HEMA PRELIMS LAB: Platelet Count (Indirect Method)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Cells which are active in blood coagulation.
Platelets
Functions of platelets
Aids in vasoconstriction
Formation of Hemostatic Plug
Thromboplastic Activity
Clot Retraction
The smallest formed elements in the blood.
Platelets
Size of Platelets
2-4µm
Platelets are difficult count due to its affinity for adhering to glass. What is this property called?
Adhesiveness
Platelets are difficult to count due to their tendency to clump together. what is this property of platelets called?
Aggregation
In what objective is indirect platelet count performed?
OIO
How many OIO fields should be done in indirect platelet count?
10 consecutive OIO fields.
Stain used to visualize platelets in indirect platelet count.
Wright’s or Wright-Giemsa Stain
The sequential process by which multiple plasma enzymes and cofactors interact in sequence, forming an insoluble fibrin clot
Coagulation
The smallest formed elements in blood.
Platelets
Platelets are also known as
thrombocytes
A reactive decrease in the blood vessel diameter.
vasoconstriction
What does vasoconstriction of blood vessels control?
Blood pressure
primary hemostasis
distribution of blood throughout the body
Tube of choice for indirect platelet count
EDTA evacuated tube
Total Magnification of the objective where Indirect Platelet Count is done
1000x.
Magnification of the objective where Indirect Platelet Count is done
100x
Each platelet seen per oil power field is equivalent to?
20,000 platelets/mm³
A normal platelet count consists of how many platelets in one OIF?
7-20
Reference Range for Platelet Count
150,000 to 350,000 platelets/mm³
Formula for Platelet Count

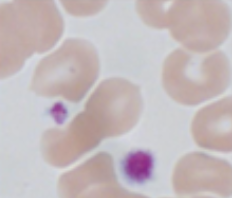
Normal Platelets
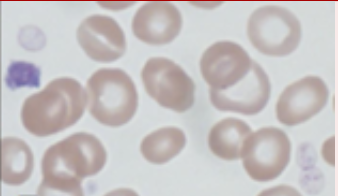
Identify the platelet morphology and the condition where it is found.
Agranular and Hypgranular Platelets in MDS
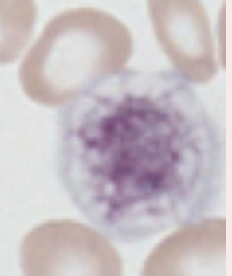
Identify the platelet morphology
Giant Platelets
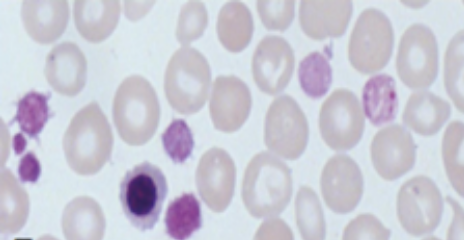
Identify the platelet morphology and in which condition it is found
