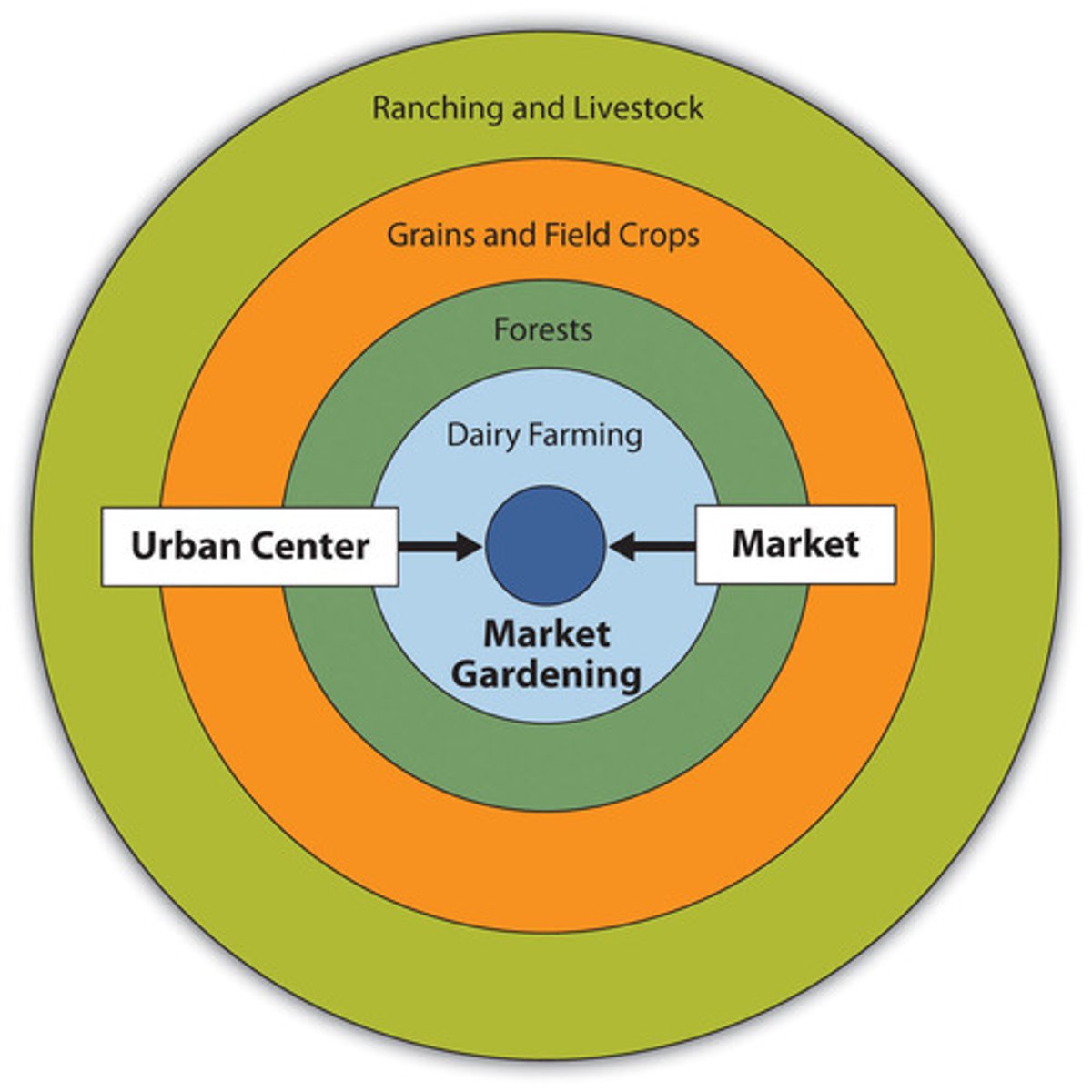
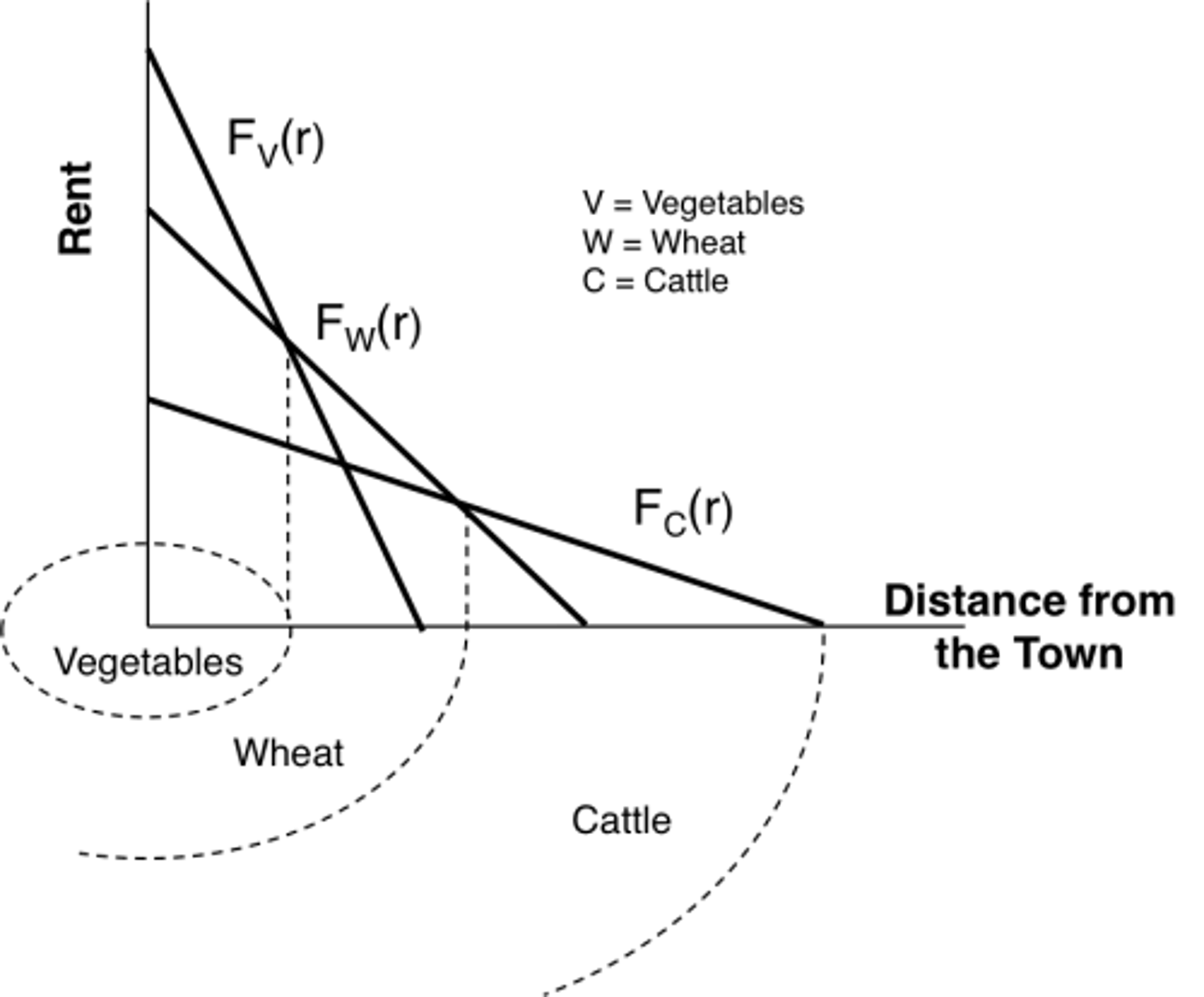
Von Thunen's model
Predicts the land-use patterns in relation to the land and transportation cost.
Similar to bid rent theory
Neolithic (First Agricultural) Revolution
(10,000 - 8,000 BCE) The development of agriculture and the domestication of plants and animals as a food source. This led to the development of permanent settlements and the start of civilization.
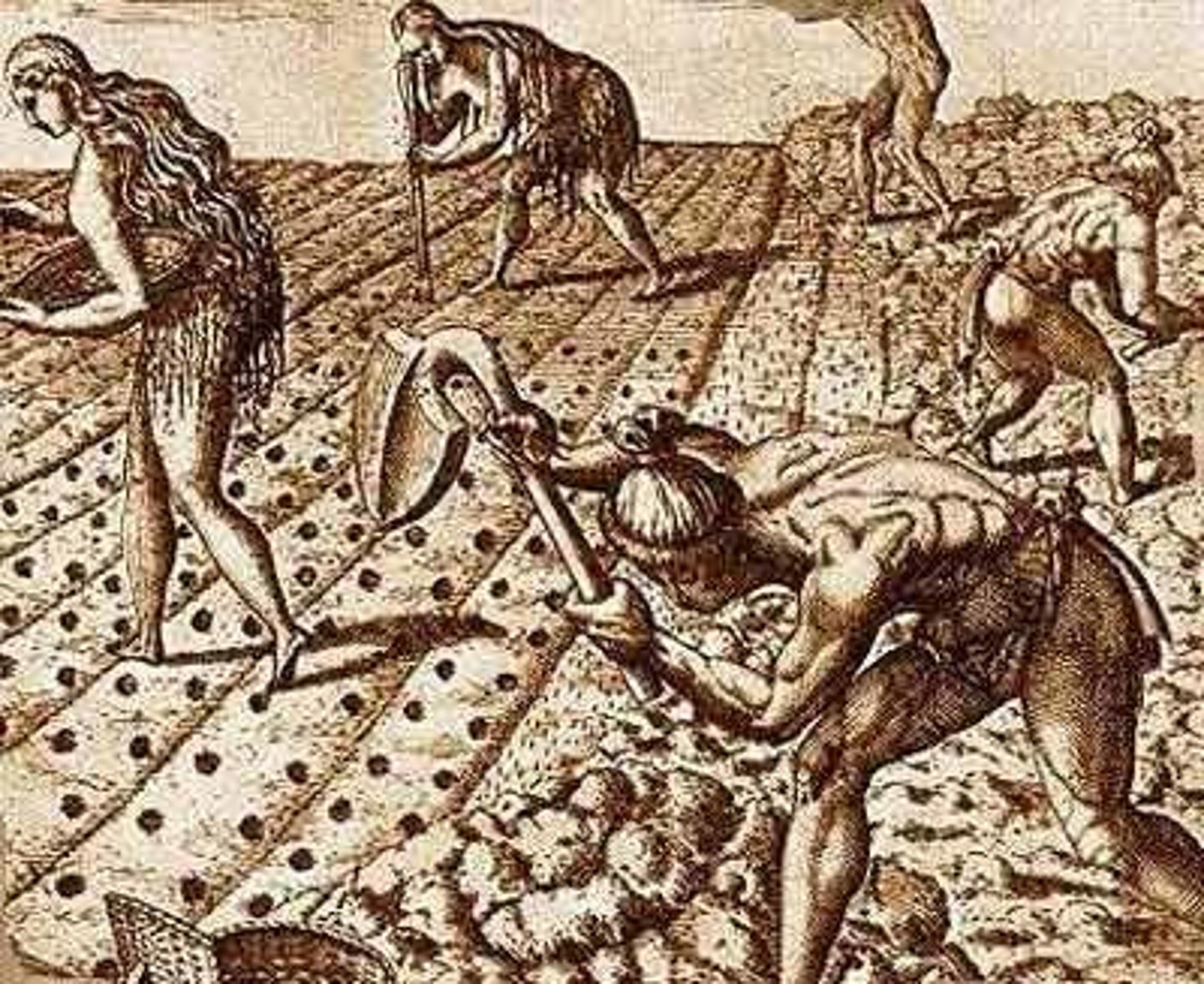

Second Agricultural Revolution
Increased land and labor productivity starting in about the 1700s. Involved crop rotation, increased use of fertilizers, reclamation of land, and new tools/machines. Improved methods of cultivation, harvesting, and storage of farm produce. Leads to increased food production, reduction in need for rural workers.

