Chapter 6: Bones and Skeletal
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Function of the skeletal system
support
movement
protection of underlying organs
mineral storage
blood-cell formation
energy metabolism
Function and structure of cartiliage
Resis compression and tension
Cartilage, firm but flexible and cells separated by abundant extracellular matrix (holds 80% water) - no blood vessls or nerves
What cells are found in cartilage?
Chondrocytes
What do chondrocytes do?
maintain cartilage tissue (mature version)
What is the Lacunae?
a cavity where the chondrocyte sits in
What are chondroblasts?
they are immature cartilage cells that are responsible for forming new cartilage. once it finishes building, it becomes a chondrocyte
What is Perichondrium?
irregular C.T. that surrounds cartilage which prevents the bone to overgrow
What are the three types of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
What is Hyaline cartilage?
most abundant cartilage; provides support through flexibility
What is Elastic cartilage?
contains many elastic fibers; able to tolerate repeated bending
What is Fibrocartilage?
resists strong compression and strong tension
Where is Hyaline cartilage found?
End of long bones
ribs
nose
trachea and larynx
growth plates
Where is elastic cartilage found?
Ear
Epiglottis
Where is fibrocartilage found?
intervertebral discs
pubic symphysis
menisci
What are the four classifications of bones?
Long bones
short bones
flat bones
irregular bones
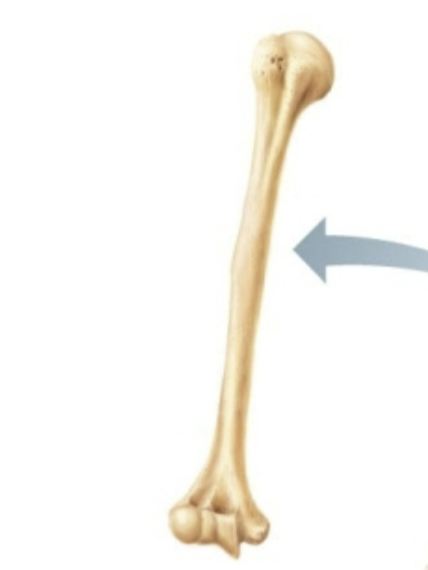
What classification of bone is this?
Long bone
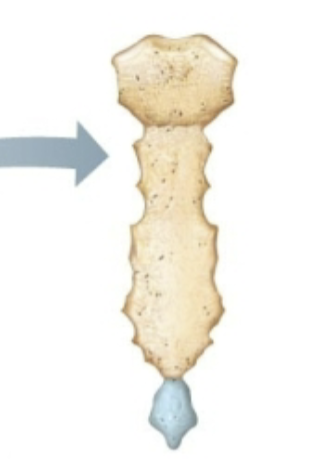
What classification of bone is this?
Flat bone
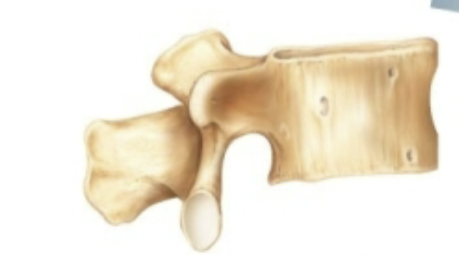
What classification of bone is this?
Irregular bone
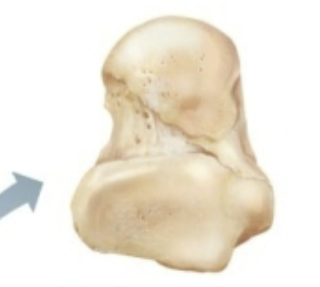
What classification of bone is this?
short bone
What are the four types of cells found in bones?
Osteocytes
Osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
Osteoprogenitor
What are Osteocytes?
mature bone cells that maintains the bone
What are Osteoblasts?
synthesize new bone matrix and then when done, becomes osteocytes
What are Osteoclasts?
dissolve bones matrix
What are osteoprogenitor?
stem cell differentiates into osteoblasts
What is Compact bone
a dense outer layer of bone; lots of calcium
What is spongy bone?
internal network of bone
What is Diploe
the spongy bone of a flat bone
What is the chemical composition of bone?
35% organic components
65% inorganic mineral salts
What do organic components consist of?
Composed of cells, fibers, and organic substances
collagen (abundant)
What do inorganic components consist of?
Primarily calcium phosphate
resists compression
What are the regulations of bone growth?
Growth hormone
thyroid hormone
sex hormone
Growth hormone
produced by the primary pituitary gland (stimulates epiphyseal plates)
Thyroid hormone
ensures that the skeleton retains proper proportions
sex hormones
Promate bone growth and later induces closure of epiphyseal plates
Where does bone deposit and remove occur
occurs at periosteal and endosteal surfaces
What is bone deposition
accomplished by osteoblasts; working to make new bone tissues and works when the body is active
What is bone reabsorption
accomplished by osteoclasts; gets rid of old bone tissue
What is bone remodeling?
helps maintain constant concentration of Ca2+ and PO43-
What is simple bone fracture?
bone breaks but does not penetrate skin
What is compound bone fracture?
bone breaks and protrudes into the skin
What is closed reduction
no surgery required
what is open reduction
surgery required
What is osteoporosis
characterized by low bone mass
Bone reabsorption outpaces bone deposition
occurs most in women after menopause
What is osteomalacia
occurs in adults
bones are inadequately mineralized
What is Rickets
a type of osteomalacia but occurs in children
analogues to osteomalacia
caused by inadequate amount of vitamin D or calcium phosphate in diet
What is Paget’s disease?
characterized by excessive rate of bone deposition and bone absorption
what is osteosarcoma
a form of bone cancer from connective tissue or muscle cell