Platelet Anisocytosis with LARGE platelets and ABNORMAL granulation; Primary Myelofibrosis
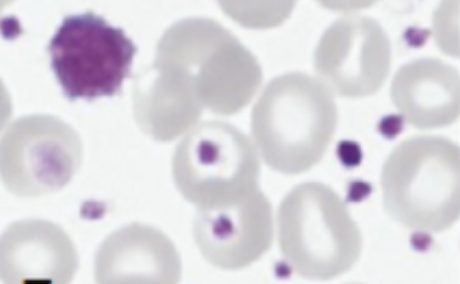
Identify the platelet morphology and condition where it is found
Platelet Anisocytosis with GIANT platelet and granulation ANOMALIES; seen in Essential Thrombocythemia
Identify the platelet morphology
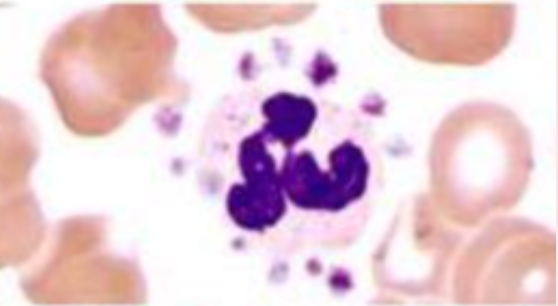
Platelet Sattelitosis
Tubes to be recollected in Platelet Sattelitosis
Citrate then EDTA
Identify the platelet morphology and condition where it is found

TINY PLATELETS (microthrombocytes) in a thrombocytopenic patient with WISKOTT- ALDRICH SYNDROME
Identify the platelet morphology and condition where it is found
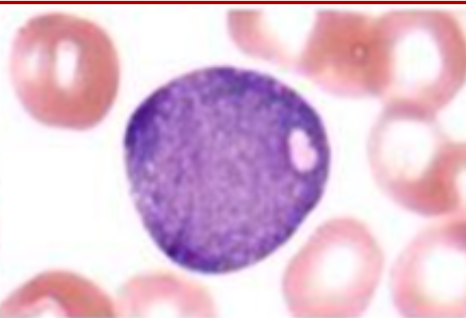
Giant Bizarre Platelets platelet with cytoplasmic vacuolization in a patient with MDS (Myelodysplastic Syndrome)
Identify the platelet morphology and condition where it is found
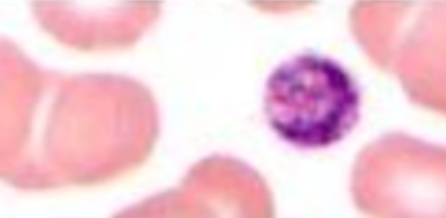
LARGE PLATELET in a patient with Bernard- Soulier Syndrome
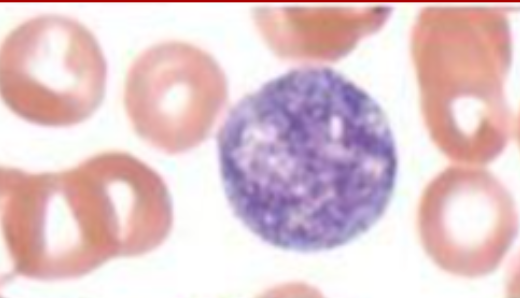
Identify the platelet morphology and condition where it is found
GIANT ADENDRITIC PLATELET, exceeding the size of background RBCs in a patient with MAY- HEGGLIN ANOMALY
Identify the platelet morphology and condition where it is found
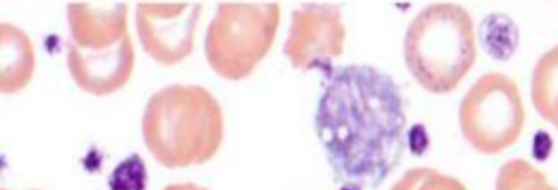
Spectrum of platelet morphology in MYELOPROLIFERATIVE NEOPLASM
Identify the platelet morphology and condition where it is found
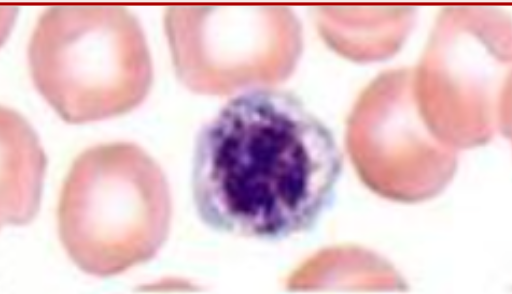
LARGE PLATELET with normal granularity in a patient with IMMUNE THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA (ITP)
GIVE THE FOLLOWING RANGE OF VALUES OF PLATELET ESTIMATES:
Markedly decreased
Moderately decreased
Slightly decreased
Low Norma
Normal
Slightly Increased
Moderately Increased
Markedly Increased
Markedly decreased: 0-49,000/μL
Moderately decreased: 50,000-99,000/μL
Slightly decreased: 100,000-149,000/μL
Low Normal: 150,000-199,000/μL
Normal: 200,000-400,000/μL
Slightly Increased: 401,000-599,000/μL
Moderately Increased: 600,000-800,000/μL
Markedly Increased: > 800,000/μL