Green Revolution aka Third Agricultural Revolution
The worldwide campaign to increase agricultural production from the 1940s to 60s, stimulated by new synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, hybridization, irrigation techniques and genetically modified foods. Spawned in part by Norman Borlaug and his research in Mexico of new strains of wheat. The movement saved millions, especially in the developing countries, from starvation.

plant domestication
deliberate tending of crops to gain certain desired attributes; began around 12,000 years ago along several fertile river valleys and cultural hearths; growing plants on purpose

animal domestication
The process of taming an animal species to be accustomed to humans and human contact
the taming of animals through generations of breeding to live in close association with humans as a pet or work animal

luxury crops
Non-subsistence crops such as tea, cacao, coffee, and tobacco. Consumed for reasons other than nutrition.

dairying
An agricultural activity involving the raising of livestock, most commonly cows and goats, for dairy products such as milk, cheese, and butter.

mediterranean agriculture
An agricultural system practiced in the Mediterranean style climates of Western Europe, California, and portions of Chile and Australia, in which diverse specialty crops such as grapes, avocados, olives, and a host of nuts, fruits, and vegetables comprise profitable agricultural operations.

organic agriculture
approach to farming and ranching that avoids the use of herbicides, pesticides, growth hormones, and other similar synthetic inputs

biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.

intertillage
the practice of mixing different seeds and seedlings in the same field

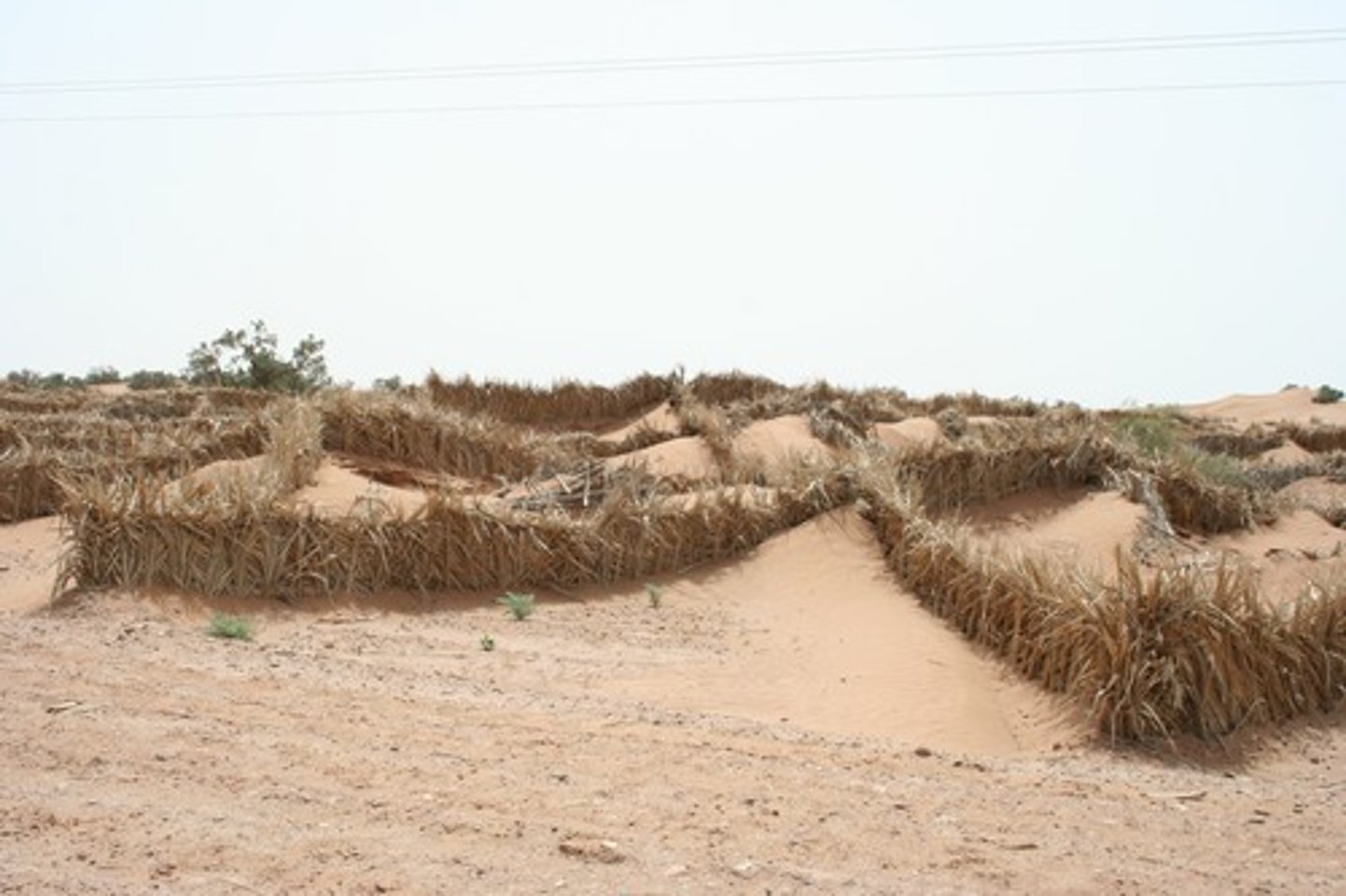
desertification
Degradation of fertile land into desert, especially in semiarid areas, due to drought and human actions like excessive crop planting, overgrazing of animals, and deforestation.

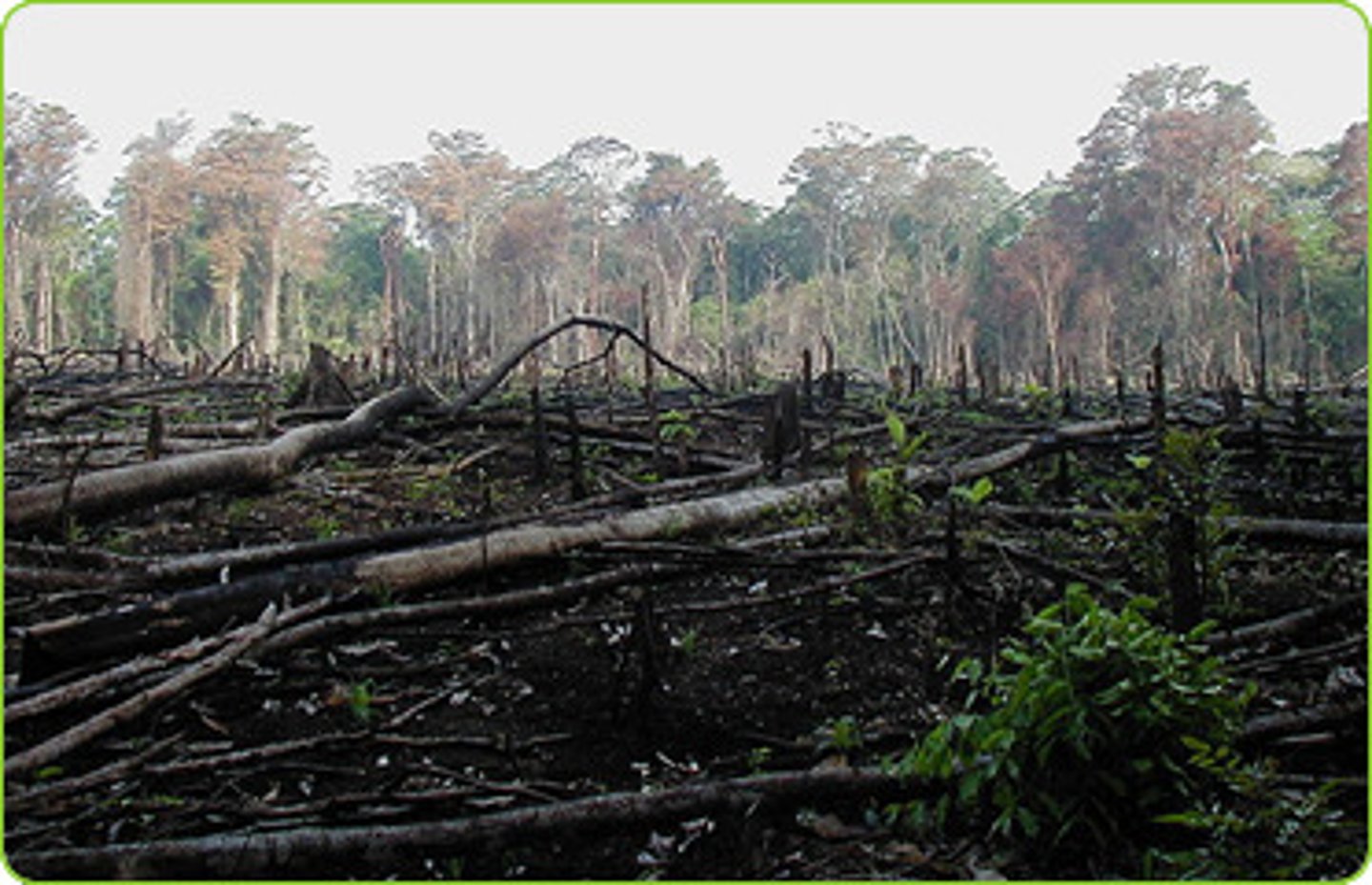
deforestation
clearing of forests for agriculture, lumber, or other uses

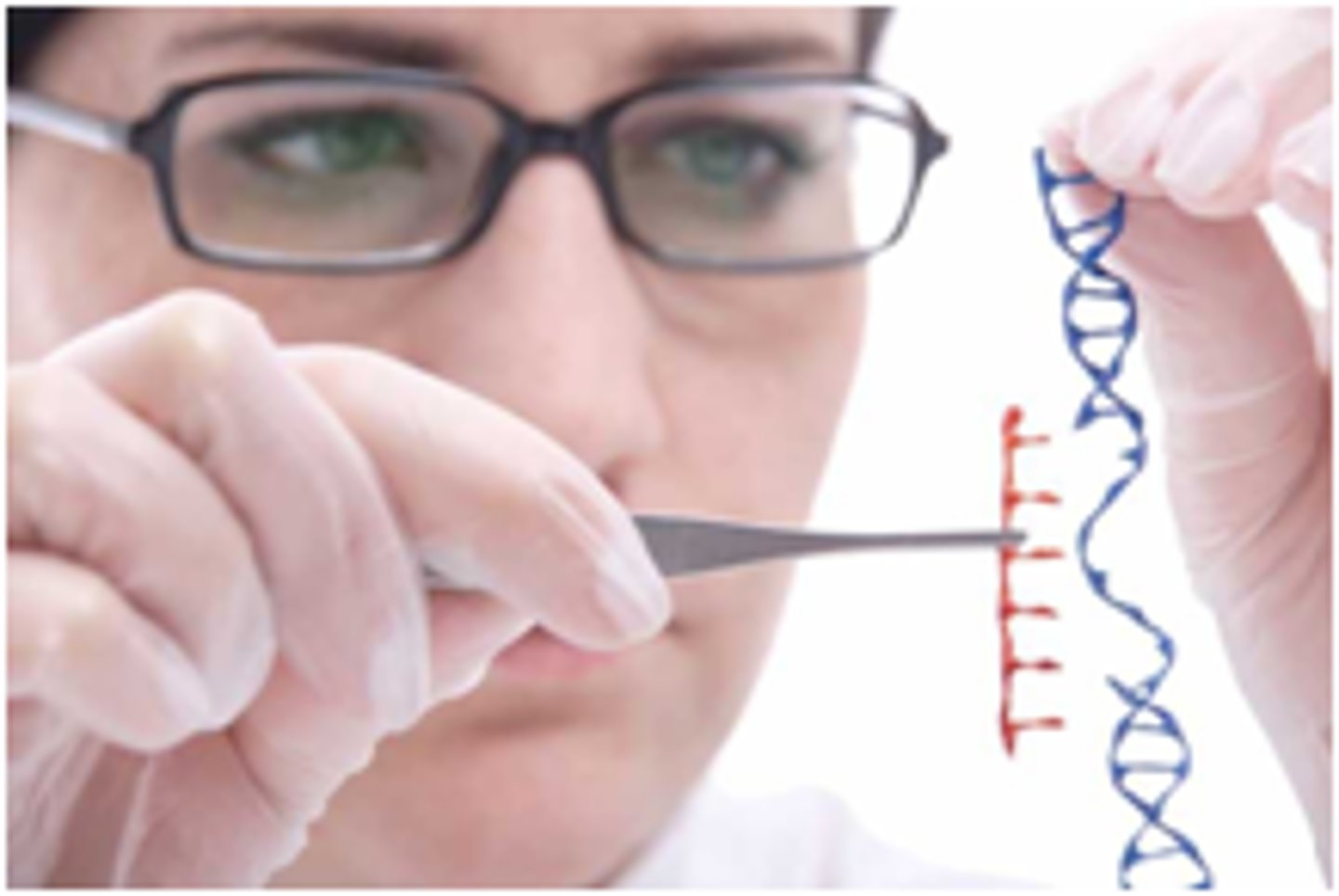
genetic modification
Branch of biotechnology that alters the genes in biological organisms to achieve a medicinal or agricultural purpose

sustainable yield
An amount of a renewable resource such as trees that can be harvested regularly without reducing the future supply

clustered rural settlements
a rural settlement in which the houses and farm buildings of each family are situated close to each other and fields surround the settlement

dispersed rural settlement
Where farmers live on individual farms isolated from neighbors rather than alongside other farmers in settlements.

linear rural settlement
Settlement clustered along a road, river, or dike to facilitate communications and transportation.
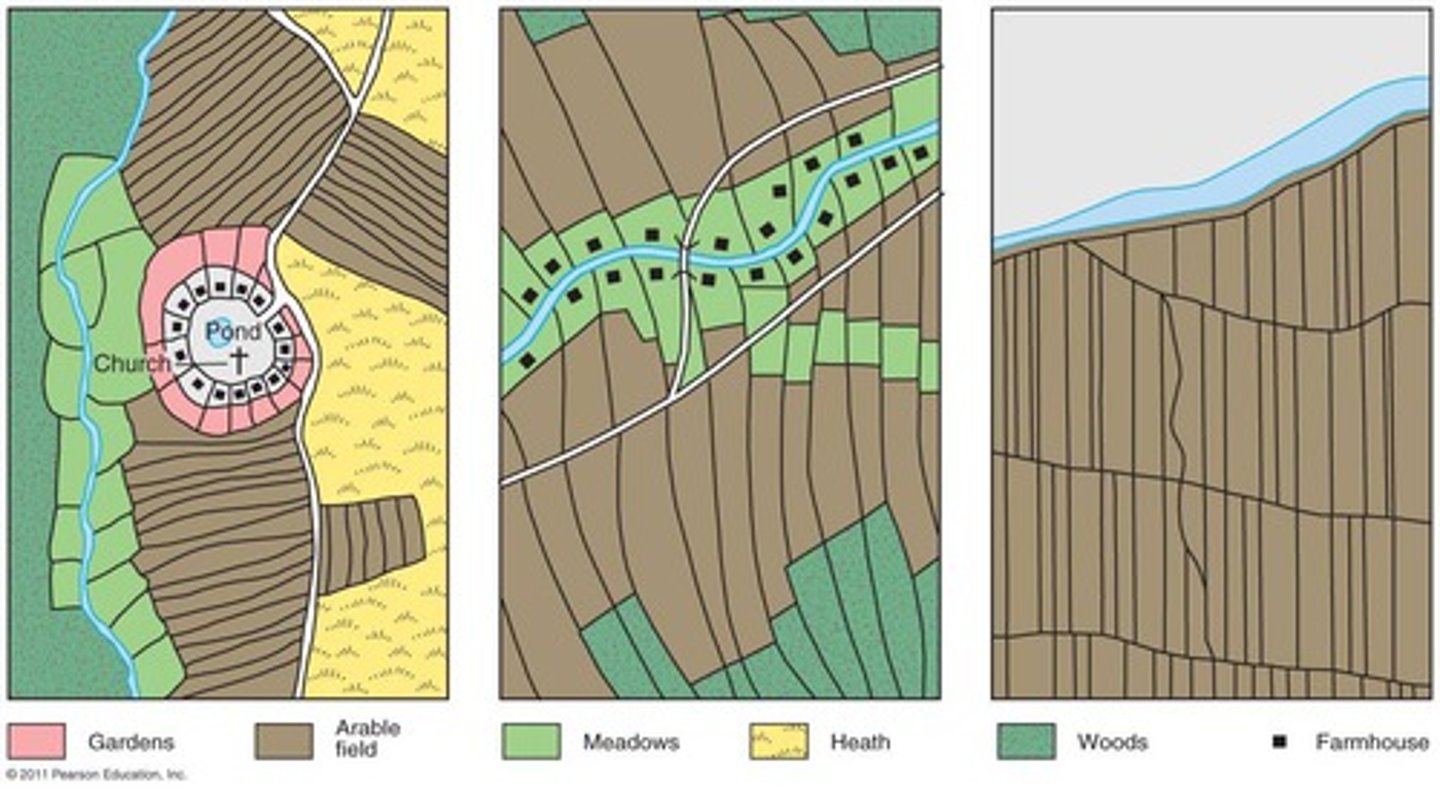
enclosure movement
The process by which British landlords consolidated or fenced in common lands to increase the production of cash crops. The Enclosure Acts led to an increase in the size of farms held by large landowners.

fallow
inactive, plowed but not sowed

extensive subsistence farming
consists of any agricultural economy in which the crops and/or animals are used nearly exclusively for local or family consumption on large areas of land and minimal labor input per acre

capital-intensive farms
Farm that makes heavy use of machinery in the farming process.
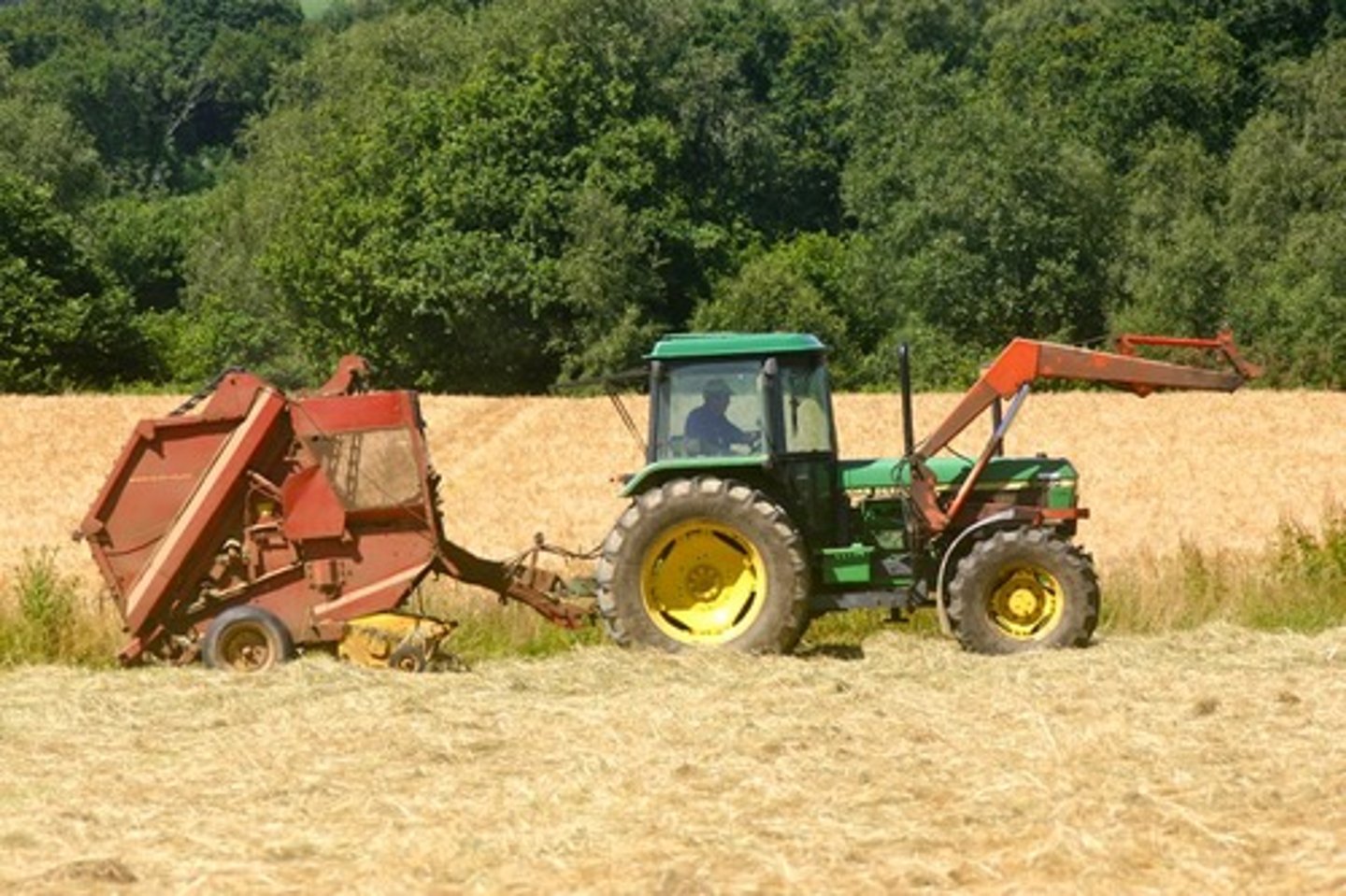

labor intensive farms
Where most of the work is done by humans, ie plantations

large scale grain production
Extensive commercial grain farm where grain is grown to be exported elsewhere for consumption

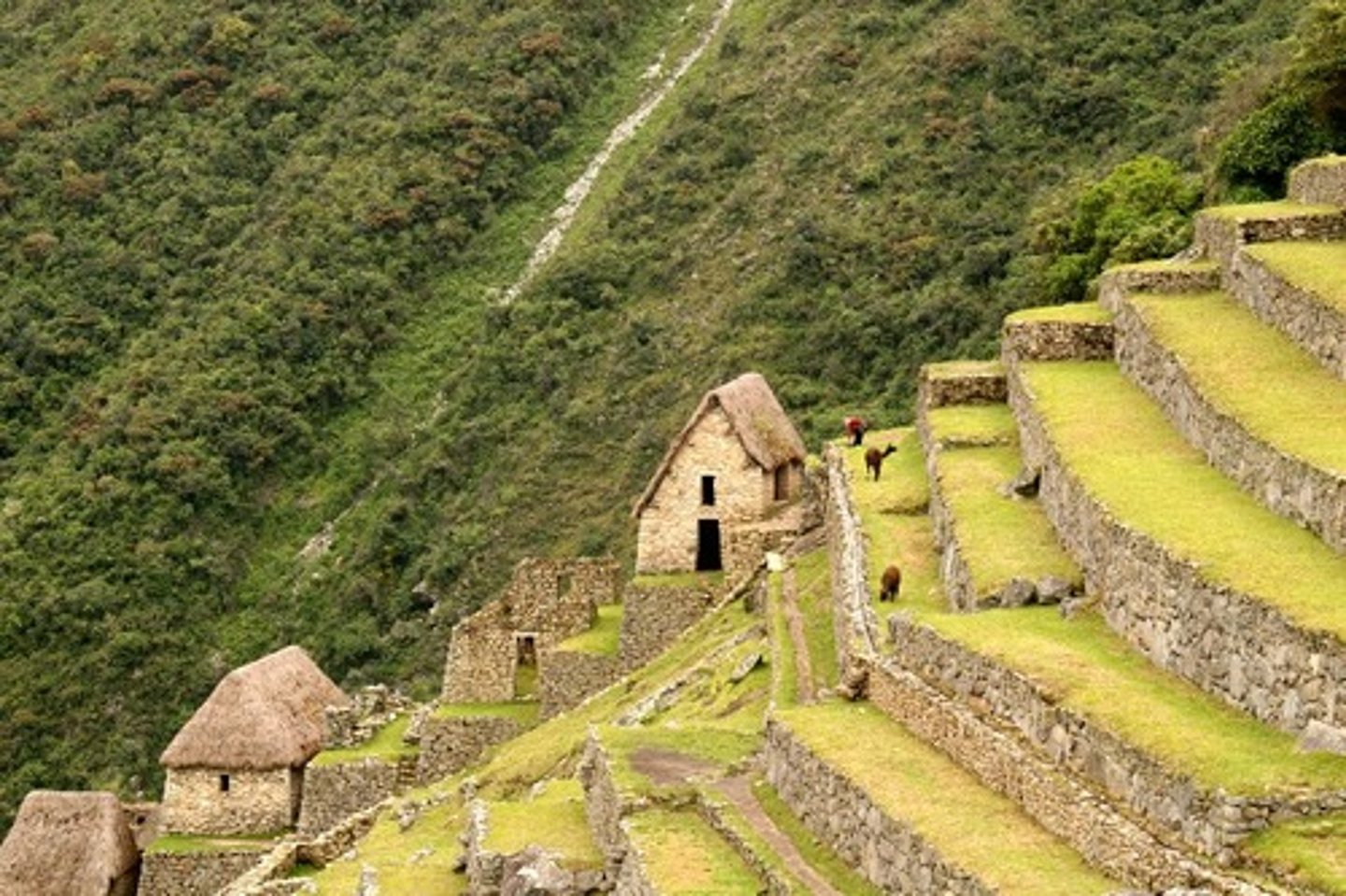
terracing
creating flat platforms in the hillside that provide a level planting surface, which reduces soil runoff from the slope and increases available land

monoculture/monocropping
The production of a single crop for commercial markets (corn, wheat, rice, etc.)

suitcase farm
A farm in which no one lives on the farm and the harvesting and planting is performed by farmers who live nearby or by migratory labor. These are common in the Midwest and Great Plains in the United States.
commodity chain/global supply chain
a linked system of processes that gather resources, convert them into goods, package them for distribution, disperse them, and sell them on the market;a series of links connecting the many places of production and distribution and resulting in a commodity exchanged on the world market
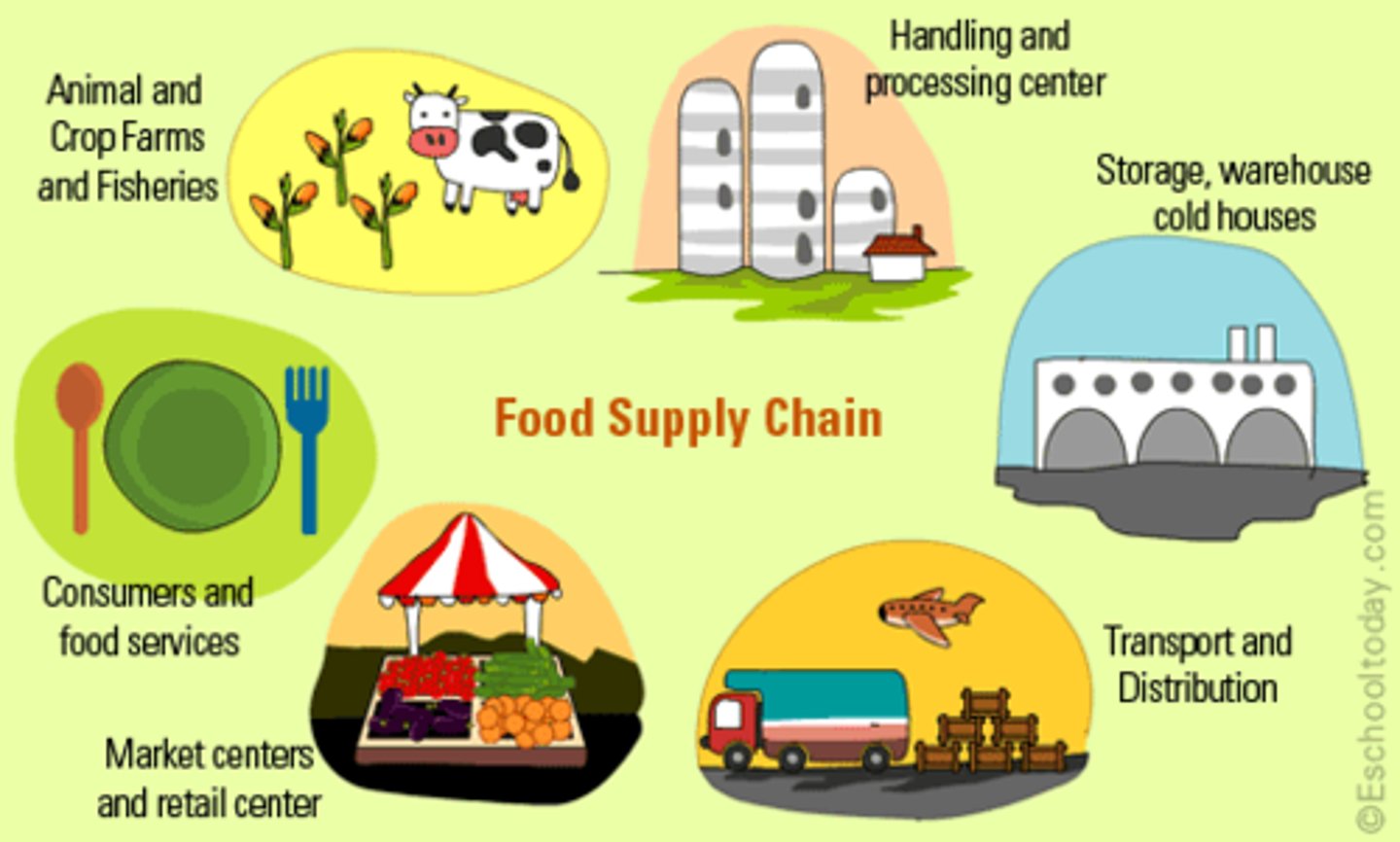
cool chain
the refrigeration and transport technologies that allow for the distribution of perishables

value-added specialty crops/products
increasing the economic value of a commodity through particular production processes, e.g., organic produce, farmer's market jams,or regionally branded products that increase consumer appeal and willingness to pay a premium over similar but undifferentiated products. i.e. free-range chickens, hormone-free beef

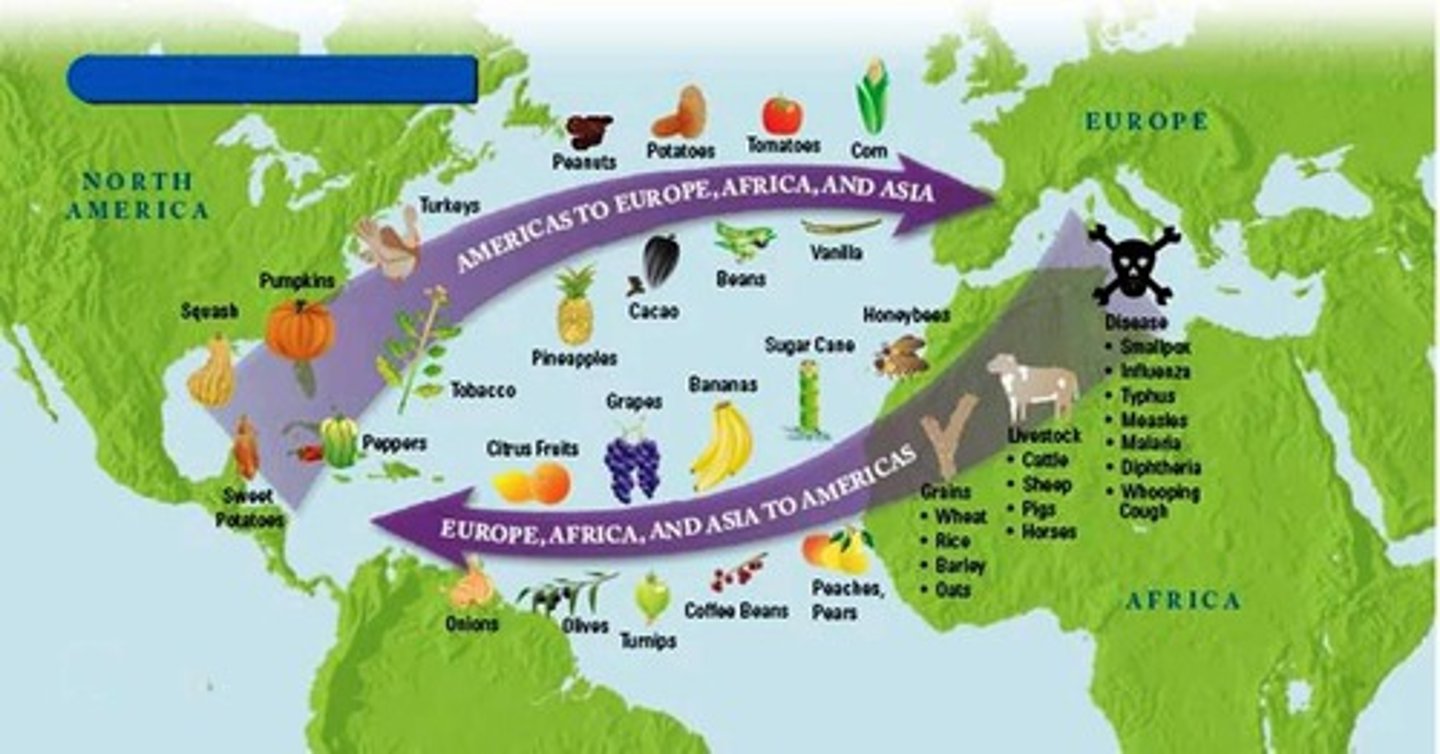
Columbian Exchange
Exchange of plants, animals, ideas, diseases, and people between the Americas, Africa, and Europe. Each region was significantly impacted as a result of trade and contact.
subsidies
a sum of money granted by the government or a public body to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain low or competitive.

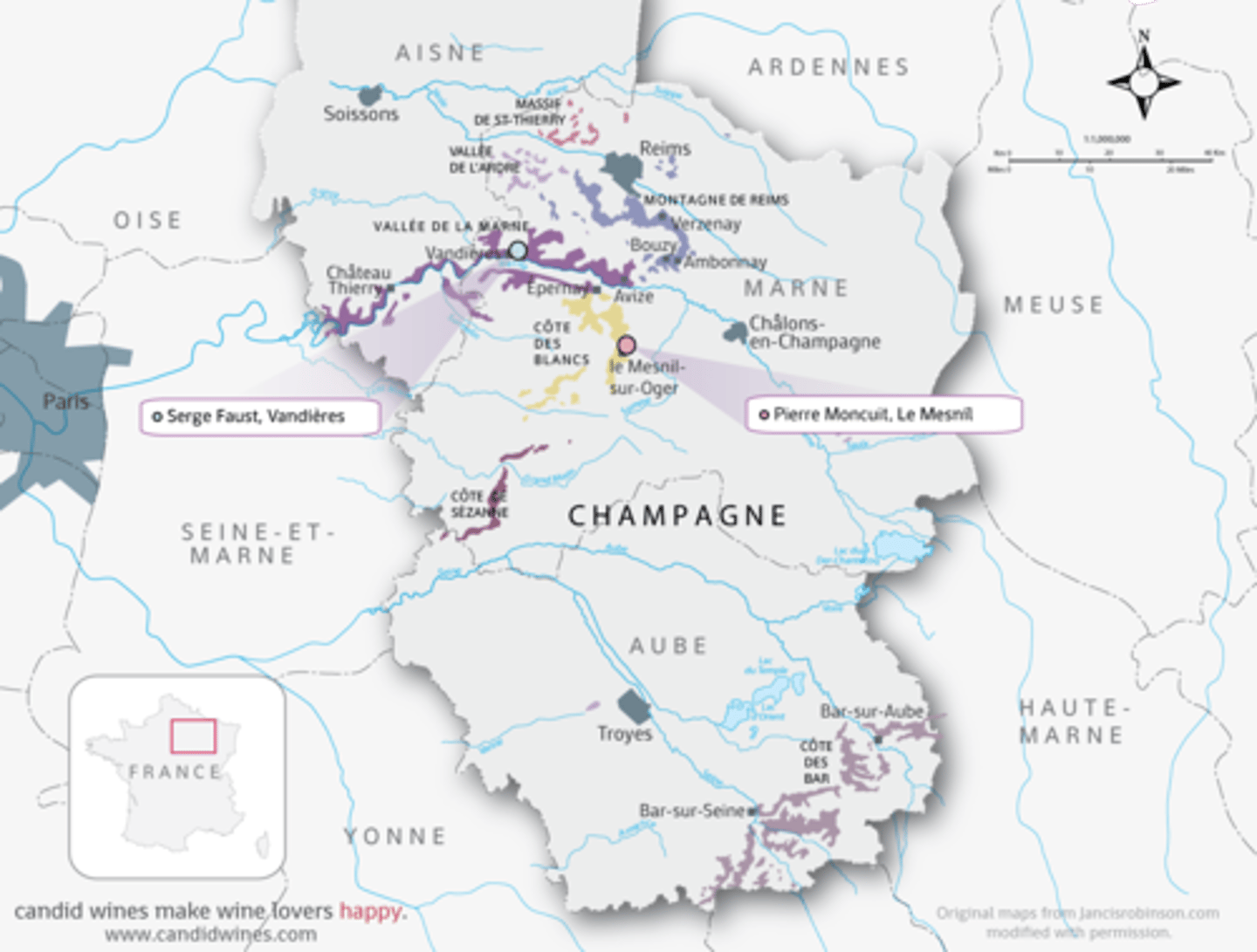
regional appellation
legally defined and protected indication used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown; other types of foods have appellations as well. The rules that govern appellations are dependent on the country in which the wine was produced.
local food movement
minimizing the distance between production and consumption, especially in relation to the modern mainstream food system. There are two primary forms of "local" when it comes to food: direct-to-consumer (farmer to you) and direct-to-retail/food service (farmer to restaurant, schools, etc.)

bid-rent theory (agriculture)
land close to settled areas has a higher value because of accessibility, since transportation costs in terms of time and money are lower.
Land farther from settled areas have lower economic value due to less accessibility and higher transport costs.
salinization of soil
the process by which water-soluble salts accumulate in the soil. It is a resource concern because excess salts hinder the growth of crops by limiting their ability to take up water. May occur naturally or because of conditions resulting from management practices

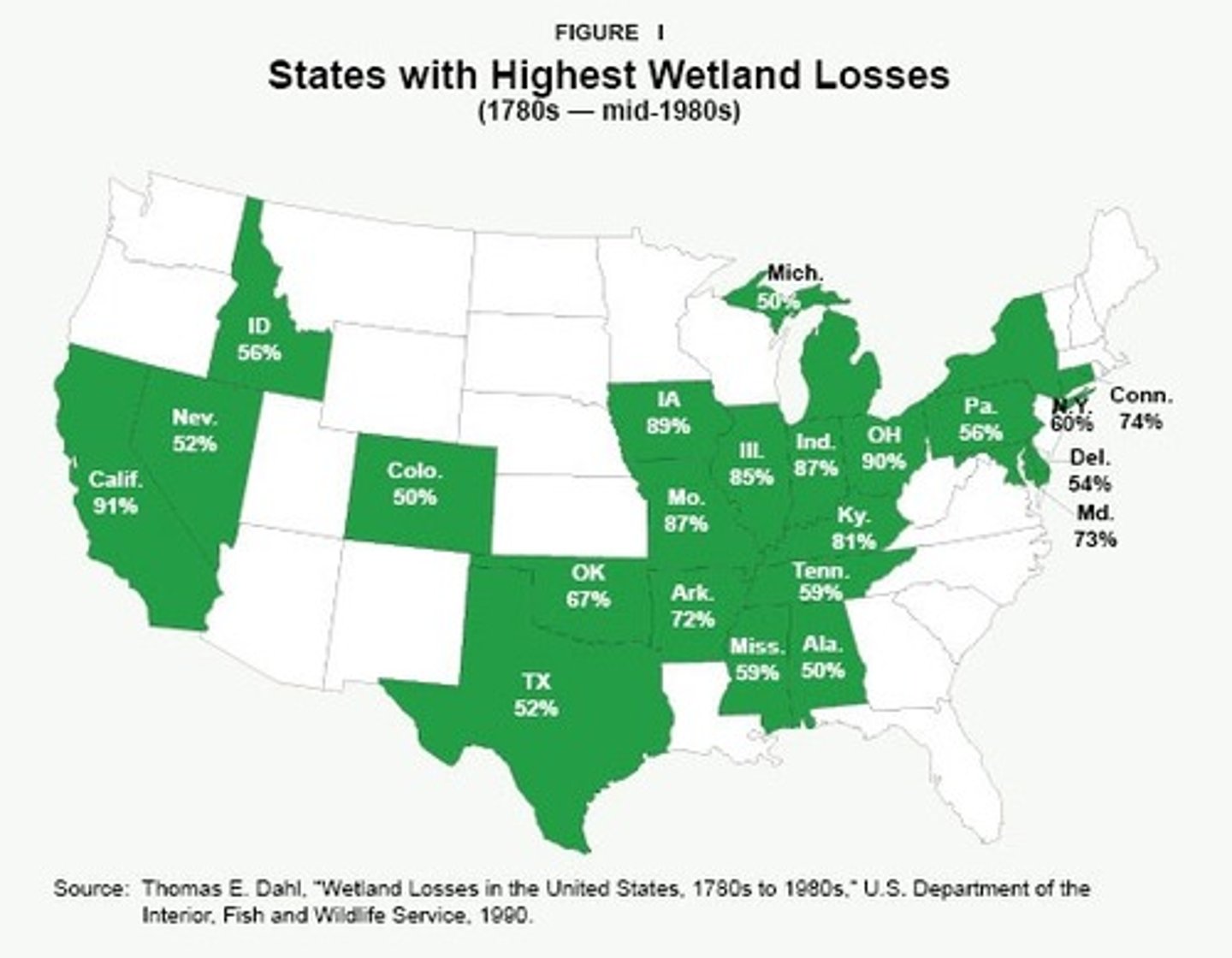
draining of wetlands
removing of water from lakes, rivers, swamps, estuaries, rice paddies, etc. in order to create land for agricultural or urban use.
community supported agriculture
Consumers and farmers work together on behalf of the earth and each other. While the farmer is tending the farm on behalf of others, consumers share the costs of supporting the farm and share the risk of variable harvests (and also share the over-abundance of a particularly fruitful years). Membership is based on shares of the harvest. Members are called shareholders and they subscribe or underwrite the harvest for the entire season in advance. Each project handles this relationship in its own fashion.

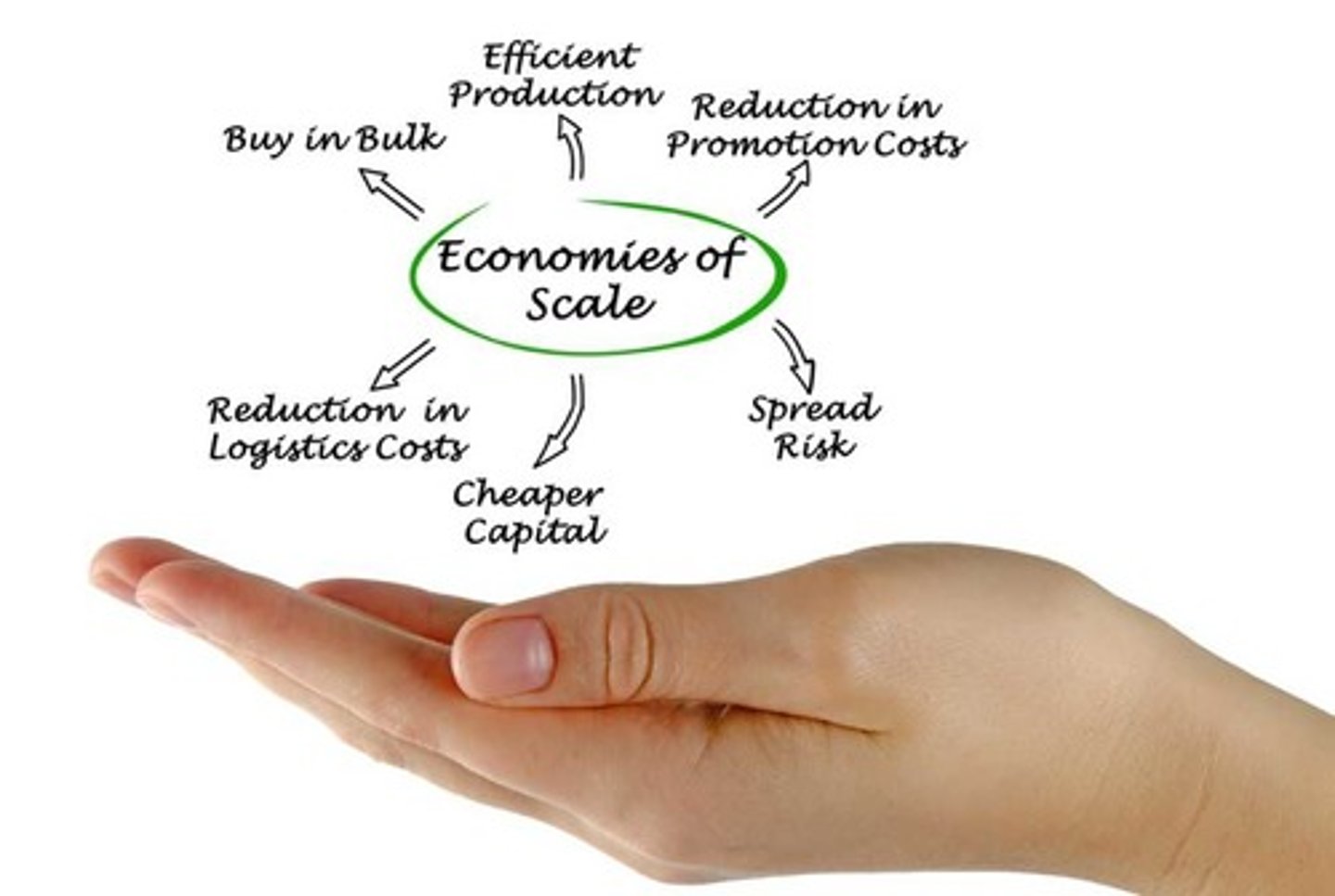
economies of scale
cost advantages gained by an agricultural producer by increasing size of operation (farm size, herd size) and thus lowering costs. This happens because costs of machinery (tractors, combines, etc), irrigation equipment, etc. are spread over larger pieces of land or more animals. Has led to consolidation of farms and reduction of "family farms".
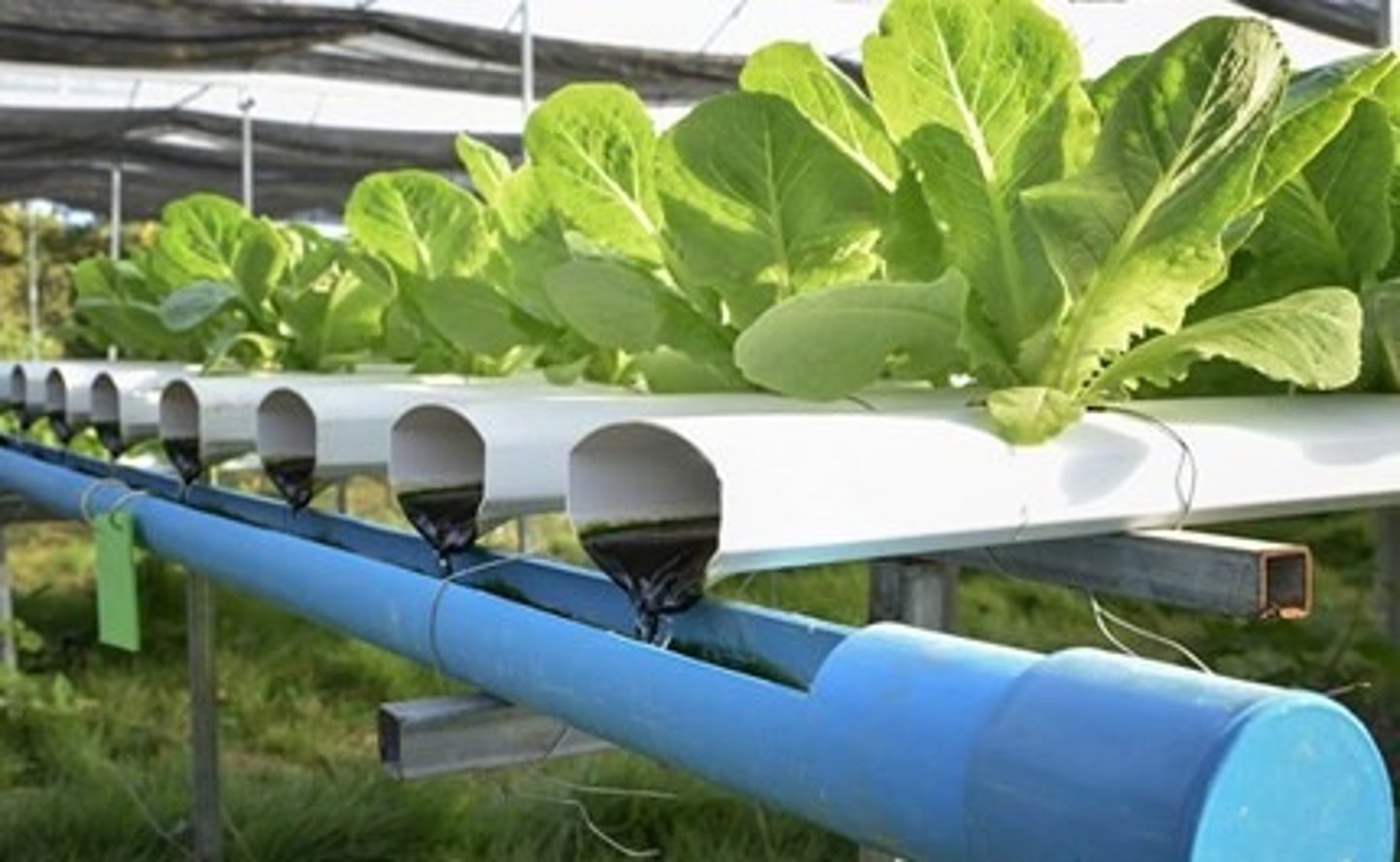
hydroponics
a form of gardening/farming that uses no soil, but instead grows plants in a solution of water and nutrients.

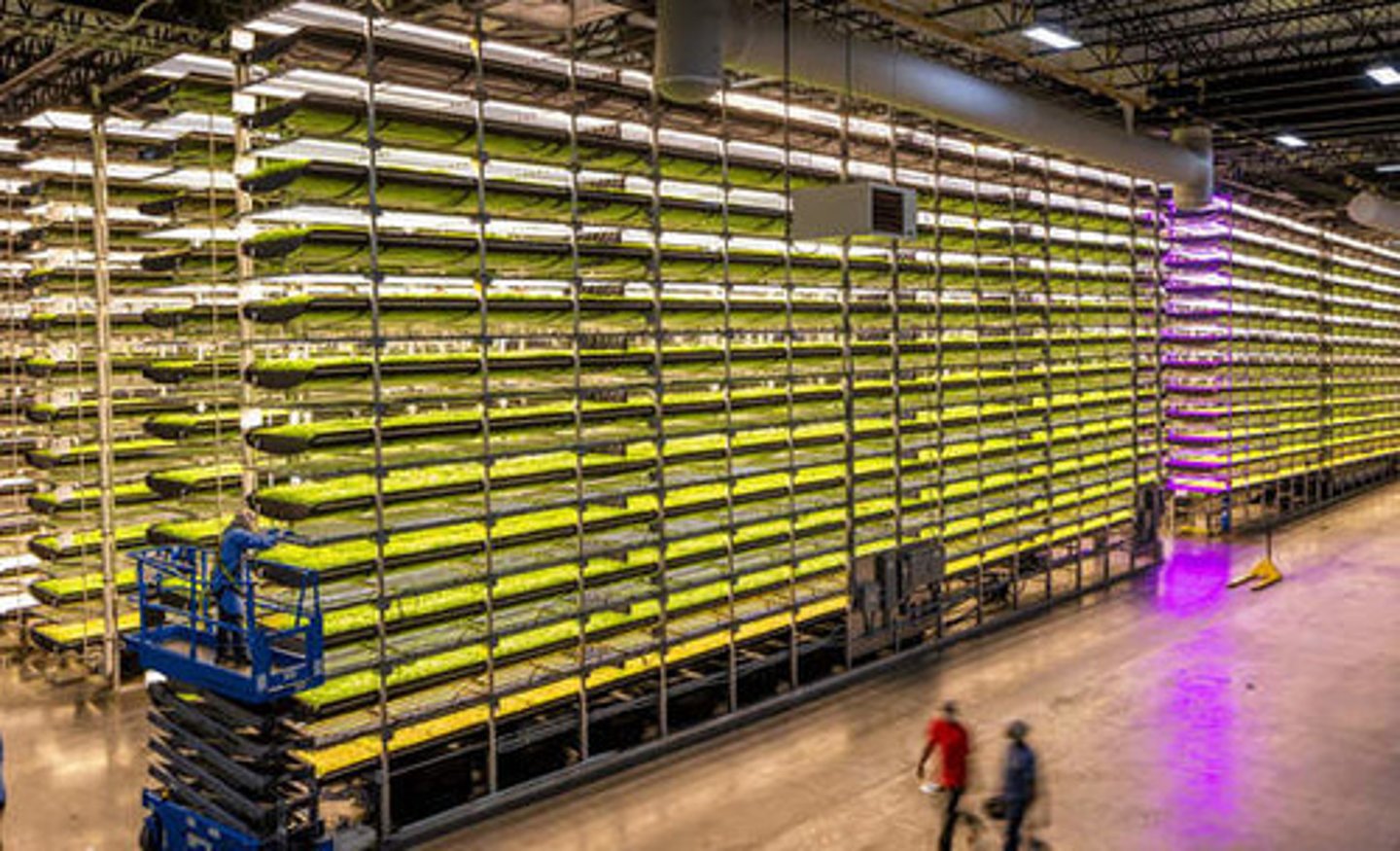
vertical farming
the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers. It often incorporates controlled-environment agriculture, which aims to optimize plant growth, and soilless farming techniques such as hydroponics.

city
An urban settlement that has been legally incorporated into an independent, self-governing unit. Tend to be socially heterogeneous, large and densely-populated compared to the surrounding area. Hubs of commercial, cultural and governmental activity.

urban area
A dense core of census tracts, densely settled suburbs, and low-density land that links the dense suburbs with the core city
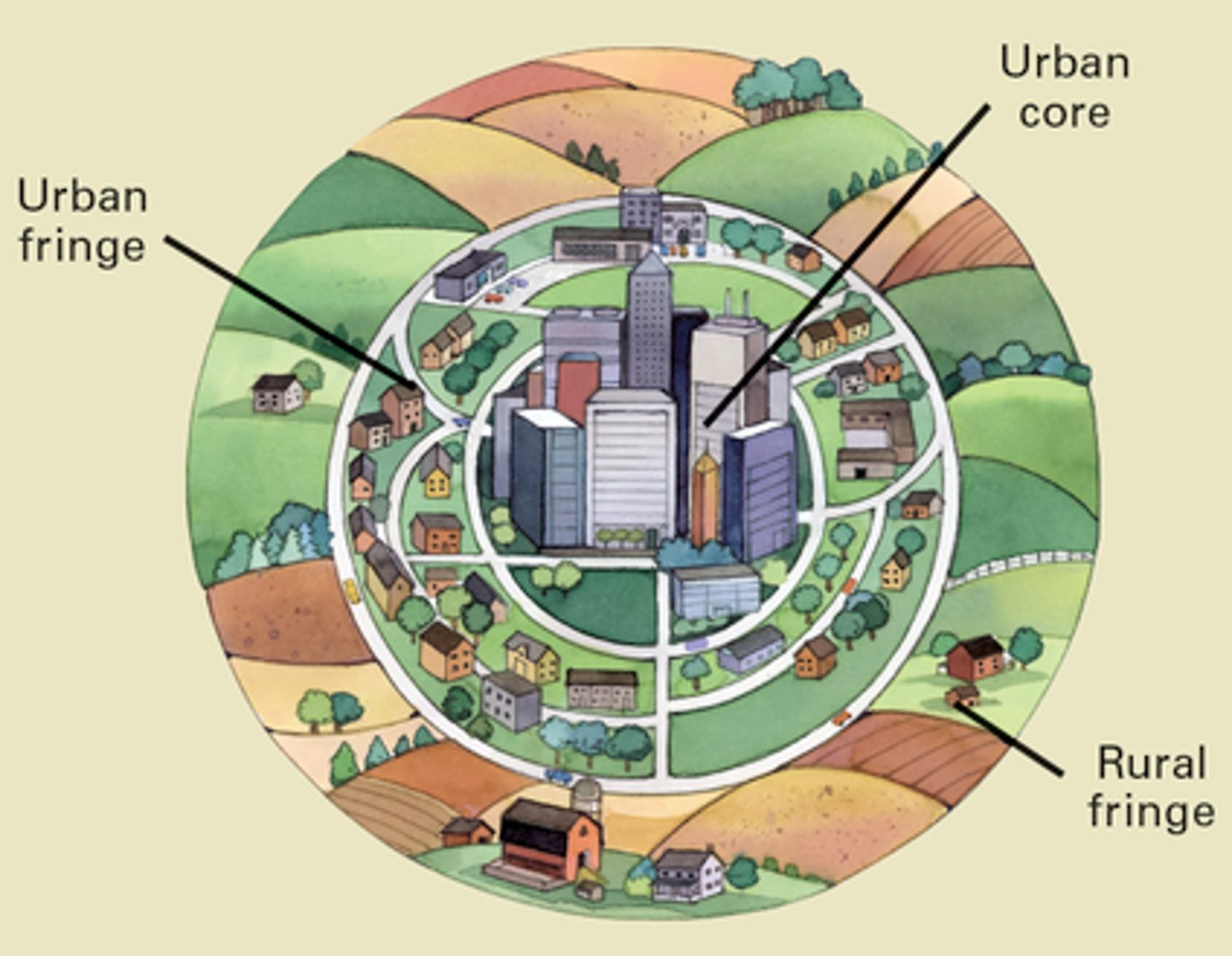
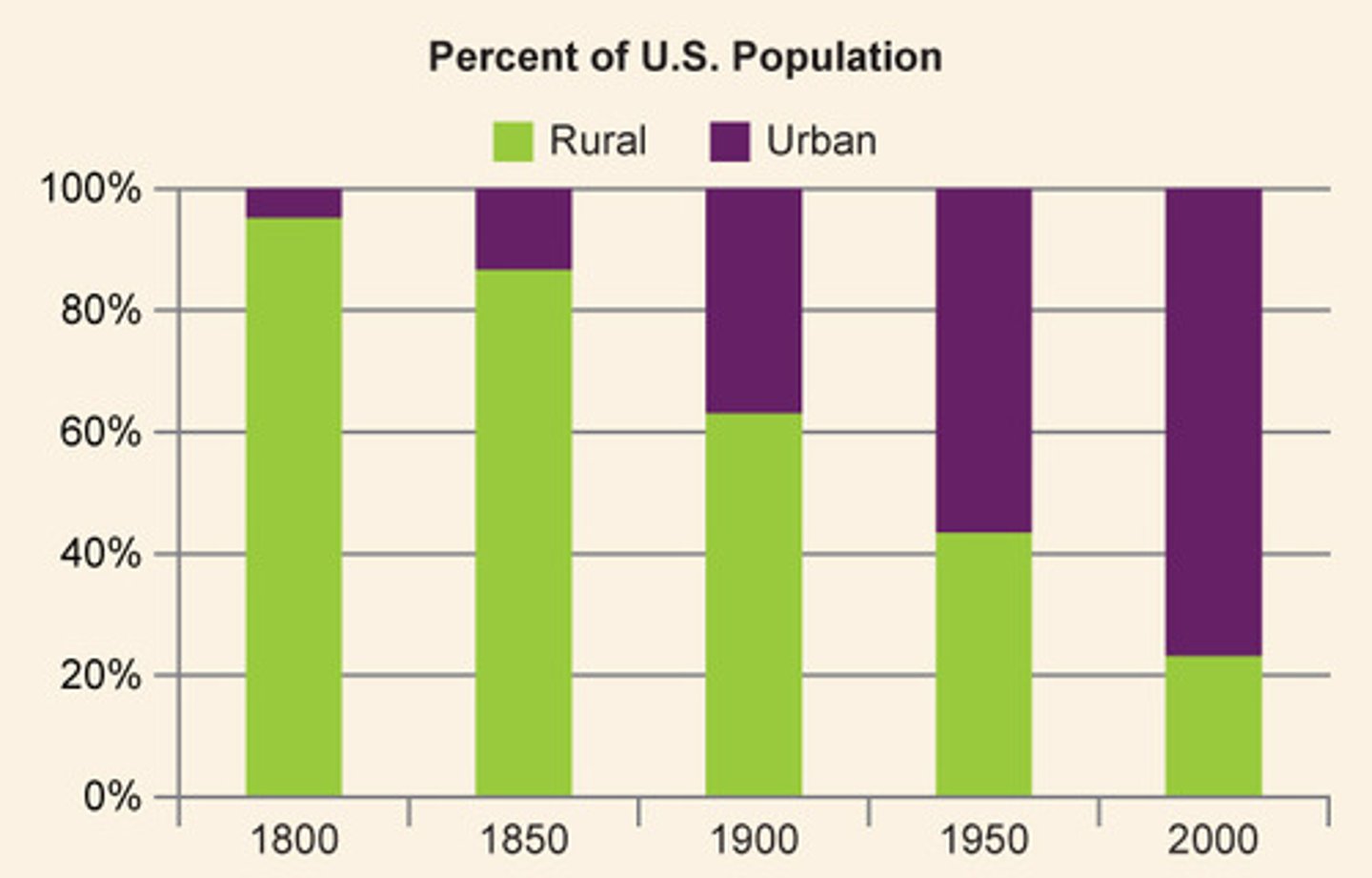
urbanization
the increase in the percentage and number of people moving into and living in urban settlements
urban morphology
the study of the physical form, layout and structure of urban places
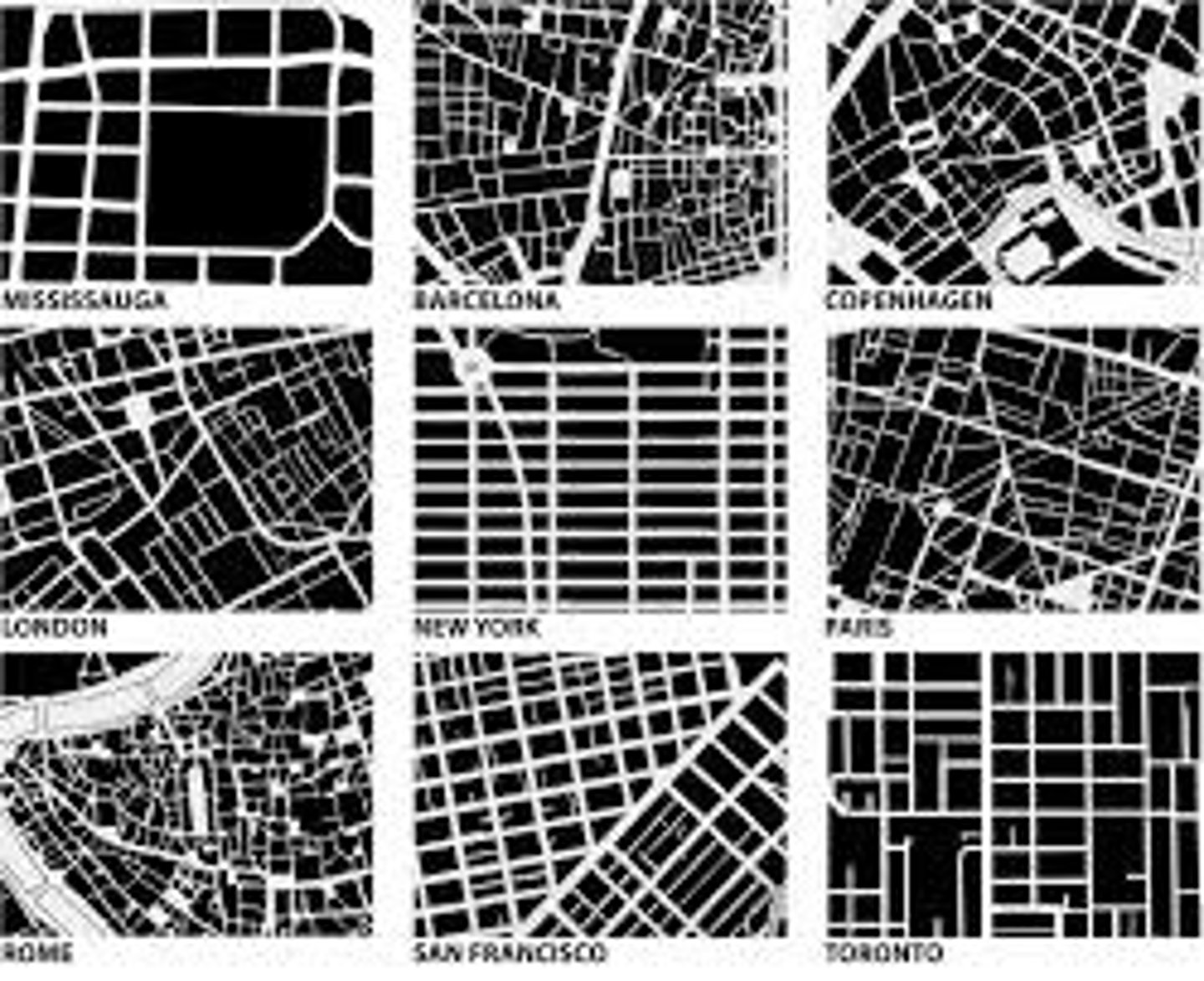

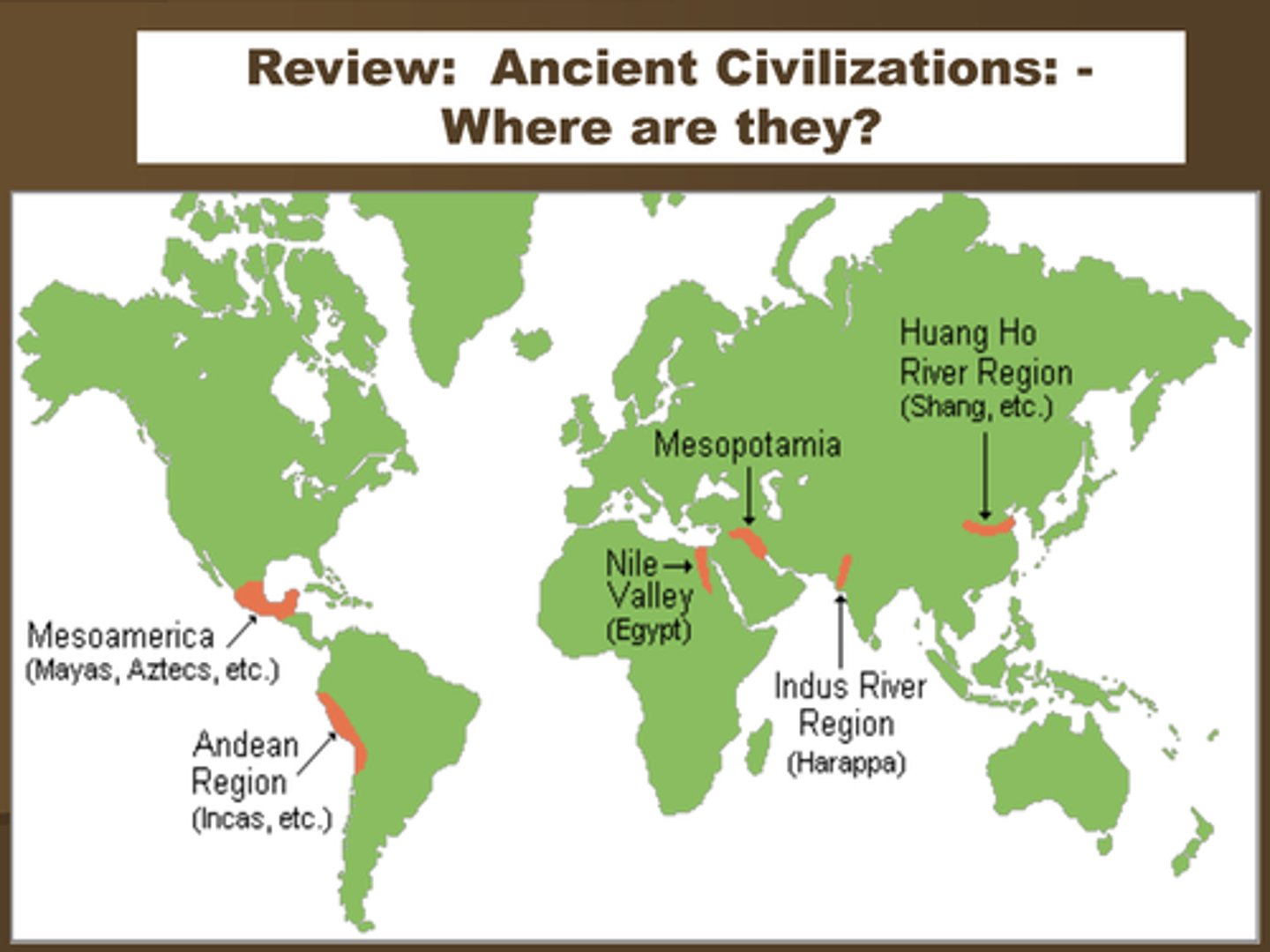
urban hearth area
areas where urban settlements began--Mesopotamia, Nile Valley, Indus Valley, Huang He River Valley, Mesoamerica--after developing surplus agricultural products and social stratification
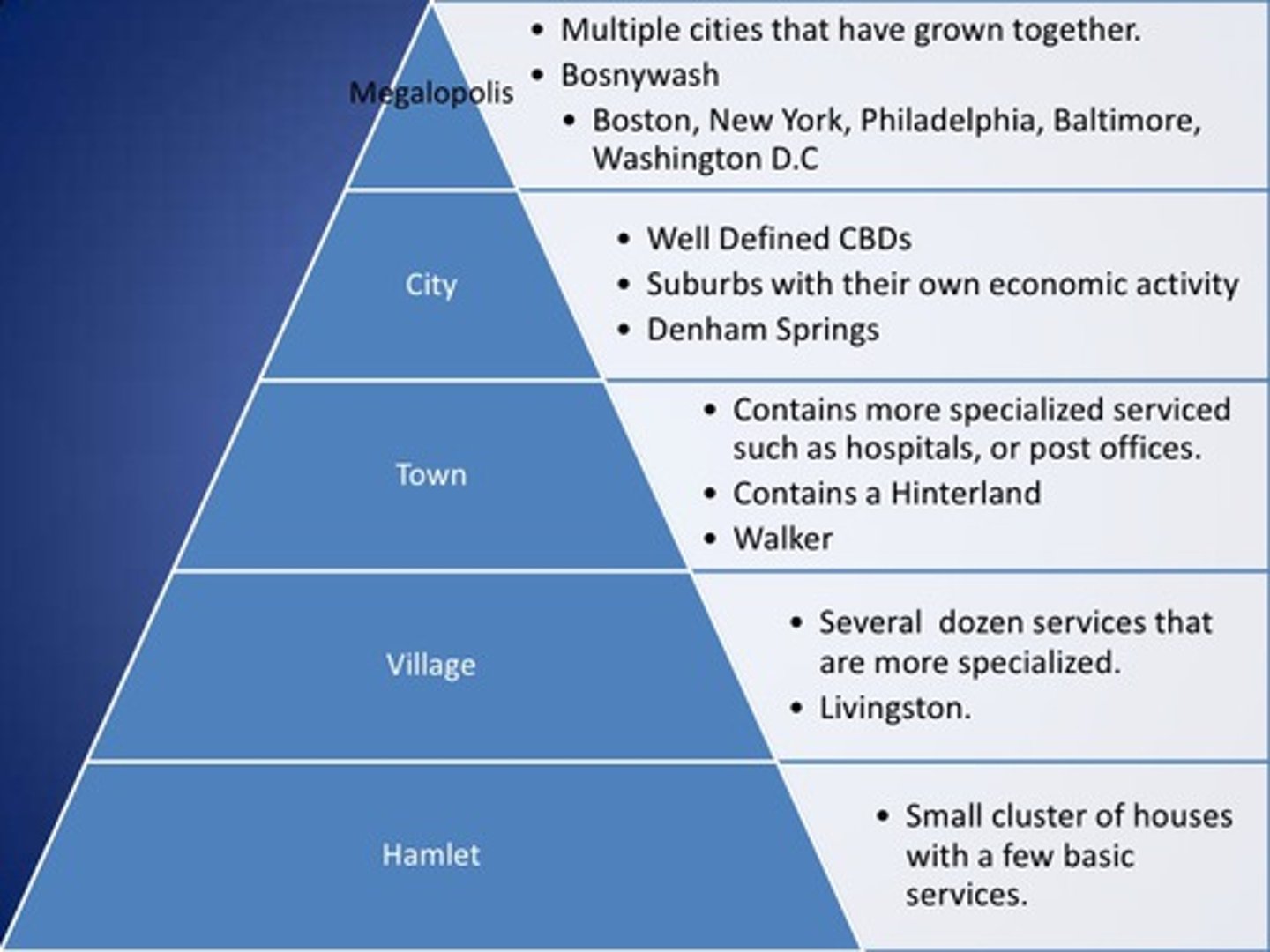
urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements (hamlet, village, town, city, metropolis) according to their size and economic functions.
colonial city
city whose primary identity is as part of a colony of an invading or conquering imperial power, often showing cultural imprints of the colonizer. Ex: Santo Domingo has imprint of Spanish colonization with its cathedrals, gridded streets and town plaza.

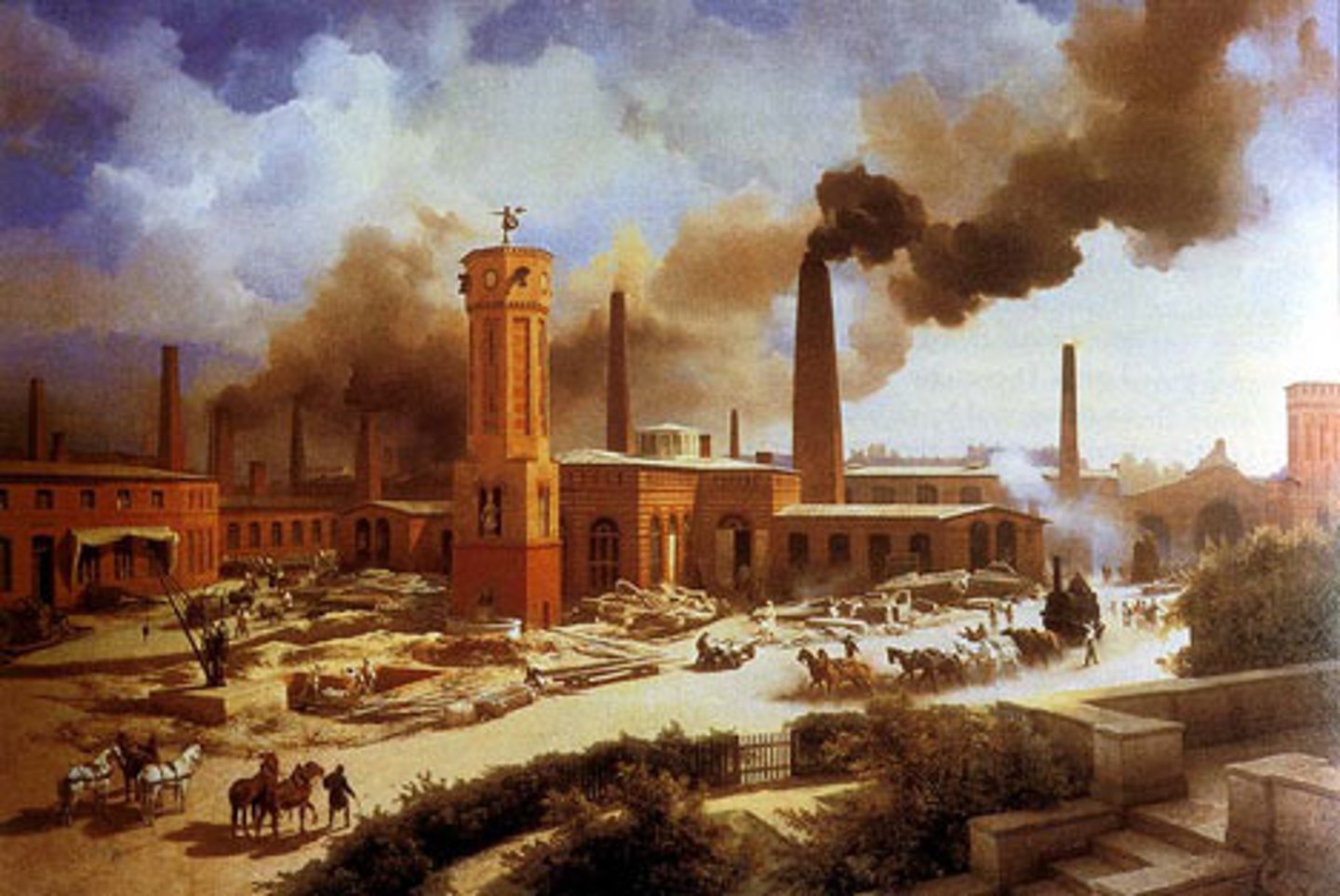
industrial city
city that grew during the Industrial Revolution. Rather than serving mainly as an administrative, religious, trade or gateway city, its function was to make and distribute manufactured products. Often these cities are densely populated and had sanitation issues. Past example is Philadelphia. Current example is Guangzhou in China.

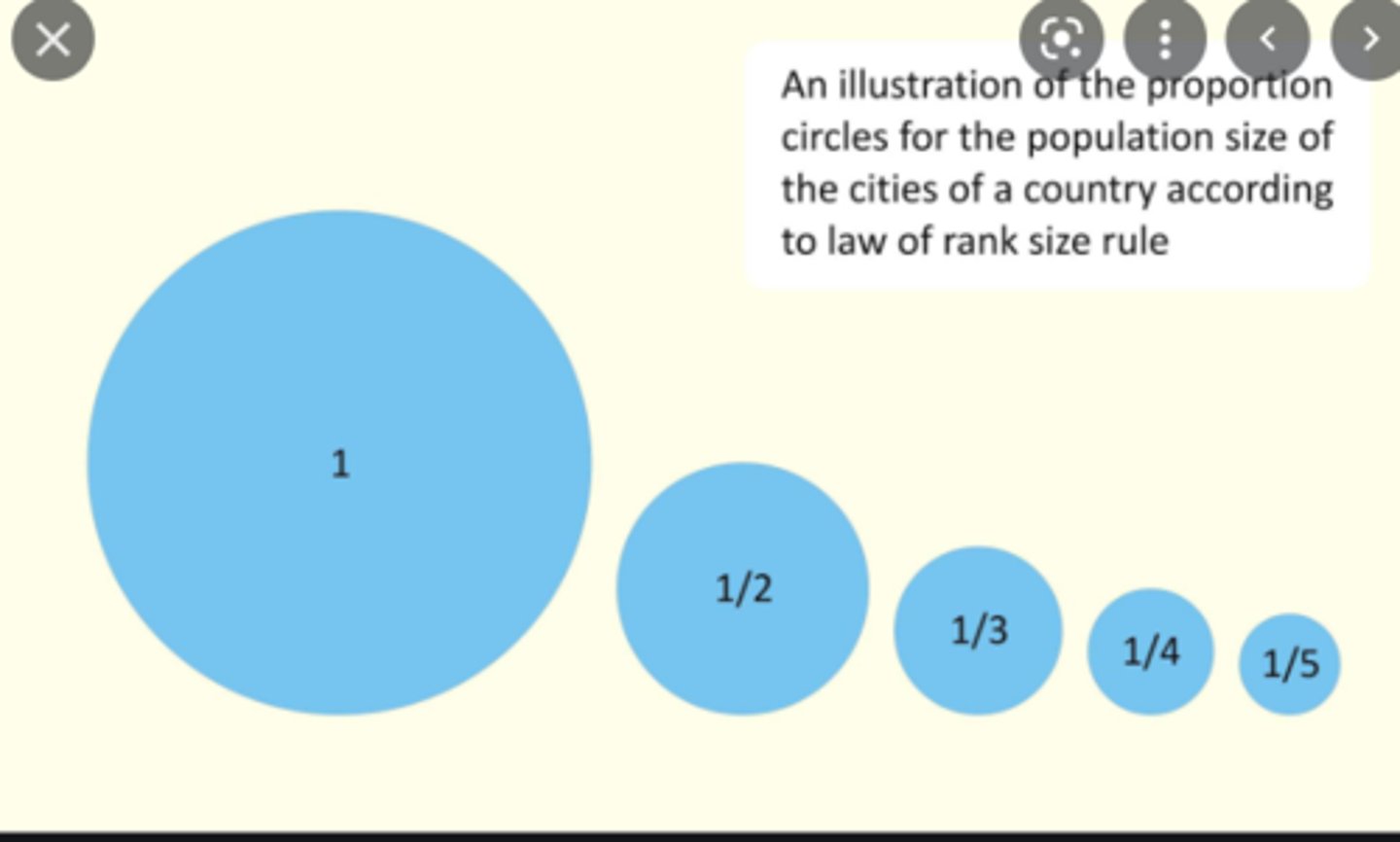
rank-size rule
In a region, the nth-largest city's population is 1/n the population of the region's largest city.
primate city
The largest settlement in a country, which has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.
Dominant city of the country

central place
urban center that provides goods or services to people living in the surrounding rural areas/hinterland
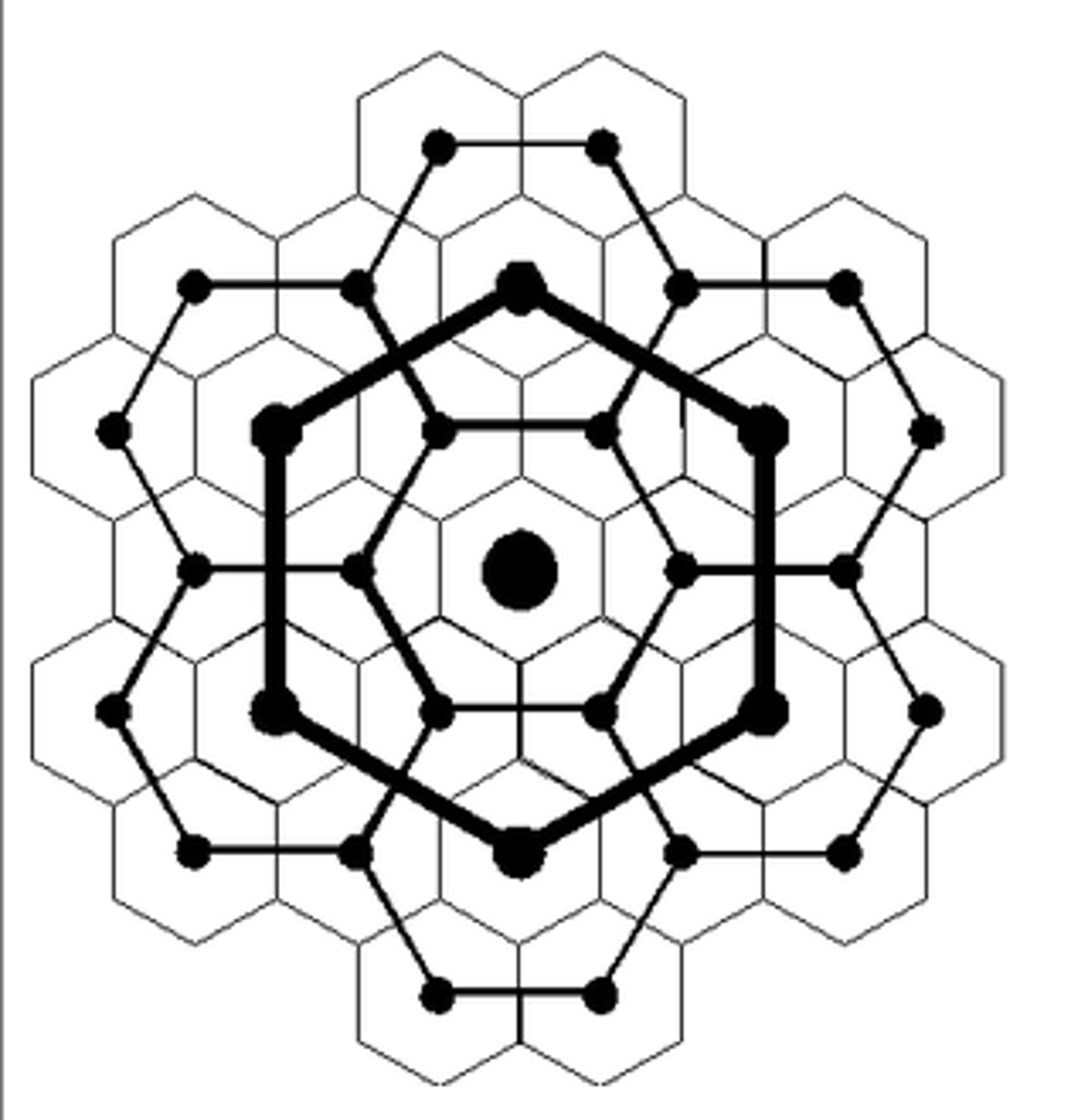
hinterland
the market area surrounding an urban center or central place , area served by an urban center
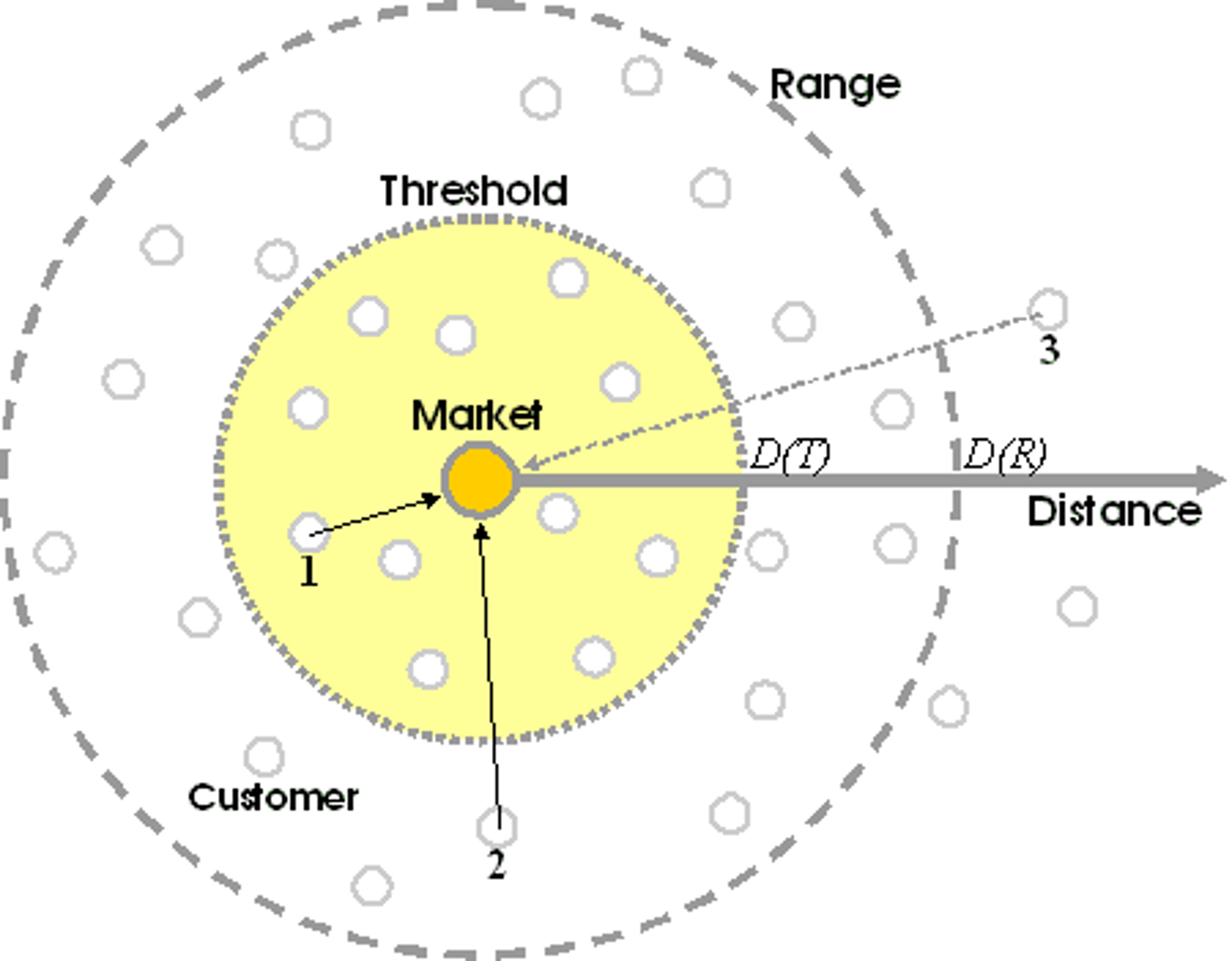
threshold
the minimum number of people needed to support a service/business